Gelatine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from
 Gelatin is nearly tasteless and odorless with a colorless or slightly yellow appearance.Budavari, S. (1996). ''Merck Index, (12th ed.)'' Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck. It is transparent and brittle, and it can come as sheets, flakes, or as a powder.
Gelatin is nearly tasteless and odorless with a colorless or slightly yellow appearance.Budavari, S. (1996). ''Merck Index, (12th ed.)'' Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck. It is transparent and brittle, and it can come as sheets, flakes, or as a powder.

 The worldwide demand of gelatin was about in 2019. On a commercial scale, gelatin is made from
The worldwide demand of gelatin was about in 2019. On a commercial scale, gelatin is made from
 Probably best known as a
Probably best known as a
 * Certain professional and theatrical lighting equipment use
* Certain professional and theatrical lighting equipment use
 Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, collagen hydrolysate, gelatine hydrolysate, hydrolyzed gelatine, and collagen peptides after it has undergone hydrolysis. It is commonly used as a gelling agent
A gel is a semi-solid that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state, although the liquid phase may still di ...
in food, beverages, medications, drug or vitamin capsules, photographic film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin photographic emulsion, emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of th ...
s, papers
Paper is a thin, flat material produced by the compression of fibres.
Paper(s) or The Paper may also refer to:
Publishing and academia
* Newspaper, a periodical publication
* ''Paper'' (magazine), an American monthly fashion and culture magazin ...
, and cosmetics.
Substances containing gelatin or functioning in a similar way are called gelatinous substances. Gelatin is an irreversibly hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
form of collagen, wherein the hydrolysis reduces protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
fibrils into smaller peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
s; depending on the physical and chemical methods of denaturation, the molecular weight of the peptides falls within a broad range. Gelatin is present in gelatin dessert
Gelatin desserts (also Jelly or Jello) are desserts made with a sweetened and flavoured processed collagen product ( gelatin). This kind of dessert was first recorded as jelly by Hannah Glasse in her 18th-century book '' The Art of Cookery'' ...
s, most gummy candy
Gummies, gummi candies, gummy candies, or jelly sweets are a broad category of gelatin-based chewable sweets. Gummi bears, Sour Patch Kids, and Jelly Babies are widely popular and are a well-known part of the sweets industry. Gummies are availabl ...
and marshmallow
Marshmallow (, ) is a type of confectionery that is typically made from sugar, water and gelatin whipped to a solid-but-soft consistency. It is used as a filling in baking or normally molded into shapes and coated with corn starch. The sugar c ...
s, ice cream
Ice cream is a sweetened frozen food typically eaten as a snack or dessert. It may be made from milk or cream and is flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit such as str ...
s, dips, and yogurt
Yogurt (; , from tr, yoğurt, also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial Fermentation (food), fermentation of milk. The bacteria used to make yogurt are known as ''yogurt cultures''. Fermentation of sugars in t ...
s. Gelatin for cooking comes as powder, granules, and sheets. Instant types can be added to the food as they are; others must soak in water beforehand.
Characteristics
Properties
Gelatin is a collection of peptides andprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s produced by partial hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of collagen extracted from the skin, bones, and connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
s of animals such as domesticated cattle, chicken, pigs, and fish. During hydrolysis, some of the bonds between and within component proteins are broken. Its chemical composition is, in many aspects, closely similar to that of its parent collagen. Photographic and pharmaceutical grades of gelatin generally are sourced from cattle bones and pig skin. Gelatin is classified as a hydrogel
A hydrogel is a crosslinked hydrophilic polymer that does not dissolve in water. They are highly absorbent yet maintain well defined structures. These properties underpin several applications, especially in the biomedical area. Many hydrogels ar ...
.
 Gelatin is nearly tasteless and odorless with a colorless or slightly yellow appearance.Budavari, S. (1996). ''Merck Index, (12th ed.)'' Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck. It is transparent and brittle, and it can come as sheets, flakes, or as a powder.
Gelatin is nearly tasteless and odorless with a colorless or slightly yellow appearance.Budavari, S. (1996). ''Merck Index, (12th ed.)'' Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck. It is transparent and brittle, and it can come as sheets, flakes, or as a powder. Polar solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for p ...
s like hot water, glycerol, and acetic acid can dissolve gelatin, but it is insoluble in organic solvents like alcohol. Gelatin absorbs 5–10 times its weight in water to form a gel. The gel formed by gelatin can be melted by reheating, and it has an increasing viscosity under stress (thixotropic
Thixotropy is a time-dependent shear thinning property. Certain gels or fluids that are thick or viscous under static conditions will flow (become thinner, less viscous) over time when shaken, agitated, shear-stressed, or otherwise stressed (ti ...
