Greenhouse gas emissions by China are the largest of any country in the world both in
production and
consumption terms, and stem mainly from
coal burning in China, including
coal-fired power station
A coal-fired power station or coal power plant is a thermal power station which burns coal to generate electricity. Worldwide, there are about 8,500 coal-fired power stations totaling over 2,000 gigawatts Nameplate capacity, capacity. They ...
s,
coal mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
,
and
blast furnaces
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric ...
producing iron and steel. When measuring production-based emissions,
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
emitted over 14 gigatonnes (
Gt)
CO2eq of
greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane ...
es in 2019, 27% of the world total.
When measuring in consumption-based terms, which adds emissions associated with imported goods and extracts those associated with exported goods, China accounts for 13 gigatonnes (
Gt) or 25% of global emissions.
Despite having the largest emissions in the world, China's large
population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction usi ...
means its per person emissions have remained considerably lower than those in the developed world.
This corresponds to over 10.1 tonnes CO
2eq emitted per person each year, slightly over the world average and the EU average but significantly lower than
the second largest emitter of greenhouse gases, the United States, with its 17.6 tonnes per person.
Accounting for historic emissions,
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
countries produced four times more CO
2 in cumulative emissions than China, due to developed countries' early start in
industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
.
The targets laid out in China's
Nationally Determined Contribution
A nationally determined contribution (NDC) or intended nationally determined contribution (INDC) is a non-binding national plan highlighting climate change mitigation, including climate-related targets for greenhouse gas emission reductions. These ...
in 2016 will likely be met, but are not enough to properly combat global warming.
China has committed to peak emissions by 2030 and
net zero
Carbon neutrality is a state of net-zero carbon dioxide emissions. This can be achieved by balancing emissions of carbon dioxide with its removal (often through carbon offsetting) or by eliminating emissions from society (the transition to the " ...
by 2060. In order to limit warming to 1.5 degrees C
coal plants in China without carbon capture must be phased out by 2045.
China continues to build coal-fired power stations in 2020 and promised to "phase down" coal use from 2026.
Greenhouse gas sources

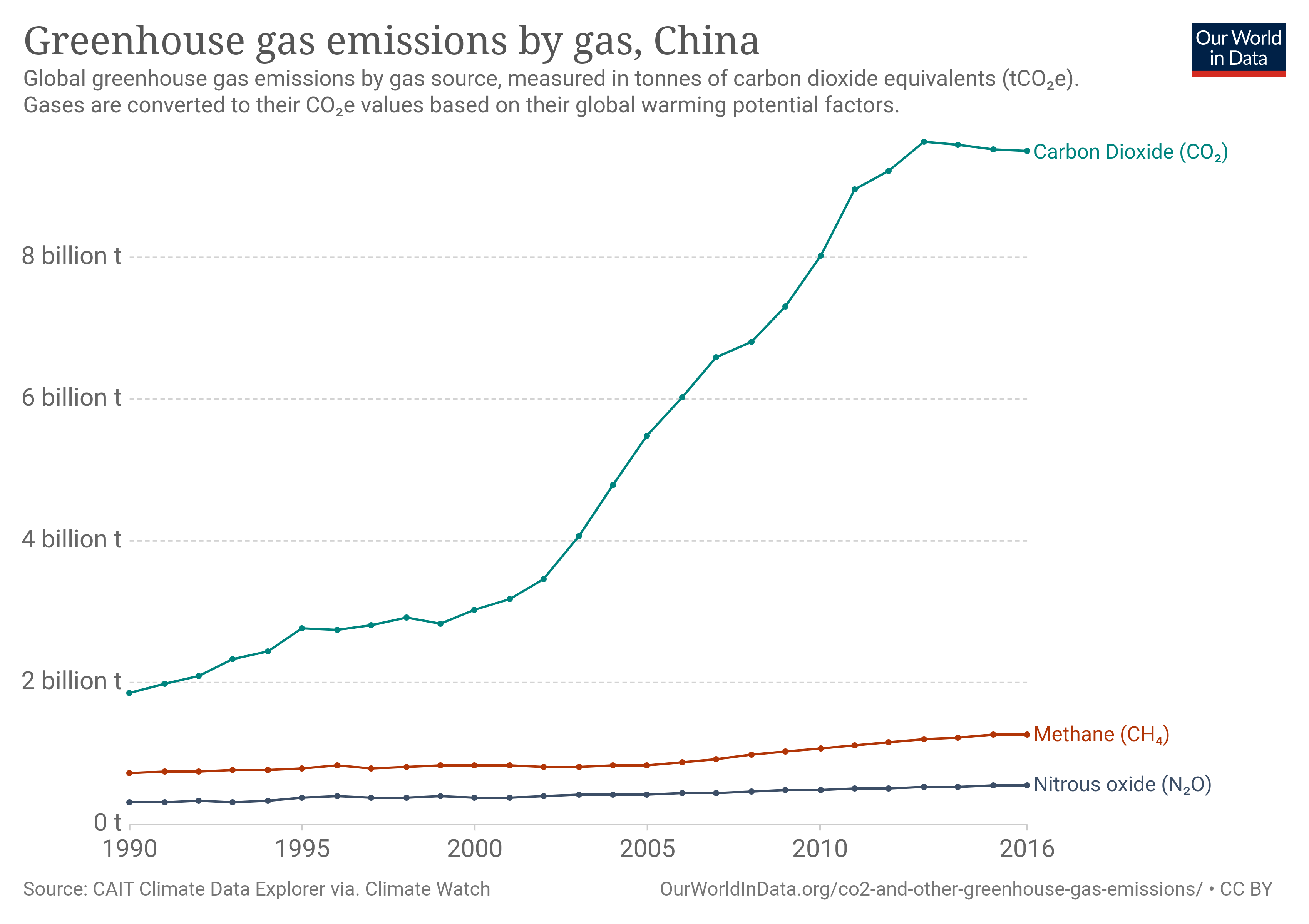


Since 2006,
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
has been the world's largest
emitter of annually. According to estimates provided by the Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency, China's carbon dioxide emissions in 2006 amounted to 6.2 billion tons, and the United States' co-production in the same year was 5.8 billion tons. In 2006, China's carbon dioxide emissions were 8 percent higher than America's, the agency said. The U.S. emitted 2% more carbon dioxide in 2005 than China. China ratified the
Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
as a
non-Annex B party without binding targets, and ratified the
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and ...
to fight
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
As the world's largest coal producer and consumer country, China worked hard to change energy structure and experienced a decrease in
coal consumption
Peak coal is the peak consumption or production of coal by a human community. Global coal consumption peaked in 2013, and had dropped slightly by the end of the 2010s.
The peak of coal's share in the global energy mix was in 2008, when coal accou ...
since 2013 to 2016.
However, China, the United States and India, the three biggest coal users, have increased coal mining in 2017.
The Chinese government has implemented several
policies to control coal consumption, and boosted the usage of
natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
and
electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describe ...
. Looking ahead, the construction and manufacturing industries of China will give way to the
service industry
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the second ...
, and the Chinese government will not set a higher goal for economic growth in 2018; thus coal consumption may not experience continuous growth in the next few years.
In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GhG, followed by the US with 11%, then India with 6.6%.
China is implementing some policies to mitigate the bad effects of climate change, most of which aim to constrain coal consumption. The Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) of China set goals and committed to peak CO
2 emissions by 2030 in the latest, and increase the use of non-
fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ma ...
energy carriers, taking up 20% of the total
primary energy
Primary energy (PE) is an energy form found in nature that has not been subjected to any human engineered conversion process. It is energy contained in raw fuels, and other forms of energy, including waste, received as input to a system. Prim ...
supply.
If China successfully reached NDC's targets, the GHG emissions level would be 12.8–14.3 Gte in 2030, reducing 64% to 70% of
emission intensity
An emission intensity (also carbon intensity or C.I.) is the emission rate of a given pollutant relative to the intensity of a specific activity, or an industrial production process; for example grams of carbon dioxide released per megajoule o ...
below 2005 levels. China has surpassed solar deployment and wind energy deployment targets for 2020.
Energy production
Electricity generation
Power is estimated as the largest emitter with 27% of 2020 GHG.
= Coal fired power stations
=
China's main power source is coal in China, which it mostly mines but also imports. According to a major 2020 study by Energy Foundation China, in order to limit warming to 1.5 degrees C coal plants without carbon capture must be phased out by 2045.
Transport fuel
Transport was estimated in 2021 to be less than 10% of emissions but growing.
