H.M. Forces on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The British Armed Forces, also known as His Majesty's Armed Forces, are the military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its

parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010
nationalarchives.gov.uk, accessed 31 December 2010
Making the Act of Union 1707
scottish.parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010 There were originally several naval and several military regular and reserve ''forces'', although most of these were consolidated into the Royal Navy or the British Army during the 19th and 20th Centuries (the
 During the later half of the seventeenth century, and in particular, throughout the eighteenth century, British foreign policy sought to contain the expansion of rival European powers through military, diplomatic and commercial means – especially of its chief competitors; Spain, the Netherlands and France. This saw Britain engage in a number of intense conflicts over colonial possessions and world trade, including a long string of Anglo-Spanish and Anglo-Dutch wars, as well as a series of "world wars" with France, such as; the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802) and the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815). During the Napoleonic wars, the Royal Navy victory at
During the later half of the seventeenth century, and in particular, throughout the eighteenth century, British foreign policy sought to contain the expansion of rival European powers through military, diplomatic and commercial means – especially of its chief competitors; Spain, the Netherlands and France. This saw Britain engage in a number of intense conflicts over colonial possessions and world trade, including a long string of Anglo-Spanish and Anglo-Dutch wars, as well as a series of "world wars" with France, such as; the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802) and the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815). During the Napoleonic wars, the Royal Navy victory at  The beginning of the twentieth century served to reduce tensions between Britain and the Russian Empire, partly due to the emergence of a unified
The beginning of the twentieth century served to reduce tensions between Britain and the Russian Empire, partly due to the emergence of a unified  Although Germany had been defeated during the First World War, by 1933 fascism had given rise to Nazi Germany, which under the leadership of Adolf Hitler re-militarised in defiance of the Treaty of Versailles. Once again tensions accumulated in European relations, and following Germany's invasion of Poland in September 1939, the Second World War began (1939–1945). The conflict was the most widespread in British history, with British Empire and
Although Germany had been defeated during the First World War, by 1933 fascism had given rise to Nazi Germany, which under the leadership of Adolf Hitler re-militarised in defiance of the Treaty of Versailles. Once again tensions accumulated in European relations, and following Germany's invasion of Poland in September 1939, the Second World War began (1939–1945). The conflict was the most widespread in British history, with British Empire and
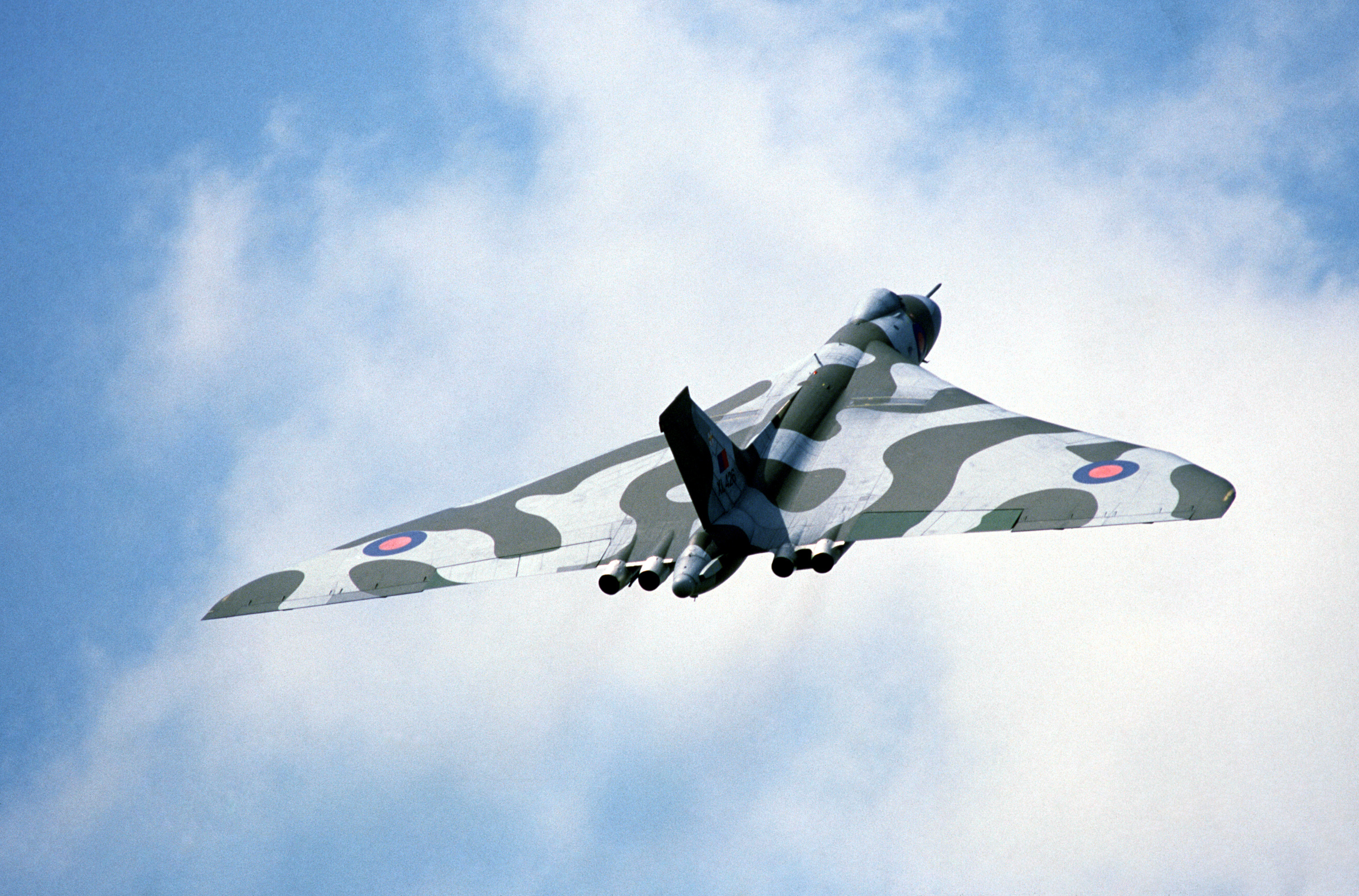 Post–Second World War economic and political decline, as well as changing attitudes in British society and government, were reflected by the armed forces' contracting global role,Focus on Europe
Post–Second World War economic and political decline, as well as changing attitudes in British society and government, were reflected by the armed forces' contracting global role,Focus on Europe
, raf.mod.uk and later epitomised by its political defeat during the
, royal-navy.mod.ukKennedy (2004), ''British Naval Strategy East of Suez, 1900–2000: Influence and Actions'', p193 The British Army of the Rhine and RAF Germany consequently represented the largest and most important overseas commitments that the armed forces had during this period, while the Royal Navy developed an anti-submarine warfare specialisation, with a particular focus on countering Soviet submarines in the Eastern Atlantic and North Sea. While NATO obligations took increased prominence, Britain nonetheless found itself engaged in a number of low-intensity conflicts, including a spate of insurgencies against colonial occupation.Chandler & Beckett (2003), pp350–351 However the
, Ministry of Defence, gov.uk, Published 31 March 2016
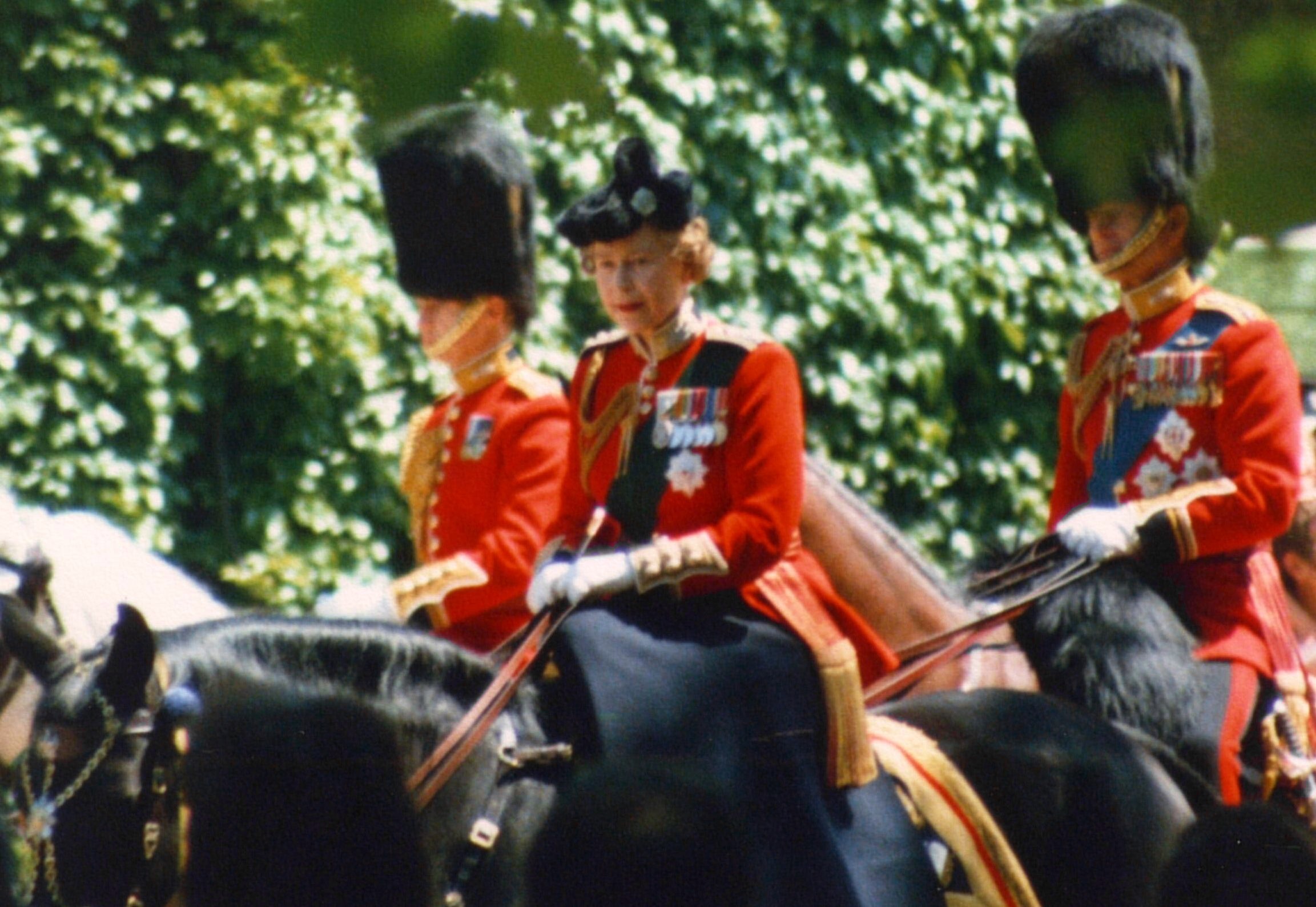

 King Charles III, sovereign of the United Kingdom, is the Head of the Armed Forces, with officers and personnel swearing allegiance to him. Long-standing constitutional convention, however, has ''de facto'' vested military authority and associated royal prerogative powers in the prime minister and the secretary of state for defence, with the former (acting with the support of the
King Charles III, sovereign of the United Kingdom, is the Head of the Armed Forces, with officers and personnel swearing allegiance to him. Long-standing constitutional convention, however, has ''de facto'' vested military authority and associated royal prerogative powers in the prime minister and the secretary of state for defence, with the former (acting with the support of the
