Gunpowder on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
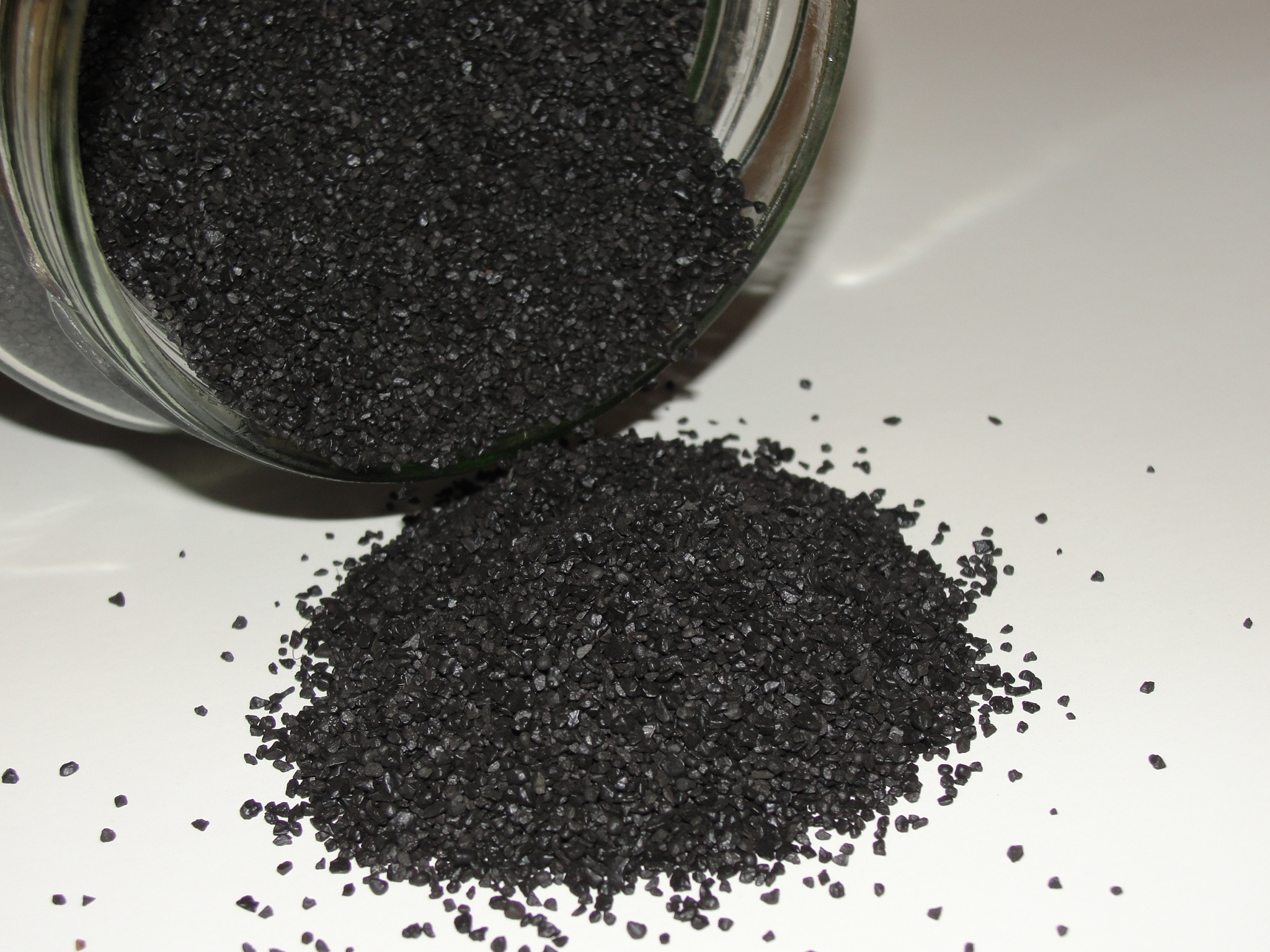


 Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern


 The earliest Western accounts of gunpowder appears in texts written by English philosopher
The earliest Western accounts of gunpowder appears in texts written by English philosopher

 Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder
Finnish smokeless powderSmokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to gunpowder ("black powder"). The combustion products are mainly gaseous, compared t ...
, is the earliest known chemical explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
. It consists of a mixture of sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
, carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
(in the form of charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ...
) and potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and ...
(saltpeter
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . This alkali metal nitrate Salt (chemistry), salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ...
). The sulfur and carbon act as fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy b ...
s while the saltpeter is an oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxi ...
. Gunpowder has been widely used as a propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the ...
in firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s, artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
, rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entir ...
ry, and pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating such things as fireworks, safety matches, oxygen candles, explosive bolts and other fasteners, parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, quarrying, and demolition ...
, including use as a blasting agent for explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
s in quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their envir ...
ing, mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
, building pipelines and road building.
Gunpowder is classified as a low explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
because of its relatively slow decomposition rate and consequently low brisance
In explosives engineering, brisance (; , ) is the shattering capability of a high explosive, determined mainly by its detonation pressure.
Practical uses
Brisance is of practical importance for determining the effectiveness of an explosion in ...
. Low explosives deflagrate
Deflagration (Lat: ''de + flagrare'', "to burn down") is subsonic combustion in which a pre-mixed flame propagates through a mixture of fuel and oxidizer. Deflagrations can only occur in pre-mixed fuels. Most fires found in daily life are diff ...
(i.e., burn at subsonic speeds), whereas high explosives
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
detonate
Detonation () is a type of combustion involving a supersonic exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front propagating directly in front of it. Detonations propagate supersonically through shock waves with ...
, producing a supersonic shockwave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a med ...
. Ignition of gunpowder packed behind a projectile
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found i ...
generates enough pressure to force the shot from the muzzle at high speed, but usually not enough force to rupture the gun barrel
A gun barrel is a crucial part of gun-type weapons such as small firearms, artillery pieces, and air guns. It is the straight shooting tube, usually made of rigid high-strength metal, through which a contained rapid expansion of high-pres ...
. It thus makes a good propellant but is less suitable for shattering rock or fortifications with its low-yield explosive power. Nonetheless, it was widely used to fill fused artillery shells (and used in mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
and civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewa ...
projects) until the second half of the 19th century, when the first high explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An ...
s were put into use.
Its use in weapons has declined due to smokeless powder replacing it, and it is no longer used for industrial purposes due to its relative inefficiency compared to newer alternatives such as dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern Germany, and patented in 1867. It rapidl ...
and ammonium nitrate/fuel oil.
Effect
Gunpowder is alow explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
: it does not detonate
Detonation () is a type of combustion involving a supersonic exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front propagating directly in front of it. Detonations propagate supersonically through shock waves with ...
, but rather deflagrates
Deflagration (Lat: ''de + flagrare'', "to burn down") is subsonic combustion in which a pre-mixed flame propagates through a mixture of fuel and oxidizer. Deflagrations can only occur in pre-mixed fuels. Most fires found in daily life are diffu ...
(burns quickly). This is an advantage in a propellant device, where one does not desire a shock that would shatter the gun and potentially harm the operator; however, it is a drawback when an explosion is desired. In that case, the propellant (and most importantly, gases produced by its burning) must be confined. Since it contains its own oxidizer and additionally burns faster under pressure, its combustion is capable of bursting containers such as a shell, grenade, or improvised "pipe bomb" or "pressure cooker" casings to form shrapnel.
In quarrying, high explosives are generally preferred for shattering rock. However, because of its low brisance
In explosives engineering, brisance (; , ) is the shattering capability of a high explosive, determined mainly by its detonation pressure.
Practical uses
Brisance is of practical importance for determining the effectiveness of an explosion in ...
, gunpowder causes fewer fractures and results in more usable stone compared to other explosives, making it useful for blasting slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
, which is fragile, or monumental stone such as granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
and marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
. Gunpowder is well suited for blank round
A blank is a firearm cartridge that, when fired, does not shoot a projectile like a bullet or pellet, but generates a muzzle flash and an explosive sound ( muzzle report) like a normal gunshot would. Firearms may need to be modified to allow a bl ...
s, signal flares, burst charge
In fireworks, a burst charge (usually black powder) is a pyrotechnic mixture placed in a shell which is ignited when the shell reaches the desired height in order to create an explosion and spread the stars. Burst charge compositions are usually ...
s, and rescue-line launches. It is also used in fireworks for lifting shells, in rockets as fuel, and in certain special effect
Special effects (often abbreviated as SFX, F/X or simply FX) are illusions or visual tricks used in the theatre, film, television, video game, amusement park and simulator industries to simulate the imagined events in a story or virtual ...
s.
Combustion converts less than half the mass of gunpowder to gas; most of it turns into particulate matter. Some of it is ejected, wasting propelling power, fouling the air, and generally being a nuisance (giving away a soldier's position, generating fog that hinders vision, etc.). Some of it ends up as a thick layer of soot
Soot ( ) is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolysed ...
inside the barrel, where it also is a nuisance for subsequent shots, and a cause of jamming an automatic weapon. Moreover, this residue is hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance' ...
, and with the addition of moisture absorbed from the air forms a corrosive substance
A corrosive substance is one that will damage or destroy other substances with which it comes into contact by means of a chemical reaction.
Etymology
The word ''corrosive'' is derived from the Latin verb ''corrodere'', which means ''to gnaw'', ...
. The soot contains potassium oxide
Potassium oxide ( K O) is an ionic compound of potassium and oxygen. It is a base. This pale yellow solid is the simplest oxide of potassium. It is a highly reactive compound that is rarely encountered. Some industrial materials, such as fertili ...
or sodium oxide
Sodium oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2 O. It is used in ceramics and glasses. It is a white solid but the compound is rarely encountered. Instead "sodium oxide" is used to describe components of various materials such as gla ...
that turns into potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
, or sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and al ...
