Ganymede (mythology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
''Antiquitates Romanae'' 1.62.2
/ref> Depending on the author, he is the brother of Ilus, Assaracus,
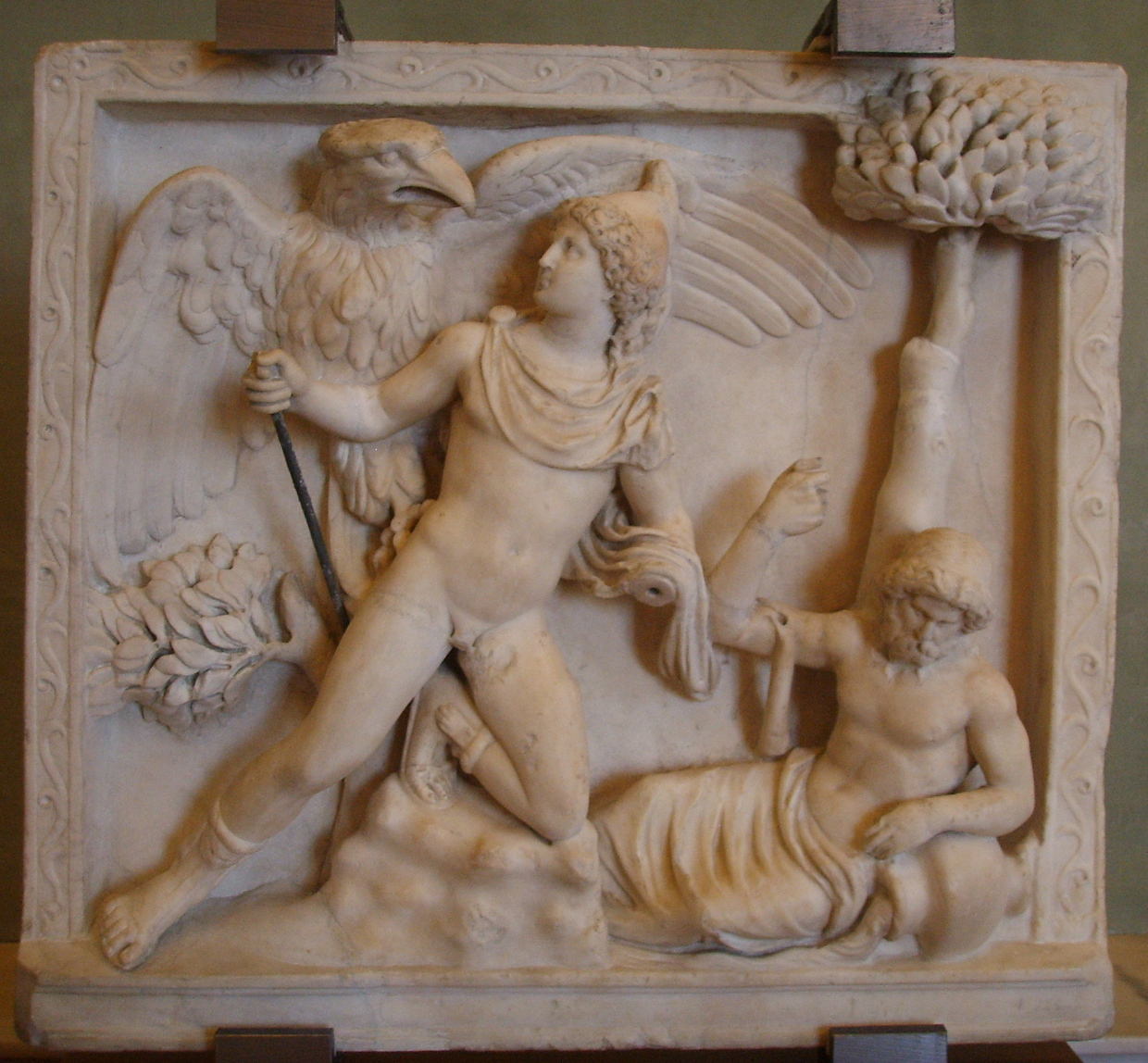 Ganymede was abducted by
Ganymede was abducted by  In the ''Iliad'', Zeus is said to have compensated Ganymede's father Tros by the gift of fine horses, "the same that carry the immortals", delivered by the messenger god
