Giant Planet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The giant planets constitute a diverse type of
The giant planets constitute a diverse type of
 A giant planet is a massive
A giant planet is a massive
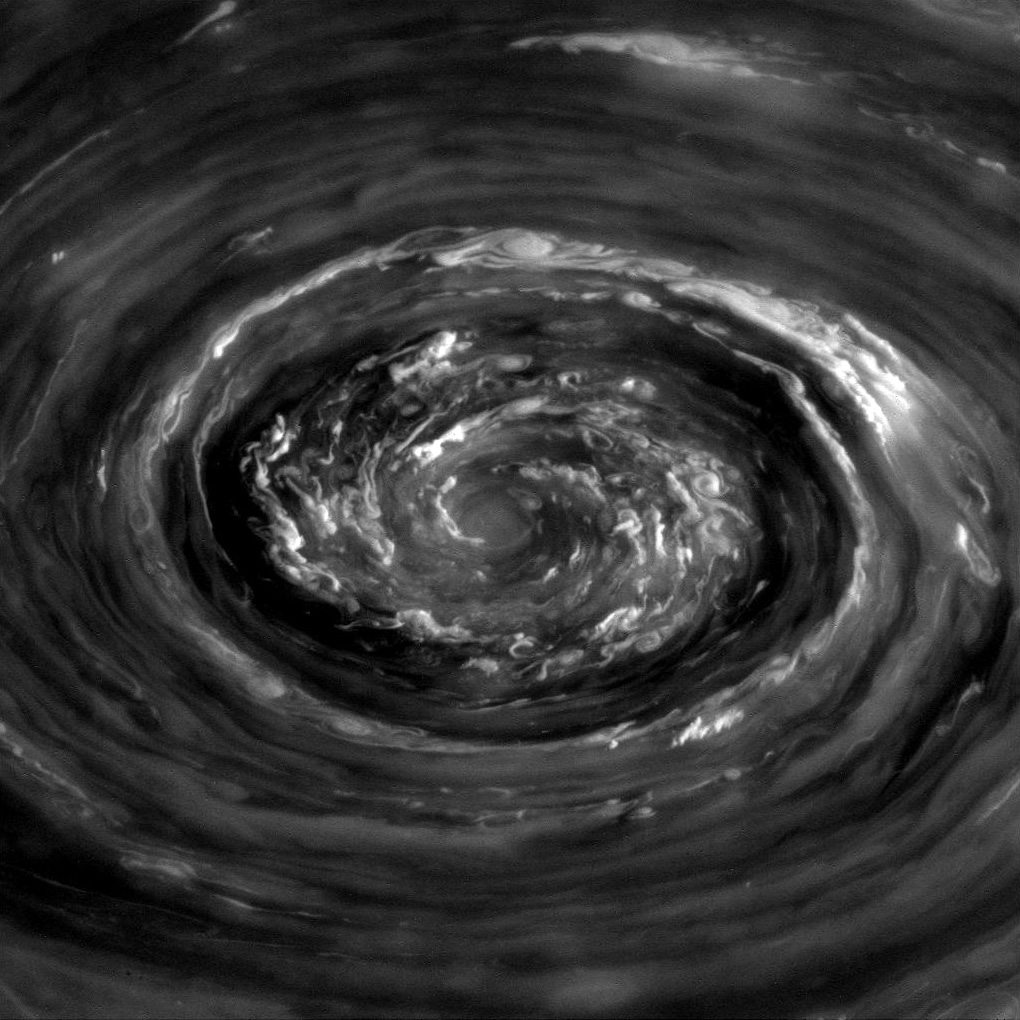 Gas giants consist mostly of hydrogen and helium. The Solar System's gas giants,
Gas giants consist mostly of hydrogen and helium. The Solar System's gas giants,
Jessica E. Libby-Roberts, Zachory K. Berta-Thompson, Jean-Michel Desert, Kento Masuda, Caroline V. Morley, Eric D. Lopez, Katherine M. Deck, Daniel Fabrycky, Jonathan J. Fortney, Michael R. Line, Roberto Sanchis-Ojeda, Joshua N. Winn, 28 Oct 2019 They are cooler and less massive than the inflated low-density hot-Jupiters. The most extreme examples known are the three planets around

 Because of the limited techniques currently available to detect
Because of the limited techniques currently available to detect
Q&A: The IAU's Proposed Planet Definition
16 August 2006 2:00 am ET * BBC News
Q&A New planets proposal
Wednesday, 16 August 2006, 13:36 GMT 14:36 UK * Gas Giants in Science Fiction
* Episode "Giants" on

planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
much larger than Earth. They are usually primarily composed of low-boiling-point materials (volatiles
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances.
