H. E. Merritt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Henry Edward Merritt
in Roland C. Bellamy & Cyrus Andrews et al. (Eds.) (1953) ''Who's Who in the Motor Industry''. Grimsby: Roland C. Bellamy.
 In 1935, Merritt joined David Brown as a research engineer, and subsequently became their chief engineer. In 1937 he was appointed Superintendent of Design (Tanks) at the Royal Arsenal, Woolwich, and was later Director of Design (Tanks) for the Ministry of Supply. He returned to David Brown in 1940. From 1945 he was a manager in the agricultural division of
In 1935, Merritt joined David Brown as a research engineer, and subsequently became their chief engineer. In 1937 he was appointed Superintendent of Design (Tanks) at the Royal Arsenal, Woolwich, and was later Director of Design (Tanks) for the Ministry of Supply. He returned to David Brown in 1940. From 1945 he was a manager in the agricultural division of
Tom Shelley, Eureka, 6 November 2003. Retrieved from archive.org 27 March 2020. Merritt also designed the epicyclic gearbox for Norbar that allowed more torque to be transmitted through the box, as well as the mechanism for their Slimline torque wrench, launched in 1963, and so called because the whole mechanism was contained within the body of the wrench unlike its predecessors which had external, break-back mechanisms. The firm continued to produce wrenches derived from Merritt's innovation for decades afterwards.
 Merritt wrote a number of books, including the standard texts ''Gears'' (1942) and its companion volume ''Gear Trains'' (1947), the later work including a Brocot table of "all useful numbers up to 200,000".Roegel, Denis. (2011)
Merritt wrote a number of books, including the standard texts ''Gears'' (1942) and its companion volume ''Gear Trains'' (1947), the later work including a Brocot table of "all useful numbers up to 200,000".Roegel, Denis. (2011)
A reconstruction of Merritt's Brocot table (1947)
'. Research Report. Retrieved from HAL 12 March 2020. Brian Hayes has commented on the significance of
Brian Hayes, '' American Scientist'', Vol. 88, No. 4 (July–Aug. 2000), pp. 296–300. Despite being a leading figure in his field and producing works of great erudition, Merritt was at pains to stress the imperfect nature of gear engineering, writing in the first edition of ''Gears'' in 1942 that it had hardly advanced since
"Automobile Gears"
'' Proceedings of the Institution of Automobile Engineers'', Vol. 20 (1926), No. 2, p. 575. * "Gear Performance II", ''Engineer'', 8 July 1932.
"Gear-tooth Stresses and Rating Formulae"
''
"Gear-Tooth Contact Phenomena"
''Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers'', Vol. 176, No. 1 (1 June 1962), pp. 141–163.
MBE Mbe may refer to:
* Mbé, a town in the Republic of the Congo
* Mbe Mountains Community Forest, in Nigeria
* Mbe language, a language of Nigeria
* Mbe' language, language of Cameroon
* ''mbe'', ISO 639 code for the extinct Molala language
Molal ...
(20 May 1899 – 28 March 1974) was a British mechanical engineer
Mechanical may refer to:
Machine
* Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement
* Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations of ...
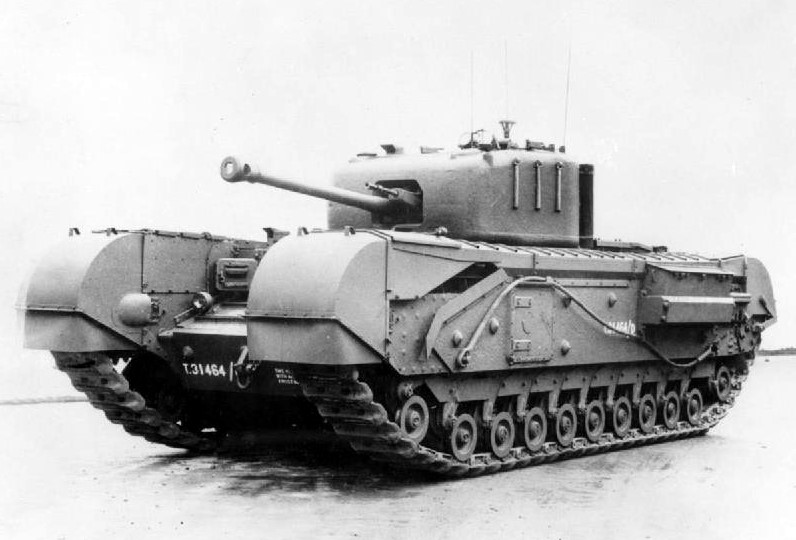
who invented the Merritt–Brown triple differential tank transmission that provided greater manoeuvrability to a generation of British tanks, starting with the Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
in 1939 and continuing into the 1980s. It allowed a tracked vehicle to change direction while on the move with less loss of power than under other steering systems, and to perform a neutral turn on the spot by rotating its tracks in opposite directions. Merritt's invention suited the faster pace of tank warfare of the Second World War, which contrasted with the more static trench warfare of the First World War, for which earlier generations of British tanks had been optimised.
