
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of
evolutionarily-related proteins that are
cell surface receptor
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral m ...
s that detect
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and b ...
s outside the
cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
and activate cellular responses. Coupling with
G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their a ...
s, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the
cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
seven times.
[ ] Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5)
license. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within transmembrane helices (Rhodopsin-like family). They are all activated by
agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
s although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed.
[
G protein-coupled receptors are found only in ]eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s, including yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
, choanoflagellate
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconne ...
s,ligands
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odor
An odor (American English) or odour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and animals can perceive via their sense ...
s, pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s, hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s, and neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neu ...
s, and vary in size from small molecules to peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. ...
s to large protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s. G protein-coupled receptors are involved in many diseases.
There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein-coupled receptors:
*the cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
signal pathway and
*the phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol (or Inositol Phospholipid) consists of a family of lipids as illustrated on the right, where red is x, blue is y, and black is z, in the context of independent variation, a class of the phosphatidylglycerides. In such molecul ...
signal pathway.G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their a ...
by exchanging the GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
bound to the G protein for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type ( Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).[
]
History and significance
With the determination of the first structure of the complex between a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) and a G-protein trimer (Gαβγ) in 2011 a new chapter of GPCR research was opened for structural investigations of global switches with more than one protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
being investigated. The previous breakthroughs involved determination of the crystal structure of the first GPCR, rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransductio ...
, in 2000 and the crystal structure of the first GPCR with a diffusible ligand (β2AR) in 2007. How the seven transmembrane helices of a GPCR are arranged into a bundle was suspected based on the low-resolution model of frog rhodopsin from cryo-electron microscopy studies of the two-dimensional crystals. The crystal structure of rhodopsin, that came up three years later, was not a surprise apart from the presence of an additional cytoplasmic helix H8 and a precise location of a loop covering retinal binding site. However, it provided a scaffold which was hoped to be a universal template for homology modeling and drug design for other GPCRs – a notion that proved to be too optimistic.
Seven years later, the crystallization of β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR) with a diffusible ligand brought surprising results because it revealed quite a different shape of the receptor extracellular side than that of rhodopsin. This area is important because it is responsible for the ligand binding and is targeted by many drugs. Moreover, the ligand binding site was much more spacious than in the rhodopsin structure and was open to the exterior. In the other receptors crystallized shortly afterwards the binding side was even more easily accessible to the ligand. New structures complemented with biochemical investigations uncovered mechanisms of action of molecular switches which modulate the structure of the receptor leading to activation states for agonists or to complete or partial inactivation states for inverse agonists.[
The 2012 ]Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz
Robert Joseph Lefkowitz (born April 15, 1943) is an American physician (internist and cardiologist) and biochemist. He is best known for his groundbreaking discoveries that reveal the inner workings of an important family G protein-coupled recep ...
for their work that was "crucial for understanding how G protein-coupled receptors function".
Classification
 The exact size of the GPCR superfamily is unknown, but at least 831 different
The exact size of the GPCR superfamily is unknown, but at least 831 different human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
(or ~ 4% of the entire protein-coding genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
) have been predicted to code for them from genome sequence analysis
In bioinformatics, sequence analysis is the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alig ...
.sequence homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a ...
between classes.
The largest class by far is class A, which accounts for nearly 85% of the GPCR genes. Of class A GPCRs, over half of these are predicted to encode olfactory receptor
Olfactory receptors (ORs), also known as odorant receptors, are chemoreceptors expressed in the cell membranes of olfactory receptor neurons and are responsible for the detection of odorants (for example, compounds that have an odor) which give r ...
s, while the remaining receptors are liganded by known endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, ...
compounds or are classified as orphan receptor
In biochemistry, an orphan receptor is a protein that has a similar structure to other identified receptors but whose endogenous ligand has not yet been identified. If a ligand for an orphan receptor is later discovered, the receptor is referred to ...
s. Despite the lack of sequence homology between classes, all GPCRs have a common structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such a ...
and mechanism of signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
. The very large rhodopsin A group has been further subdivided into 19 subgroups ( A1-A19).
According to the classical A-F system, GPCRs can be grouped into 6 classes based on sequence homology and functional similarity:
*Class A (or 1) ( Rhodopsin-like)
*Class B (or 2) (Secretin receptor family
Secretin family receptor proteins, also known as Family B or family 2 of G-protein coupled receptors are regulated by peptide hormones from the glucagon hormone family. The family is different from adhesion G protein-coupled receptors.
The secr ...
)
* Class C (or 3) ( Metabotropic glutamate/pheromone)
*Class D (or 4) ( Fungal mating pheromone receptors)
*Class E (or 5) ( Cyclic AMP receptors)
*Class F (or 6) (Frizzled
Frizzled is a family of atypical G protein-coupled receptors that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol.
Species distribution
Fr ...
/ Smoothened)
More recently, an alternative classification system called GRAFS (Glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
, Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransductio ...
, ''Adhesion'', Frizzled
Frizzled is a family of atypical G protein-coupled receptors that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol.
Species distribution
Fr ...
/ Taste2, Secretin
Secretin is a hormone that regulates water homeostasis throughout the body and influences the environment of the duodenum by regulating secretions in the stomach, pancreas, and liver. It is a peptide hormone produced in the S cells of the du ...
) has been proposed for vertebrate GPCRs.[
An early study based on available DNA sequence suggested that the human genome encodes roughly 750 G protein-coupled receptors, about 350 of which detect hormones, growth factors, and other endogenous ligands. Approximately 150 of the GPCRs found in the human genome have unknown functions.
Some web-servers and bioinformatics prediction methods]pseudo amino acid composition
Pseudo amino acid composition, or PseAAC, in molecular biology, was originally introduced by Kuo-Chen Chou in 2001 to represent protein samples for improving protein subcellular localization prediction and membrane protein type prediction. Like ...
approach.
Physiological roles
GPCRs are involved in a wide variety of physiological processes. Some examples of their physiological roles include:
# The visual sense: The opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become Retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most ...
s use a photoisomerization
In chemistry, photoisomerization is a form of isomerization induced by photoexcitation. Both reversible and irreversible photoisomerizations are known for photoswitchable compounds. The term "photoisomerization" usually, however, refers to a re ...
reaction to translate electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...
into cellular signals. Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransductio ...
, for example, uses the conversion of ''11-cis''-retinal to ''all-trans''-retinal for this purpose.
# The gustatory sense (taste): GPCRs in taste cells mediate release of gustducin
Gustducin is a G protein associated with taste and the gustatory system, found in some taste receptor cells.
Research on the discovery and isolation of gustducin is recent. It is known to play a large role in the transduction of bitter, sweet ...
in response to bitter-, umami- and sweet-tasting substances.
# The sense of smell: Receptors of the olfactory epithelium
The olfactory epithelium is a specialized epithelial tissue inside the nasal cavity that is involved in smell. In humans, it measures
9 cm2 and lies on the roof of the nasal cavity about 7 cm above and behind the nostrils. The olfactory ...
bind odorants (olfactory receptors) and pheromones (vomeronasal receptors)
# Behavioral and mood regulation: Receptors in the mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
ian brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
bind several different neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neu ...
s, including serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and va ...
, dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% o ...
, histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discover ...
, GABA, and glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
# Regulation of immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
activity and inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
: chemokine
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In additi ...
receptors bind ligands that mediate intercellular communication between cells of the immune system; receptors such as histamine receptor
The histamine receptors are a class of G protein–coupled receptors which bind histamine as their primary endogenous ligand.
There are four known histamine receptors:
* H1 receptor
* H2 receptor
* H3 receptor
* H4 receptor
Comparison
There ...
s bind inflammatory mediators and engage target cell types in the inflammatory response. GPCRs are also involved in immune-modulation, e. g. regulating interleukin induction or suppressing TLR-induced immune responses from T cells.