, which corrodes wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" ...
or steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistan ...
gun barrels. Gunpowder arms therefore require thorough and regular cleaning to remove the residue.
History
China
The first confirmed reference to what can be considered gunpowder in China occurred in the 9th century AD during theTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
, first in a formula contained in the ''Taishang Shengzu Jindan Mijue'' (太上聖祖金丹秘訣) in 808, and then about 50 years later in a Taoist text known as the '' Zhenyuan miaodao yaolüe'' (真元妙道要略). The ''Taishang Shengzu Jindan Mijue'' mentions a formula composed of six parts sulfur to six parts saltpeter to one part birthwort herb. According to the ''Zhenyuan miaodao yaolüe'', "Some have heated together sulfur, realgar
Realgar ( ), also known as "ruby sulphur" or "ruby of arsenic", is an arsenic sulfide mineral with the chemical formula α-. It is a soft, sectile mineral occurring in monoclinic crystals, or in granular, compact, or powdery form, often in asso ...
and saltpeter with honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
; smoke and flames result, so that their hands and faces have been burnt, and even the whole house where they were working burned down." Based on these Taoist texts, the invention of gunpowder by Chinese alchemists was likely an accidental byproduct from experiments seeking to create the elixir of life
The elixir of life, also known as elixir of immortality, is a potion that supposedly grants the drinker eternal life and/or eternal youth. This elixir was also said to cure all diseases. Alchemists in various ages and cultures sought the mean ...
. This experimental medicine
An experimental drug is a medicinal product (a drug or vaccine) that has not yet received approval from governmental regulatory authorities for routine use in human or veterinary medicine. A medicinal product may be approved for use in one diseas ...
origin is reflected in its Chinese name ''huoyao'' ( ), which means "fire medicine". Saltpeter
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . This alkali metal nitrate Salt (chemistry), salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ...
was known to the Chinese by the mid-1st century AD and was primarily produced in the provinces of Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
, Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-leve ...
, and Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in His ...
. There is strong evidence of the use of saltpeter and sulfur in various medicinal
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ...
combinations. A Chinese alchemical text dated 492 noted saltpeter burnt with a purple flame, providing a practical and reliable means of distinguishing it from other inorganic salts, thus enabling alchemists to evaluate and compare purification techniques; the earliest Latin accounts of saltpeter purification are dated after 1200.
The earliest chemical formula for gunpowder appeared in the 11th century Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
text, ''Wujing Zongyao
The ''Wujing Zongyao'' (), sometimes rendered in English as the ''Complete Essentials for the Military Classics'', is a Chinese military compendium written from around 1040 to 1044.
The book was compiled during the Northern Song dynasty by Z ...
'' (''Complete Essentials from the Military Classics''), written by Zeng Gongliang between 1040 and 1044. The ''Wujing Zongyao'' provides encyclopedia references to a variety of mixtures that included petrochemicals—as well as garlic and honey. A slow match for flame-throwing mechanisms using the siphon principle and for fireworks and rockets is mentioned. The mixture formulas in this book contain at most 50 % saltpeter; not enough to create an explosion, they produce an incendiary instead. The ''Essentials'' was written by a Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
court bureaucrat and there is little evidence that it had any immediate impact on warfare; there is no mention of its use in the chronicles of the wars against the Tanguts
The Tangut people ( Tangut: , ''mjɨ nja̱'' or , ''mji dzjwo''; ; ; mn, Тангуд) were a Tibeto-Burman tribal union that founded and inhabited the Western Xia dynasty. The group initially lived under Tuyuhun authority, but later submitted ...
in the 11th century, and China was otherwise mostly at peace during this century. However, it had already been used for fire arrows
Fire arrows were one of the earliest forms of weaponized gunpowder, being used from the 9th century onward. Not to be confused with earlier incendiary arrow projectiles, the fire arrow was a gunpowder weapon which receives its name from the tra ...
since at least the 10th century. Its first recorded military application dates its use to the year 904 in the form of incendiary projectiles. In the following centuries various gunpowder weapons such as bomb
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechan ...
s, fire lances
The fire lance () was a gunpowder weapon and the ancestor of modern firearms. It first appeared in 10th–12th century China and was used to great effect during the Jin-Song Wars. It began as a small pyrotechnic device attached to a polearm wea ...
, and the gun appeared in China. Explosive weapons such as bombs have been discovered in a shipwreck off the shore of Japan dated from 1281, during the Mongol invasions of Japan.
By 1083 the Song court was producing hundreds of thousands of fire arrows for their garrisons. Bombs and the first proto-guns, known as "fire lances", became prominent during the 12th century and were used by the Song during the Jin-Song Wars. Fire lances were first recorded to have been used at the Siege of De'an
The siege of De'an (德安之戰) was fought as part of the Jin-Song Wars of China in 1132, during the Jin invasion of Hubei and Shaanxi. The battle between the besiegers, a group of rebels led by Li Heng and the Song Chinese defenders is impo ...
in 1132 by Song forces against the Jin. In the early 13th century the Jin used iron-casing bombs. Projectiles were added to fire lances, and re-usable fire lance barrels were developed, first out of hardened paper, and then metal. By 1257 some fire lances were firing wads of bullets. In the late 13th-century metal fire lances became 'eruptors', proto-cannons firing co-viative projectiles (mixed with the propellant, rather than seated over it with a wad), and by 1287 at the latest, had become true guns, the hand cannon
The hand cannon ( Chinese: 手 銃 ''shŏuchòng'', or 火 銃 ''huŏchòng''), also known as the gonne or handgonne, is the first true firearm and the successor of the fire lance. It is the oldest type of small arms as well as the most mech ...
.
Middle East
According to Iqtidar Alam Khan, it was invading Mongols who introduced gunpowder to the Islamic world. TheMuslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s acquired knowledge of gunpowder some time between 1240 and 1280, by which point the Syrian Hasan al-Rammah
Hasan al-Rammah (, died 1295) was a Syrian Arab chemist and engineer during the Mamluk Sultanate who studied gunpowders and explosives, and sketched prototype instruments of warfare, including the first torpedo. Al-Rammah called his early torpedo ...
had written recipes, instructions for the purification of saltpeter, and descriptions of gunpowder incendiaries. It is implied by al-Rammah's usage of "terms that suggested he derived his knowledge from Chinese sources" and his references to saltpeter as "Chinese snow" ( ar, ثلج الصين '), fireworks as "Chinese flowers", and rockets as "Chinese arrows" that knowledge of gunpowder arrived from China. However, because al-Rammah attributes his material to "his father and forefathers", al-Hassan argues that gunpowder became prevalent in Syria and Egypt by "the end of the twelfth century or the beginning of the thirteenth". In Persia saltpeter was known as "Chinese salt" ( fa, نمک چینی) ''namak-i chīnī'') or "salt from Chinese salt marshes" ( ').
Hasan al-Rammah included 107 gunpowder recipes in his text ''al-Furusiyyah wa al-Manasib al-Harbiyya'' (''The Book of Military Horsemanship and Ingenious War Devices''), 22 of which are for rockets. If one takes the median of 17 of these 22 compositions for rockets (75% nitrates, 9.06% sulfur, and 15.94% charcoal), it is nearly identical to the modern reported ideal recipe of 75% potassium nitrate, 10% sulfur, and 15% charcoal. The text also mentions fuses, incendiary bombs, naphtha pots, fire lances, and an illustration and description of the earliest torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, ...
. The torpedo was called the "egg which moves itself and burns". Two iron sheets were fastened together and tightened using felt. The flattened pear shaped vessel was filled with gunpowder, metal filings, "good mixtures", two rods, and a large rocket for propulsion. Judging by the illustration, it was evidently supposed to glide across the water. Fire lances were used in battles between the Muslims and Mongols in 1299 and 1303.
Al-Hassan claims that in the Battle of Ain Jalut
The Battle of Ain Jalut (), also spelled Ayn Jalut, was fought between the Bahri Mamluks of Egypt and the Mongol Empire on 3 September 1260 (25 Ramadan 658 AH) in southeastern Galilee in the Jezreel Valley near what is known today as the S ...
of 1260, the Mamluks
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
used against the Mongols, in "the first cannon in history", formula with near-identical ideal composition ratios for explosive gunpowder. Other historians urge caution regarding claims of Islamic firearms use in the 1204–1324 period as late medieval Arabic texts used the same word for gunpowder, ''naft'', that they used for an earlier incendiary, naphtha.
The earliest surviving documentary evidence for cannons in the Islamic world is from an Arabic manuscript dated to the early 14th century. The author's name is uncertain but may have been Shams al-Din Muhammad, who died in 1350. Dating from around 1320-1350, the illustrations show gunpowder weapons such as gunpowder arrows, bombs, fire tubes, and fire lances or proto-guns. The manuscript describes a type of gunpowder weapon called a ''midfa'' which uses gunpowder to shoot projectiles out of a tube at the end of a stock. Some consider this to be a cannon while others do not. The problem with identifying cannons in early 14th century Arabic texts is the term ''midfa'', which appears from 1342 to 1352 but cannot be proven to be true hand-guns or bombards. Contemporary accounts of a metal-barrel cannon in the Islamic world do not occur until 1365. Needham believes that in its original form the term ''midfa'' refers to the tube or cylinder of a naphtha
Naphtha ( or ) is a flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture.