In the ''Iliad'', Zeus is said to have compensated Ganymede's father Tros by the gift of fine horses, "the same that carry the immortals", delivered by the messenger god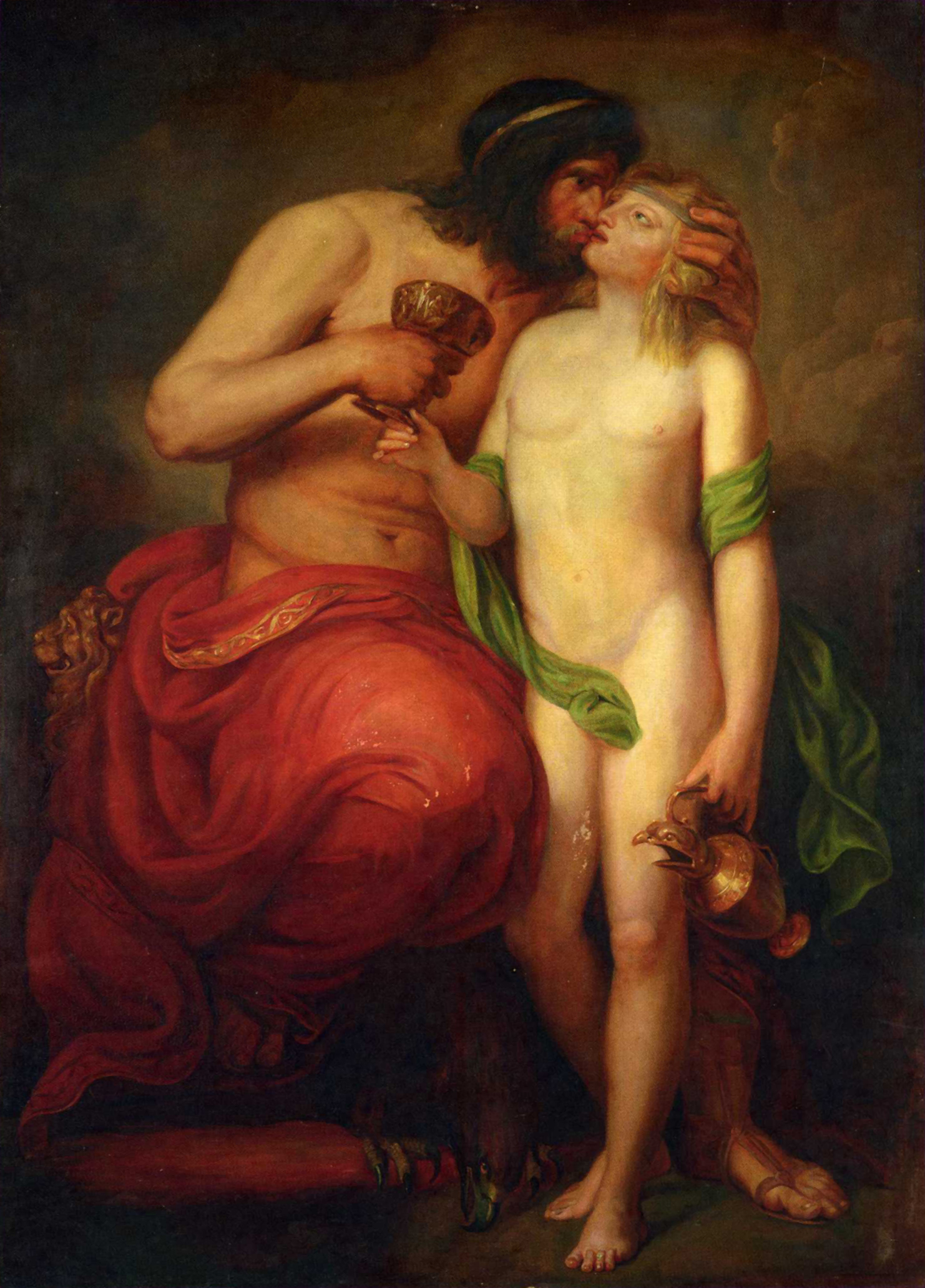 
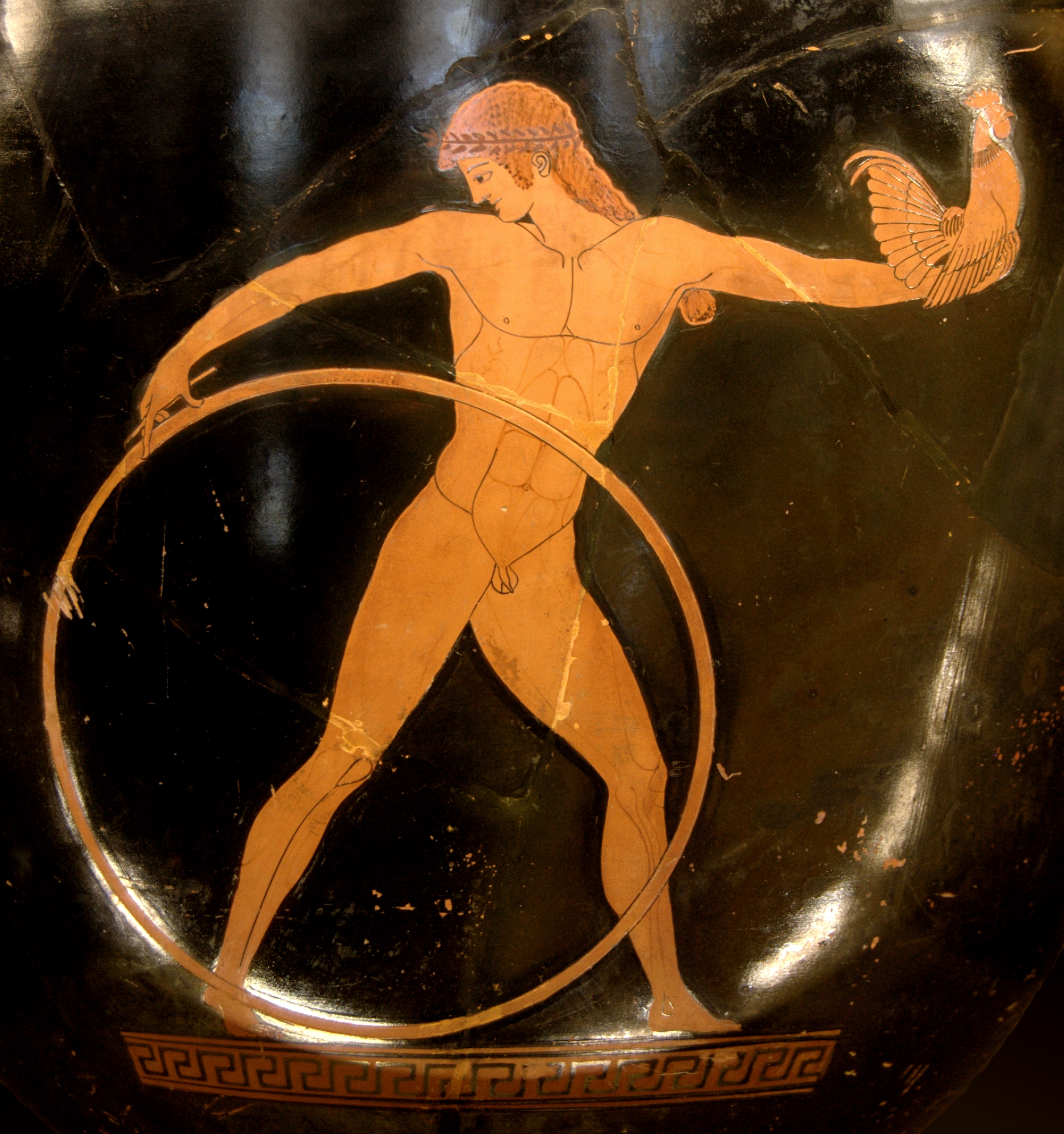 In 5th century Athens, the story of Ganymede became popular among vase-painters, which was suited to the all-male
In 5th century Athens, the story of Ganymede became popular among vase-painters, which was suited to the all-male
File:Andr37.jpg, Michelangelo's ''Ganymede''. Copy after a lost original (1532) pencil.