 The British Armed Forces are a professional force with a strength of 153,290 UK Regulars and Gurkhas, 37,420
The British Armed Forces are a professional force with a strength of 153,290 UK Regulars and Gurkhas, 37,420
UK Armed Forces: Quarterly Service Personnel Statistics. 1 April 2021. MoD. Published 27 May 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2021. See table 1, page 4. This gives a total strength of 198,880 "UK Service Personnel". As a percentage breakdown of UK Service Personnel, 77.1% are UK Regulars and Gurkhas, 18.8% are Volunteer Reserves and 4.1% are composed of Other Personnel. In addition, all ex-Regular personnel retain a "statutory liability for service" and are liable to be recalled (under Section 52 of the Reserve Forces Act (RFA) 1996) for duty during wartime, which is known as the Regular Reserve. MoD publications since April 2013 no longer report the entire strength of the Regular Reserve, instead they only give a figure for Regular Reserves who serve under a fixed-term reserve contract. These contracts are similar in nature to those of the Volunteer Reserve.gov.uk MoD – reserves and cadet strengths
, table 4 page 13. See note 2. April 2014. , Regular Reserves serving under a fixed-term contract numbered 44,600 personnel.gov.uk MoD – reserves and cadet strengths
, table 1a-page 10. 12 July 1690. The distribution of personnel between the services and categories of service on 1 April 2021 was as follows: , there were a total of 9,330 Regular service personnel stationed outside of the United Kingdom, 3,820 of those were located in Germany. 138,040 Regular service personnel were stationed in the United Kingdom, the majority located in the South East and South West of England with 37,520 and 36,790 Regular service personnel, respectively.
 According to the International Institute for Strategic Studies and the
According to the International Institute for Strategic Studies and the
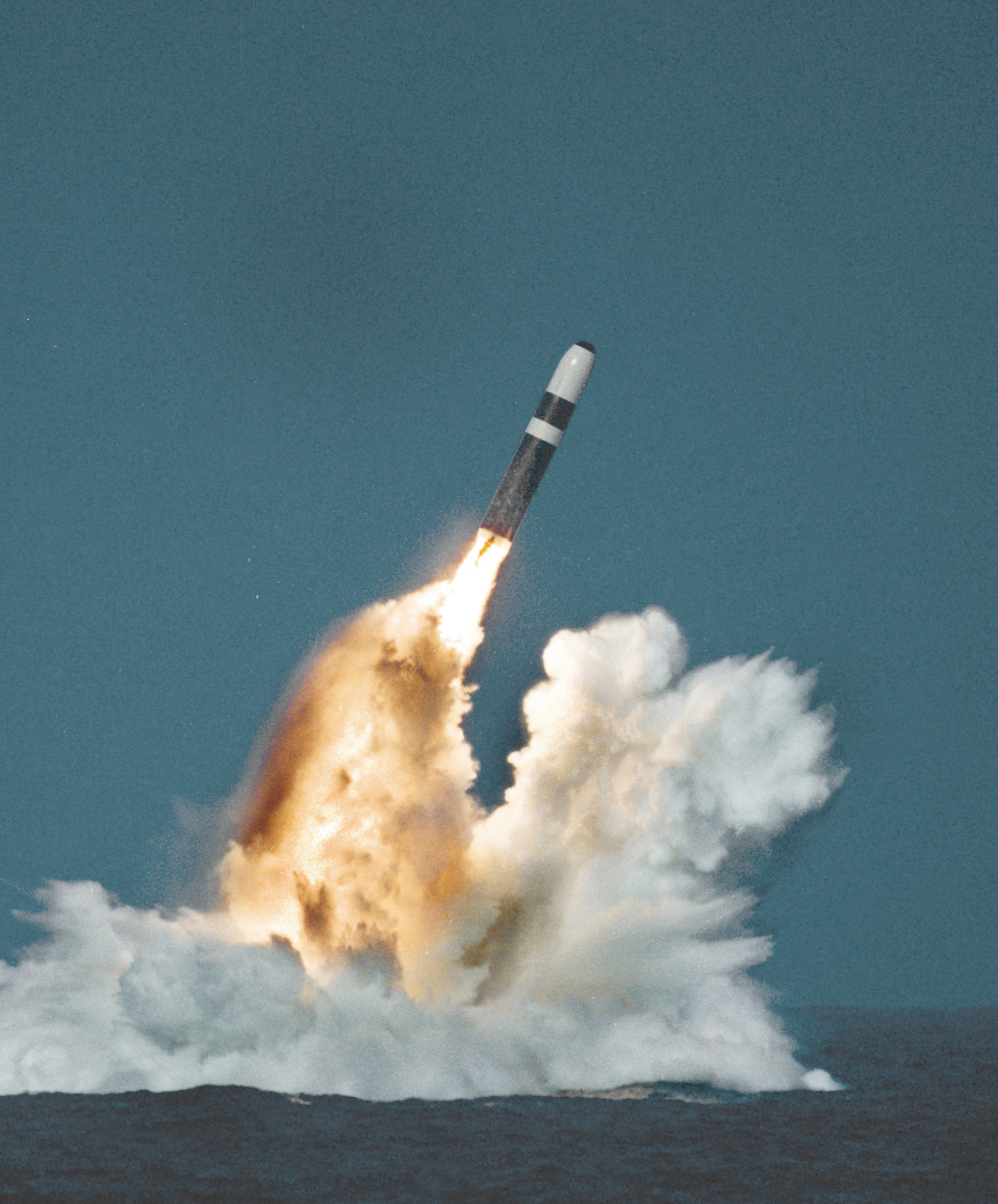 The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear weapon states under the Non-Proliferation Treaty and maintains an independent nuclear deterrent, currently consisting of four
The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear weapon states under the Non-Proliferation Treaty and maintains an independent nuclear deterrent, currently consisting of four
, royalnavy.mod.uk, Accessed 6 December 2014 According to the British Government, since the introduction of
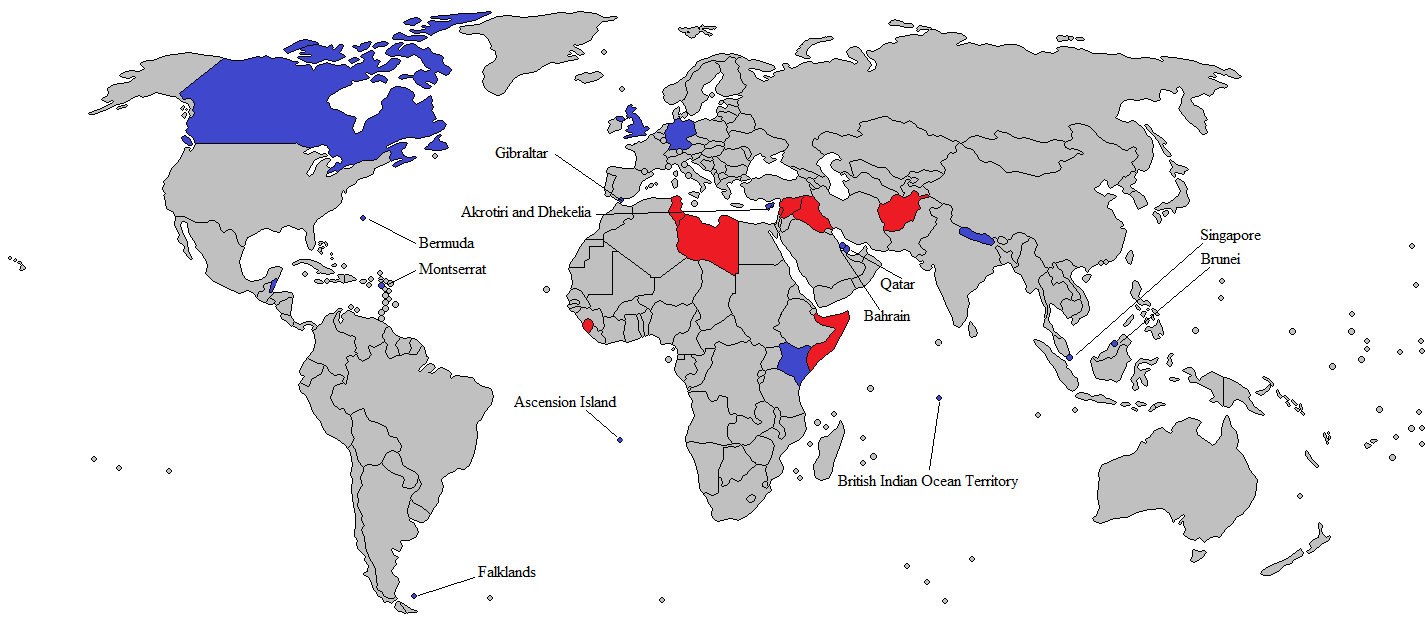 The British Armed Forces maintain a number of overseas garrisons and military facilities which enable the country to conduct operations worldwide. The majority of Britain's permanent military installations are located on
The British Armed Forces maintain a number of overseas garrisons and military facilities which enable the country to conduct operations worldwide. The majority of Britain's permanent military installations are located on
 The British Army is made up of the Regular Army and the Army Reserve. The army has a single command structure based at Andover and known as "Army Headquarters".Army Command reorganization
The British Army is made up of the Regular Army and the Army Reserve. The army has a single command structure based at Andover and known as "Army Headquarters".Army Command reorganization
Defence Marketing Intelligence, 10 November 2011 Deployable combat formations consist of two divisions ( 1st and 3rd Mechanised) and eight brigades. Within the United Kingdom, operational and non-deployable units are administered by two divisions, Force Troops Command, and
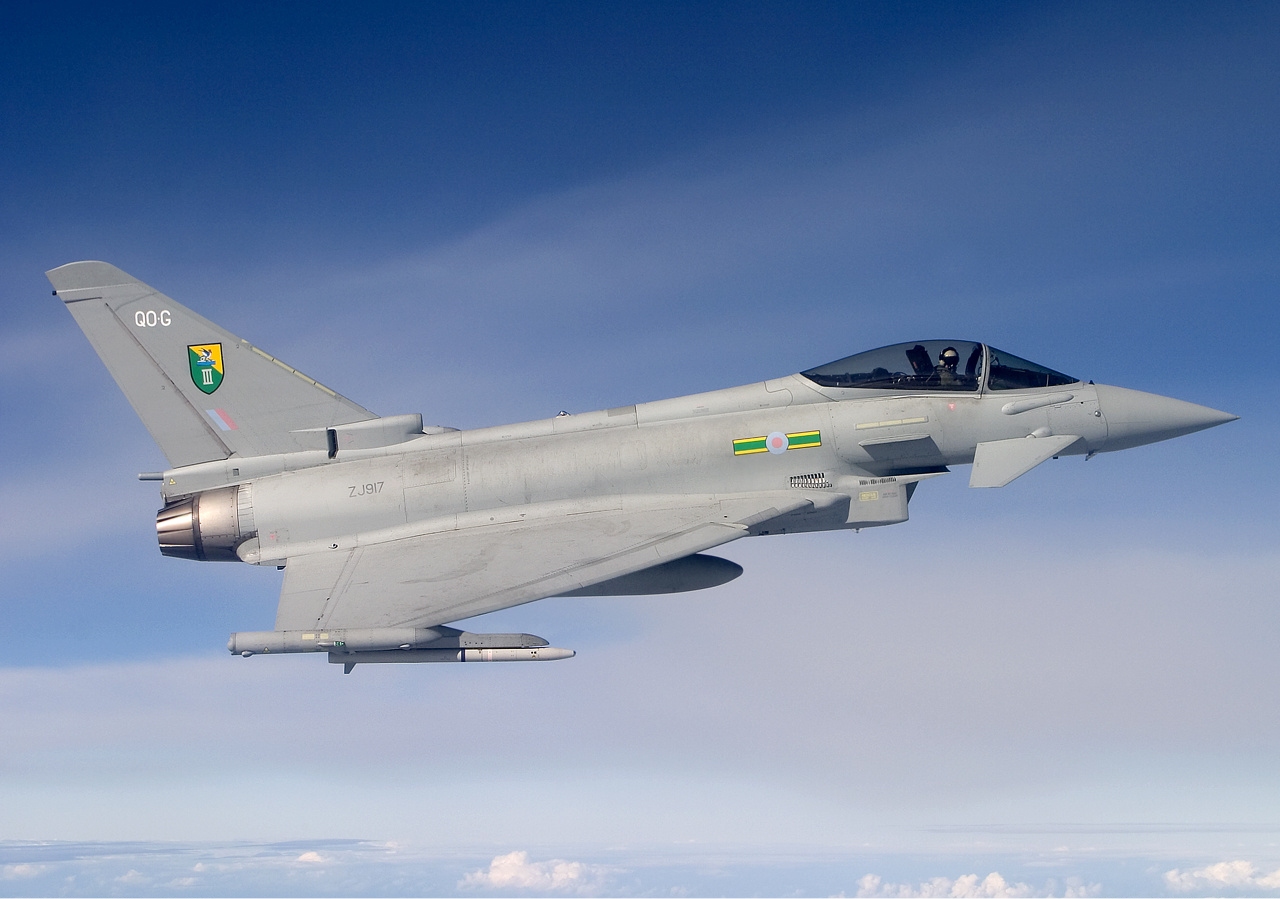 The Royal Air Force has a large operational fleet that fulfils various roles, consisting of both fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. Frontline aircraft are controlled by Air Command, which is organised into five groups defined by function: 1 Group (Air Combat), 2 Group (Air Support), 11 Group (Air and Space operations), 22 Group (training aircraft and ground facilities) and 38 Group (Royal Air Force's Engineering, Logistics, Communications and Medical Operations units). In addition 83 Expeditionary Air Group directs formations in the Middle East and the 38 Group combines the expeditionary combat support and
The Royal Air Force has a large operational fleet that fulfils various roles, consisting of both fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. Frontline aircraft are controlled by Air Command, which is organised into five groups defined by function: 1 Group (Air Combat), 2 Group (Air Support), 11 Group (Air and Space operations), 22 Group (training aircraft and ground facilities) and 38 Group (Royal Air Force's Engineering, Logistics, Communications and Medical Operations units). In addition 83 Expeditionary Air Group directs formations in the Middle East and the 38 Group combines the expeditionary combat support and
 All three services of the British Armed Forces recruit primarily from within the United Kingdom, although citizens from the Commonwealth of Nations and the Republic of Ireland are equally eligible to join.Evans (2005)
