Gustavs Klucis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gustav Klutsis ( lv, Gustavs Klucis, russian: Густав Густавович Клуцис; 4 January 1895 – 26 February 1938) was a pioneering Latvian photographer and major member of the Constructivist avant-garde in the early 20th century. He is known for the Soviet revolutionary and
 Born in Ķoņi parish, near Rūjiena, Klutsis began his artistic training in
Born in Ķoņi parish, near Rūjiena, Klutsis began his artistic training in
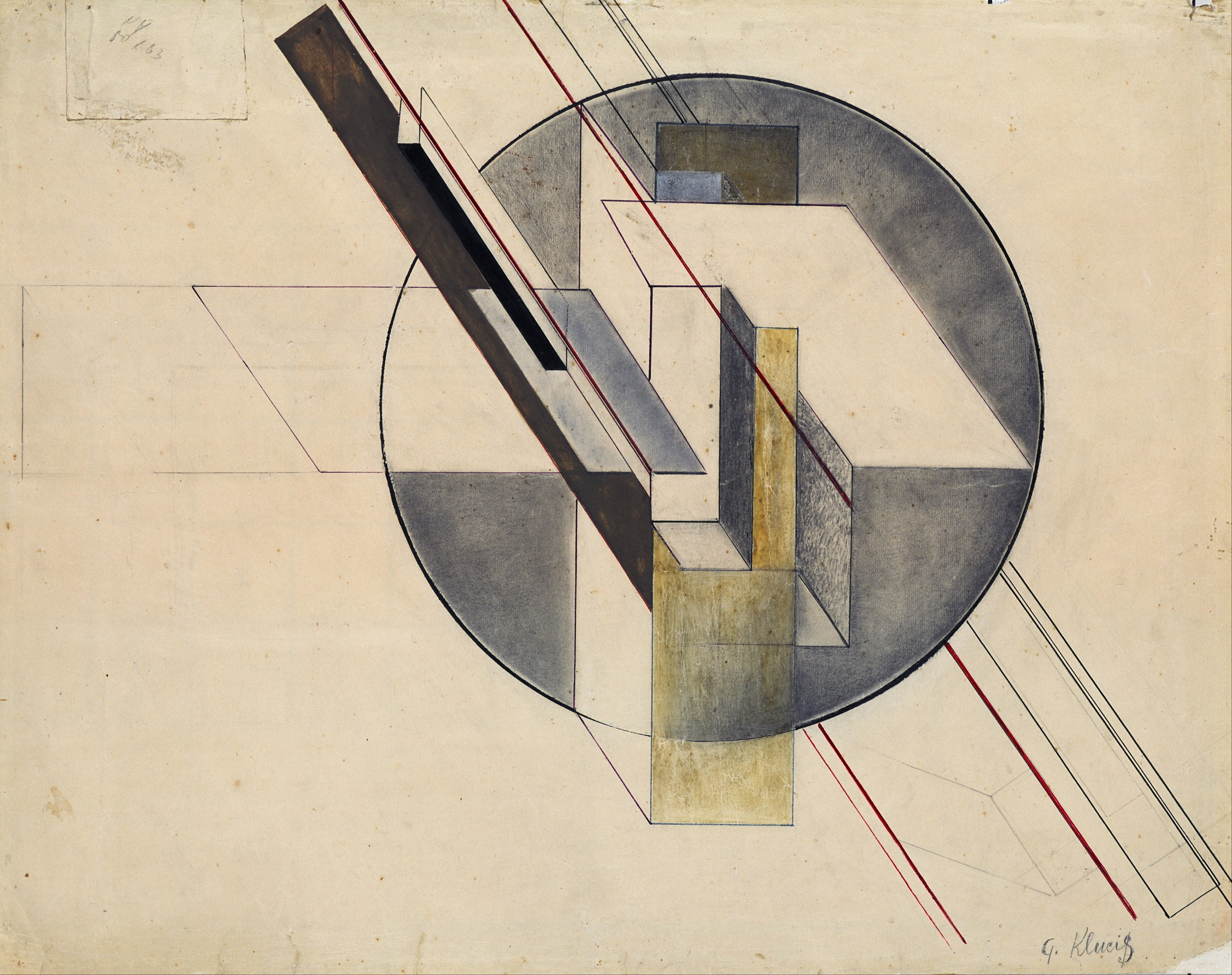 Klutsis worked in a variety of experimental media. He liked to use propaganda as a sign or revolutionary background image. His first project of note, in 1922, was a series of semi-portable multimedia agitprop kiosks to be installed on the streets of Moscow, integrating "radio-orators", film screens, and newsprint displays, all to celebrate the fifth anniversary of the Revolution. Like other Constructivists he worked in sculpture, produced exhibition installations, illustrations and ephemera.
