HD 268835 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HD 268835 (or R66) (30 SM) is one of two stars that were identified by NASA's
NASA's Spitzer Uncovers Hints of Mega Solar Systems
Nasa.gov, accessed 11 Feb 2006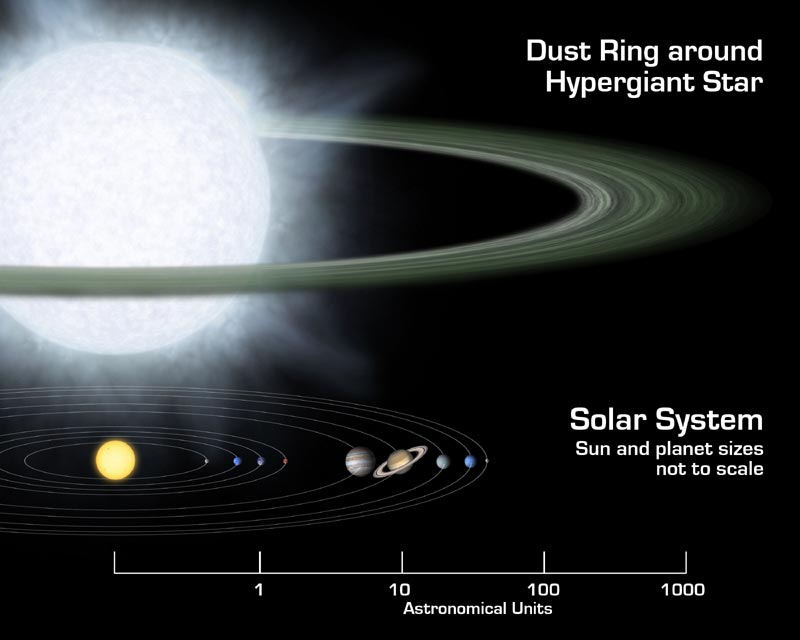
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, f ...
in the Milky Way's nearest neighbor galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), or Nubecula Major, is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of around 50 kiloparsecs (≈160,000 light-years), the LMC is the second- or third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way, after the ...
(the other being R 126 or HD 37974
HD 37974 (or R 126) a variable B hypergiant in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It is surrounded by an unexpected dust disk.
Properties
R126, formally RMC (Radcliffe observatory Magellanic Cloud) 126, is a massive luminous star with several ...
), as being circled by monstrous dust disks that are theorised to be the origin of planets.
Significance
Both HD 268835 and HD 37974 are classified ashypergiant
A hypergiant (luminosity class 0 or Ia+) is a very rare type of star that has an extremely high luminosity, mass, size and mass loss because of its extreme stellar winds. The term ''hypergiant'' is defined as luminosity class 0 (zero) in the MKK ...
s, very large and very bright. The dust cloud around them surprised astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either o ...
s because stars as big as these were thought to be inhospitable to planet formation as they have very strong winds making it difficult/impossible for the dust clouds to "condense" into planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a ...
s.
''"We do not know if planets like those in our solar system are able to form in the highly energetic, dynamic environment of these massive stars, but if they could, their existence would be a short and exciting one"'' said Charles Beichman, an astronomer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA ...
and the California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasional ...
, both in Pasadena, California.Nasa.gov, accessed 11 Feb 2006

References
* {{Stars of Mensa Stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud Mensa (constellation) Luminous blue variables B-type hypergiants 268835 022989 CD-70 00273 B(e) stars ko:R 66과 R 126 it:R 66 e R 126