Mixtures labelled ''naphtha'' have been produced from natural gas condensates, petroleum distillates, and the distillation of coal tar and peat. In different industries and regions ' ...
projector (flamethrower
A flamethrower is a ranged incendiary device designed to project a controllable jet of fire. First deployed by the Byzantine Empire in the 7th century AD, flamethrowers saw use in modern times during World War I, and more widely in World ...
), then after the invention of gunpowder it meant the tube of fire lances, and eventually it applied to the cylinder of hand-gun and cannon.
According to Paul E. J. Hammer, the Mamluks
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
certainly used cannons by 1342. According to J. Lavin, cannons were used by Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinc ...
at the siege of Algeciras
Algeciras ( , ) is a municipality of Spain belonging to the province of Cádiz, Andalusia. Located in the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula, near the Strait of Gibraltar, it is the largest city on the Bay of Gibraltar ( es, Bahía de Algeci ...
in 1343. A metal cannon firing an iron ball was described by Shihab al-Din Abu al-Abbas al-Qalqashandi between 1365 and 1376.
The musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually di ...
appeared in the Ottoman Empire by 1465. In 1598, Chinese writer Zhao Shizhen described Turkish muskets as being superior to European muskets. The Chinese military book '' Wu Pei Chih'' (1621) later described Turkish muskets that used a rack-and-pinion
A rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the ''pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert rotational motion into linear motion. Rotating the pinion causes the rack to be driven i ...
mechanism, which was not known to have been used in European or Chinese firearms at the time.
The state-controlled manufacture of gunpowder by the Ottoman Empire through early supply chain
In commerce, a supply chain is a network of facilities that procure raw materials, transform them into intermediate goods and then final products to customers through a distribution system. It refers to the network of organizations, people, activ ...
s to obtain nitre, sulfur and high-quality charcoal from oaks in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
contributed significantly to its expansion between the 15th and 18th century. It was not until later in the 19th century when the syndicalist production of Turkish gunpowder was greatly reduced, which coincided with the decline of its military might.
Europe

 The earliest Western accounts of gunpowder appears in texts written by English philosopher
The earliest Western accounts of gunpowder appears in texts written by English philosopher Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through emp ...
in 1267 called ''Opus Majus
The ''Opus Majus'' (Latin for "Greater Work") is the most important work of Roger Bacon. It was written in Medieval Latin, at the request of Pope Clement IV, to explain the work that Bacon had undertaken. The 878-page treatise ranges over all ...
'' and ''Opus Tertium''. The oldest written recipes in continental Europe were recorded under the name Marcus Graecus or Mark the Greek between 1280 and 1300 in the ''Liber Ignium
The ''Liber Ignium ad Comburendos Hostes'' (translated as ''On the Use of Fire to Conflagrate the Enemy'', or ''Book of Fires for the Burning of Enemies'', and abbreviated as ''Book of Fires'') is a medieval collection of recipes for incendiary wea ...
'', or ''Book of Fires''.
Some sources mention possible gunpowder weapons being deployed by the Mongols against European forces at the Battle of Mohi
The Battle of Mohi (11 April 1241), also known as Battle of the Sajó River''A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East'', Vol. I, ed. Spencer C. Tucker, (ABC-CLIO, 2010), 279; "Although Mongol losses in t ...
in 1241. Professor Kenneth Warren Chase credits the Mongols for introducing into Europe gunpowder and its associated weaponry. However, there is no clear route of transmission, and while the Mongols are often pointed to as the likeliest vector, Timothy May points out that "there is no concrete evidence that the Mongols used gunpowder weapons on a regular basis outside of China." However, Timothy May also points out "However... the Mongols used the gunpowder weapon in their wars against the Jin, the Song and in their invasions of Japan."
Records show that, in England, gunpowder was being made in 1346 at the Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
; a powder house
A powder tower (german: Pulverturm), occasionally also powder house (''Pulverhaus''), was a building used by the military or by mining companies, frequently a tower, to store gunpowder or, later, explosives. They were common until the 20th centu ...
existed at the Tower in 1461; and in 1515 three King's gunpowder makers worked there. Gunpowder was also being made or stored at other royal castles, such as Portchester
Portchester is a locality and suburb northwest of Portsmouth, England. It is part of the Fareham (borough), borough of Fareham in Hampshire. Once a small village, Portchester is now a busy part of the expanding conurbation between Portsmouth ...
. The English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I (" Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of r ...
(1642–1645) led to an expansion of the gunpowder industry, with the repeal of the Royal Patent in August 1641.
In late 14th century Europe, gunpowder was improved by ''corning'', the practice of drying it into small clumps to improve combustion and consistency. During this time, European manufacturers also began regularly purifying saltpeter, using wood ashes containing potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2 CO3. It is a white salt, which is soluble in water. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and gl ...
to precipitate calcium from their dung liquor, and using ox blood, alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double sulfate salt of aluminium with the general formula , where is a monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the ...
, and slices of turnip
The turnip or white turnip ('' Brassica rapa'' subsp. ''rapa'') is a root vegetable commonly grown in temperate climates worldwide for its white, fleshy taproot. The word ''turnip'' is a compound of ''turn'' as in turned/rounded on a lathe and ...
to clarify the solution.
During the Renaissance, two European schools of pyrotechnic
Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating such things as fireworks, safety matches, oxygen candles, explosive bolts and other fasteners, parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, quarrying, and demolition. ...
thought emerged, one in Italy and the other at Nuremberg, Germany. In Italy, Vannoccio Biringuccio
Vannoccio Biringuccio, sometimes spelled Vannocio Biringuccio (c. 1480 – c. 1539), was an Italian metallurgist. He is best known for his manual on metalworking, '' De la pirotechnia'', published posthumously in 1540.
20th Century translation by ...
, born in 1480, was a member of the guild ''Fraternita di Santa Barbara'' but broke with the tradition of secrecy by setting down everything he knew in a book titled ''De la pirotechnia
''De la Pirotechnia'' is considered to be one of the first printed books on metallurgy to have been published in Europe. It was written in Italian and first published in Venice in 1540. The author was Vannoccio Biringuccio, a citizen of Siena, ...
'', written in vernacular. It was published posthumously in 1540, with 9 editions over 138 years, and also reprinted by MIT Press
The MIT Press is a university press affiliated with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts (United States). It was established in 1962.
History
The MIT Press traces its origins back to 1926 when MIT publ ...
in 1966.
By the mid-17th century fireworks were used for entertainment on an unprecedented scale in Europe, being popular even at resorts and public gardens. With the publication of ''Deutliche Anweisung zur Feuerwerkerey'' (1748), methods for creating fireworks were sufficiently well-known and well-described that "Firework making has become an exact science." In 1774 Louis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
ascended to the throne of France at age 20. After he discovered that France was not self-sufficient in gunpowder, a Gunpowder Administration was established; to head it, the lawyer Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS (
CNRS (
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
. By careful testing and adjusting the proportions and grinding time, powder from mills such as at Essonne
Essonne () is a department of France in the southern Île-de-France region. It is named after the river Essonne. In 2019, it had a population of 1,301,659 across 194 communes.Andrew Noble and Frederick Abel, worked to improve the properties of gunpowder during the late 19th century. This formed the basis for the Noble-Abel gas equation for
 Gunpowder and gunpowder weapons were transmitted to India through the
Gunpowder and gunpowder weapons were transmitted to India through the  The Mughal emperor
The Mughal emperor
 Cannons were introduced to Majapahit when Kublai Khan's Chinese army under the leadership of Ike Mese sought to invade Java in 1293.
Cannons were introduced to Majapahit when Kublai Khan's Chinese army under the leadership of Ike Mese sought to invade Java in 1293.
 On the origins of gunpowder technology, historian
On the origins of gunpowder technology, historian
 The development of smokeless powders, such as
The development of smokeless powders, such as
 Modern corning first compresses the fine black powder meal into blocks with a fixed density (1.7 g/cm3). In the United States, gunpowder grains were designated F (for fine) or C (for coarse). Grain diameter decreased with a larger number of Fs and increased with a larger number of Cs, ranging from about for 7F to for 7C. Even larger grains were produced for artillery bore diameters greater than about . The standard DuPont ''Mammoth'' powder developed by Thomas Rodman and
Modern corning first compresses the fine black powder meal into blocks with a fixed density (1.7 g/cm3). In the United States, gunpowder grains were designated F (for fine) or C (for coarse). Grain diameter decreased with a larger number of Fs and increased with a larger number of Cs, ranging from about for 7F to for 7C. Even larger grains were produced for artillery bore diameters greater than about . The standard DuPont ''Mammoth'' powder developed by Thomas Rodman and
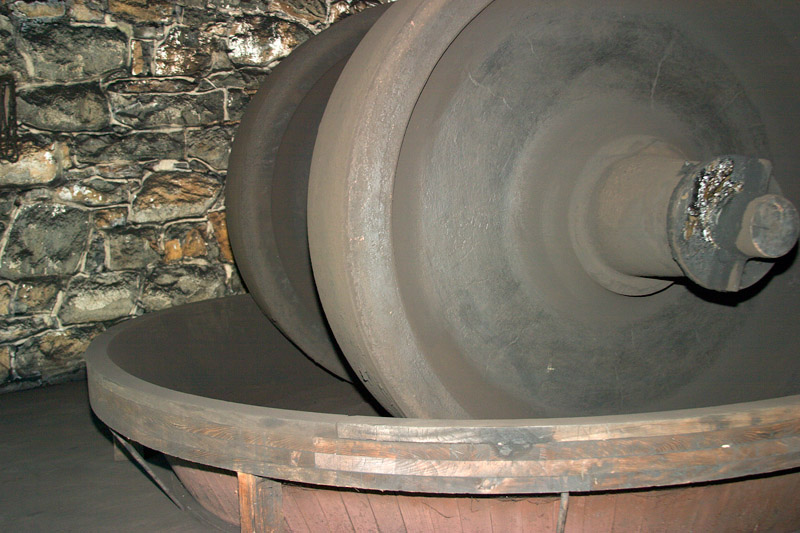


 For the most powerful black powder, meal powder, a
For the most powerful black powder, meal powder, a
Études Hygiéniques de la chair de cheval comme aliment
'',
"Confederate Boys and Peter Monkeys."