# Autonomic nervous system transmission: Both the sympathetic and parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of ...
nervous systems are regulated by GPCR pathways, responsible for control of many automatic functions of the body such as blood pressure, heart rate, and digestive processes
# Cell density sensing: A novel GPCR role in regulating cell density sensing.
# Homeostasis modulation (e.g., water balance).metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
of some types of tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s.
# Used in the endocrine system for peptide and amino-acid derivative hormones that bind to GCPRs on the cell membrane of a target cell. This activates cAMP, which in turn activates several kinases, allowing for a cellular response, such as transcription.
Receptor structure
GPCRs are integral membrane protein
An integral, or intrinsic, membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All ''transmembrane proteins'' are IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comprise a sign ...
s that possess seven membrane-spanning domains or transmembrane helices.glycosylated
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not ...
. These extracellular loops also contain two highly conserved cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, some ...
residues that form disulfide bond
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In ...
s to stabilize the receptor structure. Some seven-transmembrane helix proteins ( channelrhodopsin) that resemble GPCRs may contain ion channels, within their protein.
In 2000, the first crystal structure of a mammalian GPCR, that of bovine rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransductio ...
(), was solved.transmembrane domain
A transmembrane domain (TMD) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs generally adopt an alpha helix topological conformation, although some TMDs such as those in porins can adopt a different conformation. Because the interior of the lipid bi ...
s, such as microbial rhodopsins and adiponectin receptors 1 and 2 ( ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2). However, these 7TMH (7-transmembrane helices) receptors and channels do not associate with G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their a ...
s. In addition, ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2 are oriented oppositely to GPCRs in the membrane (i.e. GPCRs usually have an extracellular N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
, cytoplasmic C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein i ...
, whereas ADIPORs are inverted).
Structure–function relationships
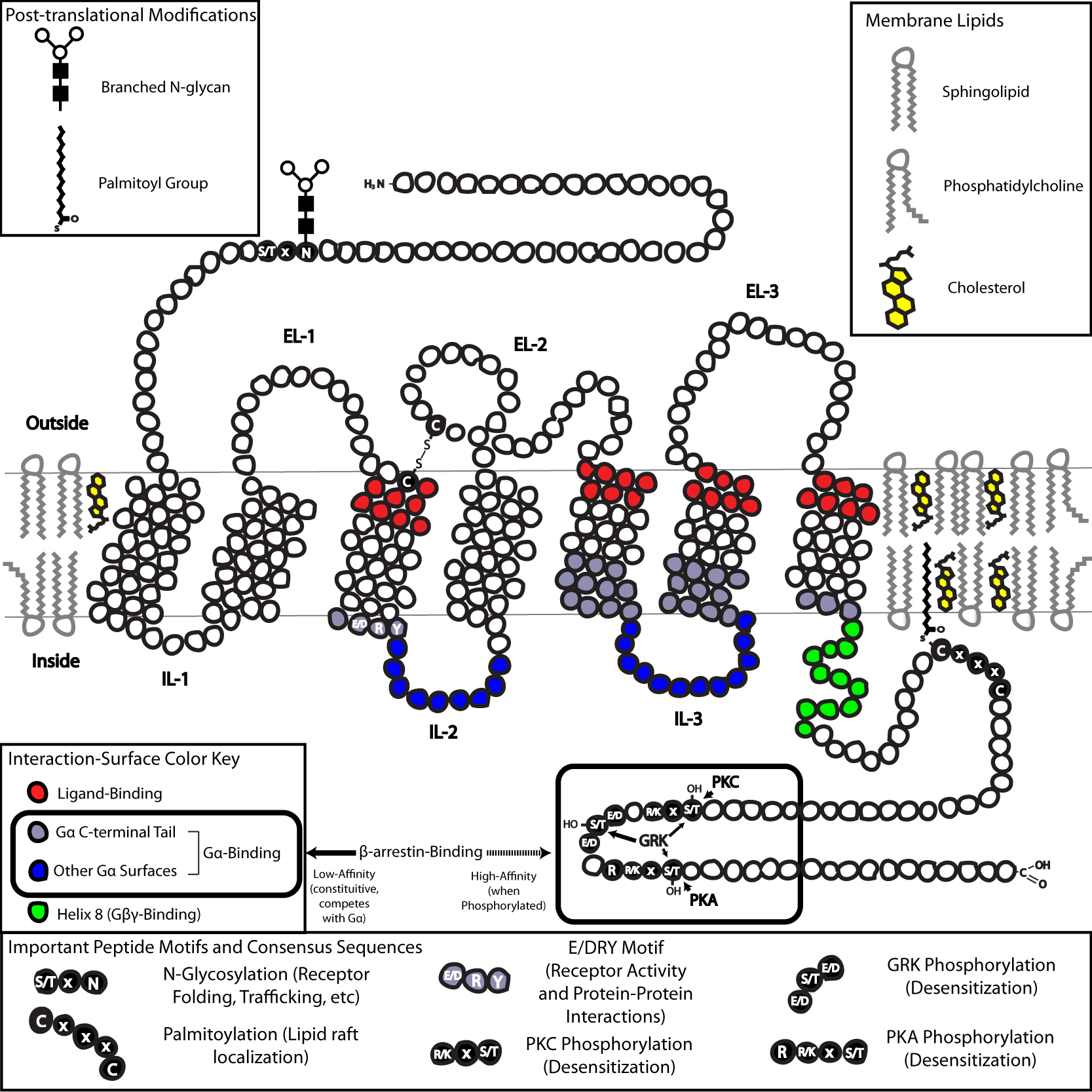 In terms of structure, GPCRs are characterized by an extracellular
In terms of structure, GPCRs are characterized by an extracellular N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
, followed by seven transmembrane
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequent ...
(7-TM) α-helices
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ear ...
(TM-1 to TM-7) connected by three intracellular (IL-1 to IL-3) and three extracellular loops (EL-1 to EL-3), and finally an intracellular C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein i ...
. The GPCR arranges itself into a tertiary structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may i ...
resembling a barrel, with the seven transmembrane helices forming a cavity within the plasma membrane that serves a ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elect ...
-binding domain that is often covered by EL-2. Ligands may also bind elsewhere, however, as is the case for bulkier ligands (e.g., protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s or large peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. ...
s), which instead interact with the extracellular loops, or, as illustrated by the class C metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), the N-terminal tail. The class C GPCRs are distinguished by their large N-terminal tail, which also contains a ligand-binding domain. Upon glutamate-binding to an mGluR, the N-terminal tail undergoes a conformational change that leads to its interaction with the residues of the extracellular loops and TM domains. The eventual effect of all three types of agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
-induced activation is a change in the relative orientations of the TM helices (likened to a twisting motion) leading to a wider intracellular surface and "revelation" of residues of the intracellular helices and TM domains crucial to signal transduction function (i.e., G-protein coupling). Inverse agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist.
A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse ago ...
s and antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist.
Etymology
The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, ri ...
s may also bind to a number of different sites, but the eventual effect must be prevention of this TM helix reorientation.[
The structure of the N- and C-terminal tails of GPCRs may also serve important functions beyond ligand-binding. For example, The C-terminus of M3 muscarinic receptors is sufficient, and the six-amino-acid polybasic (KKKRRK) domain in the C-terminus is necessary for its preassembly with Gq proteins.]serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − for ...
(Ser) or threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO� ...
(Thr) residues that, when phosphorylated
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
, increase the affinity of the intracellular surface for the binding of scaffolding proteins called β-arrestin
Arrestins (abbreviated Arr) are a small family of proteins important for regulating signal transduction at G protein-coupled receptors.
Arrestins were first discovered as a part of a conserved two-step mechanism for regulating the activity of ...
s (β-arr).sterically
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
prevent G-protein coupling and may recruit other proteins, leading to the creation of signaling complexes involved in extracellular-signal regulated kinase ( ERK) pathway activation or receptor endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. ...
