
Government incentives for plug-in electric vehicles have been established around the world to support policy-driven adoption of
plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) to store electrical power within its onboard rechargeable battery packs, which then ...
s. These incentives mainly take the form of purchase rebates, tax exemptions and
tax credit
A tax credit is a tax incentive which allows certain taxpayers to subtract the amount of the credit they have accrued from the total they owe the state. It may also be a credit granted in recognition of taxes already paid or a form of state "dis ...
s, and additional perks that range from access to bus lanes to waivers on fees (charging, parking, tolls, etc.). The amount of the financial incentives may depend on vehicle
battery size or all-electric range. Often
hybrid electric vehicles are included. Some countries extend the benefits to
fuel cell vehicle
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate e ...
s, and
electric vehicle conversion
In automobile engineering, electric vehicle conversion is the replacement of a car's combustion engine and connected components with an electric motor and batteries, to create an all-electric vehicle (AEV).
There are two main aims for converting ...
s.
More recently, some governments have also established long term regulatory signals with specific target timeframes such as
ZEV mandates, national or regional emissions regulations, stringent
fuel economy standards, and the
phase-out of internal combustion engine vehicle sales
Phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles means stopping selling and using vehicles which are powered by fossil fuels, such as gasoline (petrol), diesel, kerosene and fuel oil: it is one of the three most important parts of the general fossil fuel phas ...
.
For example, Norway set a national goal that all new car sales by 2025 should be
zero emission vehicles (
electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
or
hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
).
Other countries have announced similar targets for the electrification of their vehicle fleet, most within a timeframe between 2030 and 2050.
[
]
Asia
China
On May 21, 2022, Shanghai Municipal People's Government released and issued the "Shanghai Action Plan for Accelerating Economic Recovery and Revitalization" to promote automobile consumption. The incentive plan includes tax deduction and offers financial subsidy of 10,000 Yuan per electrical vehicle.

 The Chinese government adopted a plan in 2009 with the goal of turning the country into one of the leaders of all-electric and hybrid vehicles by 2012. The government's intention was to create a world-leading industry that would produce jobs and exports, and to reduce urban pollution and its oil dependence. However, a study found that even though local air pollution would be reduced by replacing a gasoline car with a similar-size electric car, it would reduce
The Chinese government adopted a plan in 2009 with the goal of turning the country into one of the leaders of all-electric and hybrid vehicles by 2012. The government's intention was to create a world-leading industry that would produce jobs and exports, and to reduce urban pollution and its oil dependence. However, a study found that even though local air pollution would be reduced by replacing a gasoline car with a similar-size electric car, it would reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
by only 19%, as China uses coal for 75% of its electricity production.new energy vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) to store electrical power within its onboard rechargeable battery packs, which then ...
s (NEVs) to designate plug-in electric vehicles, and only pure electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles are subject to purchase incentives.[ ''See Acronyms and Key Terms, pp. v''] On June 1, 2010, the Chinese government announced a trial program to provide incentives up to 60,000 yuan (~ in June 2011) for private purchase of new battery electric vehicles and 50,000 yuan (~ in June 2011) for plug-in hybrids in five cities.Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
, Shenzhen, Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
, Hefei and Changchun. The subsidies are paid directly to automakers rather than consumers, but the government has stated that it expected that vehicle prices will be reduced accordingly. The amount of the subsidy is to be reduced once 50,000 units are sold.[ In addition to the subsidy, the Chinese government is planning to introduce, beginning on January 1, 2012, an exemption from annual taxes for pure electric, fuel-cell, and plug-in hybrid vehicles. Hybrid vehicles were eligible for a 50% reduction only.
In 2011, only 8,159 electric cars were sold in China despite a 120,000 yuan subsidy.
Unsubsidized lead-acid EVs are produced without government approval at a rate of more than 30,000 per year in Shandong and requires no driving license because the top speed is less than 50 km/h. They cost 31,600 yuan and have been the target of criticism from major car manufacturers.]
India
 In November 2010, the Government of India (GoI), through the
In November 2010, the Government of India (GoI), through the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is a ministry of the Government of India, headed by current Union Cabinet Minister Raj Kumar Singh, that is mainly responsible for research and development, intellectual property protection, and ...
(MNRE), announced a subsidy of million for electric vehicles. The subsidy provided benefits up to 20% on the ex-factory price, with a maximum benefit of on electric cars, on two-wheelers, on high speed two-wheelers, for electric minibuses, and for three-wheelers. To claim the subsidy, manufacturers needed to certify that 30% of the components were made in India. The scheme ended on 31 March 2012.OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
report, India is regarded as a country providing the least subsidies, compared to other major markets, to renewable energy in electric vehicle and that may hamper the governments target of achieving the all-electric target by 2030.
Various state governments and cities provide their own subsidies:
* Delhi, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand and Lakshadweep don't levy VAT
* Chandigarh, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Gujarat & West Bengal offer partial rebate on VAT
* Delhi also provides a 15% subsidy of the base price of select electric cars, like REVA. It also exempts such cars from road tax and registration fees.
Japan
The Japanese government introduced the first electric vehicle incentive program in 1996, and it was integrated in 1998 with the Clean Energy Vehicles Introduction Project, which provided subsidies and tax discounts for the purchase of electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, methanol and hybrid electric vehicles. The project provided a purchase subsidy of up to 50% the incremental costs of a clean energy vehicle as compared with the price of a conventional engine vehicle. This program was extended until 2003.
In May 2009 the National Diet passed the "Green Vehicle Purchasing Promotion Measure" that went into effect on June 19, 2009, but retroactive to April 10, 2009.[ The program established tax deductions and exemptions for environmentally friendly and fuel efficient vehicles, according to a set of stipulated environmental performance criteria, and the requirements are applied equally to both foreign and domestic produced vehicles. The program provides purchasing subsidies for two type of cases, consumers purchasing a new passenger car without a trade-in (non-replacement program), and for those consumers buying a new car trading a used car registered for 13 years or more ( scrappage program).][ ''See pages 45–46''.]
Tonnage and acquisition tax reductions
 New next generation vehicles, including electric and
New next generation vehicles, including electric and fuel cell vehicle
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate e ...
s, plug-in hybrids, hybrid electric vehicles, clean diesel and natural gas vehicles are exempted from both the acquisition tax and the tonnage tax.[
These incentives were effective from April 1, 2009, until March 31, 2012, for the acquisition tax which is paid once at the time of purchase. The tonnage tax reductions were effective from April 1, 2009, until April 30, 2012, and the incentive was applicable once, at the time of the first mandatory inspection, three years after the vehicle purchase.][ As an example, the amount exempted for the purchase of a new next generation vehicle was 81,000 yen (~US$975) corresponding to the acquisition tax, and 22,500 yen (~US$271) for the tonnage tax, for a total of 103,500 yen (~US$1,246).][
]
Automobile tax reductions
Consumers purchasing new next generation electric vehicles, including fuel cell vehicles, benefited from a 50% reduction of the annual automobile tax. These incentives were in effect from April 1, 2009, until March 31, 2010, applicable only once.[
]
Incentives for purchasing new green vehicles
Subsidies for purchases of new environmentally friendly vehicles without scrapping a used car are 100,000 yen (~US$1,100) for the purchase of a standard or small car, and 50,000 yen (~US$550) for the purchase of a mini or kei vehicle. Subsidies for purchasing trucks and buses meeting the stipulated fuel efficiency and emission criteria vary between 200,000 yen (~US$2,100) to 900,000 yen (~US$9,600).[
Subsidies for purchases of new environmentally friendly vehicles in the case of owners scrapping a 13-year or older vehicle are 250,000 yen (~US$2,700) for the purchase of a standard or small car, and 125,000 yen (~US$1,300) for the purchase of a mini or kei vehicle. Subsidies for purchasing trucks and buses meeting the stipulated fuel efficiency and emission criteria vary between 400,000 yen (~US$4,300) to 1,800,000 yen (~US$19,000).][
All incentives for new purchases with or without trading were applicable in Japan's fiscal year 2009, from April 1, 2009, through March 31, 2010.]
Philippines
Under President Duterte's administration, the Tax Reform for Acceleration and Inclusion Act was signed into law, which has exemptions for anyone buying an electric vehicle alongside hybrids.
South Korea
In July 2016, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy announced a plan to make electric car batteries run longer, build a network of charging stations and make electric car purchases and ownership more affordable. The government expects that the current and future policy programs will help increase the electric car market share in South Korea to 0.5% in 2017, up from 0.2% in 2015, and to achieve 5.3% in 2020.[
The government's plan also includes the development of an electric car battery, beginning in 2016, with energy density high enough to more than double the travel distance on a charge to . The government expects to increase the global market share of South Korean electric cars to match that of South Korean gasoline and diesel cars, which reached 8.5% based on sales by South Korea's two main car exporters, Hyundai Motor Company and ]Kia Motors
Kia Corporation, commonly known as Kia (, ; formerly known as Kyungsung Precision Industry and Kia Motors Corporation), is a South Korean multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Seoul, South Korea. It is South Korea's second lar ...
.[
]
Europe
Electrification of transport
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery (sometimes cha ...
( electromobility) figures prominently in the Green Car Initiative (GCI), included in the European Economic Recovery Plan. DG TREN is supporting a large European "electromobility" project on EVs and related infrastructure with a total budget of around as part of the Green Car Initiative.
There are measures to promote efficient vehicles in the Directive 2009/33/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on the promotion of clean and energy-efficient road transport vehicles and in the Directive 2006/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 April 2006 on energy end-use efficiency and energy services.
As of April 2011, 15 of the 27 European Union member states provide tax incentives for electrically chargeable vehicles, which includes all Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
an countries plus the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
. Also 17 countries levy carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
related taxes on passenger cars as a disincentive. The incentives consist of tax reductions and exemptions, as well as of bonus payments for buyers of PEVs, hybrid vehicles, and some alternative fuel vehicles.
Armenia
Armenia advanced an initiative to exempt VAT taxes from the import of electric cars. On January 17, the government approved the draft on the initiative on the draft law, according to which "the import of electric motor vehicles will be exempt from value added tax. The exemption is supposed to be in effect until January 1, 2022".
Armenia is also set to become the first country, the government of which will switch its fleet from petroleum-run cars to all electric cars. As the Minister of Nature Protection has stated, the Armenia has joined the Global Electric Mobility process. The country has already been granted relevant funds for undertaking this project, and as the minister states "in case of everything proceeding swiftly, all Cabinet members will be issued electric cars by year-end".
Austria
Electric vehicles are exempted from the fuel consumption tax, levied upon the first registration, and from the monthly vehicle tax. In addition to tax breaks, hybrid vehicles and other alternative fuel vehicles benefit from a fuel consumption tax that pays bonuses to passenger cars with low carbon dioxide output. Alternative fuel vehicles, including hybrids, qualify for as much as (around ) in annual bonuses. This bonus was valid from 1 July 2008 until 31 August 2012.[ Additionally, cars with no carbon emissions qualify for a deduction of the VAT (Value-Added Tax), as of January 2016.]
Belgium
The Belgian government established a personal income tax deduction of 30% of the purchase price including VAT of a new electric vehicle, up to €9,190. Plug-in hybrids are not eligible.[ This tax incentive ended on December 31, 2012. There is also available a tax deduction up to 40% for investments in external recharging stations publicly accessible, to a maximum of €250.][ The ]Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
regional government had an additional eco-bonus for cars registered before December 31, 2011.
Bulgaria
Electric vehicles, including cars, motorbikes and mopeds, are exempt from the annual circulation tax.
Cyprus
Vehicles with emissions less than 120 grams of carbon dioxide per kilometer are exempt from paying registration taxes.
Czech Republic
Electric, hybrid and other alternative fuel vehicles used for business purposes are exempt from the road tax.[
The Czech Republic has one of the lowest rates of plug-in electric vehicles on newly registered automobiles among ]OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
countries (only 0,3 % in 2018). It is becoming relevant topic for the country, especially for the Škoda auto, the Czech greatest representative of the automobile industry.
Hence, experimentally empirical research on Czech consumers’ preferences was conducted, whose aim was to evaluate the efficiency of various incentives that might promote the market with plug-in electric vehicles in the Czech Republic. The research has shown that except the price, the most relevant factors affecting the willingness to pay for the relatively expensive plug-in electric vehicles are: better fuel-efficiency (CZK 52,000 more on average for a reduction in operating costs of CZK 1 per 1 km for a new car), increase in driving range (CZK 28,000 more on average for an increase in driving range of 100 km), battery-charging time, financial support for electrical wiring in households, free parking in cities or environmental factors (26–40 thousand CZK for each 20% emission reduction). On the other hand, free motorway toll sticker or special traffic lane has non-significant effect on the incentives to buy the vehicle.
Denmark
In 2016, battery electric vehicles lost access to their registration tax exemption. The registration tax will gradually be phased back in until 2020.
Estonia
No grants towards the purchase of Plug-In or Electric vehicles as of 2016. Electric vehicles are exempt from the city public parking fees and can use bus lanes.
From 2011 to 2014 Estonia has allocated a total of in grants towards the purchase of battery electric vehicles (ended 7 August 2014). From 2011 to 2014, KredEx has allocated grants totaling ; the average grant per car was . The grant has helped the purchase of over 650 electric cars in Estonia. At that time, a country-wide quick charging network (CHAdeMO 500 V/120 A and Type2 400 V/32 A) was established.
Finland
For the period of 2018–2021, €6,000,000 annually will be allocated towards the purchase of electric cars and conversion of petrol cars to E85 and gas. An individual registering a new electric car in the period 1.1.2018–30.11.2021 is eligible for a grant of €2,000, if the purchase price of the car is €50,000 or less.
The Prime Minister of Finland (2003–2010) Mr. Matti Vanhanen
Matti Taneli Vanhanen (; born 4 November 1955) is a Finnish politician who served as Prime Minister of Finland from 2003 to 2010. He was also Chairman of the Centre Party and President of the European Council in 2006. In his earlier career, he ...
in 2010 mentioned that he wanted to see more electric cars on Finnish roads as soon as possible and with any cost to the governmental car related tax incomes.
In the end of 2017, there were 1,449 electric cars registered in Finland.
France
Since 2008 France has a bonus–malus system offering a financial incentive, or bonus, for the purchase of cars with low carbon emissions, and a fee, or malus, for the purchase of high-emission vehicles. The bonus applies to private and company vehicles purchased on or after 5 December 2007 and are deduced from the purchase price of the vehicle. The malus penalty applies to all vehicles registered after 1 January 2008, and is added at the time of registration. Since 2009, every family with more than two children receives a deduction from the malus of 20 g of per km per child.['' See Chapter 3 – Car Registration Tax ('Bonus-Malus' system) in France pp. 15-21.'']
;2012–2014
 Until July 31, 2012, a premium up to , under the bonus-malus system, was granted for the purchase of new cars with emissions of 60 g/km or less which benefited all-electric cars and any plug-in hybrid with such low emissions. Vehicles emitting up to 125 g/km or less, such as conventional hybrids and natural gas vehicles, were granted up to .
Until July 31, 2012, a premium up to , under the bonus-malus system, was granted for the purchase of new cars with emissions of 60 g/km or less which benefited all-electric cars and any plug-in hybrid with such low emissions. Vehicles emitting up to 125 g/km or less, such as conventional hybrids and natural gas vehicles, were granted up to .[ The incentive could not exceed 20% of the sales price including VAT, increased with the cost of the battery if it is rented.][
Effective on August 1, 2012, the government increased the bonus for electric cars up to but capped at 30% of the vehicle price including VAT. The price includes any battery leasing charges, and therefore, electric cars which need a battery leasing contract also are eligible for the bonus. For example, an electric car sold for including VAT was eligible for the maximum bonus of . The emission level for the maximum bonus was raised to 20 g/km or less. Cars with emission levels between 20 and 50 g/km were eligible to a bonus of up to , and between 50 and 60 g/km were eligible to a bonus of up to . After this limit, the bonus dropped to .
