Gustav Koerner on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gustav Philipp Koerner, also spelled Gustave or Gustavus Koerner (20 November 1809 – 9 April 1896), was a German-American revolutionary, journalist, lawyer, politician, judge and statesman in Illinois and Germany, and a Colonel of the
 They reached the Port of New York City on 17 June and went next to St. Louis in Missouri, a slave state that Koerner deeply abhorred. Shortly after, having departed that city, he and the Engelmanns settled down in the Shiloh Valley near Belleville, Illinois. (Demonstrating the sincerity and earnestness of Koerner's attitude toward the abolition of slavery, the 50th anniversary edition of the "Belleviller Zeitung" printed this example from "those memorable days of the anti-slavery movement: A large crowd was gathered in great excitement in Belleville's public square. Koerner, inquiring for the cause of this unusual gathering and learning that a slave was being offered for sale, rose from his horse, went to the auction stand, bought the slave, and immediately gave him freedom.")
Koerner continued his legal studies in
They reached the Port of New York City on 17 June and went next to St. Louis in Missouri, a slave state that Koerner deeply abhorred. Shortly after, having departed that city, he and the Engelmanns settled down in the Shiloh Valley near Belleville, Illinois. (Demonstrating the sincerity and earnestness of Koerner's attitude toward the abolition of slavery, the 50th anniversary edition of the "Belleviller Zeitung" printed this example from "those memorable days of the anti-slavery movement: A large crowd was gathered in great excitement in Belleville's public square. Koerner, inquiring for the cause of this unusual gathering and learning that a slave was being offered for sale, rose from his horse, went to the auction stand, bought the slave, and immediately gave him freedom.")
Koerner continued his legal studies in
 * Jesse K. Dubois
*
* Jesse K. Dubois
*
 In 1867 Koerner was appointed president of the board of trustees that organized the Illinois Soldiers' Orphans' Home at Bloomington, and in 1870 he became president of the first board of railroad commissioners of Illinois. A supporter of
In 1867 Koerner was appointed president of the board of trustees that organized the Illinois Soldiers' Orphans' Home at Bloomington, and in 1870 he became president of the first board of railroad commissioners of Illinois. A supporter of
 At the suggestion of farmer Dr. Anton Schott, a graduate in Theology and Philosophy, Koerner, together with other ''Latin Farmers,'' in 1836 founded the
At the suggestion of farmer Dr. Anton Schott, a graduate in Theology and Philosophy, Koerner, together with other ''Latin Farmers,'' in 1836 founded the
 The historical society of
The historical society of
Belleville Zeitung
(Deutsche Biographie) {{DEFAULTSORT:Korner, Gustav 1809 births 1896 deaths 19th-century American diplomats American abolitionists Ambassadors of the United States to Spain American agnostics American male writers American people of German descent Hessian emigrants to the United States German revolutionaries Heidelberg University alumni Illinois Democrats Illinois lawyers Illinois Liberal Republicans Illinois Republicans Justices of the Illinois Supreme Court Lieutenant Governors of Illinois Members of the Illinois House of Representatives People from Belleville, Illinois People of Illinois in the American Civil War Union Army colonels United States Army officers 19th-century American judges 19th-century American lawyers
U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
who was a confessed enemy of slavery. He married on 17 June 1836 in Belleville Sophia Dorothea Engelmann (16 November 1815 – 1 March 1888); they had 9 children. He belonged to the co-founders and was one of the first members of the Grand Old Party
The Republican Party, also referred to as the GOP ("Grand Old Party"), is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States. The GOP was founded in 1854 by anti-slavery activists who opposed the Kansas–Nebraska Act, ...
, and was a close confidant of Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
and his wife Mary Todd, and had an essential role in his nomination and election for president in 1860.
