Grand Trunk Railway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Grand Trunk Railway (; french: Grand Tronc) was a
The Grand Trunk Railway (; french: Grand Tronc) was a
 The company was incorporated on November 10, 1852, as the ''Grand Trunk Railway Company of Canada'' to build a railway line between Montreal and
The company was incorporated on November 10, 1852, as the ''Grand Trunk Railway Company of Canada'' to build a railway line between Montreal and  By 1860, the Grand Trunk was on the verge of bankruptcy and in no position to expand further east to Halifax. On the eve of the
By 1860, the Grand Trunk was on the verge of bankruptcy and in no position to expand further east to Halifax. On the eve of the 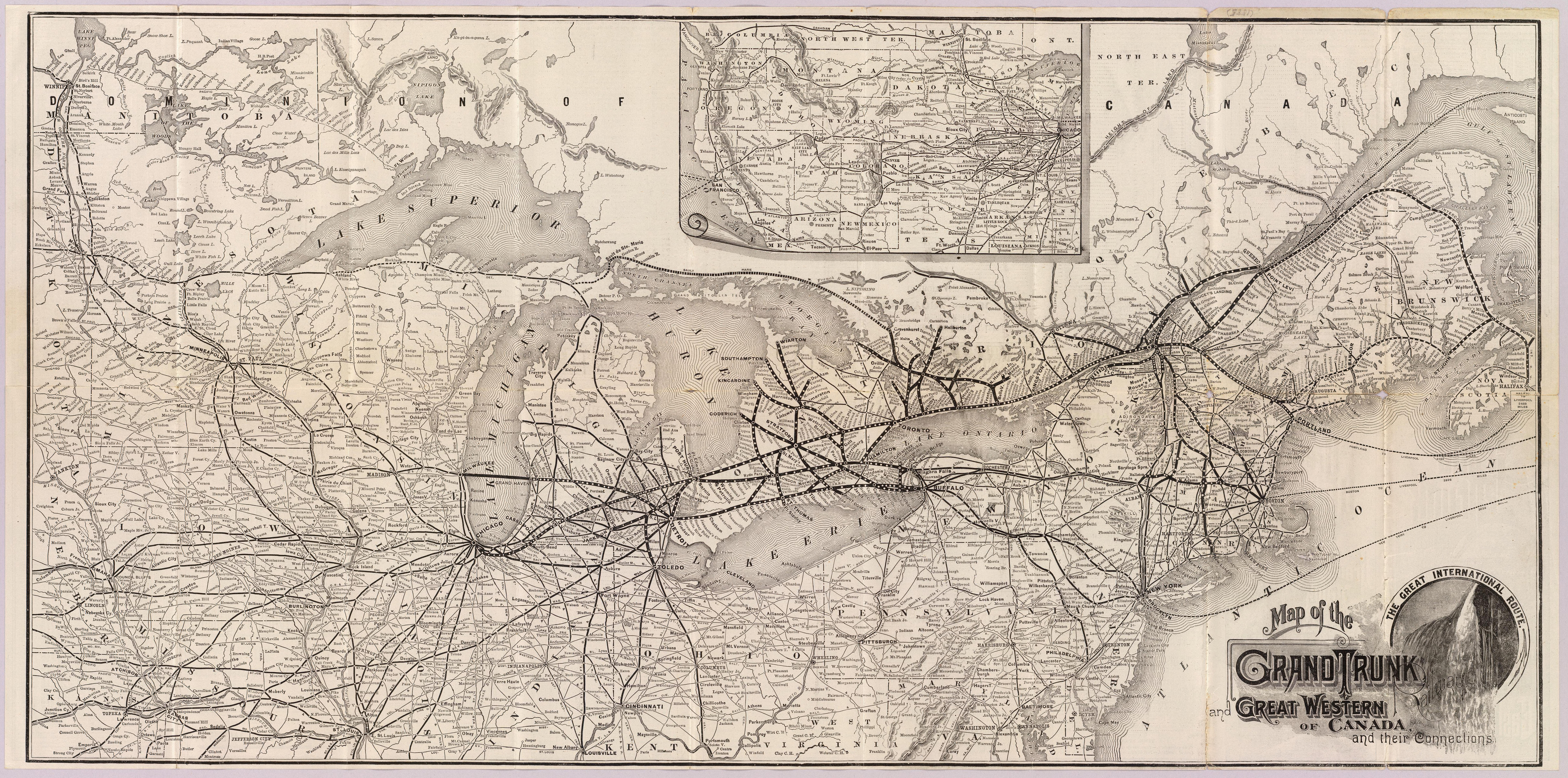
Niagara Rails - Introduction
. Home.cogeco.ca. Retrieved on 2013-07-26.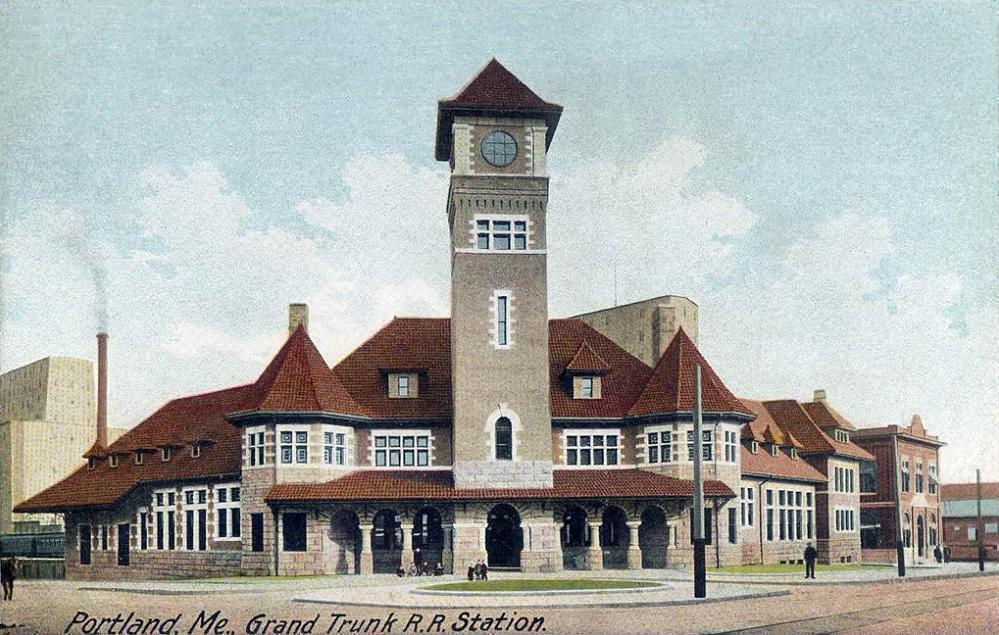 The GTR system expanded throughout
The GTR system expanded throughout
 ''
''
 The Portland, Maine-Chicago, Illinois mainline of the Grand Trunk is or was known by the following names:
*CN
The Portland, Maine-Chicago, Illinois mainline of the Grand Trunk is or was known by the following names:
*CN
online
Collections Canada: History of the Grand Trunk Railway
(Trent University Archives) * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20091027143522/http://www.geocities.com/sharut/gt_rail.html GTR Historybr>Grand Trunk Railway Collection Finding Aid, Special Collections, University of Vermont Library
* ttp://www.risksandrewards.org.uk/source_65.html Maps of the Grand Trunk Railway 1857, and its connections, c1860br>Report for submission to the shareholders of the Grand Trunk Railway in 1860
*, illustrated account of the Grand Trunk Railway {{DEFAULTSORT:Grand Trunk Railway Defunct Ontario railways Defunct Quebec railways Defunct Maine railroads Defunct New Hampshire railroads Defunct Vermont railroads History of Montreal Predecessors of the Canadian National Railway Railway companies established in 1852 Railway companies disestablished in 1923 5 ft 6 in gauge railways in the United States Defunct New York (state) railroads Defunct Michigan railroads 5 ft 6 in gauge railways in Canada Canadian companies established in 1852 Transport companies based in London Defunct companies based in London Companies based in the City of Westminster
 The Grand Trunk Railway (; french: Grand Tronc) was a
The Grand Trunk Railway (; french: Grand Tronc) was a railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
system that operated in the Canadian provinces of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
and Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
and in the American states of Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
, Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
, Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, and Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
. The railway was operated from headquarters in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
, Quebec, with corporate headquarters in London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
(4 Warwick House Street). It cost an estimated $160 million to build. The Grand Trunk, its subsidiaries, and the Canadian Government Railways
