Guillaume Du Fay on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Guillaume Du Fay ( , ; also Dufay, Du Fayt; 5 August 1397(?) – 27 November 1474) was a French composer and music theorist of the early
Guillaume Du Fay ( , ; also Dufay, Du Fayt; 5 August 1397(?) – 27 November 1474) was a French composer and music theorist of the early
 Du Fay's life is better documented than "almost any other uropeancomposer of the 15th century". The reasons for this are numerous, but especially informative are the thorough record keeping of the institutions he associated with and the many biographical or historical anecdotes integrated in his compositions. In addition, while records from many northern French cathedrals were either lost or destroyed, those from
Du Fay's life is better documented than "almost any other uropeancomposer of the 15th century". The reasons for this are numerous, but especially informative are the thorough record keeping of the institutions he associated with and the many biographical or historical anecdotes integrated in his compositions. In addition, while records from many northern French cathedrals were either lost or destroyed, those from
 From November 1418 to 1420 he was a subdeacon at
From November 1418 to 1420 he was a subdeacon at
 After the abdication of the last antipope (Felix V) in 1449, his own former employer Duke Amédée VIII of Savoy, the struggle between different factions within the Church began to heal, and Du Fay once again left Cambrai for points south. He went to Turin in 1450, shortly before the death of Duke Amédée, but returned to Cambrai later that year; and in 1452 he went back to Savoy yet again. This time he did not return to Cambrai for six years, and during that time he attempted to find either a benefice or an employment which would allow him to stay in Italy. Numerous compositions, including one of the four '' Lamentationes'' that he composed on the
After the abdication of the last antipope (Felix V) in 1449, his own former employer Duke Amédée VIII of Savoy, the struggle between different factions within the Church began to heal, and Du Fay once again left Cambrai for points south. He went to Turin in 1450, shortly before the death of Duke Amédée, but returned to Cambrai later that year; and in 1452 he went back to Savoy yet again. This time he did not return to Cambrai for six years, and during that time he attempted to find either a benefice or an employment which would allow him to stay in Italy. Numerous compositions, including one of the four '' Lamentationes'' that he composed on the
Further info and sample pages
* ''Die frühen Messenkompositionen von Guillaume Dufay'', ed. R. Bockhold, 1960, Tutzing
 Du Fay may have been the first composer to use the term "fauxbourdon" for this simpler compositional style, prominent in 15th century liturgical music in general and that of the Burgundian school in particular.
Du Fay may have been the first composer to use the term "fauxbourdon" for this simpler compositional style, prominent in 15th century liturgical music in general and that of the Burgundian school in particular.
 Two known depictions of Du Fay survive from his lifetime, both described by Planchart as "simplified likenesses", which "clearly depict the same person". The earlier, and better known, is a
Two known depictions of Du Fay survive from his lifetime, both described by Planchart as "simplified likenesses", which "clearly depict the same person". The earlier, and better known, is a
New Du Fay edition by Alejandro Planchart
downloadable from Digital Image Archive of Medieval Music {{DEFAULTSORT:Du Fay, Guillaume 1390s births 1397 births 1474 deaths 15th-century Franco-Flemish composers French classical composers French male classical composers People from Beersel
 Guillaume Du Fay ( , ; also Dufay, Du Fayt; 5 August 1397(?) – 27 November 1474) was a French composer and music theorist of the early
Guillaume Du Fay ( , ; also Dufay, Du Fayt; 5 August 1397(?) – 27 November 1474) was a French composer and music theorist of the early Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
. Considered the leading European composer of his time, his music was widely performed and reproduced. Du Fay was well-associated with composers of the Burgundian School
The Burgundian School was a group of composers active in the 15th century in what is now northern and eastern France, Belgium, and the Netherlands, centered on the court of the Dukes of Burgundy. The school inaugurated the music of Burgundy.
The ...
, particularly his colleague Gilles Binchois
Gilles de Bins dit Binchois (also Binchoys; – 20 September 1460) was a Franco-Flemish composer of early Renaissance music. A central figure of the Burgundian School, Binchois and his colleague Guillaume Du Fay were deeply influenced by the ...
, but was never a regular member of the Burgundian chapel himself.
While he is among the best-documented composers of his time, Du Fay's birth and family is shrouded with uncertainty, though he was probably the illegitimate child of a priest. He was educated at Cambrai Cathedral
Cambrai Cathedral (french: Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Grâce de Cambrai) is a Catholic church located in Cambrai, Nord, France, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Cambrai. The cathedral was registered as a '' monument historique'' on 9 August ...