Armchair General. January 2005. Adapted from a talk given to the
Gun and Gunpowder
Oare Gunpowder Works, Kent, UK
Royal Gunpowder Mills
A digital exhibit produced by the Hagley Library that covers the founding and early history of the DuPont Company powder yards in Delaware *
Video Demonstration
of the Medieval Siege Society's Guns, Including showing ignition of gunpowder
Black Powder Recipes
* {{Use dmy dates, date=December 2019 Chinese inventions Explosives Firearm propellants Pyrotechnic compositions Rocket fuels Solid fuels
internal ballistics
Internal ballistics (also interior ballistics), a subfield of ballistics, is the study of the propulsion of a projectile.
In guns, internal ballistics covers the time from the propellant's ignition until the projectile exits the gun barrel. The s ...
.
The introduction of smokeless powder
Finnish smokeless powderSmokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to gunpowder ("black powder"). The combustion products are mainly gaseous, compared t ...
in the late 19th century led to a contraction of the gunpowder industry. After the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the majority of the British gunpowder manufacturers merged into a single company, "Explosives Trades limited"; and a number of sites were closed down, including those in Ireland. This company became Nobel Industries Limited; and in 1926 became a founding member of Imperial Chemical Industries
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain.
It was formed by the merger of four leading British chemical companies in 1926.
Its headquarters were at ...
. The Home Office removed gunpowder from its list of ''Permitted Explosives''; and shortly afterwards, on 31 December 1931, the former Curtis & Harvey's Glynneath
Glynneath ( cy, Glyn-nedd "valley of the River Neath"), also spelt ''Glyn-neath'' and ''Glyn Neath'', is a small town, community and electoral ward lying on the River Neath in the county borough of Neath Port Talbot, Wales. It was formerly in th ...
gunpowder factory at Pontneddfechan
Pontneddfechan, also known as Pontneathvaughan (pronounced ) ("bridge over the Little Neath" in Welsh) is the southernmost village in the county of Brecknockshire, Wales, within the Vale of Neath, in the community of Ystradfellte and in the pri ...
, in Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, closed down, and it was demolished by fire in 1932. The last remaining gunpowder mill at the Royal Gunpowder Factory, Waltham Abbey was damaged by a German parachute mine
A parachute mine is a naval mine dropped from an aircraft by parachute. They were mostly used in the Second World War by the Luftwaffe and initially by the Royal Air Force (RAF) Bomber Command.
Frequently, they were dropped on land targets.
Histo ...
in 1941 and it never reopened. This was followed by the closure of the gunpowder section at the Royal Ordnance Factory
Royal Ordnance Factories (ROFs) was the collective name of the UK government's munitions factories during and after the Second World War. Until privatisation, in 1987, they were the responsibility of the Ministry of Supply, and later the Mini ...
, ROF Chorley, the section was closed and demolished at the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
; and ICI Nobel
Nobel Enterprises () is a chemicals business that used to be based at Ardeer, in the Ayrshire town of Stevenston, in Scotland. Specialising in nitrogen-based propellants and explosives and nitrocellulose-based products such as varnishes and inks. ...
's Roslin gunpowder factory, which closed in 1954. This left ICI Nobel's Ardeer site in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, which included a gunpowder factory, as the only factory in Great Britain producing gunpowder. The gunpowder area of the Ardeer site closed in October 1976.
India
 Gunpowder and gunpowder weapons were transmitted to India through the
Gunpowder and gunpowder weapons were transmitted to India through the Mongol invasions of India
The Mongol Empire launched several invasions into the Indian subcontinent from 1221 to 1306, with many of the later raids made by the Qaraunas of Mongol origin. The Mongols occupied parts of the subcontinent for decades. As the Mongols progresse ...
. The Mongols were defeated by Alauddin Khalji
Alaud-Dīn Khaljī, also called Alauddin Khilji or Alauddin Ghilji (), born Ali Gurshasp, was an emperor of the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrativ ...
of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
, and some of the Mongol soldiers remained in northern India after their conversion to Islam. It was written in the ''Tarikh-i Firishta'' (1606–1607) that Nasiruddin Mahmud the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate presented the envoy of the Mongol ruler Hulegu Khan with a dazzling pyrotechnics display upon his arrival in Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
in 1258. Nasiruddin Mahmud tried to express his strength as a ruler and tried to ward off any Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
attempt similar to the Siege of Baghdad (1258)
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sac ...
. Firearms known as ''top-o-tufak'' also existed in many Muslim kingdoms in India by as early as 1366. From then on the employment of gunpowder warfare
Early modern warfare is the era of warfare following medieval warfare. It is associated with the start of the widespread use of gunpowder and the development of suitable weapons to use the explosive, including artillery and firearms; for thi ...
in India was prevalent, with events such as the "Siege of Belgaum
Belgaum ( ISO: ''Bēḷagāma''; also Belgaon and officially known as Belagavi) is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka located in its northern part along the Western Ghats. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Belagavi ...
" in 1473 by Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it c ...
Muhammad Shah Bahmani.
The shipwrecked Ottoman Admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet ...
Seydi Ali Reis
Seydi Ali Reis (1498–1563), formerly also written Sidi Ali Reis and Sidi Ali Ben Hossein, was an Ottoman admiral and navigator. Known also as Katib-i Rumi, Galatalı or Sidi Ali Çelebi,Danışan, Gaye. 2019. “A Sixteenth-Century Otto ...
is known to have introduced the earliest type of matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of rope that is touched to the gunpowder by a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or trigger with his finger. Befor ...
weapons, which the Ottomans used against the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
during the Siege of Diu (1531)
The siege of Diu occurred when a combined Ottoman- Gujarati force defeated a Portuguese attempt to capture the city of Diu in 1531. The victory was partly the result of Ottoman firepower over the Portuguese besiegers deployed by Mustafa B ...
. After that, a diverse variety of firearms, large guns in particular, became visible in Tanjore
Thanjavur (), also Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is the 11th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of South Indian religion, art, and architecture. Most of the ...
, Dacca
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city i ...
, Bijapur
Bijapur, officially known as Vijayapura, is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural i ...
, and Murshidabad
Murshidabad fa, مرشد آباد (, or ) is a historical city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located on the eastern bank of the Bhagirathi River, a distributary of the Ganges. It forms part of the Murshidabad district.
Durin ...
. Guns made of bronze were recovered from Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
(1504)- the former capital of the Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
s
 The Mughal emperor
The Mughal emperor Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
mass-produced matchlocks for the Mughal Army
The Army of the Mughal Empire was the force by which the Mughal emperors established their empire in the 15th century and expanded it to its greatest extent at the beginning of the 18th century. Although its origins, like the Mughals themselves, ...
. Akbar is personally known to have shot a leading Rajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Ra ...
commander during the Siege of Chittorgarh. The Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
began to use bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
rockets (mainly for signalling) and employ sapper
A sapper, also called a pioneer or combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparin ...
s: special units that undermined heavy stone fortifications to plant gunpowder charges.
The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
is known to have introduced much more advanced matchlocks, their designs were a combination of Ottoman and Mughal designs. Shah Jahan also countered the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and other Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (20 ...
in his province of Gujarāt
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth- ...
, which supplied Europe saltpeter for use in gunpowder warfare during the 17th century."India." Encyclopædia Britannica 2008 Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2008. Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
and Mālwa participated in saltpeter production. The Dutch, French, Portuguese, and English used Chhapra
Chhapra is a city and headquarters of the Saran district in the Indian state of Bihar. It is situated near the junction of the Ghaghara River and the Ganges River.
Chhapra grew in importance as a river-based market in the 18th century when t ...
as a center of saltpeter refining.
Ever since the founding of the Sultanate of Mysore by Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali ( حیدر علی, ''Haidarālī''; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the att ...
, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
military officers were employed to train the Mysore Army. Hyder Ali and his son Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He i ...
were the first to introduce modern cannons and musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually di ...
s, their army was also the first in India to have official uniforms. During the Second Anglo-Mysore War Hyder Ali and his son Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He i ...
unleashed the Mysorean rockets at their British opponents effectively defeating them on various occasions. The Mysorean rockets inspired the development of the Congreve rocket
The Congreve rocket was a type of rocket artillery designed by British inventor Sir William Congreve in 1808.
The design was based upon the rockets deployed by the Kingdom of Mysore against the East India Company during the Second, Third, ...
, which the British widely used during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
and the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
."rocket and missile system." Encyclopædia Britannica 2008 Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2008.
Southeast Asia
 Cannons were introduced to Majapahit when Kublai Khan's Chinese army under the leadership of Ike Mese sought to invade Java in 1293.