All three services of the British Armed Forces recruit primarily from within the United Kingdom, although citizens from the Commonwealth of Nations and the Republic of Ireland are equally eligible to join.Evans (2005)
How British Army is fast becoming foreign legion
, timesonline.co.uk The minimum recruitment age is 16 years (although personnel may not serve on armed operations below 18 years, and if under 18 must also have parental consent to join); the maximum recruitment age depends whether the application is for a regular or reserve role; there are further variations in age limit for different corps/regiments. The normal term of engagement is 22 years; however, the minimum service required before resignation is 4 years, plus, in the case of the Army, any service person below the age of 18. At present, the yearly intake into the armed forces is 11,880 (per the 12 months to 31 March 2014).UK Armed Forces Quarterly Personnel Report
, gov.uk, 1 April 2014 Excluding the
British Ministry of Defence
(gov.uk)
Defence Academy of the United Kingdom
(.da.mod.uk)
Royal Navy official website
(royalnavy.mod.uk)
Royal Marines official webpage
(royalnavy.mod.uk)
British Army official website
(army.mod.uk)
Royal Air Force official website
(raf.mod.uk) {{North Atlantic Treaty Organization British Armed Forces deployments
Overseas Territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, support international peacekeeping
Peacekeeping comprises activities intended to create conditions that favour lasting peace. Research generally finds that peacekeeping reduces civilian and battlefield deaths, as well as reduces the risk of renewed warfare.
Within the United N ...
efforts and provide humanitarian aid
Humanitarian aid is material and logistic assistance to people who need help. It is usually short-term help until the long-term help by the government and other institutions replaces it. Among the people in need are the homeless, refugees, and ...
.
Since the formation of the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707 (later succeeded by the United Kingdom), the British Armed Forces have seen action in a number of major wars involving the world's great powers, including the Seven Years' War, the American Revolutionary War, the Napoleonic Wars, the 1853–1856 Crimean War, the First World War, and the Second World War. Britain's victories in most of these decisive wars, allowed it to influence world events and establish itself as one of the world's leading military and economic powers.
As of October 2022, the British Armed Forces consist of: the Royal Navy, a blue-water navy
A blue-water navy is a maritime force capable of operating globally, essentially across the deep waters of open oceans. While definitions of what actually constitutes such a force vary, there is a requirement for the ability to exercise sea cont ...
with a fleet of 72 commissioned ships, together with the Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
, a highly specialised amphibious light infantry force; the British Army, the UK's principal land warfare
Land warfare or ground warfare is the process of military operations eventuating in combat that takes place predominantly on the battlespace land surface of the planet.
Land warfare is categorized by the use of large numbers of combat personne ...
branch; and the Royal Air Force, a technologically sophisticated air force with a diverse operational fleet consisting of both fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. The British Armed Forces include standing forces, Regular Reserve, Volunteer Reserves and Sponsored Reserves
The Sponsored Reserves are a category of reserve forces in the British Armed Forces, created by the Reserve Forces Act 1996. It allows for certain support or specialist tasks to be carried out by trained civilian professionals. The Royal Fleet Aux ...
.
The head of the Armed Forces is the British monarch
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiwi ...
, currently Charles III, to whom members of the forces swear allegiance. Long-standing constitutional convention, however, has vested ''de facto'' executive authority, by the exercise of royal prerogative, in the prime minister and the secretary of state for defence. The prime minister (acting with the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
) makes the key decisions on the use of the armed forces. The UK Parliament approves the continued existence of the British Army by passing an Armed Forces Act
Armed Forces Act (with its variations) is a stock short title used for legislation in India, Malaysia and the United Kingdom relating to armed forces. The bill for an act with this short title will usually have been known as an Armed Forces Bill du ...
at least once every five years, as required by the Bill of Rights 1689. The Royal Navy, Royal Air Force, and Royal Marines among with all other forces do not require this act. The armed forces are managed by the Defence Council of the Ministry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in states ...
