Gulf of Mexico on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an


 The consensus among geologistsSalvador, A. (1991) ''Origin and development of the Gulf of Mexico basin'', in A. Salvador, ed., p. 389–444, The Gulf of Mexico Basin: The Geology of North America, v. J., Geological Society of America, Boulder, Colorado.Stern, R.J., and W.R. Dickinson (2010
The consensus among geologistsSalvador, A. (1991) ''Origin and development of the Gulf of Mexico basin'', in A. Salvador, ed., p. 389–444, The Gulf of Mexico Basin: The Geology of North America, v. J., Geological Society of America, Boulder, Colorado.Stern, R.J., and W.R. Dickinson (2010
''The Gulf of Mexico is a Jurassic backarc basin.''
Geosphere. 6(6):739–754. who have studied the geology of the Gulf of Mexico is that before the Late
''Is the Gulf's Origin Heaven Sent?''
AAPG Explorer (Dec. 2002) American Association of Petroleum Geologists. Tulsa Oklahoma. However, Gulf Coast geologists do not regard this hypothesis as having any credibility. Instead they overwhelmingly accept plate tectonics, not an asteroid impact, as having created the Gulf of Mexico as illustrated by papers authored by Kevin Mickus and others. This hypothesis is not to be confused with the
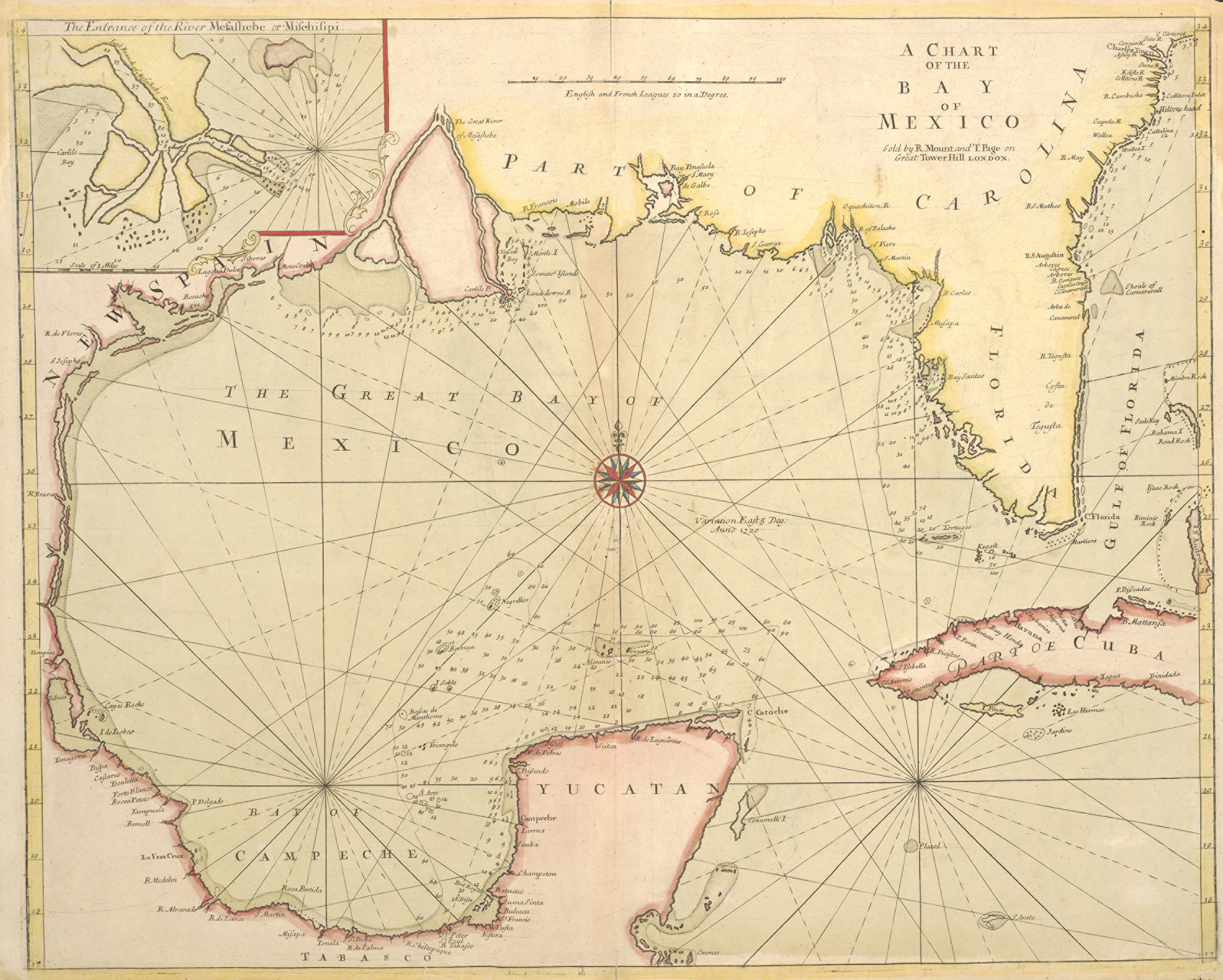
 Although the Spanish voyage of
Although the Spanish voyage of

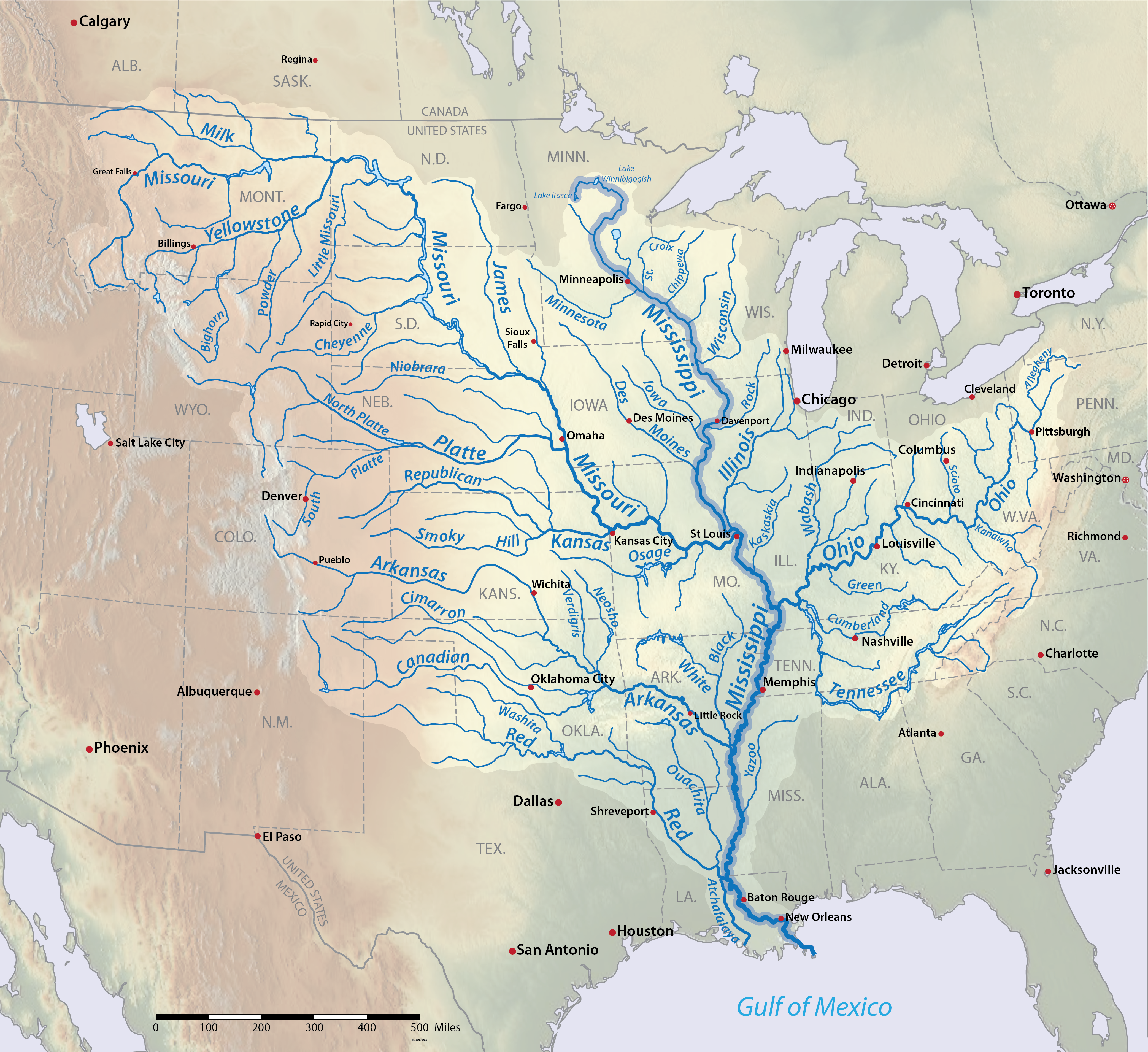

 The Gulf of Mexico's eastern, northern, and northwestern shores lie along the US states of Florida, Alabama,
The Gulf of Mexico's eastern, northern, and northwestern shores lie along the US states of Florida, Alabama,
The earthquake was described by the USGS as an
PDF
Recently, resident Bryde's whales within the gulf were classified as an endemic, unique subspecies and making them as one of the most endangered whales in the world. The Gulf of Mexico yields more finfish, shrimp, and
 The major environmental threats to the Gulf are
The major environmental threats to the Gulf are
 On April 20, 2010, the ''
On April 20, 2010, the ''
Resource Database for Gulf of Mexico Research
Gulf of Mexico Integrated Science
Mystery Mardi Gras Shipwreck
* *
Bathymetry of the Northern Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean East of Florida
The Present State of the West-Indies: Containing an Accurate Description of What Parts Are Possessed by the Several Powers in Europe
written by
BP Oil Spill
NPR {{DEFAULTSORT:Gulf Of Mexico Bodies of water of Alabama Bodies of water of Florida Bodies of water of Louisiana Bodies of water of Mississippi Bodies of water of Texas Gulfs of Mexico Gulfs of the Atlantic Ocean Gulfs of the United States Landforms of Campeche Landforms of Tabasco Landforms of Tamaulipas Landforms of Veracruz Landforms of Yucatán Marginal seas of the Atlantic Ocean Mexico–United States border
ocean basin
In hydrology, an oceanic basin (or ocean basin) is anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater. Geologically, ocean basins are large geologic basins that are below sea level.
Most commonly the ocean is divided into basins fol ...
and a marginal sea
This is a list of seas of the World Ocean, including marginal seas, areas of water, various gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.
Terminology
* Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Ocea ...
of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississ ...
; on the southwest and south by the Mexican states of Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas), is a state in the northeast region of Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entiti ...
, Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
, Tabasco
Tabasco (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tabasco), is one of the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It is located in ...
, Campeche
Campeche (; yua, Kaampech ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Campeche), is one of the 31 states which make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by ...
, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo ( , ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo), is one of the 31 states which, with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 11 mu ...
; and on the southeast by Cuba. The Southern U.S. states of Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
, Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
, and Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast
Third Coast is an American colloquialism used to describe coastal regions distinct from the East Coast and the West Coast of the United States. Generally, the term "Third Coast" refers to either the Great Lakes region or in some circles the G ...
" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
coasts).
The Gulf of Mexico took shape approximately 300 million years ago as a result of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
.Huerta, A.D., and D.L. Harry (2012) ''Wilson cycles, tectonic inheritance, and rifting of the North American Gulf of Mexico continental margin.'' Geosphere. 8(1):GES00725.1, first published on March 6, 2012, The Gulf of Mexico basin
The formation of the Gulf of Mexico, an oceanic rift basin located between North America and the Yucatan Block, was preceded by the breakup of the Supercontinent Pangaea in the Late-Triassic, weakening the lithosphere. Rifting between the North ...
is roughly oval in shape and is approximately wide. Its floor consists of sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
s and recent sediments. It is connected to part of the Atlantic Ocean through the Florida Straits
The Straits of Florida, Florida Straits, or Florida Strait ( es, Estrecho de Florida) is a strait located south-southeast of the North American mainland, generally accepted to be between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean, and between th ...
between the U.S. and Cuba, and with the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
via the Yucatán Channel
The Yucatán Channel or Straits of Yucatán (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Canal de Yucatán'') is a strait between Mexico and Cuba. It connects the Yucatán Basin of the Caribbean Sea with the Gulf of Mexico. It is just over wide and nearly deep ...
between Mexico and Cuba. Because of its narrow connection to the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf experiences very small tidal ranges. The size of the Gulf basin is approximately 1.6 million km2 (615,000 sq mi). Almost half of the basin consists of shallow continental-shelf waters. The volume of water in the basin is roughly (). The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most important offshore petroleum
Offshore drilling is a mechanical process where a wellbore is drilled below the seabed. It is typically carried out in order to explore for and subsequently extract petroleum that lies in rock formations beneath the seabed. Most commonly, the te ...
production regions in the world, making up one-sixth of the United States' total production.
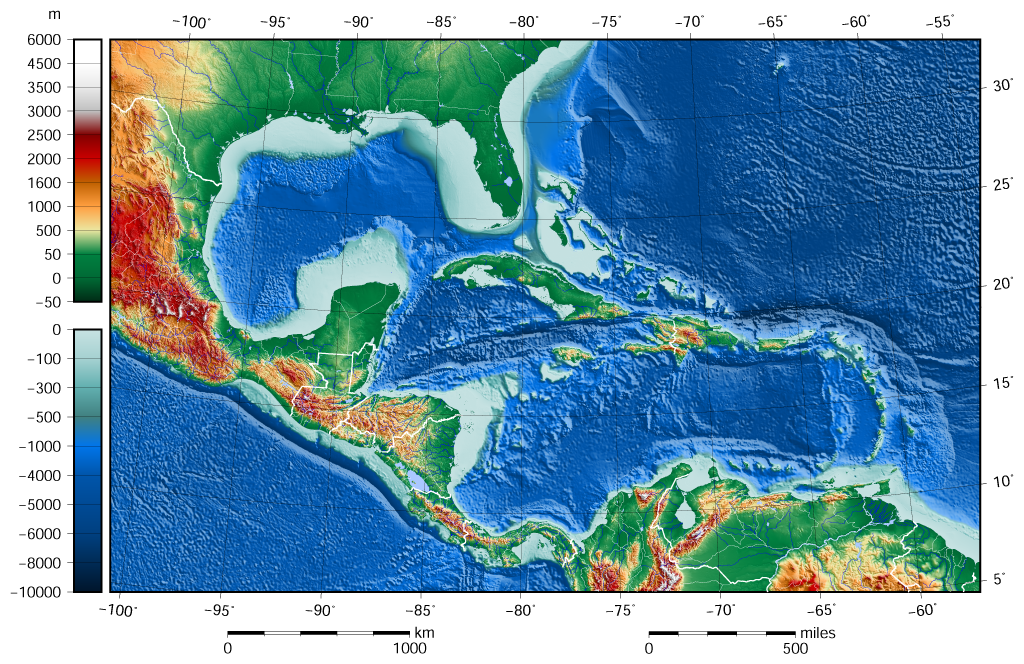
Extent
TheInternational Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) is an intergovernmental organisation representing hydrography. , the IHO comprised 98 Member States.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ensure that the world's seas, oceans and navigable waters a ...
defines the southeast limit of the Gulf of Mexico as:
A line joiningCape Catoche Cabo Catoche or Cape Catoche, in the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, is the northernmost point on the Yucatán Peninsula. It lies in the municipality of Isla Mujeres, about north of the city of Cancún. According to the International Hydrograph ...Light () with the Light on Cape San Antonio in Cuba, through this island to the meridian of 83°W and to the Northward along this meridian to the latitude of the South point of theDry Tortugas Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the seven Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most isolated of the Florida Keys. The archipelago's c ...(24°35'N), along this parallel Eastward to Rebecca Shoal (82°35'W) thence through the shoals and Florida Keys to the mainland at the eastern end ofFlorida Bay Florida Bay is the bay located between the southern end of the Florida mainland (the Florida Everglades) and the Florida Keys in the United States. It is a large, shallow estuary that while connected to the Gulf of Mexico, has limited exchange o ...and all the narrow waters between the Dry Tortugas and the mainland being considered to be within the Gulf.
