German cuisine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The cuisine of Germany () is made up of many different local or regional cuisines, reflecting the country's federal history.
The cuisine of Germany () is made up of many different local or regional cuisines, reflecting the country's federal history.
 The average annual meat consumption is per person. The most common varieties are pork, poultry and beef. Other varieties of meat are widely available, but are considered to be insignificant.
Source: Statista.com, 2017
Meat is usually
The average annual meat consumption is per person. The most common varieties are pork, poultry and beef. Other varieties of meat are widely available, but are considered to be insignificant.
Source: Statista.com, 2017
Meat is usually 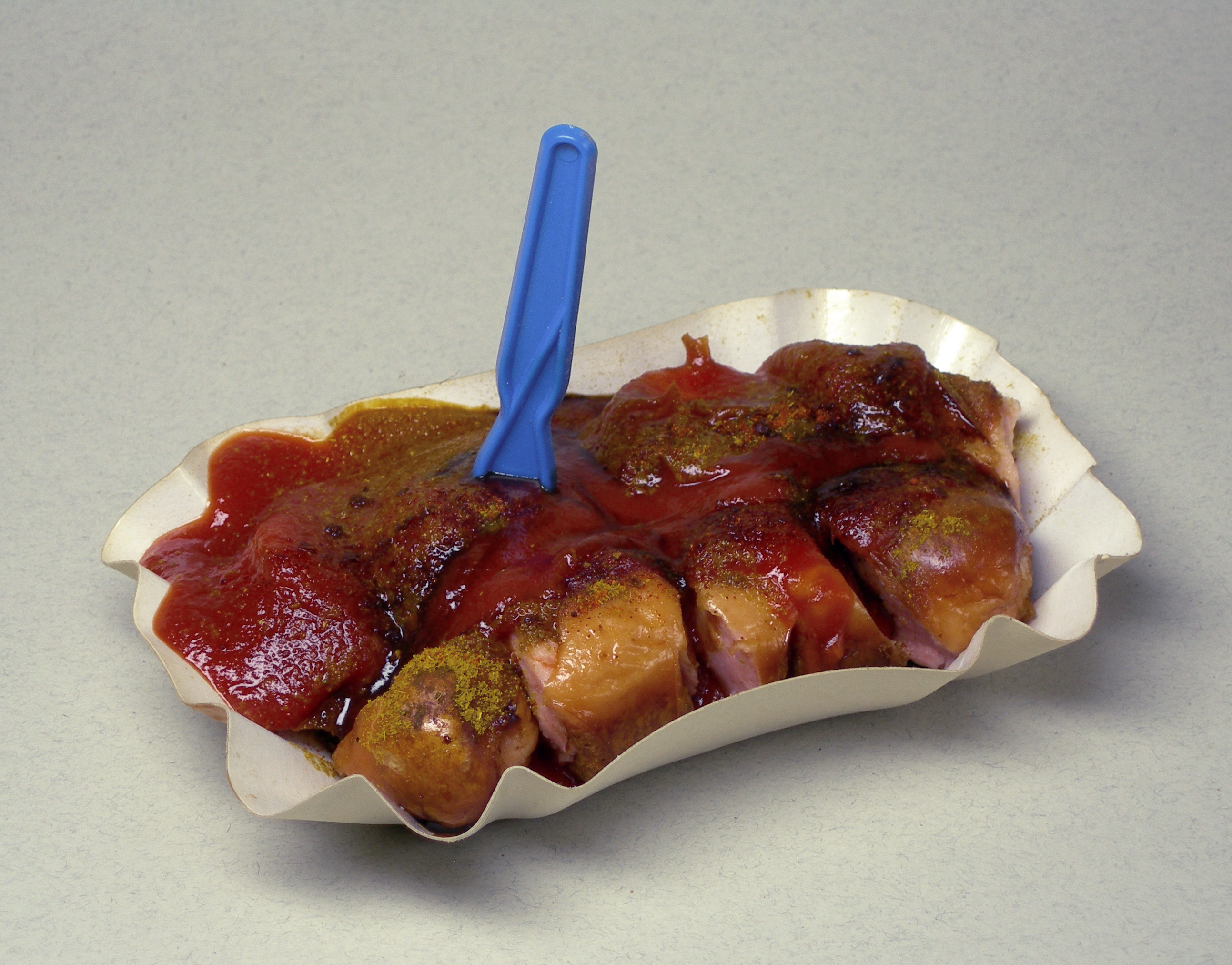 A long tradition of sausage-making exists in Germany; more than 1,500 different types of sausage (german: Wurst) are made. Most ''Wurst'' is made with natural casings of pork, sheep or lamb intestines. Among the most popular and most common are '' Bratwurst'', usually made of ground pork and spices, the ''Wiener'' (Viennese), which may be pork or beef and is smoked and fully cooked in a water bath, and ''Blutwurst'' (
A long tradition of sausage-making exists in Germany; more than 1,500 different types of sausage (german: Wurst) are made. Most ''Wurst'' is made with natural casings of pork, sheep or lamb intestines. Among the most popular and most common are '' Bratwurst'', usually made of ground pork and spices, the ''Wiener'' (Viennese), which may be pork or beef and is smoked and fully cooked in a water bath, and ''Blutwurst'' (
 Of saltwater fish, Alaska pollock is the most common. Popular freshwater fish on the German menu are
Of saltwater fish, Alaska pollock is the most common. Popular freshwater fish on the German menu are

 Noodles, made from wheat flour and egg, are usually thicker than the Italian flat pasta. Especially in the southwestern part of the country, the predominant variety of noodles are '' Spätzle'', made with a large number of eggs, and ''
Noodles, made from wheat flour and egg, are usually thicker than the Italian flat pasta. Especially in the southwestern part of the country, the predominant variety of noodles are '' Spätzle'', made with a large number of eggs, and ''
 With the exception of mustard for sausages, German dishes are rarely hot and spicy; the most popular herbs and spices are traditionally
With the exception of mustard for sausages, German dishes are rarely hot and spicy; the most popular herbs and spices are traditionally  Mustard (''Senf'') is a very common accompaniment to sausages and can vary in strength, the most common version being ''Mittelscharf'' (medium hot), which is somewhere between traditional English and French mustards in strength.
Mustard (''Senf'') is a very common accompaniment to sausages and can vary in strength, the most common version being ''Mittelscharf'' (medium hot), which is somewhere between traditional English and French mustards in strength.
 A wide variety of
A wide variety of
File:Schoko-Osterhase IMGP1551 smial wp.jpg, Chocolate Easter Bunny
File:Juravolksfest Neumarkt 2013 - 021.JPG, Oktoberfest Gingerbread
Christmas-goose-(Weihnachtsgans) 1.jpg, Roast Christmas goose
File:Cookies - Till Westermayer.jpg, Christmas cookies
File:Rotkaeppchen Sekt Riesling Trocken.jpg, New Year Sekt
Apart from Christmas, nearly all other Christian holidays and seasons have special dishes associated with them, varying regionally and by denomination. The Easter season, for instance, is typically associated with painted Easter eggs, ''Osterbrot'' and a meal of freshwater fish on Good Friday. Likewise, Saint Sylvester's Day is often celebrated with a meal of

 Since a beer tax law was changed in 1993, many breweries served this trend of mixing beer with other drinks by selling bottles of pre-mixed beverages. Examples are ''Bibob'' (by
Since a beer tax law was changed in 1993, many breweries served this trend of mixing beer with other drinks by selling bottles of pre-mixed beverages. Examples are ''Bibob'' (by
 Franconia, a major region consisting roughly of the northern half of
Franconia, a major region consisting roughly of the northern half of
 Typical for Hessen are ''Frankfurter Rippchen'', a spiked
Typical for Hessen are ''Frankfurter Rippchen'', a spiked 

 In general the cuisine is very hearty and features many peculiarities of central Germany such as a great variety of
In general the cuisine is very hearty and features many peculiarities of central Germany such as a great variety of
Facts and figures on German agricultural exports
Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture Several food products are internationally known brands.
