Galvanic corrosion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
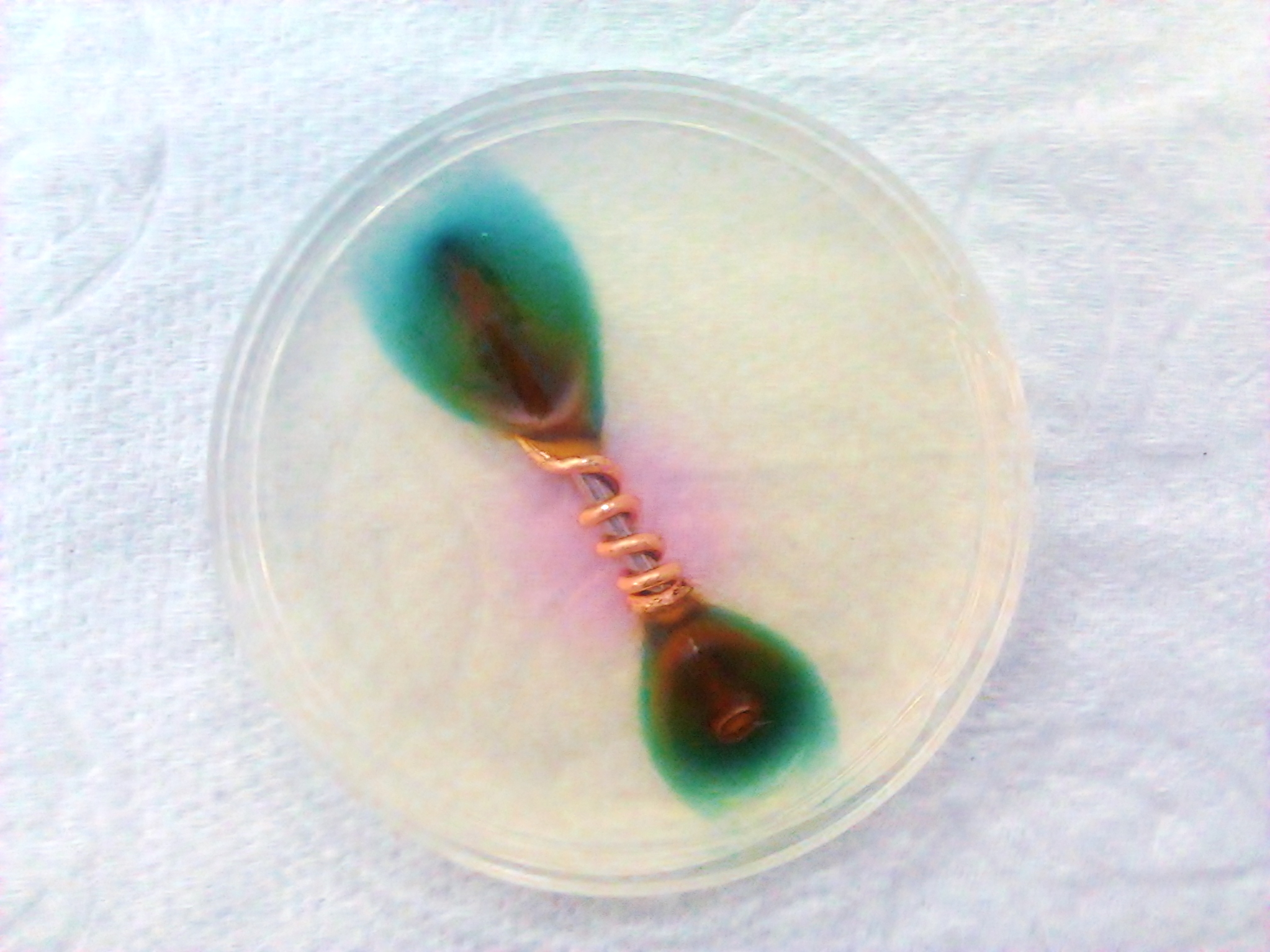 Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one
 There are several ways of reducing and preventing this form of corrosion.
* Electrically insulate the two metals from each other. If they are not in electrical contact, no galvanic coupling will occur. This can be achieved by using non-conductive materials between metals of different electropotential. Piping can be isolated with a spool of pipe made of plastic materials, or made of metal material internally coated or lined. It is important that the spool be a sufficient length to be effective. For reasons of safety, this should not be attempted where an electrical earthing system uses the pipework for its
There are several ways of reducing and preventing this form of corrosion.
