Giant Virus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A giant virus, sometimes referred to as a girus, is a very large
virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
, some of which are larger than typical bacteria. All known giant viruses belong to the phylum ''Nucleocytoviricota
''Nucleocytoviricota'' is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix - for virus phylum. These viruses are refe ...
''.
Description
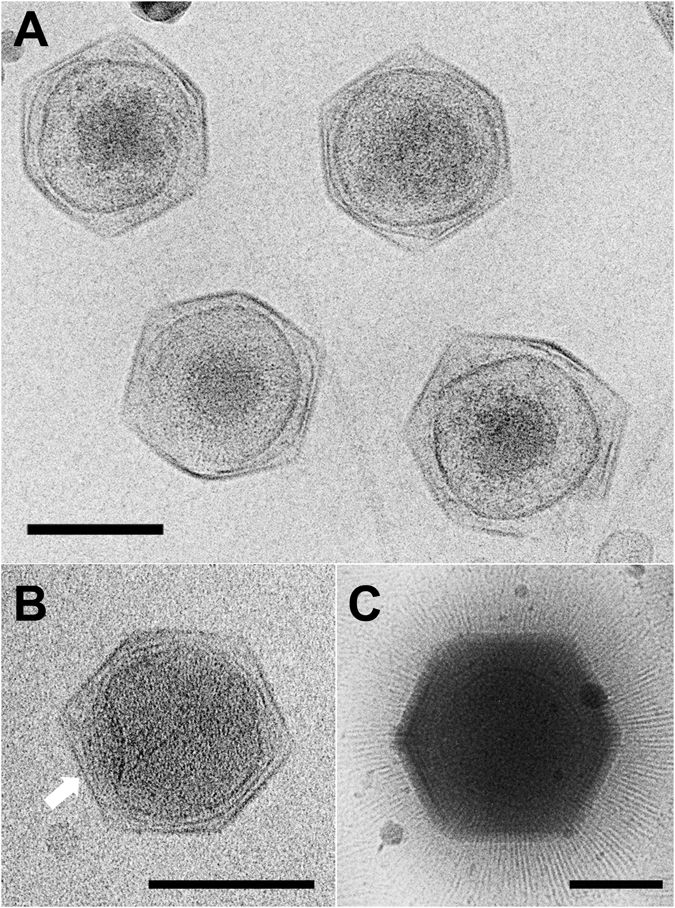
While the exact criteria as defined in the scientific literature vary, giant viruses are generally described as viruses having large, pseudo- icosahedral capsids (200 to 400 nanometers in diameter) that may be surrounded by a thick (approximately 100 nm) layer of filamentous protein fibers. The viruses have large, double-stranded DNA genomes (300 to >1000 kilobasepairs) that encode a large contingent of genes (of the order of 1000 genes). The best characterized giant viruses are the phylogenetically relatedmimivirus
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant viruses, in the family ''Mimiviridae''. Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. This genus contains a single identified species named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus'' (APMV). It also refers to a group of phylo ...
and megavirus
Megavirus is a viral genus containing a single identified species named ''Megavirus chilensis'', phylogenetically related to Acanthamoeba polyphaga Mimivirus (APMV). In colloquial speech, Megavirus chilensis is more commonly referred to as jus ...
, which belong to the family ''Mimiviridae
''Mimiviridae'' is a family of viruses. Amoeba and other protists serve as natural hosts. The family is divided in up to 4 subfamilies., UCPMS ID: 1889607PDF/ref> Fig. 4 and §Discussion: "Considering that tupanviruses comprise a sister gr ...
'' (aka ''Megaviridae''), and are distinguished by their large capsid diameters. Giant viruses from the deep ocean, terrestrial sources, and human patients contain genes encoding cytochrome P450 (CYP; P450) enzymes. The origin of these P450 genes in giant viruses remains unknown but may have been acquired from an ancient host.
The genomes of many giant viruses encode many unusual genes that are not found in other viruses, including genes involved in glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH ...
and the TCA cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins ...
, fermentation, and the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
.

History
The first giant viruses to be described were chloroviruses of the familyPhycodnaviridae
''Phycodnaviridae'' is a family of large (100–560 kb) double-stranded DNA viruses that infect marine or freshwater eukaryotic algae. Viruses within this family have a similar morphology, with an icosahedral capsid (polyhedron with 20 fac ...
. These were discovered in 1981 by Russel H. Meints, James L. Van Etten, Daniel Kuczmarski, Kit Lee, and Barbara Ang. The first chlorovirus
''Chlorovirus'', also known as Chlorella virus, is a genus of giant double-stranded DNA viruses, in the family ''Phycodnaviridae''. This genus is found globally in freshwater environments where freshwater microscopic algae serve as natural hosts ...
was initially called HVCV (Hydra viridis Chlorella virus) since it was first found to infect Chlorella-like algae.
Other giant viruses that infected marine flagellates were described later. The first mimivirus
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant viruses, in the family ''Mimiviridae''. Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. This genus contains a single identified species named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus'' (APMV). It also refers to a group of phylo ...