The fee schedule for the bonus-malus was modified in 2013. Effective November 1, 2013, the bonus was reduced from to for all-electrics and any other vehicle with emissions of less than 21 g/km. Vehicles emitting between 21 and 60 g/km, such as plug-in hybrids and conventional hybrids, were eligible to a bonus up to , and for emissions between 61 and 90 g/km up to , down from . Effective January 1, 2014, the fee schedule for the malus was increased to a maximum penalty of from for vehicles emitting over 200 g/km. Flex-fuel vehicles remained exempt from the malus fee. A neutral class applies to vehicles emitting between 91 and 130 g/km.][
;2015–2016
From April 1, 2015, a super-bonus was introduced, increasing the financial incentive to a cumulative total of , consisting of the regular bonus of for purchasing a pure electric car, plus up to for customers ]scrapping
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered me ...
a diesel-powered car in circulation before 1 January 2001. In the case of plug-in hybrids with emission levels between 21 and 60 g/km, the purchase bonus was plus the scrapping premium of . Also a specific grant was introduced for families which are below the income tax threshold who buy an ordinary new or second hand car below certain emission thresholds or a hybrid or electric car.
 Effective January 4, 2016, the bonus limited to 27% of the purchase price of vehicles emitting up to 20 g/km was kept. This bonus corresponds to pure electric vehicles and those equipped with a range extender. Vehicles emitting between 21 and 60 g/km are entitled to a bonus. This bonus corresponds to the majority of plug-in hybrids. Conventional hybrid passenger cars emitting between 61 and 110 g/km with sufficient level of hybridization, with an electric motor with an output power of not be less than 10 kW, are entitle to a bonus.
Effective January 4, 2016, the bonus limited to 27% of the purchase price of vehicles emitting up to 20 g/km was kept. This bonus corresponds to pure electric vehicles and those equipped with a range extender. Vehicles emitting between 21 and 60 g/km are entitled to a bonus. This bonus corresponds to the majority of plug-in hybrids. Conventional hybrid passenger cars emitting between 61 and 110 g/km with sufficient level of hybridization, with an electric motor with an output power of not be less than 10 kW, are entitle to a bonus.[ Diesel-powered hybrids, such as the PSA Hybrid4, are no longer eligible for the bonus, even if the car emits less than 110 g/km of .
The combined super-bonus for the purchase or lease of a new all-electric car was maintained. To be eligible for the additional scrappage bonus, the old diesel-powered car have to be owned for at least a year and in circulation before 1 January 2006. The new vehicle must not be sold within 6 months of acquisition or have traveled less than .][
]
2020–2022
The French government has canceled any bonus for cars priced above , than for the car that bonus will be in 2020 and in 2021; and in 2020 for the cars priced below . For the car that cost between and , the bonus is reduced by 50%, but French government will certainly adapt if too many people bought foreign cars. French (Zoe, E208, C4, DS-3...) EV will be on Fully supported, but other foreign car and specially Tesla is targeted by this limit of .
Germany
 " Nationale Plattform Elektromobilität" (NPE) is a German government initiative to develop Germany into a leading market for electric mobility. In May 2010, under its National Program for Electric Mobility, Chancellor
" Nationale Plattform Elektromobilität" (NPE) is a German government initiative to develop Germany into a leading market for electric mobility. In May 2010, under its National Program for Electric Mobility, Chancellor Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel (; ; born 17 July 1954) is a German former politician and scientist who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. A member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), she previously served as Leader of the Opp ...
set the goal to bring 1 million electric vehicles on German roads by 2020. However, the government also announced that it would not provide subsidies to the sales of plug-in electric cars but instead it will only fund research in the area of electric mobility. Electric vehicles and plug-ins are exempt from the annual circulation tax for a period of five years from the date of their first registration.[ ''Click under "Overzicht stimuleringsprogrammas elektrische voertuigen (Overview incentive programs electric vehicles) to download the report in pdf format (website in Dutch)''.] In 2016, the annual circulation tax exemption was extended from five to ten years, backdated to 1 January 2016.[
The private use of a company car is treated as taxable income in Germany and measured at a flat monthly rate of 1% of the vehicle's gross list price. So plug-in electric cars have been at a disadvantage since their price tag can be as much as double that of a car using a conventional internal combustion engine due to the high cost of the battery. In June 2013 German legislators approved a law that ends the tax disadvantage for corporate plug-in electric cars. The law, backdated to 1 January 2013, allows private users to offset the list price with per unit of battery size, expressed in kilowatt hours (kWh). The maximum offset was set at corresponding to a 20 kWh battery. The amount one can offset will sink annually by per kilowatt hour. The range criteria will rise to starting in 2018. As part of the package of financial incentives approved in 2016, private owners of plug-in electric vehicles that charge their cars in their employer premises are exempted from declaring this perk as a cash benefit in their income tax return. Employers who provide this perk are allowed to discount from their income tax a 25% of the lump sum value of the cash benefit. These two fiscal benefits apply only from 1 January 2017 until the end of 2020.
] In August 2014, the federal government announced its plan to introduce non-monetary incentives through new legislation to be effective by 1 February 2015. The proposed user benefits include measures to privilege battery-powered cars, fuel cell vehicles and some plug-in hybrids, just like Norway does, by granting local governments the authority to allow these vehicles into bus lanes, and to offer free parking and reserved parking spaces in locations with charging points. Not all plug-in hybrids will qualify for the benefits, only those with emissions of no more than 50 g/km or an all-electric range of over are eligible.
According to the fourth progress report of the German National Electric Mobility Platform, only about 24,000 plug-in electric cars are on German roads by the end of November 2014, well behind the target of 100,000 unit goal set for 2014. As a result, Chancellor
In August 2014, the federal government announced its plan to introduce non-monetary incentives through new legislation to be effective by 1 February 2015. The proposed user benefits include measures to privilege battery-powered cars, fuel cell vehicles and some plug-in hybrids, just like Norway does, by granting local governments the authority to allow these vehicles into bus lanes, and to offer free parking and reserved parking spaces in locations with charging points. Not all plug-in hybrids will qualify for the benefits, only those with emissions of no more than 50 g/km or an all-electric range of over are eligible.
According to the fourth progress report of the German National Electric Mobility Platform, only about 24,000 plug-in electric cars are on German roads by the end of November 2014, well behind the target of 100,000 unit goal set for 2014. As a result, Chancellor Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel (; ; born 17 July 1954) is a German former politician and scientist who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. A member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), she previously served as Leader of the Opp ...
recognized in December 2014 that the government has to provide more incentives to meet the goal of having 1 million electric cars on the country's roads by 2020. Among others, and based on the recommendations of the report, the federal government is considering to offer a tax break for zero-emission company cars, more subsidies to expand charging infrastructure, particularly to deploy more public fast chargers, and more public funding for research and development of the next generation of rechargeable batteries.[''The term electric drive used by KBA includes battery-electric, plug-in and fuel-cell cars.'']
2016–2019
At the beginning of 2016, German politicians from the three parties in Mrs. Merkel's ruling coalition and auto executives began talks to introduce a subsidy for green car buyers worth up to () to boost sales of electric and plug-in hybrid cars. , the German government proposal is for the auto industry to cover 40% of the cost of the purchase subsidy. Private buyers would get the full subsidy, while corporate buyers would receive for each electric car, and the program is expected to run until 2020, the deadline set to achieve the goal of 1 million electric cars on German roads. Incentives will fall by each year. In March 2016, Nissan Europe announced its support to the green car incentive and its commitment to double the government's E-premium incentive when buying a Nissan electric car, with a reduction of the purchase price of the same amount of the subsidy. Nissan Center Europe CEO said "''we remain convinced that the goal of one million electric cars by 2020 is still achievable''." According to Nissan if from now on electric car sales double every year until 2020, it is still possible to achieve the government goal.
 An incentive scheme to promote plug-in electric vehicle adoption was approved in April 2016 with a budget of (). A total of () is reserved for the purchase subsidies, which are expected to run until all the money is disbursed, estimated to last until 2019 at the latest. Another () are budgeted to finance the deployment of charging stations in cities and on autobahn highway stops. And another () would go toward purchasing electric cars for federal government fleets. The program is aimed to promote the sale of 400,000 electric vehicles. The cost of the purchase incentive is shared equally between the government and automakers. Electric car buyers get a () discount while buyers of plug-in hybrid vehicles get a discount of (). Premium cars, such as the Tesla Model S and
An incentive scheme to promote plug-in electric vehicle adoption was approved in April 2016 with a budget of (). A total of () is reserved for the purchase subsidies, which are expected to run until all the money is disbursed, estimated to last until 2019 at the latest. Another () are budgeted to finance the deployment of charging stations in cities and on autobahn highway stops. And another () would go toward purchasing electric cars for federal government fleets. The program is aimed to promote the sale of 400,000 electric vehicles. The cost of the purchase incentive is shared equally between the government and automakers. Electric car buyers get a () discount while buyers of plug-in hybrid vehicles get a discount of (). Premium cars, such as the Tesla Model S and BMW i8
The BMW i8 is a plug-in hybrid sports car developed by BMW. The i8 was part of BMW's electrified fleet and was marketed under the BMW i sub-brand. The production version of the BMW i8 was unveiled at the 2013 Frankfurt Motor Show and was rel ...
, are not eligible to the incentive because there is a cap of () for the purchase price. Only electric vehicles purchased after 18 May 2016 are eligible for the bonus and the owner must keep the new electric car at least nine months. The same rule applies for leasing.[ In May 2016, Nissan announced the company decided to raise the bonus with an additional () to () for customers of its all-electric Leaf car and e-NV200 utility van. The online application system to claim the bonus went into effect on 2 July 2016. , a total of 26 plug-in electric cars and vans are eligible for the purchase bonus.][ According to the Federal Office of Economics and Export Control (BAFA), a total of 4,451 applications have been made for the government subsidy for the purchase of a plug-in electric model , consisting of 2,650 all-electrics and 1,801 plug-in hybrids.]Bayern
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
(1,130), Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
(873), and Nordrhein-Westfalen
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhab ...
(726).[
, the following 26 plug-in electric cars and vans are eligible for the purchase bonus: ]Audi A3 e-tron
The Audi A3 is a subcompact executive/small family car (C-segment) manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi AG since September 1996, currently in its fourth generation.
The first two generations of the Audi A3 were based on the ...
, BMW 225xe, BMW 330e, BMW i3
The BMW i3 is a B-segment, high-roof hatchback manufactured and marketed by BMW with an electric powertrain using rear-wheel drive via a single-speed transmission and an underfloor Lithium-ion battery, lithium-ion battery pack and an optional R ...
, Citroën Berlingo Electric
Citroën () is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded in March 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën is owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired 8 ...
, Citroën C-Zero, Ford Focus Electric
The Ford Focus Electric is a 5-door hatchback electric car that was produced by Ford. The Focus Electric is Ford's second production all-electric vehicle (the first being the Ford Ranger EV), and was made from December 2011to May 2018.
The Fo ...
, Kia Soul EV
The Kia Soul EV (also known as Kia e-Soul) is an all-electric subcompact crossover SUV manufactured by Kia and based on the Kia Soul. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) official range for the 2020 Kia Soul EV is 243 miles (391 km ...
, Mercedes-Benz B-Class Electric Drive
The Mercedes-Benz B-Class is a subcompact executive car manufactured and marketed by Mercedes-Benz since 2005. Based on the A-Class with larger dimensions, the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) classifies it as a small MPV.
As ...
(B 250e), Mercedes-Benz C350 e, Mitsubishi i-MiEV
The Mitsubishi i-MiEV (MiEV is an acronym for ''Mitsubishi innovative Electric Vehicle'') is a five-door hatchback electric car produced in the 2010s by Mitsubishi Motors, and is the electric version of the Mitsubishi i. Rebadged variants of ...
, Mitsubishi Outlander P-HEV
The is a mid-size
crossover SUV manufactured by Japanese
automaker Mitsubishi Motors. It was originally known as the when it was introduced in Japan in 2001.
The original Airtrek name was chosen to "describe the vehicle's ability to transpo ...
, Nissan e-NV200 5- and 7-seater Combi, Nissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
, Peugeot iOn, Peugeot Partner Electric, Renault Kangoo Z.E., Renault Zoe, Smart Fortwo electric drive, Tesla Model 3
The Tesla Model 3 is a compact executive sedan that is battery powered and produced by Tesla. Limited production of the Model 3 began in mid-2017, with the first production vehicle rolling off the assembly line on July 7, 2017. The offici ...
, Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid
The Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid (often abbreviated as the Prius and known as the Prius Prime in North America, South Korea, and New Zealand) is a plug-in hybrid liftback manufactured by Toyota. The first-generation model was produced from 2012 t ...
, Volkswagen e-Golf
The Volkswagen Golf (Mk7) is a small family car (C-segment) produced by German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, as the seventh generation of the Golf and the successor to the Golf Mk6. It was introduced in Berlin on 4 September 2012, befor ...
, Volkswagen e-Up!
The Volkswagen Up (stylized as Volkswagen up!) is a city car, part of the Volkswagen Group New Small Family (NSF) series of models, unveiled at the 2011 International Motor Show Germany (IAA). Production of the Up started in December 2011 at th ...
, Volkswagen Golf GTE, Volkswagen Passat GTE, and Volvo V60 Plug-in Hybrid
The Volvo V60 is a compact wagon produced by Volvo Cars related to the S60. The vehicle was first released in autumn 2010, facelifted in 2014, and is in its second generation since 2018.
The second generation V60 was launched in 2018 based on t ...
.[
]
2020–2021
 As a result of the
As a result of the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching economic consequences including the COVID-19 recession, the second largest global recession in recent history, decreased business in the services sector during the COVID-19 lockdowns, the 2020 stock ...
, the government approved in June 2020 an economic recovery plan with a budget of , which included to promote electric vehicle adoption and deployment of charging infrastructure.[
There are also lower bonuses available for leasing; new cars costing between and ; and also for used cars, provided no environmental bonus was granted in a previous purchase. In addition, other tax incentives for electric vehicles were introduced. In November 2020 the government decided to keep the innovation bonus until the end of 2025, but for plug-in hybrid cars to be eligible they must have a minimum electric range of from 2022 and at least from 2025.]
Greece
From 2011 to June 2016, all electric vehicles were exempt from the registration tax.[ From 1 July 2016 onwards the registration tax for hybrid vehicles was reduced to 50%.
In June 2020, Greek ]Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
Kyriakos Mitsotakis announced the government's plan to support the adoption of new battery electric vehicles (BEV) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV) by individuals and corporations, with the aim for one-in-three new vehicles in Greece to be electric by 2030. The plan includes purchase subsidizing, exemption from the road tax
Road tax, known by various names around the world, is a tax which has to be paid on, or included with, a motorised vehicle to use it on a public road.
National implementations Australia
All states and territories require an annual vehicle registra ...
and any parking fees, as well as incentives for setting up charging stations, for pure electric private passenger cars and motorbikes, as well as for pure electric or plug-in hybrid taxis and light commercial vehicles. The government's subsidy covers the purchase of new BEVs and PHEVs with a total of 100 million euros for 18 months in the first phase, which is estimated to cover 25% of the cost of about 14.000 new electric vehicles.