, where his teachers included Nicolas Grenon
Nicolas Grenon ( – October 17, 1456) was a French composer of the early Renaissance. He wrote in all the prevailing musical forms of the time, and was a rare case of a long-lived composer who learned his craft in the late 14th century but primari ...
and Richard Loqueville, among others. For the next decade, Du Fay worked throughout Europe: as a subdeacon in Cambrai, under Carlo I Malatesta
Carlo I Malatesta (June 1368 – 13 September 1429) (also Carlo of Rimini) was an Italian condottiero during the Wars in Lombardy and lord of Rimini, Fano, Cesena and Pesaro. He was a member of the powerful House of Malatesta. Carlo's wife ...
in Rimini
Rimini ( , ; rgn, Rémin; la, Ariminum) is a city in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy and capital city of the Province of Rimini. It sprawls along the Adriatic Sea, on the coast between the rivers Marecchia (the ancient ''Ariminu ...
, for the House of Malatesta )
, type= Noble house
, country=ItalySan Marino, estates= Castel Sismondo (Rimini) Rocca Malatestiana (Cesena)
, titles=, founded=, founder=Malatesta da Verucchio, final ruler=Pandolfo IV Malatesta, deposition=, dissolution=
The House of Malatesta ...
in Pesaro
Pesaro () is a city and ''comune'' in the Italian region of Marche, capital of the Province of Pesaro e Urbino, on the Adriatic Sea. According to the 2011 census, its population was 95,011, making it the second most populous city in the Marche, ...
, and under Louis Aleman
Louis Aleman (16 September 1450) was a French Roman Catholic cardinal and a professed member of the now-suppressed Canons Regular of Saint John Baptist. He served as the Archbishop of Arles from 1423 until his resignation in 1440 when he had resi ...
in Bologna, where he was ordained priest. As his fame began to spread, he settled in Rome in 1428 as musician of the prestigious papal choir, first under Pope Martin V
Pope Martin V ( la, Martinus V; it, Martino V; January/February 1369 – 20 February 1431), born Otto (or Oddone) Colonna, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 11 November 1417 to his death in February 1431. Hi ...
and then Pope Eugene IV
Pope Eugene IV ( la, Eugenius IV; it, Eugenio IV; 1383 – 23 February 1447), born Gabriele Condulmer, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 3 March 1431 to his death in February 1447. Condulmer was a Venetian, and ...
, where he wrote the motets ''Balsamus et munda cera'', ''Ecclesie militantis'' and ''Supremum est mortalibus''. Amid Rome's finical and political disorder in the 1430s, Du Fay took a leave of absence from the choir to serve Amadeus VIII, Duke of Savoy
Amadeus VIII (4 September 1383 – 7 January 1451), nicknamed the Peaceful, was Count of Savoy from 1391 to 1416 and Duke of Savoy from 1416 to 1440. He was the son of Amadeus VII, Count of Savoy and Bonne of Berry. He was a claimant to the papac ...
.
Du Fay returned to Italy in 1436, writing his most admired work, the complex motet '' Nuper Rosarum Flores'', which celebrated the consecration of Filippo Brunelleschi
Filippo Brunelleschi ( , , also known as Pippo; 1377 – 15 April 1446), considered to be a founding father of Renaissance architecture, was an Italian architect, designer, and sculptor, and is now recognized to be the first modern engineer, p ...
's dome for the Florence Cathedral
Florence Cathedral, formally the (; in English Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower), is the cathedral of Florence, Italy ( it, Duomo di Firenze). It was begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to a design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was structurally c ...
. He later joined the recently-moved papal court in Bologna, and was associated with the House of Este
The House of Este ( , , ) is a European dynasty of North Italian origin whose members ruled parts of Italy and Germany for many centuries.
The original House of Este's elder branch, which is known as the House of Welf, included dukes of Bavaria ...
in Ferrara
Ferrara (, ; egl, Fràra ) is a city and ''comune'' in Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy, capital of the Province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main stream ...
. For the next eleven years, Du Fay was in Cambrai serving Philip the Good
Philip III (french: Philippe le Bon; nl, Filips de Goede; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) was Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonge ...
, under whom he may have written now-lost works on music theory
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (ke ...