 * José Álvarez Cubero's sculpture of Ganymede, executed in Paris in 1804, brought the Spanish sculptor immediate recognition as one of the leading sculptors of his day.
*Vollmer's ''Wörterbuch der Mythologie aller Völker'', (Stuttgart, 1874) illustrates "Ganymede" by an engraving of a "Roman relief", showing a seated bearded Zeus who holds the cup aside to draw a naked Ganymede into his embrace. That engraving however was nothing but a copy of
* José Álvarez Cubero's sculpture of Ganymede, executed in Paris in 1804, brought the Spanish sculptor immediate recognition as one of the leading sculptors of his day.
*Vollmer's ''Wörterbuch der Mythologie aller Völker'', (Stuttgart, 1874) illustrates "Ganymede" by an engraving of a "Roman relief", showing a seated bearded Zeus who holds the cup aside to draw a naked Ganymede into his embrace. That engraving however was nothing but a copy of  *In 1959
*In 1959
World History of Male Love: Zeus and Ganymede
by Andrew Calimach
Theoi Project
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (ca 200 images of Ganymede)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ganymede Greek mythological heroes Cup-bearers Consorts of Greek gods Mythological rape victims Princes in Greek mythology Trojans Metamorphoses characters Olympian deities Characters in Greek mythology LGBT themes in Greek mythology Deeds of Zeus
Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities o ...
, Ganymede () or Ganymedes (; Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
: Γανυμήδης ''Ganymēdēs'') is a divine hero
Hero cults were one of the most distinctive features of ancient Greek religion. In Homeric Greek, "hero" (, ) refers to the mortal offspring of a human and a god. By the historical period, however, the word came to mean specifically a ''dead'' ma ...
whose homeland was Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Ç ...
. Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
describes Ganymede as the most beautiful of mortals and tells the story of how he was abducted by the gods to serve as Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek relig ...
's cup-bearer in Olympus
Olympus or Olympos ( grc, Ὄλυμπος, link=no) may refer to:
Mountains
In antiquity
Greece
* Mount Olympus in Thessaly, northern Greece, the home of the twelve gods of Olympus in Greek mythology
* Mount Olympus (Lesvos), located in Le ...
.
The myth was a model for the Greek social custom of ''paiderastía'', the romantic relationship between an adult male and an adolescent male. The Latin form of the name was Catamitus (and also "Ganymedes"), from which the English word '' catamite'' is derived. According to Plato's Laws
The ''Laws'' ( Greek: Νόμοι, ''Nómoi''; Latin: ''De Legibus'') is Plato's last and longest dialogue. The conversation depicted in the work's twelve books begins with the question of who is given the credit for establishing a civilizatio ...
, the Cretans were regularly accused of inventing the myth because they wanted to justify their "unnatural pleasures".
Family
In Greek Mythology, Ganymede is the son of Tros of Dardania, whose name "Troy" is supposedly derived from, either by his wife Callirrhoe, daughter of the river god Scamander, or Acallaris, daughter of Eumedes.Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary styl ...
''Antiquitates Romanae'' 1.62.2
/ref> Depending on the author, he is the brother of Ilus, Assaracus,
Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
or Cleomestra.
The stories about Ganymede, however, differ greatly in their detail, for some called him a son of Laomedon, others a son of Ilus. In some versions he is known as Dardanus, in others as Erichthonius or Assaracus.
Mythology
Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek relig ...
from Mount Ida
In Greek mythology, two sacred mountains are called Mount Ida, the "Mountain of the Goddess": Mount Ida (Crete), Mount Ida in Crete, and Mount Ida (Turkey), Mount Ida in the ancient Troad region of western Anatolia (in modern-day Turkey), which wa ...
near Troy in Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
. Ganymede had been tending sheep which is a rustic or humble pursuit, a characteristic of a hero's boyhood before his privileged status is revealed. An eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
transported the youth to Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (; el, Όλυμπος, Ólympos, also , ) is the highest mountain in Greece. It is part of the Olympus massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located in the Olympus Range on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia, be ...
. The bird is sometimes described as being under the command of Zeus and sometimes as being the god transformed.
On Olympus, Zeus granted Ganymede eternal youth and immortality as the official cup bearer to the gods, in place of Hebe, relieved of cup-bearing duties upon her marriage to Herakles. Alternatively, the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Ody ...
'' presented Hebe (and at one instance, Hephaestus) as the cup bearer of the gods with Ganymede acting as Zeus's personal cup bearer. Edmund Veckenstedt Edmund Veckenstedt (1840–1903) was an educator, ethnologist and folklorist who published many works, sometimes under the pseudonym Heinrich Veltheim.
Albert Edmund Veckenstedt was born in Vehlitz, near Magdeburg, on 7 January 1840. His early ca ...
associated Ganymede with the creation of mead
Mead () is an alcoholic beverage made by fermenting honey mixed with water, and sometimes with added ingredients such as fruits, spices, grains, or hops. The alcoholic content ranges from about 3.5% ABV to more than 20%. The defining characte ...