, headed by the secretary of state for defence.
The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear powers, a permanent member on the United Nations Security Council, founding and leading member of the NATO military alliance, and party to the AUKUS security pact and the Five Power Defence Arrangements
The Five Power Defence Arrangements (FPDA) are a series of bilateral defence relationships established by a series of multi-lateral agreements between Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United Kingdom, all of which are Commonwe ...
. Overseas garrisons and training facilities are maintained at Ascension Island
Ascension Island is an isolated volcanic island, 7°56′ south of the Equator in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is about from the coast of Africa and from the coast of South America. It is governed as part of the British Overseas Territory o ...
, Bahrain, Belize, Bermuda, British Indian Ocean Territory
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean, halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 ...
, Brunei, Canada, Cyprus, the Falkland Islands, Germany, Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
, Kenya, Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
, Nepal, Qatar, Singapore, and the United States.
History

Organisational history
With theActs of Union 1707
The Acts of Union ( gd, Achd an Aonaidh) were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act 1707 passed by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the te ...
, the armed forces of England and Scotland were merged into the armed forces of the Kingdom of Great Britain.Acts of Union 1707parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010
nationalarchives.gov.uk, accessed 31 December 2010
Making the Act of Union 1707
scottish.parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010 There were originally several naval and several military regular and reserve ''forces'', although most of these were consolidated into the Royal Navy or the British Army during the 19th and 20th Centuries (the
Royal Naval Air Service
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British Army's Royal Flying Corps t ...
and the Royal Flying Corps
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colors =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, decorations ...
of the British Army, by contrast, were separated from their parent forces in 1918 and amalgamated to form a new force, the Royal Air Force, which would have complete responsibility for naval, military and strategic aviation until the Second World War).
''Naval'' forces included the Royal Navy, the Waterguard (subsequently HM Coastguard), and Sea Fencibles and ''River Fencibles'' formed as and when required for the duration of emergencies. The Merchant Navy and offshore fishing boat crews were also important manpower reserves to the armed naval forces (any seaman was liable to impressment, with many so conscripted especially during the two decades of conflict from the French Revolution until the end of the Napoleonic Wars, and from 1835 registered on the ''Register of Seamen'' to identify them as a potential resource), and many of their seamen would serve part time in the Royal Navy Reserve (created under the ''Naval Reserve Act of 1859'') and Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a cit ...
(created in 1903).
The British military (those parts of the British Armed Forces tasked with land warfare, as opposed to the naval forces) historically was divided into a number of military forces, of which the British Army (also referred to historically as the 'Regular Army' and the 'Regular Force') was only one. The oldest of these organisations was the Militia Force (also referred to as the ''Constitutional Force''), which (in the Kingdom of England) was originally the main military defensive force (there otherwise were originally only Royal bodyguards, including the Yeomen Warders and the Yeomen of the Guard, with armies raised only temporarily for expeditions overseas), made up of civilians embodied for annual training or emergencies, and had used various schemes of compulsory service during different periods of its long existence.
The Militia was originally an all infantry force, organised at the city or county level, and members were not required to serve outside of their recruitment area, although the area within which militia units in Britain could be posted was increased to anywhere in the Britain during the Eighteenth Century, and Militia coastal artillery, field artillery, and engineers units were introduced from the 1850s.''The Militia Artillery 1852-1909'', by Norman EH Litchfield. The Sherwood Press (Nottingham) Ltd. 1987 The Yeomanry was a mounted force that could be mobilised in times of war or emergency. Volunteer Force units were also frequently raised during wartime, which did not rely on compulsory service and hence attracted recruits keen to avoid the Militia. These were seen as a useful way to add to military strength economically during wartime, but otherwise as a drain on the Militia and so were not normally maintained in peacetime, although in Bermuda prominent propertied men were still appointed ''Captains of Forts'', taking charge of maintaining and commanding fortified coastal artillery batteries and manned by volunteers (reinforced in wartime by embodied militiamen), defending the colony's coast from the Seventeenth Century to the Nineteenth Century (when all of the batteries were taken over by the regular Royal Artillery). The Militia system was extended to a number of English (subsequently ''British'') colonies, beginning with Virginia and Bermuda. In some colonies, ''Troops of Horse'' or other mounted units similar to the Yeomanry were also created. The Militia and Volunteer units of a colony were generally considered to be separate forces from the ''Home'' Militia Force and Volunteer Force in the United Kingdom, and from the Militia Forces and Volunteer Forces of other colonies. Where a colony had more than one Militia or Volunteer unit, they would be grouped as a Militia or Volunteer Force for that colony, such as the Jamaica Volunteer Defence Force
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispanio ...
, which comprised the St. Andrew Rifle Corps
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy an ...
(or Kingston Infantry Volunteers
Kingston may refer to:
Places
* List of places called Kingston, including the five most populated:
** Kingston, Jamaica
** Kingston upon Hull, England
** City of Kingston, Victoria, Australia
** Kingston, Ontario, Canada
** Kingston upon Thames, ...
), the Jamaica Corps of Scouts
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispan ...
, and the Jamaica Reserve Regiment
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispan ...
, but not the Jamaica Militia Artillery
The Militia of the British Dominions, Self-Governing Colonies, and Crown Colonies were the principal military forces of the Dominions, Self-governing colonies (those with elected local legislatures) and Crown Colonies (those without elected local l ...
. In smaller colonies with a single militia or volunteer unit, that single unit would still be considered to be listed within a force, or in some case might be named a force rather than a regiment or corps, such as is the case for the Falkland Islands Defence Force and the Royal Montserrat Defence Force
The Royal Montserrat Defence Force is the home defence unit of the British Overseas Territory of Montserrat.
History
Raised in 1899, the unit is today a reduced force of about forty volunteer soldiers, primarily concerned with civil Defence and ...
. The Militia, Yeomanry and Volunteer Forces collectively were known as the ''Reserve Forces'', ''Auxiliary Forces'', or ''Local Forces''. Officers of these forces could not sit on Courts Martial of regular forces personnel. The Mutiny Act did not apply to members of the Reserve Forces.
The other ''regular'' military force that existed alongside the British Army was the Board of Ordnance
The Board of Ordnance was a British government body. Established in the Tudor period, it had its headquarters in the Tower of London. Its primary responsibilities were 'to act as custodian of the lands, depots and forts required for the defence ...
, which included the ''Ordnance Military Corps'' (made up of the Royal Artillery, Royal Engineers, and the Royal Sappers and Miners), as well as the originally-civilian Commissariat Stores and transport departments, as well as barracks departments, ordnance factories and various other functions supporting the various naval and military forces. The English Army, subsequently the British Army once Scottish regiments were moved onto its establishment following the Union of the Kingdoms of Scotland and England, was originally a separate force from these, but absorbed the Ordnance Military Corps and various previously civilian departments after the Board of Ordnance was abolished in 1855. The ''Reserve Forces'' (which referred to the Home Yeomanry, Militia and Volunteer Forces before the 1859 creation of the British Army ''Regular Reserve'' by Secretary of State for War
The Secretary of State for War, commonly called War Secretary, was a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, which existed from 1794 to 1801 and from 1854 to 1964. The Secretary of State for War headed the War Office and ...
Sidney Herbert, and re-organised under the ''Reserve Force Act, 1867'') were increasingly integrated with the British Army through a succession of reforms over the last two decades of the Nineteenth Century (in 1871, command of the Auxiliary Forces in the British Isles was taken from the Lords-Lieutenant of counties and transferred to the War Office, though colonial Governors retained control of their militia and volunteer forces, and by the end of the century, at the latest, any unit wholly or partly funded from Army Funds was considered part of the British Army) and the early years of the Twentieth Century, whereby the Reserve Forces units mostly lost their own identities and became numbered Territorial Force sub-units of regular British Army corps or regiments (the Home Militia had followed this path, with the Militia Infantry units becoming numbered battalions of British Army regiments, and the Militia Artillery integrating within Royal Artillery territorial divisions in 1882 and 1889, and becoming parts of the Royal Field Artillery
The Royal Field Artillery (RFA) of the British Army provided close artillery support for the infantry. It came into being when created as a distinct arm of the Royal Regiment of Artillery on 1 July 1899, serving alongside the other two arms of t ...
or Royal Garrison Artillery in 1902 (though retaining their traditional corps names), but was not merged into the Territorial Force when it was created in 1908 (by the merger of the Yeomanry and Volunteer Force). The Militia was instead renamed the ''Special Reserve'', and was permanently suspended after the First World War (although a handful of Militia units survived in the United Kingdom, its colonies, and the Crown Dependencies). Unlike the Home, Imperial Fortress and Crown Dependency Militia and Volunteer units and forces that continued to exist after the First World War, although parts of the British military, most were not considered parts of the British Army unless they received Army Funds (as was the case for the Bermuda Militia Artillery and the Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps
The Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps (BVRC) was created in 1894 as a reserve for the Regular Army infantry component of the Bermuda Garrison. Renamed the ''Bermuda Rifles'' in 1951, it was amalgamated into the Bermuda Regiment in 1965.
Formation
A ...
), which was generally only the case for those in the Channel Islands or the Imperial Fortress colonies (Nova Scotia, before Canadian confederation, Bermuda, Gibraltar, and Malta). Today, the British Army is the only Home British military force (unless the Army Cadet Force and the Combined Cadet Force
The Combined Cadet Force (CCF) is a youth organisation in the United Kingdom, sponsored by the Ministry of Defence (MOD), which operates in schools, and normally includes Army, Royal Navy and Royal Air Force sections. Its aim is to "provide a ...
are considered), including both the regular army and the forces it absorbed, though British military units organised on Territorial lines remain in British Overseas Territories that are still not considered formally part of the British Army, with only the Royal Gibraltar Regiment and the Royal Bermuda Regiment (an amalgam of the old Bermuda Militia Artillery and Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps) appearing on the British Army order of precedence and in the Army List.