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
were precursors of today's Canadian National Railway.
GTR's main line ran from Portland, Maine
Portland is the largest city in the U.S. state of Maine and the seat of Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 in April 2020. The Greater Portland metropolitan area is home to over half a million people, the 104th-largest metropo ...
to Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
, and then from Montreal to Sarnia
Sarnia is a city in Lambton County, Ontario, Canada. It had a Canada 2021 Census, 2021 population of 72,047, and is the largest city on Lake Huron. Sarnia is located on the eastern bank of the junction between the Upper and Lower Great Lakes w ...
, Ontario, where it joined its western subsidiary.
The GTR had four important subsidiaries during its lifetime:
* Grand Trunk Eastern which operated in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
and Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
.
*Central Vermont Railway
The Central Vermont Railway was a railroad that operated in the U.S. states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont, as well as the Canadian province of Quebec.
It connected Montreal, Quebec, with New London, Connect ...
which operated in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, and Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
.
*Grand Trunk Pacific Railway
The Grand Trunk Pacific Railway was a historic Canadian transcontinental railway running from Fort William, Ontario (now Thunder Bay) to Prince Rupert, British Columbia, a Pacific coast port. East of Winnipeg the line continued as the National Tra ...
which operated in Northwestern Ontario, Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
, Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
, Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, and British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
.
*Grand Trunk Western Railroad
The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company is an American subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding ...
which operated in Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
, Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
, and Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
.
A fifth subsidiary was the never-completed Southern New England Railway
The Southern New England Railway was a project of the Grand Trunk Railway (GT) to build a railroad from the GT-owned Central Vermont Railway at Palmer, Massachusetts south and east to the all-weather port of Providence, Rhode Island. Much gradin ...
, chartered in 1910, which would have run from a connection with the Central Vermont at Palmer, Massachusetts
Palmer is a city in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 12,448 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Springfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area. Palmer adopted a home rule charter in 2004 with a counc ...
, to the deep-water, all-weather port of Providence, Rhode Island
Providence is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Rhode Island. One of the oldest cities in New England, it was founded in 1636 by Roger Williams, a Reformed Baptist theologian and religious exile from the Massachusetts ...