, which had a traditional origin in Phrygia. In various literature such as the Aeneid, Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; grc-gre, Ἥρα, Hḗrā; grc, Ἥρη, Hḗrē, label=none in Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she ...
, Zeus's wife, regards Ganymede as a rival for her husband's affection. In various stories, Zeus later put Ganymede in the sky as the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellation ...
Aquarius
Aquarius may refer to:
Astrology
* Aquarius (astrology), an astrological sign
* Age of Aquarius, a time period in the cycle of astrological ages
Astronomy
* Aquarius (constellation)
* Aquarius in Chinese astronomy
Arts and entertainment ...
(the "water-carrier" or "cup-carrier"), which is adjacent to Aquila (the Eagle). The largest moon of the planet Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
(named after Zeus's Roman counterpart) was named Ganymede by the German astronomer Simon Marius.
 In the ''Iliad'', Zeus is said to have compensated Ganymede's father Tros by the gift of fine horses, "the same that carry the immortals", delivered by the messenger god
In the ''Iliad'', Zeus is said to have compensated Ganymede's father Tros by the gift of fine horses, "the same that carry the immortals", delivered by the messenger god Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orat ...
. Tros was consoled that his son was now immortal and would be the cup bearer for the gods, a position of much distinction.

Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
accounts for the pederastic aspect of the myth by attributing its origin to Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
, where the social custom of ''paiderastía'' was supposed to have originated (see " Cretan pederasty"). Athenaeus
Athenaeus of Naucratis (; grc, Ἀθήναιος ὁ Nαυκρατίτης or Nαυκράτιος, ''Athēnaios Naukratitēs'' or ''Naukratios''; la, Athenaeus Naucratita) was a Greek rhetorician and grammarian, flourishing about the end of ...
recorded a version of the myth where Ganymede was abducted by the legendary King Minos to serve as his cupbearer instead of Zeus. Some authors have equated this version of the myth to Cretan pederasty practices, as recorded by Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
and Ephoros, it involved abduction of a youth by an older lover for a period of two months before the youth was able to re-enter society as a man. Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
portrays Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no t ...
denying that Ganymede was the ''catamite'' of Zeus, instead asserting that the god loved him for his ''psychē'', "mind" or "soul," giving the etymology of his name as ''ganu-'' "taking pleasure" and ''mēd-'' "mind." Xenophon's Socrates points out that Zeus did not grant any of his lovers immortality, but that he did grant immortality to Ganymede.
In poetry, Ganymede became a symbol for the beautiful young male who attracted homosexual desire and love. He is not always portrayed as acquiescent. However, in the ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jas ...
'' of Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes ( grc, Ἀπολλώνιος Ῥόδιος ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; la, Apollonius Rhodius; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the '' Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and ...
, Ganymede is furious at the god Eros for having cheated him at the game of chance played with knucklebones
Knucklebones, also known as scatter jacks, snobs, astragalus, tali, dibs, fivestones, jacks, or jackstones, among many other names, is a game of dexterity played with a number of small objects that are thrown up, caught, and manipulated in va ...
, and Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols incl ...
scolds her son for "cheating a beginner". The Augustan poet Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: th ...
portrays the abduction with pathos: the boy's aged tutors try in vain to draw him back to Earth, and his hounds bay uselessly at the sky. The loyal hounds left calling after their abducted master is a frequent motif in visual depictions and is referenced by Statius:
Here the Phrygian hunter is borne aloft on tawny wings,Gargara Gargara ( grc, Γάργαρα) was an ancient Greek city on the southern coast of the Troad region of Anatolia. It was initially located beneath Mount Gargaron, one of the three peaks of Mount Ida, today known as Koca Kaya (). At some point in ...’s range sinks downwards as he rises, and Troy grows dim beneath him; sadly stand his comrades; vainly the hounds weary their throats with barking, pursue his shadow or bay at the clouds.'