Confusingly, and similarly to the dual meaning of the word Corps in the British Army (by example, the 1st Battalion of the King's Royal Rifle Corps
The King's Royal Rifle Corps was an infantry rifle regiment of the British Army that was originally raised in British North America as the Royal American Regiment during the phase of the Seven Years' War in North America known in the United St ...
was in 1914 part of the 6th Brigade that was part of the 2nd Infantry Division, which was itself part of 1st Army Corps), the British Army sometimes also used the term expeditionary force or field force to describe a body made up of British Army units, most notably the British Expeditionary Force, or of a mixture of British Army, Indian Army, or Imperial auxiliary units, such as the Malakand Field Force (this is similarly to the naval use of the term task force). In this usage, ''force'' is used to describe a self-reliant body able to act without external support, at least within the parameters of the task or objective for which it is employed.
Empire and World Wars
 During the later half of the seventeenth century, and in particular, throughout the eighteenth century, British foreign policy sought to contain the expansion of rival European powers through military, diplomatic and commercial means – especially of its chief competitors; Spain, the Netherlands and France. This saw Britain engage in a number of intense conflicts over colonial possessions and world trade, including a long string of Anglo-Spanish and Anglo-Dutch wars, as well as a series of "world wars" with France, such as; the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802) and the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815). During the Napoleonic wars, the Royal Navy victory at
During the later half of the seventeenth century, and in particular, throughout the eighteenth century, British foreign policy sought to contain the expansion of rival European powers through military, diplomatic and commercial means – especially of its chief competitors; Spain, the Netherlands and France. This saw Britain engage in a number of intense conflicts over colonial possessions and world trade, including a long string of Anglo-Spanish and Anglo-Dutch wars, as well as a series of "world wars" with France, such as; the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802) and the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815). During the Napoleonic wars, the Royal Navy victory at Trafalgar Trafalgar most often refers to:
* Battle of Trafalgar (1805), fought near Cape Trafalgar, Spain
* Trafalgar Square, a public space and tourist attraction in London, England
It may also refer to:
Music
* ''Trafalgar'' (album), by the Bee Gees
Pl ...
(1805) under the command of Horatio Nelson
Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte (29 September 1758 – 21 October 1805) was a British flag officer in the Royal Navy. His inspirational leadership, grasp of strategy, and unconventional tactics brought abo ...
(aboard HMS ''Victory'') marked the culmination of British maritime supremacy, and left the Navy in a position of uncontested hegemony at sea. By 1815 and the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars, Britain had risen to become the world's dominant great power and the British Empire subsequently presided over a period of relative peace, known as Pax Britannica., pp. 508–10.
With Britain's old rivals no-longer a threat, the nineteenth century saw the emergence of a new rival, the Russian Empire, and a strategic competition in what became known as The Great Game for supremacy in Central Asia. Britain feared that Russian expansionism in the region would eventually threaten the Empire in India. In response, Britain undertook a number of pre-emptive actions against perceived Russian ambitions, including the First Anglo-Afghan War (1839–1842), the Second Anglo-Afghan War (1878–1880) and the British expedition to Tibet (1903–1904). During this period, Britain also sought to maintain the balance of power in Europe, particularly against Russian expansionism, who at the expense of the waning Ottoman Empire had ambitions to "carve up the European part of Turkey". This ultimately led to British involvement in the Crimean War (1854–1856) against the Russian Empire.
 The beginning of the twentieth century served to reduce tensions between Britain and the Russian Empire, partly due to the emergence of a unified
The beginning of the twentieth century served to reduce tensions between Britain and the Russian Empire, partly due to the emergence of a unified German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
. The era brought about an Anglo-German naval arms race which encouraged significant advancements in maritime technology (e.g. Dreadnoughts, torpedoes and submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s), and in 1906, Britain had determined that its only likely naval enemy was Germany. The accumulated tensions in European relations finally broke out into the hostilities of the First World War (1914–1918), in what is recognised today, as the most devastating war in British military history, with nearly 800,000 men killed and over 2 million wounded. Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
victory resulted in the defeat of the Central Powers, the end of the German Empire, the Treaty of Versailles and the establishment of the League of Nations.
 Although Germany had been defeated during the First World War, by 1933 fascism had given rise to Nazi Germany, which under the leadership of Adolf Hitler re-militarised in defiance of the Treaty of Versailles. Once again tensions accumulated in European relations, and following Germany's invasion of Poland in September 1939, the Second World War began (1939–1945). The conflict was the most widespread in British history, with British Empire and
Although Germany had been defeated during the First World War, by 1933 fascism had given rise to Nazi Germany, which under the leadership of Adolf Hitler re-militarised in defiance of the Treaty of Versailles. Once again tensions accumulated in European relations, and following Germany's invasion of Poland in September 1939, the Second World War began (1939–1945). The conflict was the most widespread in British history, with British Empire and Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
troops fighting in campaigns from Europe and North Africa, to the Middle East and the Far East. Approximately 390,000 British Empire and Commonwealth troops lost their lives. Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
victory resulted in the defeat of the Axis powers and the establishment of the United Nations (replacing the League of nations).
The Cold War
, raf.mod.uk and later epitomised by its political defeat during the
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
(1956). Reflecting Britain's new role in the world and the escalation of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
(1947–1991), the country became a founding member of the NATO military alliance in 1949. Defence Review A Defence Review is the process by which government of the United Kingdom decides upon its overall defence policy and upon the means and resources devoted to achieving its defence objectives. Such reviews can happen when political or economic factor ...
s, such as those in 1957
1957 ( MCMLVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Gregorian calendar, the 1957th year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 957th year of the 2nd millennium, the 57th year of the 20th century, and the 8th y ...
and 1966
Events January
* January 1 – In a coup, Colonel Jean-Bédel Bokassa takes over as military ruler of the Central African Republic, ousting President David Dacko.
* January 3 – 1966 Upper Voltan coup d'état: President Maurice Yaméogo i ...
, announced significant reductions in conventional forces, the pursuement of a doctrine based on nuclear deterrence
Deterrence theory refers to the scholarship and practice of how threats or limited force by one party can convince another party to refrain from initiating some other course of action. The topic gained increased prominence as a military strategy ...
, and a permanent military withdrawal East of Suez. By the mid-1970s, the armed forces had reconfigured to focus on the responsibilities allocated to them by NATO.Vanguard to Trident 1945–2000, royal-navy.mod.ukKennedy (2004), ''British Naval Strategy East of Suez, 1900–2000: Influence and Actions'', p193 The British Army of the Rhine and RAF Germany consequently represented the largest and most important overseas commitments that the armed forces had during this period, while the Royal Navy developed an anti-submarine warfare specialisation, with a particular focus on countering Soviet submarines in the Eastern Atlantic and North Sea. While NATO obligations took increased prominence, Britain nonetheless found itself engaged in a number of low-intensity conflicts, including a spate of insurgencies against colonial occupation.Chandler & Beckett (2003), pp350–351 However the
Dhofar Rebellion
The Dhofar Rebellion, also known as the Dhofar War or the Omani Civil War, was waged from 1963 to 1976 in the province of Dhofar against the Sultanate of Muscat and Oman. The war began with the formation of the Dhofar Liberation Front, a group ...
(1962–1976) and The Troubles (1969–1998) emerged as the primary operational concerns of the armed forces. Perhaps the most important conflict during the Cold War, at least in the context of British defence policy, was the Falklands War
The Falklands War ( es, link=no, Guerra de las Malvinas) was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial de ...
(1982).
Since the end of the Cold War, an increasingly international role for the armed forces has been pursued, with re-structuring to deliver a greater focus on expeditionary warfare and power projection
Power projection (or force projection or strength projection), in international relations, is the capacity of a state to deploy and sustain forces outside its territory. The ability of a state to project its power into an area may serve as an e ...
. This entailed the armed forces often constituting a major component in peacekeeping
Peacekeeping comprises activities intended to create conditions that favour lasting peace. Research generally finds that peacekeeping reduces civilian and battlefield deaths, as well as reduces the risk of renewed warfare.
Within the United N ...
and humanitarian missions under the auspices of the United Nations, NATO, and other multinational operations, including: peacekeeping responsibilities in the Balkans and Cyprus, the 2000 intervention in Sierra Leone and participation in the UN-mandated no-fly zone over Libya (2011). Post- September 11, the armed forces have been heavily committed to the War on Terror (2001–present), with lengthy campaigns in Afghanistan (2001–2021) and Iraq (2003–2009), and more recently as part of the Military intervention against ISIL (2014–present). Britain's military intervention against Islamic State was expanded following a parliamentary vote to launch a bombing campaign over Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
; an extension of the bombing campaign requested by the Iraqi government against the same group. In addition to the aerial campaign, the British Army has trained and supplied allies on the ground and the Special Air Service
The Special Air Service (SAS) is a special forces unit of the British Army. It was founded as a regiment in 1941 by David Stirling and in 1950, it was reconstituted as a corps. The unit specialises in a number of roles including counter-terro ...
, the Special Boat Service, and the Special Reconnaissance Regiment (British special forces) has carried out various missions on the ground in both Syria and Iraq.
The armed forces have also been called upon to assist with national emergencies through the provisions of the military aid to the civil authorities (MACA) mechanism. This has seen the armed forces assist government departments and civil authorities responding to flooding, food shortages, wildfires, terrorist attacks and, most notably, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic; the armed forces' support to the latter falls under Operation Rescript, described as the UK's "biggest ever homeland military operation in peacetime" by the Ministry of Defence.