Hungary
All hybrid and electric vehicles are exempt from registration tax. The Government announced that from October 27, 2016, electric vehicles would be eligible for a 21% rebate of the gross purchase price, capped at a ( at the December 2016 exchange rate). Furthermore, to promote electric cars, the Government has added some other regulatory incentives, such as green license plates, and simplified tax and regulations on electric charge points. By 2020, the Government expects that there will be 30,000 environmentally friendly cars on Hungarian roads.
Iceland
All electric vehicles are exempt from VAT up to , and the tax is applied at the normal rate for the remainder of the price. Electric vehicles, as well as hydrogen powered vehicles, that are shorter than 5 meters also get free parking in the city center for up to 90 minutes. The free parking also applies to methane and hybrid vehicles that weigh less than 1,600 kg, although in order for hybrid vehicles to be applicable, they must have emissions of less than 50 g/km.
Ireland
 Series production EVs were exempted from VRT until December 2012. The VRT exemption was replaced by a €5000 credit against the tax. Annual motor tax for EVs is €120. The Government has set a target of 10% for all vehicles on Irish roads to be electric by 2020.
The ESB eCar electric vehicle charging network serves as the main charging network for the island of Ireland and has rapidly expanded in recent years. Currently the network is free to use with an RFID card provided by ESB to EV owners who wish to use the network. The network aims to provide rapid charging every 30 km on major routes and as of 2015 has almost 2000 standard charging points (all provide connection via
Series production EVs were exempted from VRT until December 2012. The VRT exemption was replaced by a €5000 credit against the tax. Annual motor tax for EVs is €120. The Government has set a target of 10% for all vehicles on Irish roads to be electric by 2020.
The ESB eCar electric vehicle charging network serves as the main charging network for the island of Ireland and has rapidly expanded in recent years. Currently the network is free to use with an RFID card provided by ESB to EV owners who wish to use the network. The network aims to provide rapid charging every 30 km on major routes and as of 2015 has almost 2000 standard charging points (all provide connection via IEC 62196
IEC 62196 ''Plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets – Conductive charging of electric vehicles'' is a series of international standards that define requirements and tests for plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and veh ...
Type 2 Mennekes, around half are 22 kW with the remainder a mix of 3.6 kW and 7.4 kW). There are around 100 CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO is a fast-charging system for battery electric vehicles, developed starting in 2010 by the CHAdeMO Association, formed by the Tokyo Electric Power Company and five major Japanese automakers. The name is an abbreviation of "CHArge de MOve ...
rapid chargers with over 70 located outside the Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 c ...
Metro area. All rapid chargers installed since mid-2014 have been triple standard CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO is a fast-charging system for battery electric vehicles, developed starting in 2010 by the CHAdeMO Association, formed by the Tokyo Electric Power Company and five major Japanese automakers. The name is an abbreviation of "CHArge de MOve ...
/Combined Charging System
The Combined Charging System (CCS) is a standard for charging electric vehicles. It can use or connectors to provide power at up to . These two connectors are extensions of the IEC 62196 Type 1 and Type 2 connectors, with two additional d ...
/AC 43 kW. Four rapid chargers in Dublin and two rapid chargers in Belfast were co-funded by the EU as part of the UK/Ireland RCN program. The UK charging network operated by Ecotricity
Ecotricity is a British energy company based in Stroud, Gloucestershire, England, specialising in selling green energy to consumers that it primarily generates from its 87.2 megawatt wind power portfoliothe company prefers the term windmill ra ...
has a single CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO is a fast-charging system for battery electric vehicles, developed starting in 2010 by the CHAdeMO Association, formed by the Tokyo Electric Power Company and five major Japanese automakers. The name is an abbreviation of "CHArge de MOve ...
only rapid charger at IKEA Belfast. This is the sole rapid charger on the island that is not part of the ESB eCars network.
Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland
The Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI) ( ga, Údarás Fuinnimh Inmharthana na hÉireann) is an Irish governmental body established to promote and aid in the development of sustainable energy in Ireland.
History
The SEAI was founded ...
offers a government grant of up to €5,000 for the purchase of a new electric car. Electric and hybrid vehicles had a reduction of up to off the registration tax between July 2008 and December 2010.[ However this grant is only available on vehicles on an approved list of models which must be sold by a dealer registered for the scheme. No grant applies where a vehicle is imported privately. The grant is reduced to €3,800 for business purchasers or those who require finance to purchase the vehicle, however some importers will report financed private sales as cash sales to acquire the full grant.
, plug-in electric car purchasers are eligible for a government credit worth up to (about ). Vehicle Registration Tax (VRT), up to is also waived for electric cars. Also, all-electric car owners pay the lowest rate of annual road tax, which is based on emissions. In addition, the first 2,000 electric cars registered in Ireland are eligible for installation of a free home-charging points worth about (about ).]
Italy
Electric vehicles are exempt from the annual circulation tax or ownership tax for five years from the date of their first registration. Thereafter, EVs benefit from a 75% reduction of the tax rate applied to equivalent gasoline-powered vehicles.[ Buyers of electric vehicles and other vehicles emitting 70 g/km or less of carbon dioxide are eligible to receive from €1,500 to €6,000. In the region of Lombardy, electric vehicles are exempt from the annual ownership tax.
]
Latvia
Electric vehicles, including cars, goods vehicles, buses, and motorcycles, are exempt from payment of the Vehicle Operation Tax
Luxembourg
Buyers of electric vehicles and other vehicles emitting 60 g/km
Emission standards are the legal requirements governing air pollutants released into the atmosphere. Emission standards set quantitative limits on the permissible amount of specific air pollutants that may be released from specific sources o ...
or less of carbon dioxide are eligible to receive a premium of (around ), this premium ended 31 December 2011. In order to qualify for the rebate, the owner must have concluded an agreement to buy electricity from renewable energy.[
]
Monaco
Buyers of electric vehicles and plug in hybrids are eligible to receive (around ) from the Monegasque Government. In addition vehicles owners are allowed to park free at any public parking facility.
Netherlands
 Considering the potential of plug-in electric vehicles in the country due to its relative small size and geography, the Dutch government set a target of 15,000 to 20,000 electric vehicles with three or more wheels on the roads in 2015; 200,000 vehicles in 2020; and 1 million vehicles in 2025.
Considering the potential of plug-in electric vehicles in the country due to its relative small size and geography, the Dutch government set a target of 15,000 to 20,000 electric vehicles with three or more wheels on the roads in 2015; 200,000 vehicles in 2020; and 1 million vehicles in 2025.[ The first government target was achieved in 2013, two years earlier, thanks to the sales peak that occurred at the end of 2013. According to official figures, 30,086 plug-in electric vehicles with three or more wheels have been registered in the country through 31 December 2013.][ ''See under the heading "31-12-2013" for total registrations figures at the end of December 2013.'']
Initially, the Dutch government set incentives such as the total exemption of the registration fee and road taxes, which resulted in savings of approximately for private car owners over four years,Ministry of Infrastructure and the Environment
, type = Department
, logo = Ministerie van Infrastructuur en Waterstaat Logo.png
, logo_width = 250x250px
, logo_alt = Logo of the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management
, image = Rijksgeb ...
a subsidy on the purchase of all-electric taxis or delivery vans. This subsidy increases to per vehicle in Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
, Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"Ne ...
, The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
, Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the fourth-largest city and a municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the province of Utrecht. It is located in the eastern corner of the Randstad conurbation, in the very centre of mainland Net ...
, and Arnhem-Nijmegen metropolitan area. An additional subsidy is offered by several local government for the purchase of full electric taxis and vans, in Amsterdam and in Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
and Tilburg
Tilburg () is a city and municipality in the Netherlands, in the southern province of North Brabant. With a population of 222,601 (1 July 2021), it is the second-largest city or municipality in North Brabant after Eindhoven and the seventh-larg ...
.[ ''See Financial stimulation, pp. 8.''][
] In Amsterdam EV owners also have access to parking spaces reserved for battery electric vehicles, so they avoid the current wait for a parking place in Amsterdam, which can reach up to 10 years in some parts of the city.
In Amsterdam EV owners also have access to parking spaces reserved for battery electric vehicles, so they avoid the current wait for a parking place in Amsterdam, which can reach up to 10 years in some parts of the city.[ EV owners in the city of Rotterdam are entitled to one year of free parking in downtown and enjoy subsidies of up to if they install a home charger using green electricity.][
Other factors contributing to the rapid adoption of plug-in electric vehicles are the relative small size of the country, which reduces ]range anxiety
Range anxiety is the driver's fear that a vehicle has insufficient energy storage (fuel and/or battery capacity) to cover the road distance needed to reach its intended destination, and would thus strand the vehicle's occupants mid-way. The term, ...
(the Netherlands stretches about east to west); a long tradition of environmental activism; high gasoline prices ( per gallon as of January 2013), which make the cost of running a car on electricity five times cheaper; and also some EV leasing programs provide free or discounted gasoline-powered vehicles for those who want to take a vacation driving long distances. With all of these incentives and tax breaks, plug-in electric cars have similar driving costs to conventional cars.[
Initially, sales of plug-in electric car were lower than expected, and during 2012 the segment captured a market share of less than 1% of new car sales in the country.]
Norway
 The Parliament of Norway set the goal to reach 50,000 zero emission vehicles by 2018. Among the existing incentives, all-electric cars are exempt in Norway from all non-recurring vehicle fees, including purchase taxes, which are extremely high for ordinary cars, and 25% VAT on purchase, together making electric car purchase price competitive with conventional cars.
The Parliament of Norway set the goal to reach 50,000 zero emission vehicles by 2018. Among the existing incentives, all-electric cars are exempt in Norway from all non-recurring vehicle fees, including purchase taxes, which are extremely high for ordinary cars, and 25% VAT on purchase, together making electric car purchase price competitive with conventional cars.[ As an example, by early 2013 the price of the top selling Nissan Leaf was 240,690 kroner (around ) while the purchase price of the 1.3-lt ]Volkswagen Golf
The Volkswagen Golf () is a compact car/small family car (C-segment) produced by the German automotive manufacturer Volkswagen since 1974, marketed worldwide across eight generations, in various body configurations and under various nameplates ...
was 238,000 Krone (about ).road tax
Road tax, known by various names around the world, is a tax which has to be paid on, or included with, a motorised vehicle to use it on a public road.
National implementations Australia
All states and territories require an annual vehicle registra ...
, all public parking fees, and toll payments, as well as being able to use bus lanes. In September 2013 the Norwegian Parliament approved, as part of the revised 2014 budget, an exemption from the 25% VAT for leasing electric vehicles effective on 1 January 2014. However, , the exemption has not gone into effect because the
In September 2013 the Norwegian Parliament approved, as part of the revised 2014 budget, an exemption from the 25% VAT for leasing electric vehicles effective on 1 January 2014. However, , the exemption has not gone into effect because the Minister of Finance
A finance minister is an executive or cabinet position in charge of one or more of government finances, economic policy and financial regulation.
A finance minister's portfolio has a large variety of names around the world, such as "treasury", " ...
decided to defer the measure, pending a formal consultation with the EFTA Surveillance Authority
The EFTA Surveillance Authority (ESA) monitors compliance with the Agreement on the European Economic Area (EEA) in Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway; the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) States which are a part of the EEA Agreement, allowin ...
(ESA) to ensure that the VAT exemption for leasing was not in violation of the European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade As ...
Agreement. The government's loss of revenue due to the still not implemented leasing exemption is estimated at 47 million krone (around ) per year.[
] The target of 50,000 electric cars on Norwegian roads was reached on 20 April 2015, more than two years earlier than expected.
The target of 50,000 electric cars on Norwegian roads was reached on 20 April 2015, more than two years earlier than expected.
Phase out of incentives
In May 2015 the Government decided to keep the existing incentives through 2017, and the political parties in Parliament agreed to reduced and phase out some of the incentives. Beginning in January 2018, electric car owners will be required to pay half of the yearly road license fee and the full rate as of 2020. The value-added tax (VAT) exemption for electric cars will end in 2018, but replaced by a new scheme, which may be subjected to a ceiling that could be reduced as technology develops. The agreement also gave local authorities the right to decide whether electric cars can park for free and use public transport lanes.Trondheim
Trondheim ( , , ; sma, Tråante), historically Kaupangen, Nidaros and Trondhjem (), is a city and municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. As of 2020, it had a population of 205,332, was the third most populous municipality in Norway, and ...
and Tønsberg
Tønsberg , historically Tunsberg, is a city and municipality in Vestfold og Telemark county, eastern Norway, located around south-southwest of Oslo on the western coast of the Oslofjord near its mouth onto the Skagerrak. The administrative c ...
decided to introduce full payment for EVs from 2017; the cities of Bodø and Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the ...
will introduce payment for parking in downtown but exempted parking outside the city's center; and the cities of Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population ...
, Mandal and Drammen
Drammen () is a city and municipality in Viken, Norway. The port and river city of Drammen is centrally located in the south-eastern and most populated part of Norway. Drammen municipality also includes smaller towns and villages such as Konne ...
decided to keep free parking for zero-emission vehicles.
Portugal
The Portuguese Government launched in early 2008 a national Programme for Electric Mobility called Mobi.E.
Mobi.E is deploying a national electric mobility system. The system was designed to be scalable and used in multiple geographies, overcoming the current situation of lack of communication among the different electric mobility experiences that are being deployed in Europe. By the first semester of 2011, a wide public network of 1 300 normal and 50 fast charging points will be fully implemented in the main 25 cities of the country.
EVs are fully exempt from both the Vehicle Tax due upon purchase (Imposto Sobre Veículos) and the annual Circulation Tax (Imposto Único de Circulação). Personal income tax provides an allowance of EUR 803 upon the purchase of EVs. EVs are exempt from the 5%-10% company car tax rates which are part of the Corporation Income Tax. The Budget Law provides for an increase of the depreciation costs related to the purchase of EVs for the purpose of Corporation Income Tax.
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
established a government subsidy of €5,000 for the first 5,000 new electric cars sold in the country. In addition, there is in place a €1,500 incentive if the consumer turns in a used car as part of the down payment for the new electric car.
Romania
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
offers a government grant of up to 25% of the price (up to a maximum of ) for the purchase of a new electric car.[ For hybrid vehicles, with or without plug-in capabilities, a €550 grant is offered, plus an additional €160 grant for hybrid vehicles emitting under 100g/km of . Combined with the cash-for-clunkers program, the total grant is up to €2200.
Electric and hybrid vehicles are exempt from the environmental tax, which also acts as a registration tax.
From March 2015, electric vehicles are also exempt from the annual tax, while hybrid vehicles have a 95% reduction.
In 2016, the "Rabla Plus" program offered a government grant of for the purchase of a new electric car. In 2017, the "Rabla Plus" grant program increased to EUR 10,000 for the purchase of a pure electric vehicle (BEV). Furthermore, car owners will receive an additional if they end their registration of a car older than eight years.
]
Spain
Spain's government aimed to have 1 million electric cars on the roads by 2014 as part of a plan to cut energy consumption and dependence on expensive imports, Industry Minister Miguel Sebastián said.Aragón
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises th ...
, Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
, Baleares, Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a Madrid metropolitan area, metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the Largest cities of the Europ ...
, Navarra
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
, Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
, Castilla-La Mancha, Murcia
Murcia (, , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the seventh largest city in the country. It has a population of 460,349 inhabitants in 2021 (about one ...