* Electrically insulate the two metals from each other. If they are not in electrical contact, no galvanic coupling will occur. This can be achieved by using non-conductive materials between metals of different electropotential. Piping can be isolated with a spool of pipe made of plastic materials, or made of metal material internally coated or lined. It is important that the spool be a sufficient length to be effective. For reasons of safety, this should not be attempted where an electrical earthing system uses the pipework for its
 The compatibility of two different metals may be predicted by consideration of their anodic index. This parameter is a measure of the electrochemical voltage that will be developed between the metal and gold. To find the relative voltage of a pair of metals it is only required to subtract their anodic indices.Wheeler, Gerson J., The design of electronic equipment: a manual for production and manufacturing, Prentice-Hall, 1972
To reduce galvanic corrosion for metals stored in normal environments such as storage in warehouses or non-temperature and humidity controlled environments, there should not be more than 0.25V difference in the anodic index of the two metals in contact. For controlled environments in which temperature and humidity are controlled, 0.50V can be tolerated. For harsh environments such as outdoors, high humidity, and salty environments, there should be not more than 0.15V difference in the anodic index. For example: gold and silver have a difference of 0.15V, therefore the two metals will not experience significant corrosion even in a harsh environment.
When design considerations require that dissimilar metals come in contact, the difference in anodic index is often managed by finishes and plating. The finishing and plating selected allow the dissimilar materials to be in contact, while protecting the more base materials from corrosion by the more noble. It will always be the metal with the most negative anodic index which will ultimately suffer from corrosion when galvanic incompatibility is in play. This is why sterling silver and stainless steel tableware should never be placed together in a dishwasher at the same time, as the steel items will likely experience corrosion by the end of the cycle (soap and water having served as the chemical electrolyte, and heat having accelerated the process).
The compatibility of two different metals may be predicted by consideration of their anodic index. This parameter is a measure of the electrochemical voltage that will be developed between the metal and gold. To find the relative voltage of a pair of metals it is only required to subtract their anodic indices.Wheeler, Gerson J., The design of electronic equipment: a manual for production and manufacturing, Prentice-Hall, 1972
To reduce galvanic corrosion for metals stored in normal environments such as storage in warehouses or non-temperature and humidity controlled environments, there should not be more than 0.25V difference in the anodic index of the two metals in contact. For controlled environments in which temperature and humidity are controlled, 0.50V can be tolerated. For harsh environments such as outdoors, high humidity, and salty environments, there should be not more than 0.15V difference in the anodic index. For example: gold and silver have a difference of 0.15V, therefore the two metals will not experience significant corrosion even in a harsh environment.
When design considerations require that dissimilar metals come in contact, the difference in anodic index is often managed by finishes and plating. The finishing and plating selected allow the dissimilar materials to be in contact, while protecting the more base materials from corrosion by the more noble. It will always be the metal with the most negative anodic index which will ultimately suffer from corrosion when galvanic incompatibility is in play. This is why sterling silver and stainless steel tableware should never be placed together in a dishwasher at the same time, as the steel items will likely experience corrosion by the end of the cycle (soap and water having served as the chemical electrolyte, and heat having accelerated the process).
 Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon ...
. A similar galvanic reaction is exploited in primary cells to generate a useful electrical voltage to power portable devices.
This phenomenon is named after Italian physician Luigi Galvani
Luigi Galvani (, also ; ; la, Aloysius Galvanus; 9 September 1737 – 4 December 1798) was an Italian physician, physicist, biologist and philosopher, who studied animal electricity. In 1780, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs ...
(1737-1798).