. After a brief return to both Savoy and Italy, Du Fay settled in Cambrai in 1458, where his focus shifted from song and motet, to composing English-inspired cyclic masses based on cantus firmus
In music, a ''cantus firmus'' ("fixed melody") is a pre-existing melody forming the basis of a polyphonic composition.
The plural of this Latin term is , although the corrupt form ''canti firmi'' (resulting from the grammatically incorrect tr ...
, such as the ''Missa Ave regina celorum'', the ''Missa Ecce ancilla Domini'', the ''Missa L'Homme armé'' and the ''Missa Se la face ay pale''. During his final years in Cambrai, Du Fay he wrote his now-lost requiem and both met and influenced the leading musicians of his time, including Antoine Busnois
Antoine Busnois (also Busnoys; – before 6 November 1492) was a French composer, singer and poet of early Renaissance music. Busnois and colleague Johannes Ockeghem were the leading European composers of the second half the 15th century, and ...
, Loyset Compère
Loyset Compère ( – 16 August 1518) was a Franco-Flemish composer of the Renaissance. Of the same generation as Josquin des Prez, he was one of the most significant composers of motets and chansons of that era, and one of the first musicians ...
, Johannes Tinctoris
Jehan le Taintenier or Jean Teinturier (Latinised as Johannes Tinctoris; also Jean de Vaerwere; – 1511) was a Renaissance music theorist and composer from the Low Countries. Up to his time, he is perhaps the most significant European writer ...
and particularly, Johannes Ockeghem
Johannes Ockeghem ( – 6 February 1497) was a Franco-Flemish composer and singer of early Renaissance music. Ockeghem was the most influential European composer in the period between Guillaume Du Fay and Josquin des Prez, and he was—with his ...
.
Du Fay has been described as leading the first generation of European musicians who were primarily considered 'composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and Defi ...
s' by occupation. His erratic career took him throughout Western Europe, forming a 'cosmopolitan style' and an extensive oeuvre which included representatives of virtually every polyphonic genre of his time. Like Binchois, Du Fay was deeply influenced by the ''contenance angloise
The ''Contenance angloise'', or English manner, is a distinctive style of polyphony developed in fifteenth-century England which uses full, rich harmonies based on the third and sixth. It was highly influential in the fashionable Burgundian court ...
'' style of John Dunstaple
John Dunstaple (or Dunstable, – 24 December 1453) was an English composer whose music helped inaugurate the transition from the medieval to the Renaissance periods. The central proponent of the ''Contenance angloise'' style (), Dunstaple was ...
, and synthesized it with a wide variety of other styles, including that of the famous ''Missa Caput
The ''Missa Caput'' was a musical setting of the Roman Catholic mass, dating from the 1440s, by an anonymous English composer. It circulated widely on the European continent in the mid-15th century and was one of the best-loved musical works of ...
'', and the techniques of his younger contemporaries, Ockeghem and Busnois.
Life
Background
 Du Fay's life is better documented than "almost any other uropeancomposer of the 15th century". The reasons for this are numerous, but especially informative are the thorough record keeping of the institutions he associated with and the many biographical or historical anecdotes integrated in his compositions. In addition, while records from many northern French cathedrals were either lost or destroyed, those from
Du Fay's life is better documented than "almost any other uropeancomposer of the 15th century". The reasons for this are numerous, but especially informative are the thorough record keeping of the institutions he associated with and the many biographical or historical anecdotes integrated in his compositions. In addition, while records from many northern French cathedrals were either lost or destroyed, those from Cambrai Cathedral
Cambrai Cathedral (french: Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Grâce de Cambrai) is a Catholic church located in Cambrai, Nord, France, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Cambrai. The cathedral was registered as a '' monument historique'' on 9 August ...
remain extant.
Modern scholarship generally spells the composer's surname as two words, 'Du Fay'. Before the late 20th century, however, spelling the name as single word—'Dufay'—was much more common. Archival discoveries from this period revealed that the surname was usually spelled as two words in documents of the 14th and 15th century, contrary to musical sources of that time. It seems that Du Fay's parents spelt their surname as 'Du Fayt', but for unknown reasons the composer altered the spelling while active in Italy. Documents from the composer's early years in Cambrai sometimes spelled his first name as Willaume, or a related form such as Willermus, Willem or Wilhelm.
