Geneva Act of the Lisbon Agreement on Appellations of Origin and Geographical Indications on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, neighboring_municipalities=
Federal Statistical Office spreadsheet listing the Swiss and French communes of the Geneva Functional Urban Area
Land area of the 93 Swiss communes: 555.1 km² (source
.
Land area of the 158 French communes: 1737.1 km² (source
. had a population of 1,032,750 in Jan. 2019 (Swiss estimates and French census).As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined
Federal Statistical Office spreadsheet listing the Swiss and French communes of the Geneva Functional Urban Area
Population of the 93 Swiss communes in January 2019: 599,556 (source
.
Population of the 158 French communes in January 2019: 433,194 (source
. Since 2013, the Canton of Geneva, the
*District of Nyon (307.4 km�
*Genevois français (1443.2 km²), itself made up of CA Thonon Agglomération (238.9 km�
CA Annemasse-les Voirons-Agglomération (78.2 km�
CC Arve et Salève (99.3 km�
CC du Pays Rochois (93.9 km�
CC Faucigny-Glières (150.7 km�
CC du Genevois (151.5 km�
CA du Pays de Gex (404.9 km�
and CC du Pays Bellegardien (225.8 km�
and had a population of 1,025,316 in Jan. 2019 (Swiss estimates and French census), 58.5% of them living on Swiss territory, and 41.5% on French territory.Grand Genève is made up of: *Canton of Geneva (499,480 inh. in Jan. 201
*District of Nyon (100,685 inh. in Jan. 201
*Genevois français (425,151 inh. in Jan. 2019), itself made up of CA Thonon Agglomération (90,531 inh
CA Annemasse-les Voirons-Agglomération (90,562 inh
CC Arve et Salève (20,074 inh
CC du Pays Rochois (28,369 inh
CC Faucigny-Glières (27,181 inh
CC du Genevois (48,312 inh
CA du Pays de Gex (98,257 inh
and CC du Pays Bellegardien (21,865 inh
Geneva is a global city, a financial centre, and a worldwide centre for diplomacy due to the presence of numerous

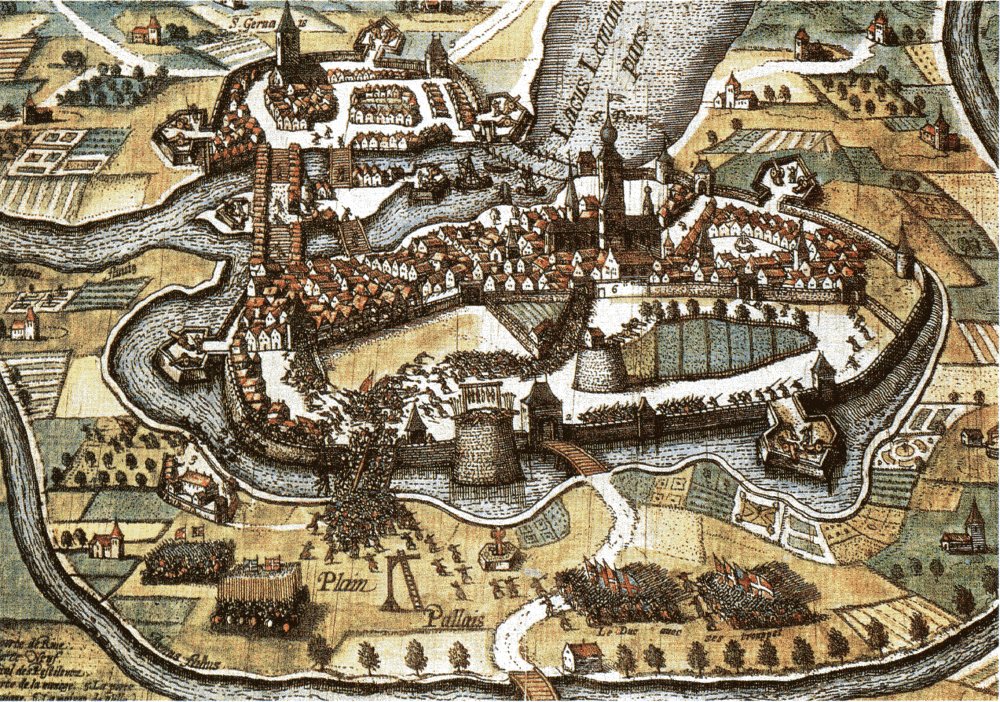 Geneva was an Allobrogian border town, fortified against the
Geneva was an Allobrogian border town, fortified against the
 Geneva is located at 46°12' North, 6°09' East, at the south-western end of
Geneva is located at 46°12' North, 6°09' East, at the south-western end of  The city covers an area of , while the area of the
The city covers an area of , while the area of the
2009 data accessed 25 March 2010. Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 3.4%, housing and buildings made up 46.2% and transportation infrastructure 25.8%, while parks, green belts and sports fields made up 15.7%. Of the agricultural land, 0.3% is used for growing crops. Of the water in the municipality, 0.2% is composed of lakes and 2.9% is rivers and streams. The altitude of Geneva is and corresponds to the altitude of the largest of the Pierres du Niton, two large rocks emerging from the lake which date from the last ice age. This rock was chosen by General
The altitude of Geneva is and corresponds to the altitude of the largest of the Pierres du Niton, two large rocks emerging from the lake which date from the last ice age. This rock was chosen by General
 The climate of Geneva is a
The climate of Geneva is a

accessed 25 April 2011/ , the gender distribution of the population was 47.8% male and 52.2% female. The population was made up of 46,284 Swiss men (24.2% of the population) and 45,127 (23.6%) non-Swiss men. There were 56,091 Swiss women (29.3%) and 43,735 (22.9%) non-Swiss women.Canton of Geneva Statistical Office
''Population résidante du canton de Genève, selon l'origine et le sexe, par commune, en mars 2011'' accessed 18 April 2011. approximately 24.3% of the population of the municipality were born in Geneva and lived there in 200043,296. A further 11,757 or 6.6% who were born in the same canton, while 27,359 or 15.4% were born elsewhere in Switzerland, and 77,893 or 43.8% were born outside of Switzerland. In , there were 1,147 live births to Swiss citizens and 893 births to non-Swiss citizens, and in the same time span there were 1,114 deaths of Swiss citizens and 274 non-Swiss citizen deaths. Ignoring immigration and emigration, the population of Swiss citizens increased by 33, while the foreign population increased by 619. There were 465 Swiss men and 498 Swiss women who emigrated from Switzerland. At the same time, there were 2933 non-Swiss men and 2662 non-Swiss women who immigrated from another country to Switzerland. The total Swiss population change in 2008 (from all sources, including moves across municipal borders) was an increase of 135 and the non-Swiss population increased by 3181 people. This represents a
accessed 19 June 2010. , children and teenagers (0–19 years old) make up 18.2% of the population, while adults (20–64 years old) make up 65.8% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 16%. , there were 78,666 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 74,205 married individuals, 10,006 widows or widowers and 15,087 individuals who are divorced.STAT-TAB Thema 40 – Eidgenössische Volkszählung (34)
accessed 2 February 2011. , there were 86,231 private households in the municipality, and an average of 1.9 persons per household. There were 44,373 households that consist of only one person and 2,549 households with five or more people. Out of a total of 89,269 households that answered this question, 49.7% were households made up of just one person and there were 471 adults who lived with their parents. Of the rest of the households, there are 17,429 married couples without children, 16,607 married couples with children. There were 5,499 single parents with a child or children. There were 1,852 households that were made up of unrelated people and 3,038 households that were made up of some sort of institution or another collective housing.
 , there were 743 single family homes (or 10.6% of the total) out of a total of 6,990 inhabited buildings. There were 2,758 multi-family buildings (39.5%), along with 2,886 multi-purpose buildings that were mostly used for housing (41.3%) and 603 other use buildings (commercial or industrial) that also had some housing (8.6%). Of the single family homes, 197 were built before 1919, while 20 were built between 1990 and 2000. The greatest number of single family homes (277) were built between 1919 and 1945.Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB – Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 – Gebäude und Wohnungen
, there were 743 single family homes (or 10.6% of the total) out of a total of 6,990 inhabited buildings. There were 2,758 multi-family buildings (39.5%), along with 2,886 multi-purpose buildings that were mostly used for housing (41.3%) and 603 other use buildings (commercial or industrial) that also had some housing (8.6%). Of the single family homes, 197 were built before 1919, while 20 were built between 1990 and 2000. The greatest number of single family homes (277) were built between 1919 and 1945.Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB – Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 – Gebäude und Wohnungen
accessed 28 January 2011. , there were 101,794 apartments in the municipality. The most common apartment size was 3 rooms of which there were 27,084. There were 21,889 single room apartments and 11,166 apartments with five or more rooms. Of these apartments, a total of 85,330 apartments (83.8% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 13,644 apartments (13.4%) were seasonally occupied and 2,820 apartments (2.8%) were empty. , the construction rate of new housing units was 1.3 new units per 1000 residents. , the average price to rent an average apartment in Geneva was 1163.30
2003 data accessed 26 May 2010. The vacancy rate for the municipality, , was 0.25%. In June 2011, the average price of an apartment in and around Geneva was 13,681 CHF per square metre (). The average can be as high as 17,589
Colors=
id:lightgrey value:gray(0.9)
id:darkgrey value:gray(0.8)
ImageSize = width:1100 height:500
PlotArea = height:350 left: 100 bottom:90 right:100
Legend = columns:3 left:220 top:70 columnwidth:160
AlignBars = justify
DateFormat = x.y
Period = from:0 till:180000
TimeAxis = orientation:vertical
AlignBars = justify
ScaleMajor = gridcolor:darkgrey increment:20000 start:0
ScaleMinor = gridcolor:lightgrey increment:5000 start:0
Colors=
id:TO value:yellowgreen legend:Total
id:FR value:teal legend:French_Speaking
id:GE value:green legend:German_Speaking
id:CA value:lightpurple legend:Catholic
id:PR value:oceanblue legend:Protestant
id:SW value:red legend:Swiss
PlotData=
color:yellowgreen width:40 mark:(line,white) align:center
bar:1850 from:start till:37724 text:"37,724" color:TO
bar:1870 from:start till:60004 text:"60,004" color:TO
bar:1888 from:start till:75709 text:"75,709" color:TO
bar:1900 from:start till:97359 text:"97,359" color:TO
bar:1910 from:start till:115243 text:"115,243" color:TO
bar:1930 from:start till:124121 text:"124,121" color:TO
bar:1950 from:start till:145473 text:"145,473" color:TO
bar:1970 from:start till:173618 text:"173,618" color:TO
bar:1990 from:start till:171042 text:"171,042" color:TO
bar:2000 from:start till:177964 text:"177,964" color:TO
LineData =
points:(300,111)(400,113) color:GE
points:(400,113)(500,118) color:GE
points:(500,118)(600,126) color:GE
points:(600,126)(700,130) color:GE
points:(700,130)(800,128) color:GE
points:(800,128)(900,109) color:GE
points:(900,109)(1000,104) color:GE
points:(300,209)(400,241) color:FR
points:(400,241)(500,259) color:FR
points:(500,259)(600,271) color:FR
points:(600,271)(700,306) color:FR
points:(700,306)(800,307) color:FR
points:(800,307)(900,309) color:FR
points:(900,309)(1000,340) color:FR
points:(100,112)(200,143) color:CA
points:(200,143)(300,153) color:CA
points:(300,153)(400,177) color:CA
points:(400,177)(500,194) color:CA
points:(500,194)(600,186) color:CA
points:(600,186)(700,204) color:CA
points:(700,204)(800,266) color:CA
points:(800,266)(900,245) color:CA
points:(900,245)(1000,219) color:CA
points:(100,141)(200,158) color:PR
points:(200,158)(300,171) color:PR
points:(300,171)(400,187) color:PR
points:(400,187)(500,198) color:PR
points:(500,198)(600,218) color:PR
points:(600,218)(700,236) color:PR
points:(700,236)(800,217) color:PR
points:(800,217)(900,157) color:PR
points:(900,157)(1000,141) color:PR
points:(100,147)(200,166) color:SW
points:(200,166)(300,182) color:SW
points:(300,182)(400,204) color:SW
points:(400,204)(500,221) color:SW
points:(500,221)(600,270) color:SW
points:(600,270)(700,321) color:SW
points:(700,321)(800,314) color:SW
points:(800,314)(900,282) color:SW
points:(900,282)(1000,284) color:SW
 Prior to the
Prior to the
Geneva saint peter.JPG, St. Pierre Cathedral
Vue aile sud College Calvin.JPG,
, www.rts.ch (page visited on 11 August 2013). An annual music festival takes place in June. Groups of artists perform in different parts of the city. In 2016 the festival celebrated its 25th anniversary. Further annual festivals are the ''Fête de l'Olivier,'' a festival of Arabic music, organized by the ICAM since 1980, and the ''Genevan Brass Festival'', founded by Christophe Sturzenegger in 2010.
 The Canton of Geneva's public school system has ''écoles primaires'' (ages 4–12) and ''cycles d'orientation'' (ages 12–15). Students can leave school at 15, but secondary education is provided by ''collèges'' (ages 15–19), the oldest of which is the
The Canton of Geneva's public school system has ''écoles primaires'' (ages 4–12) and ''cycles d'orientation'' (ages 12–15). Students can leave school at 15, but secondary education is provided by ''collèges'' (ages 15–19), the oldest of which is the  Geneva is home to the
Geneva is home to the
accessed 24 June 2010. Of the working population, 38.2% used public transportation to get to work, and 30.6% used a private car.

 The city is served by the
The city is served by the  Trains operated by
Trains operated by  In May 2013, the demonstrator electric bus system with a capacity of 133 passengers commenced between
In May 2013, the demonstrator electric bus system with a capacity of 133 passengers commenced between
 Water, natural gas and electricity are provided to the municipalities of the Canton of Geneva by the state-owned
Water, natural gas and electricity are provided to the municipalities of the Canton of Geneva by the state-owned

 Geneva is the European headquarters of the
Geneva is the European headquarters of the



 * Alfredo Aceto (born 1991), a visual artist
* Gustave Ador (1845–1928), statesman, President of the
* Alfredo Aceto (born 1991), a visual artist
* Gustave Ador (1845–1928), statesman, President of the


 *
*



 * Admiral of the Fleet Lord John Hay GCB (1827–1916), Royal Navy officer and politician
* Abraham Hermanjat (1862–1932), painter who worked in the
* Admiral of the Fleet Lord John Hay GCB (1827–1916), Royal Navy officer and politician
* Abraham Hermanjat (1862–1932), painter who worked in the