File:Gummi Bears in Action 55.JPG, Gummy bears
File:Jägermeister.jpg, Jägermeister liqueur
File:Dinkelbrezelchen.jpg, Mini pretzels
File:Ritter Sport - english.png,
German Foods Official Website
Taste Atlas: Top 100 Most Popular Foods in Germany
{{Authority control

Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
itself is part of the larger cultural region of Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, sharing many culinary traditions with neighbouring countries such as Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
. Southern regions, like Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
and Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
, share dishes with Austrian cuisine and parts of Swiss cuisine.
The Michelin Guide
The Michelin Guides ( ) are a series of guide books that have been published by the French tyre company Michelin since 1900. The Guide awards up to three Michelin stars for excellence to a select few establishments. The acquisition or loss of ...
of 2015 awarded a three-star ranking (the highest designation) to 11 restaurants in Germany, while 38 more received two-star rankings and 233 one-star rankings. , Germany had the fourth-highest number of Michelin three-star restaurants in the world, after Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
.
Hot foods
Meat
 The average annual meat consumption is per person. The most common varieties are pork, poultry and beef. Other varieties of meat are widely available, but are considered to be insignificant.
Source: Statista.com, 2017
Meat is usually
The average annual meat consumption is per person. The most common varieties are pork, poultry and beef. Other varieties of meat are widely available, but are considered to be insignificant.
Source: Statista.com, 2017
Meat is usually braised
Braising (from the French word ''braiser'') is a combination-cooking method that uses both wet and dry heats: typically, the food is first browned at a high temperature, then simmered in a covered pot in cooking liquid (such as wine, broth, coc ...
; fried dishes also exist, but these recipes usually originate from France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. Several cooking methods used to soften tough cuts have evolved into national specialties, including ''Sauerbraten
Sauerbraten is a traditional German roast of heavily marinated meat. It is regarded as a national dish of Germany, and is frequently served in German-style restaurants internationally. It can be prepared from a variety of meats, most often from ...
'' (sour roast), involving marinating beef, horse meat or venison in a vinegar or wine vinegar mixture over several days.
 A long tradition of sausage-making exists in Germany; more than 1,500 different types of sausage (german: Wurst) are made. Most ''Wurst'' is made with natural casings of pork, sheep or lamb intestines. Among the most popular and most common are '' Bratwurst'', usually made of ground pork and spices, the ''Wiener'' (Viennese), which may be pork or beef and is smoked and fully cooked in a water bath, and ''Blutwurst'' (
A long tradition of sausage-making exists in Germany; more than 1,500 different types of sausage (german: Wurst) are made. Most ''Wurst'' is made with natural casings of pork, sheep or lamb intestines. Among the most popular and most common are '' Bratwurst'', usually made of ground pork and spices, the ''Wiener'' (Viennese), which may be pork or beef and is smoked and fully cooked in a water bath, and ''Blutwurst'' (blood sausage
A blood sausage is a sausage filled with blood that is cooked or dried and mixed with a filler until it is thick enough to solidify when cooled. Most commonly, the blood of pigs, sheep, lamb, cow, chicken, or goose is used.
In Europe and the ...
) or ''Schwarzwurst'' (black sausage) made from blood (often of pigs or geese). Thousands of types of cold cuts also are available which are also called "Wurst" in German. There are many regional specialties, such as the '' Münchner Weißwurst'' (Munich white sausage) popular in Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
or the '' Currywurst'' (depending on region, either a steamed pork sausage or a version of the ''Bratwurst'', sliced and spiced with curry ketchup) popular in the metropolitan areas of Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
, Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
and the Ruhr Area
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
. Strict regulations governing what may and may not be put into them have been in force in Germany since the 13th century. In the market ordinance of Landshut in 1236, it was set down that only top-quality meat could be made into sausages. Döner kebab
Doner kebab (, ; tr, döner or , ), also spelled döner kebab, is a type of kebab, made of meat cooked on a vertical rotisserie. Seasoned meat stacked in the shape of an inverted cone is turned slowly on the rotisserie, next to a vertical cook ...
sales reach more than 3.5 billion euros each year, making it one of the most popular fast food items in the country.
Fish
trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salm ...
, pike, carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
, and European perch also are listed frequently. Seafood traditionally was restricted to the northern coastal areas, except for pickled herring
Pickled herring is a traditional way of preserving herring as food by pickling or curing.
Most cured herring uses a two-step curing process: it is first cured with salt to extract water; then the salt is removed and the herring is brined in ...
, which was often served in a Fischbrötchen, as ''Rollmops
Rollmops () are pickled herring fillets, rolled into a cylindrical shape, often around a savoury filling.
Presentation
The filling usually consists of onion, sliced pickled gherkin, or green olive with pimento. Rollmops are often skewered with ...
'' (a pickled herring fillet rolled into a cylindrical shape around a piece of pickled gherkin or onion), or '' Brathering'' (fried, marinated herring).
Today, many sea fish, such as fresh herring, tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: ...
, mackerel, salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus '' Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Onco ...
and sardines, are well established throughout the country. Prior to the industrial revolution and the ensuing pollution of the rivers, salmon were common in the rivers Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
, Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
, and Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
and only slowly started to return along with a growing consciousness for environmental questions and resulting measures, such as state-of-the-art sewage plant and reduction of agricultural deposits.
Fish fingers, known as Fischstäbchen (lit.: "fish sticklets"), are a popular processed food
Convenience food, also called tertiary processed food, is food that is commercially prepared (often through processing) to optimise ease of consumption. Such food is usually ready to eat without further preparation. It may also be easily p ...
made using whitefish such as cod, haddock or pollock, which has been battered or breaded.
Vegetables
Vegetables are often used instew
A stew is a combination of solid food ingredients that have been cooked in liquid and served in the resultant gravy. A stew needs to have raw ingredients added to the gravy. Ingredients in a stew can include any combination of vegetables a ...
s or vegetable soups, but are also served as side dishes. Carrots, cauliflower, turnips, spinach, peas, beans, broccoli and many types of cabbage are very common. Fried onions are a common addition to many meat dishes throughout the country. Circa 1900, carrots were sometimes roasted in water, with the broth used in place of coffee.
Asparagus is a popular seasonal side or main dish with a yearly per-capita consumption of . The white variety is especially popular in Germany and more common than green asparagus. Restaurants will sometimes devote an entire menu to nothing but white asparagus when it is in season. Spargel season (german: Spargelzeit or ''Spargelsaison'') traditionally begins in mid-April and ends on St. John's Day (24 June).
Structure of meals

Breakfast
Breakfast is the first meal of the day usually eaten in the morning. The word in English refers to breaking the fasting period of the previous night.Anderson, Heather Arndt (2013)''Breakfast: A History'' AltaMira Press. Various "typical" or " ...