Overview
Dissimilar metals and alloys have differentelectrode potential
In electrochemistry, electrode potential is the electromotive force of a galvanic cell built from a standard reference electrode and another electrode to be characterized. By convention, the reference electrode is the standard hydrogen electrode ...
s, and when two or more come into contact in an electrolyte, one metal (that's more reactive) acts as anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
and the other (that's less reactive) as cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
. The electropotential difference between the reactions at the two electrodes is the driving force for an accelerated attack on the anode metal, which dissolves into the electrolyte. This leads to the metal at the anode corroding more quickly than it otherwise would and corrosion at the cathode being inhibited. The presence of an electrolyte and an electrical conducting path between the metals is essential for galvanic corrosion to occur. The electrolyte provides a means for ion migration whereby ions move to prevent charge build-up that would otherwise stop the reaction. If the electrolyte contains only metal ions that are not easily reduced (such as Na+, Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, or Zn2+), the cathode reaction is the reduction of dissolved H+ to H2 or O2 to OH−. Goodisman notes that many chemistry textbooks use an incorrect model for a cell with zinc and copper electrodes in an acidic electrolyte.
In some cases, this type of reaction is intentionally encouraged. For example, low-cost household batteries typically contain carbon-zinc cells. As part of a closed circuit
Closed circuit can refer to:
*Closed-circuit television
*Closed-circuit radio
*Rebreather – breathing sets
* ''Closed Circuit'' (1978 film), a 1978 Italian film
* ''Closed Circuit'' (2013 film), a 2013 British thriller film
*An electric circuit
...
(the electron pathway), the zinc within the cell will corrode preferentially (the ion pathway) as an essential part of the battery producing electricity. Another example is the cathodic protection
Cathodic protection (CP; ) is a technique used to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the cathode of an electrochemical cell. A simple method of protection connects the metal to be protected to a more easily corroded "sacrifi ...
of buried or submerged structures as well as hot water storage tanks. In this case, sacrificial anodes work as part of a galvanic couple, promoting corrosion of the anode, while protecting the cathode metal.
In other cases, such as mixed metals in piping (for example, copper, cast iron and other cast metals), galvanic corrosion will contribute to accelerated corrosion of parts of the system. Corrosion inhibitors such as sodium nitrite
Sodium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. It is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important nitrite ...
or sodium molybdate can be injected into these systems to reduce the galvanic potential. However, the application of these corrosion inhibitors must be monitored closely. If the application of corrosion inhibitors increases the conductivity of the water within the system, the galvanic corrosion potential can be greatly increased.
Acidity or alkalinity ( pH) is also a major consideration with regard to closed loop bimetallic circulating systems. Should the pH and corrosion inhibition doses be incorrect, galvanic corrosion will be accelerated. In most HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. ...
systems, the use of sacrificial anodes and cathodes is not an option, as they would need to be applied within the plumbing of the system and, over time, would corrode and release particles that could cause potential mechanical damage to circulating pumps, heat exchangers, etc.
Examples of corrosion
A common example of galvanic corrosion occurs in galvanized iron, a sheet of iron or steel covered with a zinc coating. Even when the protectivezinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
coating is broken, the underlying steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistan ...
is not attacked. Instead, the zinc is corroded because it is less "noble". Only after it has been consumed can rusting of the base metal occur. By contrast, with a conventional tin can
A steel can, tin can, tin (especially in British English, Australian English, Canadian English and South African English),
steel packaging, or can is a container for the distribution or storage of goods, made of thin metal. Many cans ...
, the opposite of a protective effect occurs: because the tin is more noble than the underlying steel, when the tin coating is broken, the steel beneath is immediately attacked preferentially.
Statue of Liberty
A spectacular example of galvanic corrosion occurred in theStatue of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty (''Liberty Enlightening the World''; French: ''La Liberté éclairant le monde'') is a colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor in New York City, in the United States. The copper statue, ...
when regular maintenance checks in the 1980s revealed that corrosion had taken place between the outer copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
skin and the wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" ...
support structure. Although the problem had been anticipated when the structure was built by Gustave Eiffel
Alexandre Gustave Eiffel (born Bonickhausen dit Eiffel; ; ; 15 December 1832 – 27 December 1923) was a French civil engineer. A graduate of École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures, he made his name with various bridges for the French railway ...
to Frédéric Bartholdi's design in the 1880s, the insulation layer of shellac between the two metals had failed over time and resulted in rusting of the iron supports. An extensive renovation was carried out with replacement of the original insulation with PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that has numerous applications. It is one of the best-known and widely applied PFAS. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chem ...
. The structure was far from unsafe owing to the large number of unaffected connections, but it was regarded as a precautionary measure to preserve a national symbol of the United States.