Figures released by the Ministry of Defence on 31 March 2016 show that 7,185 British Armed Forces personnel have lost their lives in medal earning theatres since the end of the Second World War.UK Armed Forces Deaths: Operational deaths post World War II 3 September 1945 to 17 February 2016, Ministry of Defence, gov.uk, Published 31 March 2016
Today
Command organisation

 King Charles III, sovereign of the United Kingdom, is the Head of the Armed Forces, with officers and personnel swearing allegiance to him. Long-standing constitutional convention, however, has ''de facto'' vested military authority and associated royal prerogative powers in the prime minister and the secretary of state for defence, with the former (acting with the support of the
King Charles III, sovereign of the United Kingdom, is the Head of the Armed Forces, with officers and personnel swearing allegiance to him. Long-standing constitutional convention, however, has ''de facto'' vested military authority and associated royal prerogative powers in the prime minister and the secretary of state for defence, with the former (acting with the support of the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
) making the key decisions on the use of the armed forces. The sovereign retains the power to prevent the unconstitutional use of the armed forces, including that of its nuclear arsenal.
The Ministry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in states ...
is the government department charged with formulating and executing defence policy. It currently employs 56,860 civilian staff members as of 1 October 2015. The department is administered by the secretary of state for defence who is assisted by the Minister of State for the Armed Forces, Minister for Defence Procurement, and Minister for Veterans' Affairs. Responsibility for the management of the forces is delegated to a number of committees: the Defence Council, Chiefs of Staff Committee, Defence Management Board and three single-service boards. The Defence Council, composed of senior representatives of the services and the Ministry of Defence, provides the "formal legal basis for the conduct of defence". The three constituent single-service committees ( Admiralty Board, Army Board
The Army Board is the top single-service management committee of the British Army, and has always been staffed by senior politicians and soldiers. Until 1964 it was known as the Army Council.
Membership of the Board
The composition is as follo ...
and Air Force Board) are chaired by the secretary of state for defence.
The chief of the defence staff (CDS) is the senior-most officer of the armed forces and is an appointment that can be held by an admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, ...
, air chief marshal
Air chief marshal (Air Chf Mshl or ACM) is a high-ranking air officer originating from the Royal Air Force. The rank is used by air forces of many countries that have historical British influence. An air chief marshal is equivalent to an Admir ...
or general. Before the practice was discontinued in the 1990s, those who were appointed to the position of CDS had been elevated to the most senior rank in their respective service. The CDS, along with the permanent under secretary, are the principal military advisers to the secretary of state. All three services have their own respective professional chiefs; the First Sea Lord for the Royal Navy, the chief of the general staff for the Army and the chief of the air staff for the Royal Air Force.
Personnel
 The British Armed Forces are a professional force with a strength of 153,290 UK Regulars and Gurkhas, 37,420
The British Armed Forces are a professional force with a strength of 153,290 UK Regulars and Gurkhas, 37,420 Volunteer Reserve
Volunteering is a voluntary act of an individual or group wikt:gratis, freely giving time and labor for community service. Many volunteers are specifically trained in the areas they work, such as medicine, education, or emergency rescue. O ...
s and 8,170 "Other Personnel" .UK Armed Forces: Quarterly Service Personnel Statistics. 1 April 2021. MoD. Published 27 May 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2021. See table 1, page 4. This gives a total strength of 198,880 "UK Service Personnel". As a percentage breakdown of UK Service Personnel, 77.1% are UK Regulars and Gurkhas, 18.8% are Volunteer Reserves and 4.1% are composed of Other Personnel. In addition, all ex-Regular personnel retain a "statutory liability for service" and are liable to be recalled (under Section 52 of the Reserve Forces Act (RFA) 1996) for duty during wartime, which is known as the Regular Reserve. MoD publications since April 2013 no longer report the entire strength of the Regular Reserve, instead they only give a figure for Regular Reserves who serve under a fixed-term reserve contract. These contracts are similar in nature to those of the Volunteer Reserve.gov.uk MoD – reserves and cadet strengths
, table 4 page 13. See note 2. April 2014. , Regular Reserves serving under a fixed-term contract numbered 44,600 personnel.gov.uk MoD – reserves and cadet strengths
, table 1a-page 10. 12 July 1690. The distribution of personnel between the services and categories of service on 1 April 2021 was as follows: , there were a total of 9,330 Regular service personnel stationed outside of the United Kingdom, 3,820 of those were located in Germany. 138,040 Regular service personnel were stationed in the United Kingdom, the majority located in the South East and South West of England with 37,520 and 36,790 Regular service personnel, respectively.
Defence expenditure
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) is an international institute based in Stockholm. It was founded in 1966 and provides data, analysis and recommendations for armed conflict, military expenditure and arms trade as well a ...
, the United Kingdom has the fourth-largest defence budget in the world. For comparison's sake, this sees Britain spending more in absolute terms than France, Germany, India or Japan, a similar amount to that of Russia, but less than China, Saudi Arabia or the United States. In September 2011, according to Professor Malcolm Chalmers of the Royal United Services Institute, current "planned levels of defence spending should be enough for the United Kingdom to maintain its position as one of the world's top military powers, as well as being one of NATO-Europe's top military powers. Its edge – not least its qualitative edge – in relation to rising Asian powers seems set to erode, but will remain significant well into the 2020s, and possibly beyond." The Strategic Defence and Security Review 2015 The National Security Strategy and Strategic Defence and Security Review 2015 was published by the British government during the second Cameron ministry on 23 November 2015 to outline the United Kingdom's defence strategy up to 2025. It identified k ...
committed to spending 2% of GDP on defence and announced a £178 billion investment over ten years in new equipment and capabilities.
Nuclear weapons
 The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear weapon states under the Non-Proliferation Treaty and maintains an independent nuclear deterrent, currently consisting of four
The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear weapon states under the Non-Proliferation Treaty and maintains an independent nuclear deterrent, currently consisting of four ballistic missile submarine
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. The United States Navy's hull classification symbols for ballistic missile submarines are SSB and SSBN – t ...
s, UGM-133 Trident II submarine-launched ballistic missile
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which carries a nuclear warhead ...
s, and 160 operational thermonuclear warheads. This is known as Trident in both public and political discourse (with nomenclature taken after the UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missile). Trident is operated by the Royal Navy Submarine Service, charged with delivering a 'Continuous At-Sea Deterrent' (CASD) capability, whereby one of the ''Vanguard''-class strategic submarines is always on patrol.Royal Navy – Continuous at sea deterrent, royalnavy.mod.uk, Accessed 6 December 2014 According to the British Government, since the introduction of
Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris ( Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an apparent magnitude that ...
(Tridents predecessor) in the 1960s, from April 1969 "the Royal Navy's ballistic missile boats have not missed a single day on patrol", giving what the Defence Council described in 1980 as a deterrent "effectively invulnerable to pre-emptive attack". As of 2015, it has been British Government policy for the ''Vanguard''-class strategic submarines to carry no more than 40 nuclear warheads, delivered by eight UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missiles. In contrast with the other recognised nuclear weapon states, the United Kingdom operates only a submarine-based delivery system, having decommissioned its tactical WE.177 free-fall bombs in 1998.
The House of Commons voted on 18 July 2016 in favour of replacing the ''Vanguard''-class submarines with a new generation of s. The programme will also contribute to extending the life of the UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missiles and modernise the infrastructure associated with the CASD.
Former weapons of mass destruction possessed by the United Kingdom include both biological and chemical weapons. These were renounced in 1956 and subsequently destroyed.
Overseas military installations
 The British Armed Forces maintain a number of overseas garrisons and military facilities which enable the country to conduct operations worldwide. The majority of Britain's permanent military installations are located on
The British Armed Forces maintain a number of overseas garrisons and military facilities which enable the country to conduct operations worldwide. The majority of Britain's permanent military installations are located on British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remna ...
(BOTs) or former colonies
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature.
A former may become an integral part of the ...
which retain close diplomatic ties with the United Kingdom, and located in areas of strategic importance. The most significant of these are the "Permanent Joint Operating Bases" (PJOBs), located on the four overseas territories of Cyprus ( British Forces Cyprus), Gibraltar ( British Forces Gibraltar), the Falkland Islands ( British Forces South Atlantic Islands) and Diego Garcia (British Forces British Indian Ocean Territories
British Forces British Indian Ocean Territories (BFBIOT) is the name for the British Armed Forces Permanent Joint Operating Base (PJOB) on Diego Garcia, in the British Indian Ocean Territory.
). While not a PJOB, Ascension Island (another BOT) is home to the airbase RAF Ascension Island, notable for use as a staging post during the 1982 Falklands War
The Falklands War ( es, link=no, Guerra de las Malvinas) was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial de ...
, the territory is also the site of a joint UK-US signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ( ...
facility.
Qatar is home to RAF Al Udeid
Al Udeid Air Base ( ar, قاعدة العديد الجوية) is one of two military bases southwest of Doha, Qatar, also known as Abu Nakhlah Airport ().
It houses the Qatar Emiri Air Force, United States Air Force, Royal Air Force, and othe ...
, a Royal Air Force outpost at Al Udeid Air Base which serves as the operational headquarters for No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group
No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group is a group within the Royal Air Force, currently based at Al Udeid Air Base in Qatar.
Originally formed in 1943, during the Second World War it formed part of the 2nd Tactical Air Force (2TAF) and was known as No ...
and its operations across the Middle East. A large Royal Navy Naval Support Facility (NSF) is located in Bahrain, established in 2016 it marks the British return East of Suez. In support of the Five Power Defence Arrangements
The Five Power Defence Arrangements (FPDA) are a series of bilateral defence relationships established by a series of multi-lateral agreements between Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United Kingdom, all of which are Commonwe ...
(FPDA), the United Kingdom retains a naval repair and logistics support facility at Sembawang wharf, Singapore. ("''The White Ensign is still flying above the operations of Naval Party 1022 (NP1022), based at Sembawang Wharves in Singapore.''") Other overseas military installations include; British Forces Brunei, British Forces Germany
British Forces Germany (''BFG'') was the generic name for the three services of the British Armed Forces, made up of service personnel, UK Civil Servants, and dependents (family members), based in Germany. It was established following the Second ...
, the British Army Training Unit Kenya, British Army Training Unit Suffield
The British Army Training Unit Suffield (BATUS) is a British Army unit located at the vast training area of Canadian Forces Base Suffield near Suffield, Alberta, Canada. BATUS is the British Army's largest armoured training facility, and it can ...
in Canada, British Army Training and Support Unit Belize
British Army Training Support Unit Belize (BATSUB), the successor of the former British Forces Belize, is the name given to the current British Army Garrison in Belize. The garrison is used primarily for jungle warfare training, with access to o ...