Early life
From the evidence of his will, he was probably born in Beersel, in the vicinity ofBrussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, the illegitimate child of an unknown priest and a woman named Marie Du Fayt. She moved with her son to Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department and in the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, regio ...
early in his life, staying with a relative who was a canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western ca ...
of the cathedral there. The link between the Du Fay family and the Cathedral of Cambrai
Cambrai Cathedral (french: Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Grâce de Cambrai) is a Catholic church located in Cambrai, Nord, France, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Cambrai. The cathedral was registered as a '' monument historique'' on 9 August ...
is the sole reason a large amount of information is known about Du Fay's early life, as the institute kept detailed records on all affiliated persons. His musical gifts were noticed by the cathedral authorities, who evidently gave him a thorough training in music; he studied with Rogier de Hesdin during the summer of 1409, and he was listed as a choirboy in the cathedral from 1409 to 1412. During those years he studied with Nicolas Malin, and the authorities must have been impressed with the boy's gifts because they gave him his own copy of Villedieu's ''Doctrinale Puerorum'' in 1411, a highly unusual event for one so young. In June of 1414 he had already been given a benefice
A benefice () or living is a reward received in exchange for services rendered and as a retainer for future services. The Roman Empire used the Latin term as a benefit to an individual from the Empire for services rendered. Its use was adopted by ...
as chaplain at St. Géry, immediately adjacent to Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department and in the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, regio ...
where he studied under Nicolas Malin and Richard Loqueville. Later that year, on the evidence of music composed, and a later relationship with the Malatesta court, members of which he met on the trip, he probably went to the Council of Konstanz. He likely stayed there until 1418, at which time he returned to Cambrai.
Cambrai to Italy and Savoy
 From November 1418 to 1420 he was a subdeacon at
From November 1418 to 1420 he was a subdeacon at Cambrai Cathedral
Cambrai Cathedral (french: Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Grâce de Cambrai) is a Catholic church located in Cambrai, Nord, France, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Cambrai. The cathedral was registered as a '' monument historique'' on 9 August ...
. In 1420 he left Cambrai for Italy – first to Rimini
Rimini ( , ; rgn, Rémin; la, Ariminum) is a city in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy and capital city of the Province of Rimini. It sprawls along the Adriatic Sea, on the coast between the rivers Marecchia (the ancient ''Ariminu ...
and then to Pesaro
Pesaro () is a city and ''comune'' in the Italian region of Marche, capital of the Province of Pesaro e Urbino, on the Adriatic Sea. According to the 2011 census, its population was 95,011, making it the second most populous city in the Marche, ...
, where he worked for the Malatesta Malatesta may refer to:
People Given name
* Malatesta (I) da Verucchio (1212–1312), founder of the powerful Italian Malatesta family and a famous condottiero
* Malatesta IV Baglioni (1491–1531), Italian condottiero and lord of Perugia, Bettona, ...
family. Several of his compositions can be dated to this period; they contain colloquial references to Italy. There he met the composers Hugo
Hugo or HUGO may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Hugo'' (film), a 2011 film directed by Martin Scorsese
* Hugo Award, a science fiction and fantasy award named after Hugo Gernsback
* Hugo (franchise), a children's media franchise based on ...
and Arnold de Lantins
Arnold de Lantins ( fl. 1420s – before 2 July 1432) was a Netherlandish composer of the late medieval and early Renaissance eras. He is one of a few composers who shows aspects of both medieval and Renaissance style, and was a contemporary o ...
, who were also among the musicians of the Malatesta household. In 1424 Du Fay returned to Cambrai, because of the illness and subsequent death of the relative with whom his mother was staying. By 1426, however, he had returned to Italy. In Bologna
Bologna (, , ; egl, label= Emilian, Bulåggna ; lat, Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nat ...
, he entered the service of Cardinal Louis Aleman, the papal legate. While in Bologna he became a deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions. Major Christian churches, such as the Catholic Churc ...
, and by 1428 he was ordained priest.
Cardinal Aleman was driven from Bologna by the rival Canedoli family in 1428, and Du Fay also left, going to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. He became a member of the Papal Choir, the most prestigious musical establishment in Europe, serving first Pope Martin V
Pope Martin V ( la, Martinus V; it, Martino V; January/February 1369 – 20 February 1431), born Otto (or Oddone) Colonna, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 11 November 1417 to his death in February 1431. Hi ...
, and then after the death of Pope Martin in 1431, Pope Eugene IV
Pope Eugene IV ( la, Eugenius IV; it, Eugenio IV; 1383 – 23 February 1447), born Gabriele Condulmer, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 3 March 1431 to his death in February 1447. Condulmer was a Venetian, and ...