, Castilla y León
Castile, Castille or Castilla may refer to:
Places Spain
*Castile (historical region), a vaguely defined historical region of Spain covering most of Castile and León, all of the Community of Madrid and most of Castilla–La Mancha
*Kingdom of ...
electric vehicles are eligible to a €6,000 tax incentive and hybrids to €2,000.[
]
Sweden
In September 2011 the Swedish government approved a program, effective starting in January 2012, to provide a subsidy of per car for the purchase of electric cars and other "super green cars" with ultra-low carbon emissions (below 50 grams of carbon dioxide per km). There is also an exemption from the annual circulation tax for the first five years from the date of their first registration that benefits owners of electric vehicles with an energy consumption of 37 kWh per 100 km or less, and hybrid vehicles with emissions of 120 g/km
Emission standards are the legal requirements governing air pollutants released into the atmosphere. Emission standards set quantitative limits on the permissible amount of specific air pollutants that may be released from specific sources o ...
or less. In addition, for both electric and hybrid vehicles, the taxable value of the car for the purposes of calculating the benefit in kind of a company car under personal income tax is reduced by 40% compared with the corresponding or comparable gasoline- or diesel-powered car. The reduction of the taxable value has a cap of per year.[
, a total of 5,028 new "super clean cars" had been registered in the country since January 2012, and because the government allocated funds for a total of 5,000 super clean cars between 2012 and 2014, the fund has been exhausted.][ ''A total of 5,209 super clean cars have been registered in Sweden since 2011. Super clean cars are those with carbon dioxide emissions of up to 50 g/km. ''][ ''A total of 4,656 super clean cars and 282 all-electric vans were registered in Sweden in 2014. Super clean cars are those with carbon dioxide emissions of up to 50 g/km (two Porsche plug-in models, the Panamera S E-Hybrid and the 918 Spyder are not accounted as super clean cars, instead they are accounted with conventional hybrids). In 2011 there were 181 plug-in electric vehicles registered, 928 in 2012, 1,546 in 2013 and 4,656 super clean cars were registered during 2014. Since the introduction of the super clean car rebate in January 2012 until December 2014, a total of 7,130 super clean cars have been registered.'']
The Government raised the appropriation for the super green car rebate by for 2015 and by for 2016. Beginning in 2016, only zero emissions cars are entitled to receive the full premium, while other super green cars, plug-in hybrids, receive half premium. The exemption for the first five years of ownership from the annual circulation tax is still in place.[ In 2016, in order to promote the introduction of electricity-powered buses in the market, the Government planned to allocate for 2016 and per year between 2017 and 2019 to introduce an electric bus premium.][
The new bonus-malus system, starting 1 July 2018, will offer electric car buyers a bonus of 60 000 SEK.
The bonus of SEK 70,000 offered to electric car buyers was abolished in November 2022 by the new right-wing government.
]
Switzerland
Switzerland has a car import tax which is 4% of the purchase price (before adding the VAT) which is waived for electric cars.Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
(GL), Solothurn
Solothurn ( , ; french: Soleure ; it, Soletta ; rm, ) is a town, a municipality, and the capital of the canton of Solothurn in Switzerland. It is located in the north-west of Switzerland on the banks of the Aare and on the foot of the Weissens ...
(SO), Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
(TI) and Zurich (ZH) are completely waiving the tax for plug-in electric vehicles.
;Calculation example for Zurich
Based on a usual car with the following specification:
* Engine: 2 L
* Total weight: 1800 kg
* Energy efficiency: C
* Year: 2013
The resulting tax to be paid per year will be . Hence when calculating with a life expectancy of 10 years, the car owner in this example might save around when buying a plug-in electric car.
However, since the tax on fossil fuels are relatively high in all European countries, including Switzerland, there is still an indirect, but quite strong incentive for car buyers to decide for energy efficient vehicles.
Based on the following examples:
* Fuel economy: unleaded
* Driving habits: per year
* Fuel tax: per liter ( per gallon)
* Carbon tax (since January 1, 2014): per liter ( per gallon)
The resulting taxes on the burned fuels will be around per year, which results in over the car's 10-year lifetime.
United Kingdom
Plug-in Car Grant
The Plug-in Car Grant (PiCG) started on 1 January 2011 and is available across the UK. The program reduces the up-front cost of eligible cars by providing a 25% grant towards the cost of new plug-in cars capped at ().[
] The government announced in April 2014 that funding for the full grant of up to will remain in place until either 50,000 grants have been issued or 2017, whichever is first.
The government announced in April 2014 that funding for the full grant of up to will remain in place until either 50,000 grants have been issued or 2017, whichever is first.[ As forecasts estimated that the scheme will reach its 50,000 limit around November 2015, the government announced in August 2015 that the Plug-in Car Grant will continue until at least February 2016 for all plug-in cars with emissions of 75 g/km of under.][
* Vehicle type: Only ultra-low emission cars are eligible ( vehicle category M1). Motorbikes, quadricycles and vans are not covered.
* Carbon dioxide exhaust emissions: Vehicles must emit equal or less than 75 grams of carbon dioxide () per kilometre driven.
* Range: Electric vehicles (EVs) must be able to travel a minimum of between charges. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) must have a minimum all-electric range of .
* Minimum top speed: Vehicles must be able to reach a speed of or more.
* Warranty: Vehicles must have a 3-year or vehicle warranty (guarantee) and a 3-year battery and electric drive train warranty, with the option of extending the battery warranty for an extra 2 years('drive train' means the parts that send power from the engine to the wheels. These include the clutch, transmission (gear box), drive shafts, U-joints and differential).
* Battery performance: Vehicles must have either a minimum 5-year warranty on the battery and electric drive train as standard, or extra evidence of battery performance to show reasonable performance after 3 years of use
* Electrical safety: Vehicles must comply with certain regulations (UN-ECE Reg 100.01) that show that they are electrically safe.
* Crash safety: To make sure cars will be safe in a crash, they must either have: EC whole vehicle type approval (EC WVTA, not small series) or evidence that the car has appropriate levels of safety as judged by international standards.
In February 2015 the government announced that to take account of rapidly developing technology, and the growing range of ULEVs on the British market, the criteria for the plug-in car grant was updated and from April 2015, eligible ultra-low emission vehicles (ULEVs) must meet criteria in one of the following categories depending on emission levels and zero-emission-capable mileage, with a technology neutral approach, which means that hydrogen fuel cell cars are also eligible for the grant:][
* Category 1: emissions of less than 50g/km and a zero emission range of at least .
* Category 2: emissions of less than 50g/km and a zero emission range between .
* Category 3: emissions of 50–75g/km and a zero emission range of at least .
In December 2015, the Department for Transport (DfT) announced that Plug-in car grant was extended until March 2018 to encourage more than 100,000 UK motorists to buy cleaner vehicles. A total funding of (~) is available for the extension. To reflect the changes in the British market, the criteria for the Plug-in Car Grant was updated and the maximum grant drops from (~) to (~). For the extension, the amount of the grant is linked in directly with the Office for Low Emission Vehicles three vehicle categories issued in April 2015. The eligible ultra-low emission vehicles (ULEVs) must meet criteria in one of three categories depending on emission levels ( emissions bands between 50 and 75g/km) and zero-emission-capable mileage (minimum of ), with a technology neutral approach, which means that hydrogen fuel cell cars are eligible for the grant.][
A price cap is in place, with all Category 1 plug-in vehicles eligible for the full grant no matter what their purchase price, while Category 2 and 3 models with a list price of more than (~) are eligible for the grant. Vehicles with a zero-emission range of at least (category 1), including hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, get a full (~), but plug-in hybrids (categories 2 and 3) costing under (~) receive (~).][ The grant scheme will come under review when a cumulative total of 40,000 Category 1 claims, and 45,000 Category 2 and 3 combined sales have been made. Both these totals will include cars sold before March 2016.][
, the following 31 cars available in the British market are eligible for the grant according to their category:]BMW i3
The BMW i3 is a B-segment, high-roof hatchback manufactured and marketed by BMW with an electric powertrain using rear-wheel drive via a single-speed transmission and an underfloor Lithium-ion battery, lithium-ion battery pack and an optional R ...
, BYD e6
The BYD e6 is an all-electric compact crossover/compact MPV manufactured by BYD from 2009. Field testing for the first generation model began in China in May 2010 with 40 units operating as taxis in the city of Shenzhen. Sales to the general pub ...
, Citroen C-Zero, Ford Focus Electric
The Ford Focus Electric is a 5-door hatchback electric car that was produced by Ford. The Focus Electric is Ford's second production all-electric vehicle (the first being the Ford Ranger EV), and was made from December 2011to May 2018.
The Fo ...
, Hyundai Ioniq Electric, Kia Soul EV
The Kia Soul EV (also known as Kia e-Soul) is an all-electric subcompact crossover SUV manufactured by Kia and based on the Kia Soul. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) official range for the 2020 Kia Soul EV is 243 miles (391 km ...
, Mahindra e2o, Mercedes-Benz B-Class Electric Drive
The Mercedes-Benz B-Class is a subcompact executive car manufactured and marketed by Mercedes-Benz since 2005. Based on the A-Class with larger dimensions, the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) classifies it as a small MPV.
As ...
, Nissan e-NV200 5- and 7-seater Combi, Nissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
, Peugeot iOn, Renault Fluence Z.E.
The Renault Fluence Z.E. is an electric version of the Renault Fluence compact sedan, part of the Renault Z.E. program of battery electric vehicles. It was unveiled by Renault at the 2009 Frankfurt Motor Show. The Fluence Z.E. is outfitted with a ...
, Renault Zoe, Smart Fortwo electric drive, Tesla Model S, Toyota Mirai, Volkswagen e-Golf
The Volkswagen Golf (Mk7) is a small family car (C-segment) produced by German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, as the seventh generation of the Golf and the successor to the Golf Mk6. It was introduced in Berlin on 4 September 2012, befor ...
, and Volkswagen e-Up!
The Volkswagen Up (stylized as Volkswagen up!) is a city car, part of the Volkswagen Group New Small Family (NSF) series of models, unveiled at the 2011 International Motor Show Germany (IAA). Production of the Up started in December 2011 at th ...
.
;Eligible category 2 vehicles
Audi A3 e-tron
The Audi A3 is a subcompact executive/small family car (C-segment) manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi AG since September 1996, currently in its fourth generation.
The first two generations of the Audi A3 were based on the ...
(MY 2016 only), BMW 225xe, BMW 330e, Kia Optima PHEV, Mercedes-Benz C350 e, Mitsubishi Outlander P-HEV
The is a mid-size
crossover SUV manufactured by Japanese
automaker Mitsubishi Motors. It was originally known as the when it was introduced in Japan in 2001.
The original Airtrek name was chosen to "describe the vehicle's ability to transpo ...
(except GX3h 4Work), Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid
The Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid (often abbreviated as the Prius and known as the Prius Prime in North America, South Korea, and New Zealand) is a plug-in hybrid liftback manufactured by Toyota. The first-generation model was produced from 2012 t ...
, Vauxhall Ampera Ampera may refer to:
Indonesia
Ampera is generally an abbreviation for ''Amanat Penderitaan Rakyat'' andate of People's Suffering a now-rarely used colloquial name for the preamble of the Constitution of Indonesia.
* Ampera Bridge, a bridge in ...
, Volkswagen Golf GTE, Volkswagen Passat GTE, Volvo V60 Plug-in Hybrid
The Volvo V60 is a compact wagon produced by Volvo Cars related to the S60. The vehicle was first released in autumn 2010, facelifted in 2014, and is in its second generation since 2018.
The second generation V60 was launched in 2018 based on t ...
(D5 and D6 Twin Engine), and Volvo XC90 T8 Twin Engine Momentum.[
;Ineligible vehicles
Category 2 or 3 vehicles with a recommended retail price over £60,000 aren't eligible for a grant. This includes: ]BMW i8
The BMW i8 is a plug-in hybrid sports car developed by BMW. The i8 was part of BMW's electrified fleet and was marketed under the BMW i sub-brand. The production version of the BMW i8 was unveiled at the 2013 Frankfurt Motor Show and was rel ...
(category 2), Mercedes-Benz S500 Plug-in Hybrid (category 3), and Porsche Panamera S E-Hybrid
The Porsche Panamera is a mid/ full-sized luxury car (E-segment/ F-segment in Europe) manufactured and marketed by German automobile manufacturer Porsche across two generations using a front-engine, rear or all-wheel drive configuration.
Po ...
(category 3).[
The Tesla Roadster was not included in the government's list of eligible vehicles for the plug-in electric car grant. Tesla Motors stated that the company applied for the scheme, but did not complete its application.][
]
Plug-in Van Grant
 The Plug-In Van Grant (PiVG) began in February 2012. Van-buyers can receive 20% – up to – off the cost of a plug-in van. To be eligible for the scheme, vans have to meet performance criteria to ensure safety, range, and ultra-low tailpipe emissions. Consumers, both business and private will receive the discount at the point of purchase.
The Plug-In Van Grant (PiVG) began in February 2012. Van-buyers can receive 20% – up to – off the cost of a plug-in van. To be eligible for the scheme, vans have to meet performance criteria to ensure safety, range, and ultra-low tailpipe emissions. Consumers, both business and private will receive the discount at the point of purchase.[ The Plug-In Van Grant scheme was extended in October 2016 to make electric trucks above 3.5 tonnes eligible for grants of up to , when businesses switch their large trucks to an electric vehicle. The government also announced their commitment for an additional to the scheme so that all vans and trucks meeting the eligibility requirements can benefit from the grant scheme.][
The eligibility criteria for vans with a gross weight of 3.5 tonnes or less ( N1 van) are:][ '', 637 claims have been made through the plug-in van grant program.'']
* Vehicle type: only new N1 vans are eligible. This includes pre-registration conversions (normal, internal combustion engine vans that were converted to battery or hybrid versions by specialist converters before the car's first registration).
* Carbon dioxide exhaust emissions: vehicles must emit less than 75 grams of carbon dioxide () per kilometre driven.
* Range: eligible fully electric vans must be able to travel a minimum of between charges. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) must have a minimum electric range of .
* Minimum top speed: vehicles must be able to reach a speed of or more.
* Warranty: Vehicles must have a 3-year or vehicle warranty (guarantee) and a 3-year battery and electric drive train warranty, with the option of extending the battery warranty for an extra 2 years
* Battery performance: vehicles must have either a minimum 5-year warranty on the battery and electric drive train as standard
or extra evidence of battery performance to show reasonable performance after 3 years of use
* Electrical safety: vehicles must comply with certain regulations (UN-ECE Reg 100.00) that show that they are electrically safe.
* Crash safety To make sure cars will be safe in a crash, they must either have EC whole vehicle type approval (EC WVTA, not small series) or evidence that the car has appropriate levels of safety as judged by international standards.
, the number of claims made through the Plug-in Van Grant scheme totaled 2,938 units since the launch of the programme in 2012, up from 1,906 made by the end of December 2015.[ ''See graph with PIVG cumulative claims and claims by quarter''.] the following nine vans are eligible for the grant: BD Otomotive eTraffic, BD Otomotiv eDucato, Citroën Berlingo
The Citroën Berlingo and Peugeot Partner are a range of multi-purpose vehicles produced by the PSA Group and later by Stellantis. They are sold both as panel vans for use as commercial vehicles and as a passenger variant with rear seats and w ...
, Mercedes-Benz Vito E-Cell, Mitsubishi Outlander GX3h 4Work, Nissan e-NV200, Peugeot ePartner, Renault Kangoo Z.E., and Smith Electric Edison.[
]
Number of beneficiaries
The number of eligible registered plug-in electric vehicles passed the 25,000 unit milestone in January 2015.plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) to store electrical power within its onboard rechargeable battery packs, which then ...
s have been registered in the UK up until December 2016, including over 85,000 plug-in hybrids and all-electric cars, and about 4,000 plug-in commercial vans. Not all vehicles were eligible for the grant schemes.