(internalization). As the phosphorylation of these Ser and Thr residues often occurs as a result of GPCR activation, the β-arr-mediated G-protein-decoupling and internalization of GPCRs are important mechanisms of desensitization.palmitoylation
Palmitoylation is the covalent attachment of fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, to cysteine (''S''-palmitoylation) and less frequently to serine and threonine (''O''-palmitoylation) residues of proteins, which are typically membrane prot ...
of one or more sites of the C-terminal tail or the intracellular loops. Palmitoylation is the covalent modification of cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, some ...
(Cys) residues via addition of hydrophobic acyl group
In chemistry, an acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group (). In organic chemistry, the acyl group (IUPA ...
s, and has the effect of targeting the receptor to cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
- and sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because o ...
-rich microdomains of the plasma membrane called lipid raft
The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids, cholesterol and protein receptors organised in glycolipoprotein lipid microdomains termed lipid rafts. Their existence in cellular membranes remains somewhat controversial ...
s. As many of the downstream transducer and effector molecules of GPCRs (including those involved in negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by othe ...
pathways) are also targeted to lipid rafts, this has the effect of facilitating rapid receptor signaling.
GPCRs respond to extracellular signals mediated by a huge diversity of agonists, ranging from proteins to biogenic amines
A biogenic amine is a biogenic substance with one or more amine groups. They are basic nitrogenous compounds formed mainly by decarboxylation of amino acids or by amination and transamination of aldehydes and ketones. Biogenic amines are organic ...
to protons
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron m ...
, but all transduce this signal via a mechanism of G-protein coupling. This is made possible by a guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is ...
-nucleotide exchange factor (GEF
Gef ( ), also referred to as the Talking Mongoose or the Dalby Spook, was the name given to an allegedly talking mongoose which was claimed to inhabit a farmhouse owned by the Irving family. The Irvings' farm was located at Cashen's Gap near ...
) domain primarily formed by a combination of IL-2 and IL-3 along with adjacent residues of the associated TM helices.
Mechanism
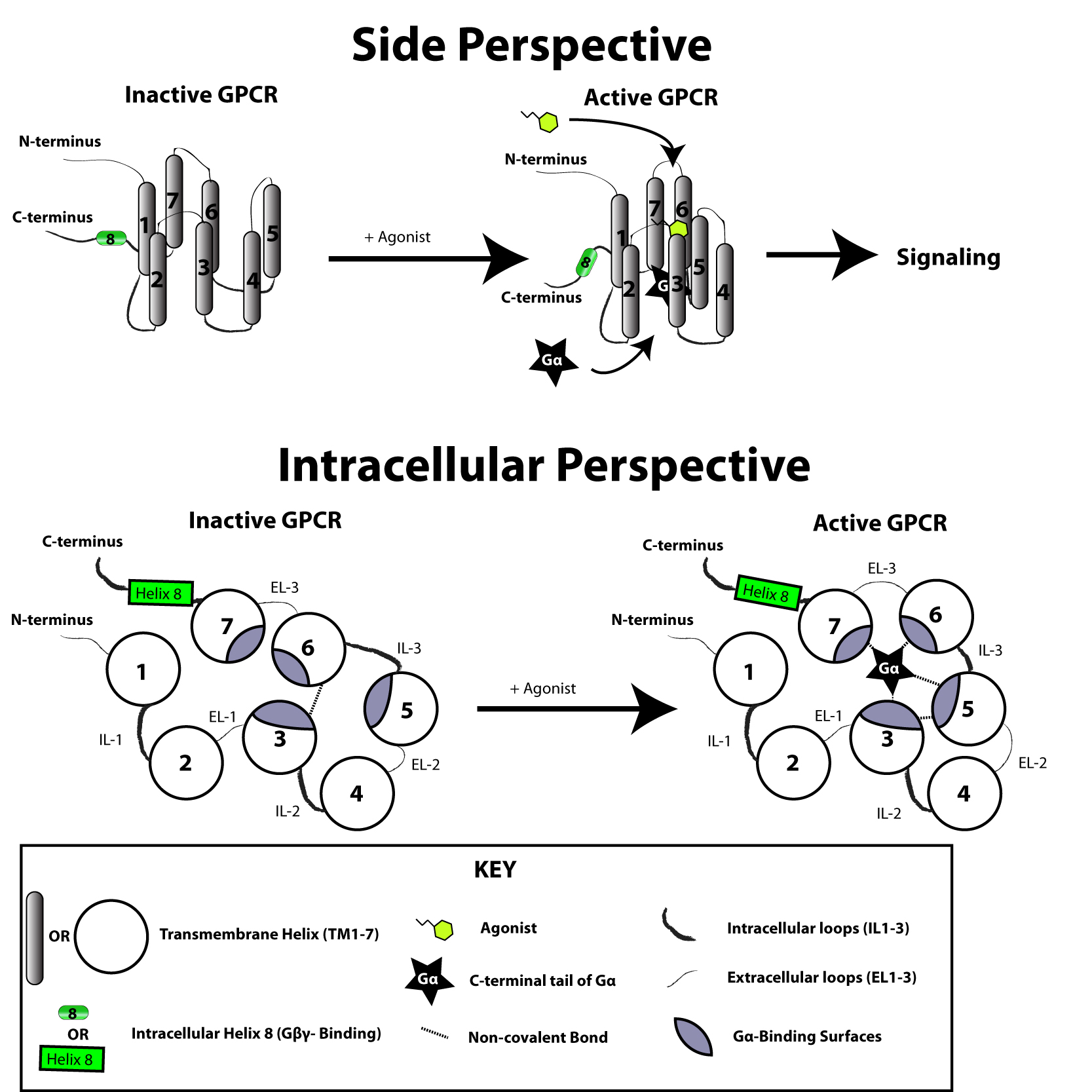 The G protein-coupled receptor is activated by an external signal in the form of a ligand or other signal mediator. This creates a conformational change in the receptor, causing activation of a
The G protein-coupled receptor is activated by an external signal in the form of a ligand or other signal mediator. This creates a conformational change in the receptor, causing activation of a G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their a ...
. Further effect depends on the type of G protein. G proteins are subsequently inactivated by GTPase activating proteins, known as RGS proteins.
Ligand binding
GPCRs include one or more receptors for the following ligands:
sensory signal mediators (e.g., light and olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, ...
stimulatory molecules);
adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building ...
, bombesin
Bombesin is a 14-amino acid peptide originally isolated from the skin of the European fire-bellied toad (''Bombina bombina'')
by Vittorio Erspamer ''et al.'' and named after its source. NIHMSID 45053. It has two known homologs in mammals called ...
, bradykinin
Bradykinin (BK) (Greek brady-, slow; -kinin, kīn(eîn) to move) is a peptide that promotes inflammation. It causes arterioles to dilate (enlarge) via the release of prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor an ...
, endothelin
Endothelins are peptides with receptors and effects in many body organs. Endothelin constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. The endothelins are normally kept in balance by other mechanisms, but when overexpressed, they contribute ...
, γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA), hepatocyte growth factor ( HGF), melanocortin
The melanocortins are a family of neuropeptide hormones which are the ligands of the melanocortin receptorsEricson, M.D., et al., ''Bench-top to clinical therapies: A review of melanocortin ligands from 1954 to 2016.'' Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basi ...
s, neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. NPY has been identified as the most abundant peptide present in the ma ...
, opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use ...
peptides, opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become Retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most ...
s, somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-cou ...
, GH, tachykinins, members of the vasoactive intestinal peptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide, also known as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP, is a peptide hormone that is vasoactive in the intestine. VIP is a peptide of 28 amino acid residues that belongs to a glucagon/secretin superfamily, the lig ...
family, and vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then trave ...
;
biogenic amine
A biogenic amine is a biogenic substance with one or more amine groups. They are basic nitrogenous compounds formed mainly by decarboxylation of amino acids or by amination and transamination of aldehydes and ketones. Biogenic amines are organic ...
s (e.g., dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% o ...
, epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
, norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad ...
, histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discover ...
, serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and va ...
, and melatonin
Melatonin is a natural product found in plants and animals. It is primarily known in animals as a hormone released by the pineal gland in the brain at night, and has long been associated with control of the sleep–wake cycle.
In vertebrat ...
);
glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
(metabotropic
A metabotropic receptor, also referred to by the broader term G-protein-coupled receptor, is a type of membrane receptor that initiates a number of metabolic steps to modulate cell activity. The nervous system utilizes two types of receptors: met ...
effect);
glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to tre ...
;
acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
( muscarinic effect);
chemokines
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In addition ...
;
lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
mediators of inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
(e.g., prostaglandins
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are deri ...
, prostanoid
Prostanoids are active lipid mediators that regulate inflammatory response. Prostanoids are a subclass of eicosanoids consisting of the prostaglandins (mediators of inflammatory and anaphylactic reactions), the thromboxanes (mediators of vasocons ...
s, platelet-activating factor, and leukotrienes
Leukotrienes are a family of eicosanoid inflammatory mediators produced in leukocytes by the oxidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and the essential fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by the enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase.
Leukotri ...
);
peptide hormones (e.g., calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the ...
, C5a anaphylatoxin, follicle-stimulating hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, ...
SH gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released ...
nRH neurokinin
Tachykinin peptides are one of the largest families of neuropeptides, found from amphibians to mammals. They were so named due to their ability to rapidly induce contraction of gut tissue. The tachykinin family is characterized by a common C-termi ...
, thyrotropin-releasing hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a hypophysiotropic hormone produced by neurons in the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin from the anterior pituitary.
TRH has been used clinicall ...
RH and oxytocin
Oxytocin (Oxt or OT) is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. It plays a role in social bonding, reproduction, childbirth, and the period after childbirth. Oxytoc ...
);
and endocannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tet ...
s.
GPCRs that act as receptors for stimuli that have not yet been identified are known as orphan receptor
In biochemistry, an orphan receptor is a protein that has a similar structure to other identified receptors but whose endogenous ligand has not yet been identified. If a ligand for an orphan receptor is later discovered, the receptor is referred to ...
s.
However, in contrast to other types of receptors that have been studied, wherein ligands bind externally to the membrane, the ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elect ...
s of GPCRs typically bind within the transmembrane domain. However, protease-activated receptor
Protease-activated receptors (PAR) are a subfamily of related G protein-coupled receptors that are activated by cleavage of part of their extracellular domain. They are highly expressed in platelets, and also on endothelial cells, myocytes an ...
s are activated by cleavage of part of their extracellular domain.
Conformational change
 The transduction of the signal through the membrane by the receptor is not completely understood. It is known that in the inactive state, the GPCR is bound to a
The transduction of the signal through the membrane by the receptor is not completely understood. It is known that in the inactive state, the GPCR is bound to a heterotrimeric G protein
Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the ''"large" G proteins'' (as opposed to the subclass of smaller, monomeric small GTPases) are membrane-associated G proteins that form a heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-structu ...
complex. Binding of an agonist to the GPCR results in a conformational change
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors.
A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. Its shape can change in response to changes in its environment or oth ...
in the receptor that is transmitted to the bound Gα subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein via protein domain dynamics. The activated Gα subunit exchanges GTP in place of GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
which in turn triggers the dissociation of Gα subunit from the Gβγ dimer and from the receptor. The dissociated Gα and Gβγ subunits interact with other intracellular proteins to continue the signal transduction cascade while the freed GPCR is able to rebind to another heterotrimeric G protein to form a new complex that is ready to initiate another round of signal transduction.inverse agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist.
A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse ago ...
s are ligands that shift the equilibrium in favour of inactive states; and neutral antagonists are ligands that do not affect the equilibrium. It is not yet known how exactly the active and inactive states differ from each other.
G-protein activation/deactivation cycle
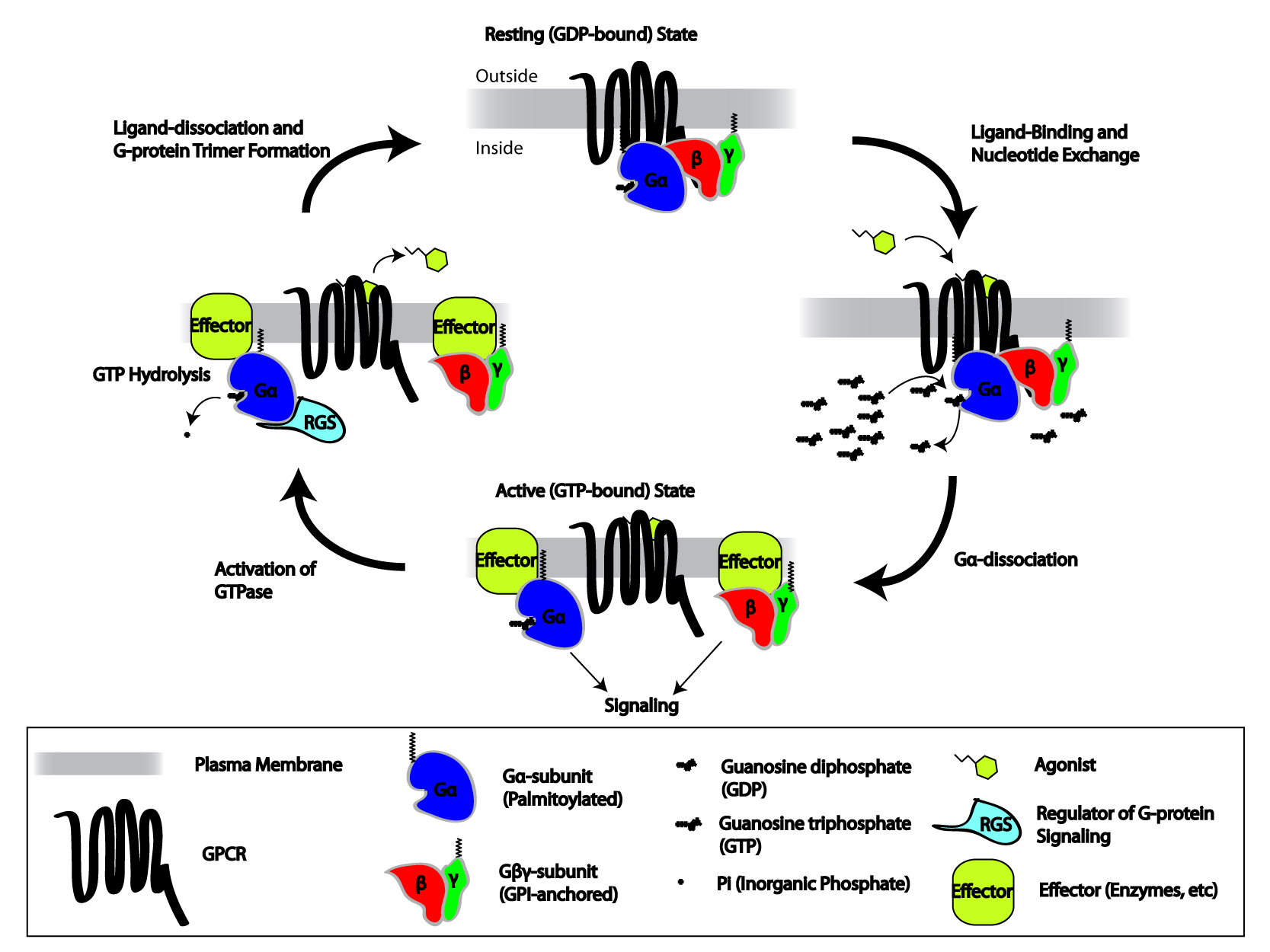 When the receptor is inactive, the
When the receptor is inactive, the GEF
Gef ( ), also referred to as the Talking Mongoose or the Dalby Spook, was the name given to an allegedly talking mongoose which was claimed to inhabit a farmhouse owned by the Irving family. The Irvings' farm was located at Cashen's Gap near ...
domain may be bound to an also inactive α-subunit of a heterotrimeric G-protein
Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the ''"large" G proteins'' (as opposed to the subclass of smaller, monomeric small GTPases) are membrane-associated G proteins that form a heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-struct ...