Home energy
Energy consumption
According to the 2016 Chinese Statistical Yearbook published by
China's National Bureau of Statistics, China's energy consumption was 430,000 (10,000 tons of Standard Coal Equivalent), including 64% coal, 18.1% crude oil, 5.9% natural gas, 12.0% primary electricity, and other energy. Since 2011, the percentage of coal has decreased, and the percentage of crude oil, natural gas, primary electricity, and other energy have increased.
China experienced an increase in electricity demand and usage in 2017 as the economy accelerated. According to the Climate Data Explorer published by
World Resources Institute
The World Resources Institute (WRI) is a global research non-profit organization established in 1982 with funding from the MacArthur Foundation under the leadership of James Gustave Speth. WRI's activities are focused on seven areas: food, for ...
, China, the European Union, and the U.S. contributed to more than 50% of global
greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
.
In 2016, China's greenhouse gas emissions accounted for 26% of total global emissions. The energy industry has been the biggest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions since the last decade.
Although China has large countrywide emissions, its per capita carbon dioxide emissions are still lower than those of some other developed and developing countries.
Industry
Manufacturing industry is estimated at 19% of 2020 emissions.
Cement
Cement is estimated to be 15% of emissions but only a tenth of companies are reporting data as of 2021.
Iron and steel
Steel is estimated at 15% to 20% of emissions and consolidation of the industry may help.
Agriculture
Agriculture is estimated at 13% of 2020 GHG.
Slightly over half of agricultural emissions are estimated to be
nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and ha ...
and almost all the rest
methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
.
Waste
Waste is estimated at 6% of 2020 emissions.
Most municipal solid waste is sent to landfill.
Coal mine methane
China is by far the largest emitter of
methane from coal mines.
Mitigation
A 2011
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), commonly referred to as the Berkeley Lab, is a United States national laboratory that is owned by, and conducts scientific research on behalf of, the United States Department of Energy. Located in ...
report predicted that Chinese emissions will peak around 2030. This because in many areas such as infrastructure, housing, commercial building, appliances per household, fertilizers, and cement production a maximum intensity will be reached and replacement will take the place of new demand. The 2030 emissions peak also became China's pledge at the Paris COP21 summit. Carbon emission intensity may decrease as policies become strengthened and more effectively implemented, including by more effective financial incentives, and as less carbon intensive energy supplies are deployed. In a "baseline" computer model emissions were predicted to peak in 2033; in an "Accelerated Improvement Scenario" they were predicted to peak in 2027. China also established 10 binding environmental targets in its Thirteenth Five-Year Plan (2016-2020). These include an aim to reduce carbon intensity by 18% by 2020, as well as a binding target for renewable energy at 15% of total energy, raised from under 12% in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan. According to
BloombergNEF
Bloomberg L.P. is a privately held financial, software, data, and media company headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It was co-founded by Michael Bloomberg in 1981, with Thomas Secunda, Duncan MacMillan, Charles Zegar, and a ...
the
levelized cost of electricity from new large-scale solar power has been below existing coal-fired power stations since 2021.
Policy
The climate change mitigation policy in China is an important environmental protection strategy since the 2010s after rapid domestic developments. Having emitted the second-largest amount of greenhouse gas and having the most people, China published a series of policies and laws to mitigate environmental impacts, such as reduce atmospheric pollution, transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy, and achieve carbon neutrality.
In the past 20 years, China has published 4 legislative laws and 5 executive plans as outlines regarding the climate change issues. Government departments and local governments also developed their own special plans and implementation methods based on the national outline. In 2015 China joined the
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and ...
to globally constrain the temperature rise and greenhouse gas emission.
In 2020 China created th
14th FYP(Five Year Plan). The key climate- and energy-related ideas in the FYP will be critical to China's energy transition and global efforts to tackle climate change.
In April, 2021, the United States and China decided to cooperate and reduce the global climate change. Series of international and domestic mitigation and adaption strategies was published based on the Paris Agreement.
Policy and Law
Forest Law of the People's Republic of China (1998)
The aim of this law was to conserve and rationally exploit forest resources. It accelerated territorial afforestation and cultivation while also ensuring forest product management, production, and supply in order to meet socialist construction requirements.
Energy Conservation Law (2007)
The aim of this law was to strengthen
energy conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (f ...
, especially for key energy-using institutions, as well as to encourage energy efficiency and energy-saving technology. The legislation allowed the government to promote and facilitate the use of renewable energy in a variety of applications.