 *
*


 *
*
Geneva public transport
Geneva Tourist Information OfficeGeneva Tourist ShoppingGeneva Historical & Genealogical Society Collection
{{Portal bar, Switzerland, Europe, Geography, Cities in Switzerland Cantonal capitals of Switzerland Populated places established in the 1st millennium BC Associates of the Old Swiss Confederacy Former theocracies Counties of the Holy Roman Empire Populated places on the Rhône Populated places on Lake Geneva Populated riverside places in Switzerland Municipalities of the canton of Geneva
Carouge
Carouge () is a municipality in the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland.
History
Carouge is first mentioned in the Early Middle Ages as ''Quadruvium'' and ''Quatruvio''. In 1248 it was mentioned as ''Carrogium'' while in the 14th Century it was kno ...
, Chêne-Bougeries
Chêne-Bougeries is a municipality in the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland.
History
Chêne-Bougeries is first mentioned in 1270 as ''Quercus''. In 1801 it was mentioned as ''Chêne-les-Bougeries''.
Chêne-Bougeries was inhabited for most of its his ...
, Cologny
Cologny () is a municipality in the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland.
History
Cologny is first mentioned in 1208 as ''Colognier''.
The oldest trace of a settlement in the area is a Neolithic lake side village which was discovered near the village ...
, Lancy
Lancy is a municipality of the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland.
History
Lancy is first mentioned in 1097 as ''Lanciaco'' meaning "fearless".
Geography
Lancy has an area, , of . Of this area, or 5.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while or ...
, Grand-Saconnex
Le Grand-Saconnex () is a municipality of the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland.
Several international organizations and permanent missions to the United Nations are located in Grand Saconnex. Consequently, the population of Grand Saconnex is quite ...
, Pregny-Chambésy
Pregny-Chambésy is a commune in the canton of Geneva in Switzerland. It is located directly north of the city of Geneva, on the south-western shore of Lake Geneva.
A number of foreign permanent missions are located in Pregny-Chambésy due to i ...
, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
(after Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zü ...
) and the most populous city of Romandy
Romandy (french: Romandie or )Before World War I, the term French Switzerland (french: Suisse française) waalso used german: Romandie or , it, Romandia, rm, Romanda) is the French-speaking part of western Switzerland. In 2020, about 2 milli ...
, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situated in the south west of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial lak ...
, it is the capital of the Republic and Canton of Geneva
The Canton of Geneva, officially the Republic and Canton of Geneva (french: link=no, République et canton de Genève; frp, Rèpublica et canton de Geneva; german: Republik und Kanton Genf; it, Repubblica e Cantone di Ginevra; rm, Republica e ...
.
The city of Geneva () had a population 201,818 in 2019 (Jan. estimate) within its small municipal territory of , but the Canton of Geneva
The Canton of Geneva, officially the Republic and Canton of Geneva (french: link=no, République et canton de Genève; frp, Rèpublica et canton de Geneva; german: Republik und Kanton Genf; it, Repubblica e Cantone di Ginevra; rm, Republica e ...
(the city and its closest Swiss suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separat ...
s and exurb
An exurb (or alternately: exurban area) is an area outside the typically denser inner suburban area, at the edge of a metropolitan area, which has some economic and commuting connection to the metro area, low housing density, and growth. It s ...
s) had a population of 499,480 (Jan. 2019 estimate) over , and together with the suburbs and exurbs located in the canton of Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital c ...
and in the French departments of Ain
Ain (, ; frp, En) is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in Eastern France. Named after the Ain river, it is bordered by the Saône and Rhône rivers. Ain is located on the country's eastern edge, on the Swiss border, where it ...
and Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie (; Arpitan: ''Savouè d'Amont'' or ''Hiôta-Savouè''; en, Upper Savoy) or '; it, Alta Savoia. is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of Southeastern France, bordering both Switzerland and Italy. Its prefecture is Ann ...
the cross-border Geneva metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport net ...
as officially defined by Eurostat
Eurostat ('European Statistical Office'; DG ESTAT) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statistical information to ...
, which extends over ,As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined Functional Urban Area
The larger urban zone (LUZ), or functional urban area (FUA), is a measure of the population and expanse of metropolitan and surrounding areas which may or may not be exclusively urban. It consists of a city and its commuting zone outside it.
The ...
of Geneva was made up of 93 Swiss communes and 158 French communesFederal Statistical Office spreadsheet listing the Swiss and French communes of the Geneva Functional Urban Area
Land area of the 93 Swiss communes: 555.1 km² (source
.
Land area of the 158 French communes: 1737.1 km² (source
. had a population of 1,032,750 in Jan. 2019 (Swiss estimates and French census).As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined
Functional Urban Area
The larger urban zone (LUZ), or functional urban area (FUA), is a measure of the population and expanse of metropolitan and surrounding areas which may or may not be exclusively urban. It consists of a city and its commuting zone outside it.
The ...
of Geneva was made up of 93 Swiss communes and 158 French communesFederal Statistical Office spreadsheet listing the Swiss and French communes of the Geneva Functional Urban Area
Population of the 93 Swiss communes in January 2019: 599,556 (source
.
Population of the 158 French communes in January 2019: 433,194 (source
. Since 2013, the Canton of Geneva, the
Nyon District
Nyon District is a district in the canton of Vaud, Switzerland. The seat of the district is the city of Nyon.
Geography
Nyon has an area, , of . Of this area, or 42.0% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 44.7% is forested. Of the r ...
(in the canton of Vaud), and the (literally 'Metropolitan hub of the French Genevan territory'), this last one a federation of eight French intercommunal councils, have formed ("Greater Geneva"), a Local Grouping of Transnational Cooperation ( in French, a public entity under Swiss law) in charge of organizing cooperation within the cross-border metropolitan area of Geneva (in particular metropolitan transports). The extends over Grand Genève is made up of:
*Canton of Geneva (245.8 km�*District of Nyon (307.4 km�
*Genevois français (1443.2 km²), itself made up of CA Thonon Agglomération (238.9 km�
CA Annemasse-les Voirons-Agglomération (78.2 km�
CC Arve et Salève (99.3 km�
CC du Pays Rochois (93.9 km�
CC Faucigny-Glières (150.7 km�
CC du Genevois (151.5 km�
CA du Pays de Gex (404.9 km�
and CC du Pays Bellegardien (225.8 km�
and had a population of 1,025,316 in Jan. 2019 (Swiss estimates and French census), 58.5% of them living on Swiss territory, and 41.5% on French territory.Grand Genève is made up of: *Canton of Geneva (499,480 inh. in Jan. 201
*District of Nyon (100,685 inh. in Jan. 201
*Genevois français (425,151 inh. in Jan. 2019), itself made up of CA Thonon Agglomération (90,531 inh
CA Annemasse-les Voirons-Agglomération (90,562 inh
CC Arve et Salève (20,074 inh
CC du Pays Rochois (28,369 inh
CC Faucigny-Glières (27,181 inh
CC du Genevois (48,312 inh
CA du Pays de Gex (98,257 inh
and CC du Pays Bellegardien (21,865 inh
Geneva is a global city, a financial centre, and a worldwide centre for diplomacy due to the presence of numerous
international organization
An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states an ...
s, including the headquarters of many agencies of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
and the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, an ...
. Geneva hosts the highest number of international organizations in the world. It is also where the Geneva Conventions
upright=1.15, Original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are four treaties, and three additional protocols, that establish international legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war. The singular term ''Geneva Conve ...
were signed, which chiefly concern the treatment of wartime non-combatants and prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of w ...
. Together with, for instance, New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
(global headquarters of the UN), Basel
Basel ( , ), also known as Basle ( ),french: Bâle ; it, Basilea ; rm, label= Sutsilvan, Basileia; other rm, Basilea . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine. Basel is Switzerland's third-most-populous city (after Zürich a ...
(Bank for International Settlements), and Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
(Council of Europe), Geneva is a city serving as the headquarters of one of the most important international organizations, without being the capital of a country.
In 2021, Geneva was ranked as the world's ninth most important financial centre
A financial centre ( BE), financial center ( AE), or financial hub, is a location with a concentration of participants in banking, asset management, insurance or financial markets with venues and supporting services for these activities to ...
for competitiveness by the Global Financial Centres Index
The Global Financial Centres Index (GFCI) is a ranking of the competitiveness of financial centres based on over 29,000 financial centre assessments from an online questionnaire together with over 100 indices from organisations such as the World ...
, fifth in Europe behind London, Zürich, Frankfurt and Luxembourg. In 2019, Geneva was ranked among the ten most liveable cities in the world by Mercer
Mercer may refer to:
Business
* Mercer (car), a defunct American automobile manufacturer (1909–1925)
* Mercer (consulting firm), a large human resources consulting firm headquartered in New York City
* Mercer (occupation), a merchant or trade ...
together with Zürich and Basel
Basel ( , ), also known as Basle ( ),french: Bâle ; it, Basilea ; rm, label= Sutsilvan, Basileia; other rm, Basilea . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine. Basel is Switzerland's third-most-populous city (after Zürich a ...
. The city has been referred to as the world's most compact metropolis and the "Peace Capital". In 2019, Mercer ranked Geneva as the thirteenth most expensive city in the world. In a UBS
UBS Group AG is a multinational investment bank and financial services company founded and based in Switzerland. Co-headquartered in the cities of Zürich and Basel, it maintains a presence in all major financial centres as the largest Sw ...
ranking of global cities in 2018, Geneva was ranked first for gross earnings, second most expensive, and fourth in purchasing power
Purchasing power is the amount of goods and services that can be purchased with a unit of currency. For example, if one had taken one unit of currency to a store in the 1950s, it would have been possible to buy a greater number of items than would ...
.
Name
The city was mentioned inLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
texts, by Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
, with the spelling ''Genava'', probably from the Celtic from the stem ("bend, knee"), in the sense of a bending river or estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environme ...
, an etymology shared with the Italian port city of Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of G ...
(in Italian ''Genova'').John T. Koch, ''Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia'', ABC-CLIO, 2006, p. 1513.
The medieval county of Geneva
The County of Geneva, largely corresponding to the later Genevois province, originated in the tenth century, in the Burgundian Kingdom of Arles (Arelat) which fell to the Holy Roman Empire in 1032.
History
Several nobles had held the title of a ...
in Middle Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned ...
was known as ''pagus major Genevensis'' or ''Comitatus Genevensis'' (also ''Gebennensis''). After 1400 it became the '' Genevois'' province of Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Sa ...
(albeit not extending to the city proper, until the reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
of the seat of the Bishop of Geneva
The Catholic Diocese of Geneva was a Latin Catholic diocese in part of Switzerland and Savoy from 400 to 1801 when it merged with the Diocese of Chambéry. The merged diocese later lost Swiss territory to the Catholic Diocese of Lausanne, Geneva a ...
).
History

 Geneva was an Allobrogian border town, fortified against the
Geneva was an Allobrogian border town, fortified against the Helvetii
The Helvetii ( , Gaulish: *''Heluētī''), anglicized as Helvetians, were a Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their contact with the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. According to Juliu ...
tribe, when the Romans took it in 121 BC. It became Christian under the Late Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medit ...
, and acquired its first bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or offic ...
in the 5th century, having been connected to the Bishopric of Vienne in the 4th.
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Geneva was ruled by a count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York ...
under the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
until the late 14th century, when it was granted a charter giving it a high degree of self-governance. Around this time, the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule o ...
came to at least nominally dominate the city. In the 15th century, an oligarchic republican government emerged with the creation of the Grand Council. In the first half of the 16th century, the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
reached the city, causing religious strife, during which Savoy rule was thrown off and Geneva allied itself with the Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy or Swiss Confederacy (Modern German: ; historically , after the Reformation also , "Confederation of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or In the charters of the 14th century ...
.
In 1541, with Protestantism on the rise, John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
, the Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
Reformer and proponent of Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John ...
, became the spiritual leader of the city and established the Republic of Geneva
The Canton of Geneva, officially the Republic and Canton of Geneva (french: link=no, République et canton de Genève; frp, Rèpublica et canton de Geneva; german: Republik und Kanton Genf; it, Repubblica e Cantone di Ginevra; rm, Republica e ...
. By the 18th century, Geneva had come under the influence of Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
France, which cultivated the city as its own. France tended to be at odds with the ordinary townsfolk, which inspired the failed Geneva Revolution of 1782 The Geneva Revolution of 1782 (french: La révolution genevoise de 1782)
was a short-lived attempt to broaden the franchise and include men of modest means in the republican government of the oligarchic Genevan city-state.
Background
In 1782 the c ...
, an attempt to win representation in the government for men of modest means. In 1798, revolutionary France under the Directory
Directory may refer to:
* Directory (computing), or folder, a file system structure in which to store computer files
* Directory (OpenVMS command)
* Directory service, a software application for organizing information about a computer network's u ...
annexed Geneva. At the end of the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
, on 1June 1814, Geneva was admitted to the Swiss Confederation
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
. In 1907, the separation of Church and State was adopted. Geneva flourished in the 19th and 20th centuries, becoming the seat of many international organizations.
Geography
Topography
 Geneva is located at 46°12' North, 6°09' East, at the south-western end of
Geneva is located at 46°12' North, 6°09' East, at the south-western end of Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial lak ...
, where the Rhône flows out. It is surrounded by three mountain chains, each belonging to the Jura: the Jura main range lies north-westward, the Vuache southward, and the Salève south-eastward.
 The city covers an area of , while the area of the
The city covers an area of , while the area of the canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ente ...
is , including the two small exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
s of Céligny
Céligny is a municipality in the canton of Geneva, Switzerland. It consists of two small exclaves of the Canton of Geneva surrounded by the Canton of Vaud, near Crans-près-Céligny.
History
Céligny is first mentioned in 1163 as ''Siliniacum' ...
in Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital c ...
. The part of the lake that is attached to Geneva has an area of and is sometimes referred to as ''petit lac'' (small lake). The canton has only a border with the rest of Switzerland. Of of border, 103 are shared with France, the Département de l'Ain to the north and west and the Département de la Haute-Savoie to the south and east.
Of the land in the city, , or 1.5%, is used for agricultural purposes, while , or 3.1%, is forested. The rest of the land, , or 91.8%, is built up (buildings or roads), , or 3.1%, is either rivers or lakes and , or 0.1%, is wasteland.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics2009 data accessed 25 March 2010. Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 3.4%, housing and buildings made up 46.2% and transportation infrastructure 25.8%, while parks, green belts and sports fields made up 15.7%. Of the agricultural land, 0.3% is used for growing crops. Of the water in the municipality, 0.2% is composed of lakes and 2.9% is rivers and streams.
Guillaume Henri Dufour
Guillaume Henri Dufour (15 September 178714 July 1875) was a Swiss military officer, structural engineer and topographer. He served under Napoleon I and held the Swiss office of General four times in his career, firstly in 1847 when he led the ...
as the reference point for surveying in Switzerland. The second main river of Geneva is the Arve
The Arve (french: L'Arve, ) is a river in France (''département'' of Haute-Savoie), and Switzerland (canton of Geneva). A left tributary of the Rhône, it is long, of which 9 km in Switzerland. Its catchment area is , of which 80 km ...
, which flows into the Rhône just west of the city centre. Mont Blanc
Mont Blanc (french: Mont Blanc ; it, Monte Bianco , both meaning "white mountain") is the highest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe, rising above sea level. It is the second-most prominent mountain in Europe, after Mount Elbrus, and it ...
can be seen from Geneva and is an hour's drive from the city.
Climate
 The climate of Geneva is a
The climate of Geneva is a temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
, more specifically an oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
( Köppen climate classification: Cfb). Winters are cool, usually with light frosts at night and thawing conditions during the day. Summers are relatively warm. Precipitation is adequate and is relatively well-distributed throughout the year, although autumn is slightly wetter than other seasons. Ice storms near Lac Léman are normal in the winter: Geneva can be affected by the Bise, a north-easterly wind. This can lead to severe icing in winter.
In summer, many people swim in the lake and patronise public beaches such as Genève Plage and the Bains des Pâquis. The city, in certain years, receives snow during colder months. The nearby mountains are subject to substantial snowfall and are suitable for skiing. Many world-renowned ski resorts such as Verbier
Verbier is a village located in south-western Switzerland in the canton of Valais. It is a holiday resort and ski area in the Swiss Alps and is recognised as one of the premier off-piste resorts in the world. Some areas are covered with snow all ...
and Crans-Montana
Crans-Montana is a municipality in the district of Sierre in the canton of Valais, Switzerland. On 1 January 2017 the former municipalities of Chermignon, Mollens, Montana and Randogne merged to form the new municipality of Crans-Montana.
...
are less than three hours away by car. Mont Salève (), just across the border in France, dominates the southerly view from the city centre, and Mont Blanc
Mont Blanc (french: Mont Blanc ; it, Monte Bianco , both meaning "white mountain") is the highest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe, rising above sea level. It is the second-most prominent mountain in Europe, after Mount Elbrus, and it ...
, the highest of the Alpine range, is visible from most of the city, towering high above Chamonix
Chamonix-Mont-Blanc ( frp, Chamôni), more commonly known as Chamonix, is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of southeastern France. It was the site of the first Winter Olympics in 1924. In 2019, it had ...
, which, along with Morzine, Le Grand Bornand, La Clusaz, and resorts of the Grand Massif such as Samoens, Morillon, and Flaine, are the closest French skiing destinations to Geneva.
During the years 2000–2009, the mean yearly temperature was 11 °C and the mean number of sunshine-hours per year was 2003.
The highest temperature recorded in Genève–Cointrin was in July 2015, and the lowest temperature recorded was −20.0 °C (−4.0 °F) in February 1956.
Politics
Coat of arms