Life
Early life and education
Gustav was the son of the Frankfurt publisher, bookseller and art dealer Bernhard Körner (1776–1829) and his wife Maria Magdalena Kämpfe (1776–1847), daughter of another Frankfurt bookseller. He graduated withAbitur
''Abitur'' (), often shortened colloquially to ''Abi'', is a qualification granted at the end of secondary education in Germany. It is conferred on students who pass their final exams at the end of ISCED 3, usually after twelve or thirteen yea ...
from the Gymnasium Francofurtanum. Then he studied law at the universities in Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a popu ...
, Munich and Heidelberg and graduated 1832 from the University of Heidelberg
}
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg, (german: Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg; la, Universitas Ruperto Carola Heidelbergensis) is a public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, ...
as Dr. iuris utriusque, doctor as well as German and Roman law.
Escape from Persecution in Germany
OnChristmas Eve
Christmas Eve is the evening or entire day before Christmas Day, the festival commemorating the birth of Jesus. Christmas Day is observed around the world, and Christmas Eve is widely observed as a full or partial holiday in anticipatio ...
1830 in Munich, Koerner was involved in a somewhat drunken snowball fight that led to a confrontation with the Gendarmerie of that city in royal Bavaria where an officer was knocked down and wounded. Because of his participation in these so-called "Christmas riots," he was taken into custody for four months, later recalling that during the time of his captivity he learned more about the law than during the whole of his two-years of study at the University of Jena. Owing to this event the University of Munich
The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich or LMU; german: Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It is Germany's sixth-oldest university in continuous operati ...
was temporarily closed and after his custody, Koerner changed to the university in Heidelberg.
Koerner was one of the participants at the Hambach Festival
The Hambacher Festival was a German national democratic festival celebrated from 27 May to 30 May 1832 at Hambach Castle, near Neustadt an der Weinstraße, in present-day Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The event was disguised as a nonpolitical ...
in the spring of 1832 which was held to prepare a free, democratic, and unified state in Germany. The German Confederation
The German Confederation (german: Deutscher Bund, ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, w ...
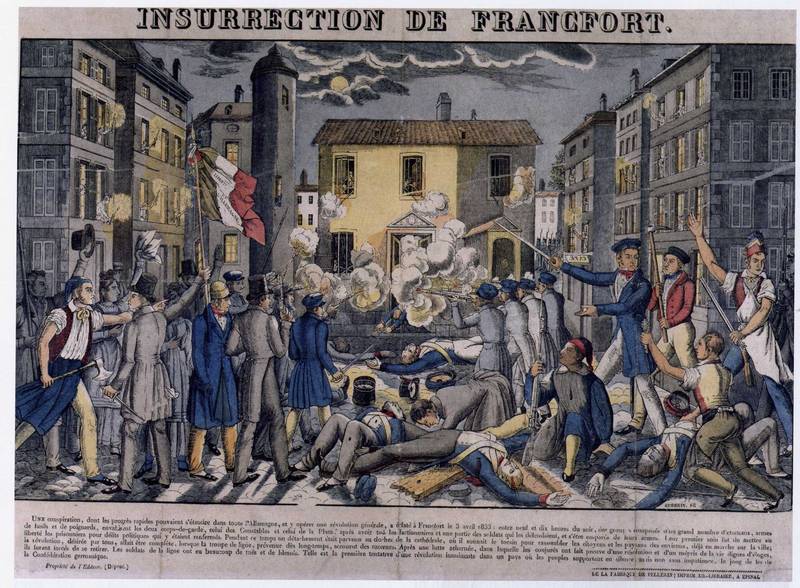
's legation of sovereigns, the Bundestag (officially called the Bundesversammlung, ''Federal Assembly''), was located in the '' Palais Thurn und Taxis'' in the center of Frankfurt, Koerner's native city. During the Frankfurter Wachensturm in 1833, a failed attempt by students to start a revolution in all states of the German Confederation, Koerner was injured and, to avoid being prosecuted by the authorities and held captive for high treason which would threaten capital punishment, he escaped in female dress to France. A warrant was out for him. He is counted as one of the Dreissiger.