Plugged-in Places
On 19 November 2009, Andrew Adonis
Andrew Adonis, Baron Adonis, (born Andreas Adonis; 22 February 1963) is a British Labour Party (UK), Labour Party politician and journalist who served in HM Government for five years in the Third Blair ministry, Blair ministry and the Brown mi ...
, the Secretary of State for Transport, announced a scheme called "Plugged-in-Places", making available £30 million to be shared between three and six cities to investigate further the viability of providing power supply for electric vehicles, and encouraging local government and business to participate and bid for funds.
The UK government is supporting the "Plugged-In Places" program to install vehicle recharging points across the UK. The scheme offers match-funding to consortia of businesses and public sector partners to support the installation of EV recharging infrastructure in lead places across the UK.
London congestion charge
All-electric vehicles (BEVs) and eligible plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) qualify for a 100% discount from the London congestion charge. A plug-in electric drive vehicle qualifies if the vehicle is registered with the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency
The Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA; cy, Asiantaeth Trwyddedu Gyrwyr a Cherbydau) is the organisation of the UK government responsible for maintaining a database of drivers in Great Britain and a database of vehicles for the entire ...
(DVLA) and has a fuel type of 'electric', or alternatively, if the vehicle is a 'plug-in hybrid' and is on the Government's list of PHEVs eligible for the OLEV grant. , approved PHEVs include all extended-range cars such as the BMW i3 with range extender and Vauxhall Ampera Ampera may refer to:
Indonesia
Ampera is generally an abbreviation for ''Amanat Penderitaan Rakyat'' andate of People's Suffering a now-rarely used colloquial name for the preamble of the Constitution of Indonesia.
* Ampera Bridge, a bridge in ...
, and plug-in hybrids that emit 75g/km or less of and that meet the Euro 5
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards for pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and EEA member states and the UK, and ships in EU waters. The standards are defined in a seri ...
standard for air quality, such as the Audi A3 Sportback e-tron, BMW i8
The BMW i8 is a plug-in hybrid sports car developed by BMW. The i8 was part of BMW's electrified fleet and was marketed under the BMW i sub-brand. The production version of the BMW i8 was unveiled at the 2013 Frankfurt Motor Show and was rel ...
, Mitsubishi Outlander P-HEV
The is a mid-size
crossover SUV manufactured by Japanese
automaker Mitsubishi Motors. It was originally known as the when it was introduced in Japan in 2001.
The original Airtrek name was chosen to "describe the vehicle's ability to transpo ...
, and Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid
The Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid (often abbreviated as the Prius and known as the Prius Prime in North America, South Korea, and New Zealand) is a plug-in hybrid liftback manufactured by Toyota. The first-generation model was produced from 2012 t ...
.
The original Greener Vehicle Discount was substituted by the Ultra Low Emission Discount (ULED) scheme that went into effect on 1 July 2013. The ULED introduced more stringent emission standards that limited the free access to the congestion charge zone to any car or van that emits 75g/km or less of CO2 and meets the Euro 5
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards for pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and EEA member states and the UK, and ships in EU waters. The standards are defined in a seri ...
emission standards for air quality. there are no internal combustion
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combust ...
-only vehicles that meet this criteria. The measure is designed to limit the growing number of diesel vehicles on London's roads. Mayor Boris Johnson approved the new scheme in April 2013, after taking into account a number of comments received during the 12-week public consultation that took place. About 20,000 owners of vehicles registered for the Greener Vehicle Discount by June 2013 were granted a three-year sunset period (until 24 June 2016) before they have to pay the full congestion charge.
Effective from 8 April 2019, the ULED scheme will be replaced with the Cleaner Vehicle Discount. This means that from April 2019, only vehicles which are Euro 6, emit up to 75g/km of and have a minimum 20 mile zero emission range, will qualify for the discount. A further phase from October 2021 will mean that only zero-emission vehicle
A zero-emission vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that does not emit exhaust gas or other pollutants from the onboard source of power. The California definition also adds that this includes under any and all possible operational modes and conditions ...
s ( pure electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles) will qualify for the discount, which will be phased out completely from December 2025.
North America
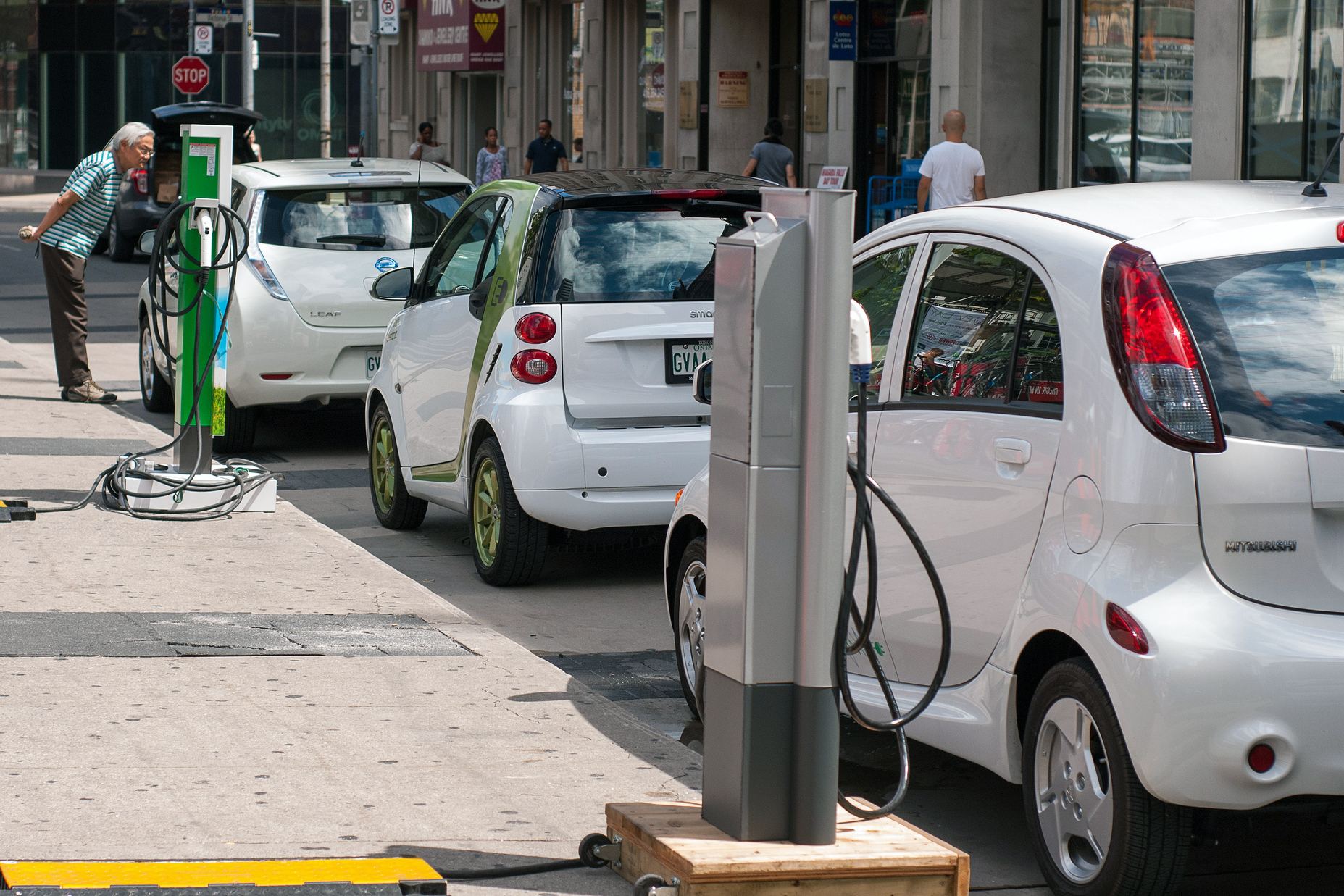

Canada
The Government of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown ...
introduced a federal Incentive for Zero Emission Vehicles (iZEV) program on May 1, 2019. Under iZEV, the purchaser or lessee is entitled to a rebate of up to on the after-tax cost of an eligible new electric- or hydrogen-powered vehicle in addition to any provincial incentive programs. The amount of the rebate is determined by Transport Canada
Transport Canada (french: Transports Canada) is the department within the Government of Canada responsible for developing regulations, policies and services of road, rail, marine and air transportation in Canada. It is part of the Transporta ...
based on the vehicle's battery capacity and electric range, and all eligible vehicles must have a list price
The list price, also known as the manufacturer's suggested retail price (MSRP), or the recommended retail price (RRP), or the suggested retail price (SRP) of a product is the price at which its manufacturer notionally recommends that a retailer ...
of or less ( or less if the vehicle seats seven or more passengers).
Simultaneously, the federal government launched a federal Zero-Emission Vehicle Infrastructure Program administered by Natural Resources Canada
Natural Resources Canada (NRCan; french: Ressources naturelles Canada; french: RNCan, label=none)Natural Resources Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Natural Resources (). is the dep ...
. The program provides rebates to businesses and governments for new electric vehicle charging stations in public places, workplaces, multi-family residential
Multifamily residential (also known as multidwelling unit or MDU) is a classification of housing where multiple separate housing units for residential inhabitants are contained within one building or several buildings within one complex. Units ca ...
buildings, and in public transit and delivery fleets.
Ontario
;Former rebate program
The Ontario Ministry of Transportation (MTO) established the Electric Vehicle Incentive Program (EVIP) – later renamed the Electric and Hydrogen Vehicle Incentive Program (EHVIP) – in 2010. To qualify, Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) had to be purchased or leased from a seller in Ontario and owned or leased for at least 12 months. Leased vehicles with 12-month terms received 33% of the incentive, 24-month lease terms received 66%, and lease terms 36 months or longer received the full incentive. Vehicles were required to be on a government-developed list of approved vehicles to qualify, and vehicles with a Manufacturer's Suggested Retail Price (MSRP) of or greater were not eligible for the incentive. Electric vehicles with a battery size of 5 -16 kWh were eligible for incentives from to . Vehicles with a battery size exceeding 16 kWh qualified for to . Vehicles with five or more seats were eligible for an additional . Demonstration vehicles under a specified mileage and used exclusively for test drives at dealerships or leasing companies were also eligible. Applications for incentives were required to be submitted within 3 months of the vehicle's provincial registration. Prior to the cancellation of the program, the Government of Ontario included rebates of up to for electric and hybrid vehicles. The EHVIP was financed by proceeds from Ontario's participation with Quebec and California in the Western Climate Initiative
Western Climate Initiative, Inc. (WCI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit corporation which administers the shared emissions trading market between the American state of California and the Canadian province of Quebec as well as separately administering th ...
(WCI) cap and trade
Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). Carbon emission t ...
program.
The program (and the companion incentive program to encourage private businesses to install charging stations) was cancelled on July 11, 2018, after the government of Premier Doug Ford
Douglas Robert Ford Jr. (born November 20, 1964) is a Canadian politician and businessman who has served as the 26th and current premier of Ontario since June 2018 and leader of the Progressive Conservative (PC) Party since March 2018. He ...
began the withdrawal of Ontario from the WCI. Rebates were still issued if the vehicle had been delivered to the consumer, registered, and plated on or before July 11; or if the vehicle was in the inventory of a dealership on or before July 11 or was ordered directly from the manufacturer before that date, provided that the vehicle was delivered to the consumer, registered, and plated by September 10, 2018.
;Green vehicle plates
 Electric vehicles in Ontario are eligible for special license plates, officially called Green Vehicle License Plates, from the Ministry of Transportation. In addition to a green colour scheme distinct from the province's typical blue and white license plates, these green plates permit BEV and PHEV owners to travel in the province's
Electric vehicles in Ontario are eligible for special license plates, officially called Green Vehicle License Plates, from the Ministry of Transportation. In addition to a green colour scheme distinct from the province's typical blue and white license plates, these green plates permit BEV and PHEV owners to travel in the province's high-occupancy vehicle
A high-occupancy vehicle lane (also known as an HOV lane, carpool lane, diamond lane, 2+ lane, and transit lane or T2 or T3 lanes) is a restricted traffic lane reserved for the exclusive use of vehicles with a driver and one or more passengers, i ...
(HOV) and travel at no cost in the high-occupancy toll
A high-occupancy toll lane (or HOT lane) is a type of traffic lane or roadway that is available to high-occupancy vehicles and other exempt vehicles without charge; other vehicles are required to pay a variable fee that is adjusted in response t ...
(HOT) lanes, regardless of the number of passengers in the vehicle.
Quebec
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
began offering rebates of up to (~ ) beginning on January 1, 2012, for the purchase of new plug-in electric vehicles equipped with a minimum of 4 kWh battery, and new hybrid electric vehicles were eligible for a rebate. All-electric vehicles with high-capacity battery packs were eligible for the full rebate, and lower incentives were set for low-range electric cars and plug-in hybrids. Quebec's government earmarked (~ ) for the program, and the maximum rebate amount was set to be slowly reduced every year until a maximum of in 2015, but the rebates would continue until the fund runs out. There was also a ceiling for the maximum number of eligible vehicles: 10,000 for all-electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids, and 5,000 for conventional hybrids. In November 2013, the provincial government announced its decision to earmark in 2014 an additional (~ ) to fund a three-year extension to the electric-vehicle rebate program. The maximum rebate was kept at , but a graded scale was introduced in order to spread the incentive over 10,000 or more vehicles.
In November 2013, the provincial government announced its decision to earmark in 2014 an additional (~ ) to fund a three-year extension to the electric-vehicle rebate program. The maximum rebate was kept at , but a graded scale was introduced in order to spread the incentive over 10,000 or more vehicles.[
Also in 2013, the provincial government announced it support to deploy 5,000 new charging stations. A total of 500 stations were to be located around various cities and along the province's so-called Electric Circuit route, another 1,000 near government buildings, and 3,500 at various workplaces for employee use. Businesses are eligible for a 75% rebate on installation costs up to for Level 1 or Level 2 charging stations. In addition, a 50% rebate will continue to be offered to individuals for installation of home charging stations, with a maximum of .][ Also the government announced an initiative for the gradual electrification of the provincial government's own vehicle fleet. The goal is to replace vehicles of the provincial government's 34 ministers (cabinet-level officials) with plug-in hybrid or pure electric vehicles by March 2017. The government expects to bring 2,000 plug-in vehicles into the provincial fleet over the same time.][
In October 2016, the ]National Assembly of Quebec
The National Assembly of Quebec (officially in french: link=no, Assemblée nationale du Québec) is the legislative body of the province of Quebec in Canada. Legislators are called MNAs (Members of the National Assembly; french: link=no, déput ...
passed a new zero emission vehicle legislation that obliges any carmaker who sells in the Canadian province more than 4,500 new vehicles per year over a three-year average, to offer their customers a minimum number of plug-in hybrid and all-electric models. Under the new law, 3.5% of the total number of autos sold by carmakers in Quebec have to be zero emissions vehicle
A zero-emission vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that does not emit exhaust gas or other pollutants from the onboard source of power. The California definition also adds that this includes under any and all possible operational modes and conditions ...
s (ZEV) starting in 2018, rising to 15.5% in 2020. A tradable credit system was created for those carmakers not fulfilling their quotas to avoid financial penalties. The quotas will be determined by Quebec's Ministry of Sustainable Development. Quebec became the first Canadian province to pass such legislation, joining ten U.S. states, including California, that have similar ZEV laws. Quebec aims to have 100,000 zero emission vehicles on the road by 2020.[
]
British Columbia
 As of June 22, 2019,
As of June 22, 2019, British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
's Clean Energy Vehicle (CEV) Program, funded by the Government of British Columbia and administered by the New Car Dealers of British Columbia industry group, was renewed with funding for approximately 12,000 vehicles. This program will expire when the current 26.5 million in new funding is depleted. The current levels of incentives for vehicles under CA$55,000 are: for an EV (min 85 km range), for a plug-in hybrid or an extended range vehicle with a smaller battery capacity (less than 85 km range) these amounts may be reduced annually. All vehicles must be new and purchased in BC, each claim is processed by the dealer at the Point of Sale and deducted from the vehicle price after taxes. The previous program that provided funding to cover part of the cost of installing home EV charging equipment has been discontinued.