Renewable Energy Act (2009)
This Act outlines the responsibilities of the government, businesses, and other users in the production and use of renewable energy. It includes policies and targets relating to mandatory grid connectivity, market control legislation, differentiated pricing, special funds, and tax reliefs, as well as a target of 15 percent renewable energy by 2020.
12th Five-Year Plan (2011-2015)
The 12th Five-Year Plan sought to make domestic consumption and development more economically equitable and environmentally friendly. It also shifted the economy's focus away from heavy industry and resource-intensive manufacturing and into a more consumer-driven, resource-efficient economy.
The National Strategy for Climate Change Adaptation (2013)
The strategy established clear guidelines and principles for adapting to and mitigating climate change. It includes interventions such as early-warning identification and information-sharing systems at the national and regional levels, an ocean disaster monitoring system, and coastal restoration to protect water supplies, reduce soil erosion, and improve disaster prevention.
National Plan For Tackling Climate Change (2014-2020)
The National Plan For Tackling Climate Change is a national law that includes prevention, adaptation, scientific study, and public awareness. By 2020, China plans to reduce carbon emissions per unit of GDP by 40-45 percent compared to 2005 levels, raise the share of non-fossil fuels in primary energy consumption to 15%, and increase forest area and stock volume by 40 million hectares and 1.3 million m3, respectively, compared to 2005 levels.
Energy Development Strategy Action Plan (2014-2020)
This plan aimed to reduce China's high energy consumption per unit of GDP through a series of steps and mandatory goals, encouraging more productive, self-sufficient, renewable, and creative energy production and consumption.
Law on the Prevention and Control of Atmospheric Pollution (2016)
The aim of this law is to preserve and improve the environment, prevent and regulate air pollution, protect public health, advance ecological civilization, and promote economic and social growth that is sustainable. It demands that robust emission control initiatives be implemented against the pollution caused by the burning of coal, industrial production, motor vehicles and vessels, dust as well as agricultural activities.
13th Five-Year Plan (2016-2020)
The 13th Five Year Plan published the strategy and pathway for China's development during 2016-2020 and set specific environmental and productivity goals. Peak goals for carbon emissions, energy use, and water use were established in the 13th Five Year Plan. It also stated objectives for increasing industry productivity, removing obsolete or overcapacity production facilities, increasing renewable energy production, and improving green infrastructure.
Mitigation Approach
Emissions Trading
Vehicles
Vehicles account for around 8% of the heat-trapping gases released annually in China. As the Chinese vehicle stock rises and heavy manufacturing as a percentage of the overall economy declines, this percentage will rise in the coming years. Fuel performance regulations and funding for electric vehicles are two of the Chinese government's key policies on vehicle emissions. The government refers to vehicles fueled by non-petroleum fuels as "new energy vehicles," or "NEVs." Almost all NEVs in China today are battery-powered plug-in electric vehicles.
Future Plans
14th Five Year Plan (2021-2025)
The 14th FYP(Five Year Plan) was created in September, 2020 as the key climate- and energy-related plan that is critical to China's energy transition and global efforts to tackle climate change.
On September 22, 2020, Chinese leader Xi Jinping stated: "China will increase its nationally determined contributions, adopt more powerful policies and measures, strive to reach the peak of carbon dioxide emissions by 2030, and strive to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060."
Of particular interest is how China will integrate into the FYP to achieve peak carbon before 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. The plan will be seen by many as a test of how seriously the pledge is being taken at the policy level.
Unlike most nations that have committed to carbon neutrality, China's economy grows rapidly. China is still a developing country and, as of 2020, growth was still linked to carbon emissions. In the 14th Five Year Plan, the Chinese government revealed climate mitigation goals including higher share of non-fossil fuels in the energy mix, reduction of emissions per unit of GDP, carbon cap for the power sector, reduction of fine particle pollution in key cities, and greater forest coverage. These goals cover industrial production, transportation, forestry, and citizens’ daily life aspects.
U.S.-China Cooperation
On April 15 and 16, 2021, U.S. Special Presidential Envoy for Climate John Kerry and China Special Envoy for Climate Change Xie Zhenhua met in Shanghai to discuss aspects of the climate crisis. U.S. and China Finally released joint statement and decided to cooperating with each other and with other countries to tackle the climate crisis. According to the joint statement on U.S. Department of State, "This includes both enhancing their respective actions and cooperating in multilateral processes, including the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and the Paris Agreement."
In short term, The United States and China take following actions to further address the climate crisis:
* Both countries intend to develop by COP 26 in Glasgow their respective long-term strategies aimed at net zero GHG emissions/carbon neutrality.