But Klutsis and Kulagina are primarily known for their photomontages. The names of some of their best posters, such as "Electrification of the whole country" (1920), "There can be no revolutionary movement without a revolutionary theory" (1927), and "Field shock workers into the fight for the socialist reconstruction" (1932), belied the fresh, powerful, and sometimes eerie images. For economy they often posed for, and inserted themselves into, these images, disguised as shock workers or peasants. Their dynamic compositions, distortions of scale and space, angled viewpoints and colliding perspectives make them perpetually modern.
Klutsis is one of four artists with a claim to having invented the subgenre of political photo montage in 1918 (along with the German Dadaists Hannah Höch and Raoul Hausmann, and the Russian El Lissitzky). He worked alongside Lissitzky on the ''
Klutsis worked in a variety of experimental media. He liked to use propaganda as a sign or revolutionary background image. His first project of note, in 1922, was a series of semi-portable multimedia agitprop kiosks to be installed on the streets of Moscow, integrating "radio-orators", film screens, and newsprint displays, all to celebrate the fifth anniversary of the Revolution. Like other Constructivists he worked in sculpture, produced exhibition installations, illustrations and ephemera.
But Klutsis and Kulagina are primarily known for their photomontages. The names of some of their best posters, such as "Electrification of the whole country" (1920), "There can be no revolutionary movement without a revolutionary theory" (1927), and "Field shock workers into the fight for the socialist reconstruction" (1932), belied the fresh, powerful, and sometimes eerie images. For economy they often posed for, and inserted themselves into, these images, disguised as shock workers or peasants. Their dynamic compositions, distortions of scale and space, angled viewpoints and colliding perspectives make them perpetually modern.
Klutsis is one of four artists with a claim to having invented the subgenre of political photo montage in 1918 (along with the German Dadaists Hannah Höch and Raoul Hausmann, and the Russian El Lissitzky). He worked alongside Lissitzky on the ''
Gustav Klutsis and Valentina Kulagina: Photography and Montage After Constructivism
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20160408153831/http://briviba.org/2016/03/30/photomontage-as-a-new-form-of-agitation-art/ Essay “Photomontage as a new form of agitation art” by Gustav Klutsis {{DEFAULTSORT:Klutsis, Gustav 1895 births 1938 deaths People from Valmiera Municipality People from Kreis Wolmar Communist Party of the Soviet Union members Latvian graphic designers Latvian photographers Soviet photographers Collage artists Constructivism (art) Academic staff of Vkhutemas Latvian Riflemen Russian military personnel of World War I Soviet military personnel of the Russian Civil War Latvian Operation of the NKVD Members of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union executed by the Soviet Union Great Purge victims from Latvia Soviet rehabilitations
Stalinist
Stalinism is the means of governing and Marxist-Leninist policies implemented in the Soviet Union from 1927 to 1953 by Joseph Stalin. It included the creation of a one-party totalitarian police state, rapid industrialization, the theory o ...
propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
he produced with his wife Valentina Kulagina
Valentina Kulagina, full name Valentina Nikiforovna Kulagina-Klutsis (russian: Валентина Никифоровна Кулагина-Клуцис, 1902–1987) was a Russian painter and book, poster, and exhibition designer. She was a centra ...
and for the development of photomontage techniques.
Biography
 Born in Ķoņi parish, near Rūjiena, Klutsis began his artistic training in
Born in Ķoņi parish, near Rūjiena, Klutsis began his artistic training in Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
in 1912. In 1915 he was drafted into the Russian Army, serving in a Latvian riflemen detachment, then went to Moscow in 1917. As a soldier of the 9th Latvian Riflemen Regiment, Klutsis served among Vladimir Lenin's personal guard in the Smolny
Smolny is a place name in central Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is a compound of historically interrelated buildings erected in 18th and 19th centuries. As the most widely known of the buildings, the Smolny Institute, has been used as the seat of t ...
in 1917-1918 and was later transferred to Moscow to serve as part of the guard of the Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty, Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of th ...
(1919-1924).
In 1918-1921 he began art studies under Kazimir Malevich
Kazimir Severinovich Malevich ; german: Kasimir Malewitsch; pl, Kazimierz Malewicz; russian: Казими́р Севери́нович Мале́вич ; uk, Казимир Северинович Малевич, translit=Kazymyr Severynovych ...
and Antoine Pevsner, joined the Communist Party, met and married longtime collaborator Valentina Kulagina, and graduated from the state-run art school VKhUTEMAS. He would continue to be associated with VKhUTEMAS as a professor of color theory from 1924 until the school closed in 1930.
