Growth Chart on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A growth chart is used by 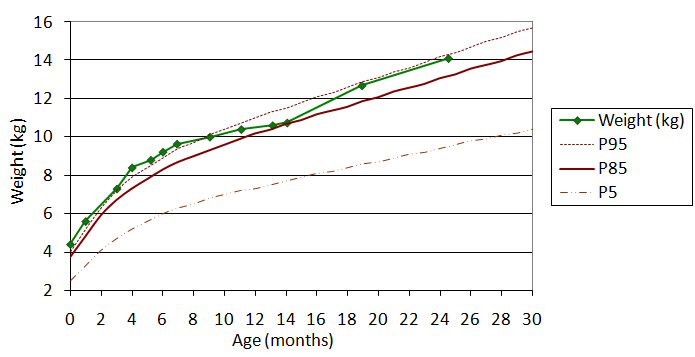 Growth charts are different for persons assigned male at birth and female at birth, due in part to pubertal differences and disparity in final adult height. In addition, children born prematurely and children with chromosomal abnormalities such as
Growth charts are different for persons assigned male at birth and female at birth, due in part to pubertal differences and disparity in final adult height. In addition, children born prematurely and children with chromosomal abnormalities such as
CDC information on growth charts
The WHO Child Growth Standards
Pediatrics
pediatricians
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the ...
and other health care providers to follow a child's growth over time. Growth charts have been constructed by observing the growth of large numbers of healthy children over time. The height
Height is measure of vertical distance, either vertical extent (how "tall" something or someone is) or vertical position (how "high" a point is).
For example, "The height of that building is 50 m" or "The height of an airplane in-flight is abou ...
, weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
Some standard textbooks define weight as a Euclidean vector, vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weigh ...
, and head circumference of a child can be compared to the expected parameters of children of the same age and sex to determine whether the child is growing appropriately. Growth charts can also be used to predict the expected adult height and weight of a child because, in general, children maintain a fairly constant growth curve. When a child deviates from his or her previously established growth curve, investigation into the cause is generally warranted. Parameters used to analyze growth charts include weight velocity (defined as rate of change in weight over time), height velocity (defined as rate of change in stature over time), and whether someone's growth chart crosses percentiles. For instance, endocrine disorders can be associated with a decrease in height velocity and preserved weight velocity while normal growth variants are associated with a decrease in height and weight velocity that are proportional to each other.
It's important to note that other parameters are more commonly used such as waist circumference for assessing obesity and skin fold difference for assessing malnutrition. Growth charts can also be compiled with a portion of the population deemed to have been raised in more or less ideal environments, such as nutrition that conforms to pediatric guidelines, and no maternal smoking. Charts from these sources end up with slightly taller but thinner averages.
 Growth charts are different for persons assigned male at birth and female at birth, due in part to pubertal differences and disparity in final adult height. In addition, children born prematurely and children with chromosomal abnormalities such as
Growth charts are different for persons assigned male at birth and female at birth, due in part to pubertal differences and disparity in final adult height. In addition, children born prematurely and children with chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual dis ...
and Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hair ...
follow distinct growth curves which deviate significantly from children without these conditions. As such, growth charts have been created to describe the expected growth patterns of several developmental conditions.
Since there are differences in normal growth rates between breastfed and formula-fed babies, the World Health Organization growth charts, which better reflect the growth pattern of the healthy, breastfed infant are considered the standard for U.S. children under age two.
History and Revisions to Growth Chart
The growth chart was first developed by theNational Center for Health Statistics
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) is a U.S. government agency that provides statistical information to guide actions and policies to improve the public health of the American people. It is a unit of the Centers for Disease Control ...
(NCHS) in 1977 to clinically analyze child development. The 1977 growth chart was subsequently used by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
for dissemination to healthcare systems abroad. In order to accommodate for heterogenous populations internationally, the WHO made an effort to gather data from different regions in every continent. Data used to calculate the CDC's growth chart percentiles was accumulated periodically since the 1960s by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a survey research program conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States, and t ...
. Updated and more comprehensive data was later used to revise the existing growth chart and construct the 2000 CDC growth charts. The revised growth charts include revision of the 14 existing charts as well as introduction of 2 new BMI-for-age charts.