In the arts
Ancient visual arts
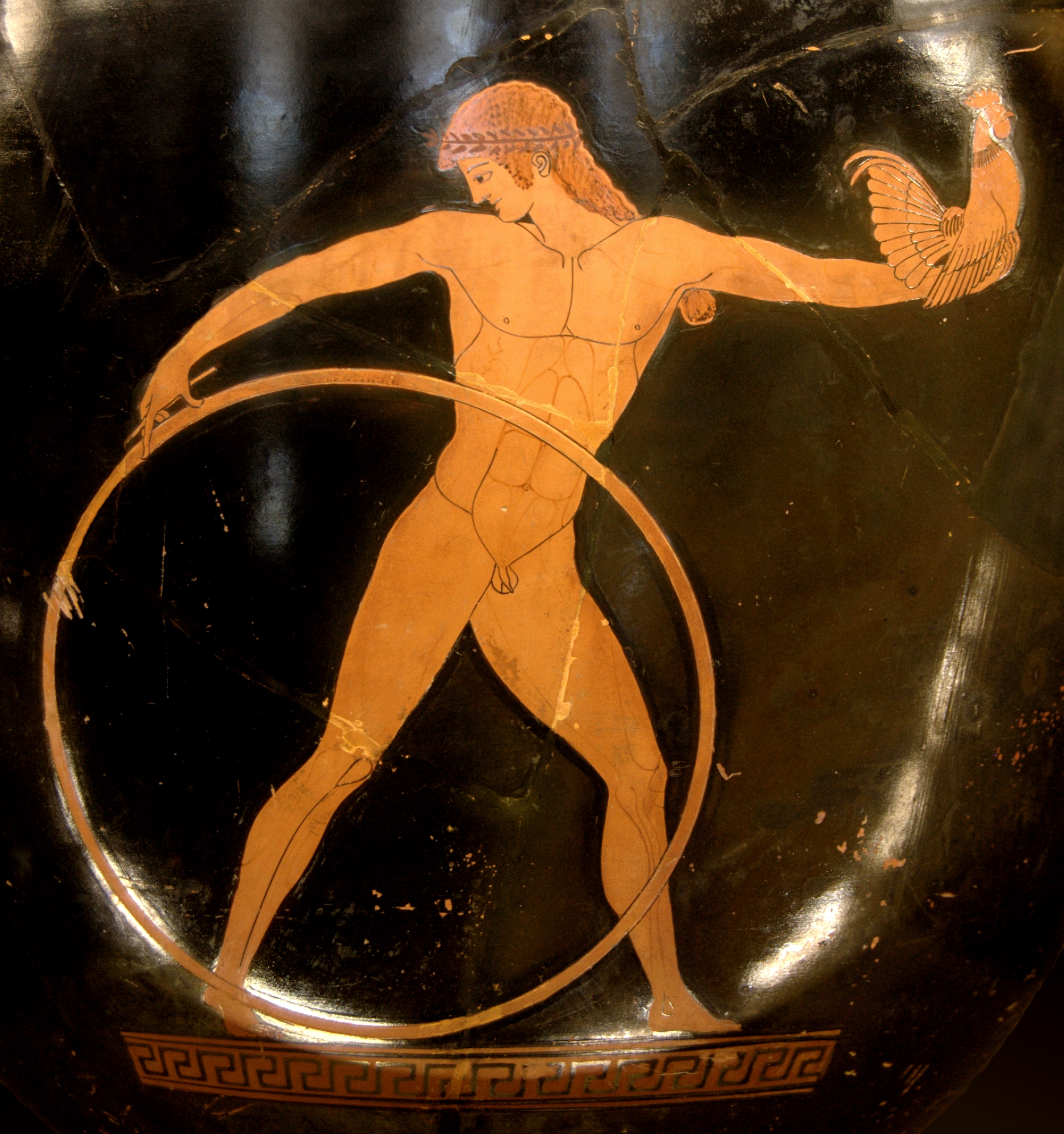 In 5th century Athens, the story of Ganymede became popular among vase-painters, which was suited to the all-male
In 5th century Athens, the story of Ganymede became popular among vase-painters, which was suited to the all-male symposium
In ancient Greece, the symposium ( grc-gre, συμπόσιον ''symposion'' or ''symposio'', from συμπίνειν ''sympinein'', "to drink together") was a part of a banquet that took place after the meal, when drinking for pleasure was acc ...
. Ganymede was usually depicted as a muscular young man, although Greek and Roman sculpture typically depicted his physique as less developed than athletes'.
One of the earliest depictions of Ganymede is a red-figure krater by the Berlin Painter
The Berlin Painter (active c. 490–460s BCE) is the conventional name given to an Attic Greek vase-painter who is widely regarded as a rival to the Kleophrades Painter, among the most talented vase painters of the early 5th century BCE (see P ...
in the Musée du Louvre. Zeus pursues Ganymede on one side, while the youth runs away on the other side, rolling along a hoop while holding aloft a crowing cock. The Ganymede myth was depicted in recognizable contemporary terms, illustrated with common behavior of homoerotic courtship rituals, as on a vase by the "Achilles Painter" where Ganymede also flees with a cock. Cocks were common gifts from older male suitors to younger men they were interested in romantically in 5th century Athens. Leochares (ca. 350 B.C.E.), a Greek sculptor of Athens who was engaged with Scopas on the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus or Tomb of Mausolus ( grc, Μαυσωλεῖον τῆς Ἁλικαρνασσοῦ; tr, Halikarnas Mozolesi) was a tomb built between 353 and 350 BC in Halicarnassus (present Bodrum, Turkey) for Mausolus, a ...
cast a lost bronze group of Ganymede and the Eagle, a work that was held remarkable for its ingenious composition. It is apparently copied in a well-known marble group in the Vatican. Such Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
gravity-defying feats were influential in the sculpture of the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
.
Ganymede and Zeus in the guise of an eagle were a popular subject on Roman funerary monuments with at least 16 sarcophagi depicting this scene.
Renaissance and Baroque
Ganymede was a major symbol of homosexual love in the visual and literary arts from theRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
to the Late Victorian era, until when Antinous
Antinous, also called Antinoös, (; grc-gre, Ἀντίνοος; 27 November – before 30 October 130) was a Greek youth from Bithynia and a favourite and probable lover of the Roman emperor Hadrian. Following his premature death before his ...
, the reported lover of the Roman Emperor Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania ...
, became a more popular subject.
In Shakespeare's ''As You Like It
''As You Like It'' is a pastoral comedy by William Shakespeare believed to have been written in 1599 and first published in the First Folio in 1623. The play's first performance is uncertain, though a performance at Wilton House in 1603 h ...
'' (1599), a comedy about misunderstandings in the magical setting of the Forest of Arden, Celia, dressed as a shepherdess, becomes "Aliena" (Latin "stranger", Ganymede's sister) and Rosalind, because she is "more than common tall", dresses up as a boy, Ganymede, a well-known image to the audience. She plays on her ambiguous charm to seduce Orlando, but also (involuntarily) the shepherdess Phoebe. Thus behind the conventions of Elizabethan theater in its original setting, the young boy played the girl Rosalind who dresses up as a boy and is then courted by another boy playing Phoebe. Ganymede also appears in the opening of Christopher Marlowe
Christopher Marlowe, also known as Kit Marlowe (; baptised 26 February 156430 May 1593), was an English playwright, poet and translator of the Elizabethan era. Marlowe is among the most famous of the Elizabethan playwrights. Based upon t ...
play '' Dido, Queen of Carthage'', where his and Zeus's affectionate banter is interrupted by an angry Aphrodite (Venus). In later Jacobean tragedy, '' Women Beware Women'', Ganymede, Hebe, and Hymen briefly appear to serve as cup bearers to the court, one of which has been poisoned in an assassination attempt, although the plan goes awry.