. By this time his fame had spread, and he had become one of the most respected musicians in Europe. As a consequence, honors in the form of benefices came to him from churches in his homeland. In 1434 he was appointed ''maistre de chappelle'' in Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Savo ...
, where he served Duke Amédée VIII. He had left Rome because of a crisis in the finances of the papal choir while seeking to escape the turbulence and uncertainty during the struggle between the papacy and the Council of Basel
The Council of Florence is the seventeenth ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held between 1431 and 1449. It was convoked as the Council of Basel by Pope Martin V shortly before his death in February 1431 and took place in ...
. By 1435 he was again in the service of the papal chapel, but this time it was in Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...
– Pope Eugene having been driven from Rome in 1434 by the establishment of an insurrectionary republic there, sympathetic to the Council of Basel and the Conciliar movement
Conciliarism was a reform movement in the 14th-, 15th- and 16th-century Catholic Church which held that supreme authority in the Church resided with an ecumenical council, apart from, or even against, the pope.
The movement emerged in response to ...
. In 1436 Du Fay composed the festive motet '' Nuper rosarum flores'', one of his most famous compositions, dedicated to and performed at the cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnight ...
in Florence, featuring Filippo Brunelleschi
Filippo Brunelleschi ( , , also known as Pippo; 1377 – 15 April 1446), considered to be a founding father of Renaissance architecture, was an Italian architect, designer, and sculptor, and is now recognized to be the first modern engineer, p ...
's renowned dome. Eugene at this time lived in exile at the nearby church of Santa Maria Novella.
The papal court moved to Bologna in April 1436, and by 10 May 1437 Du Fay was in possession of a university law degree. Since there is no evidence that Du Fay had studied law at Bologna, it is likely that the degree was granted by papal fiat. In September 1436, Du Fay achieved what he had long sought for, a lucrative benefice near the place of his birth. A certain Jehan Vivien went on to become the bishop of Nevers, vacating his canonicate at Cambrai in the process, and Du Fay was given Vivien's canonicate by both ''motu proprio
In law, ''motu proprio'' (Latin for "on his own impulse") describes an official act taken without a formal request from another party. Some jurisdictions use the term ''sua sponte'' for the same concept.
In Catholic canon law, it refers to a do ...
'' and Papal bull. Although the law degree was not necessary in holding the canonicate at Cambrai, Du Fay regarded both titles important enough to be mentioned in his funeral monument.
During this period Du Fay also began his long association with the Este family in Ferrara
Ferrara (, ; egl, Fràra ) is a city and ''comune'' in Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy, capital of the Province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main stream ...
, some of the most important musical patrons of the Renaissance, and with which he probably had become acquainted during the days of his association with the Malatesta family; Rimini and Ferrara are not only geographically close, but the two families were related by marriage, and Du Fay composed at least one ballade
Ballad is a form of narrative poetry, often put to music, or a type of sentimental love song in modern popular music.
Ballad or Ballade may also refer to:
Music Genres and forms
* Ballade (classical music), a musical setting of a literary ballad ...
for Niccolò III, Marquis of Ferrara. In 1437 Du Fay visited the town. When Niccolò died in 1441, the next Marquis maintained the contact with Du Fay, and not only continued financial support for the composer but copied and distributed some of his music.
Return to Cambrai
The struggle between the papacy and the Council of Basel continued through the 1430s, and evidently Du Fay realised that his own position might be threatened by the spreading conflict, especially since Pope Eugene was deposed in 1439 by the council and replaced by Duke Amédée of Savoy himself, as Pope (Antipope
An antipope ( la, antipapa) is a person who makes a significant and substantial attempt to occupy the position of Bishop of Rome and leader of the Catholic Church in opposition to the legitimately elected pope. At times between the 3rd and mid- ...
) Felix V
Amadeus VIII (4 September 1383 – 7 January 1451), nicknamed the Peaceful, was Count of Savoy from 1391 to 1416 and Duke of Savoy from 1416 to 1440. He was the son of Amadeus VII, Count of Savoy and Bonne of Berry. He was a claimant to the papac ...
. At this time Du Fay returned to his homeland, arriving in Cambrai by December of that year. One of the first documents mentioning him in Cambrai is dated 27 December 1440, when he received a delivery of 36 lots of wine for the feast of St. John the Evangelist.