. These "G-proteins" are a trimer of α, β, and γ subunits (known as Gα, Gβ, and Gγ, respectively) that is rendered inactive when reversibly bound to Guanosine diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine.
GDP is the product ...
(GDP) (or, alternatively, no guanine nucleotide) but active when bound to guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only ...
(GTP). Upon receptor activation, the GEF domain, in turn, allosterically
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation (or allosteric control) is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site.
The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric site ...
activates the G-protein by facilitating the exchange of a molecule of GDP for GTP at the G-protein's α-subunit. The cell maintains a 10:1 ratio of cytosolic GTP:GDP so exchange for GTP is ensured. At this point, the subunits of the G-protein dissociate from the receptor, as well as each other, to yield a Gα-GTP monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; '' mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
...
and a tightly interacting Gβγ dimer, which are now free to modulate the activity of other intracellular proteins. The extent to which they may diffuse
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
, however, is limited due to the palmitoylation
Palmitoylation is the covalent attachment of fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, to cysteine (''S''-palmitoylation) and less frequently to serine and threonine (''O''-palmitoylation) residues of proteins, which are typically membrane prot ...
of Gα and the presence of an isoprenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpene ...
moiety that has been covalently
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
added to the C-termini of Gγ.
Because Gα also has slow GTP→GDP hydrolysis capability, the inactive form of the α-subunit (Gα-GDP) is eventually regenerated, thus allowing reassociation with a Gβγ dimer to form the "resting" G-protein, which can again bind to a GPCR and await activation. The rate of GTP hydrolysis is often accelerated due to the actions of another family of allosteric modulating proteins called Regulators of G-protein Signaling, or RGS proteins, which are a type of GTPase-Activating Protein GTPase-activating proteins or GTPase-accelerating proteins (GAPs) are a family of regulatory proteins whose members can bind to activated G proteins and stimulate their GTPase activity, with the result of terminating the signaling event. GAPs are ...
, or GAP. In fact, many of the primary effector
Effector may refer to:
*Effector (biology), a molecule that binds to a protein and thereby alters the activity of that protein
* ''Effector'' (album), a music album by the Experimental Techno group Download
* ''EFFector'', a publication of the El ...
proteins (e.g., adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
s) that become activated/inactivated upon interaction with Gα-GTP also have GAP activity. Thus, even at this early stage in the process, GPCR-initiated signaling has the capacity for self-termination.
Crosstalk
 GPCRs downstream signals have been shown to possibly interact with
GPCRs downstream signals have been shown to possibly interact with integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle ...
signals, such as FAK. Integrin signaling will phosphorylate FAK, which can then decrease GPCR Gαs activity.
Signaling
 If a receptor in an active state encounters a
If a receptor in an active state encounters a G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their a ...
, it may activate it. Some evidence suggests that receptors and G proteins are actually pre-coupled.adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
is an example of a cellular protein that can be regulated by a G protein, in this case the G protein Gs. Adenylate cyclase activity is activated when it binds to a subunit of the activated G protein. Activation of adenylate cyclase ends when the G protein returns to the GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
-bound state.
Adenylate cyclases (of which 9 membrane-bound and one cytosolic forms are known in humans) may also be activated or inhibited in other ways (e.g., Ca2+/Calmodulin
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the bin ...
binding), which can modify the activity of these enzymes in an additive or synergistic fashion along with the G proteins.
The signaling pathways activated through a GPCR are limited by the primary sequence
Biomolecular structure is the intricate folded, three-dimensional shape that is formed by a molecule of protein, DNA, or RNA, and that is important to its function. The structure of these molecules may be considered at any of several length ...
and tertiary structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may i ...
of the GPCR itself but ultimately determined by the particular conformation stabilized by a particular ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elect ...
, as well as the availability of transducer
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another.
Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and con ...
molecules. Currently, GPCRs are considered to utilize two primary types of transducers: G-proteins
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their ac ...
and β-arrestins. Because β-arr's have high affinity only to the phosphorylated
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
form of most GPCRs (see above or below), the majority of signaling is ultimately dependent upon G-protein activation. However, the possibility for interaction does allow for G-protein-independent signaling to occur.
G-protein-dependent signaling
There are three main G-protein-mediated signaling pathways, mediated by four sub-classes of G-proteins distinguished from each other by sequence homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a ...
( Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, and Gα12/13). Each sub-class of G-protein consists of multiple proteins, each the product of multiple genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
or splice variations that may imbue them with differences ranging from subtle to distinct with regard to signaling properties, but in general they appear reasonably grouped into four classes. Because the signal transducing properties of the various possible βγ combinations do not appear to radically differ from one another, these classes are defined according to the isoform of their α-subunit.functional selectivity
Functional selectivity (or “agonist trafficking”, “biased agonism”, “biased signaling”, "ligand bias" and “differential engagement”) is the ligand-dependent selectivity for certain signal transduction pathways relative to a referen ...
(also known as agonist-directed trafficking, or conformation-specific agonism). However, the binding of any single particular agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
may also initiate activation of multiple different G-proteins, as it may be capable of stabilizing more than one conformation of the GPCR's GEF
Gef ( ), also referred to as the Talking Mongoose or the Dalby Spook, was the name given to an allegedly talking mongoose which was claimed to inhabit a farmhouse owned by the Irving family. The Irvings' farm was located at Cashen's Gap near ...
domain, even over the course of a single interaction. In addition, a conformation that preferably activates one isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some is ...
of Gα may activate another if the preferred is less available. Furthermore, feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled ...
pathways may result in receptor modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) that alter the G-protein preference. Regardless of these various nuances, the GPCR's preferred coupling partner is usually defined according to the G-protein most obviously activated by the endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, ...
ligand under most physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemica ...
or experimental
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a ...
conditions.
Gα signaling
# The effector of both the Gαs and Gαi/o pathways is the cyclic-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-generating enzyme adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
, or AC. While there are ten different AC gene products in mammals, each with subtle differences in tissue distribution or function, all catalyze
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
the conversion of cytosolic
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrio ...
adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms ...
(ATP) to cAMP, and all are directly stimulated by G-proteins of the Gαs class. In contrast, however, interaction with Gα subunits of the Gαi/o type inhibits AC from generating cAMP. Thus, a GPCR coupled to Gαs counteracts the actions of a GPCR coupled to Gαi/o, and vice versa. The level of cytosolic cAMP may then determine the activity of various ion channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of i ...
as well as members of the ser/thr-specific protein kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulatio ...
(PKA) family. Thus cAMP is considered a second messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first m ...
and PKA a secondary effector
Effector may refer to:
*Effector (biology), a molecule that binds to a protein and thereby alters the activity of that protein
* ''Effector'' (album), a music album by the Experimental Techno group Download
* ''EFFector'', a publication of the El ...
.
# The effector of the Gαq/11 pathway is phospholipase C-β (PLCβ), which catalyzes the cleavage of membrane-bound phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of ...
(PIP2) into the second messengers inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as s ...
(DAG). IP3 acts on IP3 receptors found in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
(ER) to elicit Ca2+ release from the ER, while DAG diffuses along the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
where it may activate any membrane localized forms of a second ser/thr kinase called protein kinase C
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and ...
(PKC). Since many isoforms of PKC are also activated by increases in intracellular Ca2+, both these pathways can also converge on each other to signal through the same secondary effector. Elevated intracellular Ca2+ also binds and allosterically
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation (or allosteric control) is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site.
The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric site ...
activates proteins called calmodulin
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the bin ...
s, which in turn tosolic small GTPase
Small GTPases (), also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotr ...