Allusions to Ganymede occur with some frequency in 17th century Spanish theater. In ''El castigo sin venganza'' (1631) by Lope de Vega
Félix Lope de Vega y Carpio ( , ; 25 November 156227 August 1635) was a Spanish playwright, poet, and novelist. He was one of the key figures in the Spanish Golden Age of Baroque literature. His reputation in the world of Spanish literatur ...
, Federico, the son of the Duke of Mantua, rescues Casandra, his future step-mother, and the pair will later develop an incestuous relationship. To emphasize the non-normative relation, the work includes a long passage, possibly an ekphrasis derived from Italian art, in which Jupiter in the form of an eagle abducts Ganymede. Two plays by Tirso de Molina, and in particular ''La prudencia en la mujer,'' include intriguing references to Ganymede. In this particular play, a Jewish doctor who seeks to poison the future king, carries a cup which is compared to Ganymede's.
One of the earliest surviving non-ancient depictions of Ganymede is a woodcut from the first edition of ''Emblemata
Usually known simply as the ''Emblemata'', the first emblem book appeared in Augsburg (Germany) in 1531 under the title ''Viri Clarissimi D. Andreae Alciati Iurisconsultiss. Mediol. Ad D. Chonradum Peutingerum Augustanum, Iurisconsultum Emblema ...
'' (ca. 1531), which shows the youth riding the eagle as opposed to being carried away. However, this composition is uncommon, with only sketches by Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was ins ...
that survived depicting Ganymede being carried. Painter-architect Baldassare Peruzzi
Baldassare Tommaso Peruzzi (7 March 1481 – 6 January 1536) was an Italian architect and painter, born in a small town near Siena (in Ancaiano, ''frazione'' of Sovicille) and died in Rome. He worked for many years with Bramante, Raphael, and lat ...
included a panel of ''The Rape of Ganymede'' in a ceiling at the Villa Farnesina, Rome, (ca 1509–1514), with Ganymede's long blond hair and girlish pose making him identifiable at first glance, grasping the eagle's wing without resistance. In Antonio Allegri Correggio's '' Ganymede Abducted by the Eagle'' (Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
) Ganymede's grasp is more intimate, Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
' version portrays a young man and Johann Wilhelm Baur
Johann Wilhelm Baur, Joan Guiliam Bouwer, or Bauer (Strasbourg, 31 May 1607 - Vienna, 1 January 1640) was a German engraver, etcher and miniature painter. He is famous for a series of illustrations of Ovid's ''Metamorphoses''.
Biography
Accordi ...
portrays a full-grown Ganymede confidently riding the eagle towards Olympus in ''Ganymede Triumphant'' (ca. 1640s). On the other hand,when Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (, ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally cons ...
painted the ''Rape of Ganymede'' for a Dutch Calvinist patron in 1635, a dark eagle carries aloft a plump cherubic baby (Paintings Gallery, Dresden) who is bawling and urinating in fright. A 1685 statue of Ganymede and Zeus entitled ''Ganymède Médicis'' by Pierre Laviron stands in the gardens of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, ...
.
Examples of Ganymede in 18th century France have been studied by Michael Preston Worley. The image of Ganymede was always that of a naive adolescent accompanied by an eagle and the homoerotic aspects of the legend were rarely dealt with. In fact, the story was often more sexualized. The Neoplatonic interpretation of the myth, also common in the Italian Renaissance, the rape of Ganymede represented the ascent to spiritual perfection,these however seemed to be of no interest to Enlightenment philosophers and mythographers. Jean-Baptiste Marie Pierre, Charles-Joseph Natoire
Charles-Joseph Natoire (3 March 1700 – 23 August 1777) was a French painter in the Rococo manner, a pupil of François Lemoyne and director of the French Academy in Rome, 1751–1775. Considered during his lifetime the equal of François Bouch ...
, Guillaume II Coustou, Pierre Julien
Pierre Julien (20 June 1731 – 17 December 1804) was a French sculptor who worked in a full range of rococo and neoclassical styles.
He served an early apprenticeship at Le Puy-en-Velay, near his natal village of Saint-Paulien, then at the Éco ...
, Jean-Baptiste Regnault
Jean-Baptiste Regnault (9 October 1754 – 12 November 1829) was a French painter.
Biography
Regnault was born in Paris, and began life at sea in a merchant vessel. At the age of fifteen his talent attracted attention, and he was sent to ...
and others contributed images of Ganymede to French art during this period.
Royal Collection
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King Charles III and overseen by the ...
, Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a royal residence at Windsor in the English county of Berkshire. It is strongly associated with the English and succeeding British royal family, and embodies almost a millennium of architectural history.
The original c ...
File:Ganyrubn.jpg, '' The Rape of Ganymede'' (1611) by Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
File:Rembrandt - The Abduction of Ganymede - Google Art Project - cropped.jpg, '' The Abduction of Ganymede'' (1635) by Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (, ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally cons ...
File:Einführung des Ganymed in den Olymp (van Loo).jpg, ''The Induction of Ganymede in Olympus'' (1768) by van Loo Van Loo is a Dutch toponymic surname, meaning "from the forest clearing". People with this surname include:
;A family of painters :
*Jacob van Loo (1614–1670), Dutch painter
* Louis-Abraham van Loo (1653-1712), Dutch-born French painter, son ...
File:Le chateau de versailles le jardin 114.jpg, ''Ganymède Médicis'' (1684-1685) by Pierre Laviron at Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, ...
.
Modern


 * José Álvarez Cubero's sculpture of Ganymede, executed in Paris in 1804, brought the Spanish sculptor immediate recognition as one of the leading sculptors of his day.