Cannons were introduced to Majapahit when Kublai Khan's Chinese army under the leadership of Ike Mese sought to invade Java in 1293. History of Yuan
The ''History of Yuan'' (''Yuán Shǐ''), also known as the ''Yuanshi'', is one of the official Chinese historical works known as the ''Twenty-Four Histories'' of China. Commissioned by the court of the Ming dynasty, in accordance to political ...
mentioned that the Mongol used cannons (Chinese: 炮—''Pào'') against Daha forces.Schlegel, Gustaaf (1902). "On the Invention and Use of Fire-Arms and Gunpowder in China, Prior to the Arrival of European". ''T'oung Pao''. 3: 1–11.Reid, Anthony (1993). ''Southeast Asia in the Age of Commerce, 1450-1680. Volume Two: Expansion and Crisis''. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. Cannons were used by the Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom (; th, อยุธยา, , IAST: or , ) was a Siamese kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. The Ayutthaya Kingdom is consi ...
in 1352 during its invasion of the Khmer Empire. Within a decade large quantities of gunpowder could be found in the Khmer Empire. By the end of the century firearms were also used by the Trần dynasty
The Trần dynasty, ( Vietnamese: Nhà Trần, chữ Nôm: 茹陳)also known as the House of Trần, was a Vietnamese dynasty that ruled over the Kingdom of Đại Việt from 1225 to 1400. The dynasty was founded when emperor Trần Thá ...
.
Even though the knowledge of making gunpowder-based weapon has been known after the failed Mongol invasion of Java, and the predecessor of firearms, the pole gun ( bedil tombak), was recorded as being used by Java in 1413, the knowledge of making "true" firearms came much later, after the middle of the 15th century. It was brought by the Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
ic nations of West Asia, most probably the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
. The precise year of introduction is unknown, but it may be safely concluded to be no earlier than 1460. Before the arrival of the Portuguese in Southeast Asia, the natives already possessed primitive firearms, the Java arquebus. Portuguese influence to local weaponry after the capture of Malacca (1511)
The Capture of Malacca in 1511 occurred when the governor of Portuguese India Afonso de Albuquerque conquered the city of Malacca in 1511.
The port city of Malacca controlled the narrow, strategic Strait of Malacca, through which all seagoing ...
resulted in a new type of hybrid tradition matchlock firearm, the istinggar.Andaya, L. Y. 1999. Interaction with the outside world and adaptation in Southeast Asian society 1500–1800. In ''The Cambridge history of southeast Asia''. ed. Nicholas Tarling. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 345–401.
Portuguese and Spanish invaders were unpleasantly surprised and even outgunned on occasion. Circa 1540, the Javanese, always alert for new weapons found the newly arrived Portuguese weaponry superior to that of the locally made variants. Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese Hindu-Buddhist thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was based on the island of Java (in modern-day Indonesia ...
-era cetbang cannons were further improved and used in the Demak Sultanate
The Demak Sultanate (کسلطانن دمق) was a Javanese Muslim state located on Java's north coast in Indonesia, at the site of the present-day city of Demak. A port fief to the Hindu-Buddhist Majapahit kingdom thought to have been founded i ...
period during the Demak invasion of Portuguese Malacca
Portuguese control of Malacca, a city on the Malay Peninsula, refers to the 130 year period (1511–1641) when it was a possession of the Portuguese East Indies. It was conquered from the Malacca Sultanate as part of Portuguese attempts to ...
. During this period, the iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
for manufacturing Javanese cannons was imported from Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
in northern Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The material was known by Javanese as ''wesi kurasani'' (Khorasan iron). When the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
came to the archipelago, they referred to it as ''berço'', which was also used to refer to any breech-loading swivel gun, while the Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex history, including a number of different languages, both ...
call it ''verso''. By the early 16th century, the Javanese already locally-producing large guns, some of them still survived until the present day and dubbed as "sacred cannon" or "holy cannon". These cannons varied between 180- to 260-pounders, weighing anywhere between 3–8 tons, length of them between 3–6 m.
Saltpeter harvesting was recorded by Dutch and German travelers as being common in even the smallest villages and was collected from the decomposition process of large dung hills specifically piled for the purpose. The Dutch punishment for possession of non-permitted gunpowder appears to have been amputation. Ownership and manufacture of gunpowder was later prohibited by the colonial Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
occupiers.Dipanegara, P.B.R. Carey, ''Babad Dipanagara: an account of the outbreak of the Java war, 1825–30 : the Surakarta court version of the Babad Dipanagara with translations into English and Indonesian'' volume 9: Council of the M.B.R.A.S. by Art Printing Works: 1981. According to colonel McKenzie quoted in Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles
Sir Thomas Stamford Bingley Raffles (5 July 1781 – 5 July 1826) was a British statesman who served as the Lieutenant-Governor of the Dutch East Indies between 1811 and 1816, and Lieutenant-Governor of Bencoolen between 1818 and 1824. He is ...
', '' The History of Java'' (1817), the purest sulfur was supplied from a crater from a mountain near the straits of Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and ...
.
Historiography
 On the origins of gunpowder technology, historian
On the origins of gunpowder technology, historian Tonio Andrade
Tonio Adam Andrade (born 1968) is an historian of East Asian history and the history of East Asian trading networks.
Bibliography
* ''Commerce, Culture, and Conflict: Taiwan Under European Rule, 1624–1662''. Yale University Press, 2000.
* ''H ...
remarked, "Scholars today overwhelmingly concur that the gun was invented in China." Gunpowder and the gun are widely believed by historians to have originated from China due to the large body of evidence that documents the evolution of gunpowder from a medicine to an incendiary and explosive, and the evolution of the gun from the fire lance
The fire lance () was a gunpowder weapon and the ancestor of modern firearms. It first appeared in 10th–12th century China and was used to great effect during the Jin-Song Wars. It began as a small pyrotechnic device attached to a polearm weap ...
to a metal gun, whereas similar records do not exist elsewhere. As Andrade explains, the large amount of variation in gunpowder recipes in China relative to Europe is "evidence of experimentation in China, where gunpowder was at first used as an incendiary and only later became an explosive and a propellant... in contrast, formulas in Europe diverged only very slightly from the ideal proportions for use as an explosive and a propellant, suggesting that gunpowder was introduced as a mature technology."
However, the history of gunpowder is not without controversy. A major problem confronting the study of early gunpowder history is ready access to sources close to the events described. Often the first records potentially describing use of gunpowder in warfare were written several centuries after the fact, and may well have been colored by the contemporary experiences of the chronicler. Translation difficulties have led to errors or loose interpretations bordering on artistic licence
Artistic license (alongside more contextually-specific derivative terms such as poetic license, historical license, dramatic license, and narrative license) refers to deviation from fact or form for artistic purposes. It can include the alterat ...
. Ambiguous language can make it difficult to distinguish gunpowder weapons from similar technologies that do not rely on gunpowder. A commonly cited example is a report of the Battle of Mohi
The Battle of Mohi (11 April 1241), also known as Battle of the Sajó River''A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East'', Vol. I, ed. Spencer C. Tucker, (ABC-CLIO, 2010), 279; "Although Mongol losses in t ...
in Eastern Europe that mentions a "long lance" sending forth "evil-smelling vapors and smoke", which has been variously interpreted by different historians as the "first-gas attack upon European soil" using gunpowder, "the first use of cannon in Europe", or merely a "toxic gas" with no evidence of gunpowder. It is difficult to accurately translate original Chinese alchemical texts, which tend to explain phenomena through metaphor, into modern scientific language with rigidly defined terminology in English. Early texts potentially mentioning gunpowder are sometimes marked by a linguistic process where semantic change
Semantic change (also semantic shift, semantic progression, semantic development, or semantic drift) is a form of language change regarding the evolution of word usage—usually to the point that the modern meaning is radically different from ...
occurred. For instance, the Arabic word ''naft'' transitioned from denoting naphtha
Naphtha ( or ) is a flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture.
Mixtures labelled ''naphtha'' have been produced from natural gas condensates, petroleum distillates, and the distillation of coal tar and peat. In different industries and regions ' ...
to denoting gunpowder, and the Chinese word ''pào'' changed in meaning from trebuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weight ...
to a cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
. This has led to arguments on the exact origins of gunpowder based on etymological foundations. Science and technology historian Bert S. Hall makes the observation that, "It goes without saying, however, that historians bent on special pleading, or simply with axes of their own to grind, can find rich material in these terminological thickets."
Another major area of contention in modern studies of the history of gunpowder is regarding the transmission of gunpowder. While the literary and archaeological evidence supports a Chinese origin for gunpowder and guns, the manner in which gunpowder technology was transferred from China to the West is still under debate. It is unknown why the rapid spread of gunpowder technology across Eurasia took place over several decades whereas other technologies such as paper, the compass, and printing did not reach Europe until centuries after they were invented in China.
Components
Gunpowder is a granular mixture of: * anitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insolu ...
, typically potassium nitrate (KNO3), which supplies oxygen for the reaction;
* charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ...
, which provides carbon and other fuel for the reaction, simplified as carbon (C);
* sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
(S), which, while also serving as a fuel, lowers the temperature required to ignite the mixture, thereby increasing the rate of combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combus ...
.
Potassium nitrate is the most important ingredient in terms of both bulk and function because the combustion process releases oxygen from the potassium nitrate, promoting the rapid burning of the other ingredients. To reduce the likelihood of accidental ignition by static electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material or between materials. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is na ...
, the granules of modern gunpowder are typically coated with graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
, which prevents the build-up of electrostatic charge.
Charcoal does not consist of pure carbon; rather, it consists of partially pyrolyzed
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''p ...
cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wa ...
, in which the wood is not completely decomposed. Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
differs from ordinary charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ...
. Whereas charcoal's autoignition temperature is relatively low, carbon's is much greater. Thus, a gunpowder composition containing pure carbon would burn similarly to a match head, at best.