, and British Gurkhas Nepal.
Some British Overseas Territories also maintain locally raised units and regiments; The Royal Bermuda Regiment
The Royal Bermuda Regiment (RBR), formerly the Bermuda Regiment, is the home defence unit of the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is a single territorial infantry battalion that was formed on the amalgamation in 1965 of two originally ...
, the Falkland Islands Defence Force, the Royal Gibraltar Regiment, the Royal Montserrat Defence Force
The Royal Montserrat Defence Force is the home defence unit of the British Overseas Territory of Montserrat.
History
Raised in 1899, the unit is today a reduced force of about forty volunteer soldiers, primarily concerned with civil Defence and ...
, the Cayman Islands Regiment
The Cayman Islands Regiment is the home defence unit of the British Overseas Territory of the Cayman Islands. It is a single territorial infantry and engineer battalion of the British Armed Forces that was formed in 2020.
History
2019
On 12 ...
, and the Turks and Caicos Regiment. Though their primary mission is "home defence", individuals have volunteered for operational duties. The Royal Gibraltar Regiment mobilised section-sized units for attachment to British regiments deployed during the Iraq War. The Isle of Man, a Crown dependency hosts a multi-capability recruiting and training unit of the British Army Reserve.
Since 1969 Britain has had a military satellite communications system, Skynet
Skynet may refer to:
Airlines
* Sky Net Airline, a charter airline from Armenia
* Skynet (airline), a Russian regional airline based at the Krasnoyarsk Airport
* Skynet Airlines, a defunct Irish airline that operated in 2001–2004
* Skynet, a d ...
, initially in large part to support East of Suez bases and deployments. Since 2015 Skynet has offered near global coverage.
Expeditionary forces
The British Armed Forces place significant importance in the ability to conduct expeditionary warfare. Professor of International Politics, Adrian Hyde-Price, highlights that in the post-Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
era both Britain and France have re-focused their attention ''"towards expeditionary warfare and power projection
Power projection (or force projection or strength projection), in international relations, is the capacity of a state to deploy and sustain forces outside its territory. The ability of a state to project its power into an area may serve as an e ...
. Power projection has always been an element of British and French military thinking given their residual over seas interests, but it has now moved centre stage."'' While the armed forces are expeditionary in nature, it maintains a core of "high readiness" forces trained and equipped to deploy at very short notice, these include; the Joint Expeditionary Force (Maritime) (Royal Navy), 3 Commando Brigade
3 Commando Brigade (3 Cdo Bde), previously called the 3rd Special Service Brigade, is a commando formation of the British Armed Forces. It is composed of the Royal Marine Commandos, alongside commando qualified sailors, soldiers and airmen f ...
(Royal Marines), and 16 Air Assault Brigade
16 Air Assault Brigade Combat Team, from 1999 to 2021 16 Air Assault Brigade, is a formation of the British Army based in Colchester in the county of Essex. It is the Army's rapid response airborne formation and is the only brigade in the Britis ...
(British Army). Frequently, these forces will act as part of a larger tri-service effort, under the direction of Permanent Joint Headquarters, or along with like-minded allies under the UK Joint Expeditionary Force. Similarly, under the auspices of NATO, such expeditionary forces are designed to meet Britain's obligations to the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps
The Allied Rapid Reaction Corps (ARRC) is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization High Readiness Force (Land) Headquarters ready for deployment worldwide.
History
The ARRC was created on 1 October 1992 in Bielefeld based on the former I (Britis ...
and other NATO operations.
In 2010, the governments of the United Kingdom and France signed the Lancaster House Treaties which committed both governments to the creation of a Franco-British Combined Joint Expeditionary Force. It is envisaged as a deployable joint force, for use in a wide range of crisis scenarios, up to and including high intensity combat operations. As a joint force it involves all three armed Services: a land component composed of formations at national brigade level, maritime and air components with their associated Headquarters, together with logistics and support functions.
The Armed Forces
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is a technologically sophisticated naval force, and as of October 2022 consists of 72 commissioned ships with an additional 11 support vessels of various types operated by the Royal Fleet Auxiliary. Command of deployable assets is exercised by the Fleet Commander of theNaval Service Naval Service may refer to either:
* His Majesty's Naval Service, Britain's Royal Navy plus additional services
* Naval Service (Ireland), a branch of the Irish Defence Forces
* United States Department of the Navy, United States military department ...
. Personnel matters are the responsibility of the Second Sea Lord/Commander-in-Chief Naval Home Command, an appointment usually held by a vice-admiral.
The Surface Fleet consists of aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a ...
s, amphibious warfare ships, destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s, frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and ...
s, patrol vessels, mine-countermeasure vessels, and other miscellaneous vessels. The Surface Fleet has been structured around a single fleet since the abolition of the Eastern and Western fleets in 1971. The recently built Type 45 destroyers are technologically advanced air-defence destroyers. The Royal Navy has commissioned two s, embarking an air-group including the advanced fifth-generation multi-role fighter, the F-35B.
A submarine service has existed within the Royal Navy for more than 100 years. The Submarine Service's four nuclear-powered submarines carry Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
's Trident II ballistic missiles, forming the United Kingdom's nuclear deterrent. Seven nuclear-powered attack submarines have been ordered, with five completed and two under construction. The ''Astute'' class are the most advanced and largest fleet submarines ever built for the Royal Navy, and will maintain Britain's nuclear-powered submarine fleet capabilities for decades to come.
Royal Marines
The Royal Marines are the Royal Navy's amphibious troops. Consisting of a single manoeuvre brigade (3 Commando
No. 3 Commando was a battalion-sized Commando unit raised by the British Army during the Second World War. Formed in July 1940 from volunteers for special service, it was the first such unit to carry the title of "Commando". Shortly afterwards the ...
) and various independent units, the Royal Marines specialise in amphibious
Amphibious means able to use either land or water. In particular it may refer to:
Animals
* Amphibian, a vertebrate animal of the class Amphibia (many of which live on land and breed in water)
* Amphibious caterpillar
* Amphibious fish, a fish ...
, arctic, and mountain warfare. Contained within 3 Commando Brigade are three attached army units; 383 Commando Petroleum Troop RLC, 29th Commando Regiment Royal Artillery
29 Commando Regiment, Royal Artillery is the Commando-trained unit of the British Army's Royal Artillery, based in Plymouth. The regiment is under the operational control of 3 Commando Brigade, to which it provides artillery support and gunnery ...
, a field artillery regiment based in Plymouth, and 24 Commando Regiment Royal Engineers
24 Commando Royal Engineers is a unit of the British Army's Royal Engineers supporting 3 Commando Brigade.
History
The regiment, which was formed in April 2008, is one of two British Army units attached to 3 Commando Brigade, Royal Marines, th ...
. The Commando Logistic Regiment consists of personnel from the Army, Royal Marines, and Royal Navy.
British Army
 The British Army is made up of the Regular Army and the Army Reserve. The army has a single command structure based at Andover and known as "Army Headquarters".Army Command reorganization
The British Army is made up of the Regular Army and the Army Reserve. The army has a single command structure based at Andover and known as "Army Headquarters".Army Command reorganizationDefence Marketing Intelligence, 10 November 2011 Deployable combat formations consist of two divisions ( 1st and 3rd Mechanised) and eight brigades. Within the United Kingdom, operational and non-deployable units are administered by two divisions, Force Troops Command, and
London District
London District (LONDIST) is the name given by the British Army to the area of operations encompassing the Greater London area. It was established in 1870 as ''Home District''.
History
In January 1876 a ‘Mobilization Scheme for the forces in ...
.
The Army has 50 battalions (36 regular and 14 reserve) of regular and reserve infantry, organised into 17 regiments. The majority of infantry regiments contains multiple regular and reserve battalions. Modern infantry have diverse capabilities and this is reflected in the varied roles assigned to them. There are four operational roles that infantry battalions can fulfil: air assault
Air assault is the movement of ground-based military forces by vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft—such as the helicopter—to seize and hold key terrain which has not been fully secured, and to directly engage enemy forces behind e ...
, armoured infantry, mechanised infantry
Mechanized infantry are infantry units equipped with armored personnel carriers (APCs) or infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) for transport and combat (see also mechanized force).
As defined by the United States Army, mechanized infantry is di ...
, and light role infantry. Regiments and battalions e.g.: the Parachute Regiment, exist within every corps of the Army, functioning as administrative or tactical formations.
Armoured regiments are equivalent to an infantry battalion. There are 14 armoured regiments within the army, ten regular and four yeomanry (armoured reserve), of which four are designated as " Armoured", three as " Armoured cavalry", and six as "Light Cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was primarily rai ...
". Army 2020 Refine has seen developments which will further modify the Royal Armoured Corps. with two existing regiments forming the core of two new STRIKE Brigades. These two regiments, along with the Armoured Cavalry will be equipped with the " Ajax" armoured fighting vehicle, a new £3.5 billion procurement programme. The Ajax will be employed in the task organisation and roles of both Armoured Cavalry and Medium Armour. With a slight exception of the Household Cavalry, which maintains quasi-autonomy within the Household Division, armoured regiments and their yeomanry counterparts collectively form the Royal Armoured Corps.
Arms and support units are also formed into similar collectives organised around specific purposes, such as the Corps of Royal Engineers, Army Air Corps and Royal Army Medical Corps
The Royal Army Medical Corps (RAMC) is a specialist corps in the British Army which provides medical services to all Army personnel and their families, in war and in peace. The RAMC, the Royal Army Veterinary Corps, the Royal Army Dental Corps a ...
.