Geology


 The consensus among geologistsSalvador, A. (1991) ''Origin and development of the Gulf of Mexico basin'', in A. Salvador, ed., p. 389–444, The Gulf of Mexico Basin: The Geology of North America, v. J., Geological Society of America, Boulder, Colorado.Stern, R.J., and W.R. Dickinson (2010
The consensus among geologistsSalvador, A. (1991) ''Origin and development of the Gulf of Mexico basin'', in A. Salvador, ed., p. 389–444, The Gulf of Mexico Basin: The Geology of North America, v. J., Geological Society of America, Boulder, Colorado.Stern, R.J., and W.R. Dickinson (2010''The Gulf of Mexico is a Jurassic backarc basin.''
Geosphere. 6(6):739–754. who have studied the geology of the Gulf of Mexico is that before the Late
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
, the Gulf of Mexico did not exist. Before the Late Triassic, the area now occupied by the Gulf of Mexico consisted of dry land, which included continental crust that now underlies Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate mun ...
, within the middle of the large supercontinent of Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
. This land lay south of a continuous mountain range that extended from north-central Mexico, through the Marathon Uplift
The Marathon Uplift is a Paleogene-age domal uplift, approximately in diameter, in southwest Texas. The Marathon Basin was created by erosion of Cretaceous and younger strata from the crest of the uplift.McBride, E.F. and Hayward, O.T., 1988''Ge ...
in West Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
and the Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
of Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
, and to Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
where it linked directly to the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
. It was created by the collision of continental plates that formed Pangea. As interpreted by Roy Van Arsdale and Randel T. Cox, this mountain range was breached in Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
times by the formation of the Mississippi Embayment
The Mississippi embayment is a physiographic feature in the south-central United States, part of the Mississippi Alluvial Plain. It is essentially a northward continuation of the fluvial sediments of the Mississippi River Delta to its conflue ...
.Van Arsdale, R. B. (2009) ''Adventures Through Deep Time: The Central Mississippi River Valley and Its Earthquakes.'' Special Paper no. 455, Geological Society of America, Boulder, Colorado. 107 pp.Cox, R. T., and R. B. Van Arsdale (2002) ''The Mississippi Embayment, North America: a first order continental structure generated by the Cretaceous superplume mantle event.'' Journal of Geodynamics. 34:163–176.
Geologists and other Earth scientists agree in general that the present Gulf of Mexico basin originated in Late Triassic time as the result of rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben ...
within Pangea. The rifting was associated with zones of weakness within Pangea, including sutures where the Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
, South American, and African plates collided to create it. First, there was a Late Triassic-Early Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
phase of rifting during which rift valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear d ...
s formed and filled with continental red beds. Second, as rifting progressed through Early and Middle Jurassic times, the continental crust was stretched and thinned. This thinning created a broad zone of transitional crust, which displays modest and uneven thinning with block faulting, and a broad zone of uniformly thinned transitional crust, which is half the typical thickness of normal continental crust. It was at this time that rifting first created a connection to the Pacific Ocean across central Mexico and later eastward to the Atlantic Ocean. This flooded the opening basin to create the Gulf of Mexico as an enclosed marginal sea. While the Gulf of Mexico was a restricted basin, the subsiding transitional crust was blanketed by the widespread deposition of Louann Salt
The Louann Salt is a widespread evaporite formation that formed in the Gulf of Mexico during the Callovian in the mid Jurassic. The Louann formed in a rift as the South American and North American Plates separated, from an embayment of the Pacific ...
and associated anhydrite
Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with the ...
evaporite
An evaporite () is a water- soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean ...
s. During the Late Jurassic, continued rifting widened the Gulf of Mexico and progressed to the point that sea-floor spreading and formation of oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumu ...
occurred. At this point, sufficient circulation with the Atlantic Ocean was established that the deposition of Louann Salt
The Louann Salt is a widespread evaporite formation that formed in the Gulf of Mexico during the Callovian in the mid Jurassic. The Louann formed in a rift as the South American and North American Plates separated, from an embayment of the Pacific ...
ceased.Buffler, R. T., 1991, ''Early Evolution of the Gulf of Mexico Basin'', in D. Goldthwaite, ed., pp. 1–15, Introduction to Central Gulf Coast Geology, New Orleans Geological Society, New Orleans, Louisiana.Galloway, W. E., 2008, ''Depositional evolution of the Gulf of Mexico sedimentary basin.'' in K.J. Hsu, ed., pp. 505–549, The Sedimentary Basins of the United States and Canada, Sedimentary Basins of the World. v. 5, Elsevier, The Netherlands. Seafloor spreading stopped at the end of Jurassic time, about 145–150 million years ago.
During the Late Jurassic through Early Cretaceous, the basin occupied by the Gulf of Mexico experienced a period of cooling and subsidence of the crust underlying it. The subsidence was the result of a combination of crustal stretching, cooling, and loading. Initially, the combination of crustal stretching and cooling caused about of tectonic subsidence of the central thin transitional and oceanic crust. Because subsidence occurred faster than sediment could fill it, the Gulf of Mexico expanded and deepened.Sawyer, D. S., R. T. Buffler, and R. H. Pilger, Jr., 1991, ''The crust under the Gulf of Mexico basin'', in A. Salvador, ed., pp. 53–72, The Gulf of Mexico Basin: The Geology of North America, v. J., Geological Society of America
The Geological Society of America (GSA) is a nonprofit organization dedicated to the advancement of the geosciences.
History
The society was founded in Ithaca, New York, in 1888 by Alexander Winchell, John J. Stevenson, Charles H. Hitchco ...
, Boulder, Colorado
Boulder is a home rule city that is the county seat and most populous municipality of Boulder County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 108,250 at the 2020 United States census, making it the 12th most populous city in Color ...
.
Later, loading of the crust within the Gulf of Mexico and adjacent coastal plain by the accumulation of kilometers of sediments during the rest of the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
and all of the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
further depressed the underlying crust to its current position about below sea level. Particularly during the Cenozoic, a time of relative stability for the Gulf's coastal zones, thick clastic wedge
In geology, clastic wedge usually refers to a thick assemblage of sediments--often lens-shaped in profile--eroded and deposited landward of a mountain chain; they begin at the mountain front, thicken considerably landwards of it to a peak depth, an ...
s built out the continental shelf along the northwestern and northern margins of the Gulf of Mexico.
To the east, the stable Florida platform was not covered by the sea until the latest Jurassic or the beginning of Cretaceous time. The Yucatán platform was emergent until the mid-Cretaceous. After both platforms were submerged, the formation of carbonates
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
and evaporites
An evaporite () is a water-soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean ...
has characterized the geologic history of these two stable areas. Most of the basin was rimmed during the Early Cretaceous by carbonate platforms, and its western flank was involved during the latest Cretaceous and early Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
periods in a compressive deformation episode, the Laramide Orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
, which created the Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental () is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that f ...
of eastern Mexico.