He wrote a number of books, including the standard texts ''Gears'' (1942), which received three editions, and its companion volume ''Gear Trains'' (1947), which included a Brocot table derived from the work of the French clockmaker and mathematician Achille Brocot.
He complained that gearing was a field dominated by empiricism in which science had so far played little role, so that it had hardly progressed in 150 years, but Brian Hayes found sophisticated mathematical concepts in use in the field and, for him, a surprising degree of interchange between mathematics and mechanics. By 2000, many of the problems that Merritt had wrestled with had been solved through the application of brute-force calculations by computers.
Early life
Henry Merritt was born inWest Ham
West Ham is an area in East London, located east of Charing Cross in the west of the modern London Borough of Newham.
The area, which lies immediately to the north of the River Thames and east of the River Lea, was originally an ancient ...
, London, on 20 May 1899, to Henry Merritt, a harness-maker, and his wife Jemima. He was educated at Leyton County High School and Erith Technical College before becoming a premium apprentice at Vickers Limited
Vickers Limited was a British engineering conglomerate. The business began in Sheffield in 1828 as a steel foundry and became known for its church bells, going on to make shafts and propellers for ships, armour plate and then artillery. Entir ...
at Erith from 1915 to 1920. He then took a BSc degree in engineering and became an assistant lecturer at West Ham Municipal College from 1920 to 1924. He received his DSc in engineering from the University of London in 1927."MERRITT, Henry Edward"in Roland C. Bellamy & Cyrus Andrews et al. (Eds.) (1953) ''Who's Who in the Motor Industry''. Grimsby: Roland C. Bellamy.
Career
 In 1935, Merritt joined David Brown as a research engineer, and subsequently became their chief engineer. In 1937 he was appointed Superintendent of Design (Tanks) at the Royal Arsenal, Woolwich, and was later Director of Design (Tanks) for the Ministry of Supply. He returned to David Brown in 1940. From 1945 he was a manager in the agricultural division of
In 1935, Merritt joined David Brown as a research engineer, and subsequently became their chief engineer. In 1937 he was appointed Superintendent of Design (Tanks) at the Royal Arsenal, Woolwich, and was later Director of Design (Tanks) for the Ministry of Supply. He returned to David Brown in 1940. From 1945 he was a manager in the agricultural division of Morris Motors
Morris Motors Limited was a British privately owned motor vehicle manufacturing company formed in 1919 to take over the assets of William Morris, 1st Viscount Nuffield, William Morris's WRM Motors Limited and continue production of the same veh ...
and from 1949, chief research officer at the British Transport Commission
The British Transport Commission (BTC) was created by Clement Attlee's post-war Labour government as a part of its nationalisation programme, to oversee railways, canals and road freight transport in Great Britain (Northern Ireland had the se ...
. From 1949 he was at Rootes Group
The Rootes Group or Rootes Motors Limited was a British automobile manufacturer and, separately, a major motor distributors and dealers business. Run from London's West End, the manufacturer was based in the Midlands and the distribution and de ...
.
While he was at Woolwich, Merritt revised the design of the A20 prototype tank to become the A22 which went into production as the Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
, incorporating his Merritt-Brown triple differential tank transmission (1939) which allowed a tracked vehicle to have continuously variable steering and mitigated the loss of power found when changing direction using other systems. The system also allowed a tank to perform a neutral turn on the spot by rotating its tracks in opposite directions. The greater manoeuvrability provided by Merritt's invention made British tanks more suited to the faster pace of warfare seen in the early Second World War in France and Poland which contrasted with the more static trench warfare of the First World War for which inter-war British tanks had been optimised. His design was used in several generations of post-war British tanks, the last of which was the Chieftain
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribal society or chiefdom.
Tribe
The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia.
Tribal societies are sometimes categorized a ...
.Epicyclics take more torque.Tom Shelley, Eureka, 6 November 2003. Retrieved from archive.org 27 March 2020. Merritt also designed the epicyclic gearbox for Norbar that allowed more torque to be transmitted through the box, as well as the mechanism for their Slimline torque wrench, launched in 1963, and so called because the whole mechanism was contained within the body of the wrench unlike its predecessors which had external, break-back mechanisms. The firm continued to produce wrenches derived from Merritt's innovation for decades afterwards.
