Geography of Beijing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
北京地理概貌
last accessed 11/18/08 The city is inland from the
 Two urban districts, Dongcheng and Xicheng form the urban core of Beijing. They occupy the area inside the old walled city, which used to be divided into two walled sections, ''neicheng'', the inner city and ''waicheng'', the adjoining outer city to the south. Though the city walls no longer stand, they continue to retain geographic significance. Streets that once traversed the wall are still named ''nei'' (inner) or ''wai'' (outer) in relationship to whether the street section is inside or outside the wall. Today, Line 2 loop of the
Two urban districts, Dongcheng and Xicheng form the urban core of Beijing. They occupy the area inside the old walled city, which used to be divided into two walled sections, ''neicheng'', the inner city and ''waicheng'', the adjoining outer city to the south. Though the city walls no longer stand, they continue to retain geographic significance. Streets that once traversed the wall are still named ''nei'' (inner) or ''wai'' (outer) in relationship to whether the street section is inside or outside the wall. Today, Line 2 loop of the  Beyond the 2nd Ring Road, the city spreads out in a checkerboard fashion marked by concentric ring roads. Four other districts, Haidian, Chaoyang, Fengtai and
Beyond the 2nd Ring Road, the city spreads out in a checkerboard fashion marked by concentric ring roads. Four other districts, Haidian, Chaoyang, Fengtai and
 The city of Beijing lies on low and flat land, with elevation generally between above sea level. The highest point inside the old walled city is at the top of Coal Hill in
The city of Beijing lies on low and flat land, with elevation generally between above sea level. The highest point inside the old walled city is at the top of Coal Hill in  To the west is Xishan, also known as the Western Hills, which are visible from the city on clear days. Xishan forms the eastern flank of the
To the west is Xishan, also known as the Western Hills, which are visible from the city on clear days. Xishan forms the eastern flank of the
last accessed 11/16/08 Xishan covers nearly all of Fangshan and Mentougou Districts west of the city. East Lingshan (elevation ), a Xishan peak on the border with Hebei, is the highest point in Beijing Municipality. It is located from the city. Xishan is also known for high mountain meadows and scenic river gorges, including Shidu, Beijing, Shidu. The mountains north of Beijing including
The mountains north of Beijing including
 Several major
Several major  Downtown Beijing has several
Downtown Beijing has several
陈平, 三、什刹海与陶然湖、古蓟城
June 6, 2008 A major flood in 295 A.D. devastated part of Beijing, then known as Ji. Just west of
 Today, an aqueduct draws water from the Yongding through Yuyuantan Park to the western city moat, which empties into Liangshui River south of the city. Another aqueduct draws water from Kunming Lake in the