, Rho
Rho (uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ; el, ρο or el, ρω, label=none) is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Phoenician letter res . Its uppercase form uses the sa ...
. Once bound to GTP, Rho can then go on to activate various proteins responsible for cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is co ...
regulation such as Rho-kinase (ROCK). Most GPCRs that couple to Gα12/13 also couple to other sub-classes, often Gαq/11.
Gβγ signaling
The above descriptions ignore the effects of Gβγ–signalling, which can also be important, in particular in the case of activated Gαi/o-coupled GPCRs. The primary effectors of Gβγ are various ion channels, such as G-protein-regulated inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRKs), P/ Q- and N-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, as well as some isoforms of AC and PLC, along with some phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) isoforms.
G-protein-independent signaling
Although they are classically thought of working only together, GPCRs may signal through G-protein-independent mechanisms, and heterotrimeric G-proteins may play functional roles independent of GPCRs. GPCRs may signal independently through many proteins already mentioned for their roles in G-protein-dependent signaling such as β-arrs, GRKs, and Srcs. Such signaling has been shown to be physiologically relevant, for example, β-arrestin
Arrestins (abbreviated Arr) are a small family of proteins important for regulating signal transduction at G protein-coupled receptors.
Arrestins were first discovered as a part of a conserved two-step mechanism for regulating the activity ...
signaling mediated by the chemokine receptor CXCR3
Chemokine receptor CXCR3 is a Gαi protein-coupled receptor in the CXC chemokine receptor family. Other names for CXCR3 are G protein-coupled receptor 9 (GPR9) and CD183. There are three isoforms of CXCR3 in humans: CXCR3-A, CXCR3-B and chemokin ...
was necessary for full efficacy chemotaxis of activated T cells. In addition, further scaffolding proteins involved in subcellular localization The cells of eukaryotic organisms are elaborately subdivided into functionally-distinct membrane-bound compartments. Some major constituents of eukaryotic cells are: extracellular space, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi app ...
of GPCRs (e.g., PDZ-domain-containing proteins) may also act as signal transducers. Most often the effector is a member of the MAPK
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine (i.e., a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase). MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses to ...
family.
Examples
In the late 1990s, evidence began accumulating to suggest that some GPCRs are able to signal without G proteins. The ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase, a key signal transduction mediator downstream of receptor activation in many pathways, has been shown to be activated in response to cAMP-mediated receptor activation in the slime mold
Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to several kinds of unrelated eukaryotic organisms with a life cycle that includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores. Spores are often produced in macroscopic mul ...
''D. discoideum'' despite the absence of the associated G protein α- and β-subunits.
In mammalian cells, the much-studied β2-adrenoceptor has been demonstrated to activate the ERK2 pathway after arrestin-mediated uncoupling of G-protein-mediated signaling. Therefore, it seems likely that some mechanisms previously believed related purely to receptor desensitisation are actually examples of receptors switching their signaling pathway, rather than simply being switched off.
In kidney cells, the bradykinin receptor B2 has been shown to interact directly with a protein tyrosine phosphatase. The presence of a tyrosine-phosphorylated ITIM
''Itim'' ( Filipino for "black"), released overseas as ''The Rites of May'', is a 1976 Filipino thriller film and the directorial debut of Mike de Leon, with a screenplay by Clodualdo del Mundo Jr. and Gil Quito. The film stars Tommy Abuel a ...
(immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif) sequence in the B2 receptor is necessary to mediate this interaction and subsequently the antiproliferative effect of bradykinin.
GPCR-independent signaling by heterotrimeric G-proteins
Although it is a relatively immature area of research, it appears that heterotrimeric G-proteins may also take part in non-GPCR signaling. There is evidence for roles as signal transducers in nearly all other types of receptor-mediated signaling, including integrins
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, ...
, receptor tyrosine kinases
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high- affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinas ...
(RTKs), cytokine receptors ( JAK/STATs), as well as modulation of various other "accessory" proteins such as GEFs
Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+) is a syndromic autosomal dominant disorder where affected individuals can exhibit numerous epilepsy phenotypes. GEFS+ can persist beyond early childhood (i.e., 6 years of age). GEFS+ is a ...
, guanine-nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs) and protein phosphatases. There may even be specific proteins of these classes whose primary function is as part of GPCR-independent pathways, termed activators of G-protein signalling (AGS). Both the ubiquity of these interactions and the importance of Gα vs. Gβγ subunits to these processes are still unclear.
Details of cAMP and PIP2 pathways


 There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein-linked receptors: the
There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein-linked receptors: the cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol (or Inositol Phospholipid) consists of a family of lipids as illustrated on the right, where red is x, blue is y, and black is z, in the context of independent variation, a class of the phosphatidylglycerides. In such molecul ...
signal pathway.
cAMP signal pathway
The cAMP signal transduction contains 5 main characters: stimulative hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
receptor (Rs) or inhibitory hormone receptor
A hormone receptor is a receptor molecule that binds to a specific chemical messenger . Hormone receptors are a wide family of proteins made up of receptors for thyroid and steroid hormones, retinoids and Vitamin D, and a variety of other recepto ...
(Ri); stimulative regulative G-protein (Gs) or inhibitory regulative G-protein (Gi); adenylyl cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
; protein kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulatio ...
(PKA); and cAMP phosphodiesterase
A phosphodiesterase (PDE) is an enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, ''phosphodiesterase'' refers to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below. However, there are many ot ...
.
Stimulative hormone receptor (Rs) is a receptor that can bind with stimulative signal molecules, while inhibitory hormone receptor (Ri) is a receptor that can bind with inhibitory signal molecules.
Stimulative regulative G-protein is a G-protein linked to stimulative hormone receptor (Rs), and its α subunit upon activation could stimulate the activity of an enzyme or other intracellular metabolism. On the contrary, inhibitory regulative G-protein is linked to an inhibitory hormone receptor, and its α subunit upon activation could inhibit the activity of an enzyme or other intracellular metabolism.
Adenylyl cyclase is a 12-transmembrane glycoprotein that catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cAMP with the help of cofactor Mg2+ or Mn2+. The cAMP produced is a second messenger in cellular metabolism and is an allosteric activator of protein kinase A.
Protein kinase A is an important enzyme in cell metabolism due to its ability to regulate cell metabolism by phosphorylating specific committed enzymes in the metabolic pathway. It can also regulate specific gene expression, cellular secretion, and membrane permeability. The protein enzyme contains two catalytic subunits and two regulatory subunits. When there is no cAMP,the complex is inactive. When cAMP binds to the regulatory subunits, their conformation is altered, causing the dissociation of the regulatory subunits, which activates protein kinase A and allows further biological effects.
These signals then can be terminated by cAMP phosphodiesterase, which is an enzyme that degrades cAMP to 5'-AMP and inactivates protein kinase A.
Phosphatidylinositol signal pathway
In the phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol (or Inositol Phospholipid) consists of a family of lipids as illustrated on the right, where red is x, blue is y, and black is z, in the context of independent variation, a class of the phosphatidylglycerides. In such molecul ...
signal pathway, the extracellular signal molecule binds with the G-protein receptor (Gq) on the cell surface and activates phospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role ...
, which is located on the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
. The lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually ...
hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of ...
(PIP2) into two second messengers: inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as s ...
(DAG). IP3 binds with the IP3 receptor
Inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R) is a membrane glycoprotein complex acting as a Ca2+ channel activated by inositol trisphosphate (InsP3). InsP3R is very diverse among organisms, and is necessary for the control of cellular and physio ...
in the membrane of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria to open Ca2+ channels. DAG helps activate protein kinase C
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and ...
(PKC), which phosphorylates many other proteins, changing their catalytic activities, leading to cellular responses.
The effects of Ca2+ are also remarkable: it cooperates with DAG in activating PKC and can activate the CaM kinase pathway, in which calcium-modulated protein calmodulin
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the bin ...