On planet Earth, the term ...
), rather than rock or other solid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structur ...
matter, but massive solid planet
This page describes exoplanet orbital and physical parameters.
Orbital parameters
Most known extrasolar planet candidates have been discovered using indirect methods and therefore only some of their physical and orbital parameters can be determi ...
s can also exist. There are four known giant planets in the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
: Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
. Many extrasolar
An ''extrasolar object'' ({{ety, la, extra, outside or beyond, , solaris, of the Sun) is an astronomical object that exists outside the Solar System. It is not applied to stars, or any other celestial object that is larger than a star or the Sol ...
giant planets have been identified orbiting other star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s.
They are also sometimes called jovian planets, after Jupiter ("Jove" being another name for the Roman god "Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
"). They are also sometimes known as gas giants. However, many astronomers now apply the latter term only to Jupiter and Saturn, classifying Uranus and Neptune, which have different compositions, as ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary ...
s.
Both names are potentially misleading: all of the giant planets consist primarily of fluids above their critical points, where distinct gas and liquid phases do not exist. The principal components are hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
in the case of Jupiter and Saturn, and water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
in the case of Uranus and Neptune.
The defining differences between a very low-mass brown dwarf and a gas giant () are debated. One school of thought is based on formation; the other, on the physics of the interior. Part of the debate concerns whether "brown dwarfs" must, by definition, have experienced nuclear fusion at some point in their history.
Terminology
The term ''gas giant'' was coined in 1952 by the science fiction writer James Blish and was originally used to refer to all giant planets. Arguably it is something of a misnomer, because throughout most of the volume of these planets the pressure is so high that matter is not in gaseous form. Other than the upper layers of the atmosphere, all matter is likely beyond the critical point, where there is no distinction between liquids and gases. ''Fluid planet'' would be a more accurate term. Jupiter also has metallic hydrogen near its center, but much of its volume is hydrogen, helium, and traces of other gases above their critical points. The observable atmospheres of all these planets (at less than unitoptical depth
In physics, optical depth or optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to ''transmitted'' radiant power through a material.
Thus, the larger the optical depth, the smaller the amount of transmitted radiant power throug ...
) are quite thin compared to their radii, only extending perhaps one percent of the way to the center. Thus the observable portions are gaseous (in contrast to Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
and Earth, which have gaseous atmospheres through which the crust can be seen).
The rather misleading term has caught on because planetary scientists typically use ''rock'', ''gas'', and ''ice'' as shorthands for classes of elements and compounds commonly found as planetary constituents, irrespective of the matter's phase. In the outer Solar System, hydrogen and helium are referred to as ''gases''; water, methane, and ammonia as ''ices''; and silicates and metals as ''rock''. When deep planetary interiors are considered, it may not be far off to say that, by ''ice'' astronomers mean oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
and carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
, by ''rock'' they mean silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
, and by ''gas'' they mean hydrogen and helium. The many ways in which Uranus and Neptune differ from Jupiter and Saturn have led some to use the term only for the planets similar to the latter two. With this terminology in mind, some astronomers have started referring to Uranus and Neptune as ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary ...
s to indicate the predominance of the ''ices'' (in fluid form) in their interior composition.
The alternative term ''jovian planet'' refers to the Roman god Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
—the genitive form of which is ''Jovis'', hence ''Jovian''—and was intended to indicate that all of these planets were similar to Jupiter.