Today, an aqueduct draws water from the Yongding through Yuyuantan Park to the western city moat, which empties into Liangshui River south of the city. Another aqueduct draws water from Kunming Lake in the
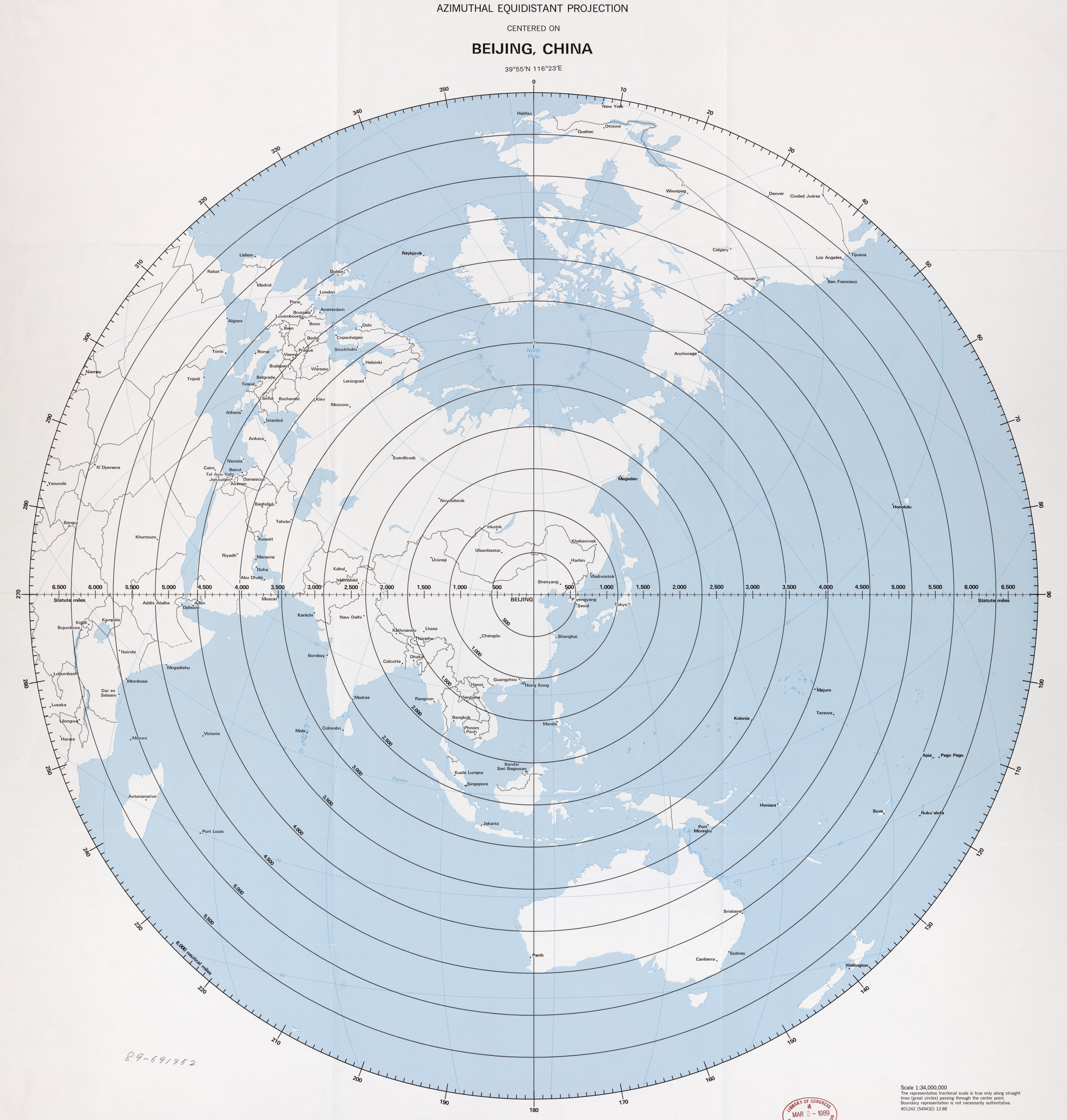 With coordinates of 39° 54' 50 N and 116° 23' 30" E, Beijing shares roughly the same latitude as
With coordinates of 39° 54' 50 N and 116° 23' 30" E, Beijing shares roughly the same latitude as
Image:Beijing urban landsat.jpg , Beijing's urban extent
Image:Beijing SPOT 1059.jpg , Satellite image of the city of Beijing, with the
"Peking"
a map from 1914 {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Beijing Articles containing video clips
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
is a municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the ...
located in North China
North China, or Huabei () is a geographical region of China, consisting of the provinces of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia. Part of the larger region of Northern China (''Beifang''), it lies north of the Qinling–Hu ...
at the northern tip of the North China Plain
The North China Plain or Huang-Huai-Hai Plain () is a large-scale downfaulted rift basin formed in the late Paleogene and Neogene and then modified by the deposits of the Yellow River. It is the largest alluvial plain of China. The plain is border ...
, near the meeting point of the Xishan and Yanshan Yanshan may refer to:
Places
*Yanshan County, Hebei ()
*Yanshan County, Jiangxi ()
*Yanshan County, Yunnan ()
*Yanshan District (), Guilin, Guangxi
**Yanshan Subdistrict (), in Yanshan District
*Yanshan Avenue Subdistrict (), Haigang District, Qinh ...
mountain ranges
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
. The city itself lies on flat land (elevation ) that opens to the east and south. The municipality's outlying districts and counties extend into the mountains that surround the city from the southwest to the northeast. The highest peaks are over .
Beijing Municipality consists of six city districts (previously eight, see Xuanwu and Chongwen), eight suburban districts and two rural counties. It covers a total area of
. By land area, the municipality is slightly larger than the country of Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
, though much of the municipality outside the urban core are sparsely populated mountains and farmland. The terrain is roughly 38% flat and 62% mountainous.(Chinese北京地理概貌
last accessed 11/18/08 The city is inland from the
Bohai Sea
The Bohai Sea () is a marginal sea approximately in area on the east coast of Mainland China. It is the northwestern and innermost extension of the Yellow Sea, to which it connects to the east via the Bohai Strait. It has a mean depth of ...
via Tianjin Municipality in the southeast. Aside from Tianjin, Beijing is bordered on all other sides by Hebei Province
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0 ...