(CaM) binds Ca2+, undergoes a change in conformation, and activates CaM kinase II, which has unique ability to increase its binding affinity to CaM by autophosphorylation, making CaM unavailable for the activation of other enzymes. The kinase then phosphorylates target enzymes, regulating their activities. The two signal pathways are connected together by Ca2+-CaM, which is also a regulatory subunit of adenylyl cyclase and phosphodiesterase in the cAMP signal pathway.
Receptor regulation
GPCRs become desensitized when exposed to their ligand for a long period of time. There are two recognized forms of desensitization: 1) homologous desensitization
Homologous desensitization occurs when a receptor decreases its response to an agonist at high concentration. It is a process through which, after prolonged agonist exposure, the receptor is uncoupled from its signaling cascade and thus the cell ...
, in which the activated GPCR is downregulated; and 2) heterologous desensitization Heterologous desensitization (also known as cross-desensitization) is the term for the unresponsiveness of cells to one or more agonists to which they are normally responsive. Typically, desensitization is a receptor (biochemistry)-based phenomeno ...
, wherein the activated GPCR causes downregulation of a different GPCR. The key reaction of this downregulation is the phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
of the intracellular (or cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
ic) receptor domain by protein kinase
A protein kinase is a kinase which selectively modifies other proteins by covalently adding phosphates to them (phosphorylation) as opposed to kinases which modify lipids, carbohydrates, or other molecules. Phosphorylation usually results in a fu ...
s.
Phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinases
Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases (protein kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulatio ...
) are activated by the signal chain coming from the G protein (that was activated by the receptor) via adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
and cyclic AMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal tra ...
(cAMP). In a ''feedback mechanism'', these activated kinases phosphorylate the receptor. The longer the receptor remains active the more kinases are activated and the more receptors are phosphorylated. In β2-adrenoceptors, this phosphorylation results in the switching of the coupling from the Gs class of G-protein to the Gi class.
Phosphorylation by GRKs
The G protein-coupled receptor kinases
G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GPCRKs, GRKs) are a family of protein kinases within the AGC (protein kinase A, protein kinase G, protein kinase C) group of kinases. Like all AGC kinases, GRKs use ATP to add phosphate to Serine and Threonine ...
(GRKs) are protein kinases that phosphorylate only active GPCRs.Arrestin
Arrestins (abbreviated Arr) are a small family of proteins important for regulating signal transduction at G protein-coupled receptors.
Arrestins were first discovered as a part of a conserved two-step mechanism for regulating the activity of ...
linking'': The phosphorylated receptor can be linked to ''arrestin'' molecules that prevent it from binding (and activating) G proteins, in effect switching it off for a short period of time. This mechanism is used, for example, with rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransductio ...
in retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which the ...
cells to compensate for exposure to bright light. In many cases, arrestin's binding to the receptor is a prerequisite for translocation. For example, beta-arrestin bound to β2-adrenoreceptors acts as an adaptor for binding with clathrin, and with the beta-subunit of AP2 (clathrin adaptor molecules); thus, the arrestin here acts as a scaffold assembling the components needed for clathrin-mediated endocytosis of β2-adrenoreceptors.
Mechanisms of GPCR signal termination
As mentioned above, G-proteins may terminate their own activation due to their intrinsic GTP→GDP hydrolysis capability. However, this reaction proceeds at a slow rate (≈.02 times/sec) and, thus, it would take around 50 seconds for any single G-protein to deactivate if other factors did not come into play. Indeed, there are around 30 isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some iso ...
of RGS proteins that, when bound to Gα through their GAP domain, accelerate the hydrolysis rate to ≈30 times/sec. This 1500-fold increase in rate allows for the cell to respond to external signals with high speed, as well as spatial resolution due to limited amount of second messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first m ...
that can be generated and limited distance a G-protein can diffuse in 0.03 seconds. For the most part, the RGS proteins are promiscuous
Promiscuity is the practice of engaging in sexual activity frequently with different partners or being indiscriminate in the choice of sexual partners. The term can carry a moral judgment. A common example of behavior viewed as promiscuous by ma ...
in their ability to activate G-proteins, while which RGS is involved in a given signaling pathway seems more determined by the tissue and GPCR involved than anything else. In addition, RGS proteins have the additional function of increasing the rate of GTP-GDP exchange at GPCRs, (i.e., as a sort of co-GEF) further contributing to the time resolution of GPCR signaling.
In addition, the GPCR may be desensitized itself. This can occur as:
# a direct result of ligand occupation, wherein the change in conformation allows recruitment of GPCR-Regulating Kinases (GRKs), which go on to phosphorylate
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, ...
various serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − for ...
/threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO� ...
residues of IL-3 and the C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
tail. Upon GRK phosphorylation, the GPCR's affinity for β-arrestin
Arrestins (abbreviated Arr) are a small family of proteins important for regulating signal transduction at G protein-coupled receptors.
Arrestins were first discovered as a part of a conserved two-step mechanism for regulating the activity ...
(β-arrestin-1/2 in most tissues) is increased, at which point β-arrestin may bind and act to both sterically
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
hinder G-protein coupling as well as initiate the process of receptor internalization through clathrin-mediated endocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME), also called clathrin-mediated endocytosis, is a process by which cells absorb metabolites, hormones, proteins – and in some cases viruses – by the inward budding of the plasma membrane (invagination). This ...
. Because only the liganded receptor is desensitized by this mechanism, it is called homologous desensitization
Homologous desensitization occurs when a receptor decreases its response to an agonist at high concentration. It is a process through which, after prolonged agonist exposure, the receptor is uncoupled from its signaling cascade and thus the cell ...
# the affinity for β-arrestin may be increased in a ligand occupation and GRK-independent manner through phosphorylation of different ser/thr sites (but also of IL-3 and the C-terminal tail) by PKC and PKA. These phosphorylations are often sufficient to impair G-protein coupling on their own as well.heterologous desensitization Heterologous desensitization (also known as cross-desensitization) is the term for the unresponsiveness of cells to one or more agonists to which they are normally responsive. Typically, desensitization is a receptor (biochemistry)-based phenomeno ...
. GRKs may also have GAP domains and so may contribute to inactivation through non-kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
mechanisms as well. A combination of these mechanisms may also occur.
Once β-arrestin is bound to a GPCR, it undergoes a conformational change allowing it to serve as a scaffolding protein for an adaptor complex termed AP-2, which in turn recruits another protein called clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1976. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When ...
. If enough receptors in the local area recruit clathrin in this manner, they aggregate and the membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. ...
buds inwardly as a result of interactions between the molecules of clathrin, in a process called opsonization
Opsonins are extracellular proteins that, when bound to substances or cells, induce phagocytes to phagocytose the substances or cells with the opsonins bound. Thus, opsonins act as tags to label things in the body that should be phagocytosed (i.e. ...
. Once the pit has been pinched off the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
due to the actions of two other proteins called amphiphysin
Amphiphysin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AMPH'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a protein associated with the cytoplasmic surface of synaptic vesicles. A subset of patients with stiff person syndrome who were also affected ...
and dynamin
Dynamin is a GTPase responsible for endocytosis in the eukaryotic cell. Dynamin is part of the "dynamin superfamily", which includes classical dynamins, dynamin-like proteins, Mx proteins, OPA1, mitofusins, and GBPs. Members of the dynamin fami ...
, it is now an endocytic
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. ...
vesicle
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry)
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form nat ...
. At this point, the adapter molecules and clathrin have dissociated
Dissociation in chemistry is a general process in which molecules (or ionic compounds such as salts, or complexes) separate or split into other things such as atoms, ions, or radicals, usually in a reversible manner. For instance, when an acid ...
, and the receptor is either trafficked
''Trafficked'' is a 2017 American thriller drama film directed by Will Wallace and starring Ashley Judd, Sean Patrick Flanery and Anne Archer.