*Vollmer's ''Wörterbuch der Mythologie aller Völker'', (Stuttgart, 1874) illustrates "Ganymede" by an engraving of a "Roman relief", showing a seated bearded Zeus who holds the cup aside to draw a naked Ganymede into his embrace. That engraving however was nothing but a copy of
* José Álvarez Cubero's sculpture of Ganymede, executed in Paris in 1804, brought the Spanish sculptor immediate recognition as one of the leading sculptors of his day.
*Vollmer's ''Wörterbuch der Mythologie aller Völker'', (Stuttgart, 1874) illustrates "Ganymede" by an engraving of a "Roman relief", showing a seated bearded Zeus who holds the cup aside to draw a naked Ganymede into his embrace. That engraving however was nothing but a copy of Raphael Mengs
Anton Raphael Mengs (22 March 1728 – 29 June 1779) was a German painter, active in Dresden, Rome, and Madrid, who while painting in the Rococo period of the mid-18th century became one of the precursors to Neoclassical painting, which replace ...
's counterfeit Roman fresco, painted as a practical joke on the eighteenth-century art critic Johann Winckelmann who was growing desperate in his search for homoerotic Greek and Roman antiquities. This story is very briefly told by Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as tr ...
in his ''Italienische Reise''.
*At Chatsworth in the nineteenth century the bachelor Duke of Devonshire
Duke of Devonshire is a title in the Peerage of England held by members of the Cavendish family. This (now the senior) branch of the Cavendish family has been one of the wealthiest British aristocratic families since the 16th century and ha ...
added to his sculpture gallery Adamo Tadolini
Adamo Tadolini (21 December 1788 – 16 February 1863) was an Italian sculptor. One of a family of sculptors, he studied in Rome with the neo-classical sculptor Antonio Canova and is linked to him in style.
Life
Adamo was born in Bologna ...
's Neoclassic "Ganymede and the Eagle", in which a luxuriously reclining Ganymede, embraced by one wing, prepares to exchange a peck with the eagle. The delicate cup in his hand is made of gilt-bronze, lending an unsettling immediacy and realism to the white marble group.
*In the early years of the twentieth century, the topos of Ganymede's abduction by Zeus was drafted into the service of commercial enterprise. Adapting an 1892 lithograph by Frank Kirchbach
Johann Frank Kirchbach (2 June 1859, London – 19 March 1912, Schliersee), was a German historical-, portrait-, genre- and landscape-painter; who also operated as a graphic designer and illustrator.
Biography
His father was the artist, Ernst ...
, the brewery of Anheuser-Busch
Anheuser-Busch Companies, LLC is an American brewing company headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri. Since 2008, it has been wholly owned by Anheuser-Busch InBev SA/NV ( AB InBev), now the world's largest brewing company, which owns multiple ...
launched in 1904 an ad campaign publicizing the successes of Budweiser beer. Collectibles featuring the graphics of the poster continued to be produced into the early 1990s.
*The poem “ Ganymed” by Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as tr ...
was set to music by Franz Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short lifetime, Schubert left behind a vast ''oeuvre'', including more than 600 secular vocal wo ...
in 1817; published in his Opus 19, no. 3 (D. 544). Also set by Hugo Wolf.
*The Portuguese sculptor António Fernandes de Sá represented the abduction of Ganymede in 1898. The sculpture can be found in Jardim da Cordoaria, in Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropo ...
(Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
).
*In stories by P. G. Wodehouse, the Junior Ganymede is a servants' club, analogous to the Drones, to which Jeeves
Jeeves (born Reginald Jeeves, nicknamed Reggie) is a fictional character in a series of comedic short stories and novels by English author P. G. Wodehouse. Jeeves is the highly competent valet of a wealthy and idle young Londoner named Berti ...
belongs. Wodehouse named it after Ganymede presumably in reference to his role of cup-bearer.
*Ganymede is a reluctant music fan in Kurtis Blow's 1980 song "Way Out West". After hours of rap by "The Stranger" (Kurtis), he eventually gets up to dance.
*American artist Henry Oliver Walker painted a mural in the Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The libra ...
in Washington D.C. circa 1900, depicting an adolescent, nude Ganymede on the back of an eagle.
*Ganymede and the god Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; grc, wikt:Διόνυσος, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstas ...
make an appearance in ''Everworld VI: Fear the Fantastic'', of K.A. Applegate's fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
series Everworld
''Everworld'' is a fantasy novel series co-authored by K. A. Applegate and Michael Grant and published by Scholastic between 1999 and 2001. It consists of twelve books and a companion music CD titled ''The Everworld Experience''.
Main characte ...
. Ganymede is described as attracting both males and females.
My first thought, my first flash was that it was a beautiful woman.... The angel was beautiful, with a face dominated by immense, lustrous green eyes and framed by golden ringlets, and with a bow mouth and full lips and brilliant white teeth.
And only then, only after I had felt that first rush of improbable carnal lust, did it occur to me that this angel was a man. Applegate, K. A., ''Everworld VI: Fear the Fantastic'', p. 50.
 *In 1959
*In 1959 Robert Rauschenberg
Milton Ernest "Robert" Rauschenberg (October 22, 1925 – May 12, 2008) was an American painter and graphic artist whose early works anticipated the Pop art movement. Rauschenberg is well known for his Combines (1954–1964), a group of artwor ...
referenced the myth in one of his best-known works, ''Canyon'' and in another work, ''Pail for Ganymede''. In "Canyon", a photo of Rauschenberg's son Christopher beautifully reiterates the infant portrayed by Rembrandt in the 17th century. A stuffed eagle emerges from the flat picture plane with a pillow tied to a piece of string very near his claw. The pillow also reflects upon the young boy's body and Rembrandt's painting.