In 2002 geologist Michael Stanton published a speculative essay suggesting an impact origin for the Gulf of Mexico at the close of the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
, which could have caused the Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–T, P–Tr) extinction event, also known as the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian Extinction and colloquially as the Great Dying, formed the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, as ...
.Stanton, M. S., 2002''Is the Gulf's Origin Heaven Sent?''
AAPG Explorer (Dec. 2002) American Association of Petroleum Geologists. Tulsa Oklahoma. However, Gulf Coast geologists do not regard this hypothesis as having any credibility. Instead they overwhelmingly accept plate tectonics, not an asteroid impact, as having created the Gulf of Mexico as illustrated by papers authored by Kevin Mickus and others. This hypothesis is not to be confused with the
Chicxulub Crater
The Chicxulub crater () is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore near the community of Chicxulub, after which it is named. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when a large a ...
, a large impact crater on the coast of the Gulf of Mexico on the Yucatán Peninsula. Increasingly, the Gulf of Mexico is regarded as a back-arc basin behind the Jurassic Nazas Arc of Mexico.
In 2014 Erik Cordes of Temple University
Temple University (Temple or TU) is a public state-related research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was founded in 1884 by the Baptist minister Russell Conwell and his congregation Grace Baptist Church of Philadelphia then called Ba ...
and others discovered a brine pool
A brine pool, sometimes called an underwater lake, deepwater or brine lake, is a volume of brine collected in a seafloor depression. The pools are dense bodies of water that have a salinity that is three to eight times greater than the surrou ...
below the gulf's surface, with a circumference of and feet deep, which is four to five times saltier than the rest of the water. The first exploration of the site was unmanned, using Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
and in 2015 a team of three used the deep submergence vehicle
A deep-submergence vehicle (DSV) is a deep-diving crewed submersible that is self-propelled. Several navies operate vehicles that can be accurately described as DSVs. DSVs are commonly divided into two types: research DSVs, which are used for ex ...
. The site cannot sustain any kind of life other than bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other ...
s with a symbiotic relationship
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
, tube worm
A tubeworm is any worm-like sessile invertebrate that anchors its tail to an underwater surface and secretes around its body a mineral tube, into which it can withdraw its entire body.
Tubeworms are found among the following taxa:
* Annelida, the ...
s and certain kinds of shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
. It has been called the "Jacuzzi of Despair". Because it is warmer than the surrounding water ( compared to ), animals are attracted to it, but cannot survive once they enter it.
Today, the Gulf of Mexico has the following seven main areas:
* Gulf of Mexico basin
The formation of the Gulf of Mexico, an oceanic rift basin located between North America and the Yucatan Block, was preceded by the breakup of the Supercontinent Pangaea in the Late-Triassic, weakening the lithosphere. Rifting between the North ...
, which contains the Sigsbee Deep
The Sigsbee DeepThe name "Sigsbee Deep" has sometimes been applied to Sigsbee Basin, a U. S. Board on Geographic Names approved name for a feature nominally a42° 58' 00" N 069° 13' 00" Win the Gulf of Maine. See multiple features named for Sigsbe ...
and can be further divided into the continental rise, the Sigsbee Abyssal Plain, and the Mississippi Cone.
* Northeast Gulf of Mexico, which extends from a point east of the Mississippi River Delta near Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in and one of two county seats of Harrison County, Mississippi, United States (the other being the adjacent city of Gulfport). The 2010 United States Census recorded the population as 44,054 and in 2019 the estimated popu ...
to the eastern side of Apalachee Bay
Apalachee Bay is a bay in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico occupying an indentation of the Florida coast to the west of where the Florida peninsula joins the United States mainland. It is bordered by Taylor County, Florida, Taylor, Jefferson Coun ...
.
* South Florida Continental Shelf and Slope, which extends along the coast from Apalachee Bay to the Straits of Florida
The Straits of Florida, Florida Straits, or Florida Strait ( es, Estrecho de Florida) is a strait located south-southeast of the North American mainland, generally accepted to be between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean, and between t ...
and includes the Florida Keys and Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the seven Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most isolated of the Florida Keys. The archipelago's c ...
* Campeche Bank
Campeche Bank is part of the Gulf of Mexico and extends from the Yucatan Straits in the east to the Tabasco-Campeche Basin in the west.Campeche Bankin Geonames.org (cc-by)/ref> The Campeche ocean bank is from Mexico's geography of Campeche na ...
, which extends from the Yucatán Straits in the east to the Tabasco
Tabasco (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tabasco), is one of the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It is located in ...
– Campeche Basin in the west and includes Arrecife Alacran.
* Bay of Campeche, which is an isthmian embayment
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a na ...
extending from the western edge of Campeche Bank to the offshore regions just east of the port of Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
.
* Western Gulf of Mexico, which is located between Veracruz to the south and the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
to the north.
* Northwest Gulf of Mexico, which extends from Alabama to the Rio Grande.
History
Pre-Columbian
As early as theMaya Civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, archit ...
, the Gulf of Mexico was used as a trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
off the coast of the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
and present-day Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
.
Spanish exploration

 Although the Spanish voyage of
Although the Spanish voyage of Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
was credited with the discovery of the Americas by Europeans, the ships in his four voyages never reached the Gulf of Mexico. Instead, the Spanish sailed into the Caribbean around Cuba and Hispaniola. The first alleged European exploration of the Gulf of Mexico was by Amerigo Vespucci in 1497. Columbus is purported to have followed the coastal land mass of Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
before returning to the Atlantic Ocean via the Straits of Florida between Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
and Cuba. However, this first voyage of 1497 is widely disputed and many historians doubt that it took place as described. In his letters, Vespucci described this trip, and once Juan de la Cosa
Juan de la Cosa (c. 1450 – 28 February 1510) was a Castilian navigator and cartographer, known for designing the earliest European world map which incorporated the territories of the Americas discovered in the 15th century.
De la Cosa was th ...
returned to Spain, a famous world map, depicting Cuba as an island, was produced.
In 1506, Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of w ...
took part in the conquest of Hispaniola and Cuba, receiving a large estate of land and indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
slaves for his effort. In 1510, he accompanied Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar, an aide of the governor of Hispaniola, in his expedition to conquer Cuba. In 1518 Velázquez put him in command of an expedition to explore and secure the interior of Mexico for colonization.
In 1517, Francisco Hernández de Córdoba Francisco Hernández de Córdoba may refer to:
* Francisco Hernández de Córdoba (Yucatán conquistador) (died 1517)
* Francisco Hernández de Córdoba (founder of Nicaragua) (died 1526)
{{hndis, name=Hernandez de Cordoba, Francisco ...
discovered the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
. This was the first European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
encounter with an advanced civilization in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, with solidly built buildings and a complex social organization which they recognized as being comparable to those of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by the ...
; they also had reason to expect that this new land would have gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
. All of this encouraged two further expeditions, the first in 1518 under the command of Juan de Grijalva
Juan de Grijalva (; born c. 1490 in Cuéllar, Crown of Castile – 21 January 1527 in Honduras) was a Spanish conquistador, and a relative of Diego Velázquez.Diaz, B., 1963, The Conquest of New Spain, London: Penguin Books, He went to Hispanio ...
, and the second in 1519 under the command of Hernán Cortés, which led to the Spanish exploration, military invasion, and ultimately settlement and colonization known as the Conquest of Mexico
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the eve ...
. Hernández did not live to see the continuation of his work: he died in 1517, the year of his expedition, as the result of the injuries and the extreme thirst suffered during the voyage, and disappointed in the knowledge that Diego Velázquez
Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez (baptized June 6, 1599August 6, 1660) was a Spanish painter, the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV of Spain and Portugal, and of the Spanish Golden Age. He was an individualistic artist of th ...
had given precedence to Grijalva as the captain of the next expedition to Yucatán.