The current standard composition for the gunpowder manufactured by pyrotechnicians was adopted as long ago as 1780. Proportions by weight are 75% potassium nitrate (known as saltpeter or saltpetre), 15% softwood charcoal, and 10% sulfur. These ratios have varied over the centuries and by country, and can be altered somewhat depending on the purpose of the powder. For instance, power grades of black powder, unsuitable for use in firearms but adequate for blasting rock in quarrying operations, are called blasting powder rather than gunpowder with standard proportions of 70% nitrate, 14% charcoal, and 16% sulfur; blasting powder may be made with the cheaper sodium nitrate
Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Chile saltpeter (large deposits of which were historically mined in Chile) to distinguish it from ordinary saltpeter, potassium nitrate. ...
substituted for potassium nitrate and proportions may be as low as 40% nitrate, 30% charcoal, and 30% sulfur. In 1857, Lammot du Pont solved the main problem of using cheaper sodium nitrate formulations when he patented DuPont "B" blasting powder. After manufacturing grains from press-cake in the usual way, his process tumbled the powder with graphite dust for 12 hours. This formed a graphite coating on each grain that reduced its ability to absorb moisture.
Neither the use of graphite nor sodium nitrate was new. Glossing gunpowder corns with graphite was already an accepted technique in 1839, and sodium nitrate-based blasting powder had been made in Peru for many years using the sodium nitrate mined at Tarapacá (now in Chile). Also, in 1846, two plants were built in south-west England to make blasting powder using this sodium nitrate. The idea may well have been brought from Peru by Cornish miners returning home after completing their contracts. Another suggestion is that it was William Lobb
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
, the plant collector, who recognised the possibilities of sodium nitrate during his travels in South America. Lammot du Pont would have known about the use of graphite and probably also knew about the plants in south-west England. In his patent he was careful to state that his claim was for the combination of graphite with sodium nitrate-based powder, rather than for either of the two individual technologies.
French war powder in 1879 used the ratio 75% saltpeter, 12.5% charcoal, 12.5% sulfur. English war powder in 1879 used the ratio 75% saltpeter, 15% charcoal, 10% sulfur. The British Congreve rockets used 62.4% saltpeter, 23.2% charcoal and 14.4% sulfur, but the British Mark VII gunpowder was changed to 65% saltpeter, 20% charcoal and 15% sulfur. The explanation for the wide variety in formulation relates to usage. Powder used for rocketry can use a slower burn rate since it accelerates the projectile for a much longer time—whereas powders for weapons such as flintlocks, cap-locks, or matchlocks need a higher burn rate to accelerate the projectile in a much shorter distance. Cannons usually used lower burn-rate powders, because most would burst with higher burn-rate powders.
Other compositions
Besides black powder, there are other historically important types of gunpowder. "Brown gunpowder" is cited as composed of 79% nitre, 3% sulfur, and 18% charcoal per 100 of dry powder, with about 2% moisture. Prismatic Brown Powder is a large-grained product theRottweil
Rottweil (; Alemannic: ''Rautweil'') is a town in southwest Germany in the state of Baden-Württemberg. Rottweil was a free imperial city for nearly 600 years.
Located between the Black Forest and the Swabian Alps, Rottweil has nearly 25,00 ...
Company introduced in 1884 in Germany, which was adopted by the British Royal Navy shortly thereafter. The French navy adopted a fine, 3.1 millimeter, not prismatic grained product called ''Slow Burning Cocoa'' (SBC) or "cocoa powder". These brown powders reduced burning rate even further by using as little as 2 percent sulfur and using charcoal made from rye straw that had not been completely charred, hence the brown color.
Lesmok powder was a product developed by DuPont in 1911, one of several semi-smokeless products in the industry containing a mixture of black and nitrocellulose powder. It was sold to Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
and others primarily for .22 and .32 small calibers. Its advantage was that it was believed at the time to be less corrosive than smokeless powders then in use. It was not understood in the U.S. until the 1920s that the actual source of corrosion was the potassium chloride residue from potassium chlorate sensitized primers. The bulkier black powder fouling better disperses primer residue. Failure to mitigate primer corrosion by dispersion caused the false impression that nitrocellulose-based powder caused corrosion. Lesmok had some of the bulk of black powder for dispersing primer residue, but somewhat less total bulk than straight black powder, thus requiring less frequent bore cleaning. It was last sold by Winchester in 1947.
Sulfur-free powders
 The development of smokeless powders, such as
The development of smokeless powders, such as cordite
Cordite is a family of smokeless propellants developed and produced in the United Kingdom since 1889 to replace black powder as a military propellant. Like modern gunpowder, cordite is classified as a low explosive because of its slow burn ...
, in the late 19th century created the need for a spark-sensitive priming charge, such as gunpowder. However, the sulfur content of traditional gunpowders caused corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
problems with Cordite Mk I and this led to the introduction of a range of sulfur-free gunpowders, of varying grain sizes. They typically contain 70.5 parts of saltpeter and 29.5 parts of charcoal. Like black powder, they were produced in different grain sizes. In the United Kingdom, the finest grain was known as ''sulfur-free mealed powder'' (''SMP''). Coarser grains were numbered as sulfur-free gunpowder (SFG n): 'SFG 12', 'SFG 20', 'SFG 40' and 'SFG 90', for example; where the number represents the smallest BSS sieve mesh size, which retained no grains.
Sulfur's main role in gunpowder is to decrease the ignition temperature. A sample reaction for sulfur-free gunpowder would be:
: 6 KNO3 + C7H4O → 3 K2CO3 + 4 CO2 + 2 H2O + 3 N2
Smokeless powders
The term ''black powder'' was coined in the late 19th century, primarily in the United States, to distinguish prior gunpowder formulations from the new smokeless powders and semi-smokeless powders. Semi-smokeless powders featured bulk volume properties that approximated black powder, but had significantly reduced amounts of smoke and combustion products. Smokeless powder has different burning properties (pressure vs. time) and can generate higher pressures and work per gram. This can rupture older weapons designed for black powder. Smokeless powders ranged in color from brownish tan to yellow to white. Most of the bulk semi-smokeless powders ceased to be manufactured in the 1920s.Granularity
Serpentine
The original dry-compounded powder used in 15th-century Europe was known as "Serpentine", either a reference to Satan or to a common artillery piece that used it. The ingredients were ground together with a mortar and pestle, perhaps for 24 hours, resulting in a fine flour. Vibration during transportation could cause the components to separate again, requiring remixing in the field. Also if the quality of the saltpeter was low (for instance if it was contaminated with highlyhygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance' ...
calcium nitrate
Calcium nitrate, also called ''Norgessalpeter'' (Norwegian salpeter), is an inorganic compound with the formula Ca(NO3)2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound, which is rarely encountered, absorbs moisture from the air to give the tetrahydrate. Both anhyd ...
), or if the powder was simply old (due to the mildly hygroscopic nature of potassium nitrate), in humid weather it would need to be re-dried. The dust from "repairing" powder in the field was a major hazard.
Loading cannons or bombards before the powder-making advances of the Renaissance was a skilled art. Fine powder loaded haphazardly or too tightly would burn incompletely or too slowly. Typically, the breech-loading powder chamber in the rear of the piece was filled only about half full, the serpentine powder neither too compressed nor too loose, a wooden bung pounded in to seal the chamber from the barrel when assembled, and the projectile placed on. A carefully determined empty space was necessary for the charge to burn effectively. When the cannon was fired through the touchhole, turbulence from the initial surface combustion caused the rest of the powder to be rapidly exposed to the flame.
The advent of much more powerful and easy to use ''corned'' powder changed this procedure, but serpentine was used with older guns into the 17th century.
Corning
For propellants to oxidize and burn rapidly and effectively, the combustible ingredients must be reduced to the smallest possible particle sizes, and be as thoroughly mixed as possible. Once mixed, however, for better results in a gun, makers discovered that the final product should be in the form of individual dense grains that spread the fire quickly from grain to grain, much asstraw
Straw is an agricultural byproduct consisting of the dry stalks of cereal plants after the grain and chaff have been removed. It makes up about half of the yield of cereal crops such as barley, oats, rice, rye and wheat. It has a number ...
or twig
A twig is a thin, often short, branch of a tree or bush.
The buds on the twig are an important diagnostic characteristic, as are the abscission scars where the leaves have fallen away. The color, texture, and patterning of the twig bark ar ...
s catch fire more quickly than a pile of sawdust
Sawdust (or wood dust) is a by-product or waste product of woodworking operations such as sawing, sanding, milling, planing, and routing. It is composed of small chippings of wood. These operations can be performed by woodworking machine ...
.
In late 14th century Europe and China, gunpowder was improved by wet grinding; liquid, such as distilled spirits was added during the grinding-together of the ingredients and the moist paste dried afterwards. The principle of wet mixing to prevent the separation of dry ingredients, invented for gunpowder, is used today in the pharmaceutical industry. It was discovered that if the paste was rolled into balls before drying the resulting gunpowder absorbed less water from the air during storage and traveled better. The balls were then crushed in a mortar by the gunner immediately before use, with the old problem of uneven particle size and packing causing unpredictable results. If the right size particles were chosen, however, the result was a great improvement in power. Forming the damp paste into ''corn''-sized clumps by hand or with the use of a sieve instead of larger balls produced a product after drying that loaded much better, as each tiny piece provided its own surrounding air space that allowed much more rapid combustion than a fine powder. This "corned" gunpowder was from 30% to 300% more powerful. An example is cited where of serpentine was needed to shoot a ball, but only of corned powder.
Because the dry powdered ingredients must be mixed and bonded together for extrusion and cut into grains to maintain the blend, size reduction and mixing is done while the ingredients are damp, usually with water. After 1800, instead of forming grains by hand or with sieves, the damp ''mill-cake'' was pressed in molds to increase its density and extract the liquid, forming ''press-cake''. The pressing took varying amounts of time, depending on conditions such as atmospheric humidity. The hard, dense product was broken again into tiny pieces, which were separated with sieves to produce a uniform product for each purpose: coarse powders for cannons, finer grained powders for muskets, and the finest for small hand guns and priming. Inappropriately fine-grained powder often caused cannons to burst before the projectile could move down the barrel, due to the high initial spike in pressure. ''Mammoth'' powder with large grains, made for Rodman's 15-inch cannon, reduced the pressure to only 20 percent as high as ordinary cannon powder would have produced.