, including a piece wedged between Beijing and Tianjin.
Historically, Beijing was situated on the border between sedentary
Sedentary lifestyle is a lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while engaged in an activity like soci ...
agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
areas to the south and pastoralist regions beyond the mountains to the north. The Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand Li (unit), ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against Eurasian noma ...
of China was built across the mountains north of Beijing to guard against nomadic invasions. In modern times, the same mountains that shielded Beijing from the Gobi
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast ...
steppes
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grassland ...
also form a semi-circular basin which catches the city's air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
. Severe smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words '' smoke'' and ''fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odor. The word was then int ...
problems develop in the summer as the hot and humid air pressure from monsoons
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscill ...
in the south prevent air pollutants from leaving the basin. Smog is less severe in the fall and winter when the direction of the wind currents reverse course as the vast anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from ...
high pressure system takes hold and brings cold, dry air from Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
. In the spring, the northerly winds, pick up dust from desertifying areas of western China and bring occasionally severe dust storms
A dust storm, also called a sandstorm, is a meteorological phenomenon common in arid and semi-arid regions. Dust storms arise when a gust front or other strong wind blows loose sand and dirt from a dry surface. Fine particles are trans ...
to Beijing. The city's climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
is characterized by hot, humid summers and cold, windy, and dry winters.
Layout of Beijing's administrative divisions
In imperial times, the old walled city of Beijing occupied . The physical size of the city has grown more than tenfold in recent decades to about . The inner suburbs (), and outer suburbs () provide further space for growth. The remaining of the municipality consists of rural areas, nature reserves and lightly populated mountains. Two urban districts, Dongcheng and Xicheng form the urban core of Beijing. They occupy the area inside the old walled city, which used to be divided into two walled sections, ''neicheng'', the inner city and ''waicheng'', the adjoining outer city to the south. Though the city walls no longer stand, they continue to retain geographic significance. Streets that once traversed the wall are still named ''nei'' (inner) or ''wai'' (outer) in relationship to whether the street section is inside or outside the wall. Today, Line 2 loop of the
Two urban districts, Dongcheng and Xicheng form the urban core of Beijing. They occupy the area inside the old walled city, which used to be divided into two walled sections, ''neicheng'', the inner city and ''waicheng'', the adjoining outer city to the south. Though the city walls no longer stand, they continue to retain geographic significance. Streets that once traversed the wall are still named ''nei'' (inner) or ''wai'' (outer) in relationship to whether the street section is inside or outside the wall. Today, Line 2 loop of the Beijing Subway
The Beijing Subway is the rapid transit system of Beijing Municipality that consists of 25 lines including 20 rapid transit lines, two airport rail links, one maglev line and 2 light rail lines, and 463 stations. The rail network extends ...
traces the inner city wall. The 2nd Ring Road
The 2nd Ring Road () is the innermost ring road highway which encircles the city center of Beijing, People's Republic of China. (The first ring road had been a circular tram route.)
The ring road can be divided into two parts: the original ring ...
outlines the combined walled city including the outer city.
The inner city is divided into eastern and western halves by Dongcheng and Xicheng Districts. The Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrifi ...
, where emperors once lived, and Tiananmen Square
Tiananmen Square or Tian'anmen Square (; 天安门广场; Pinyin: ''Tiān'ānmén Guǎngchǎng''; Wade–Giles: ''Tʻien1-an1-mên2 Kuang3-chʻang3'') is a city square in the city center of Beijing, China, named after the eponymous Tiananm ...
, the center of the city, both belong to Dongcheng. But the Zhongnanhai
Zhongnanhai () is a former imperial garden in the Imperial City, Beijing, adjacent to the Forbidden City; it serves as the central headquarters for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the State Council (central government) of China. Zhongn ...
Compound, next door to the Forbidden City, where China's current leaders now reside, and the Great Hall of the People
The Great Hall of the People is a state building located at the western edge of Tiananmen Square in Beijing. It is used for legislative and ceremonial activities by the government of the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the ruling Chinese C ...