In 1523, a treasure ship was wrecked en route along the coast of Padre Island
Padre Island is the largest of the Texas barrier islands and the world's longest barrier island. The island is located along Texas's southern coast of the Gulf of Mexico and is noted for its white sandy beaches. Meaning ''father'' in Spanish, it ...
, Texas. When word of the disaster reached Mexico City, the viceroy requested a rescue fleet and immediately sent Ángel de Villafañe
Ángel de Villafañe (b. c. 1504) was a Spanish conquistador of Florida, Mexico, and Guatemala, and was an explorer, expedition leader, and ship captain (with Hernán Cortés), who worked with many 16th-century settlements and shipwrecks alo ...
, in Mexico City with Cortés, marching overland to find the treasure-laden vessels. Villafañe traveled to Pánuco and hired a ship to transport him to the site, which had already been visited from that community. He arrived in time to greet García de Escalante Alvarado (a nephew of Pedro de Alvarado), commander of the salvage operation, when Alvarado arrived by sea on July 22, 1554. The team labored until September 12 to salvage the Padre Island treasure. This loss, in combination with other ship disasters around the Gulf of Mexico, gave rise to a plan for establishing a settlement on the northern Gulf Coast to protect shipping and more quickly rescue castaways. As a result, the expedition of Tristán de Luna y Arellano
Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510 – September 16, 1573) was a Spanish explorer and Conquistador of the 16th century.Herbert Ingram Priestley, Tristan de Luna: Conquistador of the Old South: A Study of Spanish Imperial Strategy (1936). http://palm ...
was sent and landed at Pensacola Bay
Pensacola Bay is a bay located in the northwestern part of Florida, United States, known as the Florida Panhandle.
The bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, is located in Escambia County and Santa Rosa County, adjacent to the city of Pensacola ...
on August 15, 1559.
On December 11, 1526, Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
granted Pánfilo de Narváez
Pánfilo de Narváez (; 147?–1528) was a Spanish '' conquistador'' and soldier in the Americas. Born in Spain, he first embarked to Jamaica in 1510 as a soldier. He came to participate in the conquest of Cuba and led an expedition to Camagü ...
a license to claim what is now the Gulf Coast of the United States, known as the Narváez expedition
The Narváez expedition was a Spanish journey of exploration and colonization started in 1527 that intended to establish colonial settlements and garrisons in Florida. The expedition was initially led by Pánfilo de Narváez, who died in 1528. M ...
. The contract gave him one year to gather an army, leave Spain, be large enough to found at least two towns of 100 people each, and garrison two more fortresses anywhere along the coast. On April 7, 1528, they spotted land north of what is now Tampa Bay
Tampa Bay is a large natural harbor and shallow estuary connected to the Gulf of Mexico on the west-central coast of Florida, comprising Hillsborough Bay, McKay Bay, Old Tampa Bay, Middle Tampa Bay, and Lower Tampa Bay. The largest freshwater in ...
. They turned south and traveled for two days looking for a great harbor the master pilot Miruelo knew of. Sometime during these two days, one of the five remaining ships was lost on the rugged coast, but nothing else is known of it.
In 1697, Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (16 July 1661 – 9 July 1706) or Sieur d'Iberville was a French soldier, explorer, colonial administrator, and trader. He is noted for founding the colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal to French ...
sailed for France and was chosen by the Minister of Marine to lead an expedition to rediscover the mouth of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
and to colonize Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
which the English coveted. Iberville's fleet sailed from Brest on October 24, 1698. On January 25, 1699, Iberville reached Santa Rosa Island in front of Pensacola
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal ci ...
founded by the Spanish; he sailed from there to Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The ...
and explored Massacre Island, later renamed Dauphin Island
Dauphin Island is an island town in Mobile County, Alabama, United States, on a barrier island of the same name, in the Gulf of Mexico. It incorporated in 1988. The population was 1,778 at the 2020 census, up from 1,238 at the 2010 census. The t ...
. He cast anchor between Cat Island and Ship Island
Ship Island is a barrier island off the Gulf Coast of Mississippi, one of the Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands. Hurricane Camille split the island into two separate islands (West Ship Island and East Ship Island) in 1969. In early 2019, ...
; and on February 13, 1699, he went to the mainland, Biloxi, with his brother Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville
Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville (; ; February 23, 1680 – March 7, 1767), also known as Sieur de Bienville, was a French colonial administrator in New France. Born in Montreal, he was an early governor of French Louisiana, appointed four ...
. On May 1, 1699, he completed a fort on the north-east side of the Bay of Biloxi, a little to the rear of what is now Ocean Springs, Mississippi
Ocean Springs is a city in Jackson County, Mississippi, United States, approximately east of Biloxi and west of Gautier. It is part of the Pascagoula, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 17,225 at the 2000 U.S. Census. ...
. This fort was known as Fort Maurepas
Fort Maurepas, later known as Old Biloxi,
"Pierre Le Moyne, Sieur d'Iberville" (biography),
''Catholic Encyclopedia'', 1907, webpage:
gives dates: 13 Feb. 1699, went to the mainland Biloxi,
with fort completion May 1, 1699; sailed f ...
or Old Biloxi. A few days later, on May 4, Pierre Le Moyne sailed for France leaving his teenage brother, Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne, as second in command to the French commandant.
Geography



 The Gulf of Mexico's eastern, northern, and northwestern shores lie along the US states of Florida, Alabama,
The Gulf of Mexico's eastern, northern, and northwestern shores lie along the US states of Florida, Alabama, Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
, Louisiana, and Texas. The US portion of the Gulf coastline spans , receiving water from 33 major rivers that drain 31 states. The Gulf's southwestern and southern shores lie along the Mexican state
The states of Mexico are first-level administrative territorial entities of the country of Mexico, which is officially named Mexico, United Mexican States. There are 32 federal entities in Mexico (31 states and the capital, Mexico City, as a sepa ...
s of Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas), is a state in the northeast region of Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entiti ...
, Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
, Tabasco
Tabasco (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tabasco), is one of the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It is located in ...
, Campeche
Campeche (; yua, Kaampech ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Campeche), is one of the 31 states which make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by ...
, Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate mun ...
, and the northernmost tip of Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo ( , ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo), is one of the 31 states which, with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 11 mu ...
. The Mexican portion of the Gulf coastline spans 1,743 miles (2,805 km). On its southeast quadrant, the Gulf is bordered by Cuba. It supports major American, Mexican and Cuban fishing industries. The outer margins of the wide continental shelves of Yucatán and Florida receive cooler, nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
-enriched waters from the deep by a process known as upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nut ...
, which stimulates plankton growth in the euphotic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
. This attracts fish, shrimp, and squid. River
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
drainage and atmospheric fallout from industrial coastal cities also provide nutrients to the coastal zone.
The Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
, a warm Atlantic Ocean current and one of the strongest ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, s ...
s known, originates in the gulf, as a continuation of the Caribbean Current
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
-Yucatán Current-Loop Current
A parent to the Florida Current, the Loop Current is a warm ocean current that flows northward between Cuba and the Yucatán Peninsula, moves north into the Gulf of Mexico, loops east and south before exiting to the east through the Florida Stra ...
system. Other circulation features include the anticyclonic gyre
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction dete ...
s which are shed by the Loop Current and travel westward where they eventually dissipate and a permanent cyclonic gyre in the Bay of Campeche. The Bay of Campeche in Mexico constitutes a major arm of the Gulf of Mexico. Additionally, the gulf's shoreline is fringed by numerous bays and smaller inlets. A number of rivers empty into the gulf, most notably the Mississippi River and the Rio Grande in the northern gulf, and the Grijalva and Usumacinta
The Usumacinta River (; named after the howler monkey) is a river in southeastern Mexico and northwestern Guatemala. It is formed by the junction of the Pasión River, which arises in the Sierra de Santa Cruz (in Guatemala) and the Salinas ...
rivers in the southern gulf. The land that forms the gulf's coast, including many long, narrow barrier islands, is almost uniformly low-lying and is characterized by marshes and swamps as well as stretches of sandy beach.