). The upper melting point of gelatin is below human body temperature
Normal human body-temperature (normothermia, euthermia) is the typical temperature range found in humans. The normal human body temperature range is typically stated as .
Human body temperature varies. It depends on sex, age, time of day, exert ...
, a factor that is important for mouthfeel
Mouthfeel refers to the physical sensations in the mouth caused by food or drink, making it distinct from taste. It is a fundamental sensory attribute which, along with taste and smell, determines the overall flavor of a food item. Mouthfeel is ...
of foods produced with gelatin. The viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
of the gelatin-water mixture is greatest when the gelatin concentration is high and the mixture is kept cool at about . Commercial gelatin will have a gel strength of around 90 to 300 grams Bloom using the Bloom
Bloom or blooming may refer to:
Science and technology Biology
* Bloom, one or more flowers on a flowering plant
* Algal bloom, a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in an aquatic system
* Jellyfish bloom, a collective n ...
test of gel strength. Gelatin's strength (but not viscosity) declines if it is subjected to temperatures above , or if it is held at temperatures near 100 °C for an extended period of time.
Gelatins have diverse melting points and gelation temperatures, depending on the source. For example, gelatin derived from fish has a lower melting and gelation point than gelatin derived from beef or pork.
Composition
When dry, gelatin consists of 98–99% protein, but it is not a nutritionally complete protein since it is missingtryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic ...
and is deficient in isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprot ...
, threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO� ...
, and methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
. The amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
content of hydrolyzed collagen is the same as collagen. Hydrolyzed collagen contains 19 amino acids, predominantly glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogeni ...
(Gly) 26–34%, proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the prot ...
(Pro) 10–18%, and hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelatin. ...
(Hyp) 7–15%, which together represent around 50% of the total amino acid content.Poppe, J. (1997). Gelatin, in A. Imeson (ed.) ''Thickening and Gelling Agents for Food (2nd ed.)'': 144–68. London: Blackie Academic and Professional. Glycine is responsible for close packing of the chains. Presence of proline restricts the conformation. This is important for gelation properties of gelatin. Other amino acids that contribute highly include: alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side c ...
(Ala) 8–11%; arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the am ...
(Arg) 8–9%; aspartic acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
(Asp) 6–7%; and glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
(Glu) 10–12%.
Research
Digestibility
A 2005 study in humans found hydrolyzed collagen absorbed as smallpeptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
in the blood.
Effects on skin
Ingestion of hydrolyzed collagen may affect the skin by increasing the density of collagen fibrils andfibroblasts
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells o ...
, thereby stimulating collagen production. It has been suggested, based on mouse and in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology an ...
studies, that hydrolyzed collagen peptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
have chemotactic properties on fibroblasts or an influence on growth of fibroblasts.
Joint effects
Some clinical studies report that the oral ingestion of hydrolyzed collagen decreases joint pain, those with the most severe symptoms showing the most benefit. However, other clinical trials have yielded mixed results. In 2011, theEuropean Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies concluded that "a cause and effect relationship has not been established between the consumption of collagen hydrolysate and maintenance of joints". Four other studies reported benefit with no side effects; however, the studies were not extensive, and all recommended further controlled study. One study found that oral collagen only improved symptoms in a minority of patients and reported nausea as a side effect. Another study reported no improvement in disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Another study found that collagen treatment may actually cause an exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involv ...
symptoms.
Safety concerns
Hydrolyzed collagen, like gelatin, is made from animalby-products
A by-product or byproduct is a secondary product derived from a production process, manufacturing process or chemical reaction; it is not the primary product or service being produced.
A by-product can be useful and marketable or it can be consid ...
from the meat industry
The meat industry are the people and companies engaged in modern industrialized livestock agriculture for the production, packing, preservation and marketing of meat (in contrast to dairy products, wool, etc.). In economics, the meat industry is ...
or sometimes animal carcasses removed and cleared by knacker
A knacker (), knackerman or knacker man is a person who removes and clears animal carcasses (dead, dying, injured) from private farms or public highways and renders the collected carcasses into by-products such as fats, tallow (yellow grease ...
s, including skin, bones, and connective tissue.