. A new line to Providence would have allowed for more extensive port facilities than were possible for the Central Vermont at New London, Connecticut
New London is a seaport city and a port of entry on the northeast coast of the United States, located at the mouth of the Thames River in New London County, Connecticut. It was one of the world's three busiest whaling ports for several decade ...
. Construction began in 1910 and continued in fits and starts for more than 20 years until finally abandoned in the early 1930s because of the Great Depression. The loss of the SNER's strongest proponent, Grand Trunk Railway president Charles Melville Hays
Charles Melville Hays (May 16, 1856 – April 15, 1912) was the president of the Grand Trunk Railway. He began working in the railroad business as a clerk at the age of 17 and quickly rose through the ranks of management to become the General M ...
, on in 1912 may have been the major reason that this new route to the sea was never completed. Another important factor was the unrelenting opposition of the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad , commonly known as The Consolidated, or simply as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to December 31, 1968. Founded by the merger of ...
, which fiercely protected its virtual monopoly control of rail traffic in southern New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
.
History
Charter, construction, and expansion
 The company was incorporated on November 10, 1852, as the ''Grand Trunk Railway Company of Canada'' to build a railway line between Montreal and
The company was incorporated on November 10, 1852, as the ''Grand Trunk Railway Company of Canada'' to build a railway line between Montreal and Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
.
The charter was soon extended east to Portland, Maine and west to Sarnia, Canada West
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the ...
. In 1853 the GTR purchased the St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad
The St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad , known as St-Laurent et Atlantique Quebec in Canada, is a short-line railway operating between Portland, Maine, on the Atlantic Ocean, and Montreal, Quebec, on the St. Lawrence River. It crosses the C ...
from Montreal to the Canada East – Vermont border, and the parent company Atlantic and St. Lawrence Railroad
The St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad , known as St-Laurent et Atlantique Quebec in Canada, is a short-line railway operating between Portland, Maine, on the Atlantic Ocean, and Montreal, Quebec, on the St. Lawrence River. It crosses the C ...
through to the harbour facilities at Portland. A line was also built to Lévis, via Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, Virginia, the capital of Virginia, United States
* Richmond, London, a part of London
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town in England
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, California, ...
from Montreal in 1855, part of the much-talked about "Maritime
Maritime may refer to:
Geography
* Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps
* Maritime Region, a region in Togo
* Maritime Southeast Asia
* The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prin ...
connection" in British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestow ...
. In the same year it purchased the Toronto and Guelph Railroad, whose railway was already under construction. But the Grand Trunk Railway Company changed the original route of the T&G and extended the line to Sarnia, a hub for Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
-bound traffic. By July, 1856, the section from Sarnia to Toronto opened, and the section from Montreal to Toronto opened in October of that year. By 1859 a ferry service was established across the St. Clair River
The St. Clair River (french: Rivière Sainte-Claire) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed November 7, 2011 river in central North America which flows from Lake Huron int ...
to Fort Gratiot (now Port Huron, Michigan).
The Grand Trunk was one of the main factors that pushed British North America towards Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
. The original colonial economy structured along the water route from the Maritimes up the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
and the lower Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
was greatly expanded by the duplicate route of the Grand Trunk. The explosive growth in trade during the 1850s within the United Province of Canada and further east by water to the Maritimes demanded that a railway link the entire geopolitical region together. During this time the GTR extended its line to Lévis further east to Rivière-du-Loup
Rivière-du-Loup (; 2021 population 20,118) is a small city on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec. The city is the seat for the Rivière-du-Loup Regional County Municipality and the judicial district of Kamouraska. Its one of ...
.
 By 1860, the Grand Trunk was on the verge of bankruptcy and in no position to expand further east to Halifax. On the eve of the
By 1860, the Grand Trunk was on the verge of bankruptcy and in no position to expand further east to Halifax. On the eve of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, it stretched from Sarnia
Sarnia is a city in Lambton County, Ontario, Canada. It had a Canada 2021 Census, 2021 population of 72,047, and is the largest city on Lake Huron. Sarnia is located on the eastern bank of the junction between the Upper and Lower Great Lakes w ...
in the west to Rivière-du-Loup in the east and Portland in the southeast. Colonists in the United Province of Canada, some who experienced their territory being attacked by the United States fifty years earlier (in the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
), were uncomfortably close to the giant Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. It proved essential to th ...
and faced terrorist attacks during the mid-19th century in the form of Fenian raids.
Such security concerns led to demands for a year-round transportation system that British reinforcements could use should their territory be attacked during winter when the St. Lawrence River was frozen, and the only railway for British reinforcements to use would be the Grand Trunk connection at Portland, in the United States. Many citizens thought that the only way to finish the Grand Trunk – and protect the country – would be to unite all the colonies into a federation so that they could share the costs of an expanded railway system. Thus the British North America Act, 1867
The ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (french: Loi constitutionnelle de 1867),''The Constitution Act, 1867'', 30 & 31 Victoria (U.K.), c. 3, http://canlii.ca/t/ldsw retrieved on 2019-03-14. originally enacted as the ''British North America Act, 186 ...
included the provision for an Intercolonial Railway
The Intercolonial Railway of Canada , also referred to as the Intercolonial Railway (ICR), was a historic Canadian railway that operated from 1872 to 1918, when it became part of Canadian National Railways. As the railway was also completely o ...
to link with the Grand Trunk at Rivière-du-Loup.
The end of the American Civil War saw British North America on the verge of uniting in a single federation, and the GTR's financial prospects improved as the railway was well-positioned to take advantage of increased population and economic growth. By 1867, it had become the largest railroad system in the world by accumulating more than of track that connected locations between its ocean port at Portland, Maine
Portland is the largest city in the U.S. state of Maine and the seat of Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 in April 2020. The Greater Portland metropolitan area is home to over half a million people, the 104th-largest metropo ...
, its river port at Rivière-du-Loup, the three northern New England states, and much of the southern areas of the new provinces of Quebec and Ontario. By 1880, the Grand Trunk Railway system stretched all the way from Portland in the east to Chicago, Illinois, in the west (by means of the Grand Trunk Western Railroad
The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company is an American subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding ...
between Port Huron and Chicago).
Several impressive construction feats were associated with the GTR: the first successful bridging of the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
on August 25, 1860, with the opening of the first Victoria Bridge at Montreal (replaced by the present structure in 1898); the bridging of the Niagara River between Fort Erie, Ontario and Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York (behind only New York City) and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is across the Canadian border from Sou ...
; and the construction of a tunnel beneath the St. Clair River
The St. Clair River (french: Rivière Sainte-Claire) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed November 7, 2011 river in central North America which flows from Lake Huron int ...
, connecting Sarnia, Ontario, and Port Huron, Michigan. The latter work opened in August 1890 and replaced the railcar ferry at the same location.

Heyday
Common during 19th century railway construction in British colonies, GTR built to a broad gauge (''Provincial Gauge
Indian gauge is a broad track gauge of , used in India, Pakistan, western Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Argentina, Chile, and on BART in San Francisco, United States.
In North America, it is called Indian Gauge, Provincial, Portland, or Texas gauge. ...
'') of ; however, this was changed to the standard gauge of between 1872 and 1885 to facilitate interchange with U.S. railroads. To overcome the gauge difference, the GTR experimented with a form of variable-gauge axles called "adjustable gauge trucks", but these proved unreliable.. Home.cogeco.ca. Retrieved on 2013-07-26.
 The GTR system expanded throughout
The GTR system expanded throughout southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
, western Quebec, and the U.S. state of Michigan over the years by purchasing and absorbing numerous smaller railway companies, as well as building new lines. GTR's largest purchase came on August 12, 1882, when it bought the Great Western Railway, running from Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Fall ...
to Toronto, and connecting to London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, Windsor
Windsor may refer to:
Places Australia
* Windsor, New South Wales
** Municipality of Windsor, a former local government area
* Windsor, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane, Queensland
**Shire of Windsor, a former local government authority around Wi ...
, and communities in the Bruce Peninsula
The Bruce Peninsula is a peninsula in Ontario, Canada, that divides Georgian Bay of Lake Huron from the lake's main basin. The peninsula extends roughly northwestwards from the rest of Southwestern Ontario, pointing towards Manitoulin Island, ...
.
The company sold the line along the St. Lawrence River between Rivière-du-Loup
Rivière-du-Loup (; 2021 population 20,118) is a small city on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec. The city is the seat for the Rivière-du-Loup Regional County Municipality and the judicial district of Kamouraska. Its one of ...
and Lévis in 1879 to the federal government-owned Intercolonial Railway
The Intercolonial Railway of Canada , also referred to as the Intercolonial Railway (ICR), was a historic Canadian railway that operated from 1872 to 1918, when it became part of Canadian National Railways. As the railway was also completely o ...
(IRC), and granted running rights in 1889 to the IRC on trackage between Lévis and Montreal (via Richmond); however, the IRC's construction of a more direct line from Lévis to Saint-Hyacinthe
Saint-Hyacinthe (; French: ) is a city in southwestern Quebec east of Montreal on the Yamaska River. The population as of the 2021 Canadian census was 57,239. The city is located in Les Maskoutains Regional County Municipality of the Montérég ...
in 1899 saw most of this traffic transferred to that line.
Bankruptcy and nationalization
As the dominant railway in British North America, GTR was reportedly asked by the federal government soon afterConfederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
to consider building a rail line to the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
coast at British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
but refused, forcing the government to enact legislation creating the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) to meet British Columbia's conditions for joining Confederation. By the early 20th century, GTR desired to operate in Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West or the Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada� ...
, particularly given the virtual monopoly of service that CPR maintained and the lucrative increasing flows of immigrants west of Ontario. The federal government encouraged GTR to co-operate with a local railway company operating on the Prairies
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
, the Canadian Northern Railway
The Canadian Northern Railway (CNoR) was a historic Canadian transcontinental railway. At its 1923 merger into the Canadian National Railway , the CNoR owned a main line between Quebec City and Vancouver via Ottawa, Winnipeg, and Edmonton.
Man ...
(CNoR), but an agreement was never reached.
CNoR decided to build its own transcontinental system at this time, forcing GTR in 1903 to enter into an agreement with Wilfrid Laurier
Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier, ( ; ; November 20, 1841 – February 17, 1919) was a Canadian lawyer, statesman, and politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Canada from 1896 to 1911. The first French Canadian prime minis ...
's government to build a third railway system from the Atlantic to the Pacific. GTR would build (with federal assistance) and operate the Grand Trunk Pacific Railway (GTPR) from Winnipeg, Manitoba
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749,6 ...
to Prince Rupert, British Columbia
Prince Rupert is a port city in the province of British Columbia, Canada. Its location is on Kaien Island near the Alaskan panhandle. It is the land, air, and water transportation hub of British Columbia's North Coast, and has a population of 12 ...
