Galathea expeditions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
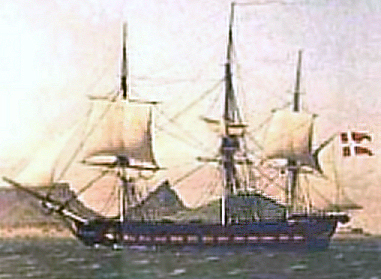 The ''Galathea'' expeditions comprise a series of three Danish ship-based scientific research expeditions in the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries, carried out with material assistance from the Royal Danish Navy and, with regard to the second and third expeditions, under the auspices of the Danish Expedition Foundation. All three expeditions
The ''Galathea'' expeditions comprise a series of three Danish ship-based scientific research expeditions in the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries, carried out with material assistance from the Royal Danish Navy and, with regard to the second and third expeditions, under the auspices of the Danish Expedition Foundation. All three expeditions
 The ''Galathea'' left Copenhagen on 24 June 1845 and, after a provisioning stop at
The ''Galathea'' left Copenhagen on 24 June 1845 and, after a provisioning stop at
 The third expedition took place during 2006–2007, using the offshore patrol
The third expedition took place during 2006–2007, using the offshore patrol
Scientific Results of The Danish Deep-Sea Expedition GALATHEA 2
Global expeditions Oceanographic expeditions Science and technology in Denmark Royal Danish Navy Exploration ships Research vessels Expeditions from Denmark
circumnavigated
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical body (e.g. a planet or moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth.
The first recorded circumnavigation of the Earth was the ...
the world from west to east and followed similar routes.
First expedition
Preparations
The first ''Galathea'' Expedition took place from 1845 to 1847 and had political and scientific objectives. It was initiated by the King of Denmark, Christian VIII, with its main purposes the handover of the Danish colonies in India, following their sale to theBritish East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
, as well as a final Danish attempt to explore and recolonise the Nicobar Islands
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located southeast of the Indian ...
in the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
. Additional aims were the expansion of trade with China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and the discovery of new trading opportunities, as well as making extensive scientific collections.Balsved (27 February 2006).Historical Perspective: Galathea 1.
The ''Galathea'' was a three-masted sailing ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships ...
, a naval corvette which had been built in 1831 at the Gammelholm naval shipyard in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
. It was in length and had a draught of . When it departed on its voyage under the leadership of Captain Steen Andersen Bille it carried 231 seamen and scientists, 36 guns, and supplies for one year.
The scientists included physician and assistant botanist Didrik Ferdinand Didrichsen, botanist Bernhard Casper Kamphøvener, entomologist
Entomology () is the scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such as ara ...
Carl Emil Kiellerup Carl may refer to:
* Carl, Georgia, city in USA
* Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
*Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name
* Carl², a TV series
* "Carl", an episode of ...
, geologist Hinrich Johannes Rink and zoologists Wilhelm Friedrich Georg Behn
Wilhelm Friedrich Georg Behn (25 December 1808, Kiel – 14 May 1878, Dresden) was a German anatomist and zoologist. For eight years he was president of the German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina.
From 1828 he studied medicine at the Universiti ...
and Johannes Theodor Reinhardt, not all of whom remained for the duration of the voyage, as well as sketch artist
A sketch (ultimately from Greek σχέδιος – ''schedios'', "done extempore") is a rapidly executed freehand drawing that is not usually intended as a finished work.Dian ...
Johan Christian Thornam Johan
* Johan (given name)
* ''Johan'' (film), a 1921 Swedish film directed by Mauritz Stiller
* Johan (band), a Dutch pop-group
** ''Johan'' (album), a 1996 album by the group
* Johan Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada
* Jo-Han, a ...
and genre painter Poul August Plum
Poul is a Danish masculine given name. It is the Danish cognate of the name Paul. Poul may refer to:
People
* Poul Andersen (1922–2006), Danish printer
* Poul Anderson (1926–2001), American writer
* Poul Erik Andreasen (born 1949), Danish fo ...
.Maule (1974).
It was an expensive undertaking, with a budget of nearly half a million Rixdollars, equivalent to 3% of Denmark's annual state revenues at the time.
The voyage
Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
, sailed southwards around Africa to India, where she visited Tranquebar, Pondicherry, Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
and Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, commer ...
. In Calcutta an additional ship, the steamboat ''Ganges'', was purchased and the carrier ''Christine'' hired, to assist with work in the Nicobar Islands. Considerable time and effort was expended at the Nicobars; most of January 1846 was spent in the northern Nicobar islands, and February in the southern. As well as scientific surveys and collecting, preparations were made for a new colony based at Pulo Milu. Several people, including the geologist Rink, remained there when the expedition departed, though the nascent colony was abandoned only two years later.
The ''Galathea'' proceeded to Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, calling at Penang, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, Batavia, and Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
before heading for the Chinese coast and visiting Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a List of cities in China, city and Special administrative regions of China, special ...
, Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a pop ...
, Canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ente ...
, Amoy, and Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the ...
. An attempt to stop at Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
was rebuffed by the authorities there. The ship then crossed the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
, visiting the Hawaiian archipelago
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost K ...
and Tahiti on the way, to Valparaiso, Callao, and Lima
Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of ...
in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
, before rounding Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
. Further visits were made to Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, Montevideo, Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, and Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-larges ...