The Gulf of Mexico is an excellent example of a passive margin
A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting cre ...
. The continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
is quite wide at most points along the coast, most notably at the Florida and Yucatán Peninsulas. The shelf is exploited for its oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
by means of offshore drilling rigs, most of which are situated in the western gulf and in the Bay of Campeche. Another important commercial activity is fishing; major catches include red snapper
Red snapper is a common name of several fish species. It may refer to:
* Several species from the genus ''Lutjanus'':
** ''Lutjanus campechanus'', Northern red snapper, commonly referred to as red snapper in the Gulf of Mexico and western Atlanti ...
, amberjack
Amberjacks are Atlantic and Pacific fish in the genus '' Seriola'' of the family Carangidae. They are widely consumed across the world in various cultures, most notably for Pacific amberjacks in Japanese cuisine; they are most often found in th ...
, tilefish
250px, Blue blanquillo, ''Malacanthus latovittatus''
Tilefishes are mostly small perciform marine fish comprising the family Malacanthidae. They are usually found in sandy areas, especially near coral reefs.
Commercial fisheries exist for th ...
, swordfish, and various grouper
Groupers are fish of any of a number of genera in the subfamily Epinephelinae of the family Serranidae, in the order Perciformes.
Not all serranids are called "groupers"; the family also includes the sea basses. The common name "grouper" is ...
, as well as shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
and crabs
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
. Oysters are also harvested on a large scale from many of the bays and sounds. Other important industries along the coast include shipping, petrochemical processing and storage, military use, paper manufacture, and tourism.
The gulf's warm water temperature can feed powerful Atlantic hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s causing extensive human death and other destruction as happened with Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a destructive Category 5 Atlantic hurricane that caused over 1,800 fatalities and $125 billion in damage in late August 2005, especially in the city of New Orleans and the surrounding areas. It was at the time the cost ...
in 2005. In the Atlantic, a hurricane will draw up cool water from the depths and making it less likely that further hurricanes will follow in its wake (warm water being one of the preconditions necessary for their formation). However, the Gulf is shallower; when a hurricane passes over the water temperature may drop but it soon rebounds and becomes capable of supporting another tropical storm.
The Gulf is considered aseismic
In geology, aseismic creep or fault creep is measurable surface displacement along a fault in the absence of notable earthquakes. Aseismic creep may also occur as "after-slip" days to years after an earthquake. Notable examples of aseismic slip in ...
; however, mild tremors have been recorded throughout history (usually 5.0 or less on the Richter magnitude scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 ...
). Earthquakes may be caused by interactions between sediment loading on the sea floor and adjustment by the crust.
2006 earthquake
On September 10, 2006, the U.S. Geological Survey National Earthquake Information Center reported that a magnitude 6.0earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
occurred about west-southwest of Anna Maria, Florida
Anna Maria is a city in Manatee County, Florida, United States. The population was 968 at the 2020 census, down from 1,503 in 2010. The city occupies the northern part of Anna Maria Island and is one of three municipalities on the island. The ...
, around 10:56 am EDT. The quake was reportedly felt from Louisiana to Florida in the Southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern por ...
. There were no reports of damage or injuries. Items were knocked from shelves and seiche
A seiche ( ) is a standing wave in an enclosed or partially enclosed body of water. Seiches and seiche-related phenomena have been observed on lakes, reservoirs, swimming pools, bays, harbors, caves and seas. The key requirement for formation of ...
s were observed in swimming pools in parts of Florida.United States Geological Survey, September 11, 2006The earthquake was described by the USGS as an
intraplate earthquake
The term intraplate earthquake refers to a variety of earthquake that occurs ''within the interior'' of a tectonic plate; this stands in contrast to an interplate earthquake, which occurs ''at the boundary'' of a tectonic plate. Intraplate earth ...
, the largest and most widely felt recorded in the past three decades in the region. According to the September 11, 2006 issue of ''The Tampa Tribune
''The Tampa Tribune'' was a daily newspaper published in Tampa, Florida. Along with the competing ''Tampa Bay Times'', the ''Tampa Tribune'' was one of two major newspapers published in the Tampa Bay area.
The newspaper also published a ''St. Pe ...
'', earthquake tremors were last felt in Florida in 1952, recorded in Quincy, northwest of Tallahassee
Tallahassee ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Florida. It is the county seat and only incorporated municipality in Leon County. Tallahassee became the capital of Florida, then the Florida Territory, in 1824. In 2020, the population ...
.
Maritime boundary delimitation agreements
Cuba and Mexico: Exchange of notes constituting an agreement on thedelimitation
Boundary delimitation (or simply delimitation) is the drawing of boundaries, particularly of electoral precincts, states, counties or other municipalities.
of the exclusive economic zone of Mexico in the sector adjacent to Cuban maritime areas (with map), of July 26, 1976.
Cuba and United States: Maritime boundary
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Boun ...
agreement between the United States of America and the Republic of Cuba, of December 16, 1977.
Mexico and United States: Treaty to resolve pending boundary differences and maintain the Rio Grande and Colorado River as the international boundary, of November 23, 1970; Treaty on maritime boundaries between the United States of America and the United Mexican States (Caribbean Sea and Pacific Ocean), of May 4, 1978, and Treaty between the Government of the United States of America and the Government of the United Mexican States on the delimitation of the continental shelf in the Western Gulf of Mexico beyond , of June 9, 2000.
On December 13, 2007, Mexico submitted information to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS) regarding the extension of Mexico's continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles. Mexico sought an extension of its continental shelf in the Western Polygon based on international law, UNCLOS, and bilateral treaties with the United States, in accordance with Mexico's domestic legislation. On March 13, 2009, the CLCS accepted Mexico's arguments for extending its continental shelf up to into the Western Polygon. Since this would extend Mexico's continental shelf well into territory claimed by the United States, however, Mexico and the U.S. would need to enter a bilateral agreement based on international law that delimits their respective claims.
Shipwrecks
A ship now called the ''Mardi Gras'' sank around the early 19th century about off the coast of Louisiana in of water. She is believed to have been aprivateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
or trader. The shipwreck, whose real identity remains a mystery, lay forgotten at the bottom of the sea until it was discovered in 2002 by an oilfield inspection crew working for the Okeanos Gas Gathering Company (OGGC). In May 2007, an expedition, led by Texas A&M University and funded by OGGC under an agreement with the Minerals Management Service (now BOEM
The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior, established in 2010 by Secretarial Order.
The Outer Continental Shelf Lands Act (OCSLA) states: "...the outer Continental Shelf is a vi ...
), was launched to undertake the deepest scientific archaeological excavation ever attempted at that time to study the site on the seafloor and recover artifacts for eventual public display in the Louisiana State Museum
The Louisiana State Museum (LSM), founded in New Orleans in 1906, is a statewide system of National Historic Landmarks and modern structures across Louisiana, housing thousands of artifacts and works of art reflecting Louisiana's legacy of historic ...
. As part of the project educational outreach Nautilus Productions
Nautilus Productions LLC is an American video production, stock footage, and photography company incorporated in Fayetteville, North Carolina in 1997. The principals are producer/director Rick Allen and photographer Cindy Burnham. Nautilus specia ...
in partnership with BOEM, Texas A&M University, the Florida Public Archaeology Network
The Florida Public Archaeology Network, or FPAN, is a state supported organization of regional centers dedicated to public outreach and assisting Florida municipalities and the Florida Division of Historical Resources "to promote the stewardship ...
and Veolia Environmental produced a one-hour HD documentary about the project, short videos for public viewing and provided video updates during the expedition. Video footage from the ROV was an integral part of this outreach and used extensively in the ''Mystery Mardi Gras Shipwreck'' documentary.