In the mid-19th century, measurements were made determining that the burning rate within a grain of black powder (or a tightly packed mass) is about 6 cm/s (0.20 feet/s), while the rate of ignition propagation from grain to grain is around 9 m/s (30 feet/s), over two orders of magnitude faster.
Modern types
 Modern corning first compresses the fine black powder meal into blocks with a fixed density (1.7 g/cm3). In the United States, gunpowder grains were designated F (for fine) or C (for coarse). Grain diameter decreased with a larger number of Fs and increased with a larger number of Cs, ranging from about for 7F to for 7C. Even larger grains were produced for artillery bore diameters greater than about . The standard DuPont ''Mammoth'' powder developed by Thomas Rodman and
Modern corning first compresses the fine black powder meal into blocks with a fixed density (1.7 g/cm3). In the United States, gunpowder grains were designated F (for fine) or C (for coarse). Grain diameter decreased with a larger number of Fs and increased with a larger number of Cs, ranging from about for 7F to for 7C. Even larger grains were produced for artillery bore diameters greater than about . The standard DuPont ''Mammoth'' powder developed by Thomas Rodman and Lammot du Pont
Lammot du Pont I (April 13, 1831 – March 29, 1884) was a chemist and a key member of the du Pont family and its company in the mid-19th century.
Early life
Du Pont was born in 1831 in New Castle County, Delaware, the son of Margaretta Elizabeth ...
for use during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
had grains averaging in diameter with edges rounded in a glazing barrel. Other versions had grains the size of golf and tennis balls for use in Rodman gun
Drawing comparing Model 1844 8-inch columbiad and Model 1861 10-inch "Rodman" columbiad. The powder chamber on the older columbiad is highlighted by the red box.
The Rodman gun is any of a series of American Civil War–era columbiads designed b ...
s.Brown, G.I. (1998) ''The Big Bang: A history of Explosives'' Sutton Publishing pp. 22, 32 In 1875 DuPont introduced ''Hexagonal'' powder for large artillery, which was pressed using shaped plates with a small center core—about diameter, like a wagon wheel nut, the center hole widened as the grain burned. By 1882 German makers also produced hexagonal grained powders of a similar size for artillery.
By the late 19th century manufacturing focused on standard grades of black powder from Fg used in large bore rifles and shotguns, through FFg (medium and small-bore arms such as muskets and fusils), FFFg (small-bore rifles and pistols), and FFFFg (extreme small bore, short pistols and most commonly for priming flintlock
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism itself, also know ...
s). A coarser grade for use in military artillery blanks was designated A-1. These grades were sorted on a system of screens with oversize retained on a mesh of 6 wires per inch, A-1 retained on 10 wires per inch, Fg retained on 14, FFg on 24, FFFg on 46, and FFFFg on 60. Fines designated FFFFFg were usually reprocessed to minimize explosive dust hazards. In the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, the main service gunpowders were classified RFG (rifle grained fine) with diameter of one or two millimeters and RLG (rifle grained large) for grain diameters between two and six millimeters. Gunpowder grains can alternatively be categorized by mesh size: the BSS sieve mesh size, being the smallest mesh size, which retains no grains. Recognized grain sizes are Gunpowder G 7, G 20, G 40, and G 90.
Owing to the large market of antique and replica black-powder firearms in the US, modern black powder substitute
A black powder substitute is a replacement for black powder used in muzzleloading and cartridge firearms. Black powder substitutes offer a number of advantages over black powder, primarily including reduced sensitivity as an explosive and in ...
s like Pyrodex
A black powder substitute is a replacement for black powder used in muzzleloading and cartridge firearms. Black powder substitutes offer a number of advantages over black powder, primarily including reduced sensitivity as an explosive and incr ...
, Triple Seven and Black Mag3 pellets have been developed since the 1970s. These products, which should not be confused with smokeless powders, aim to produce less fouling (solid residue), while maintaining the traditional volumetric measurement system for charges. Claims of less corrosiveness of these products have been controversial however. New cleaning products for black-powder guns have also been developed for this market.
Chemistry
A simple, commonly cited,chemical equation
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and chemical formulas. The reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side with a plus sign between ...
for the combustion of gunpowder is:
: 2 KNO3 + S + 3 C → K2S + N2 + 3 CO2.
A balanced, but still simplified, equation is:
: 10 KNO3 + 3 S + 8 C → 2 K2CO3 + 3 K2SO4 + 6 CO2 + 5 N2.
The exact percentages of ingredients varied greatly through the medieval period as the recipes were developed by trial and error, and needed to be updated for changing military technology.
Gunpowder does not burn as a single reaction, so the byproducts are not easily predicted. One study showed that it produced (in order of descending quantities) 55.91% solid products: potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2 CO3. It is a white salt, which is soluble in water. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and gl ...
, potassium sulfate
Potassium sulfate (US) or potassium sulphate (UK), also called sulphate of potash (SOP), arcanite, or archaically potash of sulfur, is the inorganic compound with formula K2SO4, a white water-soluble solid. It is commonly used in fertilizers, prov ...
, potassium sulfide
Potassium sulfide is an inorganic compound with the formula K2 S. The colourless solid is rarely encountered, because it reacts readily with water, a reaction that affords potassium hydrosulfide (KSH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH). Most commonl ...
, sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
, potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and ...
, potassium thiocyanate
Potassium thiocyanate is the chemical compound with the molecular formula KSCN. It is an important salt of the thiocyanate anion, one of the pseudohalides. The compound has a low melting point relative to most other inorganic salts.
Use in che ...
, carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
, ammonium carbonate
Ammonium carbonate is a salt with the chemical formula (NH4)2CO3. Since it readily degrades to gaseous ammonia and carbon dioxide upon heating, it is used as a leavening agent and also as smelling salt. It is also known as baker's ammonia and is ...
and 42.98% gaseous products: carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
, nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simpl ...
, hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The under ...
, hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
, methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
, 1.11% water.
Gunpowder made with less-expensive and more plentiful sodium nitrate instead of potassium nitrate (in appropriate proportions) works just as well. However, it is more hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance' ...
than powders made from potassium nitrate. Muzzleloader
A muzzleloader is any firearm into which the projectile and the propellant charge is loaded from the muzzle of the gun (i.e., from the forward, open end of the gun's barrel). This is distinct from the modern (higher tech and harder to make) desig ...
s have been known to fire after hanging on a wall for decades in a loaded state, provided they remained dry. By contrast, gunpowder made with sodium nitrate must be kept sealed to remain stable.
Gunpowder releases 3 megajoules per kilogram
The kilogram (also kilogramme) is the unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo colloquially. ...
and contains its own oxidant. This is less than TNT
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagen ...
(4.7 megajoules per kilogram), or gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
(47.2 megajoules per kilogram in combustion, but gasoline requires an oxidant; for instance, an optimized gasoline and O2 mixture releases 10.4 megajoules per kilogram, taking into account the mass of the oxygen).
Gunpowder also has a low energy density
In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or .
Often only the ''useful'' or extrac ...
compared to modern "smokeless" powders, and thus to achieve high energy loadings, large amounts are needed with heavy projectiles.
Production

 For the most powerful black powder, meal powder, a
For the most powerful black powder, meal powder, a wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
charcoal, is used. The best wood for the purpose is Pacific willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
, but others such as alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few sp ...
or buckthorn
''Rhamnus'' is a genus of about 110 accepted species of shrubs or small trees, commonly known as buckthorns, in the family Rhamnaceae. Its species range from tall (rarely to ) and are native mainly in east Asia and North America, but found thr ...
can be used. In Great Britain between the 15th and 19th centuries charcoal from alder buckthorn was greatly prized for gunpowder manufacture; cottonwood was used by the American Confederate States
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
. The ingredients are reduced in particle size and mixed as intimately as possible. Originally, this was with a mortar-and-pestle or a similarly operating stamping-mill, using copper, bronze or other non-sparking materials, until supplanted by the rotating ball mill
A ball mill is a type of grinder used to grind or blend materials for use in mineral dressing processes, paints, pyrotechnics, ceramics, and selective laser sintering. It works on the principle of impact and attrition: size reduction is done ...
principle with non-sparking bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids suc ...
or lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
. Historically, a marble or limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
edge runner mill, running on a limestone bed, was used in Great Britain; however, by the mid 19th century this had changed to either an iron-shod stone wheel or a cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron– carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuri ...
wheel running on an iron bed. The mix was dampened with alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
or water during grinding to prevent accidental ignition. This also helps the extremely soluble saltpeter to mix into the microscopic pores of the very high surface-area charcoal.
Around the late 14th century, European powdermakers first began adding liquid during grinding to improve mixing, reduce dust, and with it the risk of explosion. The powder-makers would then shape the resulting paste of dampened gunpowder, known as mill cake, into corns, or grains, to dry. Not only did corned powder keep better because of its reduced surface area, gunners also found that it was more powerful and easier to load into guns. Before long, powder-makers standardized the process by forcing mill cake through sieves instead of corning powder by hand.
The improvement was based on reducing the surface area of a higher density composition. At the beginning of the 19th century, makers increased density further by static pressing. They shoveled damp mill cake into a two-foot square box, placed this beneath a screw press and reduced it to half its volume. "Press cake" had the hardness of slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
. They broke the dried slabs with hammers or rollers, and sorted the granules with sieves into different grades. In the United States, Eleuthere Irenee du Pont, who had learned the trade from Lavoisier, tumbled the dried grains in rotating barrels to round the edges and increase durability during shipping and handling. (Sharp grains rounded off in transport, producing fine "meal dust" that changed the burning properties.)