Administrative divisions
The city is divided into eight ''quartiers'', or districts, sometimes composed of several neighbourhoods. On the left bank are: (1) Jonction, (2) Centre,Plainpalais
Plainpalais is a neighbourhood in Geneva, Switzerland, and a former municipality of the Canton of Geneva.
It is mentioned in Mary Shelley's ''Frankenstein'' in chapter 6, volume 1.
Argentine author Jorge Luis Borges' ashes are buried in the cem ...
, and Acacias; (3) Eaux-Vives; and (4) Champel. The right bank includes: (1) Saint-Jean and Charmilles; (2) Servette and Petit-Saconnex; (3) Grottes and Saint-Gervais; and (4) Paquis and Nations.
Government
The Administrative Council (Conseil administratif) constitutes the executive government of the city of Geneva and operates as a collegiate authority. It is composed of five councilors (french: link=no, Conseiller administratif/ Conseillère administrative), each presiding over a department. The president of the executive department acts as mayor (''la maire/le maire''). In the governmental year 2021–2022, the Administrative Council is presided over by ''Madame la maire de Genève'' Frédérique Perler. Departmental tasks, coordination measures and implementation of laws decreed by the Municipal Council are carried out by the Administrative Council. Elections for the Administrative Council are held every five years. The current term of (''la législature'') is from 1June 2020 to 31May 2025. The delegates are elected by means of a system of Majorz. The mayor and vice change each year, while the heads of the other departments are assigned by the collegiate. The executive body holds its meetings in the Palais Eynard, near the Parc des Bastions. , Geneva's Administrative Council is made up of two representatives each of theSocial Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
F ...
(PS) and the Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation ...
(PES), and one member of the Christian Democratic Party
__NOTOC__
Christian democratic parties are political parties that seek to apply Christian principles to public policy. The underlying Christian democracy movement emerged in 19th-century Europe, largely under the influence of Catholic social tea ...
(PDC). This gives the left-wing parties four out of the five seats and, for the first time in history, a female majority. The last election was held on 15March/5April 2020. Except for the mayor, all other councillors have been elected for the first time.
Parliament
The Municipal Council (Conseil municipal) holdslegislative power
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known ...
. It is made up of 80 members, with elections held every five years. The Municipal Council makes regulations and by-laws that are executed by the Administrative Council and the administration. The delegates are selected by means of a system of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
with a seven percent threshold.
The sessions of the Municipal Council are public. Unlike members of the Administrative Council, members of the Municipal Council are not politicians by profession, and they are paid a fee based on their attendance. Any resident of Geneva allowed to vote can be elected as a member of the Municipal Council. The Council holds its meetings in the Town Hall (''Hôtel de Ville''), in the old city.
The last election of the Municipal Council was held on 15March 2020 for the (''législature'') of 2020–2025. Currently, the Municipal Council consists of: 19 members of the Social Democratic Party (PS), 18 Green Party (PES), 14 Les Libéraux-Radicaux (PLR), 8 Christian Democratic People's Party (PDC); 7 Geneva Citizens' Movement (MCG), 7 ''Ensemble à Gauche'' (an alliance of the left parties PST-POP (''Parti Suisse du Travail – Parti Ouvrier et Populaire'') and solidaritéS), 6 Swiss People's Party
The Swiss People's Party (german: Schweizerische Volkspartei, SVP; rm, Partida populara Svizra, PPS), also known as the Democratic Union of the Centre (french: Union démocratique du centre, UDC; it, Unione Democratica di Centro, UDC), is a nati ...
(UDC).
Elections
National Council
In the 2019 federal election for theSwiss National Council
The National Council (german: Nationalrat; french: Conseil national; it, Consiglio nazionale; rm, Cussegl naziunal) is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland, the upper house being the Council of States. With 200 seats, the ...
the most popular party was the Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation ...
which received 26% (+14.6) of the vote. The next seven most popular parties were the PS (17.9%, -5.9), PLR (15.1%, -2.4), the UDC (12.6%, -3.7), the PdA/ solidaritéS (10%, +1.3), the PDC (5.4%, -5.3), the pvl (5%, +2.9), and MCR (4.9%, -2.7). In the federal election a total of 34,319 votes were cast, and the voter turnout
In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate (often defined as those who cast a ballot) of a given election. This can be the percentage of registered voters, eligible voters, or all voting-age people. According to Stanford Uni ...
was 39.6%.
In the 2015 federal election for the Swiss National Council
The National Council (german: Nationalrat; french: Conseil national; it, Consiglio nazionale; rm, Cussegl naziunal) is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland, the upper house being the Council of States. With 200 seats, the ...
the most popular party was the PS which received 23.8% of the vote. The next five most popular parties were the PLR (17.6%), the UDC (16.3%), the Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation ...
(11.4%), the PDC (10.7%), and the solidaritéS (8.8%). In the federal election a total of 36,490 votes were cast, and the voter turnout
In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate (often defined as those who cast a ballot) of a given election. This can be the percentage of registered voters, eligible voters, or all voting-age people. According to Stanford Uni ...
was 44.1%.
Metropolitan cooperation
The city centre of Geneva is located only from the border of France. As a result, theurban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
and the metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport net ...
largely extend across the border on French territory. Due to the small size of the municipality of Geneva () and extension of the urban area over an international border, official bodies of transnational cooperation were developed as early as the 1970s to manage the cross-border Greater Geneva area at a metropolitan level.
In 1973, a Franco-Swiss agreement created the ''Comité régional franco-genevois'' ("Franco-Genevan Regional Committee", CRFG in French). In 1997 an 'Urban planning charter' of the CRFG defined for the first time a planning territory called ''agglomération franco-valdo-genevoise'' ("Franco-Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital c ...
-Genevan urban area"). 2001 saw the creation of a ''Comité stratégique de développement des transports publics régionaux'' ("Strategic Committee for the Development of Regional Public Transports", DTPR in French), a committee which adopted in 2003 a 'Charter for Public Transports', first step in the development of a metropolitan, cross-border commuter rail network (see Léman Express).
In 2004, a public transnational body called ''Projet d’agglomération franco-valdo-genevois'' ("Franco-Vaud-Genevan urban area project") was created to serve as the main body of metropolitan cooperation for the planning territory defined in 1997, with more local French councils taking part in this new public body than in the CRFG created in 1973. Finally in 2012 the ''Projet d’agglomération franco-valdo-genevois'' was renamed '' Grand Genève'' ("Greater Geneva"), and the following year it was transformed into a Local Grouping of Transnational Cooperation (GLCT in French), a public entity under Swiss law, which now serves as the executive body of the ''Grand Genève''.
The ''Grand Genève'' GLCT is made up of the Canton of Geneva
The Canton of Geneva, officially the Republic and Canton of Geneva (french: link=no, République et canton de Genève; frp, Rèpublica et canton de Geneva; german: Republik und Kanton Genf; it, Repubblica e Cantone di Ginevra; rm, Republica e ...
, the Nyon District
Nyon District is a district in the canton of Vaud, Switzerland. The seat of the district is the city of Nyon.
Geography
Nyon has an area, , of . Of this area, or 42.0% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 44.7% is forested. Of the r ...
(in the canton of Vaud), and the ''Pôle métropolitain du Genevois français'' (literally "Metropolitan hub of the French Genevan territory"), this last one a federation of eight French intercommunal councils in Ain
Ain (, ; frp, En) is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in Eastern France. Named after the Ain river, it is bordered by the Saône and Rhône rivers. Ain is located on the country's eastern edge, on the Swiss border, where it ...
and Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie (; Arpitan: ''Savouè d'Amont'' or ''Hiôta-Savouè''; en, Upper Savoy) or '; it, Alta Savoia. is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of Southeastern France, bordering both Switzerland and Italy. Its prefecture is Ann ...
. The ''Grand Genève'' GLCT extends over
and had a population of 1,025,316 in Jan. 2019 (Swiss estimates and French census), 58.5% of them living on Swiss territory, and 41.5% on French territory.
International relations
Geneva does not have anysister
A sister is a woman or a girl who shares one or more parents with another individual; a female sibling. The male counterpart is a brother. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer t ...
relationships with other cities. It declares itself related to the entire world.
Demographics
Population
The city of Geneva (''ville de Genève'') had a population 201,818 in 2019 (Jan. estimate) within its small municipal territory of . The city of Geneva is at the centre of the Genevametropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport net ...
, a Functional Urban Area
The larger urban zone (LUZ), or functional urban area (FUA), is a measure of the population and expanse of metropolitan and surrounding areas which may or may not be exclusively urban. It consists of a city and its commuting zone outside it.
The ...
(as per Eurostat
Eurostat ('European Statistical Office'; DG ESTAT) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statistical information to ...
methodology) which extends over Swiss territory (entire Canton of Geneva
The Canton of Geneva, officially the Republic and Canton of Geneva (french: link=no, République et canton de Genève; frp, Rèpublica et canton de Geneva; german: Republik und Kanton Genf; it, Repubblica e Cantone di Ginevra; rm, Republica e ...
and part of the canton of Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital c ...
) and French territory (parts of the departments of Ain
Ain (, ; frp, En) is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in Eastern France. Named after the Ain river, it is bordered by the Saône and Rhône rivers. Ain is located on the country's eastern edge, on the Swiss border, where it ...
and Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie (; Arpitan: ''Savouè d'Amont'' or ''Hiôta-Savouè''; en, Upper Savoy) or '; it, Alta Savoia. is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of Southeastern France, bordering both Switzerland and Italy. Its prefecture is Ann ...
). The Geneva Functional Urban Area covers a land area of (24.2% in Switzerland, 75.8% in France) and had 1,032,750 inhabitants in Jan. 2019 (Swiss estimates and French census), 58,1% of them on Swiss territory and 41.9% on French territory.
The Geneva metropolitan area is one of the fastest growing in Europe. Its population rose from 870,208 in Jan. 2008 to 1,032,750 in Jan. 2019, which means the metropolitan area registered a population growth rate of +1.57% per year during those 11 years. Growth is higher in the French part of the metropolitan area (+2.01% per year between 2008 and 2019) than in the Swiss part (+1.29% per year between 2008 and 2019), as Geneva attracts many French commuters due to high Swiss salaries and a favorable Franco-Swiss tax regime for French residents working in Switzerland.
The official language of Geneva (both the city and the canton) is French. English is also common due to the high number of anglophone immigrants and foreigners working in international institutions and in the bank sector. , 128,622 or 72.3% of the population speaks French as a first language, with English being the second most common (7,853 or 4.4%) language. 7,462 inhabitants speak Spanish (or 4.2%), 7,320 speak Italian (4.1%), 7,050 speak German (4.0%) and 113 people who speak Romansh. As a result of immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, ...
flows in the 1960s and 1980s, Portuguese is also spoken by a considerable proportion of the population.
In the city of Geneva, , 48% of the population are resident foreign nationals. For a list of the largest groups of foreign residents see the cantonal overview. Over the last 10 years (1999–2009), the population has changed at a rate of 7.2%; a rate of 3.4% due to migration and at a rate of 3.4% due to births and deaths.Swiss Federal Statistical Officeaccessed 25 April 2011/ , the gender distribution of the population was 47.8% male and 52.2% female. The population was made up of 46,284 Swiss men (24.2% of the population) and 45,127 (23.6%) non-Swiss men. There were 56,091 Swiss women (29.3%) and 43,735 (22.9%) non-Swiss women.Canton of Geneva Statistical Office
''Population résidante du canton de Genève, selon l'origine et le sexe, par commune, en mars 2011'' accessed 18 April 2011. approximately 24.3% of the population of the municipality were born in Geneva and lived there in 200043,296. A further 11,757 or 6.6% who were born in the same canton, while 27,359 or 15.4% were born elsewhere in Switzerland, and 77,893 or 43.8% were born outside of Switzerland. In , there were 1,147 live births to Swiss citizens and 893 births to non-Swiss citizens, and in the same time span there were 1,114 deaths of Swiss citizens and 274 non-Swiss citizen deaths. Ignoring immigration and emigration, the population of Swiss citizens increased by 33, while the foreign population increased by 619. There were 465 Swiss men and 498 Swiss women who emigrated from Switzerland. At the same time, there were 2933 non-Swiss men and 2662 non-Swiss women who immigrated from another country to Switzerland. The total Swiss population change in 2008 (from all sources, including moves across municipal borders) was an increase of 135 and the non-Swiss population increased by 3181 people. This represents a
population growth rate
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 t ...
of 1.8%.Swiss Federal Statistical Office – Superweb database – Gemeinde Statistics 1981–2008accessed 19 June 2010. , children and teenagers (0–19 years old) make up 18.2% of the population, while adults (20–64 years old) make up 65.8% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 16%. , there were 78,666 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 74,205 married individuals, 10,006 widows or widowers and 15,087 individuals who are divorced.STAT-TAB Thema 40 – Eidgenössische Volkszählung (34)
accessed 2 February 2011. , there were 86,231 private households in the municipality, and an average of 1.9 persons per household. There were 44,373 households that consist of only one person and 2,549 households with five or more people. Out of a total of 89,269 households that answered this question, 49.7% were households made up of just one person and there were 471 adults who lived with their parents. Of the rest of the households, there are 17,429 married couples without children, 16,607 married couples with children. There were 5,499 single parents with a child or children. There were 1,852 households that were made up of unrelated people and 3,038 households that were made up of some sort of institution or another collective housing.