On July 30, 1942, the ''Robert E. Lee'', captained by William C. Heath, was torpedoed by the . She was sailing southeast of the entrance to the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
when the explosion destroyed the #3 hold, vented through the B and C decks and damaged the engines, the radio compartment and the steering gear. After the attack she was under escort by USS ''PC-566'', captained by Lieutenant Commander Herbert G. Claudius, en route to New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
. ''PC-566'' began dropping Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
depth charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive Shock factor, hydraulic shock. Most depth ...
s on a sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect o ...
contact, sinking ''U-166''. The badly damaged ''Robert E. Lee'' first listed to port then to starboard and finally sank within about 15 minutes of the attack. One officer, nine crewmen and 15 passengers were lost. The passengers aboard ''Robert E. Lee'' were primarily survivors of previous torpedo attacks by German U-boats. The wreck's precise location was discovered during the C & C Marine survey that located the ''U-166''.
The German submarine ''U-166'' was a Type IXC U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role ...
of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
's ''Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the a ...
'' during World War II. The submarine was laid down on December 6, 1940, at the Seebeckwerft (part of Deutsche Schiff- und Maschinenbau AG
Deutsche Schiff- und Maschinenbau Aktiengesellschaft (abbreviated Deschimag) was a cooperation of eight German shipyards in the period 1926 to 1945. The leading company was the shipyard AG Weser in Bremen.
History
The Deschimag was founded in 1 ...
, Deschimag) at Wesermünde
Bremerhaven (, , Low German: ''Bremerhoben'') is a city at the seaport of the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, a state of the Federal Republic of Germany.
It forms a semi-enclave in the state of Lower Saxony and is located at the mouth of the ...
(modern Bremerhaven) as yard number 705, launched on November 1, 1941, and commissioned on March 23, 1942, under the command of ''Oberleutnant zur See
''Oberleutnant zur See'' (''OLt zS'' or ''OLZS'' in the German Navy, ''Oblt.z.S.'' in the '' Kriegsmarine'') is traditionally the highest rank of Lieutenant in the German Navy. It is grouped as OF-1 in NATO.
The rank was introduced in the Imp ...
'' Hans-Günther Kuhlmann. After training with the 4th U-boat Flotilla, ''U-166'' was transferred to the 10th U-boat Flotilla for front-line service on June 1, 1942. The U-boat sailed on only two war patrols and sank four ships totalling . She was sunk on July 30, 1942, in Gulf of Mexico.
In 2001 the wreck of ''U-166'' was found in of water, less than from where it had attacked ''Robert E. Lee''. An archaeological survey of the seafloor before the construction of a natural gas pipeline led to the discoveries by C & C Marine archaeologists Robert A. Church and Daniel J. Warren. The sonar contacts consisted of two large sections lying approximately apart at either end of a debris field that indicated the presence of a U-boat.
Biota
Various biota includechemosynthetic
In biochemistry, chemosynthesis is the biological conversion of one or more carbon-containing molecules (usually carbon dioxide or methane) and nutrients into organic matter using the oxidation of inorganic compounds (e.g., hydrogen gas, hydro ...
communities near cold seep
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature of the see ...
s and non chemosynthetic communities such as bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and other micro – benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.meiofauna
Meiobenthos, also called meiofauna, are small benthic invertebrates that live in both marine and fresh water environments. The term ''meiofauna'' loosely defines a group of organisms by their size, larger than microfauna but smaller than macrof ...
, macrofauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoo ...
, and megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
(larger organisms such as crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s, sea pen
Sea pens are colonial marine cnidarians belonging to the order Pennatulacea. There are 14 families within the order; 35 extant genera, and it is estimated that of 450 described species, around 200 are valid. Sea pens have a co ...
s, crinoid
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are ...
s, demersal fish, cetaceans, and the extinct Caribbean monk seal
The Caribbean monk seal (''Neomonachus tropicalis''), also known as the West Indian seal or sea wolf, was a species of seal native to the Caribbean which is now believed to be extinct. The main predators of Caribbean monk seals were sharks and h ...
) are living in the Gulf of Mexico.Minerals Management Service
The Minerals Management Service (MMS) was an agency of the United States Department of the Interior that managed the nation's natural gas, oil and other mineral resources on the outer continental shelf (OCS).
Due to perceived conflict of inter ...
Gulf of Mexico OCS Region (November 2006). "Gulf of Mexico OCS Oil and Gas Lease Sales: 2007–2012. Western Planning Area Sales 204, 207, 210, 215, and 218. Central Planning Area Sales 205, 206, 208, 213, 216, and 222. Draft Environmental Impact Statement. Volume I: Chapters 1–8 and Appendices". U.S. Department of the Interior, Minerals Management Service, Gulf of Mexico OCS Region, New Orleans. page 3-27–3-3Recently, resident Bryde's whales within the gulf were classified as an endemic, unique subspecies and making them as one of the most endangered whales in the world. The Gulf of Mexico yields more finfish, shrimp, and
shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater envir ...
annually than the south
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
and mid-Atlantic, Chesapeake Chesapeake often refers to:
*Chesapeake people, a Native American tribe also known as the Chesepian
* The Chesapeake, a.k.a. Chesapeake Bay
*Delmarva Peninsula, also known as the Chesapeake Peninsula
Chesapeake may also refer to:
Populated plac ...
, and New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
areas combined.
The Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
Gulf of Mexico holdings are expected to provide an important baseline of understanding for future scientific studies on the impact of the ''Deepwater Horizon'' oil spill. In Congressional testimony, Dr. Jonathan Coddington, associate director of Research and Collections at the Smithsonian's National Museum of Natural History
The National Museum of Natural History is a natural history museum administered by the Smithsonian Institution, located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., United States. It has free admission and is open 364 days a year. In 2021, with 7 ...
, provides a detailed overview of the Gulf collections and their sources which Museum staff have made available on an online map. The samples were collected for years by the former Minerals Management Service (renamed the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, Regulation and Enforcement
The Minerals Management Service (MMS) was an agency of the United States Department of the Interior that managed the nation's natural gas, oil and other mineral resources on the outer continental shelf (OCS).
Due to perceived conflict of intere ...
) to help predict the potential impacts of future oil/gas explorations. Since 1979, the specimens have been deposited in the national collections of the National Museum of Natural History.
Pollution
 The major environmental threats to the Gulf are
The major environmental threats to the Gulf are agricultural runoff
Agricultural pollution refers to biotic and abiotic byproducts of farming practices that result in contamination or degradation of the environment and surrounding ecosystems, and/or cause injury to humans and their economic interests. The pol ...
and oil drilling
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may ...
.
There are frequent "red tide
A harmful algal bloom (HAB) (or excessive algae growth) is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural phycotoxin, algae-produced toxins, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are ...
" algae blooms that kill fish and marine mammals and cause respiratory problems in humans and some domestic animals when the blooms reach close to shore. This has especially been plaguing the southwest and southern Florida coast, from the Florida Keys to north of Pasco County, Florida
Pasco County is located on the west central coast of the U.S. state of Florida. According to the 2020 census, the population was 561,691. Its county seat is Dade City, and its largest city is Zephyrhills. The county is named after Samuel Pas ...
.
In 1973 the United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it be ...
prohibited the dumping of undiluted chemical waste by manufacturing interests into the Gulf and the military confessed to similar behavior in waters off Horn Island.