, while the government would build and own the National Transcontinental Railway (NTR) from Winnipeg to Moncton, New Brunswick via Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
, which the GTR would also operate.
As part of this program, the federal government encouraged the GTR to purchase the Canada Atlantic Railway
The Canada Atlantic Railway (CAR) was a North American railway located in Ontario, southwestern Quebec and northern Vermont. It connected Georgian Bay on Lake Huron with the northern end of Lake Champlain via Ottawa. It was formed in 1897 throu ...
(CAR) with lines southeast from Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
to Vermont, and west from Ottawa to Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To ...
. The GTR took effective control of the CAR in 1905, although the purchase was not ratified by Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
until 1914.
The routing of these systems was extremely speculative, as GTPR's main line was located farther north than the profitable CPR main line in the Prairies, and NTR was located even farther north of populous centres in Ontario and Quebec. Construction costs on the GTPR escalated, despite having the most favourable crossing of the Continental Divide in North America at Yellowhead Pass
The Yellowhead Pass is a mountain pass across the Continental Divide of the Americas in the Canadian Rockies. It is located on the provincial boundary between the Canadian provinces of Alberta and British Columbia, and lies within Jasper ...
. GTR's cost-conscious president Charles Melville Hays
Charles Melville Hays (May 16, 1856 – April 15, 1912) was the president of the Grand Trunk Railway. He began working in the railroad business as a clerk at the age of 17 and quickly rose through the ranks of management to become the General M ...
was one of the victims on board RMS ''Titanic'' on April 15, 1912. His death is speculated to have contributed to poor management of GTR over the ensuing decade, and also contributed to the abandonment of the uncompleted Southern New England Railway
The Southern New England Railway was a project of the Grand Trunk Railway (GT) to build a railroad from the GT-owned Central Vermont Railway at Palmer, Massachusetts south and east to the all-weather port of Providence, Rhode Island. Much gradin ...
to Providence, Rhode Island
Providence is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Rhode Island. One of the oldest cities in New England, it was founded in 1636 by Roger Williams, a Reformed Baptist theologian and religious exile from the Massachusetts ...
, begun in 1910.
Construction started on the GTPR/NTR in 1905, and the GTPR opened to traffic in 1914, followed by the NTR in 1915. It was a transcontinental system, with the only exception being the NTR's ill-fated Quebec Bridge
The Quebec Bridge (french: pont de Québec) is a road, rail, and pedestrian bridge across the lower Saint Lawrence River between Sainte-Foy (a former suburb that in 2002 became a western area of Quebec City) and Lévis, in Quebec, Canada. The p ...
, which would not be completed for several more years.
The first indication the arrangement with the government was faltering came when GTR refused to operate the NTR, citing economic reasons. With the enormous cost of building the GTPR and the limited financial returns being realized, GTR defaulted on loan payments to the federal government in 1919. GTPR was nationalized on March 7 of that year, being operated under a federal government Board of Management until finally being placed under the control of the Crown corporation Canadian National Railways (CNR) on July 20, 1920.
GTR underwent serious financial difficulties as a result of the GTPR, and its shareholders, primarily in the United Kingdom, were determined to prevent the company from being nationalized as well. Eventually on July 12, 1920, GTR was placed under control of another federal government Board of Management while legal battles continued for several more years. Finally, on January 20, 1923, GTR was fully absorbed into the CNR on a date when all constituent companies were merged into the Crown corporation.
At the time that the GTR was fully merged into CNR, approximately 125 smaller railway companies comprised the Grand Trunk system, totalling in Canada and in the United States.
Accident
Canada's worst railway accident based on loss of life happened on the GTR, occurring on June 29, 1864, when a passenger train operating between Lévis and Montreal missed a signal for an open drawbridge on theRichelieu River
The Richelieu River () is a river of Quebec, Canada, and a major right-bank tributary of the St. Lawrence River. It rises at Lake Champlain, from which it flows northward through Quebec and empties into the St. Lawrence. It was formerly kn ...
near the present-day town of Mont-Saint-Hilaire, Quebec
Mont-Saint-Hilaire () is an off-island suburb of Montreal in southeastern Quebec, Canada, on the Richelieu River in the Regional County Municipality of La Vallée-du-Richelieu. The population as of the Canada 2011 Census was 18,200. The cit ...
, plunging onto a passing barge and killing 99 German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
immigrants.
Legacy
 ''
''Canadian Rail
The Canadian Railroad Historical Association (CRHA) (french: L'Association canadienne d'histoire ferroviaire (ACHF)) is a non-profit organization established in 1932 in Canada and is "devoted to preserving and interpreting Canada's railway heritage ...
'' speculated in 1963 that an independent GTR might have survived had it always used standard gauge. The GTR was a private company headquartered in England that received heavy Canadian government subsidies and was never profitable because of competition from shipping and American railways. (In 1880 40% of the Grand Trunk traffic was from one or another American city to and from Chicago, taking a shortcut across Ontario.) Inflated construction costs, overestimated revenues, and an inadequate initial capitalization threatened bankruptcy for the Grand Trunk.