accessed 28 January 2011. , there were 101,794 apartments in the municipality. The most common apartment size was 3 rooms of which there were 27,084. There were 21,889 single room apartments and 11,166 apartments with five or more rooms. Of these apartments, a total of 85,330 apartments (83.8% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 13,644 apartments (13.4%) were seasonally occupied and 2,820 apartments (2.8%) were empty. , the construction rate of new housing units was 1.3 new units per 1000 residents. , the average price to rent an average apartment in Geneva was 1163.30
Swiss franc
The Swiss franc is the currency and legal tender of Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It is also legal tender in the Italian exclave of Campione d'Italia which is surrounded by Swiss territory. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) issues banknotes and the fe ...
s (CHF) per month (US$930, £520, €740 approx. exchange rate from 2003). The average rate for a one-room apartment was 641.60 CHF (US$510, £290, €410), a two-room apartment was about 874.46 CHF (US$700, £390, €560), a three-room apartment was about 1126.37 CHF (US$900, £510, €720) and a six or more room apartment cost an average of 2691.07 CHF (US$2150, £1210, €1720). The average apartment price in Geneva was 104.2% of the national average of 1116 CHF.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Rental prices2003 data accessed 26 May 2010. The vacancy rate for the municipality, , was 0.25%. In June 2011, the average price of an apartment in and around Geneva was 13,681 CHF per square metre (). The average can be as high as 17,589
Swiss franc
The Swiss franc is the currency and legal tender of Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It is also legal tender in the Italian exclave of Campione d'Italia which is surrounded by Swiss territory. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) issues banknotes and the fe ...
s (CHF) per square metre () for a luxury apartment and as low as 9,847 Swiss francs (CHF) for an older or basic apartment. For houses in and around Geneva, the average price was 11,595 Swiss francs (CHF) per square metre () (June 2011), with a lowest price per square metre () of 4,874 Swiss francs (CHF), and a maximum price of 21,966 Swiss francs (CHF).
Historical population
William Monter calculates that the city's total population was 12,000–13,000 in 1550, doubling to over 25,000 by 1560. The historical population is given in the following chart:Religion
The recorded 66,491 residents (37.4% of the population) as Catholic, while 41,289 people (23.20%) belonged to no church or were agnostic oratheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
, 24,105 (13.5%) belonged to the Swiss Reformed Church
The Protestant Church in Switzerland (PCS), (EKS); french: Église évangélique réformée de Suisse (EERS); it, Chiesa evangelica riformata in Svizzera (CERiS); rm, Baselgia evangelica refurmada da la Svizra (BRRS) formerly named Federation o ...
, and 8,698 (4.89%) were Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
. There were also 3,959 members of an Orthodox church (2.22%), 220 individuals (or about 0.12% of the population) who belonged to the Christian Catholic Church of Switzerland
The Christian Catholic Church of Switzerland is an Old Catholic denomination in Switzerland. This denomination is part of the Union of Utrecht (Old Catholic).
Recent developments
In 1871 the Zürich Catholic community planned to build a c ...
, 2,422 (1.36%) who belonged to another Christian church, and 2,601 people (1.46%) who were Jewish. There were 707 individuals who were Buddhist, 474 who were Hindu and 423 who belonged to another church. 26,575 respondents (14.93%) did not answer the question.
According to 2012 statistics by Swiss Bundesamt für Statistik 49.2% of the population were Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
, (34.2% Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, 8.8% Swiss Reformed (organized in the Protestant Church of Geneva
The Protestant Church of Geneva (EPG, french: link=no, Église protestante de Genève) is an organization of congregations in the Canton of Geneva. It was founded in 1536 during the Protestant Reformation. It was the state church of Geneva from its ...
) and 6.2% other Christians, mostly other Protestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
), 38% of Genevans were non-religious
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and ant ...
, 6.1% were Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
and 1.6% were Jews.
Geneva has historically been considered a Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
city and was known as the ''Protestant Rome'' due to it being the base of John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
, William Farel, Theodore Beza
Theodore Beza ( la, Theodorus Beza; french: Théodore de Bèze or ''de Besze''; June 24, 1519 – October 13, 1605) was a French Calvinist Protestant theologian, reformer and scholar who played an important role in the Protestant Reformatio ...
and other Protestant reformers
Protestant Reformers were those theologians whose careers, works and actions brought about the Protestant Reformation of the 16th century.
In the context of the Reformation, Martin Luther was the first reformer (sharing his views publicly in 15 ...
. Over the past century, substantial immigration from France and other predominantly Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
countries, as well as general secularization, has changed its religious landscape. As a result, three times as many Roman Catholics as Protestants lived in the city in 2000, while a large number of residents were members of neither group. Geneva forms part of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Lausanne, Geneva and Fribourg
The Diocese of Lausanne, Geneva and Fribourg ( la, Dioecesis Lausannensis, Genevensis et Friburgensis) is a Latin Catholic diocese in Switzerland, which is (as all sees in the Alpine country) exempt (i.e. immediately subject to the Holy See, not p ...
.
The World Council of Churches
The World Council of Churches (WCC) is a worldwide Christian inter-church organization founded in 1948 to work for the cause of ecumenism. Its full members today include the Assyrian Church of the East, the Oriental Orthodox Churches, most jur ...
and the Lutheran World Federation
The Lutheran World Federation (LWF; german: Lutherischer Weltbund) is a global communion of national and regional Lutheran denominations headquartered in the Ecumenical Centre in Geneva, Switzerland. The federation was founded in the Swedish ...
both have their headquarters at the Ecumenical Centre
The Ecumenical Centre in Geneva, Switzerland, is located in the vicinity of the International Labour Organization, International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, and the World Health Organization and serves as the base for the following chu ...
in Grand-Saconnex
Le Grand-Saconnex () is a municipality of the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland.
Several international organizations and permanent missions to the United Nations are located in Grand Saconnex. Consequently, the population of Grand Saconnex is quite ...
, Geneva. The World Communion of Reformed Churches
The World Communion of Reformed Churches (WCRC) is the largest association of Calvinist churches in the world. It has 230 member denominations in 108 countries, together claiming an estimated 80 million people, thus being the fourth-largest Chris ...
, a worldwide organization of Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their na ...
, Continental Reformed
Continental Reformed Protestantism is a part of the Calvinist tradition within Protestantism that traces its origin in the European continent. Prominent subgroups are the Dutch Reformed, the Swiss Reformed, the French Reformed (Huguenots), the ...
, Congregational
Congregational churches (also Congregationalist churches or Congregationalism) are Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition practising congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs it ...
and other Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John ...
churches gathering more than 80 million people around the world was based here from 1948 until 2013. The executive committee of the World Communion of Reformed Churches
The World Communion of Reformed Churches (WCRC) is the largest association of Calvinist churches in the world. It has 230 member denominations in 108 countries, together claiming an estimated 80 million people, thus being the fourth-largest Chris ...
voted in 2012 to move its offices to Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German States of Germany, state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germa ...
, Germany, citing the high costs of running the ecumenical organization in Geneva, Switzerland. The move was completed in 2013. Likewise, the Conference of European Churches
The Conference of European Churches (CEC) was founded in 1959 to promote reconciliation, dialogue and friendship between the churches of Europe at a time of growing Cold War political tensions and divisions.
In its commitment to Europe as a who ...
have moved their headquarters from Geneva to Brussels.
"Protestant Rome"
 Prior to the
Prior to the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
the city was ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. Reaction to the new movement varied across Switzerland. John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
went to Geneva in 1536 after William Farel encouraged him to do so. In Geneva, the Catholic bishop had been obliged to seek exile in 1532. Geneva became a stronghold of Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John ...
. Some of the tenets created there influenced Protestantism as a whole. St. Pierre Cathedral was where Calvin and his Protestant reformers
Protestant Reformers were those theologians whose careers, works and actions brought about the Protestant Reformation of the 16th century.
In the context of the Reformation, Martin Luther was the first reformer (sharing his views publicly in 15 ...
preached. It constituted the epicentre of the newly developing Protestant thought that would later become known as the Reformed tradition
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Calv ...
. Many prominent Reformed theologians operated there, including William Farel and Theodore Beza
Theodore Beza ( la, Theodorus Beza; french: Théodore de Bèze or ''de Besze''; June 24, 1519 – October 13, 1605) was a French Calvinist Protestant theologian, reformer and scholar who played an important role in the Protestant Reformatio ...
, Calvin's successor who progressed Reformed thought after his death.
Geneva was a shelter for Calvinists, but at the same time it persecuted Roman Catholics and others considered heretics. The case of Michael Servetus
Michael Servetus (; es, Miguel Serveto as real name; french: Michel Servet; also known as ''Miguel Servet'', ''Miguel de Villanueva'', ''Revés'', or ''Michel de Villeneuve''; 29 September 1509 or 1511 – 27 October 1553) was a Spanish th ...
, an early Nontrinitarian
Nontrinitarianism is a form of Christianity that rejects the mainstream Christian doctrine of the Trinity—the belief that God is three distinct hypostases or persons who are coeternal, coequal, and indivisibly united in one being, or essence ...
, is notable. Condemned by both Catholics and Protestants alike, he was arrested in Geneva and burnt at the stake as a heretic by order of the city's Protestant governing council. John Calvin and his followers denounced him, and possibly contributed to his sentence.
In 1802, during its annexation to France under Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, the Diocese of Geneva was united with the Diocese of Chambéry, but the 1814 Congress of Vienna and the 1816 Treaty of Turin stipulated that in the territories transferred to a now considerably extended Geneva, the Catholic religion was to be protected and that no changes were to be made in existing conditions without an agreement with the Holy See. Napoleon's common policy was to emancipate Catholics in Protestant-majority areas, and the other way around, as well as emancipating Jews. In 1819, the city of Geneva and 20 parishes were united to the Diocese of Lausanne by Pope Pius VII
Pope Pius VII ( it, Pio VII; born Barnaba Niccolò Maria Luigi Chiaramonti; 14 August 1742 – 20 August 1823), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 14 March 1800 to his death in August 1823. Chiaramonti was also a ...
and in 1822, the non-Swiss territory was made into the Diocese of Annecy. A variety of concord with the civil authorities came as a result of the separation of church and state
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular sta ...
, enacted with strong Catholic support in 1907.
Crime
In 2014 the incidence of crimes listed in theSwiss Criminal Code
The Swiss Criminal Code (SR/RS 311, german: Strafgesetzbuch (StGB), french: Code pénal suisse (CP), it, Codice penale svizzero (CP), rm, Cudesch penal svizzer) is a portion of the third part (SR/RS 3) of the internal Swiss law ("Private law - ...
in Geneva was 143.9 per thousand residents. During the same period the rate of drug crimes was 33.6 per thousand residents. The rate of violations of immigration, visa and work permit laws was 35.7 per thousand residents.
Cityscape
Heritage sites of national significance
There are 82 buildings or sites in Geneva that are listed as Swiss heritage sites of national significance, and the entire old city of Geneva is part of theInventory of Swiss Heritage Sites
The Federal Inventory of Heritage Sites (ISOS) is part of a 1981 Ordinance of the Swiss Federal Council implementing the Federal Law on the Protection of Nature and Cultural Heritage.
Sites of national importance
Types
The types are based on t ...
.
Religious buildings: Cathedral St-Pierre et Chapel des Macchabés, Notre-Dame Church, Russian church, St-Germain Church, Temple de la Fusterie, Temple de l'Auditoire
Civic buildings: Former Arsenal and Archives of the City of Genève, Former Crédit Lyonnais, Former Hôtel Buisson, Former Hôtel du Résident de France et Bibliothèque de la Société de lecture de Genève, Former école des arts industriels, Archives d'État de Genève (Annexe), Bâtiment des forces motrices, Bibliothèque de Genève
The Bibliothèque de Genève (BGE, English: Geneva Library, Library of Geneva), founded in 1559, was known as ''Bibliothèque publique et universitaire'' (BPU, English: Public and University Library) from 1907 to 2006.
It occupies different build ...
, Library juive de Genève «Gérard Nordmann», Cabinet des estampes, Centre d'Iconographie genevoise, Collège Calvin
The Collège Calvin, formerly the Collège de Genève, is the oldest public secondary school in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by John Calvin.
History
On February 24, 1428, the ''Conseil Général'' of Geneva decided to establish ...
, École Geisendorf, University Hospital of Geneva (HUG), Hôtel de Ville et tour Baudet, Immeuble Clarté at Rue Saint-Laurent 2 and 4, Immeubles House Rotonde at Rue Charles-Giron 11–19, Immeubles at Rue Beauregard 2, 4, 6, 8, Immeubles at Rue de la Corraterie 10–26, Immeubles at Rue des Granges 2–6, Immeuble at Rue des Granges 8, Immeubles at Rue des Granges 10 and 12, Immeuble at Rue des Granges 14, Immeuble and Former Armory at Rue des Granges 16, Immeubles at Rue Pierre Fatio 7 and 9, House de Saussure at Rue de la Cité 24, House Des arts du Grütli at Rue du Général-Dufour 16, House Royale et les deux immeubles à côté at Quai Gustave Ador 44–50, Tavel House at Rue du Puits-St-Pierre 6, Turrettini House at Rue de l'Hôtel-de-Ville 8 and 10, Brunswick Monument, Palais de Justice, Palais de l'Athénée, Palais des Nations with library and archives of the SDN and ONU, Palais Eynard et Archives de la ville de Genève, Palais Wilson
The Palais Wilson (Wilson Palace) in Geneva, Switzerland, is the current headquarters of the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights. It was also the headquarters of the League of Nations from 1 November 1920 until that bod ...
, Parc des Bastions avec Mur des Réformateurs, Place de Neuve et Monument du Général Dufour, Pont de la Machine, Pont sur l'Arve, Poste du Mont-Blanc, Quai du Mont-Blanc, Quai et Hôtel des Bergues, Quai Général Guisan and English Gardens, Quai Gustave-Ador and Jet d'eau
The Jet d'Eau (, ''Water-Jet'') is a large fountain in Geneva, Switzerland and is one of the city's most famous landmarks, being featured on the city's official tourism web site and on the official logo for Geneva's hosting of group stage matches ...
, Télévision Suisse Romande
Télévision Suisse Romande ("Swiss Television Romandy") was a TV network with two channels: TSR 1 and TSR 2 (the two channels became RTS Un and RTS Deux after 2012). They were the main French language channels in Switzerland, part of SRG ...
, University of Geneva
The University of Geneva (French: ''Université de Genève'') is a public research university located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by John Calvin as a theological seminary. It remained focused on theology until the 17th centur ...
, Victoria Hall.
Archeological sites:
Foundation Baur and Museum of the arts d'Extrême-Orient, Parc et campagne de la Grange and Library (neolithic shore settlement/Roman villa), Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pr ...
shore settlement of Plonjon, Temple de la Madeleine archeological site, Temple Saint-Gervais archeological site, Old City with Celtic, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
and medieval villages.
Museums, theaters, and other cultural sites: Conservatoire de musique at Place Neuve 5, Conservatoire et Jardin botaniques, Fonds cantonal d'art contemporain, Ile Rousseau and statue, Institut et Musée Voltaire with Library and Archives, Mallet House and Museum international de la Réforme, Musée Ariana, Museum of Art and History, Museum d'art moderne et contemporain, Museum d'ethnographie, Museum of the International Red Cross, Musée Rath, Natural History Museum, Plainpalais Commune Auditorium, Pitoëff Theatre, Villa Bartholoni at the Museum of History and Science.
International organizations: International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
(ILO), International Committee of the Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signator ...
, United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integrat ...
(UNHCR), World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Internat ...
, World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
, International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Union ...
, World YMCA
YMCA, sometimes regionally called the Y, is a worldwide youth organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, with more than 64 million beneficiaries in 120 countries. It was founded on 6 June 1844 by George Williams in London, originally ...
.
Collège Calvin
The Collège Calvin, formerly the Collège de Genève, is the oldest public secondary school in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by John Calvin.
History
On February 24, 1428, the ''Conseil Général'' of Geneva decided to establish ...
IKRK Hauptquartier.jpg, International Committee of the Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signator ...
(CICR)
Botanical Garden Geneva 2006 803.JPG, Conservatory and Botanical Garden of the City of Geneva
The Conservatory and Botanical Garden of the city of Geneva () is a museum and an institution of the City of Geneva.
Establishment and location
It was founded in 1817 in a former area of ''Bastions Park'' in 1817 by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle ...
Basilique Notre-Dame, Genève.jpg, Notre-Dame Church
Eglise Orthodoxe Russe de Geneve.jpg, Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
Genf UNHCR.JPG, United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integrat ...
(UNHCR)
Hotel de Ville Geneva.jpg, Hôtel de Ville and the Tour Baudet
Voltaire Museum.JPG, Institut et Musée Voltaire
Musee Reforme.JPG, Mallet House and Museum international de la Réforme
Tavel House.JPG, Tavel House
Brunswick Monument.jpg, Brunswick Monument
Musée d'Art et d'Histoire (46745210785).jpg, Musée d'Art et d'Histoire
Villa La Grange.jpg, The Villa La Grange
Society and culture
Media
The city's main newspaper is the daily ''Tribune de Genève
The ''Tribune de Genève'' (English: ''Geneva Tribune'') is a Swiss French-language, regional daily newspaper, published in Berliner format by Edipresse in Geneva.
History and operations
The ''Tribune de Genève'' was first published by Jam ...
'', with a readership of about 187,000. '' Le Courrier'' mainly focuses on Geneva. Both ''Le Temps
''Le Temps'' (literally "The Time") is a Swiss French-language daily newspaper published in Berliner format in Geneva by Le Temps SA. It is the sole nationwide French-language non-specialised daily newspaper of Switzerland. Since 2021, it has b ...
'' (headquartered in Geneva) and '' Le Matin'' are widely read in Geneva, but cover the whole of Romandy
Romandy (french: Romandie or )Before World War I, the term French Switzerland (french: Suisse française) waalso used german: Romandie or , it, Romandia, rm, Romanda) is the French-speaking part of western Switzerland. In 2020, about 2 milli ...
.
Geneva is the main media center for French-speaking Switzerland. It is the headquarters for the numerous French language radio and television networks of the Swiss Broadcasting Corporation
The Swiss Broadcasting Corporation (german: Schweizerische Radio- und Fernsehgesellschaft; french: Société suisse de radiodiffusion et télévision; it, Società svizzera di radiotelevisione; rm, Societad Svizra da Radio e Televisiun; SRG ...
, known collectively as Radio Télévision Suisse
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmit ...
. While both networks cover the whole of Romandy
Romandy (french: Romandie or )Before World War I, the term French Switzerland (french: Suisse française) waalso used german: Romandie or , it, Romandia, rm, Romanda) is the French-speaking part of western Switzerland. In 2020, about 2 milli ...
, special programs related to Geneva are sometimes broadcast on some of the local radio frequencies. Other local radio stations broadcast from the city, including YesFM ( FM 91.8 MHz), Radio Cité (non-commercial radio, FM 92.2 MHz), OneFM (FM 107.0 MHz, also broadcast in Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital c ...
), and World Radio Switzerland (FM 88.4 MHz). Léman Bleu is a local TV channel, founded in 1996 and distributed by cable. Due to the proximity to France, many French television channels are also available.
Traditions and customs
Geneva observes '' Jeûne genevois'' on the first Thursday following the first Sunday in September. By local tradition, this commemorates the date news of theSt. Bartholomew's Day massacre
The St. Bartholomew's Day massacre (french: Massacre de la Saint-Barthélemy) in 1572 was a targeted group of assassinations and a wave of Catholic mob violence, directed against the Huguenots (French Calvinist Protestants) during the French Wa ...
of Huguenots reached Geneva.
Geneva celebrates ''L'Escalade
''L'Escalade'', or ''Fête de l'Escalade'' (from escalade, the act of scaling defensive walls), is an annual festival in Geneva, Switzerland, held each December commemorating the defeat of an attempt to conquer the Protestant city-state by th ...
'' on the weekend nearest 12 December, celebrating the defeat of the surprise attack of troops sent by Charles Emmanuel I, Duke of Savoy
Charles Emmanuel I ( it, Carlo Emanuele di Savoia; 12 January 1562 – 26 July 1630), known as the Great, was the Duke of Savoy from 1580 to 1630. He was nicknamed (, in context "the Hot-Headed") for his rashness and military aggression.
Bein ...
during the night of 11–12 December 1602. Festive traditions include chocolate cauldrons filled with vegetable-shaped marzipan treats and the Escalade procession on horseback in seventeenth century armour. Geneva has also been organizing a 'Course de l'Escalade', which means 'Climbing Race'. This race takes place in Geneva's Old Town, and has been popular across all ages. Non-competitive racers dress up in fancy costumes, while walking in the race.
Since 1818, a particular chestnut tree has been used as the official "herald of the spring" in Geneva. The ''sautier'' (secretary of the Parliament of the Canton of Geneva) observes the tree and notes the day of arrival of the first bud. While this event has no practical effect, the sautier issues a formal press release
A press release is an official statement delivered to members of the news media for the purpose of providing information, creating an official statement, or making an announcement directed for public release. Press releases are also consider ...
and the local newspaper will usually mention the news.
As this is one of the world's oldest records of a plant's reaction to climatic conditions, researchers have been interested to note that the first bud has been appearing earlier and earlier in the year. During the 19th century many dates were in March or April. In recent years, they have usually been in late February (sometimes earlier). In 2002, the first bud appeared unusually early, on 7 February, and then again on 29 December of the same year. The following year, one of the hottest years recorded in Europe, was a year with no bud. In 2008, the first bud also appeared early, on 19 February.
Music and festivals
Theopera house
An opera house is a theatre building used for performances of opera. It usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, and backstage facilities for costumes and building sets.
While some venues are constructed specifically fo ...
, the Grand Théâtre de Genève
Grand Théâtre de Genève is an opera house in Geneva, Switzerland.
As with many other opera houses, the Grand Théâtre de Genève is both a venue and an institution. The venue is a majestic building, towering over Place Neuve, official ...
, which officially opened in 1876, was partly destroyed by a fire in 1951 and reopened in 1962. It has the largest stage in Switzerland. It features opera and dance performances, recitals, concerts and, occasionally, theatre. The Victoria Hall is used for classical music concerts. It is the home of the Orchestre de la Suisse Romande
The Orchestre de la Suisse Romande (OSR) is a Swiss symphony orchestra, based in Geneva at the Victoria Hall. In addition to symphony concerts, the OSR performs as the opera orchestra in productions at the Grand Théâtre de Genève.
History
E ...
.
Every summer the Fêtes de Genève (Geneva Festival) are organised in Geneva. According to Radio Télévision Suisse
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmit ...
in 2013 hundreds of thousands of people came to Geneva to see the annual hour-long grand firework
Fireworks are a class of Explosive, low explosive Pyrotechnics, pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a l ...
display of the Fêtes de Genève."Une heure de feux genevois sur le thème des conquêtes", www.rts.ch (page visited on 11 August 2013). An annual music festival takes place in June. Groups of artists perform in different parts of the city. In 2016 the festival celebrated its 25th anniversary. Further annual festivals are the ''Fête de l'Olivier,'' a festival of Arabic music, organized by the ICAM since 1980, and the ''Genevan Brass Festival'', founded by Christophe Sturzenegger in 2010.
Education
 The Canton of Geneva's public school system has ''écoles primaires'' (ages 4–12) and ''cycles d'orientation'' (ages 12–15). Students can leave school at 15, but secondary education is provided by ''collèges'' (ages 15–19), the oldest of which is the
The Canton of Geneva's public school system has ''écoles primaires'' (ages 4–12) and ''cycles d'orientation'' (ages 12–15). Students can leave school at 15, but secondary education is provided by ''collèges'' (ages 15–19), the oldest of which is the Collège Calvin
The Collège Calvin, formerly the Collège de Genève, is the oldest public secondary school in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by John Calvin.
History
On February 24, 1428, the ''Conseil Général'' of Geneva decided to establish ...
, which could be considered one of the oldest public schools in the world, ''écoles de culture générale'' (15–18/19) and the ''écoles professionnelles'' (15–18/19). The ''écoles professionnelles'' offer full-time courses and part-time study as part of an apprenticeship. Geneva also has a number of private schools.
In 2011 89,244 (37.0%) of the population had completed non-mandatory upper secondary education, and 107,060 or (44.3%) had completed additional higher education (either university or a Fachhochschule). Of the 107,060 who completed tertiary schooling, 32.5% were Swiss men, 31.6% were Swiss women, 18.1% were non-Swiss men and 17.8% were non-Swiss women.
During the 2011–2012 school year, there were a total of 92,311 students in the Geneva school system (primary to university). The education system in the Canton of Geneva has eight years of primary school, with 32,716 students. The secondary school program consists of three lower, obligatory years of schooling, followed by three to five years of optional, advanced study. There were 13,146 lower-secondary students who attended schools in Geneva. There were 10,486 upper-secondary students from the municipality along with 10,330 students who were in a professional, non-university track program. An additional 11,797 students were attending private schools.
 Geneva is home to the
Geneva is home to the University of Geneva
The University of Geneva (French: ''Université de Genève'') is a public research university located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by John Calvin as a theological seminary. It remained focused on theology until the 17th centur ...
where approximately 16,500 students are regularly enrolled. In 1559 John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
founded the Geneva Academy, a theological and humanist seminary. In the 19th century the academy lost its ecclesiastic links and in 1873, with the addition of a medical faculty, it became the University of Geneva. In 2011 it was ranked European university.
The Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies
The Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies, or the Geneva Graduate Institute (french: Institut de hautes études internationales et du développement), abbreviated IHEID, is a government-accredited postgraduate institution ...
was among the first academic institutions in the world to teach international relations. It is one of Europe's most prestigious institutions, offering MA and PhD programmes in anthropology and sociology, law, political science, history, economics, international affairs, and development studies.
The oldest international school in the world is the International School of Geneva
The International School of Geneva (in French: ''Ecole Internationale de Genève''), also known as "Ecolint" or "The International School", is a private, non-profit international school based in Geneva, Switzerland.
Founded in 1924 in the serv ...
, founded in 1924 along with the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
. The Geneva School of Diplomacy and International Relations is a private, for-profit university in the grounds of the Château de Penthes.
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Gene ...
(the European Organization for Nuclear Research) is probably the best known of Geneva's educational and research facilities, most recently for the Large Hadron Collider
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle collider. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and hundre ...
. Founded in 1954, CERN was one of Europe's first joint ventures and has developed as the world's largest particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
laboratory. Physicists from around the world travel to CERN to research matter and explore the fundamental forces and materials that form the universe.
Geneva is home to five major libraries, the ''Bibliothèques municipales Genève'', the ''Haute école de travail social, Institut d'études sociales'', the ''Haute école de santé'', the ''Ecole d'ingénieurs de Genève'' and the ''Haute école d'art et de design''. There were () 877,680 books or other media in the libraries, and in the same year 1,798,980 items were loaned.
Economy
Geneva's economy is largely service-driven and closely linked to the rest of the canton. The city is one of the global leaders in financial centres. Three main sectors dominate the financial sector: commodity trading; trade finance, and wealth management. Around a third of the world's free traded oil, sugar, grains and oil seeds is traded in Geneva. Approximately 22% of the world's cotton is traded in the Lake Geneva region. Other major commodities traded in the canton include steel, electricity, or coffee. Large trading companies have their regional or global headquarters in the canton, such as Bunge,Cargill
Cargill, Incorporated, is a Privately held company, privately held American global food corporation based in Minnetonka, Minnesota, Minnetonka, Minnesota, and incorporated in Wilmington, Delaware. Founded in 1865, it is the largest privatel ...
, Vitol
Vitol is a Swiss-based multinational energy and commodity trading company that was founded in Rotterdam in 1966 by Henk Viëtor and Jacques Detiger. Though trading, logistics and distribution are at the core of its business, these are complement ...
, Gunvor, BNP Paribas
BNP Paribas is a French international banking group, founded in 2000 from the merger between Banque Nationale de Paris (BNP, "National Bank of Paris") and Paribas, formerly known as the Banque de Paris et des Pays-Bas. The full name of the gro ...
, Trafigura
Trafigura Group Pte. Ltd. is a Singaporean-based Swiss multinational commodity trading company founded in 1993 that trades in base metals and energy. It is the world's largest private metals trader and second-largest oil trader having built or ...
or Mercuria Energy Group
Mercuria Energy Group Ltd is a Cypriot-domiciled multinational commodity trading company active in a wide spectrum of global energy markets including crude oil and refined petroleum products, natural gas (including LNG), power, biodiesel, base ...
, in addition to being home to the world's largest shipping company, Mediterranean Shipping Company
Mediterranean Shipping Company S.A. (MSC) is an international shipping line founded by Gianluigi Aponte in Italy in 1970, with headquarters in Switzerland since 1978. The privately held company is owned by the Aponte family. It has been the lar ...
. Commodity trading is sustained by a strong trade finance sector, with large banks such as BCGE, BCP, BNP Paribas, BCV, Crédit Agricole
Crédit Agricole Group (), sometimes called La banque verte ( en, The green bank) due to its historical ties to farming, is a French international banking group and the world's largest cooperative financial institution. It is France's second lar ...
, Credit Suisse
Credit Suisse Group AG is a global investment bank and financial services firm founded and based in Switzerland. Headquartered in Zürich, it maintains offices in all major financial centers around the world and is one of the nine global " ...
, ING
Ing, ING or ing may refer to:
Art and media
* '' ...ing'', a 2003 Korean film
* i.n.g, a Taiwanese girl group
* The Ing, a race of dark creatures in the 2004 video game '' Metroid Prime 2: Echoes''
* "Ing", the first song on The Roches' 1992 ...
, Société Générale
Société Générale S.A. (), colloquially known in English as SocGen (), is a French-based multinational financial services company founded in 1864, registered in downtown Paris and headquartered nearby in La Défense.
Société Générale ...
, and UBS
UBS Group AG is a multinational investment bank and financial services company founded and based in Switzerland. Co-headquartered in the cities of Zürich and Basel, it maintains a presence in all major financial centres as the largest Sw ...
, all having their headquarters in the area for this business.
Wealth management is dominated by non-publicly listed banks and private banks, particularly Pictet, Lombard Odier
The Lombard Odier Group is an independent Swiss banking group based in Geneva. Its operations are organised into three divisions: private banking (wealth management), asset management, and IT and back and middle office services for other financi ...
, Edmond de Rothschild Group
The Edmond de Rothschild Group is a financial institution specialized in private banking and asset management. Based in Geneva, the group is family-owned and independent, and encompasses the Edmond de Rothschild Foundations (philanthropic arm), ...
, Union Bancaire Privée
Union Bancaire Privée (UBP SA) is a private bank and wealth management firm headquartered in Geneva. UBP is one of the largest private banks in Switzerland, and serves private and institutional clients. The bank was founded in 1969 by Edgar de Pi ...
, Mirabaud Group
Mirabaud is an international banking and financial group based in Geneva, Switzerland. Founded in 1819, it gradually developed into the third largest private bank in the city.
Six partners are involved in the group's day-to-day management. Mira ...
, Dukascopy Bank, Bordier & Cie, Banque SYZ, or REYL & Cie. In addition, the canton is home to the largest concentration of foreign-owned banks in Switzerland, such as HSBC Private Bank, JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase & Co. is an American multinational investment bank and financial services holding company headquartered in New York City and incorporated in Delaware. As of 2022, JPMorgan Chase is the largest bank in the United States, the w ...
, or Arab Bank
Arab Bank is one of the largest financial institutions in the Middle East, founded in 1930 in Jerusalem, Mandatory Palestine, as the first private sector financial institution in the Arab world. Headquartered today in Amman, Jordan, it serves cl ...
.
Behind the financial sector, the next largest major economic sector is watchmaking, dominated by luxury firms Rolex
Rolex SA () is a British-founded Swiss watch designer and manufacturer based in Geneva, Switzerland. Founded in 1905 as ''Wilsdorf and Davis'' by Hans Wilsdorf and Alfred Davis in London, the company registered ''Rolex'' as the brand name of ...
, Richemont
Compagnie Financière Richemont S.A., commonly known as Richemont, is a Switzerland-based luxury goods holding company founded in 1988 by South African businessman Johann Rupert. Through its various subsidiaries, Richemont produces and sells je ...
, Patek Philippe
Patek Philippe SA is a Swiss luxury watch and clock manufacturer, located in the Canton of Geneva and the Vallée de Joux. Established in 1839, it is named after two of its founders, Antoni Patek and Adrien Philippe. Since 1932, the company has ...
, Piaget, Roger Dubuis, and others, whose factories are concentrated in the Les Acacias neighbourhood, as well as the neighbouring municipalities of Plan-les-Ouates
Plan-les-Ouates () is a municipality of the canton of Geneva in Switzerland.
History
Plan-les-Ouates is first mentioned in 1537 as ''Plan-des-Vuattes''. In 1851 it became an independent municipality when the municipality of Compesières disso ...
, Satigny, and Meyrin
Meyrin () is a municipality of the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland.
The main site of CERN, the European particle physics research organisation, is in Meyrin. Meyrin was originally a small agricultural village until the 1950s, when construction of CE ...
.
Trade finance, wealth management, and watchmaking, approximately contribute two thirds of the corporate tax paid in the canton
Other large multinationals are also headquartered in the city and canton, such as Firmenich
Firmenich SA is a private Swiss company in the fragrance and flavor business. It is the largest privately owned company in the field and ranks number two worldwide. Firmenich has created perfumes for over 125 years and produced a number of well-k ...
(in Satigny), and Givaudan
Givaudan () is a Swiss multinational manufacturer of flavours, fragrances and active cosmetic ingredients. As of 2008, it is the world's largest company in the flavour and fragrance industries.
Overview
The company's scents and flavours are de ...
(in Vernier), the world's two largest manufacturers of flavours, fragrances and active cosmetic ingredients; SGS, the world's largest inspection, verification, testing and certification services company; Temenos
A ''temenos'' (Greek: ; plural: , ''temenē''). is a piece of land cut off and assigned as an official domain, especially to kings and chiefs, or a piece of land marked off from common uses and dedicated to a god, such as a sanctuary, holy gro ...
, a large banking software provider; or the local headquarters for Procter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational Final good, consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio, founded in 1837 by William Procter (industrialist), William Procter and James Gamble (industr ...
, Japan Tobacco International
JTI - Japan Tobacco International is the international tobacco division of Japan Tobacco, a leading international tobacco product manufacturer. The holding company is JT International SA and headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and sells its ...
, or L'Oréal
L'Oréal S.A. () is a French personal care company headquartered in Clichy, Hauts-de-Seine with a registered office in Paris. It is the world's largest cosmetics company and has developed activities in the field concentrating on hair color, s ...
(in Vernier).
Although they do not directly contribute to the local economy, the city of Geneva is also host to the world's largest concentration of international organisations and UN agencies, such as the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, an ...
, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
, the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
, the International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Union ...
, the World Intellectual Property Organization
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO; french: link=no, Organisation mondiale de la propriété intellectuelle (OMPI)) is one of the 15 specialized agencies of the United Nations (UN). Pursuant to the 1967 Convention Establishin ...
, the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Internat ...
, and the International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
, as well as the European headquarters of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
.
Its international mindedness, well-connected airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surfac ...
, and centrality in the continent, also make Geneva a good destination for congresses and trade fairs, of which the largest is the Geneva Motor Show
The Geneva International Motor Show is an annual auto show held in March in the Swiss city of Geneva. The show is hosted at the Palexpo, a convention centre located next to the Geneva Cointrin International Airport. The Salon is organised by th ...
held in Palexpo
Palexpo is a convention center in Geneva, Switzerland. The buildings are owned by the canton of Geneva while the company is a semi-private foundation. The center is located close to Geneva International Airport. There are seven halls, and 102,000 ...
.
Agriculture is commonplace in the hinterlands of Geneva, particularly wheat and wine. Despite its relatively small size, the canton produces around 10% of the Swiss wine and has the highest vineyard density in the country. The largest strains grown in Geneva are gamay, chasselas, pinot noir, gamaret, and chardonnay.
, Geneva had an unemployment rate of 3.9%. , there were five people employed in the primary economic sector and about three businesses involved in this sector. 9,783 people were employed in the secondary sector
In macroeconomics, the secondary sector of the economy is an economic sector in the three-sector theory that describes the role of manufacturing. It encompasses industries that produce a finished, usable product or are involved in constructio ...
and there were 1,200 businesses in this sector. 134,429 people were employed in the tertiary sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the second ...
, with 12,489 businesses in this sector. There were 91,880 residents of the municipality who were employed in some capacity, with women making up 47.7% of the workforce.
, the total number of full-time equivalent
Full-time equivalent (FTE), or whole time equivalent (WTE), is a unit that indicates the workload of an employed person (or student) in a way that makes workloads or class loads comparable across various contexts. FTE is often used to measure a w ...
jobs was 124,185. The number of jobs in the primary sector was four, all of which were in agriculture. The number of jobs in the secondary sector was 9,363 of which 4,863 or (51.9%) were in manufacturing and 4,451 (47.5%) were in construction. The number of jobs in the tertiary sector was 114,818. In the tertiary sector; 16,573 or 14.4% were in wholesale or retail sales or the repair of motor vehicles, 3,474 or 3.0% were in the movement and storage of goods, 9,484 or 8.3% were in a hotel or restaurant, 4,544 or 4.0% were in the information industry, 20,982 or 18.3% were the insurance or financial industry, 12,177 or 10.6% were technical professionals or scientists, 10,007 or 8.7% were in education and 15,029 or 13.1% were in health care.
, there were 95,190 workers who commuted into the municipality and 25,920 workers who commuted away. The municipality is a net importer of workers, with about 3.7 workers entering the municipality for every one leaving. About 13.8% of the workforce coming into Geneva are coming from outside Switzerland, while 0.4% of the locals commute out of Switzerland for work.Swiss Federal Statistical Office – Statwebaccessed 24 June 2010. Of the working population, 38.2% used public transportation to get to work, and 30.6% used a private car.
Sport
Ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice h ...
is one of the most popular sports in Geneva. Geneva is home to Genève-Servette HC
The Genève-Servette HC (also called Servette or GSHC) is a professional ice hockey club based in Geneva, Switzerland and competing in the National League (NL), the top tier of the Swiss hockey league system. The team plays their home games at the ...
, which plays in the National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team s ...
(NL). They play their home games in the 7,135-seat Patinoire des Vernets
Patinoire des Vernets is an indoor arena located in Geneva, Switzerland. It is primarily used for ice hockey and is the home arena of Genève-Servette HC. Opened in 1958, it has a seating capacity for 7,135 people.
History
When it opened in 1958 ...
. In 2008, 2010 and 2021 the team made it to the league finals but lost to the ZSC Lions
The Zürcher Schlittschuh Club Lions (ZSC Lions) are a professional ice hockey team located in Zürich, Switzerland, playing in the National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL) ...
, SC Bern
Schlittschuh Club Bern (''Ice-skating Club Bern'' in English) is an ice hockey team based in Bern, Switzerland. They play in the National League (NL), the top tier of the Swiss hockey league system. For the 18th year in a row, the club is the most ...
and EV Zug
EV Zug is a professional men's ice hockey team from Zug, Switzerland. It is a member of the National League and plays its home games at the Bossard Arena.
History
EV Zug won its first championship in the 1997–98 season, and the second one in ...
respectively. The team was by far the most popular one in both the city and the canton of Geneva, drawing three times more spectators than the football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, Kick (football), kicking a Football (ball), ball to score a Goal (sport), goal. Unqualified, Football (word), the word ''football'' normally means the form of football tha ...
team in 2017. Since the return of Servette FC
Servette FC is a Swiss football club based in Geneva, founded in March 1890 with rugby as its first sporting activity, and named after the Geneva district of the same name. The football section was created on 17 January 1900. They play in the ...
in the Swiss Super League
The Swiss Super League (known as the Credit Suisse Super League for sponsorship reasons) is a Swiss professional league in the top tier of the Swiss football league system and has been played in its current format since the 2003–04 season ...
, however, both teams have similar attendance numbers.
The town is home to Servette FC
Servette FC is a Swiss football club based in Geneva, founded in March 1890 with rugby as its first sporting activity, and named after the Geneva district of the same name. The football section was created on 17 January 1900. They play in the ...
, a football club founded in 1890 and named after a borough on the right bank of the Rhône. It is the most successfull football club in Romandy
Romandy (french: Romandie or )Before World War I, the term French Switzerland (french: Suisse française) waalso used german: Romandie or , it, Romandia, rm, Romanda) is the French-speaking part of western Switzerland. In 2020, about 2 milli ...
, and the third in Switzerland overall, with 17 league titles and 7 Swiss Cups. The home of Servette FC is the 30,000-seat Stade de Genève. Servette FC plays in the Credit Suisse Super League. Étoile Carouge FC and Urania Genève Sport also play in the city.
Geneva is home to the basketball team Lions de Genève, 2013 and 2015 champions of the Swiss Basketball League
The Swiss Basketball League, also known as SB League or SBL, is the top-tier professional club basketball league in Switzerland. It is organized by Swiss Basketball. The winners of the SBL are crowned Swiss national basketball champions. Curren ...
. The team plays its home games in the ''Pavilion des Sports''.
Geneva Jets Australian Football Club have been playing Australian Football
Australian football, also called Australian rules football or Aussie rules, or more simply football or footy, is a contact sport played between two teams of 18 players on an oval field, often a modified cricket ground. Points are scored by k ...
in the AFL Switzerland league since 2019.
Infrastructure
Transportation