The Gulf contains a hypoxic
Hypoxia means a lower than normal level of oxygen, and may refer to:
Reduced or insufficient oxygen
* Hypoxia (environmental), abnormally low oxygen content of the specific environment
* Hypoxia (medical), abnormally low level of oxygen in the t ...
dead zone that runs east–west along the Texas-Louisiana coastline. In July 2008, researchers reported that between 1985 and 2008, the area roughly doubled in size. It was in 2017, the largest ever recorded. Poor agricultural practices in the northern portion of the Gulf of Mexico have led to a tremendous increase of nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
and phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
in neighboring marine ecosystems, which has resulted in algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
blooms and a lack of available oxygen. Occurrences of masculinization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens.
Virilization is most commonly used in three medical and biology ...
and estrogen suppression were observed as a result. An October 2007 study of the Atlantic croaker
The Atlantic croaker (''Micropogonias undulatus'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Sciaenidae and is closely related to the black drum ('' Pogonias cromis''), the silver perch ('' Bairdiella chrysoura''), the spot c ...
found a disproportioned sex ratio of 61% males to 39% females in hypoxic Gulf sites. This was compared with a 52% to 48% male-female ratio found in reference sites, showing an impairment of reproductive output for fish populations inhabiting hypoxic coastal zones.
Microplastics within semi-enclosed seas like the Gulf have been reported in high concentrations and the Gulf's first such study estimated concentrations that rival the highest globally reported.
There are 27,000 abandoned oil and gas wells beneath the Gulf. These have generally not been checked for potential environmental problems.
''Ixtoc I'' explosion and oil spill
In June 1979, the '' Ixtoc I''oil platform
An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platfor ...
in the Bay of Campeche suffered a blowout leading to a catastrophic explosion, which resulted in a massive oil spill that continued for nine months before the well was finally capped. This was ranked as the largest oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico until the ''Deepwater Horizon'' oil spill in 2010.
''Deepwater Horizon'' explosion and oil spill
 On April 20, 2010, the ''
On April 20, 2010, the ''Deepwater Horizon
''Deepwater Horizon'' was an ultra-deepwater, dynamically positioned, semi-submersible offshore drilling rig owned by Transocean and operated by BP. On 20 April 2010, while drilling at the Macondo Prospect, a blowout caused an explosion ...
'' oil platform, located in the Mississippi Canyon
The Mississippi Canyon is an undersea canyon, part of the Mississippi Submarine Valley in the North-central Gulf of Mexico, south of Louisiana. According to the U.S. Geological Survey GLORIA Mapping Program, it is the dominant feature of the nor ...
about off the Louisiana coast, suffered a catastrophic explosion; it sank a day and a half later. It was in the process of being sealed with cement for temporary abandonment, to avoid environmental problems. Although initial reports indicated that relatively little oil had leaked, by April 24, it was claimed by BP that approximately of oil per day were issuing from the wellhead
A wellhead is the component at the surface of an oil or gas well that provides the structural and pressure-containing interface for the drilling and production equipment.
The primary purpose of a wellhead is to provide the suspension point and ...
, about below the surface on the ocean floor. On April 29, the U.S. government revealed that approximately per day, five times the original estimate, were pouring into the Gulf from the wellhead. The resulting oil slick
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into th ...
quickly expanded to cover hundreds of square miles of ocean surface, posing a serious threat to marine life and adjacent coastal wetlands and to the livelihoods of Gulf Coast shrimpers and fishermen. Coast Guard Rear Adm. Sally Brice O'Hare stated that the US government will be "employing booms, skimmers, chemical dispersants and controlled burns" to combat the oil spill. By May 1, 2010, the oil spill cleanup efforts were underway but hampered by rough seas and the "tea like" consistency of the oil. Cleanup operations were resumed after conditions became favorable. On May 27, 2010, The USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, a ...
had revised the estimate of the leak from to 12,000– an increase from earlier estimates. On July 15, 2010, BP announced that the leak stopped for the first time in 88 days.
In July 2015 BP reached an $18.7bn settlement with the US government, the states of Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi and Texas, as well as 400 local authorities. To date, BP's cost for the clean-up, environmental and economic damages and penalties has reached $54bn.
Minor oil spills
According to theNational Response Center
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, mul ...
, the oil industry has thousands of minor accidents in the Gulf of Mexico every year.
''Brutus'' oil spill
On May 12, 2016, a release of oil from subsea infrastructure on Shell's ''Brutus'' oil rig released 2,100 barrels of oil. This leak created a visible oil slick in the sea about south of Port Fourchon,Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, according to the U.S. Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement.
See also
*American Mediterranean Sea
The American Mediterranean Sea is a scientific name for the mediterranean dilution basin which includes the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. The name, which has been employed particularly by German oceanographers, is not recognized by the ...
* Charlotte Harbor (estuary), an estuary in Florida
* Green Canyon
Green Canyon is an area in the Gulf of Mexico that is rich in oil fields and under the jurisdiction of the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management. Among other oil fields Green Canyon consist of Atlantis (blocks 699, 700, 742, 743, and 744) operated b ...
, a US Gulf of Mexico petroleum exploration area
* Gulf Coast of the United States
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississ ...
* Gulf of Mexico Foundation The Gulf of Mexico Foundation is a nonprofit organization that was founded in 1990 by citizens concerned with the health and productivity of the Gulf of Mexico.
Programs
Based in Corpus Christi, Texas, the Foundation operates several programs to ...
* Jack 2 (a test well in the deep waters of the Gulf of Mexico)
* Keathley Canyon
Keathley Canyon is an undersea canyon in the United States Exclusive Economic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico. The canyon is named for the hydrographic survey ship USNS ''Sergeant George D. Keathley'' (T-AGS-35).
The Canyon is rich in oil fields. T ...
, a US Gulf of Mexico petroleum exploration area
* Nepheloid layer A nepheloid layer or nepheloid zone is a layer of water in the deep ocean basin, above the ocean floor, that contains significant amounts of suspended sediment. It is from 200 to 1000 m thick. The name comes from Greek: ''nephos'', "cloud". The part ...
* Orca Basin
The Orca Basin is a mid-slope, silled, mini-basin in the northern Gulf of Mexico some 300 km southwest of the Mississippi River mouth on the Louisiana continental slope.Meckler, A. N., et al.''Glacial to Holocene terrigenous organic matter in ...
* Outer Continental Shelf
The Outer Continental Shelf (OCS) is a feature of the geography of the United States. The OCS is the part of the internationally recognized continental shelf of the United States which does not fall under the jurisdictions of the individual U. ...
* Sigsbee Escarpment
The Sigsbee Escarpment is a major bathymetric feature of the Gulf of Mexico, extending for about . It separates the lower continental slope of the northern gulf from the abyssal plain of the Sigsbee Deep and has up to of relief across it. It has ...
, a US Gulf of Mexico petroleum exploration area
* Territorial evolution of the Caribbean
* Tunica Mound
References
External links
Resource Database for Gulf of Mexico Research
Gulf of Mexico Integrated Science
Mystery Mardi Gras Shipwreck
* *
Bathymetry of the Northern Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean East of Florida
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
The Present State of the West-Indies: Containing an Accurate Description of What Parts Are Possessed by the Several Powers in Europe
written by
Thomas Kitchin
Thomas Kitchin (also Kitchen; 1718–1784) was an United Kingdom, English engraver and cartographer, who became hydrographer to the king. He was also a writer, who wrote about the history of the West Indies.
Life
He was born in Southwark, and wa ...
, 1778, in which Kitchin discusses, in chapter 1, why the Gulf should have been called the "West Indian Sea."
BP Oil Spill
NPR {{DEFAULTSORT:Gulf Of Mexico Bodies of water of Alabama Bodies of water of Florida Bodies of water of Louisiana Bodies of water of Mississippi Bodies of water of Texas Gulfs of Mexico Gulfs of the Atlantic Ocean Gulfs of the United States Landforms of Campeche Landforms of Tabasco Landforms of Tamaulipas Landforms of Veracruz Landforms of Yucatán Marginal seas of the Atlantic Ocean Mexico–United States border