(''Frühstück'') commonly consists of bread, toast, or bread rolls with butter or margarine, cold cuts, cheeses, jam (''Konfitüre'' or more commonly called ''Marmelade''), honey and eggs (typically boiled). Common drinks at breakfast are coffee, tea, milk, cocoa (hot or cold) or fruit juices. It is very common to eat hearty toppings at breakfast, including deli meats like ham, salted meats, salami and meat-based spreads such as '' Leberwurst'' (liver sausage),''Teewurst'' or ''Mettwurst'' and cheeses such as Gouda, ''Frischkäse'' (cream cheese), Brie, ''Harzer Roller'', ''Bergkäse'' and more. Most bakeries tend to sell ''belegte Brötchen'' (sandwiches from bread rolls), especially in the morning, for people on the go.
Traditionally, the main meal of the day has been lunch (''Mittagessen''), eaten around noon. Dinner (''Abendessen'' or ''Abendbrot'') was always a smaller meal, often consisting only of a variety of breads, meat or sausages, cheese and some kind of vegetables, similar to breakfast, or possibly sandwiches. Smaller meals added during the day bear names such as ''Vesper'' (in the south), ''Brotzeit'' (bread time, also in the south), ''Kaffee und Kuchen'' (, literally for "coffee and cake"), or ''Kaffeetrinken''. It is a very German custom and comparable with the English five-o'clock tea. It takes time between lunch and dinner, often on Sundays with the entire family.
However, in Germany, as in other parts of Europe, dining habits have changed over the last 50 years. Today, many people eat only a small meal in the middle of the day at work, often also a second breakfast, and enjoy a hot dinner in the evening at home with the whole family.
For others, the traditional way of eating is still rather common, not only in rural areas. Breakfast is still very popular and may be elaborate and extended on weekends, with friends invited as guests; the same holds for coffee and cake. Since the 1990s, the Sunday brunch
Brunch is a meal eaten between 10:00 a.m. and 2:00 p.m., sometimes accompanied by alcoholic drinks (typically champagne or a cocktail). The meal originated in the British hunt breakfast. The word ''brunch'' is a portmanteau of ''breakfast'' ...
has also become common, especially in city cafés.
Side dishes
 Noodles, made from wheat flour and egg, are usually thicker than the Italian flat pasta. Especially in the southwestern part of the country, the predominant variety of noodles are '' Spätzle'', made with a large number of eggs, and ''
Noodles, made from wheat flour and egg, are usually thicker than the Italian flat pasta. Especially in the southwestern part of the country, the predominant variety of noodles are '' Spätzle'', made with a large number of eggs, and ''Maultaschen
(singular ''Maultasche'' , ) are a kind of large meat-filled dumpling in Swabian cuisine. They consist of sheets of pasta dough filled with minced meat, smoked meat, spinach, bread crumbs and onions and flavored with various herbs and spices ...
'', traditional stuffed noodles reminiscent of ravioli.
Besides noodles, potatoes are common. Potatoes entered the German cuisine in the late 17th century, and were almost ubiquitous in the 19th century and since. They most often are boiled (in salt water, ), but mashed
Mashed may refer to:
* Mashed, that created from mash ingredients
* Mashed, the result of a mashing
* Mashed, the result of a mashup (music)
* ''Mashed'' (album), a 2007 mashup album
* ''Mashed'' (video game), a vehicular combat video game
* M ...
( or ''Kartoffelbrei'') and pan-roasted potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
es () also are traditional. French fries, called , (spoken as "Pom fritz" or, respectively, "Pommès", deviating from the French pronunciation which would be "Pom freet" or "Pom") or regionally as in German, are a common style of fried potatoes; they are traditionally offered with either ketchup or mayonnaise, or, as (lit. fries red/white), with both.
Also common are dumpling
Dumpling is a broad class of dishes that consist of pieces of dough (made from a variety of starch sources), oftentimes wrapped around a filling. The dough can be based on bread, flour, buckwheat or potatoes, and may be filled with meat, ...
s (including ''Klöße'' as the term in the north or ''Knödel'' as the term in the south) and in southern Germany potato noodles, including '' Schupfnudeln'', which are similar to Italian '' gnocchi''.
Salad
A salad is a dish consisting of mixed, mostly natural ingredients with at least one raw ingredient. They are typically served at room temperature or chilled, though some can be served warm. Condiments and salad dressings, which exist in a va ...
s, also modern variations, as well as vegetarian dishes are increasingly popular in Germany.
Spices and condiments
 With the exception of mustard for sausages, German dishes are rarely hot and spicy; the most popular herbs and spices are traditionally
With the exception of mustard for sausages, German dishes are rarely hot and spicy; the most popular herbs and spices are traditionally parsley
Parsley, or garden parsley (''Petroselinum crispum'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae that is native to the central and eastern Mediterranean region (Sardinia, Lebanon, Israel, Cyprus, Turkey, southern Italy, Greece, ...
, thyme
Thyme () is the herb (dried aerial parts) of some members of the genus ''Thymus'' of aromatic perennial evergreen herbs in the mint family Lamiaceae. Thymes are relatives of the oregano genus '' Origanum'', with both plants being mostly indigen ...
, laurel, chive
Chives, scientific name ''Allium schoenoprasum'', is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaryllidaceae that produces edible leaves and flowers. Their close relatives include the common onions, garlic, shallot, leek, scallion, an ...
s, black pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, known as a peppercorn, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in dia ...
(used in small amounts), juniper berries, nutmeg
Nutmeg is the seed or ground spice of several species of the genus ''Myristica''. ''Myristica fragrans'' (fragrant nutmeg or true nutmeg) is a dark-leaved evergreen tree cultivated for two spices derived from its fruit: nutmeg, from its seed, an ...
, and caraway. Cardamom
Cardamom (), sometimes cardamon or cardamum, is a spice made from the seeds of several plants in the genera '' Elettaria'' and '' Amomum'' in the family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to the Indian subcontinent and Indonesia. They ar ...
, anise seed
Anise (; '), also called aniseed or rarely anix is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to Eurasia.
The flavor and aroma of its seeds have similarities with some other spices and herbs, such as star anise, fennel, licorice, and tar ...
, and cinnamon are often used in sweet cakes or beverages associated with Christmas time, and sometimes in the preparation of sausages, but are otherwise rare in German meals. Other herbs and spices, such as basil, sage, oregano
Oregano (, ; ''Origanum vulgare'') is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae. It was native to the Mediterranean region, but widely naturalised elsewhere in the temperate Northern Hemisphere.
Oregano is a woody perennial ...
, and hot chili pepper
Chili peppers (also chile, chile pepper, chilli pepper, or chilli), from Nahuatl '' chīlli'' (), are varieties of the berry-fruit of plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for ...
s, have become popular since the early 1980s. Fresh dill is very common in a green salad
A salad is a dish consisting of mixed, mostly natural ingredients with at least one raw ingredient. They are typically served at room temperature or chilled, though some can be served warm. Condiments and salad dressings, which exist in a va ...
or fish fillet.
 Mustard (''Senf'') is a very common accompaniment to sausages and can vary in strength, the most common version being ''Mittelscharf'' (medium hot), which is somewhere between traditional English and French mustards in strength.
Mustard (''Senf'') is a very common accompaniment to sausages and can vary in strength, the most common version being ''Mittelscharf'' (medium hot), which is somewhere between traditional English and French mustards in strength. Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf ( , , ; often in English sources; Low Franconian and Ripuarian: ''Düsseldörp'' ; archaic nl, Dusseldorp ) is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in ...
, similar to French's Deli Mustard with a taste that is very different from Dijon, and the surrounding area are known for its particularly spicy mustard, which is used both as a table condiment and in local dishes such as ''Senfrostbraten'' (pot roast with mustard). In the southern parts of the country, a sweet variety of mustard is made which is almost exclusively served with the Bavarian speciality ''Weißwurst
A Weisswurst (German ''Weißwurst'' , literally ''white sausage''; bar, Weißwuascht) is a traditional Bavarian sausage made from minced veal and pork back bacon. It is usually flavored with parsley, lemon, mace, onions, ginger and cardamom, ...
''. German mustard is usually considerably less acidic than American varieties.
Horseradish is commonly used as a condiment either on its own served as a paste, enriched with cream (''Sahnemeerrettich''), or combined with mustard. In some regions of Germany, it is used with meats and sausages where mustard would otherwise be used. Its use in Germany has been documented to the 16th century, when it was used as medicine, and as a food, whereby its leaves were consumed as a vegetable.
Garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus '' Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Welsh onion and Chinese onion. It is native to South Asia, Central Asia and northeas ...
has never played a large role in traditional German cuisine, but has risen in popularity in recent decades due to the influence of French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, Greek, and Turkish cuisines. Ramson
''Allium ursinum'', known as wild garlic, ramsons, cowleekes, cows's leek, cowleek, buckrams, broad-leaved garlic, wood garlic, bear leek, Eurasian wild garlic or bear's garlic, is a bulbous perennial flowering plant in the amaryllis family Amary ...
, a rediscovered herb from earlier centuries, has become quite popular again since the 1990s.
Desserts
 A wide variety of
A wide variety of cake
Cake is a flour confection made from flour, sugar, and other ingredients, and is usually baked. In their oldest forms, cakes were modifications of bread, but cakes now cover a wide range of preparations that can be simple or elaborate ...
s, tarts and pastries
Pastry is baked food made with a dough of flour, water and shortening (solid fats, including butter or lard) that may be savoury or sweetened. Sweetened pastries are often described as '' bakers' confectionery''. The word "pastries" suggest ...
are served throughout the country, most commonly made with fresh fruit. Apples, plums, strawberries, and cherries are used regularly in cakes. Cheesecake is also very popular, often made with quark
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly ...
. ''Schwarzwälder Kirschtorte
Black Forest gâteau or Black Forest cake (American English) is a chocolate sponge cake with a rich cherry filling based on the German dessert (), literally "Black Forest Cherry-torte".
Typically, Black Forest gateau consists of several laye ...
'' (Black Forest cake, made with cherries) is probably the most well-known example of a wide variety of typically German tortes filled with whipped or butter cream.
German doughnuts (which have no hole) are usually balls of yeast dough with jam or other fillings, and are known as '' Berliner'', ''Pfannkuchen'' (in Berlin and Eastern Germany), '' Kreppel'' or '' Krapfen'', depending on the region. ''Eierkuchen'' or ''Pfannkuchen'' are large (usually around 20–24 cm in diameter), and relatively thin (~5mm) pancakes, comparable to the French '' crêpes''. They are served covered with sugar, jam or syrup. Salty variants with cheese, ground meat or bacon exist as well as variants with apple slices baked in (called ''Apfelpfannkuchen'', literally for ''apple pancakes''), but they are usually considered to be main dishes rather than desserts. In some regions, ''Eierkuchen'' are filled and then wrapped; in others, they are cut into small pieces and arranged in a heap (called '' Kaiserschmarrn'', often including raisins baked in). The word ''Pfannkuchen'' means pancake in most parts of Germany.
A popular dessert in northern Germany is '' Rote Grütze'', red fruit pudding, which is made with black and red currants, raspberries and sometimes strawberries or cherries cooked in juice with corn starch as a thickener. It is traditionally served with cream, but also is served with vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus '' Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla ('' V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the plants produce the fruit from whic ...
sauce, milk or whipped cream. ''Rhabarbergrütze'' (rhubarb pudding) and ''Grüne Grütze'' (gooseberry fruit pudding) are variations of the ''Rote Grütze''. A similar dish, ''Obstkaltschale'', may also be found all around Germany.
Ice cream
Ice cream is a sweetened frozen food typically eaten as a snack or dessert. It may be made from milk or cream and is flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit such as ...
and sorbets are also very popular. Italian-run ice cream parlours were the first large wave of foreign-run eateries in Germany, which began around the mid-1850s, becoming widespread in the 1920s. '' Spaghettieis'', which resembles spaghetti, tomato sauce, and ground cheese on a plate, is a popular ice cream dessert.
Holidays
On the Christmas Days following Christmas Eve, roast goose is a staple of Christmas Day meals. It is sometimes replaced with European carp, particularly in Southern areas. The carp is cut into pieces, coated in breadcrumbs and fried in fat. Common side dishes are potato salad, cucumber salad or potatoes.carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
. The fasting season, which lasts from Ash Wednesday
Ash Wednesday is a holy day of prayer and fasting in many Western Christian denominations. It is preceded by Shrove Tuesday and falls on the first day of Lent (the six weeks of penitence before Easter). It is observed by Catholics in the ...
to Easter Sunday, is observed in many areas, especially Catholic ones. The preceding carnival season is known for ''Berliner Pfannkuchen (German doughnuts)''. The last months of the year, especially the Advent and Christmas season, is often associated with ''Weihnachtsgebäck'' (literally Christmas bakery products), which includes sweet and spicy foods like '' Weihnachts-/Christstollen'', ''Lebkuchen
(), or , are a honey-sweetened German cake molded cookie or bar cookie that has become part of Germany's Christmas traditions. It is similar to gingerbread.
Etymology
The etymology of ''Leb-'' in the term ''Lebkuchen'' is uncertain. Pro ...
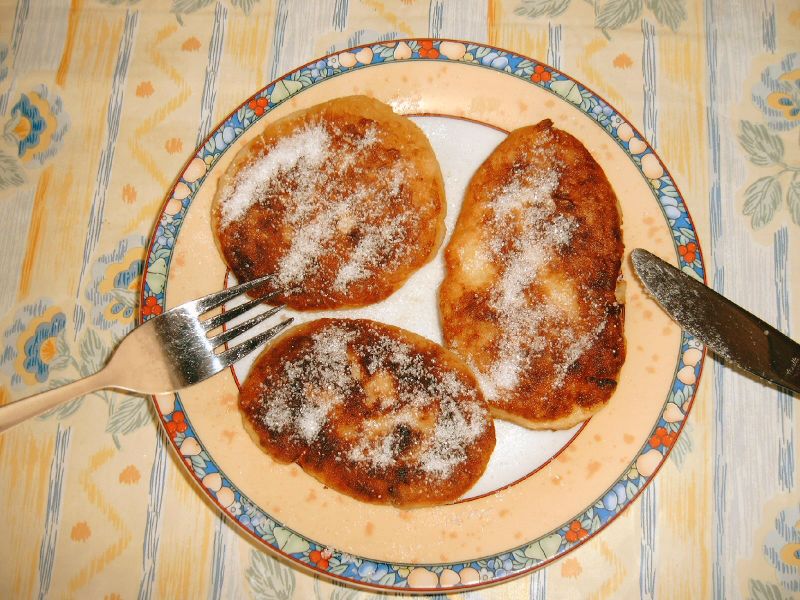
'', '' Spekulatius'', '' Marzipan'', '' Weihnachtsplätzchen'', '' Vanillekipferl'', '' Zimtsterne'' and '' Dominosteine''. German supermarkets also sell these products during this period. Another popular confectioneries are '' Crêpe'', ''Reibekuchen
Reibekuchen () are German potato pancakes, also known as Kartoffelpuffer (). They are common in many areas of Germany, the name "Reibekuchen" being characteristic to the Rheinland area. Reibekuchen may be served with apple sauce, pumpernickel b ...
'' and '' Eier-/Pfannkuchen'', which are sold in Christmas markets.
Bread
Bread
Bread is a staple food prepared from a dough of flour (usually wheat) and water, usually by baking. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cultures' diet. It is one of the oldest human-made f ...
(''Brot'') is a significant part of German cuisine, with the largest bread diversity in the world. Around 3000 types of breads and 1,200 different types of pastries and rolls are produced in about 13,000 bakeries.
Bread is served usually for breakfast (often replaced by bread rolls) and in the evening as (open) sandwiches, but rarely as a side dish for the main meal (popular, for example, with '' Eintopf'' or soup). The importance of bread in German cuisine is also illustrated by words such as ''Abendbrot'' (meaning supper, literally evening bread) and '' Brotzeit'' (snack, literally bread time). In fact, one of the major complaints of the German expatriate
An expatriate (often shortened to expat) is a person who resides outside their native country. In common usage, the term often refers to educated professionals, skilled workers, or artists taking positions outside their home country, either ...
s in many parts of the world is their inability to find acceptable local breads.
Regarding bread
Bread is a staple food prepared from a dough of flour (usually wheat) and water, usually by baking. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cultures' diet. It is one of the oldest human-made f ...
, German cuisine is more varied than that of any other culture. Bread types range from white wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
bread (''Weißbrot'') to grey (''Graubrot'') to black (''Schwarzbrot''), actually dark brown rye bread. Some breads contain both wheat and rye flour (hence ''Mischbrot
Mischbrot ( ) is German bread made from the mixture of wheat and rye flour with sourdough or yeast. It is known as "Gray bread" in some regions of Germany (e.g., parts of North Rhine-Westphalia, Bavaria and Hesse) or as "Black bread" in south ...
'', mixed bread), and often also wholemeal and whole seeds such as linseed, sunflower seed
The sunflower seed is the seed of the sunflower (''Helianthus annuus''). There are three types of commonly used sunflower seeds: linoleic (most common), high oleic, and sunflower oil seeds. Each variety has its own unique levels of monounsat ...
, or pumpkin seed (''Vollkornbrot''). Darker, rye-dominated breads, such as ''Vollkornbrot'' or ''Schwarzbrot'', are typical of German cuisine. ''Pumpernickel
Pumpernickel (; ) is a typically heavy, slightly sweet rye bread traditionally made with sourdough starter and coarsely ground rye. It is sometimes made with a combination of rye flour and whole rye grains ("rye berries").
At one time it was ...
'', sweet-tasting bread created by long-time-steaming instead of regular baking, is internationally well known, although not representative of German black bread as a whole. Most German breads are made with sourdough
Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by the fermentation of dough using wild lactobacillaceae and yeast. Lactic acid from fermentation imparts a sour taste and improves keeping qualities.
History
In the ''Encyclopedia of Food Microbio ...
. Whole grain is also preferred for high fiber. Germans use almost all available types of grain for their breads: wheat, rye, barley, spelt, oats, millet, corn and rice. Some breads are even made with potato starch flour. A lot of breads are Multigrain breads.
Among Germany's most popular breads are spelt (''Dinkelbrot''), rye (''Roggenbrot''), rye-wheat (''Roggenmischbrot
Mischbrot ( ) is German bread made from the mixture of wheat and rye flour with sourdough or yeast. It is known as "Gray bread" in some regions of Germany (e.g., parts of North Rhine-Westphalia, Bavaria and Hesse) or as "Black bread" in south ...
''), wheat-rye (''Weizenmischbrot''), wheat (''Weißbrot''), toast (''Toastbrot''), whole-grain (''Vollkornbrot''), wheat-rye-oats with sesame or linseed (''Mehrkornbrot''), sunflower seeds in dark rye bread
Rye bread is a type of bread made with various proportions of flour from rye grain. It can be light or dark in color, depending on the type of flour used and the addition of coloring agents, and is typically denser than bread made from wheat ...
(''Sonnenblumenkernbrot''), pumpkin seeds in dark rye bread (''Kürbiskernbrot''), potato bread (''Kartoffelbrot'') and roasted onions in light wheat-rye bread (''Zwiebelbrot'').
Bread rolls
Bread rolls, known in Germany as ''Brötchen'', which is a diminutive of ''Brot'', with regional linguistic varieties being ''Semmel'' (in South Germany), ''Schrippe'' (especially in Berlin), ''Rundstück'' (in the North and Hamburg) or ''Wecken'', ''Weck'', ''Weckle'', ''Weckli'' and ''Weckla'' (inBaden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
, Switzerland, parts of Southern Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are ...
and northern Bavaria), are common in German cuisine. A typical serving is a roll cut in half, and spread with butter or margarine. Cheese, honey, jam, Nutella, cold cuts such as ham, fish, or preserves are then placed between the two halves, or on each half separately, known as a ''belegtes Brötchen''.
Rolls are also used for snacks, or as a hotdog-style roll for '' Bratwurst, Brätel, Fleischkäse'' or ''Schwenker
Schwenker is a local term from the German state of Saarland, the Mosel Valley and big parts of Rheinland Pfalz and is used in three ways, all relating to the same grilled meat:
# Schwenker or ''Schwenkbraten'' is a marinated pork neck steak whi ...
''/''Schwenkbraten''.
'' Franzbrötchen'', which originated in the area of Hamburg, is a small, sweet pastry roll baked with butter and cinnamon.
Beverages
Alcoholic drinks

Beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
is very common throughout all parts of Germany, with many local and regional breweries producing a wide variety of beers. The pale lager
Pale lager is a very pale-to- golden-colored lager beer with a well- attenuated body and a varying degree of noble hop bitterness.
The brewing process for this beer developed in the mid-19th century, when Gabriel Sedlmayr took pale ale bre ...
pilsner, a style developed in the mid-19th century, is predominant in most parts of the country today, whereas wheat beer ('' Weißbier''/''Weizen'') and other types of lager are common, especially in Bavaria. A number of regions have local specialties, many of which, like ''Weißbier'', are more traditionally brewed ale
Ale is a type of beer brewed using a warm fermentation method, resulting in a sweet, full-bodied and fruity taste. Historically, the term referred to a drink brewed without hops.
As with most beers, ale typically has a bittering agent to bala ...
s. Among these are '' Altbier'', a dark beer available around Düsseldorf and the lower Rhine, '' Kölsch'', a similar style, but light in color, in the Cologne area, and the low-alcohol '' Berliner Weiße'', a sour beer made in Berlin that is often mixed with raspberry or woodruff syrup. Since the reunification of 1990, ''Schwarzbier
, black beer, is a dark lager that originated in Germany. It has an opaque, black colour with hints of chocolate or coffee flavours, and is generally around 5% ABV. It is similar to stout in that it is made from roasted malt, which gives it its ...
'', which was common in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In t ...
, but could hardly be found in West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 ...
, has become increasingly popular in Germany as a whole. Beer may also be mixed with other beverages such as pils or lager and carbonated lemonade: '' Radler'' (lit: cyclist), ''Alsterwasser'' (lit: water from the river Alster).
 Since a beer tax law was changed in 1993, many breweries served this trend of mixing beer with other drinks by selling bottles of pre-mixed beverages. Examples are ''Bibob'' (by
Since a beer tax law was changed in 1993, many breweries served this trend of mixing beer with other drinks by selling bottles of pre-mixed beverages. Examples are ''Bibob'' (by Köstritzer
The Köstritzer brewery is one of the oldest producers of Schwarzbier (black beer) in Germany. It is in Bad Köstritz, close to Gera in Thuringia.
History
The brewery was first mentioned in inheritance tax documents as "Köstritzer Inheritan ...
), ''Veltins V+'', ''Mixery'' (by Karlsberg), Dimix (by Diebels) and ''Cab'' (by Krombacher).
Cider is also popular in Germany. It is called ''Most'' or ''Ebbelwoi''. In Hessen, people drink it in a Bembel.
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
is also popular throughout the country. German wine
German wine is primarily produced in the west of Germany, along the river Rhine and its tributaries, with the oldest plantations going back to the Roman era. Approximately 60 percent of German wine is produced in the state of Rhineland-Pala ...
comes predominantly from the areas along the upper and middle Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
and its tributaries. Riesling and Silvaner are among the best-known varieties of white wine, while Spätburgunder and Dornfelder
Dornfelder is a dark-skinned variety of grape of German origin used for red wine.
are important German red wines. The sweet German wines sold in English-speaking countries seem mostly to cater to the foreign market, as they are rare in Germany.
''Korn
Korn (stylized as KoЯn, or occasionally KoRn) is an American nu metal band from Bakersfield, California, formed in 1993. The band is notable for pioneering the nu metal genre and bringing it into the mainstream.
Originally formed in 1993 ...
'', a German spirit made from malt (wheat, rye or barley), is consumed predominantly in the middle and northern parts of Germany. ''Obstler'', on the other hand, distilled from apples and pears, plums, cherries ('' Kirschwasser''), or mirabelle plums, is preferred in the southern parts. The term ''Schnaps'' refers to both kinds of hard liquors.
All cold drinks in bars and restaurants are sold in glasses with a calibration mark (''Eichstrich'') that is frequently checked by the ''Eichamt'' (~ Bureau of Weights and Measures) to ensure the guest is getting as much as is offered in the menu.
Non-alcoholic drinks
Coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
is also very common, not only for breakfast, but also accompanying a piece of cake (''Kaffee und Kuchen'') in the afternoon, usually on Sundays or special occasions and birthdays. It is generally filter coffee
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
, which is weaker than espresso
Espresso (, ) is a coffee-brewing method of Italian origin, in which a small amount of nearly boiling water (about ) is forced under of pressure through finely-ground coffee beans. Espresso can be made with a wide variety of coffee beans a ...
. Coffeeshops are also very common in Germany. Tea is more common in the northwest. East Frisians traditionally have their tea with cream and rock candy (''Kluntje''). Germany has the tenth highest per capita coffee consumption worldwide.
Popular soft drinks include '' Schorle'', juice or wine mixed with sparkling mineral water, with ''Apfelschorle
Apfelschorle () (Apple Spritzer), also Apfelsaftschorle (Apple juice spritzer) or Apfelsaft gespritzt (Splashed apple juice) in German, is a popular soft drink in Switzerland, Germany, and Austria. It consists of carbonated mineral water and a ...
'' being popular all over Germany, and '' Spezi'', made with cola and an orange-flavored drink such as Fanta
Fanta is an American-owned German brand of fruit-flavored carbonated soft drinks created by Coca-Cola Deutschland under the leadership of German businessman Max Keith. There are more than 200 flavors worldwide. Fanta originated in Germany as ...
. Germans are unique among their neighbors in preferring bottled, carbonated mineral water, either plain (''Sprudel'') or flavored (usually lemon) to noncarbonated ones.
Drinking water of excellent quality is available everywhere and at any time in Germany. Water provided by the public water utilities can be had without hesitation directly from the tap. Usually, no chlorine is added. Drinking water is controlled by state authority to ensure it is potable. Regulations are even stricter than those for bottled water (see Trinkwasserverordnung).
Regional cuisine
German regional cuisine can be divided into many varieties such as Bavarian cuisine (southern Germany) orThuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
n (central Germany) and Lower Saxon cuisine.
Baden-Württemberg
This southwest German state is divided into Baden and Swabia, whose cuisines are slightly different. Due to Baden's physiogeographical situation in theUpper Rhine Plain
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben (German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the s ...
, with Germany's warmest climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
and fruitful volcanic soils, it had good prerequisites to develop a high-quality gastronomy. Nationwide, this region features the highest density of star-rated restaurants; the municipality of Baiersbronn
Baiersbronn is a municipality and a village in the district of Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is situated in the Black Forest on the Murg river. Nearby is the mountain of Rinkenkopf (759.6 m) with its hillfort, t ...
is especially well-known for its fine-dining restaurants. Swabian cuisine tends to be heavier than Badish cuisine. Famous dishes of Baden-Württemberg are Maultaschen
(singular ''Maultasche'' , ) are a kind of large meat-filled dumpling in Swabian cuisine. They consist of sheets of pasta dough filled with minced meat, smoked meat, spinach, bread crumbs and onions and flavored with various herbs and spices ...
, Spätzle and Black Forest cake.
Bavaria
The Bavarian dukes, especially theWittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate ...
family, developed Bavarian cuisine and refined it to be presentable to the royal court. This cuisine has belonged to wealthy households, especially in cities, since the 19th century. The (old) Bavarian cuisine is closely connected to Czech cuisine and Austrian cuisine (especially from Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
and Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
), mainly through the Wittelsbach and Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
families. Already in the beginning, Bavarians were closely connected to their neighbours in Austria through linguistic, cultural and political similarities, which also reflected on the cuisine.
A characteristic Bavarian cuisine was further developed by both groups, with a distinct similarity to Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper ...
n and Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
n cuisine. A Bavarian speciality is the Brotzeit, a savoury snack, which would originally be eaten between breakfast and lunch.
Bavaria is a part of Southeastern Germany, including the city of Munich and spreading to Germany's borders with Austria and the Czech Republic. The region is located at higher elevations, and is known for yielding beet and potato crops and also for the production of fine beers.