Sir Joseph Hickson
Sir Joseph Hickson (23 January 1830 – 4 January 1897) was a Canadian railway executive. He was Secretary-Treasurer, and afterwards President, of the Grand Trunk Railway Company of Canada. He was knighted by Queen Victoria 20 January 1890. He ...
was a key executive from 1874 to 1890 based in Montreal who kept it afloat financially and formed an alliance with the Conservative party. Carlos and Lewis (1995) show that it managed to survive because its British investors accurately assessed the corporation's value and prospects, which included the likelihood that the Canadian government would bail out the railway should it ever default on its bonds. The government had guaranteed a very large loan and had enacted legislation authorizing debt restructuring. These arrangements allowed the company to float new bond issues to replace existing debt and to issue securities in lieu of interest.
American executive Charles Melville Hays
Charles Melville Hays (May 16, 1856 – April 15, 1912) was the president of the Grand Trunk Railway. He began working in the railroad business as a clerk at the age of 17 and quickly rose through the ranks of management to become the General M ...
(1856-1912) joined the Grand Trunk in 1895 as general manager (and in 1909, president, based in Montreal). Hays was the architect of the great expansion during a colourful and free-spending era. He upgraded the tracks, bridges, shops and rolling stock, but was best known for building huge grain elevators and elaborate tourist hotels such as the Château Laurier in Ottawa. Hays blundered in 1903 by building a subsidiary, the Grand Trunk Pacific Railway Company some long; it reached Prince Rupert in northern British Columbia in 1914. The government built and the Grand Trunk was to operate the National Transcontinental to link the main Grand Trunk with its Pacific subsidiary. The very expensive subsidiary was far north of major population centres and had too little traffic.
Nearing bankruptcy in 1919, the entire system was nationalized: the government merged the Grand Trunk, the Grand Trunk Pacific, and the National Transcontinental lines into the new Canadian National Railways. The process was completed in 1923. The Grand Trunk lines in the United States, however, kept their distinctive name.
The Grand Trunk legacy seeped into late 20th century popular culture, when a hard rock trio from Flint, Michigan, called itself Grand Funk Railroad
Grand Funk Railroad (often shortened to Grand Funk) is an American rock band formed in 1968 in Flint, Michigan, by Mark Farner (vocals, guitar), Don Brewer (drums, vocals), and Mel Schacher (bass). The band achieved peak popularity and succ ...
in 1969.
GTR hotels
Like the CPR and CNR, the GTR began building and operating hotels during the first two decades of the 20th century. Most of the hotels survived the takeover of the GTR by CNR in 1923 and were operated byCanadian National Hotels
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
:
*Château Laurier
The Fairmont Château Laurier is a hotel with 429 guest rooms in the downtown core of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, located near the intersection of Rideau Street and Sussex Drive and designed in a French Gothic Revival Châteauesque style to complem ...
(Ottawa) 1912-1923 - acquired by Canadian National Hotels and later by Canadian Pacific Hotels
Canadian Pacific Hotels (CPH) was a division of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) that primarily operated hotels across Canada. CPR restructured the division as a subsidiary in 1963.
Early hotels
Since passenger revenue made a significant ...
; now part of the Fairmont Hotels and Resorts
Fairmont Hotels & Resorts is a global chain of luxury hotels that operates more than 70 properties worldwide, with a strong presence in Canada.
The company originated from two hotel businesses established in the late 19th century, the Canadian P ...
chain
*Hotel Macdonald
The Fairmont Hotel Macdonald, formerly and commonly known as the Hotel Macdonald (colloquially known as The Mac), is a large historic luxury hotel in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. Located along 100 Street NW, south of Jasper Avenue, the hotel is situa ...
(Edmonton) 1912-1923 - acquired by Canadian National Hotels and later by Canadian Pacific Hotels; now part of the Fairmont Hotels and Resorts chain
* Fort Garry Hotel (Winnipeg) 1913-1923 - acquired by Canadian National Hotels and now independently operated
*Highland Inn
The Highland Inn (1908–1957) was a year-round resort hotel built and operated by the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR), in Ontario’s Algonquin Provincial Park. It was located near the park offices on the northern edge of Cache Lake, and was a focal po ...
(Algonquin Park) 1905–1923; sold to Government of Ontario and demolished
Grand Trunk today
Grand Trunk Railway was built fully a century before major property and highway development took place in the various jurisdictions it crossed and as such had the choice of geography in selecting the most direct routes. As a result, significant sections of GTR mainlines in Canada and Grand Trunk Western routes in the U.S. are still in active use byCanadian National
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN ...
(CN) today, particularly the Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
– Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
corridor by way of Drummondville, Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
, Kingston, Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
, London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, Sarnia
Sarnia is a city in Lambton County, Ontario, Canada. It had a Canada 2021 Census, 2021 population of 72,047, and is the largest city on Lake Huron. Sarnia is located on the eastern bank of the junction between the Upper and Lower Great Lakes w ...
/Port Huron
Port Huron is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of St. Clair County. The population was 30,184 at the 2010 census. The city is adjacent to Port Huron Township but is administered separately.
Located along the St. Clair ...
, and Battle Creek
Battle Creek is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan, in northwest Calhoun County, at the confluence of the Kalamazoo and Battle Creek rivers. It is the principal city of the Battle Creek, Michigan Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA), which en ...
.
Following deregulation of the railway industry in Canada and the United States, CN has abandoned or sold many former GTR and GTW branch lines in recent decades, including the former Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
-Montreal main line which had instigated the development of the system to a large degree. As well, a part of the original Toronto–Sarnia routing via St. Mary's Junction and Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
to Point Edward, Ontario
Point Edward is a village in the Canadian province of Ontario. Adjacent to the city of Sarnia in Lambton County, Point Edward sits opposite Port Huron, Michigan and is connected to it by the Blue Water Bridge, at the meeting point of the St. Cl ...