Royal Air Force
 The Royal Air Force has a large operational fleet that fulfils various roles, consisting of both fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. Frontline aircraft are controlled by Air Command, which is organised into five groups defined by function: 1 Group (Air Combat), 2 Group (Air Support), 11 Group (Air and Space operations), 22 Group (training aircraft and ground facilities) and 38 Group (Royal Air Force's Engineering, Logistics, Communications and Medical Operations units). In addition 83 Expeditionary Air Group directs formations in the Middle East and the 38 Group combines the expeditionary combat support and
The Royal Air Force has a large operational fleet that fulfils various roles, consisting of both fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. Frontline aircraft are controlled by Air Command, which is organised into five groups defined by function: 1 Group (Air Combat), 2 Group (Air Support), 11 Group (Air and Space operations), 22 Group (training aircraft and ground facilities) and 38 Group (Royal Air Force's Engineering, Logistics, Communications and Medical Operations units). In addition 83 Expeditionary Air Group directs formations in the Middle East and the 38 Group combines the expeditionary combat support and combat service support
The term combat service support (or CSS) is utilized by numerous military organizations throughout the world to describe entities that provide direct and indirect sustainment services to the groups that engage (or are potentially to be engaged) ...
units of the RAF. Deployable formations consist of Expeditionary Air Wings and squadrons—the basic unit of the Air Force. Independent flights are deployed to facilities in Afghanistan, the Falkland Islands, Iraq, and the United States.
The Royal Air Forces operates multi-role and single-role fighters, reconnaissance and patrol aircraft, tankers, transports, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles, and various types of training aircraft. Ground units are also maintained by the Royal Air Force, most prominently the RAF Police and the Royal Air Force Regiment (RAF Regt). The Royal Air Force Regiment essentially functions as the ground defence force of the RAF, optimised for the specialist role of fighting on and around forward airfields, which are densely packed with operationally vital aircraft, equipment, infrastructure and personnel . The Regiment contains nine regular squadrons, supported by five squadrons of the Royal Auxiliary Air Force
The Royal Auxiliary Air Force (RAuxAF), formerly the Auxiliary Air Force (AAF), together with the Air Force Reserve, is a component of His Majesty's Reserve Air Forces (Reserve Forces Act 1996, Part 1, Para 1,(2),(c)). It provides a primary rein ...
Regiment. In addition, it provides the UK's specialist Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear capability. It also provides half of the UK's Forward Air Controllers and the RAF's contribution to the Special Forces Support Group. By March 2008, the three remaining Ground Based Air Defence squadrons (equipped with Rapier Field Standard C) had disbanded or re-roled and their responsibilities transferred to the British Army's Royal Artillery.
Ministry of Defence
The Ministry of Defence maintains a number civilian agencies in support of the British Armed Forces. Although they are civilian, they play a vital role in supporting Armed Forces operations, and in certain circumstances are under military discipline: * The Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) operates 13 ships which primarily serve to replenish Royal Navy warships at sea, and also augment the Royal Navy's amphibious warfare capabilities through its three vessels. It is manned by 1,850 civilian personnel and is funded and run by the Ministry of Defence. * The Ministry of Defence Police (MDP) has an established strength of 2,700 police officers which provide armed security, counter terrorism, uniformed policing and investigative services to Ministry of Defence property, personnel, and installations throughout the United Kingdom. * The Defence Equipment and Support (DE&S) is the merged procurement and support organisation within the UK Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom). It came into being on 2 April 2007, bringing together the MoD's Defence Procurement Agency and the Defence Logistics Organisation under the leadership of General Sir Kevin O'Donoghue as the firstChief of Defence Materiel
The Chief Executive Officer of Defence Equipment and Support, formerly the Chief of Defence Materiel, is a senior post in the UK Ministry of Defence created in April 2007. It merges the roles of Chief of Defence Procurement and Chief of Defence Log ...
. it has a civilian and military workforce of approx. 20,000 personnel. DE&S is overseen by the Minister for Defence Equipment, Support and Technology.
* The UK Hydrographic Office (UKHO) is an organisation within the UK government responsible for providing navigational and other hydrographic information for national, civil and defence requirements. The UKHO is located in Taunton, Somerset, on Admiralty Way and has a workforce of approximately 1,000 staff.
Recruitment
 All three services of the British Armed Forces recruit primarily from within the United Kingdom, although citizens from the Commonwealth of Nations and the Republic of Ireland are equally eligible to join.Evans (2005)
All three services of the British Armed Forces recruit primarily from within the United Kingdom, although citizens from the Commonwealth of Nations and the Republic of Ireland are equally eligible to join.Evans (2005)How British Army is fast becoming foreign legion
, timesonline.co.uk The minimum recruitment age is 16 years (although personnel may not serve on armed operations below 18 years, and if under 18 must also have parental consent to join); the maximum recruitment age depends whether the application is for a regular or reserve role; there are further variations in age limit for different corps/regiments. The normal term of engagement is 22 years; however, the minimum service required before resignation is 4 years, plus, in the case of the Army, any service person below the age of 18. At present, the yearly intake into the armed forces is 11,880 (per the 12 months to 31 March 2014).UK Armed Forces Quarterly Personnel Report
, gov.uk, 1 April 2014 Excluding the
Brigade of Gurkhas
The Brigade of Gurkhas is the collective name which refers to all the units in the British Army that are composed of Nepalese Gurkha soldiers. The brigade draws its heritage from Gurkha units that originally served in the British Indian Army ...
and the Royal Irish Regiment, as of 1 April 2014 there are approximately 11,200 Black and Minority Ethnic (BME) persons serving as Regulars across the three service branches; of those, 6,610 were recruited from outside the United Kingdom. In total, Black and Minority Ethnic persons represent 7.1% of all service personnel, an increase from 6.6% in 2010.
Since the year 2000, sexual orientation has not been a factor considered in recruitment, and homosexuals can serve openly in the armed forces. All branches of the forces have actively recruited at Gay Pride events. The forces keep no formal figures concerning the number of gay and lesbian serving soldiers, saying that the sexual orientation of personnel is considered irrelevant and not monitored.
Role of women
Women have been part of the armed forces, on and off, for centuries, more fully integrated since the early 1990s, including flying fast jets and commanding warships or artillery batteries. As of 1 April 2014, there were approximately 15,840 women serving in the armed forces, representing 9.9% of all service personnel. The first female military pilot wasFlight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in air forces that use the Royal Air Force (RAF) system of ranks, especially in Commonwealth countries. It has a NATO rank code of OF-2. Flight lieutenant is abbreviated as Flt Lt in the India ...
Julie Ann Gibson while Flight Lieutenant Jo Salter
Joanna Mary Salter (born 27 August 1968, in Bournemouth) is a former Royal Air Force pilot, and was Britain's first female fast jet pilot flying the Panavia Tornado ground attack aircraft with 617 Squadron. She later became an inspirational spe ...
was the first fast-jet pilot, the former flying a Tornado GR1 on missions patrolling the then Northern Iraqi No-Fly Zone. Flight Lieutenant Juliette Fleming and Squadron Leader Nikki Thomas recently were the first Tornado GR4 crew. While enforcing the Libyan No-Fly Zone, Flight Lieutenant Helen Seymour was identified as the first female Eurofighter Typhoon pilot. In August 2011, it was announced that a female lieutenant commander, Sarah West, was to command the frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and ...
. In July 2016, it was announced that women would be allowed to serve in close combat, starting with the Royal Armoured Corps. In July 2017, the Secretary of Defence announced that women would be allowed to enlist in the RAF Regiment
The Royal Air Force Regiment (RAF Regiment) is part of the Royal Air Force and functions as a specialist corps. Founded by royal warrant in 1942, the Corps carries out soldiering tasks relating to the delivery of air power. Examples of such ta ...
from September 2017, a year ahead of schedule. In 2018, women were allowed to apply for all roles in the British military, including the special forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
. , the most senior serving woman is three-star Air Marshal Sue Gray.
March
See also
* Armed Forces Day (United Kingdom) *List of military equipment of the United Kingdom
This is a list of all military equipment ever used by the United Kingdom which includes weapons, ships and aircraft. This includes lists of specific types of current and former military equipment of the UK, and military equipment lists for certai ...
* Atholl Highlanders – The only legal private army in Europe under the command of the Duke of Atholl in Scotland
* Banknotes of the British Armed Forces
* British Forces Broadcasting Service
The British Forces Broadcasting Service (BFBS) provides radio and television programmes for His Majesty's Armed Forces, and their dependents worldwide. Editorial control is independent of the Ministry of Defence and the armed forces themselv ...
* Community Cadet Forces
* Military Covenant
The Military Covenant or Armed Forces Covenant is a term introduced in 2000 into British public life to refer to the mutual obligations between the United Kingdom and His Majesty's Armed Forces. According to ''The Guardian'', "it is an informal un ...
– The mutual obligations between the nation and its Armed Forces.
* Network-enabled capability
Network-enabled capability, or NEC, is the name given to the United Kingdom Ministry of Defence long-term intent to achieve enhanced military effect through the better use of information systems towards the goal of "right information, right place ...
– British military concept of achieving enhanced military effect through the better use of information systems. Similar to the US concept of network-centric warfare.
* The Championships, Wimbledon#Services stewards
* Uniforms of the British Armed Forces Each branch of the British Armed Forces has its own uniform regulations. Many of these uniforms are also the template for those worn in the British cadet forces.
*Uniforms of the British Army
*Uniforms of the Royal Navy
*Uniforms of the Royal Mar ...
* Military history of Scotland
* Armed forces of Wales
The Armed forces in Wales refers to military bases and organisation in Wales or associated with Wales. This includes servicemen and women from Wales and Welsh regiments and brigades of the British Armed Forces.
The Military in Wales includes the t ...
Notes
References
External links
British Ministry of Defence
(gov.uk)
Defence Academy of the United Kingdom
(.da.mod.uk)
Royal Navy official website
(royalnavy.mod.uk)
Royal Marines official webpage
(royalnavy.mod.uk)
British Army official website
(army.mod.uk)
Royal Air Force official website
(raf.mod.uk) {{North Atlantic Treaty Organization British Armed Forces deployments