There is also a separate privately funded "SCRAP-IT" program with incentives for scrapping conventional gas-powered vehicles. Basic incentives range from bus passes to co-op car-share membership credits, or in cash. However, there is also the option of applying for a rebate cheque when buying used EV (min. 15 kWh capacity) and a rebate cheque when buying a new EV (min. 15 kWh capacity). There is a requirement of 6 months of continuous driving insurance on the vehicle being scrapped from the application date backwards. Incentives are limited yearly (in 2019, there were 1,300 new and 200 used incentives). The "SCRAP-IT" rebate program currently brings the combined provincial incentives available to buyers of a qualifying new EV in BC to . There is an MSRP limit of CA$77,000. SCRAP-IT also introduced a home charging station program on October 18, 2018, called ZapBC. This program covers the cost of a Level 2 ChargePoint charging station. Applicants must pay taxes on the charging station and installation costs. An estimate is provided once the application is submitted.
Since 2016, PHEV and BEV owners can apply for a special decal which permits access to high-occupancy vehicle lanes regardless of the number of passengers in the vehicle.
Mexico
Mexico has set a minimum goal of clean energies as part of the electric power generation mix in for the next years (25% in 2018, 30% in 2021 and 35% in 2024) as a strategy to reach Greenhouse Gases (GHG) emission cuts. Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a ra ...
is also regarded as one of the greater cost-benefit potential alternatives to achieve GHG reduction.
Federal
In Mexico, there are several existing incentives regarding Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV) at a federal level. Fiscal incentives for end-consumers include higher daily lease tax deductions per car ($285 versus $200 MXN), higher tax deduction caps per car ($250,000 versus $175,000 MXN), and fiscal credits for up to 30% of investments for charging stations located in public places. Furthermore, PHEVs are exempt of the tax on new vehicles (paid by the manufacturer, assembler or dealer).
Also, the electrical power service contract for residential charging stations can be independent of household consumption under a commercial rate, which can save up to 40% on electricity compared to consolidating billing in the same meter.
Regional
In Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
, Mexico State
The State of Mexico ( es, Estado de México; ), officially just Mexico ( es, México), is one of the 32 federal entities of the United Mexican States. Commonly known as Edomex (from ) to distinguish it from the name of the whole country, it is ...
and Jalisco, PHEVs are exempt from vehicular emission verification.Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
, Durango, Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
, Mexico State
The State of Mexico ( es, Estado de México; ), officially just Mexico ( es, México), is one of the 32 federal entities of the United Mexican States. Commonly known as Edomex (from ) to distinguish it from the name of the whole country, it is ...
, Nayarit
Nayarit (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Nayarit), is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its ...
, Tlaxcala
Tlaxcala (; , ; from nah, Tlaxcallān ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tlaxcala ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tlaxcala), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 60 municipaliti ...
and Querétaro.
Charging station network
As of January 2017, in Mexico there were 700 public access charging stations for PHEVs that are privately owned. The Ministry of Energy A Ministry of Energy or Department of Energy is a government department in some countries that typically oversees the production of fuel and electricity; in the United States, however, it manages nuclear weapons development and conducts energy-rel ...
and the state owned electric power utility, Comision Federal de Electricidad, will destine $25 million MXN to install 100 more charging stations through 2017–2018 in the metropolitan areas of Guadalajara, Monterrey and Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
. As of now, users of the existing network can charge their PHEVs for free, as the cost of electricity is absorbed by the owners of the establishments where the charging stations are located.
United States
Federal government
In his 2011 State of the Union address
The State of the Union Address (sometimes abbreviated to SOTU) is an annual message delivered by the president of the United States to a joint session of the United States Congress near the beginning of each calendar year on the current conditi ...
, President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the ...
set the goal for the U.S. to become the first country to have one million electric vehicles on the road by 2015.[ For this purpose, his administration pledged billion in federal grants to support the development of next-generation electric vehicles and batteries.]truck stop
A truck stop, known as a service station in the United Kingdom, and a travel center by major chains in the United States, is a commercial facility which provides refueling, rest ( parking), and often ready-made food and other services to motor ...
charging station, electric rail
A railway electrification system supplies electric power to Rail transport, railway trains and trams without an on-board Prime mover (locomotive), prime mover or local fuel supply.
Electric railways use either electric locomotives (hauling pa ...
, and training for technicians to build and repair electric vehicles ( greencollar jobs).
Considering that actual plug-in car sales were lower than initially expected, as of early 2013, several industry observers have concluded that Obama's one million goal was unattainable.[ ''See other figures in graphs.''] According to a July 2012 study by Pike Research, cumulative sales would reach the one million goal set by the Obama Administration only in 2018,[ ]Secretary of Energy
The United States secretary of energy is the head of the United States Department of Energy, a member of the Cabinet of the United States, and fifteenth in the presidential line of succession. The position was created on October 1, 1977, when Pr ...
, Ernest Moniz
Ernest Jeffrey Moniz, GCIH (; born December 22, 1944) is an American nuclear physicist and former government official. From May 2013 to January 2017, he served as the 13th United States secretary of Energy in the Obama Administration. Prior to ...
, said in January 2016 that the one million goal may not be reached until 2020. According to the Secretary purchases have fallen well below President Barack Obama's goal due to low gasoline prices, which had a negative impact on sales. Also improvements in battery technology are required as lowering battery costs is "absolutely critical" to boost electric vehicle sales.
In March 2018, a group of America's largest electric utilities sided with U.S. automakers and asked Congress to preserve the tax credit in order to support the continued growth of sales of electric vehicles. Currently, there are hundreds of thousands of electric vehicles on the road. However, the auto industry is approaching a point at which the tax incentives will begin to expire. According to ''Daily Energy Insider'', "The utilities' efforts occur at a time when growth in electric sales is sluggish and electric companies see a possible opportunity to apply the latest battery technology to help serve their customers."
= New plug-in electric vehicles
=
The Energy Improvement and Extension Act of 2008
Public Law 110-343 () is a US Act of Congress signed into law by U.S. President George W. Bush, which was designed to mitigate the growing financial crisis of the late-2000s by giving relief to so-called "Troubled Assets."
Three divisions ...
granted tax credits for new qualified plug-in electric drive motor vehicles.American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) (), nicknamed the Recovery Act, was a stimulus package enacted by the 111th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama in February 2009. Developed in response to the Gr ...
(ARRA) also authorized federal tax credits
A tax credit is a tax incentive which allows certain taxpayers to subtract the amount of the credit they have accrued from the total they owe the state. It may also be a credit granted in recognition of taxes already paid or a form of state "disc ...
for converted plug-ins, though the credit is lower than for new PEVs.Nissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
electric vehicle and the Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid manufactured by General Motors, also marketed in rebadged variants as the Holden Volt in Australia and New Zealand and the Buick Velite 5 in China, and with a different fascia as the Vauxhall Ampera in th ...
plug-in hybrid, launched in December 2010, are eligible for the maximum $7,500 tax credit.Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid
The Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid (often abbreviated as the Prius and known as the Prius Prime in North America, South Korea, and New Zealand) is a plug-in hybrid liftback manufactured by Toyota. The first-generation model was produced from 2012 t ...
, released in January 2012, was eligible for a $2,500 tax credit due to its smaller battery capacity of 5.2 kWh. All Tesla cars and Chevrolet Bolt
The Chevrolet Bolt or Chevrolet Bolt EV is a battery electric subcompact hatchback produced by General Motors under the Chevrolet marque. It was developed and manufactured in partnership with LG Corporation. A rebadged European variant was ...
s were eligible for the $7,500 tax credit.
As granted by the 2009 ARRA, electric vehicles produced after 2010 are eligible for an IRS tax credit from $2,500 to $7,500. There are some limitations and rules however that go along with the applied tax credit from electric vehicles. When an electric vehicle is leased, the tax credit is held by the manufacturer offering the lease, not by the lessee. Other restrictions that affect PEV tax credit include limitation of credit for electric vehicles used in reselling purposes, terms requiring the vehicle to remain in the United States, and production by qualified sellers.
;Phaseout
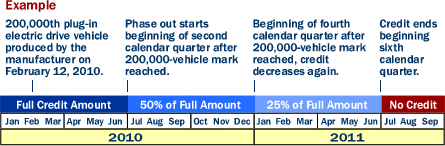 These granted tax credits on PEV vehicles will phase out once 200,000 plug-in vehicles are sold by each manufacturer in the U.S. During this phase out period after 200,000 plug-in car sales, qualified producers will experience a drop in a tax credit of $7,500 to $3,750 for the next 6 months followed by a drop to $1,875 for another 6 months until the credit is run out completely.
The qualified plug-in electric vehicle credit phases out for a PEV manufacturer over the one-year period beginning with the second calendar quarter after the calendar quarter in which at least 200,000 qualifying vehicles from that manufacturer have been sold for use in the U.S. Cumulative sales started counting sales after December 31, 2009. After reaching the cap, qualifying PEVs for one quarter still earn the full credit, the second quarter after that quarter PEVS are eligible for 50% of the credit for six months, then 25% of the credit for another six months and finally the credit is phased out.
These granted tax credits on PEV vehicles will phase out once 200,000 plug-in vehicles are sold by each manufacturer in the U.S. During this phase out period after 200,000 plug-in car sales, qualified producers will experience a drop in a tax credit of $7,500 to $3,750 for the next 6 months followed by a drop to $1,875 for another 6 months until the credit is run out completely.
The qualified plug-in electric vehicle credit phases out for a PEV manufacturer over the one-year period beginning with the second calendar quarter after the calendar quarter in which at least 200,000 qualifying vehicles from that manufacturer have been sold for use in the U.S. Cumulative sales started counting sales after December 31, 2009. After reaching the cap, qualifying PEVs for one quarter still earn the full credit, the second quarter after that quarter PEVS are eligible for 50% of the credit for six months, then 25% of the credit for another six months and finally the credit is phased out.University of California, Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a public land-grant research university near Davis, California. Named a Public Ivy, it is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University of California system. The inst ...
found that the federal tax credit was the reason behind more than 30% of the plug-in electric sales. The impact of the federal tax incentive is higher among owners of the Nissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
, with up to 49% of sales attributable to the federal incentive. The study, based on a stated preference survey of more than 2,882 plug-in vehicle owners in 11 states, also found that the federal tax credit shifts buyers from internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal c ...
vehicles to plug-in vehicles and advances the purchase timing of new vehicles by a year or more.
= Plug-in conversion kits
=
 The 2009 ARRA provided a tax credit for plug-in electric drive conversion kits. The credit is equal to 10% of the cost of converting a vehicle to a qualified plug-in electric vehicle and in service after February 17, 2009. The maximum amount of the credit is $4,000. The credit does not apply to conversions made after December 31, 2011.
The 2009 ARRA provided a tax credit for plug-in electric drive conversion kits. The credit is equal to 10% of the cost of converting a vehicle to a qualified plug-in electric vehicle and in service after February 17, 2009. The maximum amount of the credit is $4,000. The credit does not apply to conversions made after December 31, 2011.
= Charging equipment
=
Through 2010, there was a federal tax credit equal to 50% of the cost to buy and install a home-based charging station with a maximum credit of for each station. Businesses qualified for tax credits up to $50,000 for larger installations.
= New proposals
=
 Two separate initiatives were pursued in 2011 to transform the tax credit into an instant cash rebate; these did not pass. The objective of both initiatives was to make new qualifying
Two separate initiatives were pursued in 2011 to transform the tax credit into an instant cash rebate; these did not pass. The objective of both initiatives was to make new qualifying plug-in electric car
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) to store electrical power within its onboard rechargeable battery packs, which th ...
s more accessible to buyers by making the incentive more effective. The rebate would have been available at the point of sale allowing consumers to avoid a wait of up to a year to apply the tax credit against income tax returns.Debbie Stabenow
Deborah Ann Stabenow ( ; née Greer, born April 29, 1950) is an American politician serving as the senior United States senator from Michigan, a seat she has held since 2001. A member of the Democratic Party, she became the state's first female ...
who reintroduced the "Charging America Forward Act." This bill was introduced in August 2010 but was not voted by the full Senate.[ The bill would have turned the tax credit into a rebate worth up to for plug-in electric vehicles and also would have provided businesses with a tax credit for purchasing medium or heavy duty plug-in hybrid trucks. The other initiative was from the Obama Administration and was submitted in the FY2012 Budget as a provision to transform the existing credit into a rebate that would have been claimable by dealers and passed along to the consumers, this was not included in the Budget.][
Another change plug-in tax credit was proposed by Senator Carl Levin and Representative ]Sander Levin
Sander Martin Levin (born September 6, 1931) is an American politician who served in the United States House of Representatives from 1983 to 2019, representing (numbered as the from 1983 to 1993 and as the from 1993 to 2013). Levin, a member ...
who proposed to raise the existing cap on the number of plug-in vehicles eligible for the tax credit. The proposal would have raised that limit from the existing 200,000 PEVs per manufacturer to 500,000 units, this was not passed.[
In March 2014 the Obama Administration included a provision in the FY2015 Budget to increase the maximum tax credit for plug-in electric vehicles and other advanced vehicles to . However, the new maximum tax credit would not apply to luxury vehicles with a sales price of over , which would be capped at . The proposal sought to remove the 200,000 vehicle cap per manufacturer after which the credit phases out over a year. Instead, the incentives would begin to phase outfalling to 75% of the current creditstarting in 2019 for all manufacturers, and would be completely phased out by 2022; this did not get included in the Budget.
In November 2017, House Republicans proposed scrapping the $7,500 tax credit as part of a sweeping tax overhaul, but the final bill passed left the credit intact.
]
In California
 The Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP), initially funded with a total of million by the
The Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP), initially funded with a total of million by the California Environmental Protection Agency
The California Environmental Protection Agency, or CalEPA, is a state cabinet-level agency within the government of California. The mission of CalEPA is to restore, protect and enhance the environment, to ensure public health, environmental qu ...
's Air Resources Board (ARB), was established in order to promote the production and use of zero-emission vehicle
A zero-emission vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that does not emit exhaust gas or other pollutants from the onboard source of power. The California definition also adds that this includes under any and all possible operational modes and conditions ...
s (ZEVs), including plug-in electric and fuel cell vehicle
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate e ...
s. The program was created from Assembly Bill 118 that was signed by Governor Schwarzenegger in October 2007. The funding is provided on a first-come, first-served basis, and the project is expected to go through 2015. Eligible vehicles include only new ARB-certified or approved zero-emission or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. A list of eligible vehicles can be found on the California Center for Sustainable Energy web site.
Eligible vehicles include only new ARB-certified or approved zero-emission or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. A list of eligible vehicles can be found on the California Center for Sustainable Energy web site.[ Among the eligible vehicles are neighborhood electric vehicles, battery electric, plug-in hybrid electric, and fuel cell vehicles including cars, trucks, medium- and heavy-duty commercial vehicles, and zero-emission motorcycles. Vehicles must be purchased or leased on or after March 15, 2010. Rebates of up to $5,000 per light-duty vehicle are available for individuals and business owners who purchase or lease new eligible vehicles. Certain zero-emission commercial vehicles are also eligible for rebates up to $20,000.] As of early September 2012, private individuals accounted for 88% of rebate funds reimbursed. As of early March 2013, CARB has issued about 18,000 rebates totaling million.