In 1997, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA), with support from the TSE (transmissible spongiform encephalopathy
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) are a group of progressive and fatal conditions that are associated with prions and affect the brain and nervous system of many animals, including humans, cattle, and sheep. According to the most ...
) Advisory Committee, began monitoring the potential risk of transmitting animal diseases, especially bovine spongiform encephalopathy
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly known as mad cow disease, is an incurable and invariably fatal neurodegenerative disease of cattle. Symptoms include abnormal behavior, trouble walking, and weight loss. Later in the course of t ...
(BSE), commonly known as ''mad cow disease''. An FDA study from that year stated: "...steps such as heat, alkaline treatment, and filtration could be effective in reducing the level of contaminating TSE agents; however, scientific evidence is insufficient at this time to demonstrate that these treatments would effectively remove the BSE infectious agent if present in the source material." On 18 March 2016 the FDA finalized three previously-issued interim final rules designed to further reduce the potential risk of BSE in human food. The final rule clarified that "gelatin is not considered a prohibited cattle material if it is manufactured using the customary industry processes specified."
The Scientific Steering Committee (SSC) of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
in 2003 stated that the risk associated with bovine bone gelatin is very low or zero.
In 2006, the European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
stated that the SSC opinion was confirmed, that the BSE risk of bone-derived gelatin was small, and that it recommended removal of the 2003 request to exclude the skull, brain, and vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
e of bovine origin older than 12 months from the material used in gelatin manufacturing.
Production
by-product
A by-product or byproduct is a secondary product derived from a production process, manufacturing process or chemical reaction; it is not the primary product or service being produced.
A by-product can be useful and marketable or it can be consid ...
s of the meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chic ...
and leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
industries.
Most gelatin is derived from pork skins, pork and cattle bones, or split cattle hides. Gelatin made from fish by-products avoids some of the religious objections to gelatin consumption. The raw materials are prepared by different curing, acid, and alkali processes that are employed to extract the dried collagen hydrolysate. These processes may take several weeks, and differences in such processes have great effects on the properties of the final gelatin products.
Gelatin also can be prepared at home. Boiling certain cartilaginous cuts of meat or bones results in gelatin being dissolved into the water. Depending on the concentration, the resulting stock (when cooled) will form a jelly or gel naturally. This process is used for aspic
Aspic or meat jelly () is a savory gelatin made with a meat stock or broth, set in a mold to encase other ingredients. These often include pieces of meat, seafood, vegetable, or eggs. Aspic is also sometimes referred to as ''aspic gelée'' or ...
.
While many processes exist whereby collagen may be converted to gelatin, they all have several factors in common. The intermolecular and intramolecular bonds that stabilize insoluble collagen must be broken, and also, the hydrogen bonds that stabilize the collagen helix
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, ...
must be broken. The manufacturing processes of gelatin consists of several main stages:
# Pretreatments to make the raw materials ready for the main extraction step and to remove impurities that may have negative effects on physicochemical properties of the final gelatin product.
# Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of collagen into gelatin.
# Extraction of gelatin from the hydrolysis mixture, which usually is done with hot water or dilute acid solutions as a multistage process.
# The refining and recovering treatments including filtration, clarification, evaporation, sterilization, drying, rutting, grinding, and sifting to remove the water from the gelatin solution, to blend the gelatin extracted, and to obtain dried, blended, ground final product.
Pretreatments
If the raw material used in the production of the gelatin is derived frombone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
s, dilute acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
solutions are used to remove calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
and other salts. Hot water or several solvents may be used to reduce the fat content, which should not exceed 1% before the main extraction step. If the raw material consists of hides and skin; size reduction, washing, removal of hair from hides, and degreasing are necessary to prepare the hides and skins for the hydrolysis step.
Hydrolysis
After preparation of the raw material, i.e., removing some of the impurities such as fat and salts, partially purified collagen is converted into gelatin through hydrolysis. Collagen hydrolysis is performed by one of three different methods:acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
-, alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
-, and enzymatic hydrolysis
In biochemistry, enzymatic hydrolysis is a process in which enzymes facilitate the cleavage of bonds in molecules with the addition of the elements of water (i.e. hydrolysis). It plays an important role in the digestion of food.
It may be used t ...