Royal Navy and HMS ''Alarm''
In the 17th century,Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys (; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English diarist and naval administrator. He served as administrator of the Royal Navy and Member of Parliament and is most famous for the diary he kept for a decade. Pepys had no mariti ...
(then serving as Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
Secretary) agreed to the removal of lead sheathing from English Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
vessels to prevent the mysterious disintegration of their rudder-irons and bolt-heads, though he confessed himself baffled as to the reason the lead caused the corrosion.
The problem recurred when vessels were sheathed in copper to reduce marine weed accumulation and protect against shipworm
The shipworms are marine bivalve molluscs in the family Teredinidae: a group of saltwater clams with long, soft, naked bodies. They are notorious for boring into (and commonly eventually destroying) wood that is immersed in sea water, including ...
. In an experiment, the Royal Navy in 1761 had tried fitting the hull of the frigate HMS ''Alarm'' with 12-ounce copper plating. Upon her return from a voyage to the West Indies, it was found that although the copper remained in fine condition and had indeed deterred shipworm, it had also become detached from the wooden hull in many places because the iron nails used during its installation "were found dissolved into a kind of rusty Paste". To the surprise of the inspection teams, however, some of the iron nails were virtually undamaged. Closer inspection revealed that water-resistant brown paper trapped under the nail head had inadvertently protected some of the nails: "Where this covering was perfect, the Iron was preserved from Injury". The copper sheathing had been delivered to the dockyard wrapped in the paper which was not always removed before the sheets were nailed to the hull. The conclusion therefore reported to the Admiralty in 1763 was that iron should not be allowed direct contact with copper in sea water.
US Navy littoral combat ship ''Independence''
Serious galvanic corrosion has been reported on the latest US Navy attack littoral combat vessel the USS ''Independence'' caused by steel water jet propulsion systems attached to an aluminium hull. Without electrical isolation between the steel and aluminium, the aluminium hull acts as an anode to the stainless steel, resulting in aggressive galvanic corrosion.Corroding lighting fixtures
The unexpected fall in 2011 of a heavy light fixture from the ceiling of the Big Dig vehicular tunnel inBoston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
revealed that corrosion had weakened its support. Improper use of aluminium in contact with stainless steel had caused rapid corrosion in the presence of salt water. The electrochemical potential difference between stainless steel and aluminium is in the range of 0.5 to 1.0V, depending on the exact alloys involved, and can cause considerable corrosion within months under unfavorable conditions. Thousands of failing lights would have to be replaced, at an estimated cost of $54 million.
Lasagna cell
A " lasagna cell" is accidentally produced when salty moist food such as lasagna is stored in a steel baking pan and is covered with aluminium foil. After a few hours the foil develops small holes where it touches the lasagna, and the food surface becomes covered with small spots composed of corroded aluminium. In this example, the salty food (lasagna) is the electrolyte, the aluminium foil is the anode, and the steel pan is the cathode. If the aluminium foil touches the electrolyte only in small areas, the galvanic corrosion is concentrated, and corrosion can occur fairly rapidly. If the aluminium foil was not used with a dissimilar metal container, the reaction was probably a chemical one. It is possible for heavy concentrations of salt, vinegar or some other acidic compounds to cause the foil to disintegrate. The product of either of these reactions is an aluminium salt. It does not harm the food, but any deposit may impart an undesired flavor and color.Electrolytic cleaning
The common technique of cleaningsilver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
ware by immersion of the silver or sterling silver (or even just silver plated objects) and a piece of aluminium (foil is preferred because of its much greater surface area than that of ingots, although if the foil has a "non-stick" face, this must be removed with steel wool first) in a hot electrolytic bath (usually composed of water and sodium bicarbonate, i.e., household baking soda) is an example of galvanic corrosion. Silver darkens and corrodes in the presence of airborne sulfur molecules, and the copper in sterling silver corrodes under a variety of conditions. These layers of corrosion can be largely removed through the electrochemical reduction of silver sulfide molecules: the presence of aluminium (which is less noble than either silver or copper) in the bath of sodium bicarbonate strips the sulfur atoms off the silver sulfide and transfers them onto and thereby corrodes the piece of aluminium foil (a much more reactive metal), leaving elemental silver behind. No silver is lost in the process.
Preventing galvanic corrosion

ground
Ground may refer to:
Geology
* Land, the surface of the Earth not covered by water
* Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth
Electricity
* Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical c ...
or has equipotential bonding.