, on the west side of Tiananmen Square, both are part of Xicheng. The outer city, adjacent and south of the inner city, comprises the former Xuanwu and Chongwen districts, merged with Xicheng and Dongcheng respectively in July 2010. Chongwen is home to the Temple of Heaven
The Temple of Heaven () is a complex of imperial religious buildings situated in the southeastern part of central Beijing. The complex was visited by the Emperors of the Ming and Qing dynasties for annual ceremonies of prayer to Heaven for a ...
. Xuanwu is oldest continuously inhabited part of Beijing. Some of its neighborhoods including those around the Niujie Mosque
The Niujie Mosque ( "Oxen Street House of Worship" or "Oxen Street Mosque") is the oldest mosque in Beijing, China. It was first built in 996 during the Liao dynasty and was reconstructed as well as enlarged under the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661– ...
(b. 996 A.D.) and Pagoda of Tianning Temple (b. 1119 A.D.) predate the Yuan capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
. Unlike in most other parts of the city, most narrow lanes in Xuanwu are called ''jie'' instead of ''hutong
''Hutong'' () are a type of narrow street or alley commonly associated with northern Chinese cities, especially Beijing.
In Beijing, hutongs are alleys formed by lines of ''siheyuan'', traditional courtyard residences. Many neighbourhoods wer ...
s''. Each of the two core city districts has population density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopu ...
of over 20000 persons/km2 (51800 persons/sq. mi.)
 Beyond the 2nd Ring Road, the city spreads out in a checkerboard fashion marked by concentric ring roads. Four other districts, Haidian, Chaoyang, Fengtai and
Beyond the 2nd Ring Road, the city spreads out in a checkerboard fashion marked by concentric ring roads. Four other districts, Haidian, Chaoyang, Fengtai and Shijingshan
Shijingshan District () is an urban district of the municipality of Beijing. It lies to the west of the urban core of Beijing, and is part of the Western Hills area, bordering the districts of Haidian to the northeast and east, Fengtai to the s ...
, were once considered on the city's outskirts, but are now integral parts of the city inside the 5th Ring Road
Beijing's 5th Ring Road (, China Road Numbering: S50 (Beijing) is a ring road encircling the city about away from the city centre. It takes the form of an expressway and is in length. Being a ring road, it has no natural start or end point, ...
. All four have population densities above 4500 persons/km2 (11,600 persons/km2). The vast Haidian District to the northwest is home to the Old
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
* Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, M ...
and New Summer Palace
The Summer Palace () is a vast ensemble of lakes, gardens and palaces in Beijing. It was an imperial garden in the Qing dynasty. Inside includes Longevity Hill () Kunming Lake and Seventeen Hole Bridge. It covers an expanse of , three-quarter ...
, the university district, and Zhongguancun
Zhongguancun () is a major technology hub in Haidian District, Beijing, China.
Zhongguancun occupies a band between the northwestern Third Ring Road and the northwestern Fourth Ring Road, in the northwestern part of Beijing. Zhongguancun is ...
, the city's high-technology silicon village. The even bigger Chaoyang District embraces the city from the north and east. Its possessions include Beijing Central Business District (CBD), the Olympic Green
The Olympic Green () is an Olympic Park in Chaoyang District, Beijing, China constructed for the 2008 Summer Olympics. Since then, the streets around the park have been used for an exhibition street race of the FIA GT1 World Championship in 2 ...
, and even the Beijing Capital International Airport
Beijing Capital International Airport is one of two international airports serving Beijing, the other one being Beijing Daxing International Airport (PKX). It is located northeast of Beijing's city center, in an exclave of Chaoyang District ...
. Shijingshan is a heavily industrialized district in the foothills of the Western Hills. Fengtai spans across the south of urban Beijing.
Of the suburban districts further afield, Tongzhou and Shunyi
Shunyi District () is an administrative district of Beijing, located to the northeast of the city's urban core. As of 2014, the population of the district is around 983,000, of which approximately 601,000 have local residency permits. The Beiji ...
in the east are rapidly urbanizing. Mentougou and Fangshan lie to the west, in Xishan, also known as the Western Hills. Fangshan is home to two of the oldest prehistoric sites in Beijing Municipality: the caves at Zhoukoudian
Zhoukoudian Area () is a town and an area located on the east Fangshan District, Beijing, China. It borders Nanjiao and Fozizhuang Townships to its north, Xiangyang, Chengguan and Yingfeng Subdistricts to its east, Shilou and Hangcunhe Towns t ...