Du Fay was to remain in Cambrai through the 1440s, and during this time he was also in the service of the Duke of Burgundy. While in Cambrai he collaborated with Nicolas Grenon
Nicolas Grenon ( – October 17, 1456) was a French composer of the early Renaissance. He wrote in all the prevailing musical forms of the time, and was a rare case of a long-lived composer who learned his craft in the late 14th century but primari ...
on a complete revision of the liturgical musical collection of the cathedral, which included writing an extensive collection of polyphonic music for services. In addition to his musical work, he was active in the general administration of the cathedral. In 1444 his mother Marie died, and was buried in the cathedral; and in 1445 Du Fay moved into the house of the previous canon, which was to remain his primary residence for the rest of his life. Planchart speculates that around this time Du Fay might have written his works on music theory
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (ke ...
, both of which are lost.
Travels to Savoy and Italy
 After the abdication of the last antipope (Felix V) in 1449, his own former employer Duke Amédée VIII of Savoy, the struggle between different factions within the Church began to heal, and Du Fay once again left Cambrai for points south. He went to Turin in 1450, shortly before the death of Duke Amédée, but returned to Cambrai later that year; and in 1452 he went back to Savoy yet again. This time he did not return to Cambrai for six years, and during that time he attempted to find either a benefice or an employment which would allow him to stay in Italy. Numerous compositions, including one of the four '' Lamentationes'' that he composed on the
After the abdication of the last antipope (Felix V) in 1449, his own former employer Duke Amédée VIII of Savoy, the struggle between different factions within the Church began to heal, and Du Fay once again left Cambrai for points south. He went to Turin in 1450, shortly before the death of Duke Amédée, but returned to Cambrai later that year; and in 1452 he went back to Savoy yet again. This time he did not return to Cambrai for six years, and during that time he attempted to find either a benefice or an employment which would allow him to stay in Italy. Numerous compositions, including one of the four '' Lamentationes'' that he composed on the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
in 1453, his famous mass based on ''Se la face ay pale'', as well as a letter to Lorenzo de' Medici
Lorenzo di Piero de' Medici (; 1 January 1449 – 8 April 1492) was an Italian statesman, banker, ''de facto'' ruler of the Florentine Republic and the most powerful and enthusiastic patron of Renaissance culture in Italy. Also known as Lorenzo ...
, survive from this period: but as he was unable to find a satisfactory position for his retirement, he returned north in 1458. While in Savoy he served more-or-less officially as choirmaster for Louis, Duke of Savoy
Ludovico I or Louis I ( Italian: Lodovico; 24 February 1413 – 29 January 1465) was Duke of Savoy from 1440 until his death in 1465.
Life
He was born at Geneva the son of Amadeus VIII, Duke of Savoy and Mary of Burgundy; he was the first to ...
, but he was more likely in a ceremonial role, since the records of the chapel never mention him.
Final years in Cambrai
When he returned to Cambrai for his final years, he was appointed canon of the cathedral. He was now the most renowned composer in Europe. Once again he established close ties to the court of Burgundy, and continued to compose music for them; in addition he received many visitors, includingBusnois
Antoine Busnois (also Busnoys; – before 6 November 1492) was a French composer, singer and poet of early Renaissance music. Busnois and colleague Johannes Ockeghem were the leading European composers of the second half the 15th century, and ...
, Ockeghem, Tinctoris
Jehan le Taintenier or Jean Teinturier (Latinised as Johannes Tinctoris; also Jean de Vaerwere; – 1511) was a Renaissance music theorist and composer from the Low Countries. Up to his time, he is perhaps the most significant European writer ...
, and Loyset Compère
Loyset Compère ( – 16 August 1518) was a Franco-Flemish composer of the Renaissance. Of the same generation as Josquin des Prez, he was one of the most significant composers of motets and chansons of that era, and one of the first musicians ...
, all of whom were decisive in the development of the polyphonic style of the next generation. During this period he probably wrote his mass based on '' L'homme armé'', and he may be the author of the chanson ''Il sera par vous – L'homme armé'', which uses the same cantus firmus; the latter composition may have been inspired by Philip the Good
Philip III (french: Philippe le Bon; nl, Filips de Goede; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) was Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonge ...
's call for a new crusade against the Turks, who had recently captured Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. He also wrote a Requiem
A Requiem or Requiem Mass, also known as Mass for the dead ( la, Missa pro defunctis) or Mass of the dead ( la, Missa defunctorum), is a Mass of the Catholic Church offered for the repose of the soul or souls of one or more deceased persons, ...
mass around 1460, which is lost.