* Metal boats connected to a shore line electrical power feed will normally have to have the hull connected to earth for safety reasons. However the end of that earth connection is likely to be a copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
rod buried within the marina, resulting in a steel-copper "battery" of about 0.5 V. Additionally, the hull of each boat is connected to the hull of all other boats, resulting in further "batteries" between propellers (which may be made of bronze) and steel hulls, which may cause corrosion of the expensive propellers. For such cases, the use of a galvanic isolator is essential, typically two semiconductor diodes in series, in parallel with two diodes conducting in the opposite direction (antiparallel). This device is inserted in the protective earth connection between the hull and the shoreline protective conductor. This prevents any current in the protective conductor while the applied voltage is ''less'' than 1.4 V (i.e. 0.7 V per diode), but allows a full current in the case of an electrical fault. There will still be a very minor leakage of current through the diodes, which may result in slightly faster corrosion than normal.
* Ensure there is no contact with an electrolyte. This can be done by using water-repellent compounds such as greases, or by coating the metals with an impermeable protective layer, such as a suitable paint, varnish, or plastic. If it is not possible to coat both, the coating should be applied to the more noble, the material with higher potential. This is advisable because if the coating is applied only on the more active material, in case of damage to the coating there will be a large cathode area and a very small anode area, and for the exposed anodic area the corrosion rate will be correspondingly high.
* Using antioxidant paste is beneficial for preventing corrosion between copper and aluminium electrical connections. The paste consists of a lower nobility metal than aluminium or copper.
* Choose metals that have similar electropotentials. The more closely matched the individual potentials, the smaller the potential difference and hence the smaller the galvanic current. Using the same metal for all construction is the easiest way of matching potentials.
* Electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
or other plating can also help. This tends to use more noble metals that resist corrosion better. Chrome, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
, silver and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
can all be used. Galvanizing with zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
protects the steel base metal by sacrificial anodic action.
* Cathodic protection
Cathodic protection (CP; ) is a technique used to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the cathode of an electrochemical cell. A simple method of protection connects the metal to be protected to a more easily corroded "sacrifi ...
uses one or more sacrificial anode
A galvanic anode, or sacrificial anode, is the main component of a galvanic cathodic protection system used to protect buried or submerged metal structures from corrosion.
They are made from a metal alloy with a more "active" voltage (more n ...
s made of a metal which is more active than the protected metal. Alloys of metals commonly used for sacrificial anodes include zinc, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
, and aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
. This approach is commonplace in water heaters and many buried or immersed metallic structures.
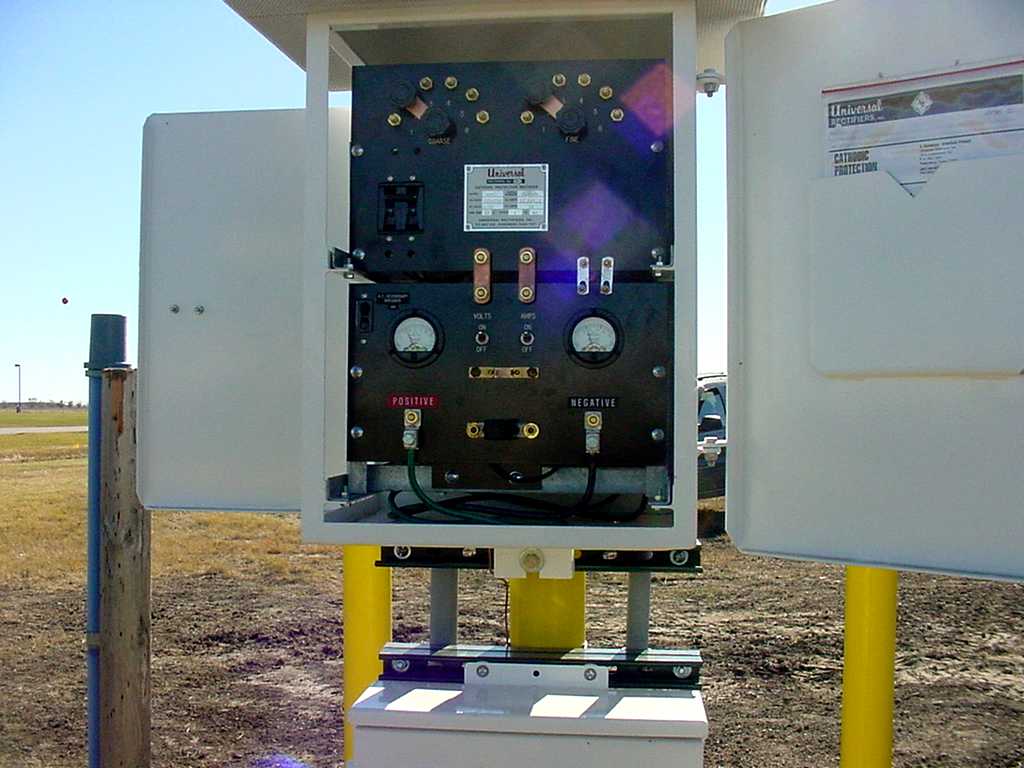
* Cathodic protection can also be applied by connecting a direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or ev ...