* Both countries intend to take appropriate actions to maximize international investment and finance in support of the transition from carbon-intensive fossil fuel based energy to green, low-carbon and renewable energy in developing countries.
* They will each implement the phasedown of hydrofluorocarbon production and consumption reflected in the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol.
In addition, both countries will continue to discuss concrete actions in the 2020s to reduce emissions aimed at keeping the Paris Agreement-aligned temperature limit within reach. Potential areas include policies, measures, and technologies to decarbonize industry and power; Increased deployment of renewable energy; Green and climate resilient agriculture; Energy efficient buildings; Green, low-carbon transportation; Cooperation on addressing emissions of methane and other non- greenhouse gases; Cooperation on addressing emissions from international civil aviation and maritime activities; and other near-term policies and measures, including with respect to reducing emissions from coal, oil, and gas.
Energy efficiency
In 2004, Premier
Wen Jiabao
Wen Jiabao (born 15 September 1942) is a retired Chinese politician who served as the Premier of the State Council from 2003 to 2013. In his capacity as head of government, Wen was regarded as the leading figure behind China's economic polic ...
promised to use an "iron hand" to make China more
energy efficient.
Energy efficiency improvements have somewhat offset increases in energy output as China continues to develop. Since 2006, the Chinese government has increased export taxes on energy-inefficient industries, reduced import tariffs on certain non-renewable energy resources, and closed down a number of inefficient power and industrial plants. In 2009, for example, for every two new plants (in terms of energy generation capacity) built, one inefficient plant was closed. China is unique in its closing of so many inefficient plants.
Renewable energy
China is the world's leading investor in
wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. ...
s and other renewable energy technologies and produces more
wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. ...
s and
solar panel
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photo ...
s each year than any other country.
[Bradsher, Keith, 30 January 2010]
China leads global race to make clean energy
, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''
As the current largest greenhouse gas contributor in the world, coal burning is the major cause of global warming in China. Therefore, China has tried to transit from fossil fuels toward renewable energy since 2010.
China is the world leader in renewable energy deployment, with more than twice the ability of any other nation. China accounted for 43% of global renewable energy capacity additions in 2018.
For decades, hydropower has been a major source of energy in China. In the last ten years, wind and solar power have risen significantly. Renewables accounted for approximately a quarter of China's electricity generation in 2018, with 18% coming from hydropower, 5% from wind, and 3% from solar.
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
is planned to be rapidly expanded. By mid-century
fast neutron reactors are seen as the main nuclear power technology which allows much more efficient use of fuel resources.
China has also dictated tough new energy standards for lighting and gas kilometrage for cars. China could push
electric cars to curb its dependence on imported
petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
(oil) and foreign automobile technology.
Co-benefits
Like India, cutting greenhouse gas emissions together with
air pollution in China, saves enough lives to easily cover the cost.
Impact of 2019–20 coronavirus outbreak
A temporary slowdown in manufacturing, construction, transportation, and overall economic activity during the beginning of the
2019–20 coronavirus outbreak reduced China's greenhouse gas emissions by "about a quarter," as reported in February 2020. Nonetheless, for the year April 1, 2020 – March 31, 2021, China's emissions reached a record high: nearly 12 billion metric tons. Additionally, China's carbon emissions during the first quarter of 2021 were higher than in the first quarters of both 2019 and 2020.
Targets
The targets laid out in China's
Intended Nationally Determined Contribution
A nationally determined contribution (NDC) or intended nationally determined contribution (INDC) is a non-binding national plan highlighting climate change mitigation, including climate-related targets for greenhouse gas emission reductions. Thes ...
(INDC) in 2016 will likely be met, but are not enough to properly combat global warming.
China also established 10 binding environmental targets in its Thirteenth Five-Year Plan (2016-2020). These include an aim to reduce carbon intensity by 18% by 2020, as well as a binding target for renewable energy at 15% of total energy, raised from under 12% in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan. The Thirteenth Five-Year Plan also set, for the first time, a cap on total energy use from all sources: no more than 5 billion tons of coal through 2020.
See also
*
*
List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions
This is a list of countries by total greenhouse gas (GHG) annual emissions in 2016. It is based on data for carbon dioxide, methane (), nitrous oxide (), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) emissions ...
References
Sources
*
*
External links
{{Asia topic, Greenhouse gas emissions by
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
Climate change in China