(BV-PW1) was described in 1995, but was not recognized as such until its sequenced genome was released as Cafeteria roenbergensis virus
''Cafeteria roenbergensis virus'' (CroV) is a giant virus that infects the marine bicosoecid flagellate ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'', a member of the microzooplankton community.
History
The virus was isolated from seawater samples collected from ...
(CroV) in 2010. Subsequently, the Giant Virus ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga'' Mimivirus was characterized (which had been mistaken as a bacterium in 1993), and then sequenced. The term "girus" was coined to refer to the group in 2006.
Genetics and evolution
The genomes of giant viruses are the largest known for viruses, and contain genes that encode for important elements oftranslation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
machinery, a characteristic that had previously been believed to be indicative of cellular organisms. These genes include multiple genes encoding a number of aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its pre ...
s, enzymes that catalyze the esterification
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
of specific amino acids or their precursors to their corresponding cognate tRNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino ac ...
s to form an aminoacyl tRNA
Aminoacyl-tRNA (also aa-tRNA or charged tRNA) is tRNA to which its cognate amino acid is chemically bonded (charged). The aa-tRNA, along with particular elongation factors, deliver the amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into the polypept ...
that is then used during translation. The presence of four aminoacyl tRNA synthetase encoding genes in mimivirus and mamavirus
Mamavirus is a large and complex virus in the Group I family ''Mimiviridae''. The virus is exceptionally large, and larger than many bacteria. Mamavirus and other mimiviridae belong to nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus (NCLDVs) family. Mamavirus ...
genomes, both species within the ''Mimiviridae'' family, as well as the discovery of seven aminoacyl tRNA synthetase genes in the megavirus genome (including those in ''Mimiviridae'') provide evidence that these large DNA viruses may have evolved from a shared cellular genome ancestor by means of genome reduction
Genome size is the total amount of DNA contained within one copy of a single complete genome. It is typically measured in terms of mass in picograms (trillionths (10−12) of a gram, abbreviated pg) or less frequently in daltons, or as the total ...
.
The discovery and subsequent characterization of giant viruses has triggered debate on their evolutionary origins. The two main hypotheses are that they evolved from small viruses by picking up DNA from host organisms; or that they evolved from very complicated organisms via genome reduction
Genome size is the total amount of DNA contained within one copy of a single complete genome. It is typically measured in terms of mass in picograms (trillionths (10−12) of a gram, abbreviated pg) or less frequently in daltons, or as the total ...
, losing various functions including self-reproduction. The possible complicated ancestral organism is also a topic of debate: by one proposal, it might represent a fourth domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
**Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* Do ...
of life, but this has been largely discounted.
Comparison of largest known giant viruses
The whole list is in the Giant Virus Toplist created by theGiant Virus Finder
The Giant Virus Finder is a free bioinformatics software for finding giant viruses in metagenomes.
Applications
The Giant Virus Finder tool integrates and applies thGiant Virus Toplist the list of the largest virus genomes. With the tool, gia ...
software.
1Mutator S (MutS) and its homologs are a family of DNA mismatch repair proteins involved in the mismatch repair system that acts to correct point mutations or small insertion/deletion loops produced during DNA replication, increasing the fidelity of replication.
2A stargate is a five-pronged star structure present on the viral capsid forming the portal through which the internal core of the particle is delivered to the host's cytoplasm.
See also
*Cafeteria roenbergensis virus
''Cafeteria roenbergensis virus'' (CroV) is a giant virus that infects the marine bicosoecid flagellate ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'', a member of the microzooplankton community.
History
The virus was isolated from seawater samples collected from ...
* Klosneuvirus
''Klosneuvirus'' (KNV, also KloV) is a new type of giant virus found by the analysis of low-complexity metagenomes from a wastewater treatment plant in Klosterneuburg, Austria. It has a 1.57-Mb genome coding unusually high number of genes typic ...
* Mimivirus
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant viruses, in the family ''Mimiviridae''. Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. This genus contains a single identified species named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus'' (APMV). It also refers to a group of phylo ...
* Nucleocytoviricota
''Nucleocytoviricota'' is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix - for virus phylum. These viruses are refe ...
* Pandoravirus
''Pandoravirus'' is a genus of giant virus, first discovered in 2013. It is the second largest in physical size of any known viral genus. Pandoraviruses have double stranded DNA genomes, with the largest genome size (2.5 million base pairs) of ...
* Pithovirus
''Pithovirus'', first described in a 2014 paper, is a genus of giant virus known from two species, ''Pithovirus sibericum'', which infects amoebas and ''Pithovirus massiliensis''. It is a double-stranded DNA virus, and is a member of the nucle ...
* Mamavirus
Mamavirus is a large and complex virus in the Group I family ''Mimiviridae''. The virus is exceptionally large, and larger than many bacteria. Mamavirus and other mimiviridae belong to nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus (NCLDVs) family. Mamavirus ...
References
{{Self-replicating organic structures Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses