George Paulet (1553–1608) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sir George Paulet (1553–1608), also known as Pawlett, Pawlet, or Powlet, was an English soldier and administrator. He served as governor of
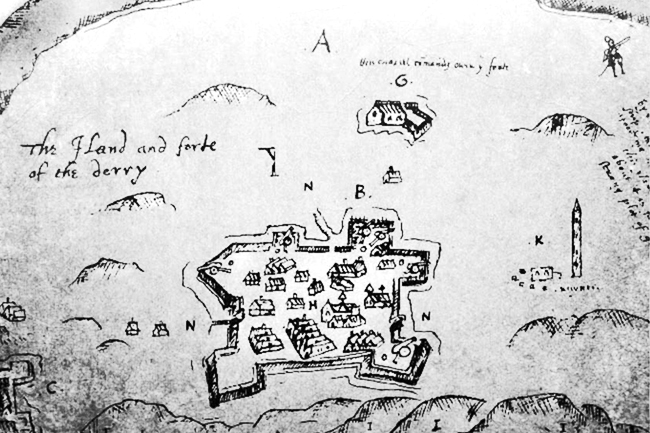 Paulet began at Derry by buying land from Docwra, who had built a town there more than thirty years after the destruction of Randolph's settlement. Docwra incurred the hostility of
Paulet began at Derry by buying land from Docwra, who had built a town there more than thirty years after the destruction of Randolph's settlement. Docwra incurred the hostility of
Derry
Derry, officially Londonderry (), is the second-largest city in Northern Ireland and the fifth-largest city on the island of Ireland. The name ''Derry'' is an anglicisation of the Old Irish name (modern Irish: ) meaning 'oak grove'. The ...
in Ireland. His arrogant and insolent behaviour caused O'Doherty's Rebellion in 1608. Paulet was killed by the rebels during the Burning of Derry
The Burning of Derry took place on 19 April 1608 during O'Doherty's Rebellion when Sir Cahir O'Doherty led a force of rebels to storm Derry in Ulster. He launched his rebellion with an attack on the garrison town of Derry, which was taken tha ...
.
Birth and origins
George was born in 1553 in England, a son of Sir George Paulet and his third wife Elizabeth Windsor. His father was Sir George Paulet (died 1558) ofCrondall
Crondall () is a village and large civil parish in the north east of Hampshire in England, in the Crondall Hundred (division), Hundred surveyed in the Domesday Book of 1086. The village is on the gentle slopes of the low western end of the North ...
, Hampshire. His father's eldest brother William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
was created Earl of Wiltshire
The title Earl of Wiltshire is one of the oldest in the Peerage of England, going back to the 12th century. It is currently held by the Marquess of Winchester, and is used as a courtesy title for the eldest son of the marquess.
The earldom was fi ...
in 1550 and Marquess of Winchester
Marquess of Winchester is a title in the Peerage of England that was created in 1551 for the prominent statesman William Paulet, 1st Earl of Wiltshire. It is the oldest of six surviving English marquessates; therefore its holder is considered th ...
1551.
George's mother was a daughter of William Windsor, 2nd Baron Windsor
Earl of Plymouth is a title that has been created three times: twice in the Peerage of England and once in the Peerage of the United Kingdom.
History
The first creation was in 1675 for Charles FitzCharles, one of the dozens of illegitima ...
.
George was one of 10 siblings.
Early life
Paulet was educated atEton Eton most commonly refers to Eton College, a public school in Eton, Berkshire, England.
Eton may also refer to:
Places
*Eton, Berkshire, a town in Berkshire, England
* Eton, Georgia, a town in the United States
* Éton, a commune in the Meuse dep ...
, 1564–72, and at King's College, Cambridge
King's College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. Formally The King's College of Our Lady and Saint Nicholas in Cambridge, the college lies beside the River Cam and faces out onto King's Parade in the centre of the city ...
, 1572-5. His contemporaries call Paulet a gentleman of Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English citi ...
.
Marriage and children
Before 1586 Paulet married Joan Kyme, daughter of Richard Kyme ofLewes
Lewes () is the county town of East Sussex, England. It is the police and judicial centre for all of Sussex and is home to Sussex Police, East Sussex Fire & Rescue Service, Lewes Crown Court and HMP Lewes. The civil parish is the centre of ...
, Sussex, and his wife Margery Humphrey. George and Joan had a son and a daughter: Nothing seems to be know about the son. The daughter's name was Frances.
Later life
Paulet was aJustice of the peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or ''puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sa ...
in Hampshire 1593–1601.
In 1606 he was appointed governor of Derry
Derry, officially Londonderry (), is the second-largest city in Northern Ireland and the fifth-largest city on the island of Ireland. The name ''Derry'' is an anglicisation of the Old Irish name (modern Irish: ) meaning 'oak grove'. The ...
in Ireland by letters of 20 and 23 July 1606 from King James I
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
to Mountjoy, the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland. These letters speak of his service in the wars. The appointment was obtained through the influence of his cousin John Paulet, 2nd Marquess of Winchester
John Paulet, 2nd Marquess of Winchester ( – 4 November 1576), styled The Honourable John Paulet between 1539 and 1550, Lord St John between 1550 and 1551 and Earl of Wiltshire between 1551 and 1555, was an English peer. He was the eldest son ...
, who knew Mountjoy, the Lord Deputy of Ireland. Paulet replaced Henry Docwra
Henry Docwra, 1st Baron Docwra of Culmore (1564 – 18 April 1631) was a leading English-born soldier and statesman in early seventeenth-century Ireland. He is often called "the founder of Derry", due to his role in establishing the city.
Ba ...
 Paulet began at Derry by buying land from Docwra, who had built a town there more than thirty years after the destruction of Randolph's settlement. Docwra incurred the hostility of
Paulet began at Derry by buying land from Docwra, who had built a town there more than thirty years after the destruction of Randolph's settlement. Docwra incurred the hostility of Charles Blount, 8th Baron Mountjoy
Charles Blount, 1st Earl of Devonshire, KG (pronounced ''Blunt''; 15633 April 1606) was an English nobleman and soldier who served as Lord Deputy of Ireland under Queen Elizabeth I, and later as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland under King James I. ...
(who became Earl of Devonshire), Lord Deputy of Ireland
The Lord Deputy was the representative of the monarch and head of the Irish executive (government), executive under English rule, during the Lordship of Ireland and then the Kingdom of Ireland. He deputised prior to 1523 for the Viceroy of Ireland ...
, by supporting Donnell Ballagh O'Cahan
Donnell Ballagh O'Cahan (died 1627) was an Irish landowner in Ulster. A vassal of Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone, O'Cahan was frequently in rebellion alongside his lord in the closing years of the 16th century. Although he did not go into exile wit ...
, Sir Cahir O'Doherty
Sir Cahir O'Doherty ( ga, Cathaoir Ó Dochartaigh or ga, label=none, Caṫaoir Ó Doċartaiġ; 1587–5 July 1608) was the last Gaelic Chief of the Name of Clan O'Doherty and Lord of Inishowen, in what is now County Donegal. O'Doherty was a n ...
, and Niall Garve O'Donnell
Niall Garve O'Donnell ( ga, Niall Garbh Ó Domhnaill; 1569 – 1626) was an Irish chieftain, alternately an ally of and rebel against English rule in Ireland. He is best known for siding with the English against his kinsman Hugh Roe O'Donnel ...
, who he thought had been ill-treated. James I agreed with Devonshire on Irish policy, about the desirability of ruling Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United King ...
through Hugh Ó Neill, 2nd Earl of Tyrone
Hugh O'Neill (Irish: ''Aodh Mór Ó Néill''; literally ''Hugh The Great O'Neill''; – 20 July 1616), was an Irish Gaelic lord, Earl of Tyrone (known as the Great Earl) and was later created ''The Ó Néill Mór'', Chief of the Name. O'Neill ...
and Rory Ó Donnell, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell
Rory O'Donnell (; 1575 – 30 July 1608), younger brother of Hugh Roe O'Donnell, was the last King of Tyrconnell and 1st Earl of Tyrconnell.An apparent original of the letters patent of the Earldom were in the possession of Count Maximilian Ka ...
, without much regard for minor chiefs. Devonshire died 3 April 1606; but he had previously approved the sale of Docwra's property to Paulet, whom he knew well. Docwra accordingly sold him his house, land which he had bought, and his company of foot, at a low price. The vice-provostship of Derry was thrown in without extra charge.
The new governor was established at Derry in the early winter of 1606, and on 20 February following Sir Arthur Chichester
Arthur Chichester, 1st Baron Chichester (May 1563 – 19 February 1625; known between 1596 and 1613 as Sir Arthur Chichester), of Carrickfergus in Ireland, was an English administrator and soldier who served as Lord Deputy of Ireland from 160 ...
, the new Lord Deputy, told Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury
Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury, (1 June 156324 May 1612), was an English statesman noted for his direction of the government during the Union of the Crowns, as Tudor England gave way to Stuart period, Stuart rule (1603). Lord Salisbury s ...
that he was unfit for the place, and that there had been many dissensions since his arrival. He fell out with George Montgomery, the new bishop of Derry
The Bishop of Derry is an Episcopal polity, episcopal title which takes its name after the monastic settlement originally founded at Daire Calgach and later known as Daire Colm Cille, Anglicised as Derry. In the Roman Catholic Church it remains a ...
, over land claims. Tyrone and Tyrconnell fled from Ireland early in September 1607 (the Flight of the Earls
The Flight of the Earls ( ir, Imeacht na nIarlaí)In Irish, the neutral term ''Imeacht'' is usually used i.e. the ''Departure of the Earls''. The term 'Flight' is translated 'Teitheadh na nIarlaí' and is sometimes seen. took place in Sep ...
); O'Cahan, who ruled the greater part of what is now County Londonderry
County Londonderry ( Ulster-Scots: ''Coontie Lunnonderrie''), also known as County Derry ( ga, Contae Dhoire), is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the thirty two counties of Ireland and one of the nine counties of Ulster. B ...
, and of O'Doherty, the chief of Inishowen
Inishowen () is a peninsula in the north of County Donegal in Ireland. Inishowen is the largest peninsula on the island of Ireland.
The Inishowen peninsula includes Ireland's most northerly point, Malin Head. The Grianan of Aileach, a ringfor ...
in County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ga, Contae Dhún na nGall) is a county of Ireland in the province of Ulster and in the Northern and Western Region. It is named after the town of Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconne ...
, came under some suspicion. Docwra had tried to divide these chiefs from the Earls, but Paulet had his own ideas on handling them.
Paulet was knighted in 1607.
O'Doherty put some armed men on Tory Island
Tory Island, or simply Tory (officially known by its Irish name ''Toraigh''),Toraigh/Tory Island
at
at
Lifford
Lifford (, historically anglicised as ''Liffer'') is the county town of County Donegal, Ireland, the administrative centre of the county and the seat of Donegal County Council, although the town of Letterkenny is often mistaken as holding this ...
in Donegal, recounts that O'Doherty left Burt Castle
Burt Castle is a ruined castle located close to Newtowncunningham and Burt, two villages in the east of County Donegal in Ulster, Ireland. Historically it was sometimes spelt as Birt Castle. It is also known by the name O'Doherty's Castle, and s ...
, on Lough Swilly
Lough Swilly () in Ireland is a glacial fjord or sea inlet lying between the western side of the Inishowen, Inishowen Peninsula and the Fanad Peninsula, in County Donegal. Along with Carlingford Lough and Killary Harbour it is one of three glaci ...
, at the end of October to superintend the felling of timber for building; but that this gave rise to a report that he was in rebellion. He then began to arm about seventy followers, refusing all recruits from outside his own district. Paulet made an unsuccessful attempt to seize Burt in the chief's absence, and reported everything to Chichester. O'Doherty remonstrated with him in a temperate letter; Paulet then (falsely) denied strongly that he had ever intended to surprise Burt, and accused O'Doherty of treason. O'Doherty went to Dublin early in December and made his excuses to Chichester, who accepted them, but without much confidence. On 18 April the privy council ordered him to be fully restored to such of his ancestral lands as were still withheld, but this order did not reach the Irish government until he was actually in rebellion.
O'Doherty's Rebellion
The ''Annals of the Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' ( ga, Annála Ríoghachta Éireann) or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' (''Annála na gCeithre Máistrí'') are chronicles of medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Deluge, dated as 2,24 ...
'' state that Paulet struck O'Doherty; there is more support for the idea that Paulet provoked O'Doherty into rebellion by insults. Paulet's carelessness invited attack, though Chichester warned him repeatedly to keep good watch. On the night of Monday, 18 April 1608, O'Doherty, at the head of fewer than a hundred men, seized the outpost at Culmore
Culmore () is a village and townland in Derry, County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. It is at the mouth of the River Foyle. In the 2011 Census it had a population of 3,465 people. It is situated within Derry and Strabane district.
History Ni ...
by a trick, and surprised Derry itself an hour before daybreak. Paulet was killed by O'Doherty's foster-father Phelim Reagh MacDavitt
Phelim Reagh MacDavitt or Phelim Reagh MacDevitt (Irish: ''Feidhlimidh Riabhach Mac Dhaibheid'', or Brindled Felim - probably a reference to a white streak or streaks in his hair) was a Gaelic Irish warrior and landowner notable for his partici ...
, and the city was sacked and burned. Sir Josias Bodley
Sir Josias Bodley (1550-1618) was an English military engineer noted for his service in Ireland during the Nine Years' War. Following the end of the war he remained in Ireland where he oversaw the rebuilding of several major forts. In 1609 he was ...
, not however an eye-witness, reported that Paulet fell fighting valiantly; but the English government spoke of his cowardice. Paulet had been warned by Richard Hansard, who held his own against the rebels at Lifford.
Despite the early success at Derry, O'Doherty's Rebellion was defeated by the swift response of the Dublin government. A force was sent out which recovered the ruins of Derry and killed O'Doherty at the Battle of Kilmacrennan
The Battle of Kilmacrennan was a skirmish fought near Kilmacrennan, County Donegal in 1608 during O'Doherty's Rebellion. Sir Cahir O'Doherty was a traditional supporter of the Crown whose treatment at the hands of local officials had led him to ...
.
Paulet's wife was with him at Derry, and the contemporary tract ''Newes from Ireland concerning the late treacherous Action''; (London, 1608) says he had children there also. Lady Paulet was held captive by the O'Doherties for a short time; but her husband's death left her in poverty, which was partly relieved out of the Tyrone forfeitures. She was alive in 1617.
Notes and references
Notes
Citations
;AttributionSources
* * * * – U to Z * – M to Z * * – Knights bachelors & Index * – Kaile to RyvesFurther reading
*''The Flight of the Earls, An Illustrated History,'' 2007, by Dr. John McCavitt FRHistS. *''O'Doherty's Rebellion,'' 2008, by Rob Dougherty. {{DEFAULTSORT:Paulet, George 1553 births 1608 deaths Alumni of King's College, Cambridge English army officers English knights 16th-century English soldiers 17th-century soldiersGeorge
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd Presiden ...
Willoughby familyFam
17th-century English soldiers
People of O'Doherty's rebellion
Younger sons of marquesses
English military personnel killed in action
English emigrants to Ireland
People from Hart District
Military personnel from Hampshire