Another advance was the manufacture of kiln charcoal by distilling wood in heated iron retorts instead of burning it in earthen pits. Controlling the temperature influenced the power and consistency of the finished gunpowder. In 1863, in response to high prices for Indian saltpeter, DuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
chemists developed a process using potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water- soluble form.
or mined potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt ...
to convert plentiful Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
an sodium nitrate to potassium nitrate.
The following year (1864) the Gatebeck Low Gunpowder Works in Cumbria (Great Britain) started a plant to manufacture potassium nitrate by essentially the same chemical process. This is nowadays called the 'Wakefield Process', after the owners of the company. It would have used potassium chloride from the Staßfurt mines, near Magdeburg, Germany, which had recently become available in industrial quantities.
During the 18th century, gunpowder factories became increasingly dependent on mechanical energy. Despite mechanization, production difficulties related to humidity control, especially during the pressing, were still present in the late 19th century. A paper from 1885 laments that "Gunpowder is such a nervous and sensitive spirit, that in almost every process of manufacture it changes under our hands as the weather changes." Pressing times to the desired density could vary by a factor of three depending on the atmospheric humidity.
Legal status
TheUnited Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
Model Regulations on the Transportation of Dangerous Goods
Dangerous goods, abbreviated DG, are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials ( syllabi ...
and national transportation authorities, such as United States Department of Transportation
The United States Department of Transportation (USDOT or DOT) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is headed by the secretary of transportation, who reports directly to the President of the United States and ...
, have classified gunpowder (black powder) as a ''Group A: Primary explosive substance'' for shipment because it ignites so easily. Complete manufactured devices containing black powder are usually classified as ''Group D: Secondary detonating substance, or black powder, or article containing secondary detonating substance'', such as firework, class D model rocket
A model rocket are small rockets designed to reach low altitudes (e.g., for model) and be recovered by a variety of means.
According to the United States National Association of Rocketry (NAR) Safety Code, model rockets are constructed of ...
engine, etc., for shipment because they are harder to ignite than loose powder. As explosives, they all fall into the category of Class 1 .
Other uses
Besides its use as a propellant in firearms and artillery, black powder's other main use has been as a blasting powder in quarrying, mining, and road construction (including railroad construction). During the 19th century, outside of war emergencies such as the Crimean War or the American Civil War, more black powder was used in these industrial uses than in firearms and artillery.Dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern Germany, and patented in 1867. It rapidl ...
gradually replaced it for those uses. Today, industrial explosives for such uses are still a huge market, but most of the market is in newer explosives rather than black powder.
Beginning in the 1930s, gunpowder or smokeless powder was used in rivet guns, stun guns for animals, cable splicers and other industrial construction tools. The "stud gun", a powder-actuated tool
A powder-actuated tool (PAT, often generically called a Hilti gun or a Ramset gun after their manufacturing companies) is a type of nail gun used in construction and manufacturing to join materials to hard substrates such as steel and concret ...
, drove nails or screws into solid concrete, a function not possible with hydraulic tools, and today is still an important part of various industries, but the cartridges usually use smokeless powders. Industrial shotgun
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge known as a shotshell, which usually discharges numerous small pellet-like spherical sub- pr ...
s have been used to eliminate persistent material rings in operating rotary kilns (such as those for cement, lime, phosphate, etc.) and clinker in operating furnaces, and commercial tools make the method more reliable.
Gunpowder has occasionally been employed for other purposes besides weapons, mining, fireworks and construction:
* After the Battle of Aspern-Essling
In the Battle of Aspern-Essling (21–22 May 1809), Napoleon I of France, Napoleon crossed the Danube near Vienna, but the French and their allies were attacked and forced back across the river by the Austrian Empire, Austrians under Archduke ...
(1809), Dominique-Jean Larrey
Baron Dominique Jean Larrey (; 8 July 1766 – 25 July 1842) was a French surgeon and military doctor, who distinguished himself in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. An important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, ...
, the surgeon of the Napoleonic Army, lacking salt, seasoned a horse meat
Horse meat forms a significant part of the culinary traditions of many countries, particularly in Eurasia. The eight countries that consume the most horse meat consume about 4.3 million horses a year. For the majority of humanity's early existen ...
bouillon for the wounded under his care with gunpowder.Larrey is quoted in French at Dr Béraud, Études Hygiéniques de la chair de cheval comme aliment
'',
Musée des Familles
''Musée des familles'' (''"Museum of Families"'') was an illustrated French literary magazine that was published in Paris from 1833 to 1900. It was founded by Émile de Girardin.
Contributors of the magazine included Alexandre Dumas, Théophile ...
(1841–42). It was also used for sterilization in ships when there was no alcohol.
* British sailors used gunpowder to create tattoo
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing ...
s when ink wasn't available, by pricking the skin and rubbing the powder into the wound in a method known as traumatic tattooing.
* Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists o ...
experimented with gunpowder in 1673 in an early attempt to build an gunpowder engine, but he did not succeed. Modern attempts to recreate his invention were similarly unsuccessful.
* Near London in 1853, Captain Shrapnel demonstrated a mineral processing
In the field of extractive metallurgy, mineral processing, also known as ore dressing, is the process of separating commercially valuable minerals from their ores.
History
Before the advent of heavy machinery the raw ore was broken up using ...
use of black powder in a method for crushing gold-bearing ores by firing them from a cannon into an iron chamber, and "much satisfaction was expressed by all present". He hoped it would be useful on the goldfields
Goldfield or Goldfields may refer to:
Places
* Goldfield, Arizona, the former name of Youngberg, Arizona, a populated place in the United States
* Goldfield, Colorado, a community in the United States
* Goldfield, Iowa, a city in the United Sta ...
of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
. Nothing came of the invention, as continuously-operating crushing machines that achieved more reliable comminution
Comminution is the reduction of solid materials from one average particle size to a smaller average particle size, by crushing, grinding, cutting, vibrating, or other processes. In geology, it occurs naturally during faulting in the upper part ...
were already coming into use.''Mining Journal'' 22 January 1853, p. 61
* Starting in 1967, Los Angeles-based artist Ed Ruscha
Edward Joseph Ruscha IV (, ''roo-SHAY''; born December 16, 1937) is an American artist associated with the pop art movement. He has worked in the media of painting, printmaking, drawing, photography and film. He is also noted for creating severa ...
began using gunpowder as an artistic medium for a series of works on paper.
See also
*Ballistics
Ballistics is the field of mechanics concerned with the launching, flight behaviour and impact effects of projectiles, especially ranged weapon munitions such as bullets, unguided bombs, rockets or the like; the science or art of designing a ...
* Berthold Schwarz
* Black powder rocket motor
* Black powder substitute
A black powder substitute is a replacement for black powder used in muzzleloading and cartridge firearms. Black powder substitutes offer a number of advantages over black powder, primarily including reduced sensitivity as an explosive and in ...
* Bulk loaded liquid propellants
* Faversham explosives industry
Faversham, in Kent, England, has claims to be the cradle of the UK's explosives industry: it was also to become one of its main centres. The first gunpowder plant in the UK was established in the 16th century, possibly at the instigation of the ...
* Gunpowder magazine
A gunpowder magazine is a magazine (building) designed to store the explosive gunpowder in wooden barrels for safety. Gunpowder, until superseded, was a universal explosive used in the military and for civil engineering: both applications ...
* Gunpowder Plot
The Gunpowder Plot of 1605, in earlier centuries often called the Gunpowder Treason Plot or the Jesuit Treason, was a failed assassination attempt against King James I by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby who sough ...
* Gunpowder warfare
Early modern warfare is the era of warfare following medieval warfare. It is associated with the start of the widespread use of gunpowder and the development of suitable weapons to use the explosive, including artillery and firearms; for thi ...
* Technology of the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; 960–1279 CE) invented some technological advances in Chinese history, many of which came from talented statesmen drafted by the government through imperial examinations.
The ingenuity of advanced mechanical engineeri ...
Notes
References
* . * . * . * . * . * . * * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * * . * . * . * Hadden, R. Lee. 2005"Confederate Boys and Peter Monkeys."
Armchair General. January 2005. Adapted from a talk given to the
Geological Society of America
The Geological Society of America (GSA) is a nonprofit organization dedicated to the advancement of the geosciences.
History
The society was founded in Ithaca, New York, in 1888 by Alexander Winchell, John J. Stevenson, Charles H. Hitch ...
on 25 March 2004.
* .
* .
* .
*
* .
*
* .
* .
*
* .
* .
* .
* .
*
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* Schmidtchen, Volker (1977a), "Riesengeschütze des 15. Jahrhunderts. Technische Höchstleistungen ihrer Zeit", ''Technikgeschichte'' 44 (2): 153–73 (153–57)
* Schmidtchen, Volker (1977b), "Riesengeschütze des 15. Jahrhunderts. Technische Höchstleistungen ihrer Zeit", ''Technikgeschichte'' 44 (3): 213–37 (226–28).
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
*
External links
Gun and Gunpowder
Oare Gunpowder Works, Kent, UK
Royal Gunpowder Mills
A digital exhibit produced by the Hagley Library that covers the founding and early history of the DuPont Company powder yards in Delaware *
Video Demonstration
of the Medieval Siege Society's Guns, Including showing ignition of gunpowder
Black Powder Recipes
* {{Use dmy dates, date=December 2019 Chinese inventions Explosives Firearm propellants Pyrotechnic compositions Rocket fuels Solid fuels