, home of the Peking Man
Peking Man (''Homo erectus pekinensis'') is a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' which inhabited the Zhoukoudian Cave of northern China during the Middle Pleistocene. The first fossil, a tooth, was discovered in 1921, and the Zhoukoudian Cave has s ...
, and Liulihe, the site of the capital of the Yan Kingdom during the Western Zhou dynasty
The Western Zhou ( zh, c=, p=Xīzhōu; c. 1045 BC – 771 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the first half of the Zhou dynasty. It began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye and ended when the Quanrong n ...
. Daxing District
Daxing District () is a district of Beijing, covering the southern suburbs of the city. It borders the Beijing districts of Tongzhou to the east/northeast, Fangshan to the west, Fengtai to the northwest, Chaoyang to the northeast, and the Heb ...
, to the south, is largely agricultural but is also developing its own technology park in Yizhuang. Changping just north of the city ranges from densely urbanized Tiantongyuan
Tiantongyuan () is a suburb in northern Beijing's Changping District. As of April 2008, it was said to have over 400,000 residents. As of 2019, the population of Tiantongyuan had jumped to 700,000, making it the largest Xiaoqu (housing communi ...
in the south to the Juyongguan Great Wall in the north. In between are the Thirteen Ming Tombs.
Far north of the municipality in the Yanshan range are Yanqing and Miyun Counties, and Huairou
Huairou District () is situated in northern Beijing about from the city center (about a 1½ to 2 hour drive).
History
In 1995 during the United Nation's 4th World's Women Conference in Beijing, the Civil Society community was forced to meet in t ...
and Pinggu District
Pinggu District (), formerly Pinggu County (), lies in the far east of Beijing Municipality. It has an area of and a population of 396,701 (2000 Census). The district is subdivided into 2 subdistricts, 14 towns, and 2 townships. It borders the Be ...
s, both of which were rural counties until 2001. The far north is rugged, rural and sparsely populated. Yanqing, Huairou and Miyun all have fewer than 200 residents per km2 (518/sq. mi.). They are perhaps best known for stretches of the Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand Li (unit), ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against Eurasian noma ...
, with Badaling
Badaling () is the site of the most visited section of the Great Wall of China, approximately northwest of Beijing's city center, in Badaling Town, Yanqing District (within Beijing municipality). The portion of the wall running through the ...
and Shuiguan in Yanqing, Mutianyu, Huanghuacheng and Jiankou
Jiankou () is a section of the Great Wall of China. In English, 'Jiankou,' is translated to 'Arrow Nock' as the shape of the mountain resembles an arrow with the collapsed ridge opening up, reminiscent of an arrow nock. The wall is 20 k ...
in Huairou, and Gubeikou
Gubeikou Town () is a town of Miyun District in northeastern Beijing, traversed by , bordering with Luanping County, Hebei to the north and the Beijing towns of Gaoling () to the west, Xinchengzi () to the east and Taishitun (). The area is one ...
and Simatai
Simatai (), a section of the Great Wall of China located in the north of Miyun County, 120 km northeast of Beijing, holds the access to Gubeikou, a strategic pass in the eastern part of the Great Wall. It was closed in June 2010 but has ...
in Miyun, and Jiangjunguan in Pinggu.
Topography
 The city of Beijing lies on low and flat land, with elevation generally between above sea level. The highest point inside the old walled city is at the top of Coal Hill in
The city of Beijing lies on low and flat land, with elevation generally between above sea level. The highest point inside the old walled city is at the top of Coal Hill in Jingshan Park
Jingshan Park is an imperial park covering immediately north of the Forbidden City in the Imperial City area of Beijing, China. The focal point is the artificial hill Jingshan (), literally "Prospect Hill". Formerly a private imperial garden at ...
, which rises to and overlooks the Forbidden City. Longevity Hill in the Summer Palace
The Summer Palace () is a vast ensemble of lakes, gardens and palaces in Beijing. It was an imperial garden in the Qing dynasty. Inside includes Longevity Hill () Kunming Lake and Seventeen Hole Bridge. It covers an expanse of , three-quarte ...
reaches an elevation of . The plains from Beijing extend to the east as far as Shanhaiguan on the Bohai Sea and as far south as Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and t ...