Objects large enough to start deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one ...
fusion (above 13 Jupiter masses for solar composition) are called brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs (also called failed stars) are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen ( 1H) into helium in their cores, unlike a main-sequence star. Instead, they have a mass between the most ...
s, and these occupy the mass range between that of large giant planets and the lowest-mass star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s. The 13-Jupiter-mass () cutoff is a rule of thumb rather than something of precise physical significance. Larger objects will burn most of their deuterium and smaller ones will burn only a little, and the value is somewhere in between. The amount of deuterium burnt depends not only on the mass but also on the composition of the planet, especially on the amount of helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
and deuterium present. The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia includes objects up to 60 Jupiter masses, and the Exoplanet Data Explorer up to 24 Jupiter masses.
Description
 A giant planet is a massive
A giant planet is a massive planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
and has a thick atmosphere of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
. They may have a dense molten core of rocky elements, or the core may have completely dissolved and dispersed throughout the planet if the planet is hot enough. In "traditional" giant planets such as Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
(the gas giants) hydrogen and helium constitute most of the mass of the planet, whereas they only make up an outer envelope on Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
, which are instead mostly composed of water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
, and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
and therefore increasingly referred to as "ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary ...
s".
Extrasolar giant planets that orbit very close to their stars are the exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
s that are easiest to detect. These are called hot Jupiter
Hot Jupiters (sometimes called hot Saturns) are a class of gas giant exoplanets that are inferred to be physically similar to Jupiter but that have very short orbital periods (). The close proximity to their stars and high surface-atmosphere t ...
s and hot Neptunes because they have very high surface temperatures. Hot Jupiters were, until the advent of space-borne telescopes, the most common form of exoplanet known, due to the relative ease of detecting them with ground-based instruments.
Giant planets are commonly said to lack solid surfaces, but it is more accurate to say that they lack surfaces altogether since the gases that constitute them simply become thinner and thinner with increasing distance from the planets' centers, eventually becoming indistinguishable from the interplanetary medium. Therefore, landing on a giant planet may or may not be possible, depending on the size and composition of its core.
Subtypes
Gas giants
 Gas giants consist mostly of hydrogen and helium. The Solar System's gas giants,
Gas giants consist mostly of hydrogen and helium. The Solar System's gas giants, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, have heavier elements making up between 3 and 13 percent of their mass.The Interior of Jupiter, Guillot et al., in ''Jupiter: The Planet, Satellites and Magnetosphere'', Bagenal et al., editors, Cambridge University Press, 2004 Gas giants are thought to consist of an outer layer of molecular hydrogen, surrounding a layer of liquid metallic hydrogen, with a probable molten core with a rocky composition.
Jupiter and Saturn's outermost portion of the hydrogen atmosphere has many layers of visible clouds that are mostly composed of water and ammonia. The layer of metallic hydrogen makes up the bulk of each planet, and is referred to as "metallic" because the very high pressure turns hydrogen into an electrical conductor. The core is thought to consist of heavier elements at such high temperatures (20,000 K) and pressures that their properties are poorly understood.
Ice giants
Ice giants have distinctly different interior compositions from gas giants. The Solar System's ice giants,Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
, have a hydrogen-rich atmosphere that extends from the cloud tops down to about 80% (Uranus) or 85% (Neptune) of their radius. Below this, they are predominantly "icy", i.e. consist mostly of water, methane, and ammonia. There is also some rock and gas, but various proportions of ice–rock–gas could mimic pure ice, so that the exact proportions are unknown.
Uranus and Neptune have very hazy atmospheric layers with small amounts of methane, giving them aquamarine colors; light blue and ultramarine respectively. Both have magnetic fields that are sharply inclined to their axes of rotation.
Unlike the other giant planets, Uranus has an extreme tilt that causes its seasons to be severely pronounced. The two planets also have other subtle but important differences. Uranus has more hydrogen and helium than Neptune despite being less massive overall. Neptune is therefore denser and has much more internal heat and a more active atmosphere. The Nice model, in fact, suggests that Neptune formed closer to the Sun than Uranus did, and should therefore have more heavy elements.