* Ganymede is a reluctant son in W.H.Auden's poem of that name, but he adores the eagle which teaches him how to kill.
* Felice Picano's 1981 novel ''An Asian Minor ''An Asian Minor'' is a novel by Felice Picano in which he re-invents the myth of Ganymede. In Greek Mythology, Ganymede was the cup-bearer of Olympus and the beloved of Zeus, chief of the gods. In the novel, told in the first person from the vi ...
'' reinvents the story of Ganymede.
*In the 2016 video game ''Overwatch
''Overwatch'' is a multimedia franchise centered on a series of online multiplayer first-person shooter (FPS) video games developed by Blizzard Entertainment: '' Overwatch'' released in 2016, and ''Overwatch 2'' released in 2022. Both games fe ...
,'' the character Bastion has a bird named Ganymede.
*A character in the Terra Ignota series by Ada Palmer is named Ganymede de la Trémoille
*The opening of Will Self's 2017 novel ''Phone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into ele ...
'' refers to 'agents of Ganymede' (p. 6) to explore caution within the homosexual community in previous decades.
*The first poem in Jericho Brown
Jericho Brown (born April 14, 1976) is an American poet and writer. Born and raised in Shreveport, Louisiana, Brown has worked as an educator at institutions such as University of Houston, San Diego State University, and Emory University. His poe ...
's Pulitzer Prize for Poetry-winning 2019 book ''The Tradition
The Tradition (known as the Regions Tradition for sponsorship reasons) is an event on the PGA Tour Champions. First staged in 1989, the PGA Tour recognizes the event as one of the five senior major golf championships. Unlike the U.S. Senior Op ...
'' is titled "Ganymede". Brown, who frequently interrogates topics of sexuality and race, brings the Greek abduction myth into contact with the history of American slavery.
Family tree
Notes
References
Sources
Ancient sources
Ganymede is named by various ancient Greek and Roman authors: *Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
– Iliad 5.265; Iliad 20.232;
*Homerica – The Little Iliad, Frag 7;
*Homeric Hymns
The ''Homeric Hymns'' () are a collection of thirty-three anonymous ancient Greek hymns celebrating individual gods. The hymns are "Homeric" in the sense that they employ the same epic meter— dactylic hexameter—as the ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'' ...
– Hymn V, To Aphrodite, 203–217;
*Theognis
Theognis of Megara ( grc-gre, Θέογνις ὁ Μεγαρεύς, ''Théognis ho Megareús'') was a Greek lyric poet active in approximately the sixth century BC. The work attributed to him consists of gnomic poetry quite typical of the time, ...
– Fragments 1.1345;
*Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar ...
– Olympian Odes
Olympian or Olympians may refer to:
Religion
* Twelve Olympians, the principal gods and goddesses in ancient Greek religion
* Olympian spirits, spirits mentioned in books of ceremonial magic
Fiction
* ''Percy Jackson & the Olympians'', fictio ...
1; 11;
*Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars ...
– Iphigenia at Aulis 1051;
*Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
– Phaedrus 255; Laws 636c
* Apollonios Rhodios – Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jas ...
3.112f;
*ps-Apollodorus – '' Bibliotheke'' 2.104; 3.141;
*Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
– Geography 13.1.11;
* Pausanias – Guide to Greece V.24.5; V.26.2–3;
*Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which ...
– The Library of History 4.75.3;
* Hyginus
**Fabulae 89; 224; 271;
**Astronomica 2.16; 2.29;
*Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom ...
– Metamorphoses
The ''Metamorphoses'' ( la, Metamorphōsēs, from grc, μεταμορφώσεις: "Transformations") is a Latin narrative poem from 8 CE by the Roman poet Ovid. It is considered his '' magnum opus''. The poem chronicles the history of the ...
10.152;
*Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: th ...
– Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; la, Aenē̆is or ) is a Latin epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Trojan who fled the fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of ...
1.28; 5.252;
*Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
– De Natura Deorum
''De Natura Deorum'' (''On the Nature of the Gods'') is a philosophical dialogue by Roman Academic Skeptic philosopher Cicero written in 45 BC. It is laid out in three books that discuss the theological views of the Hellenistic philosophies o ...
1.40;
* Valerius Flaccus – Argonautica 2.414; 5.690;
* Statius
**Thebaid
The Thebaid or Thebais ( grc-gre, Θηβαΐς, ''Thēbaïs'') was a region in ancient Egypt, comprising the 13 southernmost nomes of Upper Egypt, from Abydos to Aswan.
Pharaonic history
The Thebaid acquired its name from its proximity to ...
1.549;
** Silvae 3.4.13;
* Apuleius – The Golden Ass 6.15; 6.24;
*Quintus Smyrnaeus
Quintus Smyrnaeus (also Quintus of Smyrna; el, Κόϊντος Σμυρναῖος, ''Kointos Smyrnaios'') was a Greek epic poet whose '' Posthomerica'', following "after Homer", continues the narration of the Trojan War. The dates of Quintus S ...
– Fall of Troy 8.427; 14.324;
* Nonnus – Dionysiaca 8.93; 10.258; 10.308; 12.39; 14.430; 15.279; 17.76; 19.158; 25.430; 27.241; 31.252; 33.74; 39.67; 47.98;
*''Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; grc-x-medieval, Σοῦδα, Soûda; la, Suidae Lexicon) is a large 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia of the ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas (Σούδας) or Souida ...
'' – Ilion; Minos;
Modern sources
*External links
World History of Male Love: Zeus and Ganymede
by Andrew Calimach
Theoi Project
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (ca 200 images of Ganymede)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ganymede Greek mythological heroes Cup-bearers Consorts of Greek gods Mythological rape victims Princes in Greek mythology Trojans Metamorphoses characters Olympian deities Characters in Greek mythology LGBT themes in Greek mythology Deeds of Zeus