Gunungapi Wetar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
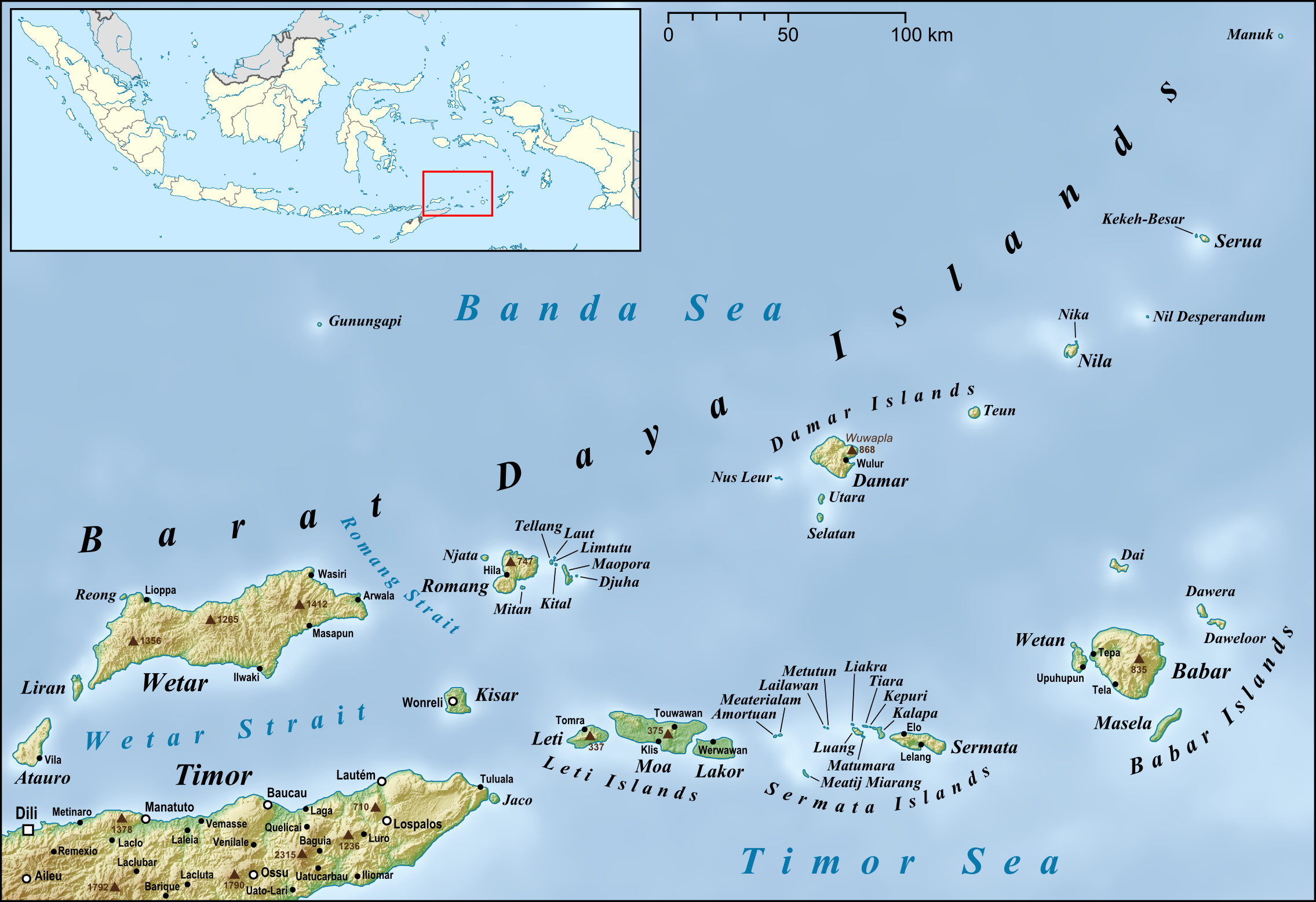 Gunungapi Wetar is an isolated
Gunungapi Wetar is an isolated
 Gunungapi Wetar is an isolated
Gunungapi Wetar is an isolated volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
island to the north of Wetar
Wetar is a tropical island which belongs to the Indonesian province of Maluku and is the largest island of the Maluku Barat Daya Islands (literally ''Southwest Islands'') of the Maluku Islands. It lies east of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which in ...
island in the Banda Sea
The Banda Sea ( id, Laut Banda, pt, Mar de Banda, tet, Tasi Banda) is one of four seas that surround the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, connected to the Pacific Ocean, but surrounded by hundreds of islands, including Timor, as well as the Halma ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. The island, a stratovolcano, only extends 239 m above sea level, but the total height of the summit from the sea bed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
is over 5000 m. Explosions in 1512 and 1699 are the only historical eruptions of the volcano.
See also
*List of volcanoes in Indonesia
The geography of Indonesia is dominated by volcanoes that are formed due to subduction zones between the Eurasian plate and the Indo-Australian plate. Some of the volcanoes are notable for their eruptions, for instance, Krakatoa for its globa ...
References
Active volcanoes of Indonesia Stratovolcanoes of Indonesia Volcanoes of the Lesser Sunda Islands Landforms of Maluku (province) Banda Sea Holocene stratovolcanoes {{Maluku-geo-stub