Klutsis taught, wrote, and produced political art for the Soviet state for the rest of his life. As the political background degraded through the 1920s and 1930s, Klutsis and Kulagina came under increasing pressure to limit their subject matter and techniques. Once joyful, revolutionary and utopian, by 1935 their art was devoted to furthering Joseph Stalin's cult of personality
A cult of personality, or a cult of the leader, Mudde, Cas and Kaltwasser, Cristóbal Rovira (2017) ''Populism: A Very Short Introduction''. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 63. is the result of an effort which is made to create an id ...
.
Despite his active and loyal service to the party, Klutsis was arrested in Moscow on 16 January 1938, as a part of the so-called " Latvian Operation" as he prepared to leave for the New York World's Fair. Kulagina agonized for months, then years, over his disappearance. His sentence was passed by the NKVD Commission and the USSR Prosecutor’s Office on 11 February 1938, and he was executed on 26 February 1938, at the Butovo NKVD training ground near Moscow. He was rehabilitated on 25 August 1956 for lack of corpus delicti.
Work
 Klutsis worked in a variety of experimental media. He liked to use propaganda as a sign or revolutionary background image. His first project of note, in 1922, was a series of semi-portable multimedia agitprop kiosks to be installed on the streets of Moscow, integrating "radio-orators", film screens, and newsprint displays, all to celebrate the fifth anniversary of the Revolution. Like other Constructivists he worked in sculpture, produced exhibition installations, illustrations and ephemera.
But Klutsis and Kulagina are primarily known for their photomontages. The names of some of their best posters, such as "Electrification of the whole country" (1920), "There can be no revolutionary movement without a revolutionary theory" (1927), and "Field shock workers into the fight for the socialist reconstruction" (1932), belied the fresh, powerful, and sometimes eerie images. For economy they often posed for, and inserted themselves into, these images, disguised as shock workers or peasants. Their dynamic compositions, distortions of scale and space, angled viewpoints and colliding perspectives make them perpetually modern.
Klutsis is one of four artists with a claim to having invented the subgenre of political photo montage in 1918 (along with the German Dadaists Hannah Höch and Raoul Hausmann, and the Russian El Lissitzky). He worked alongside Lissitzky on the ''
Klutsis worked in a variety of experimental media. He liked to use propaganda as a sign or revolutionary background image. His first project of note, in 1922, was a series of semi-portable multimedia agitprop kiosks to be installed on the streets of Moscow, integrating "radio-orators", film screens, and newsprint displays, all to celebrate the fifth anniversary of the Revolution. Like other Constructivists he worked in sculpture, produced exhibition installations, illustrations and ephemera.
But Klutsis and Kulagina are primarily known for their photomontages. The names of some of their best posters, such as "Electrification of the whole country" (1920), "There can be no revolutionary movement without a revolutionary theory" (1927), and "Field shock workers into the fight for the socialist reconstruction" (1932), belied the fresh, powerful, and sometimes eerie images. For economy they often posed for, and inserted themselves into, these images, disguised as shock workers or peasants. Their dynamic compositions, distortions of scale and space, angled viewpoints and colliding perspectives make them perpetually modern.
Klutsis is one of four artists with a claim to having invented the subgenre of political photo montage in 1918 (along with the German Dadaists Hannah Höch and Raoul Hausmann, and the Russian El Lissitzky). He worked alongside Lissitzky on the ''Pressa
''Pressa'' was an International Press Exhibition held in Cologne between May and October, 1928.
As German exhibitors were barred from participating in the ''Exposition International des Arts Décoratifs et Industriels Modern'' held in Paris in ...
'' International exhibition in Cologne.
References
External links
Gustav Klutsis and Valentina Kulagina: Photography and Montage After Constructivism
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20160408153831/http://briviba.org/2016/03/30/photomontage-as-a-new-form-of-agitation-art/ Essay “Photomontage as a new form of agitation art” by Gustav Klutsis {{DEFAULTSORT:Klutsis, Gustav 1895 births 1938 deaths People from Valmiera Municipality People from Kreis Wolmar Communist Party of the Soviet Union members Latvian graphic designers Latvian photographers Soviet photographers Collage artists Constructivism (art) Academic staff of Vkhutemas Latvian Riflemen Russian military personnel of World War I Soviet military personnel of the Russian Civil War Latvian Operation of the NKVD Members of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union executed by the Soviet Union Great Purge victims from Latvia Soviet rehabilitations