Plot
In California, Sara is eighteen and has to leave her foster home; she is offered training to be a ...
back to the plasma membrane or targeted to lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane p ...
s for degradation
Degradation may refer to:
Science
* Degradation (geology), lowering of a fluvial surface by erosion
* Degradation (telecommunications), of an electronic signal
* Biodegradation of organic substances by living organisms
* Environmental degradatio ...
.
At any point in this process, the β-arrestins may also recruit other proteins—such as the non-receptor tyrosine kinase
A non-receptor tyrosine kinase (nRTK) is a cytosolic enzyme that is responsible for catalysing the transfer of a phosphate group from a nucleoside triphosphate donor, such as ATP, to tyrosine residues in proteins. Non-receptor tyrosine kinases a ...
(nRTK), c-SRC—which may activate ERK1/2, or other mitogen-activated protein kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine (i.e., a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase). MAPKs are involved in directing cellular response ...
(MAPK) signaling through, for example, phosphorylation of the small GTPase
Small GTPases (), also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotr ...
, Ras
Ras or RAS may refer to:
Arts and media
* RAS Records Real Authentic Sound, a reggae record label
* Rundfunk Anstalt Südtirol, a south Tyrolese public broadcasting service
* Rás 1, an Icelandic radio station
* Rás 2, an Icelandic radio sta ...
, or recruit the proteins of the ERK cascade directly (i.e., Raf-1
RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase, also known as proto-oncogene c-RAF or simply c-Raf or even Raf-1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RAF1'' gene. The c-Raf protein is part of the ERK1/2 pathway as a MAP kinase ( ...
, MEK, ERK-1/2) at which point signaling is initiated due to their close proximity to one another. Another target of c-SRC are the dynamin molecules involved in endocytosis. Dynamins polymerize
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many for ...
around the neck of an incoming vesicle, and their phosphorylation by c-SRC provides the energy necessary for the conformational change allowing the final "pinching off" from the membrane.
GPCR cellular regulation
Receptor desensitization is mediated through a combination phosphorylation, β-arr binding, and endocytosis as described above. Downregulation occurs when endocytosed receptor is embedded in an endosome that is trafficked to merge with an organelle called a lysosome. Because lysosomal membranes are rich in proton pumps, their interiors have low pH (≈4.8 vs. the pH≈7.2 cytosol), which acts to denature the GPCRs. In addition, lysosomes contain many degradative enzyme A degradative enzyme is an enzyme (in a broader sense a protein) which degrades biological molecules. Some examples of degradative enzymes:
*Lipase, which digests lipids,
*Carbohydrases, which digest carbohydrates (e.g., sugars),
*Proteases, which d ...
s, including proteases, which can function only at such low pH, and so the peptide bonds joining the residues of the GPCR together may be cleaved. Whether or not a given receptor is trafficked to a lysosome, detained in endosomes, or trafficked back to the plasma membrane depends on a variety of factors, including receptor type and magnitude of the signal.
GPCR regulation is additionally mediated by gene transcription factors. These factors can increase or decrease gene transcription and thus increase or decrease the generation of new receptors (up- or down-regulation) that travel to the cell membrane.
Receptor oligomerization
G-protein-coupled receptor oligomerisation is a widespread phenomenon. One of the best-studied examples is the metabotropic GABAB receptor. This so-called constitutive receptor is formed by heterodimerization of GABABR1 and GABABR2 subunits. Expression of the GABABR1 without the GABABR2 in heterologous systems leads to retention of the subunit in the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
. Expression of the GABABR2 subunit alone, meanwhile, leads to surface expression of the subunit, although with no functional activity (i.e., the receptor does not bind agonist and cannot initiate a response following exposure to agonist). Expression of the two subunits together leads to plasma membrane expression of functional receptor. It has been shown that GABABR2 binding to GABABR1 causes masking of a retention signal
Origin and diversification of the superfamily
Signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
mediated by the superfamily of GPCRs dates back to the origin of multicellularity
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
. Mammalian-like GPCRs are found in fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
, and have been classified according to the GRAFS classification system based on GPCR fingerprints.eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
domain, and comparison of the family-specific motifs, have shown that the superfamily of GPCRs have a common origin.Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransductio ...
'', ''Adhesion'', and ''Frizzled
Frizzled is a family of atypical G protein-coupled receptors that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol.
Species distribution
Fr ...
'', evolved from the ''Dictyostelium
''Dictyostelium'' is a genus of single- and multi-celled eukaryotic, phagotrophic bacterivores. Though they are Protista and in no way fungal, they traditionally are known as "slime molds". They are present in most terrestrial ecosystems ...
discoideum'' cAMP receptors before the split of opisthokont
The opisthokonts () are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and ...
s. Later, the ''Secretin
Secretin is a hormone that regulates water homeostasis throughout the body and influences the environment of the duodenum by regulating secretions in the stomach, pancreas, and liver. It is a peptide hormone produced in the S cells of the du ...
'' family evolved from the ''Adhesion'' GPCR receptor family before the split of nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a bro ...
s.[ Insect GPCRs appear to be in their own group and Taste2 is identified as descending from ''Rhodopsin''.][ Note that the ''Secretin''/''Adhesion'' split is based on presumed function rather than signature, as the classical Class B (7tm_2, ) is used to identify both in the studies.
]
See also
* G protein-coupled receptors database
*List of MeSH codes (D12.776)
The following is a partial list of the "D" codes for Medical Subject Headings (MeSH), as defined by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM).
This list continues the information at List of MeSH codes (D12.644). Codes following these ...
*Metabotropic receptor
A metabotropic receptor, also referred to by the broader term G-protein-coupled receptor, is a type of membrane receptor that initiates a number of metabolic steps to modulate cell activity. The nervous system utilizes two types of receptors: met ...
*Orphan receptor
In biochemistry, an orphan receptor is a protein that has a similar structure to other identified receptors but whose endogenous ligand has not yet been identified. If a ligand for an orphan receptor is later discovered, the receptor is referred to ...
* Pepducins, a class of drug candidates targeted at GPCRs
*Receptor activated solely by a synthetic ligand
A receptor activated solely by a synthetic ligand (RASSL) or designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADD), is a class of artificially engineered protein receptors used in the field of chemogenetics which are selectively activ ...
, a technique for control of cell signaling through synthetic GPCRs
*TOG superfamily The transporter-opsin-G protein-coupled receptor (TOG) superfamily is a protein superfamily of integral membrane proteins, usually of 7 or 8 transmembrane alpha-helical segments (TMSs). It includes (1) ion-translocating microbial rhodopsins and (2) ...
References
Further reading
*
*
*
External links
*
GPCR Cell Line
*
* ;
*
*
GPCR-HGmod
, a database of 3D structural models of all human G-protein coupled receptors, built by the GPCR-I-TASSER
I-TASSER (Iterative Threading ASSEmbly Refinement) is a bioinformatics method for predicting three-dimensional structure model of protein molecules from amino acid sequences. It detects structure templates from the Protein Data Bank by a technique ...
pipeline
{{G protein-coupled receptors
Biochemistry
Integral membrane proteins
Molecular biology
Protein families
Signal transduction
 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are  In terms of structure, GPCRs are characterized by an extracellular
In terms of structure, GPCRs are characterized by an extracellular  The G protein-coupled receptor is activated by an external signal in the form of a ligand or other signal mediator. This creates a conformational change in the receptor, causing activation of a
The G protein-coupled receptor is activated by an external signal in the form of a ligand or other signal mediator. This creates a conformational change in the receptor, causing activation of a  The transduction of the signal through the membrane by the receptor is not completely understood. It is known that in the inactive state, the GPCR is bound to a
The transduction of the signal through the membrane by the receptor is not completely understood. It is known that in the inactive state, the GPCR is bound to a  When the receptor is inactive, the
When the receptor is inactive, the  GPCRs downstream signals have been shown to possibly interact with
GPCRs downstream signals have been shown to possibly interact with  If a receptor in an active state encounters a
If a receptor in an active state encounters a 
 There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein-linked receptors: the
There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein-linked receptors: the