As of early September 2012, private individuals accounted for 88% of rebate funds reimbursed. As of early March 2013, CARB has issued about 18,000 rebates totaling million.[
, a total of 52,264 clean vehicle rebates have been issued by the CVRP, for a total of disbursed, with only remaining for fiscal year 2013–2014. , the CVRP was facing an estimated funding shortfall for the 2013-14 fiscal year, and uncertainty about additional funding for the 2014-15 fiscal year. CARB staff presented a proposal to the board to overcome the funding shortage and also to facilitate the rebates to benefit buyers in disadvantaged communities who live in areas with bad air quality or who can't afford high-end electric cars.
A bill signed into law in September 2014, mandated the CARB to draft a financial plan to meet California's goal of putting one million vehicles on the road while making sure that disadvantaged communities can participate. CARB had to change the Clean Vehicle Rebate program to provide an extra credit for low-income drivers who wish to purchase or lease an electric car. CARB also provides assistance to carsharing programs in low-income neighborhoods and install charging stations in apartment buildings in those communities. Under bill SB 1275, low-income residents who agree to scrap older, polluting cars will also get a clean vehicle rebate on top of existing payments for junking smog-producing vehicles.]high-occupancy toll lane
A high-occupancy toll lane (or HOT lane) is a type of traffic lane or roadway that is available to high-occupancy vehicles and other exempt vehicles without charge; other vehicles are required to pay a variable fee that is adjusted in response ...
s (HOT) lanes.[
, California added income-based caps to its rebate system. Buyers with incomes less than 300% of the ]Federal poverty level
In the United States, poverty has both social and political implications. In 2020, there were 37.2 million people in poverty. Some of the many causes include income inequality, inflation, unemployment, debt traps and poor education.Western, B ...
will get up to for a plug-in hybrid, for an all-electric car, and for a hydrogen fuel-cell car and the rebate scales down until Californian buyers with incomes over are no longer are eligible for incentives on hybrids or electric cars, however can get .[ These limits do not apply to the purchase of ]fuel cell electric vehicle
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate ele ...
s, which represent less than 1% of rebate applications.
=Access to HOV lanes
=
In California a vehicle that meets specified emissions standards may be issued Clean Air Vehicle (CAV) decals that allow the vehicle to be operated by a single occupant in California's high-occupancy vehicle lane
A high-occupancy vehicle lane (also known as an HOV lane, carpool lane, diamond lane, 2+ lane, and transit lane or T2 or T3 lanes) is a restricted traffic lane reserved for the exclusive use of vehicles with a driver and one or more passengers, i ...
s (HOV), or carpool
Carpooling (also car-sharing, ride-sharing and lift-sharing) is the sharing of Automobile, car journeys so that more than one person travels in a car, and prevents the need for others to have to drive to a location themselves.
By having more ...
or diamond lanes. All-electric vehicles are classified as Federal Inherently Low Emission Vehicles (ILEVs), and as zero emissions vehicles are entitled to an unlimited number of white CAV stickers. Green CAV stickers were initially available to a limited number of applicants that purchased or leased cars meeting California's Enhanced Advanced Technology Partial Zero Emission Vehicle (Enhanced AT PZEV) or Transitional Zero-Emission Vehicle (TZEV) requirements, for which plug-in hybrids classify. The green car sticker cap was increased several times, and since September 2016 the cap was removed.census tracts
A census tract, census area, census district or meshblock is a geographic region defined for the purpose of taking a census. Sometimes these coincide with the limits of cities, towns or other administrative areas and several tracts commonly exist ...
in California for the study, including Los Angeles, Sacramento, San Diego and San Francisco. The study concluded that the ability to use potentially time-saving HOV lanes prompted the purchase of more than 24,000 plug-in electric cars and hybrids in the four urban areas from 2010 to 2013, or about 40% of the total of such vehicles. The UCLA researcher concluded that without the policy giving plug-in vehicles access to HOV lanes, total plug-in sales in the same study areas would have been only 36,692 for the three-year period.
All states
, 37 states and Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, had established incentives and tax exemption
Tax exemption is the reduction or removal of a liability to make a compulsory payment that would otherwise be imposed by a ruling power upon persons, property, income, or transactions. Tax-exempt status may provide complete relief from taxes, redu ...
s for BEVs and PHEV
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery pack can be recharged by plugging a charging cable into an external electric power source, in addition to internally by its on-board internal combustion engin ...
s, or utility-rate breaks, and other non-monetary incentives such as free parking and high-occupancy vehicle lane
A high-occupancy vehicle lane (also known as an HOV lane, carpool lane, diamond lane, 2+ lane, and transit lane or T2 or T3 lanes) is a restricted traffic lane reserved for the exclusive use of vehicles with a driver and one or more passengers, i ...
access. All states are eligible for the $7,500 income tax credit.
Oceania
Australia
Federal incentives
An Australian National Electric Vehicle Strategy is set to be released by mid 2021 by the Federal coalition government.
State and Territory incentives
State government's offer significant electric vehicle incentives to ensure they meet their EV sales targets. Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
aim for 50% of new car sales to be electric vehicles by 2030.South Australian government
The Government of South Australia, also referred to as the South Australian Government, SA Government or more formally, His Majesty’s Government, is the Australian state democratic administrative authority of South Australia. It is modelled o ...
also aim for 100% of new car sales to be electric vehicles by 2035.
= Victoria
=
Victoria offers a subsidy of $3,000 - $5,000
= Australian Capital Territory
=
ACT offers $15,000 interest free loans.
= South Australia
=
The South Australian Liberal government aim for 100% of new car sales to be electric vehicles by 2035
= New South Wales
=
New South Wales offer $250 discount from registration fees and NSW plan stamp duty exemption for EVs saving $1,200 - $18,000
= Tasmania
=
EVs exempt from stamp duty until 2023.
= Queensland
=
EVs pay $660 less stamp duty than other vehicles
= Northern Territory
=
NT EVs only pay the small car category for registration ($665.55 a year) irrelevant of size
New Zealand
In June 2021, the New Zealand government announced a "feebate" scheme, by which electric vehicles would be subsidised, while particularly high-emitting ICE vehicles would have a cost added to them. The scheme is intended to be revenue-neutral, so that the fees on high-emitting vehicles would pay for the rebates on electric ones. The rebate system began operation on 1 July 2021, with the fee part originally intended to begin on 1 January 2022 (although this has since been delayed to 1 April 2022). This came after a 2019 proposal for a feebate was seemingly vetoed by the minority coalition member New Zealand First.
26,000 EVs were registered in New Zealand in 2020 and the government have a target of an additional 60,000 electric vehicles on New Zealand roads by 2023.
South America
Ecuador
In Ecuador, all electric vehicles are exempt from customs duties and taxes starting in June 2019. The electric vehicle offer in the country is set to increase. The Ecuadorean government has been incentivizing the use of electric vehicles with tax cuts. However, both the offer and demand remained short, encouraging the government to eliminate all duties to electric vehicles.
Africa
Morocco
Electric and hybrid vehicles are exempt from customs duties since 2017.
South Africa
Electric vehicles pay a 25% duty, this is 7% higher than fossil fuel vehicles from the EU that only pay 18%. Beyond this disincentive, there are no incentives or advantages for EV ownership in South Africa.
See also
* Electric car use by country
* Phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles
* Government incentives for fuel efficient vehicles in the United States
* Hybrid tax credit
* List of modern production plug-in electric vehicles
This is a list of battery electric vehicles that are mass-produced, formerly produced, and planned. It includes only vehicles exclusively using chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, with no secondary source of propulsion (e.g ...
* Plug In America
Plug In America (PIA) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit educational organization that promotes and advocates the use of plug-in cars, trucks and sports utility vehicles (SUVs) powered by domestic and renewable electricity which it claims will help reduce ...
References
External links
Clean Vehicle Rebate Project website
Driving Electrification – A Global Comparison of Fiscal Incentive Policy for Electric Vehicles
International Council on Clean Transportation, May 2014
Effects of Federal Tax Credits for the Purchase of Electric Vehicles
Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency within the United States Congress, legislative branch of the United States government that provides budget and economic information to Congress.
Ins ...
, September 2012
Evaluating the Impact of High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) Lane Access on Plug-In Vehicles (PEVs) Purchasing and Usage in California
University of California, Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a public land-grant research university near Davis, California. Named a Public Ivy, it is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University of California system. The inst ...
, Working Paper UCD-ITS-WP-14-01, April 2014
Federal and State Laws and Incentives for alternative fuels and vehicles
Alternative Fuels Data Center, U.S. Department of Energy
List of U.S. Electric Vehicle and EVSE Incentives by State
September 2014
New Energy Tax Credits for Electric Vehicles purchased in 2009
Overview of Tax Incentives for Electrically Chargeable Vehicles in the E.U.
Plug-in Tracker: A comprehensive list of highway-capable PEVs (cars and trucks, 2- and 3-wheeled and commercial vehicles)
UK Plug-in Car Grant website
U.S. Federal & State Incentives & Laws
State and Federal Incentives for EVs, PHEVs and Charge Stations – State and Federal Incentives – United States Incentives Map
Plug In America
Plug In America (PIA) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit educational organization that promotes and advocates the use of plug-in cars, trucks and sports utility vehicles (SUVs) powered by domestic and renewable electricity which it claims will help reduce ...
US Tax Incentives for Plug-in Hybrids and Electric Cars
UK website for government ev grant claims
– Interview of A. Mamaladze, director of AIProduction, for
Caucasian Journal
'
{{DEFAULTSORT:Plug-In Electric Vehicle
Electric vehicle conversion
Electric vehicle industry
Plug-in hybrid vehicles
Renewable energy policy
Subsidies
Taxation in the United Kingdom
Taxation in the United States
 Government incentives for plug-in electric vehicles have been established around the world to support policy-driven adoption of
Government incentives for plug-in electric vehicles have been established around the world to support policy-driven adoption of 
 The Chinese government adopted a plan in 2009 with the goal of turning the country into one of the leaders of all-electric and hybrid vehicles by 2012. The government's intention was to create a world-leading industry that would produce jobs and exports, and to reduce urban pollution and its oil dependence. However, a study found that even though local air pollution would be reduced by replacing a gasoline car with a similar-size electric car, it would reduce
The Chinese government adopted a plan in 2009 with the goal of turning the country into one of the leaders of all-electric and hybrid vehicles by 2012. The government's intention was to create a world-leading industry that would produce jobs and exports, and to reduce urban pollution and its oil dependence. However, a study found that even though local air pollution would be reduced by replacing a gasoline car with a similar-size electric car, it would reduce  In November 2010, the Government of India (GoI), through the
In November 2010, the Government of India (GoI), through the  New next generation vehicles, including electric and
New next generation vehicles, including electric and  Until July 31, 2012, a premium up to , under the bonus-malus system, was granted for the purchase of new cars with emissions of 60 g/km or less which benefited all-electric cars and any plug-in hybrid with such low emissions. Vehicles emitting up to 125 g/km or less, such as conventional hybrids and natural gas vehicles, were granted up to . The incentive could not exceed 20% of the sales price including VAT, increased with the cost of the battery if it is rented.
Effective on August 1, 2012, the government increased the bonus for electric cars up to but capped at 30% of the vehicle price including VAT. The price includes any battery leasing charges, and therefore, electric cars which need a battery leasing contract also are eligible for the bonus. For example, an electric car sold for including VAT was eligible for the maximum bonus of . The emission level for the maximum bonus was raised to 20 g/km or less. Cars with emission levels between 20 and 50 g/km were eligible to a bonus of up to , and between 50 and 60 g/km were eligible to a bonus of up to . After this limit, the bonus dropped to .
The fee schedule for the bonus-malus was modified in 2013. Effective November 1, 2013, the bonus was reduced from to for all-electrics and any other vehicle with emissions of less than 21 g/km. Vehicles emitting between 21 and 60 g/km, such as plug-in hybrids and conventional hybrids, were eligible to a bonus up to , and for emissions between 61 and 90 g/km up to , down from . Effective January 1, 2014, the fee schedule for the malus was increased to a maximum penalty of from for vehicles emitting over 200 g/km. Flex-fuel vehicles remained exempt from the malus fee. A neutral class applies to vehicles emitting between 91 and 130 g/km.
;2015–2016
From April 1, 2015, a super-bonus was introduced, increasing the financial incentive to a cumulative total of , consisting of the regular bonus of for purchasing a pure electric car, plus up to for customers
Until July 31, 2012, a premium up to , under the bonus-malus system, was granted for the purchase of new cars with emissions of 60 g/km or less which benefited all-electric cars and any plug-in hybrid with such low emissions. Vehicles emitting up to 125 g/km or less, such as conventional hybrids and natural gas vehicles, were granted up to . The incentive could not exceed 20% of the sales price including VAT, increased with the cost of the battery if it is rented.
Effective on August 1, 2012, the government increased the bonus for electric cars up to but capped at 30% of the vehicle price including VAT. The price includes any battery leasing charges, and therefore, electric cars which need a battery leasing contract also are eligible for the bonus. For example, an electric car sold for including VAT was eligible for the maximum bonus of . The emission level for the maximum bonus was raised to 20 g/km or less. Cars with emission levels between 20 and 50 g/km were eligible to a bonus of up to , and between 50 and 60 g/km were eligible to a bonus of up to . After this limit, the bonus dropped to .
The fee schedule for the bonus-malus was modified in 2013. Effective November 1, 2013, the bonus was reduced from to for all-electrics and any other vehicle with emissions of less than 21 g/km. Vehicles emitting between 21 and 60 g/km, such as plug-in hybrids and conventional hybrids, were eligible to a bonus up to , and for emissions between 61 and 90 g/km up to , down from . Effective January 1, 2014, the fee schedule for the malus was increased to a maximum penalty of from for vehicles emitting over 200 g/km. Flex-fuel vehicles remained exempt from the malus fee. A neutral class applies to vehicles emitting between 91 and 130 g/km.
;2015–2016
From April 1, 2015, a super-bonus was introduced, increasing the financial incentive to a cumulative total of , consisting of the regular bonus of for purchasing a pure electric car, plus up to for customers  An incentive scheme to promote plug-in electric vehicle adoption was approved in April 2016 with a budget of (). A total of () is reserved for the purchase subsidies, which are expected to run until all the money is disbursed, estimated to last until 2019 at the latest. Another () are budgeted to finance the deployment of charging stations in cities and on autobahn highway stops. And another () would go toward purchasing electric cars for federal government fleets. The program is aimed to promote the sale of 400,000 electric vehicles. The cost of the purchase incentive is shared equally between the government and automakers. Electric car buyers get a () discount while buyers of plug-in hybrid vehicles get a discount of (). Premium cars, such as the Tesla Model S and
An incentive scheme to promote plug-in electric vehicle adoption was approved in April 2016 with a budget of (). A total of () is reserved for the purchase subsidies, which are expected to run until all the money is disbursed, estimated to last until 2019 at the latest. Another () are budgeted to finance the deployment of charging stations in cities and on autobahn highway stops. And another () would go toward purchasing electric cars for federal government fleets. The program is aimed to promote the sale of 400,000 electric vehicles. The cost of the purchase incentive is shared equally between the government and automakers. Electric car buyers get a () discount while buyers of plug-in hybrid vehicles get a discount of (). Premium cars, such as the Tesla Model S and  As a result of the
As a result of the  Considering the potential of plug-in electric vehicles in the country due to its relative small size and geography, the Dutch government set a target of 15,000 to 20,000 electric vehicles with three or more wheels on the roads in 2015; 200,000 vehicles in 2020; and 1 million vehicles in 2025. The first government target was achieved in 2013, two years earlier, thanks to the sales peak that occurred at the end of 2013. According to official figures, 30,086 plug-in electric vehicles with three or more wheels have been registered in the country through 31 December 2013. ''See under the heading "31-12-2013" for total registrations figures at the end of December 2013.''