Quantitative Definitions
Mid-parental height (MPH) is a quantity used to predict the target height of an individual based on the heights of the two biological parents. It can be used to calculate the target height (TH) for children assigned male (AMAB) or female (AFAB) at birth. * MPH = * TH for AFAB = * TH for AMAB = Velocity is another quantity that is used to quantify growth curves. It can be used for both height and weight. In the equation provided q is either weight or height, t represents time, and Δ represents change over a defined interval. Growth velocity is defined as follows. * Body mass index (BMI) is a useful quantification that can gauge level of obesity. It is defined as follows with the given clinical ranges. * *Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
: BMI > 95th percentile
* Overweight: 85th < BMI < 95th percentile
* Underweight: BMI < 5th percentile
Bone age Bone age is the degree of a person's skeletal development. In children, bone age serves as a measure of physiological maturity and aids in the diagnosis of growth abnormalities, endocrine disorders, and other medical conditions. As a person grows fr ...
is another useful metric that complements a physician's use of a growth chart. It is particularly useful in working up growth abnormalities and can indicate a delay in onset of puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
.
Common Variants of Normal Growth
* Familial short statue: Benign variant of normal height growth. Expect a normal bone age and a trajectory that is on track for the target height. * Constitutional growth delay: Benign variant of normal height growth due to a delay in the onset of puberty. Expect a delayed bone age and a trajectory that is not on track for the target height. * Endocrine Disorders: Pathologic variant of normal growth due to hormonal abnormality. Expect a delayed height trajectory accompanied by a gain of weight.Clinical Significance
The combination of height and weight velocity can indicate underlying disease of genetic origin, endocrine cause, and/or delayed growth.Normal Growth Deficiency
One of the most common growth disorders, a growth deficiency can be due to either familial short stature or constitutional growth delay(CGD). Familial short stature is indicative when one or both parents are of a short stature, and the height and weight percentiles are under the 5 percentile threshold. The child will be concordant with the mean parental height, and the bone age should be normal. Constitutional growth delays are marked by low height and weight percentiles as early as the first 4–6 months following birth.Genetic Syndromes
A variety of genetic syndromes can result growth chart patterns with a typical pattern. Genetic diseases such asTurner's syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hair ...
, Prader Willi, and Noonan syndrome can be marked by a less than 5th percentile height and weight since birth., Other genetic disorders such as Marfan's syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints a ...
and Klinefelter's syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY, is an aneuploid genetic condition where a male has an additional copy of the X chromosome. The primary features are infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles. Usually, symptoms are s ...
are typically indicated by a height above the 90th percentile.
Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders
A decrease of height velocity with retained or increased weight velocity can be indicative of endocrine disorders includinghypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
, growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or human growth hormone deficiency, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also presen ...
, and excess of glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
s.
Variability in Growth Charts
The CDC's growth chart is utilized from a population that consists of a representative population in the USA. Charts based on a specific race or ethnicity are not useful because of the growth chart progression can be attributed to socioeconomic factors. WHO launched a revised growth in 2006 chart using children from Ghana, Oman, Norway, Brazil, and the USA that substantiated the fact that growth is highly dependent on environmental factors.See also
*Failure to thrive
Failure to thrive (FTT), also known as weight faltering or faltering growth, indicates insufficient weight gain or absence of appropriate physical growth in children. FTT is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low ...
, a growth disorder
* Weight and height percentile Weight and height percentiles are determined by growth charts and body mass index charts to compare a child's measurements with those of other children in the same age group. By doing this, doctors can track a child's growth over time and monitor ho ...
*Endocrine disease
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
Types of disease
Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups:
# Endocrin ...
*Constitutional growth delay
Constitutional delay of growth and puberty (CDGP) is a term describing a temporary delay in the skeletal growth and thus height of a child with no physical abnormalities causing the delay. Short stature may be the result of a growth pattern inher ...
*Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or human growth hormone deficiency, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also presen ...
*Intrauterine growth restriction
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's ...
*Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
CDC information on growth charts
The WHO Child Growth Standards
Pediatrics