Glaciarium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
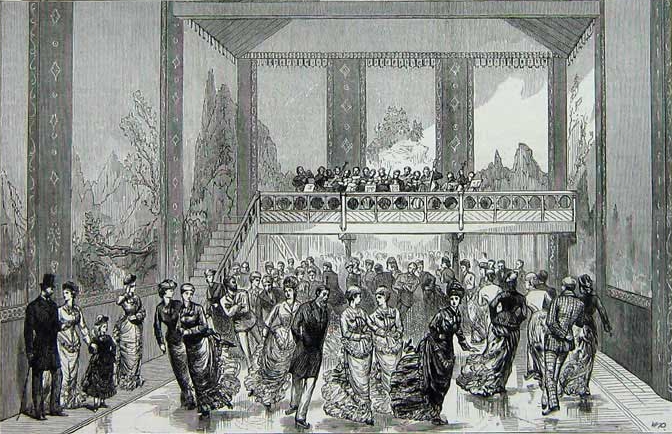
 The Glaciarium was the world's first mechanically frozen
The Glaciarium was the world's first mechanically frozen

 The Glaciarium was the world's first mechanically frozen
The Glaciarium was the world's first mechanically frozen ice rink
An ice rink (or ice skating rink) is a frozen body of water and/or an artificial sheet of ice created using hardened chemicals where people can ice skate or play winter sports. Ice rinks are also used for exhibitions, contests and ice shows. The ...
Martin C. Harris, ''Homes of British Ice Hockey'' and was located in London, England
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major s ...
. An item in the 8 June 1844 issue of Littell's Living Age headed "The Glaciarium" reported:
A later rink was opened by John Gamgee
John Gamgee (1831–1894) was a British veterinarian and inventor. He specialised in the contagious diseases of larger animals: primarily cattle and horses.
Life
Gamgee was born in 1831 in Florence, Italy, the son of Joseph Gamgee (1801–1895), ...
in a tent in a small building just off the Kings Road
King's Road or Kings Road (or sometimes the King's Road, especially when it was the king's private road until 1830, or as a colloquialism by middle/upper class London residents), is a major street stretching through Chelsea and Fulham, both ...
in Chelsea, London
Chelsea is an affluent area in west London, England, due south-west of Charing Cross by approximately 2.5 miles. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames and for postal purposes is part of the south-western postal area.
Chelsea histori ...
, on 7 January 1876. In March, it moved to a permanent venue at 379 Kings Road, where a rink measuring 40 by 24 feet was established.
The rink was based on a concrete surface, with layers of earth, cow hair and timber planks. Atop these were laid oval copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
pipes carrying a solution of glycerine
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known ...
with ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
, nitrogen peroxide, and water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
. The pipes were covered by water and the solution was pumped through, freezing the water into ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaq ...
. Gamgee had discovered the process while attempting to develop a method to freeze meat for import from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, and had patented
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A p ...
it as early as 1870.
Gamgee operated the rink on a membership-only basis and attempted to attract a wealthy clientele, experienced in open-air ice skating
Ice skating is the self-propulsion and gliding of a person across an ice surface, using metal-bladed ice skates. People skate for various reasons, including recreation (fun), exercise, competitive sports, and commuting. Ice skating may be per ...
during winters in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
. He installed an orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, c ...
gallery, which could also be used by spectators, and decorated the walls with views of the Swiss Alps
The Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps (german: Schweizer Alpen, french: Alpes suisses, it, Alpi svizzere, rm, Alps svizras), represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swiss ...
.
The rink initially proved a success, and Gamgee opened two further rinks later in the year: at Rusholme
Rusholme () is an area of Manchester, England, two miles south of the city centre. The population of the ward at the 2011 census was 13,643. Rusholme is bounded by Chorlton-on-Medlock to the north, Victoria Park and Longsight to the east, F ...
in Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
and the "Floating Glaciarium" at Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; ...
in London, this last significantly larger at 115 by 25 feet. However, the process was expensive, and mist
Mist is a phenomenon caused by small droplets of water suspended in the cold air, usually by condensation. Physically, it is an example of a dispersion. It is most commonly seen where water vapor in warm, moist air meets sudden cooling, such a ...
s rising from the ice deterred customers, forcing Gamgee to close the Glaciarium by the end of the year, and all his rinks had shut by mid-1878. However, the Southport Glaciarium
Southport is a seaside town in the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton in Merseyside, England. At the 2001 census, it had a population of 90,336, making it the eleventh most populous settlement in North West England.
Southport lies on the Iris ...
opened in 1879, using Gamgee's method.
See also
*St. Nicholas Rink
The St. Nicholas Rink, also called the St. Nicholas Arena, was an indoor ice rink, and later a boxing arena in New York City from 1896 until 1962. The rink was one of the earliest indoor ice rinks made of mechanically frozen ice in North America ( ...
References