, on the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
.
Taihang Mountains
The Taihang Mountains () are a Chinese mountain range running down the eastern edge of the Loess Plateau in Shanxi, Henan and Hebei provinces. The range extends over from north to south and has an average elevation of . The principal peak is ...
range, which run north–south up the spine of Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
province.(Chineselast accessed 11/16/08 Xishan covers nearly all of Fangshan and Mentougou Districts west of the city. East Lingshan (elevation ), a Xishan peak on the border with Hebei, is the highest point in Beijing Municipality. It is located from the city. Xishan is also known for high mountain meadows and scenic river gorges, including Shidu, Beijing, Shidu.
Foothills
Foothills or piedmont are geographically defined as gradual increases in elevation at the base of a mountain range, higher hill range or an upland area. They are a transition zone between plains and low relief hills and the adjacent topogr ...
of Xishan reach the city itself. They include Fragrant Hills
Fragrant Hills or Xiangshan Park is a public park and former imperial garden at the foot of the Western Hills in the Haidian District, Beijing, China. It was also formerly known as Jingyi Garden or "Jingyiyuan" (靜宜園). It covers and cons ...
, a major tourist attraction and Laoshan, the site of mountain bike competition in the 2008 Summer Olympics
The 2008 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXIX Olympiad () and also known as Beijing 2008 (), were an international multisport event held from 8 to 24 August 2008, in Beijing, China. A total of 10,942 athletes from 204 Nat ...
.
 The mountains north of Beijing including
The mountains north of Beijing including Badaling
Badaling () is the site of the most visited section of the Great Wall of China, approximately northwest of Beijing's city center, in Badaling Town, Yanqing District (within Beijing municipality). The portion of the wall running through the ...
, Jundu Mountains
Jundu Mountains () is a mountain range north of Beijing in China. Jundu Mountains represent the west part of the Yan Mountains. The Great Wall of China passes through Jundu Mountains with famous sections as Badaling
Badaling () is the site ...
and Fenghuanling all belong to the Yanshan Yanshan may refer to:
Places
*Yanshan County, Hebei ()
*Yanshan County, Jiangxi ()
*Yanshan County, Yunnan ()
*Yanshan District (), Guilin, Guangxi
**Yanshan Subdistrict (), in Yanshan District
*Yanshan Avenue Subdistrict (), Haigang District, Qinh ...
range, which runs east–west, across northern Hebei Province. Yanshan separates the North China Plain
The North China Plain or Huang-Huai-Hai Plain () is a large-scale downfaulted rift basin formed in the late Paleogene and Neogene and then modified by the deposits of the Yellow River. It is the largest alluvial plain of China. The plain is border ...
from the steppes
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grassland ...
and held considerable military significance in history. All of Beijing's Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand Li (unit), ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against Eurasian noma ...
sections were built in the Yanshan range, which reaches a height of at Haituoshan on the border between Yanqing County and Hebei.
The Yanshan and Xishan ranges meet at Nankou, in Changping District, northwest of the city. The intersection creates a massive fault line and rift valley through which the city's main roads and railroads to the northwest pass.
Hydrology
 Several major
Several major river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of ...
s, including the Yongding, Chaobai, Juma and Wenyu flow through Beijing Municipality. They originate in the highlands of Hebei and Shanxi, cut through the mountains west and north of the city, and eventually flow into the Hai River
The Hai River (海河, lit. "Sea River"), also known as the Peiho, ("White River"), or Hai Ho, is a Chinese river connecting Beijing to Tianjin and the Bohai Sea.
The Hai River at Tianjin is formed by the confluence of five watercourses: the ...
, which empties into the Bohai Sea
The Bohai Sea () is a marginal sea approximately in area on the east coast of Mainland China. It is the northwestern and innermost extension of the Yellow Sea, to which it connects to the east via the Bohai Strait. It has a mean depth of ...
. Over the centuries, hydrologists have channeled rivers through the city into man-made lake
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including control ...
s, moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
s, channels
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
and aqueducts, which provide water to the city and drain its refuse, but no longer threaten Beijing with flooding.