Geneva Airport
Geneva Airport ,, german: Flughafen Genf, it, Aeroporto di Ginevra, rm, Eroport de Genevra formerly and still unofficially known as Cointrin Airport, is the international airport of Geneva, the second most populous city in Switzerland. I ...
. It is connected by Geneva Airport railway station
Geneva Airport railway station (french: Gare de Genève-Aéroport) is a train station located underground next to the terminal building of Geneva International Airport (french: Aéroport international de Genève) (IATA code: GVA), in Grand-Saco ...
(french: link=no, Gare de Genève-Aéroport) to both the Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
network and the French SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (; abbreviated as SNCF ; French for "National society of French railroads") is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffi ...
network, including links to Paris, Lyon, Marseille
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Fran ...
and Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the department of Hérault. In 2018, 290,053 people l ...
by TGV. Geneva is connected to the motorway systems of both Switzerland ( A1 motorway) and France.
Public transport by bus, trolleybus or tram is provided by '' Transports Publics Genevois''. In addition to an extensive coverage of the city centre, the network extends to most of the municipalities of the Canton, with a few lines reaching into France. Public transport by boat is provided by the Mouettes Genevoises, which link the two banks of the lake within the city, and by the ''Compagnie Générale de Navigation sur le lac Léman
The ' or Lake Geneva General Navigation Company (commonly abbreviated to CGN) is a public Swiss company operating ships on Lake Geneva connecting towns in both France and Switzerland including Geneva, , , , and .
History
The CGN was formed in 1 ...
'' which serves more distant destinations such as Nyon
Nyon (; outdated German: or ; outdated Italian: , ) is a municipality in Nyon District in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland. It is located some 25 kilometers north east of Geneva's city centre, and since the 1970s it has become part of the G ...
, Yvoire, Thonon, Évian, Lausanne and Montreux
Montreux (, , ; frp, Montrolx) is a Swiss municipality and town on the shoreline of Lake Geneva at the foot of the Alps. It belongs to the district of Riviera-Pays-d'Enhaut in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland, and has a population of approxi ...
using both modern diesel vessels and vintage paddle steamers
A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine that drives paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, where the first uses were w ...
.
Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
connect the airport to the main station of Cornavin in six minutes. Regional train services are being developed towards Coppet and Bellegarde. At the city limits two new railway stations have been opened since 2002: Genève-Sécheron (close to the UN and the Botanical Gardens
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
) and Lancy-Pont-Rouge.
In 2011 work started on the CEVA rail (Cornavin – Eaux-Vives – Annemasse) project, first planned in 1884, which will connect Cornavin with the Cantonal hospital, Eaux-Vives railway station and Annemasse
Annemasse (; Arpitan: ''Anemâsse'') is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in Eastern France. Even though it covers a relatively small territory (4.98 km2 or 1.92 sq mi), it is Haute-Savoie's second ...
, in France. The link between the main railway station and the classification yard
A classification yard ( American and Canadian English (Canadian National Railway use)), marshalling yard (British, Hong Kong, Indian, Australian, and Canadian English (Canadian Pacific Railway use)) or shunting yard (Central Europe) is a railway ...
of La Praille already exists; from there, the line runs mostly underground to the Hospital and Eaux-Vives, where it links to the existing line to France. The line fully opened in December 2019, as part of the Léman Express regional rail network.
 In May 2013, the demonstrator electric bus system with a capacity of 133 passengers commenced between
In May 2013, the demonstrator electric bus system with a capacity of 133 passengers commenced between Geneva Airport
Geneva Airport ,, german: Flughafen Genf, it, Aeroporto di Ginevra, rm, Eroport de Genevra formerly and still unofficially known as Cointrin Airport, is the international airport of Geneva, the second most populous city in Switzerland. I ...
and Palexpo
Palexpo is a convention center in Geneva, Switzerland. The buildings are owned by the canton of Geneva while the company is a semi-private foundation. The center is located close to Geneva International Airport. There are seven halls, and 102,000 ...
. The project aims to introduce a new system of mass transport with electric "flash" recharging of the buses at selected stops while passengers are disembarking and embarking.
Taxis in Geneva can be difficult to find, and may need to be booked in advance, especially in the early morning or at peak hours. Taxis can refuse to take babies and children because of seating
Seating may refer to:
General plans:
* Seating plan
In theaters or stadiums:
* Bleacher seating
* Chanin's seating plan
* Club seating
* Continental seating
* Festival seating
* General seating
* Home theater seating
* Movable seating
* ...
legislation.
An ambitious project to close 200 streets in the centre of Geneva to cars was approved by the Geneva cantonal authorities in 2010 and was planned to be implemented over a span of four years (2010–2014), though , work on the project has yet to be started.
Utilities
 Water, natural gas and electricity are provided to the municipalities of the Canton of Geneva by the state-owned
Water, natural gas and electricity are provided to the municipalities of the Canton of Geneva by the state-owned Services Industriels de Genève
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a p ...
, known as SIG. Most of the drinking water (80%) is extracted from the lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
; the remaining 20% is provided by groundwater, originally formed by infiltration from the Arve. 30% of the Canton's electricity needs is locally produced, mainly by three hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined a ...
dams on the Rhône (Seujet, Verbois and Chancy-Pougny). In addition, 13% of the electricity produced in the Canton is from the burning of waste at the waste incineration facility of Les Cheneviers. The remaining needs (57%) are covered by imports from other cantons in Switzerland or other European countries; SIG buys only electricity produced by renewable methods, and in particular does not use electricity produced using nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from n ...
s or fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ...
.
Natural gas is available in the City of Geneva, as well as in about two-thirds of the municipalities of the canton, and is imported from Western Europe by the Swiss company Gaznat. SIG also provides telecommunication facilities to carriers, service provider
A service provider (SP) is an organization that provides services, such as consulting, legal, real estate, communications, storage, and processing services, to other organizations. Although a service provider can be a sub-unit of the organization t ...
s and large enterprises. From 2003 to 2005, "Voisin, voisine" a fibre to the Home
Fiber to the ''x'' (FTTX; also spelled "fibre") or fiber in the loop is a generic term for any broadband network architecture using optical fiber to provide all or part of the local loop used for last mile telecommunications. As fiber optic ...
pilot project with a triple play offering was launched to test the end-user
In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrato ...
market in the Charmilles district.
International organisations
 Geneva is the European headquarters of the
Geneva is the European headquarters of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
, in the Palace of Nations
The Palace of Nations (french: Palais des Nations, ) is the home of the United Nations Office at Geneva, located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was built between 1929 and 1938 to serve as the headquarters of the League of Nations. It has served ...
building, up the hill from the headquarters of the former League of Nations. Several agencies are headquartered in Geneva, including the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integrat ...
, the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, commonly known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) or the United Nations Human Rights Office, is a department of the Secretariat of the United Nat ...
, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
, the International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
, International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Union ...
, the International Baccalaureate Organization
The International Baccalaureate (IB), formerly known as the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO), is a nonprofit foundation headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and founded in 1968. It offers four educational programmes: the IB Dip ...
and the World Intellectual Property Organization
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO; french: link=no, Organisation mondiale de la propriété intellectuelle (OMPI)) is one of the 15 specialized agencies of the United Nations (UN). Pursuant to the 1967 Convention Establishin ...
.
Apart from the UN agencies, Geneva hosts many inter-governmental organizations
An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states an ...
, such as the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
, the South Centre, the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Internat ...
, the World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an international non-governmental and lobbying organisation based in Cologny, canton of Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded on 24 January 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab. The foundation, ...
, the International Organization for Migration
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) is a United Nations agency that provides services and advice concerning migration to governments and migrants, including internally displaced persons, refugees, and migrant workers.
The IOM was ...
, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies
The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) is a worldwide humanitarian aid organization that reaches 160 million people each year through its 192-member National Societies. It acts before, during and after disas ...
and the International Committee of the Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signator ...
.
The Maison de la Paix
The Maison de la paix (literally: ''House of Peace'') is a building owned by the Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies in Geneva, Switzerland. The building was designed by Eric Ott of Neuchâtel's IPAS firm. It serves as ...
building hosts the three Geneva centres supported by the Swiss Confederation: the International Centre for Humanitarian Demining, the Centre for the Democratic Control of Armed Forces and the Geneva Centre for Security Policy
The Geneva Centre for Security Policy (GCSP) is an international foundation that was established in 1995 under Swiss law to "promote the building and maintenance of peace, security and stability". The GCSP was founded by the Federal Department o ...
, as well as other organisations active in the field of peace, international affairs and sustainable development.
Organizations on the European level include the European Broadcasting Union
The European Broadcasting Union (EBU; french: Union européenne de radio-télévision, links=no, UER) is an alliance of public service media organisations whose countries are within the European Broadcasting Area or who are members of the Co ...
(EBU) and CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Gene ...
(the European Organization for Nuclear Research) which is the world's largest particle physics laboratory.
The Geneva Environment Network (GEN) publishes the Geneva Green Guide, an extensive listing of Geneva-based global organisations working on environmental protection and sustainable development. A website, jointly run by the Swiss Government, the World Business Council for Sustainable Development
The World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) is a CEO-led organization of over 200 international companies. The Council is also connected to 60 national and regional business councils and partner organizations.
Its origins d ...
, the United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on ...
and the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of nat ...
, includes accounts of how NGOs, business, government and the UN cooperate. By doing so, it attempts to explain why Geneva has been picked by so many NGOs and UN bodies as their headquarters' location.
The World Organization of the Scout Movement
The World Organization of the Scout Movement (WOSM ) is the largest international Scouting organization. WOSM has 173 members. These members are recognized national Scout organizations, which collectively have around 43 million participants. WOSM ...
and the World Scout Bureau Central Office are headquartered in Geneva.
Notable people
A–C