. Acid treatment is especially suitable for less fully cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural ...
ed materials such as pig skin collagen and normally requires 10 to 48 hours. Alkali treatment is suitable for more complex collagen such as that found in bovine
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship betwee ...
hides and requires more time, normally several weeks. The purpose of the alkali treatment is to destroy certain chemical crosslinks still present in collagen. Within the gelatin industry, the gelatin obtained from acid-treated raw material has been called type-A gelatin and the gelatin obtained from alkali-treated raw material is referred to as type-B gelatin.
Advances are occurring to optimize the yield of gelatin using enzymatic hydrolysis of collagen. The treatment time is shorter than that required for alkali treatment, and results in almost complete conversion to the pure product. The physical properties of the final gelatin product are considered better.
Extraction
Extraction is performed with either water or acid solutions at appropriate temperatures. All industrial processes are based on neutral or acid pH values because although alkali treatments speed up conversion, they also promote degradation processes. Acidic extraction conditions are extensively used in the industry, but the degree of acid varies with different processes. This extraction step is a multistage process, and the extraction temperature usually is increased in later extraction steps, which ensures minimum thermal degradation of the extracted gelatin.Recovery
This process includes several steps such as filtration, evaporation, drying, grinding, and sifting. These operations are concentration-dependent and also dependent on the particular gelatin used. Gelatin degradation should be avoided and minimized, so the lowest temperature possible is used for the recovery process. Most recoveries are rapid, with all of the processes being done in several stages to avoid extensive deterioration of the peptide structure. A deteriorated peptide structure would result in a low gel strength, which is not generally desired.Uses
Early history of food applications
The 10th-century '' Kitab al-Tabikh'' includes a recipe for a fish aspic, made by boiling fish heads. A recipe for jelled meat broth is found in ''Le Viandier
''Le Viandier'' (often called ''Le Viandier de Taillevent'', ) is a recipe collection generally credited to Guillaume Tirel, alias ''Taillevent''. However, the earliest version of the work was written around 1300, about 10 years before Tirel's bi ...
'', written in or around 1375.
In 15th century Britain, cattle hooves were boiled to produce a gel. By the late 17th century, the French inventor Denis Papin
Denis Papin FRS (; 22 August 1647 – 26 August 1713) was a French physicist, mathematician and inventor, best known for his pioneering invention of the steam digester, the forerunner of the pressure cooker and of the steam engine.
Early lif ...
had discovered another method of gelatin extraction via boiling of bones. An English patent for gelatin production was granted in 1754. In 1812, the chemist Jean-Pierre-Joseph d'Arcet (fr) further experimented with the use of hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
to extract gelatin from bones, and later with steam extraction, which was much more efficient. The French government viewed gelatin as a potential source of cheap, accessible protein for the poor, particularly in Paris. Food applications in France and the United States during 19th century appear to have established the versatility of gelatin, including the origin of its popularity in the US as Jell-O
Jell-O is an American brand offering a variety of powdered gelatin dessert (fruit-flavored gels/jellies), pudding, and no-bake cream pie mixes. The original gelatin dessert (genericized as jello) is the signature of the brand. "Jell-O" is a reg ...
. From the mid 1800s, Charles and Rose Knox
Rose Knox (''née'' Markward; November 18, 1857 – September 27, 1950) was an American businesswoman, who ran the Knox Gelatin Factory in Johnstown, New York, United States, after her husband died. She won wide respect as one of the leading bus ...
of New York manufactured and marketed gelatin powder, diversifying the appeal and applications of gelatin.
Culinary uses
 Probably best known as a
Probably best known as a gelling agent
A gel is a semi-solid that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state, although the liquid phase may still di ...
in cooking
Cooking, cookery, or culinary arts is the art, science and craft of using heat to Outline of food preparation, prepare food for consumption. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from grilling food over an open fire to using electric ...
, different types and grades of gelatin are used in a wide range of food and nonfood products. Common examples of foods that contain gelatin are gelatin dessert
Gelatin desserts (also Jelly or Jello) are desserts made with a sweetened and flavoured processed collagen product ( gelatin). This kind of dessert was first recorded as jelly by Hannah Glasse in her 18th-century book '' The Art of Cookery'' ...
s, trifle
Trifle is a layered dessert of English origin. The usual ingredients are a thin layer of sponge fingers or sponge cake soaked in sherry or another fortified wine, a fruit element (fresh or jelly), custard and whipped cream layered in that o ...
s, aspic
Aspic or meat jelly () is a savory gelatin made with a meat stock or broth, set in a mold to encase other ingredients. These often include pieces of meat, seafood, vegetable, or eggs. Aspic is also sometimes referred to as ''aspic gelée'' or ...