Massive solid planets
Massive solid planets can also exist. Solid planets up to thousands of Earth masses may be able to form around massive stars ( B-type and O-type stars; 5–120 solar masses), where the protoplanetary disk would contain enough heavy elements. Also, these stars have highUV radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiatio ...
and winds
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
that could photoevaporate the gas in the disk, leaving just the heavy elements.
For comparison, Neptune's mass equals 17 Earth masses, Jupiter has 318 Earth masses, and the 13 Jupiter-mass limit used in the IAU's working definition of an exoplanet equals approximately 4000 Earth masses.
Super-Puffs
A super-puff is a type ofexoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
with a mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
only a few times larger than
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
’s but a radius larger than Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
, giving it a very low mean density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematicall ...
.The Featureless Transmission Spectra of Two Super-Puff PlanetsJessica E. Libby-Roberts, Zachory K. Berta-Thompson, Jean-Michel Desert, Kento Masuda, Caroline V. Morley, Eric D. Lopez, Katherine M. Deck, Daniel Fabrycky, Jonathan J. Fortney, Michael R. Line, Roberto Sanchis-Ojeda, Joshua N. Winn, 28 Oct 2019 They are cooler and less massive than the inflated low-density hot-Jupiters. The most extreme examples known are the three planets around
Kepler-51
Kepler-51 is a Solar analog, Sun-like star that is only about 500 million years old. It is orbited by three super-puff planets—Kepler-51b, c, and d—which have the lowest known densities of any exoplanet. The planets are all Jupite ...
which are all Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
-sized but with densities below 0.1 g/cm3.
Extrasolar giant planets

exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
s, many of those found to date have been of a size associated, in the Solar System, with giant planets. Because these large planets are inferred to share more in common with Jupiter than with the other giant planets, some have claimed that "jovian planet" is a more accurate term for them. Many of the exoplanets are much closer to their parent stars and hence much hotter than the giant planets in the Solar System, making it possible that some of those planets are a type not observed in the Solar System. Considering the relative abundances of the elements in the universe (approximately 98% hydrogen and helium) it would be surprising to find a predominantly rocky planet more massive than Jupiter. On the other hand, models of planetary-system formation have suggested that giant planets would be inhibited from forming as close to their stars as many of the extrasolar giant planets have been observed to orbit.
Atmospheres
The bands seen in the atmosphere of Jupiter are due to counter-circulating streams of material called zones and belts, encircling the planet parallel to its equator. The zones are the lighter bands, and are at higher altitudes in the atmosphere. They have an internal updraft and are high-pressure regions. The belts are the darker bands, are lower in the atmosphere, and have an internal downdraft. They are low-pressure regions. These structures are somewhat analogous to the high and low-pressure cells in Earth's atmosphere, but they have a very different structure—latitudinal bands that circle the entire planet, as opposed to small confined cells of pressure. This appears to be a result of the rapid rotation and underlying symmetry of the planet. There are no oceans or landmasses to cause local heating and the rotation speed is much higher than that of Earth. There are smaller structures as well: spots of different sizes and colors. On Jupiter, the most noticeable of these features is theGreat Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is a persistent high-pressure region in the atmosphere of Jupiter, producing an anticyclonic storm that is the largest in the Solar System. Located 22 degrees south of Jupiter's equator, it produces wind-speeds up to 432&nb ...
, which has been present for at least 300 years. These structures are huge storms. Some such spots are thunderheads as well.
See also
References
Bibliography
* SPACE.com: Q&A: The IAU's Proposed Planet Definition, 16 August 2006, 2:00 AM ET * BBC News: Q&A New planets proposal Wednesday, 16 August 2006, 13:36 GMT 14:36 UKExternal links
* SPACE.comQ&A: The IAU's Proposed Planet Definition
16 August 2006 2:00 am ET * BBC News
Q&A New planets proposal
Wednesday, 16 August 2006, 13:36 GMT 14:36 UK * Gas Giants in Science Fiction
* Episode "Giants" on
The Science Channel
Science Channel (often simply branded as Science; abbreviated to SCI) is an American pay television channel owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. The channel features programming focusing on science related to wilderness survival, engineering, m ...
TV show ''Planets''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gas Giant
Types of planet