, following which the ''Galathea'' headed back to Denmark, anchoring in Copenhagen harbour on 24 August 1847 after a voyage of more than two years. During the course of the voyage 20 Danish sailors had died and several others were discharged.
Results
The expedition returned with 93 containers of "zoological, entomological, botanical and geological Objects". There were also 21 boxes of ethnographic material, a large collection fromJava
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, as well as gifts from scientists in many of the cities and ports visited by the expedition.Historical Perspective: Galathea 1 (1845–47) Results. The intention of Christian VIII was to sponsor the publication of the scientific results of the expedition. However, the King died in January 1848 and the country was thrown into the Three Years' War. Most of the boxes of collected items lay unopened for many years and, with some exceptions, were never properly processed, nor the full results formally published. The collections subsequently served mainly as reference material.
Second expedition
The second expedition was conceived in 1941 in discussions between journalist and author Hakon Mielche and oceanographer andichthyologist
Ichthyology is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish, including bony fish ( Osteichthyes), cartilaginous fish ( Chondrichthyes), and jawless fish ( Agnatha). According to FishBase, 33,400 species of fish had been described as of O ...
Anton Frederik Bruun
Anton Frederik Bruun (14 December 1901 – 13 December 1961) was a Danish oceanographer and ichthyologist.
Educated at University of Copenhagen (1926) and employed at the Danish Commission for Marine Research (Kommissionen for Danmarks Fiskeri ...
. It was originally hoped to send out a second expedition on the centenary of the first; however, World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
intervened and preparations had to be postponed. In June 1945 the two protagonists, along with explorers Eigil Knuth, Ebbe Munch and Henning Haslund-Christensen, decided to establish the Danish Expedition Foundation, which was to raise funds for the second Galathea, as well as other, expeditions.
The expedition eventually started in 1950, with its main purpose deep sea oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynami ...
. For the use of the expedition a British sloop, HMS ''Leith'', was acquired and renamed HDMS ''Galathea''. It was long and wide, with a draught of and was powered by two steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam tu ...
s that gave it a cruising speed of . ''Galathea'' 2 left Copenhagen in October 1950 carrying a crew of about 100 seamen and scientists, visiting many of the same places the original ''Galathea'' had visited over a century earlier. The main difference in the route taken from the earlier expedition was in using the Panama Canal, rather than the Drake Passage at the southern end of South America, to transit between the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic. From 1950 to 1952 the expedition carried out a program of scientific exploration; the highlight occurred in July 1951 when, while investigating the Philippine Trench
The Philippine Trench (also Philippine Deep, Mindanao Trench, and Mindanao Deep) is a submarine trench to the east of the Philippines. The trench is located in the Philippine sea of the western North Pacific Ocean and continues NNW-SSE. It has ...
, scientists secured biological material from a record depth of . The expedition returned to Copenhagen in June 1952 where the ship was welcomed by a crowd of 20,000 people.Historical Perspective: Galathea 2 (1950–52).
Results
The second Galathea expedition led to the discovery of, among other things, the fish species '' Antipodocottus galatheae'' and '' Abyssobrotula galatheae'', the snail species '' Guttula galatheae'' and, above all, livingMonoplacophora
Monoplacophora , meaning "bearing one plate", is a polyphyletic superclass of molluscs with a cap-like shell inhabiting deep sea environments . Extant representatives were not recognized as such until 1952; previously they were known only from ...
, a class of "ancestral mollusc" which until then was known only from the fossil record. The biggest sensation at the time, however, was the discovery of barnacles on a rock from the bottom of the Philippine Trench
The Philippine Trench (also Philippine Deep, Mindanao Trench, and Mindanao Deep) is a submarine trench to the east of the Philippines. The trench is located in the Philippine sea of the western North Pacific Ocean and continues NNW-SSE. It has ...
since it had been assumed that life could not exist at this sea depth. Dr Claude E. ZoBell, the 'Father of Marine Microbiology', was aboard this expedition.
Third expedition
 The third expedition took place during 2006–2007, using the offshore patrol
The third expedition took place during 2006–2007, using the offshore patrol frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed an ...
HDMS ''Vædderen'', which was refitted to serve as an expedition ship. It is a Thetis class frigate which was built at the Svendborg Shipyards in 1990 and is m long and m wide. Although the voyage was publicised as the third Galathea expedition, the ship itself was not renamed.
The expedition's main purpose was to carry out research on climate and weather changes, earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
s, tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater exp ...
s, and marine biology. It left Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
in August 2006 and visited the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
and Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland ...
, then travelled southwards through the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
along the west coast of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
to Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
. It then crossed the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
to Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
, and Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
, before sailing northwards along the west coast of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
to the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
, then sailing through the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
and visiting New York, before returning to Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
in April 2007.Balsved (12 December 2006).European Space Agency.
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * *Further reading
*{{cite book , title= The Galathea Deep Sea Expedition, 1950–52., author= Bruun, A. F. , year= 1956, publisher= Allen and Unwin , location= London , pages= 296, display-authors=etalExternal links
Scientific Results of The Danish Deep-Sea Expedition GALATHEA 2
Global expeditions Oceanographic expeditions Science and technology in Denmark Royal Danish Navy Exploration ships Research vessels Expeditions from Denmark