 Downtown Beijing has several
Downtown Beijing has several lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
s called ''hai'' or sea. During the Yuan dynasty, the Mongol rulers expanded them and built imperial palace of Dadu around them. Subsequent emperors of the Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han pe ...
and Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
dynasties used the lakes as imperial gardens. Today, the three northernmost lakes, ''Xihai'' (West Sea), '' Houhai'' (Rear Sea) and ''Qianhai'' (Front Sea), collectively known as '' Shichahai'', are lined with bars and cafés and known for nightlife. To their south, ''Beihai
Beihai (; Postal romanization: Pakhoi) is a prefecture-level city in the south of Guangxi, People's Republic of China. Its status as a seaport on the north shore of the Gulf of Tonkin has granted it historical importance as a port of internat ...
'' (North Sea) is a city park, and ''Zhonghai'' (Central Sea) and ''Nanhai'' (South Sea) are part of the Zhongnanhai
Zhongnanhai () is a former imperial garden in the Imperial City, Beijing, adjacent to the Forbidden City; it serves as the central headquarters for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the State Council (central government) of China. Zhongn ...
Compound, residence to China's leaders. This string of lakes used to form the main riverbed of the Yongding River, which now flows to the west. But 1,800 years ago, the Yongding flowed through Jishuitan and downtown Beijing and then into Longtan Lake
Longtan Lake or Longtan Tourist Pond () is a lake in Shanglin Village, Longtan District, Taoyuan City, Taiwan. The lake is known for the Buddhist temple in the centre of the lake.
History
The lake was originally built for irrigation. After the ...
and on to Tongzhou.(Chines陈平, 三、什刹海与陶然湖、古蓟城
June 6, 2008 A major flood in 295 A.D. devastated part of Beijing, then known as Ji. Just west of
Wangfujing
Wangfujing () is a shopping street in Beijing, China, located in Dongcheng District. The majority of the main area is pedestrianised. Since the middle of the Ming Dynasty there have been commercial activities in the area. In the Qing Dynas ...
, there is still a stretch of Beijing called ''Shatan'' or Sandy Beach.

Summer Palace
The Summer Palace () is a vast ensemble of lakes, gardens and palaces in Beijing. It was an imperial garden in the Qing dynasty. Inside includes Longevity Hill () Kunming Lake and Seventeen Hole Bridge. It covers an expanse of , three-quarte ...
down through the Purple Bamboo Park
Purple Bamboo Park (Chinese: 紫 竹 院 公园; pinyin: Zǐ Zhú Yuàn Gōngyuán; also called Zizhuyuan Park or Black Bamboo Park) is one of the seven largest parks in Beijing, China. It is located in the Haidian District of northwestern Beijin ...
and into the northern city moat, which also replenishes Shichahai, Beihai and Zhongnanhai. The northern moats are drained by the Ba River, which flows into the Wenyu River. The southern and eastern moats are drained by the Tonghui River, which also flow into the Wenyu.
This network of rivers and aqueducts are fed by reservoirs
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including control ...
to the north of the city. The Miyun Reservoir, the largest in the municipality, is created at the confluence of the Chao and Bai Rivers, which forms the Chaobai. The Yongding, before entering the municipality in Mentougou District, is dammed to create the vast Guanting Reservoir of Hebei Province. Despite these reservoirs, the city of Beijing faces chronic water shortages due to water-intensive agriculture, industry, and population growth. Under the South-North Water Transfer Project, the city plans to draw water from the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
through the Grand Canal, which was built 800 years ago for transportation, but now is being upgraded into a major aqueduct.
Climate
The city'sclimate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
is a rather dry, monsoon-influenced humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
''Dwa''), characterised by hot, humid summers due to the East Asian monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
, and generally cold, windy, very dry winters that reflect the influence of the vast Siberian
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from ...
. Yet during the winter, winds from the northwest must cross the mountains that shield the city, keeping the city warmer than other locations of similar latitude in China. Spring can bear witness to sandstorms blowing in from the Mongolian steppe, accompanied by rapidly warming, but generally dry, conditions. Autumn, like spring, sees little rain but is crisp and short. January averages , while July averages . Annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
is around , falling mostly in the summer months. Extremes have ranged from . In 2005, the total precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
was , a majority of which occurred in the summer.
Coordinates
 With coordinates of 39° 54' 50 N and 116° 23' 30" E, Beijing shares roughly the same latitude as
With coordinates of 39° 54' 50 N and 116° 23' 30" E, Beijing shares roughly the same latitude as Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
, Indianapolis
Indianapolis (), colloquially known as Indy, is the state capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the seat of Marion County. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the consolidated population of Indianapolis and Marion ...
, Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
(Ohio), Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
, Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, maki ...
, Bukhara
Bukhara ( Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and the city ...
, as well as Jiayuguan, Yumen, and Jiuquan
Jiuquan, formerly known as Suzhou, is a prefecture-level city in the northwesternmost part of Gansu Province in the People's Republic of China. It is more than wide from east to west, occupying , although its built-up area is mostly located in i ...
in Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
. The city lines up at about the same longitude as Xilinhot
Xilinhot ( Mongolian: , , ; ) is a county-level city which serves as the seat of government for the Xilin Gol league in Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It has a jurisdiction area of and a population of 245,886; 149,000 people live in ...
, Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
; Dezhou
Dezhou () is a prefecture-level city in northwestern Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It borders the provincial capital of Jinan to the southeast, Liaocheng to the southwest, Binzhou to the northeast, and the province of Hebei t ...
, Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in His ...
; Yongcheng
Yongcheng () is county-level city in Henan province, China, and is the easternmost county-level division of the province, bordering Anhui province on all sides except the northwest and due north. Yongcheng has significant coal deposits and some i ...
, Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is a ...
; Lu'an
Lu'an (), is a prefecture-level city in western Anhui province, People's Republic of China, bordering Henan to the northwest and Hubei to the southwest. As of the 2020 census, it had a total population of 4,393,699 inhabitants whom 1,752,537 liv ...
, Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze Riv ...
; Linchuan
Linchuan District () is one of two districts of the city of Fuzhou, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang a ...
, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
; Changting, Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its ...
; Jieyang
Jieyang () is a prefecture-level city in eastern Guangdong Province (Yuedong), People's Republic of China, part of the Chaoshan region whose people speak Chaoshan Min distinct from neighbouring Yue speakers. It is historically important as th ...
, Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
; Kota Kinabalu
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = From top, left to right, bottom:Kota Kinabalu skyline, Wawasan intersection, Tun Mustapha Tower, Kota Kinabalu Coastal Highway, the Kota Kinabalu City Mosque, the Wism ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
; and Mataram, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
. The latitude of the municipality ranges from 39° 27' to 41° 03' N and in longitude from 115° 25' to 117° 30' E.
Beijing's antipode is located in the eastern part of Río Negro Province
Río Negro (, ''Black River'') is a province of Argentina, located in northern Patagonia. Neighboring provinces are from the south clockwise Chubut, Neuquén, Mendoza, La Pampa and Buenos Aires. To the east lies the Atlantic Ocean.
Its capi ...
, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
, inland from Viedma.
Maps and satellite images
Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrifi ...
in the center, just north of Tiananmen Square
Tiananmen Square or Tian'anmen Square (; 天安门广场; Pinyin: ''Tiān'ānmén Guǎngchǎng''; Wade–Giles: ''Tʻien1-an1-mên2 Kuang3-chʻang3'') is a city square in the city center of Beijing, China, named after the eponymous Tiananm ...
and east of a string of lakes. Also visible are Yuyuantan lake in the west and the southern city moat, which once surrounded the walled outer city.
Image:Beijing ast 2007220 lrg.jpg, Satellite view of the city within the 6th Ring Road
The 6th Ring Road () is an expressway ring road in Beijing, China which runs around the city approximately from the center of the city. The 6th Ring Road is approximately long.
The road is numbered G4501 and as such is strictly speaking co ...
Image:Peking1875.jpg , The Beijing area in 1875
Image:Peking environs 1912.jpg , Beijing in 1912
Image:Peking 1916.jpg , The old city in 1916
File:Txu-oclc-10552568-nj50-2.jpg, Map of Beijing (labeled as PEI-P’ING (PEIPING) ) and nearby areas (1954)
File:Beijing 1986 Vicinity.jpg, Beijing and vicinity in 1986
Image:Beijing city wall map vectorized.svg, Map showing the old walled city, including the inner and outer cities
See also
* Neighborhoods in Beijing * Geography of China *North China Plain
The North China Plain or Huang-Huai-Hai Plain () is a large-scale downfaulted rift basin formed in the late Paleogene and Neogene and then modified by the deposits of the Yellow River. It is the largest alluvial plain of China. The plain is border ...
References
External links
"Peking"
a map from 1914 {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Beijing Articles containing video clips