(DC) electrical power supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As ...
to oppose the corrosive galvanic current. (See .)
Galvanic series
All metals can be classified into a galvanic series representing the electrical potential they develop in a given electrolyte against a standard reference electrode. The relative position of two metals on such a series gives a good indication of which metal is more likely to corrode more quickly. However, other factors such as water aeration and flow rate can influence the rate of the process markedly.Anodic index
 The compatibility of two different metals may be predicted by consideration of their anodic index. This parameter is a measure of the electrochemical voltage that will be developed between the metal and gold. To find the relative voltage of a pair of metals it is only required to subtract their anodic indices.Wheeler, Gerson J., The design of electronic equipment: a manual for production and manufacturing, Prentice-Hall, 1972
To reduce galvanic corrosion for metals stored in normal environments such as storage in warehouses or non-temperature and humidity controlled environments, there should not be more than 0.25V difference in the anodic index of the two metals in contact. For controlled environments in which temperature and humidity are controlled, 0.50V can be tolerated. For harsh environments such as outdoors, high humidity, and salty environments, there should be not more than 0.15V difference in the anodic index. For example: gold and silver have a difference of 0.15V, therefore the two metals will not experience significant corrosion even in a harsh environment.
When design considerations require that dissimilar metals come in contact, the difference in anodic index is often managed by finishes and plating. The finishing and plating selected allow the dissimilar materials to be in contact, while protecting the more base materials from corrosion by the more noble. It will always be the metal with the most negative anodic index which will ultimately suffer from corrosion when galvanic incompatibility is in play. This is why sterling silver and stainless steel tableware should never be placed together in a dishwasher at the same time, as the steel items will likely experience corrosion by the end of the cycle (soap and water having served as the chemical electrolyte, and heat having accelerated the process).
The compatibility of two different metals may be predicted by consideration of their anodic index. This parameter is a measure of the electrochemical voltage that will be developed between the metal and gold. To find the relative voltage of a pair of metals it is only required to subtract their anodic indices.Wheeler, Gerson J., The design of electronic equipment: a manual for production and manufacturing, Prentice-Hall, 1972
To reduce galvanic corrosion for metals stored in normal environments such as storage in warehouses or non-temperature and humidity controlled environments, there should not be more than 0.25V difference in the anodic index of the two metals in contact. For controlled environments in which temperature and humidity are controlled, 0.50V can be tolerated. For harsh environments such as outdoors, high humidity, and salty environments, there should be not more than 0.15V difference in the anodic index. For example: gold and silver have a difference of 0.15V, therefore the two metals will not experience significant corrosion even in a harsh environment.
When design considerations require that dissimilar metals come in contact, the difference in anodic index is often managed by finishes and plating. The finishing and plating selected allow the dissimilar materials to be in contact, while protecting the more base materials from corrosion by the more noble. It will always be the metal with the most negative anodic index which will ultimately suffer from corrosion when galvanic incompatibility is in play. This is why sterling silver and stainless steel tableware should never be placed together in a dishwasher at the same time, as the steel items will likely experience corrosion by the end of the cycle (soap and water having served as the chemical electrolyte, and heat having accelerated the process).
See also
*Corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
* Galvanic anode
* Galvanic series
* Galvanization
*
References
External links
{{Authority control Corrosion