Writing
 Merritt wrote a number of books, including the standard texts ''Gears'' (1942) and its companion volume ''Gear Trains'' (1947), the later work including a Brocot table of "all useful numbers up to 200,000".Roegel, Denis. (2011)
Merritt wrote a number of books, including the standard texts ''Gears'' (1942) and its companion volume ''Gear Trains'' (1947), the later work including a Brocot table of "all useful numbers up to 200,000".Roegel, Denis. (2011) A reconstruction of Merritt's Brocot table (1947)
'. Research Report. Retrieved from HAL 12 March 2020. Brian Hayes has commented on the significance of
number theory
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and integer-valued functions. German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) said, "Mat ...
and factoring in gear engineering as demonstrated in Merritt's work in which he suggested that the highest practical number of teeth on a gear was 127, also the largest factor of the "useful" numbers tabulated by Merritt whose table was composed of "a list of all fractions with numerator and denominator no greater than 100, ordered according to magnitude.""Computing Science: On the Teeth of Wheels"Brian Hayes, '' American Scientist'', Vol. 88, No. 4 (July–Aug. 2000), pp. 296–300. Despite being a leading figure in his field and producing works of great erudition, Merritt was at pains to stress the imperfect nature of gear engineering, writing in the first edition of ''Gears'' in 1942 that it had hardly advanced since
Robertson Buchanan
Robertson Buchanan (1770–1816) was a Scottish civil engineer from Glasgow.
Life
He was the son of the Glasgow merchant George Buchanan, and his first wife Jane Gorvie. In the early 1790s he was working at Rothesay for David Dale. His interests ...
wrote on the subject in 1808. It was a field in which "the physicist has so far played little part" and in which the practitioner "gropes dimly in the fog" relying mostly on empirical methods supplemented by elementary trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies ...
and algebra that tended to give a deceptive authority to what was often little more than educated guesswork. By the time of the third edition of ''Gears'' in 1954, knowledge had moved on somewhat but Merritt was obliged to admit that empiricism still ruled and that "the behaviour of mating tooth surfaces and their lubricant still awaits a full understanding."
In 1971 Merritt published ''Gear Engineering'', the follow-up to ''Gears'', which was praised by Paul M. Dean Jr. of Mechanical Technology Incorporated for combining strong practical and theoretical content, so allowing American engineers to access European gear techniques that were "used or are respected throughout the world".
Death and legacy
Merritt died in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, on 28 March 1974. Records relating to him are held by the British National Archives. Writing about Merritt's 1947 book on gear trains for '' American Scientist'' in 2000, Brian Hayes paid tribute to the surprising amount of interchange between mathematics and mechanics evident in the work of Camus, Brocot, and Merritt, but observed uneasily that the power of the electronic computer had "put the gearmakers out of work" as all practical combinations in a gear train could now be calculated in seconds using brute-force techniques so that it was "hardly worth the bother of being clever".Honours
* Member of the Order of the British Empire (1944 New Year Honours
The 1944 New Year Honours were appointments by many of the Commonwealth realms of King George VI to various orders and honours to reward and highlight good works by citizens of those countries. They were announced on 1 January 1944 for the Britis ...
)Fourth Supplement to ''The London Gazette
''The London Gazette'' is one of the official journals of record or government gazettes of the Government of the United Kingdom, and the most important among such official journals in the United Kingdom, in which certain statutory notices are ...
'', No. 36312 (4 January 1944), p. 67.
* James Clayton Prize of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers
The Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE) is an independent professional association and learned society headquartered in London, United Kingdom, that represents mechanical engineers and the engineering profession. With over 120,000 member ...
(1962)
* Liveryman of the Worshipful Company of Spectacle Makers
The Worshipful Company of Spectacle Makers is one of the Livery Companies of the City of London, UK.
The company was founded by a Royal Charter of Charles I in 1629 AD; it was granted the status of a Livery Company in 1809. The company was e ...
* Freeman of the City of London
Selected publications
Articles
"Automobile Gears"
'' Proceedings of the Institution of Automobile Engineers'', Vol. 20 (1926), No. 2, p. 575. * "Gear Performance II", ''Engineer'', 8 July 1932.
"Gear-tooth Stresses and Rating Formulae"
''
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers
The ''Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers'' were first published by the Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE) in 1847. The ''Proceedings'' were published under this single title until 1963, when they began to be published ...
'', Vol. 166 (1952), No. 1.
"Gear-Tooth Contact Phenomena"
''Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers'', Vol. 176, No. 1 (1 June 1962), pp. 141–163.
Books
* ''Text Book of Machine Construction and Drawing''. Bell, 1922. (With Maurice Platt) * ''Gears''. Isaac Pitman, London, 1942. (Revised 1943, 2nd 1946, 3rd 1954) * ''Gear Trains: Including a Brocot table of decimal equivalents and a table of factors of all useful numbers up to 200,000''. Isaac Pitman, London, 1947. * ''Gear Engineering''. Isaac Pitman, London, 1971. * ''The Scope of Gear Research''. Institution of Automobile Engineers, n.d.See also
* Earle BuckinghamReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Merritt, Henry 1899 births English mechanical engineers Members of the Order of the British Empire 1974 deaths English non-fiction writers Vickers people People from West Ham Alumni of the University of London Academics of the University of East London Rootes Group