 * Alfredo Aceto (born 1991), a visual artist
* Gustave Ador (1845–1928), statesman, President of the
* Alfredo Aceto (born 1991), a visual artist
* Gustave Ador (1845–1928), statesman, President of the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, an ...
(ICRC)
* David Aebischer (born 1978), ice hockey goaltender, 2001 Stanley Cup
The Stanley Cup (french: La Coupe Stanley) is the championship trophy awarded annually to the National Hockey League (NHL) playoff champion. It is the oldest existing trophy to be awarded to a professional sports franchise in North America, a ...
champion
* Jacques-Laurent Agasse
Jacques-Laurent Agasse (April 24, 1767 – December 27, 1849) was an animal and landscape painter from Switzerland.
Born at Geneva, Agasse studied in the public art school of that city. Before he turned twenty he went to Paris to study in ...
(1767–1849), animal and landscape painter
* Jeff Agoos
Jeffrey Alan Agoos (born May 2, 1968) is an American former professional soccer player who played as a defender. He is one of the all-time appearance leaders for the United States national team. Agoos served as the Sporting Director for the Ne ...
(born 1968), retired American soccer defender, 134 caps for the US team
* Henri-Frédéric Amiel (1821–1881), moral philosopher, poet and critic
* Gustave Amoudruz (1885–1963), sports shooter, bronze medallist at the 1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
* Adolphe Appia (1862–1928), architect and theorist of stage lighting
Stage lighting is the craft of lighting as it applies to the production of theater, dance, opera, and other performance arts.
and décor.
* Philip Arditti (born c. 1980), British/Jewish Sephardic theatre and television actor
* Aimé Argand (1750–1803), physicist and chemist, invented the Argand lamp
The Argand lamp is a type of oil lamp invented in 1780 by Aimé Argand. Its output is 6 to 10 candelas, brighter than that of earlier lamps. Its more complete combustion of the candle wick and oil than in other lamps required much less frequent ...
* Jean-Robert Argand Jean-Robert Argand (, , ; July 18, 1768 – August 13, 1822) was an amateur mathematician. In 1806, while managing a bookstore in Paris, he published the idea of geometrical interpretation of complex numbers known as the Argand diagram and is know ...
(1768–1822), amateur mathematician, published the Argand diagram
* Martha Argerich
Martha Argerich (; Eastern Catalan: �ɾʒəˈɾik born 5 June 1941) is an Argentine classical concert pianist. She is widely considered to be one of the greatest pianists of all time.
Early life and education
Argerich was born in Buenos A ...
(born 1941), an Argentine classical concert pianist
* John Armleder (born 1948), performance artist, painter, sculptor, critic and curator
* Germaine Aussey (1909–1979), née Agassiz, an actress of Swiss origin who settled in Geneva in 1960
* Alexandre Bardinon (born 2002), racing driver
* Pierre Bardinon (1931–2012), businessman and car collector
* Mathias Beche
Mathias Beche (born 28 June 1986 in Geneva) is a Swiss professional racing driver. He finished eighth overall and second in the LMP2 class of the 2012 24 Hours of Le Mans and is the reigning champion of the European Le Mans Series in the LMP2 clas ...
(born 1986), racing driver
* Jean-Luc Bideau
Jean-Luc Bideau (born 1 October 1940) is a Swiss film actor.
Personal life
Jean-Luc Bideau is married to Marcela Salivarova, a director of Czechoslovak origin. Together, they have two children: Nicolas, head of Presence Switzerland, and Martin ...
(born 1940), film actor
* Ernest Bloch
Ernest Bloch (July 24, 1880 – July 15, 1959) was a Swiss-born American composer. Bloch was a preeminent artist in his day, and left a lasting legacy. He is recognized as one of the greatest Swiss composers in history. As well as producing mus ...
(1880–1959), US composer of Swiss origin
* Roger Bocquet (1921–1994), footballer who won 48 caps for Switzerland
* Raoul Marie Joseph Count de Boigne (1862–1949), a French sports shooter, bronze medallist at the 1908 Summer Olympics
The 1908 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the IV Olympiad and also known as London 1908) were an international multi-sport event held in London, England, United Kingdom, from 27 April to 31 October 1908. The 1908 Games were or ...
* Caroline Boissier-Butini (1786–1836), pianist and composer
* François Bonivard
François Bonivard (or Bonnivard; 1493–1570) was a nobleman, ecclesiastic, historian, and Geneva patriot at the time of the Republic of Geneva. His life was the inspiration for Lord Byron's 1816 poem ''The Prisoner of Chillon''. He was a partis ...
(1493–1570), Geneva ecclesiastic, historian and libertine
* Charles Bonnet
Charles Bonnet (; 13 March 1720 – 20 May 1793) was a Genevan naturalist and philosophical writer. He is responsible for coining the term ''phyllotaxis'' to describe the arrangement of leaves on a plant. He was among the first to notice parth ...
(1720–1793), naturalist and philosophical writer
* Jorge Luis Borges
Jorge Francisco Isidoro Luis Borges Acevedo (; ; 24 August 1899 – 14 June 1986) was an Argentine short-story writer, essayist, poet and translator, as well as a key figure in Spanish-language and international literature. His best-known b ...
(1899–1986), Argentine short-story writer, studied at the Collège de Genève
In France, secondary education is in two stages:
* ''Collèges'' () cater for the first four years of secondary education from the ages of 11 to 15.
* ''Lycées'' () provide a three-year course of further secondary education for children between ...
* Marc-Théodore Bourrit
Marc-Théodore Bourrit (1739–1819) was a genevois traveller and writer.
Biography
Marc-Théodore Bourrit came of a family which was of French origin but had taken refuge at Geneva for reasons connected with religion. His father was a watchmak ...
(1739–1819), traveller and writer
* Nicolas Bouvier (1929–1998), writer and photographer
* Clotilde Bressler-Gianoli (1875–1912), an Italian opera singer
* Christiane Brunner (born 1947), politician, lawyer and trade union champion
* Mickaël Buffaz (born 1979), French cyclist
* Jean-Jacques Burlamaqui (1694–1748), Genevan legal and political theorist
* Cécile Butticaz (1884–1966), engineer
* Kate Burton (born 1957), actress, the daughter of actor Richard Burton
Richard Burton (; born Richard Walter Jenkins Jr.; 10 November 1925 – 5 August 1984) was a Welsh actor. Noted for his baritone voice, Burton established himself as a formidable Shakespearean actor in the 1950s, and he gave a memorable ...
* John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
(1509–1564), influential theologian, reformer
* Augustin Pyramus de Candolle
Augustin Pyramus (or Pyrame) de Candolle (, , ; 4 February 17789 September 1841) was a Swiss botanist. René Louiche Desfontaines launched de Candolle's botanical career by recommending him at a herbarium. Within a couple of years de Candolle ...
(1778–1841), botanist, worked on plant classification
* Clint Capela (born 1994), professional basketball player
* Jean de Carro (1770–1857), Vienna-based physician, promoted vaccination against smallpox
* Isaac Casaubon
Isaac Casaubon (; ; 18 February 1559 – 1 July 1614) was a classical scholar and philologist, first in France and then later in England.
His son Méric Casaubon was also a classical scholar.
Life Early life
He was born in Geneva to two F ...
(1559–1614), a classical scholar and philologist
* Méric Casaubon
Meric Casaubon (14 August 1599 in Geneva – 14 July 1671 in Canterbury), son of Isaac Casaubon, was a French-English classical scholar. He was the first to translate the ''Meditations'' of Marcus Aurelius into English.
Although biographical di ...
(1599–1671), son of Isaac Casaubon
Isaac Casaubon (; ; 18 February 1559 – 1 July 1614) was a classical scholar and philologist, first in France and then later in England.
His son Méric Casaubon was also a classical scholar.
Life Early life
He was born in Geneva to two F ...
, a French-English classical scholar
* Mike Castro de Maria (born 1972), electronic music composer
* Jean-Jacques Challet-Venel (1811–1893), politician, on the Swiss Federal Council
The Federal Council (german: Bundesrat; french: Conseil fédéral; it, Consiglio federale; rm, Cussegl federal) is the executive body of the federal government of the Swiss Confederation and serves as the collective head of state and governm ...
1864–1872
* Alfred Edward Chalon RA (1780–1860), portrait painter
* John James Chalon RA (1778–1854), painter of landscapes, marine scenes and animal life
* Marguerite Champendal (1870–1928), first Genevan to have obtained her doctorate in medicine at the University of Geneva (1900)
* Henri Christiné
Henri Marius Christiné (27 December 1867 – 25 November 1941) was a French composer of Swiss birth.
The son of a French Savoyard watchmaker, Christiné was born in Geneva, Switzerland. He began by teaching at the lycée in Geneva, while pur ...
(1867–1941), French composer of sparkling, witty, jazzy musical plays
* Victor Cherbuliez (1829–1899), novelist and author
* Étienne Clavière (1735–1793), banker and politician of the French revolution
* Paulo Coelho
Paulo Coelho de Souza (, ; born 24 August 1947) is a Brazilian lyricist and novelist and a member of the Brazilian Academy of Letters since 2002. His novel ''The Alchemist'' became an international best-seller and he has published 28 more book ...
(born 1947), Brazilian lyricist and novelist, author of '' The Alchemist'', residing in Geneva
* Renée Colliard (born 1933), former alpine skier, gold medallist at the 1956 Winter Olympics
The 1956 Winter Olympics, officially known as the VII Olympic Winter Games ( it, VII Giochi Olimpici invernali) and commonly known as Cortina d'Ampezzo 1956 ( lld, Anpezo 1956 or ), was a multi-sport event held in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy, fro ...
* Gabriel Cramer
Gabriel Cramer (; 31 July 1704 – 4 January 1752) was a Genevan mathematician. He was the son of physician Jean Cramer and Anne Mallet Cramer.
Biography
Cramer showed promise in mathematics from an early age. At 18 he received his doctorate ...
(1704–1752), Genevan mathematician
D–G