Franconia
 Franconia, a major region consisting roughly of the northern half of
Franconia, a major region consisting roughly of the northern half of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
, has its own distinct cuisine, so distinct in fact that there is said to be a "White Sausage Equator" ('' Weißwurstäquator'') that separates Franconia from the rest of Bavaria. This is a reference to the fact that those north of the Weißwurstequator do not generally eat the popular Weißwurst
A Weisswurst (German ''Weißwurst'' , literally ''white sausage''; bar, Weißwuascht) is a traditional Bavarian sausage made from minced veal and pork back bacon. It is usually flavored with parsley, lemon, mace, onions, ginger and cardamom, ...
common in southern Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
. A characteristic of Franconian food would include gravies (Soßen), food derived from potatoes, various meats, and, of course, bread. Franconia is well known throughout Germany for its heavy foods covered in gravy. A good example of Franconian food would be Schäufele
''Schäufele'' (also "Schäuferle", "Schüfeli", "Schäuferla" or "Schäufelchen") is a traditional dish from the south of Germany. It is made from the pig's shoulder meat, which gives the dish its name, "Schäufele", or the pig's scapula.
Dep ...
and Klöße, which is a pork shoulder served with traditional potato dumplings (Klöße or Knödel) covered in a gravy.
Hamburg
Due to its centuries-old history as a harbour town, the traditional cuisine ofHamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
is very diversified and sapid as the supply of ingredients was safe. Until the 20th century, it was predominantly characterized by the extensive choice of different kinds of fish
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as we ...
from the river Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
and the quick access to both the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
and the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
, both being roughly 100 kilometers away from the city center. The neighboring regions supplied the city state with fresh vegetable
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the edible flower, flowers, ...
s, fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in partic ...
came mainly from a region called Altes Land just southwest of Hamburg and until industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
, the neighbourhood of Wilhelmsburg was considered the ‘milk isle’ of Hamburg.
International trade made spice
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices a ...
s and exotic food items from Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
available since the 16th century, and these were soon incorporated into civic kitchens. From this basis, the cuisine of Hamburg developed its current characteristics thanks to the supraregional harmonization of the Northern German and Scandinavian cuisine. Due to its high economic importance, Hamburg features many internationally recognized gourmet restaurants: 11 of them were awarded a Michelin star
The Michelin Guides ( ) are a series of guide books that have been published by the French tyre company Michelin since 1900. The Guide awards up to three Michelin stars for excellence to a select few establishments. The acquisition or loss of a ...
in 2010.
Hessen
 Typical for Hessen are ''Frankfurter Rippchen'', a spiked
Typical for Hessen are ''Frankfurter Rippchen'', a spiked pork cutlet Pork cutlet may refer to:
* Tonkatsu, a Japanese breaded pork cutlet
* Dongaseu, a Korean breaded pork cutlet
* Kotlet schabowy, a Polish breaded pork cutlet
See also
* pork
* cutlet
Cutlet (derived from French ''côtelette'', ''côte'', "ri ...
, which is often served with sauerkraut
Sauerkraut (; , "sour cabbage") is finely cut raw cabbage that has been fermented by various lactic acid bacteria. It has a long shelf life and a distinctive sour flavor, both of which result from the lactic acid formed when the bacteria ...
and mashed potatoes.
Also from Hessen comes the Frankfurt green sauce (''"Grüne Sauce''"). It is a cold sauce based on sour cream with the local herbs borage, chervil, cress, parsley, pimpinelle, sorrel and chives. The start of the season is traditionally Maundy Thursday
Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday (also known as Great and Holy Thursday, Holy and Great Thursday, Covenant Thursday, Sheer Thursday, and Thursday of Mysteries, among other names) is the day during Holy Week that commemorates the Washing of th ...
(''"Gründonnerstag"''; which means ''"green Thursday"'' in German). Green sauce is mostly served with potatoes and boiled eggs.
One of the best-known specialties from Hesse is the Frankfurter Kranz, a buttercream cake whose shape is reminiscent of a crown; a reminiscence of Frankfurt as the historical coronation city of the German emperors.
Cider (''"Apfelwein"'' in German, or ''"Äppelwoi"'' in the Hessian dialect) is also very popular in and around Frankfurt. In the historic district Sachsenhausen
Sachsenhausen () or Sachsenhausen-Oranienburg was a German Nazi concentration camp in Oranienburg, Germany, used from 1936 until April 1945, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in May later that year. It mainly held political prisoners ...
there is the so-called Cider Quarter (''"Äppelwoiviertel"''), where there are numerous taverns that offer cider, especially in the summer months. In the cider taverns, '' "Handkäs mit Musik"'' is offered as a snack, a sour milk cheese served in a marinade
Marinating is the process of soaking foods in a seasoned, often acidic, liquid before cooking. The origin of the word alludes to the use of brine (''aqua marina'' or sea water) in the pickling process, which led to the technique of adding flavo ...
of onions, vinegar and spices.
Palatinate/Pfalz
The kitchen of the Palatinate, a region in the south of Rhineland-Palatinate, is largely determined by regional dishes. They are sometimes quite hearty, not least because the cooking recipes were sometimes developed in times of need or in the context of heavy physical work. You also like to eat hotter than in many other German regional kitchens. Probably the best-known dish is the Pfälzer Saumagen, a pork stomach stuffed with sausage meat, bacon, potatoes and spices. The dish became famous as the favorite meal of Federal Chancellor Helmut Kohl, who especially enjoyed serving this dish at state receptions. In the Palatinate, the salty-crustDampfnudel
A ' ( lit. "steam-noodle"; plural ', Alsatian: ) is a dumpling eaten as a meal or as a dessert in Germany, Austria and in France (Alsace- Moselle). It is a typical dish in southern Germany.
History
There are ' city gates in Freckenfeld a ...
is a traditional main dish, either with sweet side dishes (for example wine sauce, custard
Custard is a variety of culinary preparations based on sweetened milk, cheese, or cream cooked with egg or egg yolk to thicken it, and sometimes also flour, corn starch, or gelatin. Depending on the recipe, custard may vary in consistency fr ...
or boiled fruit such as plums, pears or the like) or with salty side dishes (for example potato soup, vegetable soups, goulash or pork) is eaten.
Thuringia
Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, grapes, sugarbeets, and barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
grow well, along with a variety of vegetables, which grow near Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits in ...
, the state's capital. Cauliflower [], cabbage (savoy, red, white) [], kohlrabi [], and broccoli [] grow by traditional means near Erfurt. Tomatoes, lettuce, broad beans, onions, and cucumbers are grown in the eastern portion of the region near Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
under glass centers on about of land. Thuringia is the second-largest herb
In general use, herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables and other plants consumed for macronutrients, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicina ...
-growing region in Germany; the town of Kölleda was once considered the "peppermint
Peppermint (''Mentha'' × ''piperita'') is a hybrid species of mint, a cross between watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in many regions of the world.Euro+Med Plantb ...
town", where herb growers used to congregate to study herb cultivation.
One-third of Thuringia is covered in forest, and is considered to be one of the best game-hunting regions in Germany. Anyone holding a valid hunting license and a local hunting permit for the area may hunt for game such as red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of ...
, roe deer
The roe deer (''Capreolus capreolus''), also known as the roe, western roe deer, or European roe, is a species of deer. The male of the species is sometimes referred to as a roebuck. The roe is a small deer, reddish and grey-brown, and well-adapt ...
, wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species i ...
, rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit sp ...
, duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
, and mouflon (mountain sheep). Pheasant and capercaillie
''Tetrao'' is a genus of birds in the grouse subfamily known as capercaillies. They are some of the largest living grouse.