The ''Central Federal Bureau for Investigations'' (german: link=no, Bundes-Central-Behörde für Untersuchungen) in Frankfurt was set up after the revolt against the reign of the President of the German Confederation, Francis I, Emperor of Austria, his chancellor Prince Metternich and his other vassals including King Frederick William III of Prussia. These authorities assigned him number 908 with the name Gustav Peter Philipp Koerner in their infamous "black book" of revolutionary suspects. The Free City of Frankfurt
For almost five centuries, the German city of Frankfurt was a city-state within two major Germanic entities:
*The Holy Roman Empire as the Free Imperial City of Frankfurt () (until 1806)
*The German Confederation as the Free City of Frankfurt ...
was occupied by federal troops from Austria and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
which meant a de facto total loss of its independence.
Rescued by "Angels"
On 1 May 1833, Koerner boarded a ship inLe Havre
Le Havre (, ; nrf, Lé Hâvre ) is a port city in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France. It is situated on the right bank of the estuary of the river Seine on the Channel southwest of the Pays de Caux, very ...
sailing to North America with a group of emigrants headed by the patriarch of the Engelmann family, whose son Theodor was an old friend of his from college. On the passage he became engaged to his future wife Sophie, a daughter of Engelmann's who was born in the Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine o ...
(german: link=no, Kurpfalz), a historic region of Germany. A year earlier, as a vanguard for the family, her cousin George Engelmann had explored the region of the Midwestern United States. George was also from Frankfurt, about the same age as Gustav, and had attended the same school, receiving a degree as M.D.
Doctor of Medicine (abbreviated M.D., from the Latin ''Medicinae Doctor'') is a medical degree, the meaning of which varies between different jurisdictions. In the United States, and some other countries, the M.D. denotes a professional degree. T ...
and later becoming a famous expert in the botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
of North America.
 They reached the Port of New York City on 17 June and went next to St. Louis in Missouri, a slave state that Koerner deeply abhorred. Shortly after, having departed that city, he and the Engelmanns settled down in the Shiloh Valley near Belleville, Illinois. (Demonstrating the sincerity and earnestness of Koerner's attitude toward the abolition of slavery, the 50th anniversary edition of the "Belleviller Zeitung" printed this example from "those memorable days of the anti-slavery movement: A large crowd was gathered in great excitement in Belleville's public square. Koerner, inquiring for the cause of this unusual gathering and learning that a slave was being offered for sale, rose from his horse, went to the auction stand, bought the slave, and immediately gave him freedom.")
Koerner continued his legal studies in
They reached the Port of New York City on 17 June and went next to St. Louis in Missouri, a slave state that Koerner deeply abhorred. Shortly after, having departed that city, he and the Engelmanns settled down in the Shiloh Valley near Belleville, Illinois. (Demonstrating the sincerity and earnestness of Koerner's attitude toward the abolition of slavery, the 50th anniversary edition of the "Belleviller Zeitung" printed this example from "those memorable days of the anti-slavery movement: A large crowd was gathered in great excitement in Belleville's public square. Koerner, inquiring for the cause of this unusual gathering and learning that a slave was being offered for sale, rose from his horse, went to the auction stand, bought the slave, and immediately gave him freedom.")
Koerner continued his legal studies in American law
The law of the United States comprises many levels of codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the most important is the nation's Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the federal government of the United States, as well as va ...
at Transylvania University
Transylvania University is a private university in Lexington, Kentucky. It was founded in 1780 and was the first university in Kentucky. It offers 46 major programs, as well as dual-degree engineering programs, and is accredited by the Southern ...
in Lexington, Kentucky during 1834–1835. While at the University, he got to know Mary Todd, who, a few years later, married Abraham Lincoln. From 1835 he practiced in Belleville as a lawyer in his own firm, then practiced in the office of Adam W. Snyder
Adam Wilson Snyder (October 6, 1799 – May 14, 1842) was a United States House of Representatives, U.S. Representative from Illinois as well as a member of the Illinois militia during the Black Hawk War.
Early life
Adam W. Snyder was born ...
in Belleville and from 1837 worked in the office of James Shields. In 1838 he received American citizenship
Citizenship of the United States is a legal status that entails Americans with specific rights, duties, protections, and benefits in the United States. It serves as a foundation of fundamental rights derived from and protected by the Constituti ...
.
Elected
Koerner was elected to the Illinois House of Representatives in 1842, served on theIllinois Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of Illinois is the state supreme court, the highest court of the U.S. state, State of Illinois. The court's authority is granted in Article VI of the current Illinois Constitution, which provides for seven justices elected from ...
from 1845 to 1848, and as the 12th Lieutenant Governor of Illinois from 1853 to 1857. Originally a Democrat, he became a member of the Republican Party after its formation, and helped develop its anti-slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
platform. As a friend, he took over some of Abraham Lincoln's cases when Lincoln was elected president.
Koerner was the first citizen of German extraction ever elected to the Illinois or Missouri legislatures. In 1851, in a clash with the editor of ''Anzeiger des Westens'' Henry Boernstein, he called the Forty-Eighters
The Forty-Eighters were Europeans who participated in or supported the Revolutions of 1848 that swept Europe. In the German Confederation, the Forty-Eighters favoured unification of Germany, a more democratic government, and guarantees of human ...
''Greens'' in his ''Belleviller Zeitung'' newspaper and Boernstein, in a published reply, insultingly called him ''Gray Gustav''.
Service for the Country
In 1861, Koerner was instrumental in raising the43rd Illinois Volunteer Infantry Regiment
The 43rd Regiment Illinois Volunteer Infantry, known as the "Koerner Regiment" after Gustav Körner, was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War.
Service
The 43rd Illinois Infantry was organized at Cam ...
but before its organization had been completed, he was appointed Colonel of Volunteers and assigned as aide to Gen. John C. Frémont
John Charles Frémont or Fremont (January 21, 1813July 13, 1890) was an American explorer, military officer, and politician. He was a U.S. Senator from California and was the first Republican nominee for president of the United States in 1856 ...
, upon whose removal he was assigned to Gen. Henry W. Halleck
Henry Wager Halleck (January 16, 1815 – January 9, 1872) was a senior United States Army officer, scholar, and lawyer. A noted expert in military studies, he was known by a nickname that became derogatory: "Old Brains". He was an important par ...
's staff as Brigadier General. He resigned in April 1862 due to impaired health. Shortly thereafter, he succeeded Carl Schurz
Carl Schurz (; March 2, 1829 – May 14, 1906) was a German revolutionary and an American statesman, journalist, and reformer. He immigrated to the United States after the German revolutions of 1848–1849 and became a prominent member of the new ...
as United States Ambassador to Spain
The incumbent ambassador is Julissa Reynoso Pantaleón, she was sworn in by Vice President Kamala Harris on January 7, 2022 and presented her credentials on February 2, 2022.
This is a list of United States ambassadors to Spain from 1779 to th ...
.
The expectation was that Koerner would prevent Spain from entering into the American Civil War on the side of the Southern slave states. Although Koerner, the ''Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of the United States of America'' (his precise titles as ambassador) managed to accomplish this objective, he was discontented in Spain and asked the president several times for a replacement. An important reason prompting his request was that the stipend for his ambassadorship did not nearly cover the huge financial obligations expected of him at the Spanish court. Koerner had to provide such funds from his private accounts. In 1864, he left the diplomatic service and returned to the United States.
Pallbearer
After theAssassination of Abraham Lincoln
On April 14, 1865, Abraham Lincoln, the 16th president of the United States, was assassinated by well-known stage actor John Wilkes Booth, while attending the play ''Our American Cousin'' at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C.
Shot in the hea ...
a special honour was granted him. Koerner was one of the pallbearers who carried the corpse of the president in the state funeral
A state funeral is a public funeral ceremony, observing the strict rules of protocol, held to honour people of national significance. State funerals usually include much pomp and ceremony as well as religious overtones and distinctive elements o ...
. The other men, all of them Lincoln's friends from his time in Springfield, Illinois
Springfield is the capital of the U.S. state of Illinois and the county seat and largest city of Sangamon County. The city's population was 114,394 at the 2020 census, which makes it the state's seventh most-populous city, the second largest o ...
, who conducted the coffin were:
Stephen T. Logan
Stephen Trigg Logan (February 24, 1800 – July 17, 1880) was an American lawyer and politician.
He practiced law with Abraham Lincoln from 1841 to 1843. He served as Illinois circuit court judge and in 1847 was elected to the Illinois Constitut ...
*James L. Lamb
*Samuel Hubbel Treat Jr.
Samuel H. Treat (December 17, 1815 – August 31, 1902) was a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Missouri.
Education and career
Born on December 17, 1815, in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, ...
*John Williams
*Erastus White
*J. M. Brown
*Jacob Bunn
:''This article concerns John Whitfield Bunn, Jacob Bunn, and the entrepreneurs who were interconnected with the Bunn brothers through association or familial and genealogical connection.''
John Whitfield Bunn (June 21, 1831 – June 7, 1920)Ill ...
*Charles Matheny
*Elisha Iles
*John T. Stuart
John Todd Stuart (November 10, 1807 – November 28, 1885) was a lawyer and a U.S. Representative from Illinois.
Born near Lexington, Kentucky, Stuart graduated from Centre College, Danville, Kentucky, in 1826. He then studied law, was ad ...
Last years
 In 1867 Koerner was appointed president of the board of trustees that organized the Illinois Soldiers' Orphans' Home at Bloomington, and in 1870 he became president of the first board of railroad commissioners of Illinois. A supporter of
In 1867 Koerner was appointed president of the board of trustees that organized the Illinois Soldiers' Orphans' Home at Bloomington, and in 1870 he became president of the first board of railroad commissioners of Illinois. A supporter of Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
's successful 1868 presidential election bid, in 1872 he became a supporter of the Liberal Republican Party, belonging to the nominating committee which chose Horace Greeley as its (unsuccessful) US presidential candidate.
In the same year Koerner ran for election (→ Illinois gubernatorial election, 1872) to the office of Governor of Illinois
The governor of Illinois is the head of government of Illinois, and the various agencies and departments over which the officer has jurisdiction, as prescribed in the state constitution. It is a directly elected position, votes being cast by p ...
, though the Republican Richard James Oglesby (1824–1899) won the election. He then backed the Democratic candidate Samuel J. Tilden for the U.S. presidency in a contentious election of 1876 and remained with this party afterwards.
In 1874, Koerner's wife Sophia, together with Henry Raab (1837–1901), a German immigrant (1854) from Wetzlar, a librarian in Belleville and later a well-known educator, established, with others, one of the first kindergartens. She became the first president of the ''Belleville Kindergarten Association'' which received $2,100 in contributions from 70 shareholders and, supported by 150 other women, one year later was serving 201 pupils taught by three educators. This institute followed the Julius Fröbel system of primary education for training children effortlessly. The building was finished in April 1875 for $5,000 but it was sold in 1892 to the Belleville Philharmonic Society.
Reminiscences
 At the suggestion of farmer Dr. Anton Schott, a graduate in Theology and Philosophy, Koerner, together with other ''Latin Farmers,'' in 1836 founded the
At the suggestion of farmer Dr. Anton Schott, a graduate in Theology and Philosophy, Koerner, together with other ''Latin Farmers,'' in 1836 founded the public library
A public library is a library that is accessible by the general public and is usually funded from public sources, such as taxes. It is operated by librarians and library paraprofessionals, who are also civil servants.
There are five fundament ...
in Belleville, probably the first in Illinois. Although he had never pursued agriculture as a profession, he is counted among the group of Latin farmers, which was a half-satirical, half-respectful designation for people like him, German immigrants in the United States
German Americans (german: Deutschamerikaner, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry. With an estimated size of approximately 43 million in 2019, German Americans are the largest of the self-reported ancestry groups by the Unit ...
who had received an advanced academic education.
Koerner was an active lawyer, and also wrote articles for several newspapers, among others the "Belleviller Zeitung" and the "Anzeiger des Westens
The ''Anzeiger des Westens'' (literally "Gazette of the West") was the first German-language newspaper in St. Louis, Missouri, and, along with the '' Westliche Post'' and the ''Illinois Staats-Zeitung'', one of the three most successful German-lang ...
" (published in St. Louis), American newspapers in the German language. He had great influence on the growing German community in North America in the second half of the 19th century. On the recommendation of his friend and biographer Heinrich Rattermann (1832–1923), he began at the end of 1886 to record his memoirs. Koerner did not consider publicationhe wrote down the detailed retrospective of his life as a recollection for his numerous descendants. His memoirs were published in two volumes in 1909, 13 years after his death and in the year of his 100th birthday, in Cedar Rapids, Iowa
Cedar Rapids () is the second-largest city in Iowa, United States and is the county seat of Linn County. The city lies on both banks of the Cedar River, north of Iowa City and northeast of Des Moines, the state's capital and largest city. I ...
.
Today Koerner's former home is registered in the National Register of Historic Places. It was acquired in 2001 by the City of Belleville and is being restored by the historical society of St. Clair County, Illinois (St. Clair County Historical Society) as a museum dedicated to the well-known German-American. It will illuminate Koerner's friendship with Abraham Lincoln. In 2009, Belleville celebrated Koerner's 200th birthday with a festive dinner attended by Koerner and Engelmann descendants. The following day, they planted an American white oak tree (the state tree of Illinois) at Koerner's Walnut Hill grave and presented a valuable exhibit for the planned Koerner Museum: a heavy silver tablet, given by Queen Isabella II of Spain in 1864 to Gustav Koerner for his farewell as a US ambassador to Spain.
Do right and fear no one
 The historical society of
The historical society of St. Clair County, Illinois
St. Clair County is the oldest county in Illinois; its western border is formed by the Mississippi River, bordering Missouri. It is a part of the Metro East in southern Illinois. At the 2020 United States census, it had a population of 257,40 ...
, in which Belleville is located, will restore the former home of Gustav Koerner to a museum under the motto "Do right and fear no one," which in 2009 was also the motto of his 200th birthday celebration. "Act properly and fear no one" was, however, not quite his personal motto. Rather, in his memoirs he described this phrase as the "religion" of most Burschenschaft
A Burschenschaft (; sometimes abbreviated in the German ''Burschenschaft'' jargon; plural: ) is one of the traditional (student associations) of Germany, Austria, and Chile (the latter due to German cultural influence).
Burschenschaften were ...
er (fraternity students) during his student years at Jena – though he still may have made it his own basic position as an active Burschenschafter.
One of his personal leitmotiv
A leitmotif or leitmotiv () is a "short, recurring musical phrase" associated with a particular person, place, or idea. It is closely related to the musical concepts of ''idée fixe'' or ''motto-theme''. The spelling ''leitmotif'' is an anglici ...
s was pointed out by the "Belleviller Zeitung" (the local German language newspaper) on 11 January 1899, nearly three years after his death, in a biography in the jubilee edition at the 50th anniversary of their first appearance:
See also
* Gustave Koerner House * Illinois gubernatorial election, 1852 * List of governors of Illinois * List of lieutenant governors of IllinoisExternal
Belleville Zeitung
Works
* * *''Collections of the Important General Laws of Illinois, with Comments'' (St. Louis, 1838) * *Notes
References
*External links
(Deutsche Biographie) {{DEFAULTSORT:Korner, Gustav 1809 births 1896 deaths 19th-century American diplomats American abolitionists Ambassadors of the United States to Spain American agnostics American male writers American people of German descent Hessian emigrants to the United States German revolutionaries Heidelberg University alumni Illinois Democrats Illinois lawyers Illinois Liberal Republicans Illinois Republicans Justices of the Illinois Supreme Court Lieutenant Governors of Illinois Members of the Illinois House of Representatives People from Belleville, Illinois People of Illinois in the American Civil War Union Army colonels United States Army officers 19th-century American judges 19th-century American lawyers