, marshmallow
Marshmallow (, ) is a type of confectionery that is typically made from sugar, water and gelatin whipped to a solid-but-soft consistency. It is used as a filling in baking or normally molded into shapes and coated with corn starch. The sugar c ...
s, candy corn
Candy corn is a type of small, pyramid-shaped candy, typically divided into three sections of different colors, with a waxy texture and a flavor based on honey, sugar, butter, and vanilla. It is a staple candy of the fall season and Halloween in ...
, and confections such as Peeps
Peeps are a marshmallow confection marketed since 1953 in the United States and Canada in the shape of chicks, bunnies and other animals as well as holiday shapes — by Pennsylvania-headquartered Just Born Quality Confections.
Originally ...
, gummy bear
Gummy bears (German: ''Gummibär'') are small, fruit gum candies, similar to a jelly baby in some English-speaking countries. The candy is roughly long and shaped in the form of a bear. The gummy bear is one of many gummies, popular gelat ...
s, fruit snack
A fruit snack is a type of Gummy candy, gummy snack made with fruit flavoring. They were first made by confectioner Louis Shalhoub in the 1970s as a lightweight high energy snack food for backpackers. Although they are marketed as a healthier alt ...
s, and jelly babies
Jelly Babies are a type of soft sugar jelly sweets in the shape of plump babies, sold in a variety of colours. They were first manufactured in Lancashire, England, in the nineteenth century. Their popularity waned before being revived by Basset ...
. Gelatin may be used as a stabilizer, thickener, or texturizer in foods such as yogurt, cream cheese
Cream cheese is a soft, usually mild-tasting fresh cheese made from milk and cream.Oxford English Dictionary Stabilizers such as carob bean gum and carrageenan are often added in industrial production.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration de ...
, and margarine
Margarine (, also , ) is a spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The spread was orig ...
; it is used, as well, in fat-reduced foods to simulate the mouthfeel
Mouthfeel refers to the physical sensations in the mouth caused by food or drink, making it distinct from taste. It is a fundamental sensory attribute which, along with taste and smell, determines the overall flavor of a food item. Mouthfeel is ...
of fat and to create volume. It also is used in the production of several types of Chinese soup dumplings, specifically Shanghainese soup dumplings, or ''xiaolongbao
''Xiaolongbao'' () refers to a type of small Chinese steamed bun (''baozi'') traditionally prepared in a ''xiaolong'', a small bamboo steaming basket, hence the name. ''Xiaolongbao'' are often referred to as a kind of "dumpling", but should not ...
'', as well as ''Shengjian mantou
Shengjian mantou (Wu Chinese: ssanji mhoedhou), shengjian bao, or shengjian for short, is a type of small, pan-fried ''baozi'' (steamed buns) which is a specialty of Suzhou and Shanghai. It is typically filled with pork and gelatin that melts in ...
'', a type of fried and steamed dumpling. The fillings of both are made by combining ground pork with gelatin cubes, and in the process of cooking, the gelatin melts, creating a soupy interior with a characteristic gelatinous stickiness.
Gelatin is used for the clarification of juices, such as apple juice, and of vinegar.
Isinglass
Isinglass () is a substance obtained from the dried swim bladders of fish. It is a form of collagen used mainly for the clarification or fining of some beer and wine. It can also be cooked into a paste for specialised gluing purposes.
The E ...
is obtained from the swim bladders of fish. It is used as a fining agent for wine and beer. Besides hartshorn
Hartshorn is the antler of male red deer.
Derivatives
Various nitrogen compounds were made from hartshorn shavings:
* Oil of hartshorn is a crude chemical product obtained from the destructive distillation of deer antlers.
* Salt of hartshorn r ...
jelly, from deer antlers (hence the name "hartshorn"), isinglass was one of the oldest sources of gelatin.
Cosmetics
In cosmetics, hydrolyzed collagen may be found in topical creams, acting as a product texture conditioner, and moisturizer. Collagen implants or dermal fillers are also used to address the appearance of wrinkles, contour deficiencies, and acne scars, among others. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved its use, and identifies cow (bovine) and human cells as the sources of these fillers. According to the FDA, the desired effects can last for 3–4 months, which is relatively the most short-lived compared to other materials used for the same purpose.Other technical uses
 * Certain professional and theatrical lighting equipment use
* Certain professional and theatrical lighting equipment use color gel
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
s to change the beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
color. Historically, these were made with gelatin, hence the term, color gel.