 *
* Maryam d'Abo
Maryam d'Abo is a British actress, best known as Bond girl Kara Milovy in the 1987 James Bond film '' The Living Daylights''.
Early life and education
Born in London to Georgian mother Nino Kvinitadze, daughter of General Giorgi Kvinitadze, a ...
(born 1960), English film and TV actress and Bond girl
A Bond girl is a character who is a love interest or female companion of James Bond in a novel, film or video game. Bond girls occasionally have names that are double entendres or puns, such as Pussy Galore, Plenty O'Toole, Xenia Onatopp, ...
* Jacques-Antoine Dassier (1715–1759), a Genevan medallist, active in London
* Michel Decastel (born 1955), football manager and midfielder, 314 club caps, 19 for Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
* Jean-Denis Delétraz (born 1963), racing driver
* Louis Delétraz
Louis Delétraz (born 22 April 1997) is a Swiss racing driver currently competing in the FIA World Endurance Championship and European Le Mans Series for Prema Orlen Team and in the IMSA SportsCar Championship for Tower Motorsport. He is the 20 ...
(born 1997), racing driver
* Jean-Louis de Lolme
Jean-Louis de Lolme or Delolme (174016 July 1806) was a Republic and Canton of Geneva#History, Genevan and British political philosophy, political theorist and writer on constitutional matters, born in the then independent Republic of Geneva. As a ...
(1740–1806), lawyer and constitutional writer
* Jean-André Deluc
Jean-André Deluc or de Luc (8 February 1727 – 7 November 1817) was a Swiss geologist, natural philosopher and meteorologist. He also devised measuring instruments.
Biography
Jean-André Deluc was born in Geneva. His family had come to th ...
(1727–1817), geologist, natural philosopher and meteorologist
* Giovanni Diodati (1576–1649), Italian Calvinist theologian and Bible translator
* Élie Ducommun (1833–1906), peace activist, 1902 Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiology ...
winner
* Armand Dufaux (1833–1941), aviation pioneer, flew the length of Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial lak ...
in 1910
* Henri Dufaux
Henri Dufaux (18 September 1879, Chens-sur-Léman – 25 December 1980, Geneva) was a 101-year-old Swiss painter
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "su ...
(1879–1980), French-Swiss aviation pioneer, inventor, painter and politician
* Pierre Étienne Louis Dumont
Pierre is a masculine given name. It is a French form of the name Peter. Pierre originally meant "rock" or "stone" in French (derived from the Greek word πέτρος (''petros'') meaning "stone, rock", via Latin "petra"). It is a translation ...
(1759–1829), Genevan political writer
* Henry Dunant
Henry Dunant (born Jean-Henri Dunant; 8 May 182830 October 1910), also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, and social activist. He was the visionary, promoter, and co-founder of the Red Cross. In 1901, he received th ...
(1828–1910), founded the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, an ...
, first recipient of Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiology ...
in 1901
* Emmanuel-Étienne Duvillard (1775–1832), Swiss economist
* Isabelle Eberhardt
Isabelle Wilhelmine Marie Eberhardt (17 February 1877 – 21 October 1904) was a Swiss explorer and author. As a teenager, Eberhardt, educated in Switzerland by her father, published short stories under a male pseudonym. She became interested ...
(1877–1904), Russian-Swiss explorer and travel writer
* Empress Elisabeth of Austria
Duchess Elisabeth Amalie Eugenie in Bavaria (24 December 1837 – 10 September 1898) was Empress of Austria and Queen of Hungary from her marriage to Emperor Franz Joseph I on 24 April 1854 until her assassination in 1898.
Elisabeth was ...
(1837–1898), Empress of Austria and Queen of Hungary
* Emanuele Filiberto of Savoy, Prince of Venice
Emanuele Filiberto Umberto Reza Ciro René Maria di Savoia (born 22 June 1972)''Genealogisches Handbuch des Adels, Fürstliche Häuser'' XIV. "Haus Italien". C.A. Starke Verlag, 1997, pp. 33, 38–39. .Willis, Daniel, ''The Descendants of Louis ...
(born 1972), a member of the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule o ...
* Louis Favre (1826–1879), engineer, responsible for the construction of the Gotthard Tunnel
, it, Galleria del San Gottardo
, other_name =
, line = Gotthard Line
, location = Traversing the Saint-Gotthard Massif in the middle of the Swiss Alps
, coordinates =
, os_grid_ref =
, status =
, system ...
* Philippe Favre
Philippe Favre (11 December 1961 − 6 December 2013) was a Swiss racing driver He lived in Geneva.
Favre was killed in a skiing accident at Val Thorens
Val Thorens (), is a ski town located in the Tarentaise Valley, Savoie, French Alps at an ...
(1961–2013), racing driver
* Henri Fazy (1842–1920), politician and historian
* Edmond Fleg, born Flegenheimer (1874–1963), a Swiss-French writer, thinker, novelist, essayist and playwright
* Ian Fleming
Ian Lancaster Fleming (28 May 1908 – 12 August 1964) was a British writer who is best known for his postwar ''James Bond'' series of spy novels. Fleming came from a wealthy family connected to the merchant bank Robert Fleming & Co., ...
(1908–1964), author (James Bond), studied psychology briefly in Geneva in 1931
* Sylvie Fleury
Sylvie Fleury (born 24 June 1961) is a Swiss contemporary pop artist known for her installations, sculpture, and mixed media. Her work generally depicts objects with sentimental and aesthetic attachments in consumer culture, as well as the para ...
(born 1961), a contemporary object artist of installation art
Installation art is an artistic genre of three-dimensional works that are often site-specific and designed to transform the perception of a space. Generally, the term is applied to interior spaces, whereas exterior interventions are often called ...
and mixed media
In visual art, mixed media describes artwork in which more than one medium or material has been employed.
Assemblages, collages, and sculpture are three common examples of art using different media. Materials used to create mixed media art incl ...
* Sir Augustus Wollaston Franks
Sir Augustus Wollaston Franks (20 March 182621 May 1897) was a British antiquarian and museum administrator. Franks was described by Marjorie Caygill, historian of the British Museum, as "arguably the most important collector in the history of ...
KCB FRS FSA (1826–1897), English antiquary and museum administrator
* Pierre-Victor Galland (1822–1892), painter
* Albert Gallatin
Abraham Alfonse Albert Gallatin (January 29, 1761 – August 12, 1849) was a Genevan– American politician, diplomat, ethnologist and linguist. Often described as "America's Swiss Founding Father", he was a leading figure in the early years ...
(1761–1849), an American politician of Genevan origin, diplomat, ethnologist and linguist
* Agénor de Gasparin (1810–1871), French statesman and author, also researched table-turning
* Valérie de Gasparin (1813–1894), woman of letters, regards freedom, equality and creativity
* François Gaussen (1790–1863), Protestant divine
* Marcel Golay (1927–2015), astronomer
* Claude Goretta (1929–2019), film director and television producer
* Emilie Gourd (1879–1946), journalist and activist for Women's suffrage in Switzerland
* Isabelle Graesslé (born 1959), theologian, feminist and former museum director, moderator of ministers and deacons at the Protestant Church of Geneva
The Protestant Church of Geneva (EPG, french: link=no, Église protestante de Genève) is an organization of congregations in the Canton of Geneva. It was founded in 1536 during the Protestant Reformation. It was the state church of Geneva from its ...
* Kat Graham
Katerina Alexandre Hartford Graham (born September 5, 1989) is an American actress, singer and dancer (now distributing music under the stage name Toro Gato). She is widely known for her role as Bonnie Bennett on The CW supernatural drama se ...
(born 1989), actress, singer, and model, she plays '' Bonnie Bennett'' in ''The Vampire Diaries
''The Vampire Diaries'' is an American supernatural teen drama television series developed by Kevin Williamson and Julie Plec, based on the book series of the same name written by L. J. Smith. The series premiered on The CW on September 10, ...
''
* Cédric Grand (born 1976), bobsledder, competed in four Winter Olympics, bronze medallist at the 2006 Winter Olympics
The 2006 Winter Olympics, officially the XX Olympic Winter Games ( it, XX Giochi olimpici invernali) and also known as Torino 2006, were a winter multi-sport event held from 10 to 26 February 2006 in Turin, Italy. This marked the second ...
* Romain Grosjean
Romain David Jeremie Grosjean (; born 17 April 1986) is a Swiss-French professional racing driver, competing under the French flag in the NTT IndyCar Series, driving the No. 28 Honda for Andretti Autosport. Grosjean had previously spent nine ...
(born 1986), racing driver, currently racing for Andretti Autosport
Andretti Autosport is an auto racing team that competes in the IndyCar Series, Indy Lights, Indy Pro 2000, and Formula E. The team also has a 37.5% ownership stake in the Australian Supercars Championship touring car team, Walkinshaw Andret ...
in the IndyCar Series
The IndyCar Series, currently known as the NTT IndyCar Series under sponsorship, is the highest class of regional North American open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars in the United States, which has been conducted under the auspices of ...
H–M



 * Admiral of the Fleet Lord John Hay GCB (1827–1916), Royal Navy officer and politician
* Abraham Hermanjat (1862–1932), painter who worked in the
* Admiral of the Fleet Lord John Hay GCB (1827–1916), Royal Navy officer and politician
* Abraham Hermanjat (1862–1932), painter who worked in the Fauvist
Fauvism /ˈfoʊvɪzm̩/ is the style of ''les Fauves'' (French language, French for "the wild beasts"), a group of early 20th-century modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong colour over the Representation (arts), repr ...
and Divisionist
Divisionism, also called chromoluminarism, was the characteristic style in Neo-Impressionist painting defined by the separation of colors into individual dots or patches which interacted optically..Homer, William I. ''Seurat and the Science of ...
styles
* Germain Henri Hess (1802–1850), a Swiss-Russian chemist and doctor, formulated Hess's law
* Hector Hodler (1887–1920), Esperantist
An Esperantist ( eo, esperantisto) is a person who speaks, reads or writes Esperanto. According to the Declaration of Boulogne, a document agreed upon at the first World Esperanto Congress in 1905, an Esperantist is someone who speaks Esperan ...
* Fulk Greville Howard
'Hon. Fulk or Fulke Greville Howard (3 April 1773 – 4 March 1846), of Elford Hall, Staffordshire and Castle Rising, Norfolk, was an English politician. In early life he was known as Fulk Greville Upton.
Life
He was born at Geneva, the younge ...
(1773–1846), an English politician
* Jean Huber (1721–1786), a painter, silhouettiste, soldier and author
* François Huber
François Huber (2 July 175022 December 1831), also known as Francis in English publications and Franz in German publications, was a Swiss entomologist who specialized in honey bees. His pioneering work was recognized all across Europe and base ...
(1750–1831), naturalist, studied the respiration of bees
* Marie Huber (1695–1753), translator, editor and author of theological works
* Pierre Jeanneret
Pierre Jeanneret (22 March 1896 – 4 December 1967) was a Swiss architect who collaborated with his cousin, Charles-Édouard Jeanneret (who assumed the pseudonym Le Corbusier), for about twenty years.
Early life
Arnold-André-Pierre Jea ...
(1896–1967), architect, collaborated with his cousin Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret (6 October 188727 August 1965), known as Le Corbusier ( , , ), was a Swiss-French architect, designer, painter, urban planner, writer, and one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture. He was ...
* Thomas Jouannet (born 1970), actor
* Charles Journet
Charles Journet (26 January 1891 – 15 April 1975) was a Swiss Roman Catholic theologian. He was the first Swiss named a cardinal.
Journet has been considered a figure of holiness and a candidate for canonisation; he has been accorded the title ...
(1891–1975), cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church
* Louis Jurine
Louis Jurine (; 6 February 1751 – 20 October 1819) was a Swiss physician, surgeon and naturalist mainly interested in entomology. He lived in Geneva.
Surgeon
He studied surgery in Paris and quickly acquired a great reputation for his expertis ...
(1751–1819), physician, surgeon, naturalist and entomologist
* Sonia Kacem (born 1985), Swiss-born visual artist
* Michael Krausz
Michael Krausz (born 1942) is a Swiss-born American philosopher as well as an artist and orchestral conductor. His philosophical works focus on the theory of interpretation, theory of knowledge, philosophy of science, philosophy of history, and p ...
(born 1942), American philosopher, an artist and orchestral conductor
* Adrien Lachenal
Adrien Lachenal (19 May 1849, in Geneva – 29 June 1918) was a Swiss politician and Jurist. He was president of the Swiss Confederation in 1869.
Married to Anne Louise Eggly in 1878, he had four sons. He was affiliated to the Free Democratic Pa ...
(1849–1918), politician, Federal Council of Switzerland
The Federal Council (german: Bundesrat; french: Conseil fédéral; it, Consiglio federale; rm, Cussegl federal) is the executive body of the federal government of the Swiss Confederation and serves as the collective head of state and gover ...
1892–1899
* François Lachenal (1918–1997), a publisher and diplomat
* Paul Lachenal (1884–1955), politician, co-founded Orchestre de la Suisse Romande
The Orchestre de la Suisse Romande (OSR) is a Swiss symphony orchestra, based in Geneva at the Victoria Hall. In addition to symphony concerts, the OSR performs as the opera orchestra in productions at the Grand Théâtre de Genève.
History
E ...
* Marie Laforêt
Marie Laforêt (born Maïtena Marie Brigitte Doumenach; 5 October 1939 – 2 November 2019) was a French singer and actress, particularly well known for her work during the 1960s and 1970s. In 1978, she moved to Geneva, and acquired Swiss citize ...
(born 1939), a French singer and actress
* Sarah Lahbati (born 1993), actress and singer
* François Le Fort (1656–1699), first Russian Admiral
* Georges-Louis Le Sage
Georges-Louis Le Sage (; 13 June 1724 – 9 November 1803) was a Genevan physicist and is most known for his theory of gravitation, for his invention of an electric telegraph and his anticipation of the kinetic theory of gases. Furthermore, he ...
(1724–1803), physicist, Le Sage's theory of gravitation
Le Sage's theory of gravitation is a kinetic theory of gravity originally proposed by Nicolas Fatio de Duillier in 1690 and later by Georges-Louis Le Sage in 1748. The theory proposed a mechanical explanation for Newton's gravitational force in ...
* Jean Leclerc (1657–1736), theologian and biblical scholar, promoted exegesis
Exegesis ( ; from the Greek , from , "to lead out") is a critical explanation or interpretation of a text. The term is traditionally applied to the interpretation of Biblical works. In modern usage, exegesis can involve critical interpretatio ...
* Henri Leconte
Henri Leconte (born 4 July 1963) is a French former professional tennis player. He reached the men's singles final at the French Open in 1988, won the French Open men's doubles title in 1984, and helped France win the Davis Cup in 1991. Leconte's ...
(born 1963), former French professional tennis player, men's singles finalist, French Open 1988
* Philippe Le Royer (1816-1897), French and Swiss politician and lawyer, served France as the Minister of Justice and President of the Senate
* Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
(1870–1924), lived in Geneva 1902–1905 as an exile from the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. T ...
* Jean-Étienne Liotard
Jean-Étienne Liotard (; 22 December 1702 – 12 June 1789) was a Swiss painter, art connoisseur and dealer. He is best known for his portraits in pastel, and for the works from his stay in Turkey. A Huguenot of French origin and citizen of the R ...
(1702–1789), painter, art connoisseur and dealer
* Corinne Maier (born 1963), psychoanalyst, economist, and best-selling writer
* Ella Maillart
Ella Maillart (or Ella K. Maillart; 20 February 1903, Geneva – 27 March 1997, Chandolin) was a Swiss adventurer, travel writer and photographer, as well as a sportswoman.
Early life
Ella Maillart was the second child, born to a wealthy fur t ...
(1903–1997), adventurer, travel writer and photographer, as well as a sportswoman
* Solomon Caesar Malan (1812–1894), oriental linguist and biblical scholar
* Jacques Mallet du Pan (1749–1800), Genevan-French royalist journalist
* Alexander Marcet
Alexander John Gaspard Marcet FRS (1 August 1770 – 19 October 1822), was a Genevan-born physician who became a British citizen in 1800. His wife Jane Marcet was a prolific author, whose series of books entitled 'Conversations' treated topics ...
FRS (1770–1822), physician who became a British citizen in 1800
* Jane Marcet
Jane Marcet (née Haldimand) (1 January 1769 – 28 June 1858) was an English salonnière of Swiss origin, and an innovative writer of popular, explanatory science books. She also broke ground with ''Conversations on Political Economy'' (181 ...
(1769–1858), an innovative writer of popular introductory science books
* Sebastian Marka (born 1978), German film director and editor
* Frank Martin (1890–1974), composer, editor of The Statesman's Year Book
* Nicolas Maulini (born 1981), racing driver
* Dr. Théodore Maunoir (1806–1869), co-founder of the International Committee of the Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signator ...
* Amélie Mauresmo
Amélie Simone Mauresmo (; born 5 July 1979) is a French former world No. 1 tennis player and tournament director. Mauresmo won two major singles titles at the 2006 Australian Open and Wimbledon Championships, and also won the silver medal in s ...
(born 1979), former professional tennis player and former world No.1
* Barthélemy Menn (1815–1893), a landscape painter, introduced painting en plein air
''En plein air'' (; French for 'outdoors'), or ''plein air'' painting, is the act of painting outdoors.
This method contrasts with studio painting or academic rules that might create a predetermined look. The theory of 'En plein air' painting ...
* Heinrich Menu von Minutoli (1772–1846), a Prussian Generalmajor, explorer and archaeologist
* Jacques-Barthélemy Micheli du Crest (1690–1766), military engineer, physicist and cartographer
* Giorgio Mondini (born 1980), racing driver
* Stephanie Morgenstern
Stephanie Morgenstern is a Canadian actress, filmmaker, and screenwriter for television and film. She has worked extensively on stage, film, and television in both English and French. Her most widely seen feature film credits have been '' The S ...
(born 1965), Canadian actress, filmmaker and screenwriter
* Edoardo Mortara
Edoardo "Edo" Mortara (born 12 January 1987) is a Swiss- Italian- French professional racing driver for Maserati MSG Racing. Born in Geneva, Switzerland, he holds triple nationality from all three countries. He is a former Formula Three Euro ...
(born 1987), Swiss-Italian racing driver
* Thierry Moutinho (born 1991), Swiss-Portuguese footballer
* Gustave Moynier
Gustave Moynier (21 September 1826 – 21 August 1910) was a Swiss Jurist who was active in many charitable organizations in Geneva.
He was a co-founder of the "International Committee for Relief to the Wounded", which became the International Com ...
(1826–1910), lawyer and co-founder of the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, an ...
N-R