Taxonomy
The genus ''Tetrao'' was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of hi ...
are protected game species that may not be hunted. The wooded areas also contain a wide variety of edible mushroom
Edible mushrooms are the fleshy and edible fruit bodies of several species of macrofungi (fungi which bear fruiting structures that are large enough to be seen with the naked eye). They can appear either below ground ( hypogeous) or above gro ...
s, such as chestnut mushrooms, porcini, and chanterelles, along with wild berries, such as blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, b ...
, cranberries
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry m ...
, raspberries, and blackberries, which are all traditional accompaniments to game dishes.
The most famous foods from Thuringia are Thuringian sausages and Thuringian dumplings. The state is also known for its sausage
A sausage is a type of meat product usually made from ground meat—often pork, beef, or poultry—along with salt, spices and other flavourings. Other ingredients, such as grains or breadcrumbs may be included as fillers or extenders. ...
s; steamed, scaled, and cured varieties are all prepared. Popular varieties include Thüringer '' Mettwurst'' (a spreadable cured sausage), '' Feldkieker'' (a cured, air-dried sausage dried up to eight months), Thüringer '' Leberwurst'' (a steamed pork and liver sausage), Thüringer '' Rotwurst'' (a steamed blood sausage packed in a bladder or other natural casing) and '' Mett'' (minced pork).
Saxony
 In general the cuisine is very hearty and features many peculiarities of central Germany such as a great variety of
In general the cuisine is very hearty and features many peculiarities of central Germany such as a great variety of sauce
In cooking, a sauce is a liquid, cream, or semi-solid food, served on or used in preparing other foods. Most sauces are not normally consumed by themselves; they add flavor, moisture, and visual appeal to a dish. ''Sauce'' is a French wor ...
s which accompany the main dish and the fashion to serve ''Klöße'' or Knödel
Knödel (; and ) or Klöße (; ) are boiled dumplings commonly found in Central European and East European cuisine. Central European countries in which their variant of ''Knödel'' is popular include Austria, Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, ...
as a side dish instead of potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
es, pasta
Pasta (, ; ) is a type of food typically made from an unleavened dough of wheat flour mixed with water or eggs, and formed into sheets or other shapes, then cooked by boiling or baking. Rice flour, or legumes such as beans or lentils, ...
or rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
. Also much freshwater fish
Freshwater fish are those that spend some or all of their lives in fresh water, such as rivers and lakes, with a salinity of less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine conditions in many ways, especially the difference in levels o ...
is used in Saxon cuisine, particularly carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
and trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salm ...
as is the case throughout Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
.
The rich history of the region did and still does influence the cuisine. In the blossoming and growing cities of Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label= Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth ...
and Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
an extravagant style of cuisine is cherished (one may only think of the crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all th ...
as an ingredient in the famous Leipziger Allerlei). In other, impoverished regions where the people had to work hard to yield some harvest (e.g., the Erzgebirge), peasant dishes play a major role; famous dishes originating from there include potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
es with Quark
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly ...
, potato soup or potato with bread
Bread is a staple food prepared from a dough of flour (usually wheat) and water, usually by baking. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cultures' diet. It is one of the oldest human-made f ...
and linseed oil. In the Vogtland
Vogtland (; cz, Fojtsko) is a region spanning the German states of Bavaria, Saxony and Thuringia and north-western Bohemia in the Czech Republic. It overlaps with and is largely contained within Euregio Egrensis. The name alludes to the forme ...
region, where the peasants were wealthier, the tradition of Sunday roast remains to this day.
Cereal grain
A cereal is any grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran. Cereal grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more food ...
cultivation occupies 62% of the cultivated land in Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making i ...
. Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
, oats, and rye are grown, with the rye being grown near Borde, where it is used to make '' Burger Knäckebrot'', a flatbread produced there since 1931. Another 10% of the cultivated area is planted in sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet ('' Beta vulgaris''). Together ...
s for conversion to sugar, popularized after the 19th century, when the region had an economic boom.
International influences
Elements of international cuisine (apart from influences from neighbouring countries) are a relatively recent phenomenon in German cuisine, compared with other West European states. Colonial goods shops spread only in the 19th and early 20th centuries and brought luxury goods like cocoa, coconuts, rare exotic spices, coffee and (non-herbal) tea to a wider audience. The first wave of foreigners coming to Germany specifically to sell their food specialties were ice cream makers from northern Italy, who started to arrive in noticeable numbers during the late 1920s. With the post-World War II contacts with Allied occupation troops, and especially with the influx of more and more foreign workers that began during the second half of the 1950s, many foreign dishes have been adopted into German cuisine — Italian dishes, such as spaghetti andpizza
Pizza (, ) is a dish of Italian origin consisting of a usually round, flat base of leavened wheat-based dough topped with tomatoes, cheese, and often various other ingredients (such as various types of sausage, anchovies, mushrooms, on ...
, have become staples of the German diet. In 2008, there were around 9,000 pizzerias and 7,000 Italian restaurants in Germany. The pizza is Germany's favourite fast food.
Turkish immigrants have introduced Turkish foods to Germany, notably ''döner kebab
Doner kebab (, ; tr, döner or , ), also spelled döner kebab, is a type of kebab, made of meat cooked on a vertical rotisserie. Seasoned meat stacked in the shape of an inverted cone is turned slowly on the rotisserie, next to a vertical cook ...
''. In November 2017, it was estimated that 1,500 döner kebab shops were present in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
and in circa 16,000 in whole Germany.
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
(mostly Syrian, Lebanese or Moroccan), Chinese, Balkan
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, Japanese (especially Sushi) and Greek (especially Gyros) restaurants and bars are also widespread in Germany.
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
(especially Curry
A curry is a dish with a sauce seasoned with spices, mainly associated with South Asian cuisine. In southern India, leaves from the curry tree may be included.
There are many varieties of curry. The choice of spices for each dish in trad ...
dishes), Vietnamese, Thai, and other Asian cuisines are rapidly gaining in popularity since the early 2000s. Until the late 1990s many of the more expensive restaurants served mostly French inspired dishes for decades. Since the end of the 1990s, they have been shifting to a more refined form of German cuisine.
Before 1990, the cuisine from Eastern Germany (1949-1990) was influenced by those of other nations within the former Communist bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
. East Germans traveled abroad to these countries on holiday, and soldiers coming to East Germany from these countries brought their dishes with them. A typical dish that came to the East German kitchen this way is Russian '' Soljanka''.
Food industry
Germany is the third largest agricultural producer in the European Union and the third largest agricultural exporter in the world. In 2013, German food exports were worth around EUR 66 billion.Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture Several food products are internationally known brands.
Chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec ci ...
File:German Marzipan Lübecker Vielfalt.jpg, Lübecker Marzipan
See also
*List of German cheeses
Cheeses have played a significant role in German cuisine, both historically and in contemporary times. Germany has by far the highest variety of cheeses worldwide with 9,500 cheeses coming from Germany. Cheeses are incorporated in the preparation ...
* List of German dishes
Below is a list of dishes found in German cuisine.
Famous dishes
Baden-Württemberg
Bavaria
Berlin
Bremen and Lower Saxony
East Prussia
East Prussia, as Germany's easternmost province, was very often influenced by the cuisines of ...
* List of German soups
Notes
References
*Metzger, Christine (ed.) ''Culinaria Germany''.Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
: Ullmann, 2008.
Further reading
* * *External links
*German Foods Official Website
Taste Atlas: Top 100 Most Popular Foods in Germany
{{Authority control