, was sold or abandoned, using the Great Western Railway routing instead.
Grand Trunk Corporation
CN continues to use the "Grand Trunk" name for its holding company theGrand Trunk Corporation
The Grand Trunk Corporation is the subsidiary holding company for the Canadian National Railway's properties in the United States. It is named for CN subsidiary railroad Grand Trunk Western Railroad. The Association of American Railroads has cons ...
. The corporation was created in 1971 to provide autonomy in operation for CN's US subsidiaries: Grand Trunk Western Railroad
The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company is an American subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding ...
; Duluth, Winnipeg & Pacific Railway; and the Central Vermont Railway
The Central Vermont Railway was a railroad that operated in the U.S. states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont, as well as the Canadian province of Quebec.
It connected Montreal, Quebec, with New London, Connect ...
. The main goal of the corporation, headquartered in Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
, was to make GTW profitable and keep parent CN from having to subsidize GTW's losses. CN sold off the Central Vermont in 1995 when CN became a public traded company instead of a crown corporation.
CN continued to place its US acquisitions as subsidiaries under the Grand Trunk Corporation which includes Illinois Central, Wisconsin Central, and Great Lakes Transportation. The Association of American Railroads
The Association of American Railroads (AAR) is an industry trade group representing primarily the major freight Rail transport, railroads of North America (Canada, Mexico and the United States). Amtrak and some regional Commuter rail in North Am ...
considers the Grand Trunk Corporation as a Class I railroad
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, st ...
.
Berlin Subdivision
The St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad , known as St-Laurent et Atlantique Quebec in Canada, is a short-line railway operating between Portland, Maine, on the Atlantic Ocean, and Montreal, Quebec, on the St. Lawrence River. It crosses the Can ...
, Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
to Island Pond
*CN Sherbrooke Subdivision, Island Pond to Saint-Hyacinthe
Saint-Hyacinthe (; French: ) is a city in southwestern Quebec east of Montreal on the Yamaska River. The population as of the 2021 Canadian census was 57,239. The city is located in Les Maskoutains Regional County Municipality of the Montérég ...
*CN Saint-Hyacinthe Subdivision, Saint-Hyacinthe to Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
*CN Montreal Subdivision, Montreal to Dorval
Dorval () is an on-island suburban city on the island of Montreal in southwestern Quebec, Canada. In 2016, the Canadian Census indicated that the population increased by 4.2% to 18,980. Although the city has the largest surface area in Montré ...
*CN Kingston Subdivision
Canadian National Railway's Kingston Subdivision, or Kingston Sub for short, is a major railway line connecting Toronto with Montreal that carries the majority of CN traffic between these points. The line was originally the main trunk for the Gra ...
, Dorval to Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
*CN Weston Subdivision, Toronto to Brampton
Brampton ( or ) is a city in the Canadian province of Ontario. Brampton is a city in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) and is a lower-tier municipality within Peel Region. The city has a population of 656,480 as of the 2021 Census, making it ...
*CN Halton Subdivision
The CN Halton Subdivision is a major railway line in Southern Ontario, Canada. It is owned and operated by the Canadian National Railway (CN).
Route description
The Halton Subdivision is long and runs generally northeast–southwest. Milepoint ...
, Brampton to Georgetown
*CN Guelph Subdivision
Guelph ( ; 2021 Canadian Census population 143,740) is a city in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. Known as "The Royal City", Guelph is roughly east of Kitchener and west of Downtown Toronto, at the intersection of Highway 6, Highway 7 and We ...
, Georgetown to St. Marys
*CN Forest Subdivision, St. Marys to Sarnia
Sarnia is a city in Lambton County, Ontario, Canada. It had a Canada 2021 Census, 2021 population of 72,047, and is the largest city on Lake Huron. Sarnia is located on the eastern bank of the junction between the Upper and Lower Great Lakes w ...
(St. Clair Tunnel)
*GTW Flint Subdivision, Port Huron
Port Huron is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of St. Clair County. The population was 30,184 at the 2010 census. The city is adjacent to Port Huron Township but is administered separately.
Located along the St. Clair ...
(St. Clair Tunnel) to Battle Creek
Battle Creek is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan, in northwest Calhoun County, at the confluence of the Kalamazoo and Battle Creek rivers. It is the principal city of the Battle Creek, Michigan Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA), which en ...
*GTW Southbend Subdivision, Battle Creek to Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
The Montreal-Toronto segment had been known by the following names:
*CNR Cornwall Subdivision, Dorval to Brockville
Brockville, formerly Elizabethtown, is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada, in the Thousand Islands region. Although it is the seat of the United Counties of Leeds and Grenville, it is politically independent of the county. It is included with Le ...
*CNR Gananoque Subdivision
Gananoque ( )
is a town in the Leeds and Grenville area of Ontario, Canada. The town had a population of 5,383 year-round residents in the 2021 Canadian Census, as well as summer residents sometimes referred to as "Islanders" because of the Tho ...
, Brockville to Belleville
*CNR Oshawa Subdivision
Oshawa ( , also ; 2021 population 175,383; CMA 415,311) is a city in Ontario, Canada, on the Lake Ontario shoreline. It lies in Southern Ontario, approximately east of Downtown Toronto. It is commonly viewed as the eastern anchor of the G ...
, Belleville to Toronto
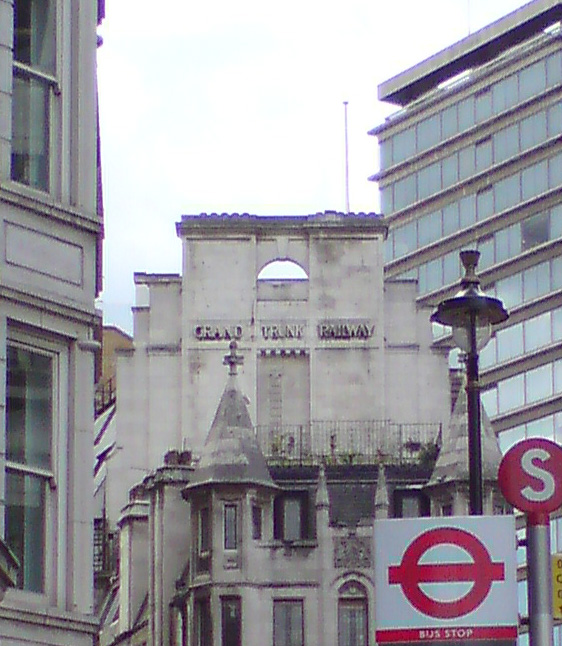
The Grand Trunk Railway Building on Warwick House Street in London continues to stand. Built by Aston Webb
Sir Aston Webb (22 May 1849 – 21 August 1930) was a British architect who designed the principal facade of Buckingham Palace and the main building of the Victoria and Albert Museum, among other major works around England, many of them in pa ...
, the 7 storey building was built in 1907 with the banner ''The Grand Trunk Railway of Canada'' on 4 Warwick House Street and ''Canadian National Railway'' on Cockspur Street. CN no longer owns the building. The current tenant on the lower floor is The Original London Tour Centre at 17–19 Cockspur Street.
In popular culture
In Series 3, Episode 1 of ''Downton Abbey
''Downton Abbey'' is a British historical drama television series set in the early 20th century, created and co-written by Julian Fellowes. The series first aired in the United Kingdom on ITV on 26 September 2010 and in the United States o ...
'', which takes place during the spring of 1920, Robert Crawley, Earl of Grantham learns that he has lost most of the fortune that he received from his wife Cora, which Lord Grantham had largely invested in Grand Trunk Railway stock.
See also
*Grand Funk Railroad
Grand Funk Railroad (often shortened to Grand Funk) is an American rock band formed in 1968 in Flint, Michigan, by Mark Farner (vocals, guitar), Don Brewer (drums, vocals), and Mel Schacher (bass). The band achieved peak popularity and succ ...
* Canada Atlantic Railway
The Canada Atlantic Railway (CAR) was a North American railway located in Ontario, southwestern Quebec and northern Vermont. It connected Georgian Bay on Lake Huron with the northern end of Lake Champlain via Ottawa. It was formed in 1897 throu ...
* Guelph Junction Railway
The Guelph Junction Railway is a shortline railway owned by the City of Guelph, Ontario, and serves the city's northwest industrial park.
The railway was the first federally chartered railway in the Commonwealth of Nations to be owned by a munic ...
* Pontiac Pacific Junction Railway
The Pontiac Pacific Junction Railway Company (PPJR) was a Canadian railway that operated in the upper Ottawa River valley in western Quebec and northeastern Ontario, Canada.
The railway ran from Aylmer through Quyon, Shawville, Fort Coulonge, ...
* List of defunct railroads of North America
The defunct railroads of North America regrouped several railroads in Canada, Mexico, and the United States. The following is a list of the past railroad companies.
Defunct railroad companies
*Algoma Central Railway (AC)
*Atchison, Topeka a ...
* Edson Joseph Chamberlin, president
* Joseph Hobson
Joseph Hobson (1834–1917) was a Canadian land surveyor and railway design engineer. Early in his career he apprenticed under various professionals and became a provincial land surveyor when he was 21 years old. He did layout work for to ...
, chief engineer from 1896
* History of rail transport in Canada
: ''This article is part of the history of rail transport by country series.''
The history of rail transport in Canada began in the early 19th century. The Canadian railway system saw several expansion "booms" throughout history, as well as a ma ...
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * . * * *Primary sources
* Canada. Legislature. Legislative Assembly. Special Committee on the Condition, Management and Prospects of the Grand Trunk. ''Report'' 1857, 263 pageonline
External links
Collections Canada: History of the Grand Trunk Railway
(Trent University Archives) * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20091027143522/http://www.geocities.com/sharut/gt_rail.html GTR Historybr>Grand Trunk Railway Collection Finding Aid, Special Collections, University of Vermont Library
* ttp://www.risksandrewards.org.uk/source_65.html Maps of the Grand Trunk Railway 1857, and its connections, c1860br>Report for submission to the shareholders of the Grand Trunk Railway in 1860
*, illustrated account of the Grand Trunk Railway {{DEFAULTSORT:Grand Trunk Railway Defunct Ontario railways Defunct Quebec railways Defunct Maine railroads Defunct New Hampshire railroads Defunct Vermont railroads History of Montreal Predecessors of the Canadian National Railway Railway companies established in 1852 Railway companies disestablished in 1923 5 ft 6 in gauge railways in the United States Defunct New York (state) railroads Defunct Michigan railroads 5 ft 6 in gauge railways in Canada Canadian companies established in 1852 Transport companies based in London Defunct companies based in London Companies based in the City of Westminster