 *
* Jacques Necker
Jacques Necker (; 30 September 1732 – 9 April 1804) was a Genevan banker and statesman who served as finance minister for Louis XVI. He was a reformer, but his innovations sometimes caused great discontent. Necker was a constitutional monarc ...
(1732–1804), banker and finance minister for Louis XVI of France
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
* Louis Albert Necker
Louis Albert Necker de Saussure FRSE MWS FGS (10 April 1786 – 20 November 1861) was a Swiss crystallographer and geographer.
He is best remembered for devising the optical illusion now known as the Necker cube.
Life
He was born in the ...
(1786–1861), a crystallographer and geographer, devised the Necker cube
The Necker cube is an optical illusion that was first published as a Rhomboid in 1832 by Swiss crystallographer Louis Albert Necker. It is a simple wire-frame, two dimensional drawing of a cube with no visual cues as to its orientation, so it ...
* Felix Neff (1798–1829), Protestant divine and philanthropist
* Alfred Newton
Alfred Newton FRS HFRSE (11 June 18297 June 1907) was an English zoologist and ornithologist. Newton was Professor of Comparative Anatomy at Cambridge University from 1866 to 1907. Among his numerous publications were a four-volume ''Diction ...
FRS HFRSE (1829–1907), English zoologist and ornithologist
* Karim Ojjeh (born 1965), Saudi Arabian businessman and racing driver
* Julie Ordon (born 1984), model and actress
* Rémy Pagani (born 1954), politician, Mayor of Geneva 2009/10 and 2012/13
* Liliane Maury Pasquier
Liliane Maury Pasquier (born 16 December 1956) is a Swiss politician, member of the Social Democratic Party of Switzerland, elected to the Swiss Council of States for the canton of Geneva in 2007, and is currently a member of a delegation that c ...
(born 1956), politician
* PATjE (born 1970), birth name Patrice Jauffret, a singer, songwriter, and musician
* Faule Petitot (1572–1629), sculptor, cabinetmaker and architect, citizen of Geneva since 1615
* Jean Petitot (1607–1691), enamel painter, son of Faule
* Carmen Perrin (born 1953), Bolivian-born Swiss visual artist, designer, and educator.
* Jean Piaget
Jean William Fritz Piaget (, , ; 9 August 1896 – 16 September 1980) was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. Piaget's theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called " genetic epistemology" ...
(1896–1980), clinical psychologist, devised genetic epistemology
Genetic epistemology or 'developmental theory of knowledge' is a study of the origins (genesis) of knowledge (epistemology) established by Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget. This theory opposes traditional epistemology and unites constructivism and ...
* Robert Pinget
Robert Pinget (Geneva, July 19, 1919 – August 25, 1997, Tours) was an avant-garde French writer, born in Switzerland, who wrote several novels and other prose pieces that drew comparison to Beckett and other major Modernist writers. He was al ...
(1919–1997), an avant-garde French modernist
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new fo ...
nouveau roman writer
* George Pitt, 1st Baron Rivers
George Pitt, 1st Baron Rivers (1 May 1721 – 7 May 1803) was an English diplomat and politician.
Background and education
He was born in Geneva, the eldest son of George Pitt of Stratfieldsaye (today rendered Stratfield Saye), Hampshire, a ...
(1721–1803), English diplomat and politician
* Barbara Polla (born 1950), medical doctor, gallery owner, art curator and writer
* James Pradier (1790–1852), Genevan and then Swiss sculptor, neoclassical style
* Jean-Louis Prévost (1838–1927), neurologist and physiologist
* Pierre Prévost (1751–1839), philosopher, physicist wrote the law of exchange in radiation
* Tariq Ramadan
Tariq Ramadan ( ar, طارق رمضان, ; born 26 August 1962) is a Swiss Muslim academic, philosopher, and writer. He was a professor of contemporary Islamic studies at St Antony's College, Oxford and the Faculty of Theology and Religion, Univ ...
(born 1962), a Swiss Muslim academic, philosopher and writer
* Marcel Raymond (1897–1981), a literary critic of French literature of the "Geneva School
The expression Geneva School refers to (1) a group of linguists based in Geneva who pioneered modern structural linguistics and (2) a group of literary theorists and critics working from a phenomenological perspective.
Geneva School of Linguist ...
"
* Flore Revalles (1889–1966), singer, dancer and actress
* Charles Pierre Henri Rieu (1820–1902), Orientalist and Professor of Arabic
* Prof Auguste Arthur de la Rive (1801–1873), a physicist, worked on the heat of gases
* Charles-Gaspard de la Rive (1770–1834), physicist, psychiatrist and politician
* François Jules Pictet de la Rive (1809–1872), zoologist and palaeontologist
* Tibor Rosenbaum
Pinchas Tibor Rosenbaum ( yi, פנחס סג"ל ליטש ראזענבוים; 1923–1980) was a Hungarian-born Swiss Jewish rabbi and businessman and one of the heads of the Jewish community in Switzerland who saved hundreds of Jews during The Ho ...
(1923–1980), rabbi and businessman
* Marc Rosset (born 1970), former pro tennis player, gold medallist at the 1992 Olympic Games
* Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revol ...
(1712–1778), writer and philosopher
* Jean Rousset
Jean Rousset (20 February 1910 – 15 September 2002) was a Swiss literary critic who worked on French literature, and in particular on Baroque literature of the late Renaissance and early seventeenth century. He is sometimes grouped with the ...
(1910–2002), literary critic and early structuralism
In sociology, anthropology, archaeology, history, philosophy, and linguistics, structuralism is a general theory of culture and methodology that implies that elements of human culture must be understood by way of their relationship to a broad ...
writer of the Geneva School
The expression Geneva School refers to (1) a group of linguists based in Geneva who pioneered modern structural linguistics and (2) a group of literary theorists and critics working from a phenomenological perspective.
Geneva School of Linguist ...
* Xavier Ruiz (born 1970), film producer and director
S–Z



 *
* Ferdinand de Saussure
Ferdinand de Saussure (; ; 26 November 1857 – 22 February 1913) was a Swiss linguist, semiotician and philosopher. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiotics in the 20th century. He is widel ...
(1857–1913), a linguist and semiotician
Semiotics (also called semiotic studies) is the systematic study of sign processes (semiosis) and meaning making. Semiosis is any activity, conduct, or process that involves signs, where a sign is defined as anything that communicates something, ...
* Horace Bénédict de Saussure
Horace Bénédict de Saussure (17 February 1740 – 22 January 1799) was a Genevan geologist, meteorologist, physicist, mountaineer and Alpine explorer, often called the founder of alpinism and modern meteorology, and considered to be the fi ...
(1740–1799), geologist, meteorologist, physicist, and Alpine explorer
* Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure (1767–1845), chemist, studied plant physiology, advanced phytochemistry
* Léon Savary Léon Savary ( Fleurier, 1895 - Boudry, 1968) was a Swiss French-speaking writer and journalist from Payerne, Vaud.
Biography
Savary was the son of a German russified aristocratic mother from the Baltic region (Von Paucker) and a father who was ...
(1895–1968), writer and journalist
* Michael Schade
Michael Schade (born 23 January 1965) is a Canadian operatic tenor, who was born in Geneva and raised in Germany and Canada. He and his wife Dee McKee, and their youngest child live in Vienna, Austria; the rest of the family lives in Canada.
...
(born 1965), a Canadian operatic tenor
* Johann Jacob Schweppe
Johann Jacob Schweppe (, ) (16 March 1740 – 18 November 1821) was a German-Swiss watchmaker and amateur scientist who developed the first practical process to manufacture bottled carbonated mineral water, based on a process discovered by Joseph ...
(1740–1821), watchmaker developed Schweppes
Schweppes (, ) is a beverage brand that originated in the Republic of Geneva; it is made, bottled and distributed worldwide by multiple international conglomerates, depending on licensing and region, that manufacture and sell soft drinks. Schwep ...
bottled carbonated water
Carbonated water (also known as soda water, sparkling water, fizzy water, club soda, water with gas, in many places as mineral water, or especially in the United States as seltzer or seltzer water) is water containing dissolved carbon dioxide gas, ...
* Marguerite Sechehaye (1887–1965), a psychotherapist, treated people with schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social with ...
* Louis Segond (1810–1885), theologian and translator, pastor in Chêne-Bougeries
Chêne-Bougeries is a municipality in the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland.
History
Chêne-Bougeries is first mentioned in 1270 as ''Quercus''. In 1801 it was mentioned as ''Chêne-les-Bougeries''.
Chêne-Bougeries was inhabited for most of its his ...
* Philippe Senderos
Philippe Sylvain Senderos (born 14 February 1985) is a Swiss retired professional footballer who played as a defender.
Senderos began his career at Servette, before moving to England as a teenager with Arsenal. He made 116 appearances over ...
(born 1985), footballer, over 200 club caps and 57 for Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
* Jean Senebier (1742–1809), pastor and voluminous writer on vegetable physiology
* Liberato Firmino Sifonia (1917-1996), an Italian composer
* Pierre Eugene du Simitiere (1737–1784), naturalist, American patriot and portrait painter.
* Michel Simon
Michel Simon (; 9 April 1895 – 30 May 1975) was a Swiss-French actor. He appeared in many notable French films, including '' La Chienne'' (1931), '' Boudu Saved from Drowning'' (1932), ''L'Atalante'' (1934), '' Port of Shadows'' (1938), '' The ...
(1895–1975), actor
* Jean Charles Léonard de Sismondi
Jean Charles Léonard de Sismondi (also known as Jean Charles Leonard Simonde de Sismondi) (; 9 May 1773 – 25 June 1842), whose real name was Simonde, was a Swiss historian and political economist, who is best known for his works on French and ...
(1773–1842), historian and political economist
* Edward Snowden
Edward Joseph Snowden (born June 21, 1983) is an American and naturalized Russian former computer intelligence consultant who leaked highly classified information from the National Security Agency (NSA) in 2013, when he was an employee and su ...
(born 1983), lived in Geneva between 2007 and 2009, while working for the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
* Pierre Soubeyran (1706–1775), engraver, etcher and Encyclopédiste
* Terry Southern
Terry Southern (May 1, 1924 – October 29, 1995) was an American novelist, essayist, screenwriter, and university lecturer, noted for his distinctive satirical style. Part of the Paris postwar literary movement in the 1950s and a companion to B ...
(1924–1995), American author, essayist and screenwriter; lived in Geneva 1956–59
* Ezekiel Spanheim (1629–1710), Prussian diplomat
* Friedrich Spanheim (1632–1701), a Calvinistic theology professor at the University of Leiden
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; nl, Universiteit Leiden) is a public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city of L ...
* Jacques Charles François Sturm Jacques Charles François Sturm (29 September 1803 – 15 December 1855) was a French mathematician.
Life and work
Sturm was born in Geneva (then part of France) in 1803. The family of his father, Jean-Henri Sturm, had emigrated from Strasbourg ...
(1803–1855), French mathematician
* Émile Taddéoli (1879–1920), Swiss aviation pioneer
* Alain Tanner
Alain Tanner (6 December 1929 – 11 September 2022) was a Swiss film director.
Early years and education
Tanner was born in Geneva, and studied economics at the University of Geneva. In 1951, he joined the film club which Claude Goretta had re ...
(born 1929), film director
* Sigismund Thalberg (1812–1871), Austrian composer and pianist
* Max Thurian (1921–1996), theologian, known as Frère Max
* Pierre Tirard (1827–1893), French politician
* Rodolphe Töpffer
Rodolphe Töpffer ( , ; 31 January 1799 – 8 June 1846) was a Swiss teacher, author, painter, cartoonist, and caricaturist. He is best known for his illustrated books (''littérature en estampes'', " graphic literature"), which are possibly ...
(1799–1846), teacher, author, painter, cartoonist and caricaturist
* Wolfgang-Adam Töpffer (1766–1847), painter of landscapes and watercolors
* Vico Torriani (1920–1998), singer, actor, show host
* Georges Trombert (1874–1949), a French fencer, silver and bronze medallist at the 1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
* Théodore Tronchin
Théodore Tronchin (24 May 1709 – 30 November 1781) was a physician from the Republic of Geneva.
Life
A native of Geneva, he studied initially at the University of Cambridge, then transferred to the University of Leiden, where he was a pupi ...
(1709–1781), a Genevan physician
* François Turrettini (1623–1687), a Genevan-Italian Reformed scholastic theologian
* Jean Alphonse Turrettini (1671–1737), reformed theologian
* Princess Vittoria of Savoy (2003), heir to the Italian throne
* François Vivares (1709–1780), French landscape-engraver, active in England
* Johann Vogel (born 1977), former footballer, played 94 games for Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
* Prince Andrei Volkonsky (1933–2008), Russian composer of classical music and harpsichordist
* Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his '' nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity— ...
(1694–1778), French philosopher, historian, dramatist and man of letters; lived at Les Délices 1755–1760
* Nedd Willard (1926–2018), writer
* R. Norris Williams
Richard "Dick" Norris Williams II (January 29, 1891 – June 2, 1968), generally known as R. Norris Williams, was an American tennis player and RMS ''Titanic'' survivor.
Biography
Williams was born in Geneva, Switzerland, the son of Philadel ...
(1891–1968), American tennis player and RMS Titanic
RMS ''Titanic'' was a British passenger liner, operated by the White Star Line, which sank in the North Atlantic Ocean on 15 April 1912 after striking an iceberg during her maiden voyage from Southampton, England, to New York City, United ...
survivor
* Pierre Wissmer (1915–1992), Swiss-French composer, pianist and music teacher
* Jean Ziegler
Jean Ziegler (; born Hans Ziegler, 19 April 1934) is a Swiss former professor of sociology at the University of Geneva and the Sorbonne, Paris, and former vice-president of the Advisory Committee to the United Nations Human Rights Council. He ...
(born 1934), politician and sociologist
* Reto Ziegler (born 1986), footballer, has played 35 games for Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
See also
* Outline of Geneva * Bibliothèque Publique et Universitaire (Geneva) * Boule de Genève * Calvin Auditory, a chapel that played a significant role in the Reformation * Circuit des Nations, the historic racetrack *Franco-Provençal language
Franco-Provençal (also Francoprovençal, Patois or Arpitan) is a language within Gallo-Romance originally spoken in east-central France, western Switzerland and northwestern Italy.
Franco-Provençal has several distinct dialects and is sepa ...
* Geneva Freeport
* Geneva Summit for Human Rights and Democracy
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * Joëlle Kuntz, ''Geneva and the call of internationalism. A history'', éditions Zoé, 2011, 96 pages ().External links
* *Geneva public transport
Geneva Tourist Information Office
{{Portal bar, Switzerland, Europe, Geography, Cities in Switzerland Cantonal capitals of Switzerland Populated places established in the 1st millennium BC Associates of the Old Swiss Confederacy Former theocracies Counties of the Holy Roman Empire Populated places on the Rhône Populated places on Lake Geneva Populated riverside places in Switzerland Municipalities of the canton of Geneva