Initially, the Dutch government set incentives such as the total exemption of the registration fee and road taxes, which resulted in savings of approximately for private car owners over four years, and for corporate owners over five years. Other vehicles including hybrid electric vehicles were also exempt from these taxes if they emit less than 95 g/km for diesel-powered vehicles, or less than 110 g/km for gasoline-powered vehicles. The exemption from the registration tax ended on January 1, 2014, and thereafter, all-electric vehicles pay a 4% registration fee and plug-in hybrids a 7% fee.
In addition, the national government offers through the
Considering the potential of plug-in electric vehicles in the country due to its relative small size and geography, the Dutch government set a target of 15,000 to 20,000 electric vehicles with three or more wheels on the roads in 2015; 200,000 vehicles in 2020; and 1 million vehicles in 2025. The first government target was achieved in 2013, two years earlier, thanks to the sales peak that occurred at the end of 2013. According to official figures, 30,086 plug-in electric vehicles with three or more wheels have been registered in the country through 31 December 2013. ''See under the heading "31-12-2013" for total registrations figures at the end of December 2013.''
Initially, the Dutch government set incentives such as the total exemption of the registration fee and road taxes, which resulted in savings of approximately for private car owners over four years, and for corporate owners over five years. Other vehicles including hybrid electric vehicles were also exempt from these taxes if they emit less than 95 g/km for diesel-powered vehicles, or less than 110 g/km for gasoline-powered vehicles. The exemption from the registration tax ended on January 1, 2014, and thereafter, all-electric vehicles pay a 4% registration fee and plug-in hybrids a 7% fee.
In addition, the national government offers through the  The Parliament of Norway set the goal to reach 50,000 zero emission vehicles by 2018. Among the existing incentives, all-electric cars are exempt in Norway from all non-recurring vehicle fees, including purchase taxes, which are extremely high for ordinary cars, and 25% VAT on purchase, together making electric car purchase price competitive with conventional cars. As an example, by early 2013 the price of the top selling Nissan Leaf was 240,690 kroner (around ) while the purchase price of the 1.3-lt
The Parliament of Norway set the goal to reach 50,000 zero emission vehicles by 2018. Among the existing incentives, all-electric cars are exempt in Norway from all non-recurring vehicle fees, including purchase taxes, which are extremely high for ordinary cars, and 25% VAT on purchase, together making electric car purchase price competitive with conventional cars. As an example, by early 2013 the price of the top selling Nissan Leaf was 240,690 kroner (around ) while the purchase price of the 1.3-lt  In September 2013 the Norwegian Parliament approved, as part of the revised 2014 budget, an exemption from the 25% VAT for leasing electric vehicles effective on 1 January 2014. However, , the exemption has not gone into effect because the
In September 2013 the Norwegian Parliament approved, as part of the revised 2014 budget, an exemption from the 25% VAT for leasing electric vehicles effective on 1 January 2014. However, , the exemption has not gone into effect because the  The target of 50,000 electric cars on Norwegian roads was reached on 20 April 2015, more than two years earlier than expected. In early March 2015 negotiations began among parties represented in the Parliament to define the future of all motor vehicles and fuel taxes. The Liberal Party wanted all the benefits to continue beyond the established quota. The Ministry of Finance also made a comprehensive review of all motor vehicle taxes. The two purchase tax exemptions cost the government about 3 billion krone (around ) in lost revenue just in 2014, and up to 4 billion krone (around ) if all the other benefits are accounted for. Despite passing the established cap of 50,000 electric cars, the tax benefits were expected to continue at least until the end of 2016.
The target of 50,000 electric cars on Norwegian roads was reached on 20 April 2015, more than two years earlier than expected. In early March 2015 negotiations began among parties represented in the Parliament to define the future of all motor vehicles and fuel taxes. The Liberal Party wanted all the benefits to continue beyond the established quota. The Ministry of Finance also made a comprehensive review of all motor vehicle taxes. The two purchase tax exemptions cost the government about 3 billion krone (around ) in lost revenue just in 2014, and up to 4 billion krone (around ) if all the other benefits are accounted for. Despite passing the established cap of 50,000 electric cars, the tax benefits were expected to continue at least until the end of 2016.
 The Plug-In Van Grant (PiVG) began in February 2012. Van-buyers can receive 20% – up to – off the cost of a plug-in van. To be eligible for the scheme, vans have to meet performance criteria to ensure safety, range, and ultra-low tailpipe emissions. Consumers, both business and private will receive the discount at the point of purchase. The Plug-In Van Grant scheme was extended in October 2016 to make electric trucks above 3.5 tonnes eligible for grants of up to , when businesses switch their large trucks to an electric vehicle. The government also announced their commitment for an additional to the scheme so that all vans and trucks meeting the eligibility requirements can benefit from the grant scheme. The extension of the Plug-In Van grant means that N2 vans (3.5 – 12 tonnes gross weight) and N3 vans (over 12 tonnes gross weight) are now eligible.
The eligibility criteria for vans with a gross weight of 3.5 tonnes or less ( N1 van) are: '', 637 claims have been made through the plug-in van grant program.''
* Vehicle type: only new N1 vans are eligible. This includes pre-registration conversions (normal, internal combustion engine vans that were converted to battery or hybrid versions by specialist converters before the car's first registration).
* Carbon dioxide exhaust emissions: vehicles must emit less than 75 grams of carbon dioxide () per kilometre driven.
* Range: eligible fully electric vans must be able to travel a minimum of between charges. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) must have a minimum electric range of .
* Minimum top speed: vehicles must be able to reach a speed of or more.
* Warranty: Vehicles must have a 3-year or vehicle warranty (guarantee) and a 3-year battery and electric drive train warranty, with the option of extending the battery warranty for an extra 2 years
* Battery performance: vehicles must have either a minimum 5-year warranty on the battery and electric drive train as standard
or extra evidence of battery performance to show reasonable performance after 3 years of use
* Electrical safety: vehicles must comply with certain regulations (UN-ECE Reg 100.00) that show that they are electrically safe.
* Crash safety To make sure cars will be safe in a crash, they must either have EC whole vehicle type approval (EC WVTA, not small series) or evidence that the car has appropriate levels of safety as judged by international standards.
, the number of claims made through the Plug-in Van Grant scheme totaled 2,938 units since the launch of the programme in 2012, up from 1,906 made by the end of December 2015. ''See graph with PIVG cumulative claims and claims by quarter''. the following nine vans are eligible for the grant: BD Otomotive eTraffic, BD Otomotiv eDucato,
The Plug-In Van Grant (PiVG) began in February 2012. Van-buyers can receive 20% – up to – off the cost of a plug-in van. To be eligible for the scheme, vans have to meet performance criteria to ensure safety, range, and ultra-low tailpipe emissions. Consumers, both business and private will receive the discount at the point of purchase. The Plug-In Van Grant scheme was extended in October 2016 to make electric trucks above 3.5 tonnes eligible for grants of up to , when businesses switch their large trucks to an electric vehicle. The government also announced their commitment for an additional to the scheme so that all vans and trucks meeting the eligibility requirements can benefit from the grant scheme. The extension of the Plug-In Van grant means that N2 vans (3.5 – 12 tonnes gross weight) and N3 vans (over 12 tonnes gross weight) are now eligible.
The eligibility criteria for vans with a gross weight of 3.5 tonnes or less ( N1 van) are: '', 637 claims have been made through the plug-in van grant program.''
* Vehicle type: only new N1 vans are eligible. This includes pre-registration conversions (normal, internal combustion engine vans that were converted to battery or hybrid versions by specialist converters before the car's first registration).
* Carbon dioxide exhaust emissions: vehicles must emit less than 75 grams of carbon dioxide () per kilometre driven.
* Range: eligible fully electric vans must be able to travel a minimum of between charges. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) must have a minimum electric range of .
* Minimum top speed: vehicles must be able to reach a speed of or more.
* Warranty: Vehicles must have a 3-year or vehicle warranty (guarantee) and a 3-year battery and electric drive train warranty, with the option of extending the battery warranty for an extra 2 years
* Battery performance: vehicles must have either a minimum 5-year warranty on the battery and electric drive train as standard
or extra evidence of battery performance to show reasonable performance after 3 years of use
* Electrical safety: vehicles must comply with certain regulations (UN-ECE Reg 100.00) that show that they are electrically safe.
* Crash safety To make sure cars will be safe in a crash, they must either have EC whole vehicle type approval (EC WVTA, not small series) or evidence that the car has appropriate levels of safety as judged by international standards.
, the number of claims made through the Plug-in Van Grant scheme totaled 2,938 units since the launch of the programme in 2012, up from 1,906 made by the end of December 2015. ''See graph with PIVG cumulative claims and claims by quarter''. the following nine vans are eligible for the grant: BD Otomotive eTraffic, BD Otomotiv eDucato, 
 Electric vehicles in Ontario are eligible for special license plates, officially called Green Vehicle License Plates, from the Ministry of Transportation. In addition to a green colour scheme distinct from the province's typical blue and white license plates, these green plates permit BEV and PHEV owners to travel in the province's
Electric vehicles in Ontario are eligible for special license plates, officially called Green Vehicle License Plates, from the Ministry of Transportation. In addition to a green colour scheme distinct from the province's typical blue and white license plates, these green plates permit BEV and PHEV owners to travel in the province's  As of June 22, 2019,
As of June 22, 2019,  These granted tax credits on PEV vehicles will phase out once 200,000 plug-in vehicles are sold by each manufacturer in the U.S. During this phase out period after 200,000 plug-in car sales, qualified producers will experience a drop in a tax credit of $7,500 to $3,750 for the next 6 months followed by a drop to $1,875 for another 6 months until the credit is run out completely.
The qualified plug-in electric vehicle credit phases out for a PEV manufacturer over the one-year period beginning with the second calendar quarter after the calendar quarter in which at least 200,000 qualifying vehicles from that manufacturer have been sold for use in the U.S. Cumulative sales started counting sales after December 31, 2009. After reaching the cap, qualifying PEVs for one quarter still earn the full credit, the second quarter after that quarter PEVS are eligible for 50% of the credit for six months, then 25% of the credit for another six months and finally the credit is phased out.
In July 2018, Tesla Inc. was the first plug-in manufacturer to pass 200,000 sales and the full tax credit was available until the end 2018, with the phase out beginning in January 2019. General Motors combined sales of plug-in electric vehicles passed 200,000 units in November 2018. The full tax credit was available until the end of March 2019 and thereafter reduced gradually until complete phase out beginning on April 1, 2020. , 21 vehicles have access to full tax credit, depending on taxpayer's conditions. Several plugin-vehicles are also approved for significant credits.
;Studies
A 2013 study published in the journal ''Energy Policy'' determined that current federal subsidies are "not aligned with the goal of decreased gasoline consumption in a consistent and efficient manner." In particular, hybrid-vehicle credit is given according to battery capacity rather than on the vehicle's all-electric range. Across the battery-capacity and charging-infrastructure scenarios examined, the lowest-cost solution is for more drivers to switch to traditional hybrid electrics or low-capacity plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). Installing charging infrastructure would provide lower gasoline savings per dollar spent than paying for increased PHEV battery capacity.
A 2016 study conducted by researchers from the
These granted tax credits on PEV vehicles will phase out once 200,000 plug-in vehicles are sold by each manufacturer in the U.S. During this phase out period after 200,000 plug-in car sales, qualified producers will experience a drop in a tax credit of $7,500 to $3,750 for the next 6 months followed by a drop to $1,875 for another 6 months until the credit is run out completely.
The qualified plug-in electric vehicle credit phases out for a PEV manufacturer over the one-year period beginning with the second calendar quarter after the calendar quarter in which at least 200,000 qualifying vehicles from that manufacturer have been sold for use in the U.S. Cumulative sales started counting sales after December 31, 2009. After reaching the cap, qualifying PEVs for one quarter still earn the full credit, the second quarter after that quarter PEVS are eligible for 50% of the credit for six months, then 25% of the credit for another six months and finally the credit is phased out.
In July 2018, Tesla Inc. was the first plug-in manufacturer to pass 200,000 sales and the full tax credit was available until the end 2018, with the phase out beginning in January 2019. General Motors combined sales of plug-in electric vehicles passed 200,000 units in November 2018. The full tax credit was available until the end of March 2019 and thereafter reduced gradually until complete phase out beginning on April 1, 2020. , 21 vehicles have access to full tax credit, depending on taxpayer's conditions. Several plugin-vehicles are also approved for significant credits.
;Studies
A 2013 study published in the journal ''Energy Policy'' determined that current federal subsidies are "not aligned with the goal of decreased gasoline consumption in a consistent and efficient manner." In particular, hybrid-vehicle credit is given according to battery capacity rather than on the vehicle's all-electric range. Across the battery-capacity and charging-infrastructure scenarios examined, the lowest-cost solution is for more drivers to switch to traditional hybrid electrics or low-capacity plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). Installing charging infrastructure would provide lower gasoline savings per dollar spent than paying for increased PHEV battery capacity.
A 2016 study conducted by researchers from the  The 2009 ARRA provided a tax credit for plug-in electric drive conversion kits. The credit is equal to 10% of the cost of converting a vehicle to a qualified plug-in electric vehicle and in service after February 17, 2009. The maximum amount of the credit is $4,000. The credit does not apply to conversions made after December 31, 2011.
The 2009 ARRA provided a tax credit for plug-in electric drive conversion kits. The credit is equal to 10% of the cost of converting a vehicle to a qualified plug-in electric vehicle and in service after February 17, 2009. The maximum amount of the credit is $4,000. The credit does not apply to conversions made after December 31, 2011.
 Two separate initiatives were pursued in 2011 to transform the tax credit into an instant cash rebate; these did not pass. The objective of both initiatives was to make new qualifying
Two separate initiatives were pursued in 2011 to transform the tax credit into an instant cash rebate; these did not pass. The objective of both initiatives was to make new qualifying  Eligible vehicles include only new ARB-certified or approved zero-emission or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. A list of eligible vehicles can be found on the California Center for Sustainable Energy web site. Among the eligible vehicles are neighborhood electric vehicles, battery electric, plug-in hybrid electric, and fuel cell vehicles including cars, trucks, medium- and heavy-duty commercial vehicles, and zero-emission motorcycles. Vehicles must be purchased or leased on or after March 15, 2010. Rebates of up to $5,000 per light-duty vehicle are available for individuals and business owners who purchase or lease new eligible vehicles. Certain zero-emission commercial vehicles are also eligible for rebates up to $20,000.
Eligible vehicles include only new ARB-certified or approved zero-emission or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. A list of eligible vehicles can be found on the California Center for Sustainable Energy web site. Among the eligible vehicles are neighborhood electric vehicles, battery electric, plug-in hybrid electric, and fuel cell vehicles including cars, trucks, medium- and heavy-duty commercial vehicles, and zero-emission motorcycles. Vehicles must be purchased or leased on or after March 15, 2010. Rebates of up to $5,000 per light-duty vehicle are available for individuals and business owners who purchase or lease new eligible vehicles. Certain zero-emission commercial vehicles are also eligible for rebates up to $20,000.