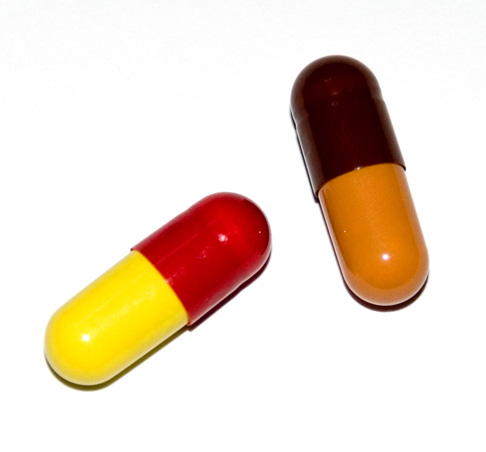
* Originally, gelatin constituted the shells of all drug and vitamin capsules to make them easier to swallow. Now, a vegetarian
Vegetarianism is the practice of abstaining from the consumption of meat (red meat, poultry, seafood, insects, and the flesh of any other animal). It may also include abstaining from eating all by-products of animal slaughter.
Vegetarianism m ...
-acceptable alternative to gelatin, hypromellose
Hypromellose ( INN), short for hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), is a semisynthetic, inert, viscoelastic polymer used in eye drops, as well as an excipient and controlled-delivery component in oral medicaments, found in a variety of commerci ...
, is also used, and is less expensive than gelatin to produce.
* Some animal glue
Animal glue is an adhesive that is created by prolonged boiling of animal connective tissue in a process called rendering. In addition to being used as an adhesive it is used for coating and sizing, in decorative composition ornaments, and as a ...
s such as hide glue may be unrefined gelatin.
* It is used to hold silver halide
A silver halide (or silver salt) is one of the chemical compounds that can form between the element silver (Ag) and one of the halogens. In particular, bromine (Br), chlorine (Cl), iodine (I) and fluorine (F) may each combine with silver to prod ...
crystals in an emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Althoug ...
in virtually all photographic film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin photographic emulsion, emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of th ...
s and photographic paper
Photographic paper is a paper coated with a light-sensitive chemical formula, like photographic film, used for making photographic prints. When photographic paper is exposed to light, it captures a latent image that is then developed to form a v ...
s. Despite significant effort, no suitable substitutes with the stability and low cost of gelatin have been found.
* Used as a carrier, coating, or separating agent for other substances, for example, it makes β-carotene
β-Carotene is an organic, strongly coloured red-orange pigment abundant in fungi, plants, and fruits. It is a member of the carotenes, which are terpenoids (isoprenoids), synthesized biochemically from eight isoprene units and thus having 40 ...
water-soluble, thus imparting a yellow color to any soft drink
A soft drink (see § Terminology for other names) is a drink that usually contains water (often carbonated), a sweetener, and a natural and/or artificial flavoring. The sweetener may be a sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, fruit juice, a su ...
s containing β-carotene.
* Ballistic gelatin
Ballistic gelatin is a testing medium designed to simulate the effects of bullet wounds in animal muscle tissue. It was developed and improved by Martin Fackler and others in the field of wound ballistics. It is calibrated to match porcine muscl ...
is used to test and measure the performance of bullets
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and con ...
shot from firearms
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes c ...
.
* Gelatin is used as a binder in match
A match is a tool for starting a fire. Typically, matches are made of small wooden sticks or stiff paper. One end is coated with a material that can be ignited by friction generated by striking the match against a suitable surface. Wooden matc ...
heads and sandpaper
upright=1.35, Sheets of sandpaper with different grit sizes (40 (coarse), 80, 150, 240, 600 (fine)).
Sandpaper and glasspaper are names used for a type of coated abrasive that consists of sheets of paper or cloth with abrasive material glued to ...
.
* Cosmetics
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protect ...
may contain a non-gelling variant of gelatin under the name hydrolyzed collagen (hydrolysate).
* Gelatin was first used as an external surface sizing
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption ...
for paper in 1337 and continued as a dominant sizing agent of all European papers through the mid-nineteenth century. In modern times, it is mostly found in watercolor paper, and occasionally in glossy printing papers, artistic papers, and playing cards. It maintains the wrinkles in crêpe paper
Crêpe paper is tissue paper that has been coated with sizing (a glue-like substance). It can then be creased in a way similar to party streamers to create gathers, giving it a crinkly texture like that of crêpe. This creasing process is called ...
.
* Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
: Gelatin is also used in synthesizing hydrogel
A hydrogel is a crosslinked hydrophilic polymer that does not dissolve in water. They are highly absorbent yet maintain well defined structures. These properties underpin several applications, especially in the biomedical area. Many hydrogels ar ...
s for tissue engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of Cell (biology), cells, engineering, Materials science, materials methods, and suitable biochemistry, biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintai ...
applications. Gelatin is also used as a saturating agent in immunoassay
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoass ...
s, and as a coat. Gelatin degradation assay allows visualizing and quantifying invasion at the subcellular level instead of analyzing the invasive behavior of whole cells, for the study of cellular protrusions called invadopodia
Invadopodia are actin-rich protrusions of the plasma membrane that are associated with degradation of the extracellular matrix in cancer invasiveness and metastasis. Very similar to podosomes, invadopodia are found in invasive cancer cells and are ...
and podosome
Podosomes are conical, actin-rich structures found on the outer surface of the plasma membrane of animal cells. Their size ranges from approximately 0.5 µm to 2.0 µm in diameter. While usually situated on the periphery of the cellular ...
s, which are protrusive structures in cancer cells and play an important role in cell attachment and remodeling of the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide stru ...
(ECM).
Religious considerations
The consumption of gelatin from particular animals may be forbidden by religious rules or cultural taboos.Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the mai ...
halal
''Halal'' (; ar, حلال, ) is an Arabic word that translates to "permissible" in English. In the Quran, the word ''halal'' is contrasted with ''haram'' (forbidden). This binary opposition was elaborated into a more complex classification kno ...
and Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""Th ...
ish kosher
(also or , ) is a set of dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed kosher ( in English, yi, כּשר), fro ...
customs generally require gelatin from sources other than pigs, such as cattle that have been slaughtered according to religious regulations (halal or kosher), or fish (that Jews and Muslims are allowed to consume).
On the other hand, some Islamic jurists have argued that the chemical treatment "purifies" the gelatin enough to always be halal, an argument most common in the field of medicine.
It has similarly been argued that gelatin in medicine is permissible in Judaism, as it is not used as food. According to ''The Jewish Dietary Laws'', the book of kosher guidelines published by the Rabbinical Assembly
The Rabbinical Assembly (RA) is the international association of Conservative rabbis. The RA was founded in 1901 to shape the ideology, programs, and practices of the Conservative movement. It publishes prayerbooks and books of Jewish interest, an ...
, the organization of Conservative Jewish
Conservative Judaism, known as Masorti Judaism outside North America, is a Jewish religious movement which regards the authority of ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions as coming primarily from its people and community through the generatio ...
rabbis, all gelatin is kosher and pareve
In ''kashrut'', the dietary laws of Judaism, pareve (from yi, פאַרעוו for "neutral", in Hebrew , and also parve and other variant English spellings) is a classification of edible substances that contain neither dairy nor meat ingredients. ...
because the chemical transformation undergone in the manufacturing process renders it a different physical and chemical substance.
Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
, Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, and Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
customs may require gelatin alternatives from sources other than animals, as many Hindus, most Jains and some Sikhs are vegetarian.
See also
*Agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori (''Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" (''Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar is ...
*Carrageenan
Carrageenans or carrageenins ( ; ) are a family of natural linear sulfated polysaccharides that are extracted from red edible seaweeds. Carrageenans are widely used in the food industry, for their gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties. T ...
*Konjac
Konjac (or konjak, ) is a common name of the East and Southeast Asian plant ''Amorphophallus konjac'' ( syn. ''A. rivieri''), which has an edible corm (bulbo-tuber). It is also known as konjaku, konnyaku potato, devil's tongue, voodoo lily, sn ...
*Pectin
Pectin ( grc, πηκτικός ': "congealed" and "curdled") is a heteropolysaccharide, a structural acid contained in the primary lamella, in the middle lamella, and in the cell walls of terrestrial plants. The principal, chemical component of ...
References
External links
{{Authority control Animal products Conservation and restoration materials Dietary supplements Edible thickening agents Excipients Gels Skin care Structural proteins