After an illness of several weeks, Du Fay died on 27 November 1474. He had requested that his motet ''Ave regina celorum'' be sung for him at his deathbed, but time was insufficient for this to be arranged. Instead, his now-lost Requiem Mass was performed during his funeral service. Du Fay was buried in the chapel of St. Étienne in the cathedral of Cambrai; his portrait was carved onto his tombstone. After the destruction of the cathedral during the French Revolution the tombstone was lost, but it was found in 1859 (it was being used to cover a well), and is now in the Palais des Beaux Arts
The Centre for Fine Arts (french: Palais des Beaux-Arts, nl, Paleis voor Schone Kunsten) is a multi-purpose cultural venue in Brussels, Belgium. It is often referred to as BOZAR (a homophone of ''Beaux-arts'') in French or PSK in Dutch. The ...
museum in Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region, the Pref ...
.
Music
Du Fay composed in most of the common forms of the day, including masses,motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the pre-eminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to Margar ...
s, Magnificat
The Magnificat (Latin for "
s, y soul
Y, or y, is the twenty-fifth and penultimate letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. According to some authorities, it is the sixth (or sevent ...
magnifies he Lord
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
) is a canticle, also known as the Song of Mary, the Canticle of Mary and, in the Eastern Christianity, Byzantine tradition, the Ode of the Theotokos (). It is traditionally incorporated ...hymn
A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn'' ...
s, simple chant settings in fauxbourdon
Fauxbourdon (also fauxbordon, and also commonly two words: faux bourdon or faulx bourdon, and in Italian falso bordone) – French for ''false drone'' – is a technique of musical harmonisation used in the late Middle Ages and early Renaissance, ...
, and antiphon
An antiphon (Greek ἀντίφωνον, ἀντί "opposite" and φωνή "voice") is a short chant in Christian ritual, sung as a refrain. The texts of antiphons are the Psalms. Their form was favored by St Ambrose and they feature prominently ...
s within the area of sacred music, and rondeaux, ballades, virelai
A ''virelai'' is a form of medieval French verse used often in poetry and music. It is one of the three ''formes fixes'' (the others were the ballade and the rondeau) and was one of the most common verse forms set to music in Europe from the lat ...
s and a few other chanson types within the realm of secular music. None of his surviving music is specifically instrumental, although instruments were certainly used for some of his secular music, especially for the lower parts; all of his sacred music is vocal. Instruments may have been used to reinforce the voices in actual performance for almost any of his works. Seven complete Masses, 28 individual Mass movements, 15 settings of chant used in Mass propers, three Magnificats, two Benedicamus Domino settings, 15 antiphon settings (six of them Marian antiphon
Marian hymns are Christian songs focused on Mary, mother of Jesus. They are used in both devotional and liturgical services, particularly by the Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, and Lutheran churches. They are often used in the mont ...
s), 27 hymns, 22 motets (13 of these isorhythm
Isorhythm (from the Greek for "the same rhythm") is a musical technique using a repeating rhythmic pattern, called a ''talea'', in at least one voice part throughout a composition. ''Taleae'' are typically applied to one or more melodic patterns o ...
ic in the more angular, austere 14th-century style which gave way to more melodic, sensuous treble-dominated part-writing with phrases ending in the "under-third" cadence in Du Fay's youth) and 87 chansons definitely by him have survived. Of Du Fay's masses, his ''Missa se la face ay pale'' and ''Missa L'Homme armé'' are listed on AllMusic
AllMusic (previously known as All Music Guide and AMG) is an American online music database. It catalogs more than three million album entries and 30 million tracks, as well as information on musicians and bands. Initiated in 1991, the databas ...
as essential compositions. Editions of Du Fay's music include:
* Guillaume Dufay, ''Opera omnia'' (collected works in six volumes), ed. Heinrich Besseler with revisions by David Fallows. ''Corpus mensurabilis musicae'' CMM 1, Rome: American Institute of Musicology
The American Institute of Musicology (AIM) is a musicological organization that researches, promotes and produces publications on early music. Founded in 1944 by Armen Carapetyan, the AIM's chief objective is the publication of modern editions ...
, 1951–1995Further info and sample pages
* ''Die frühen Messenkompositionen von Guillaume Dufay'', ed. R. Bockhold, 1960, Tutzing
Chant settings
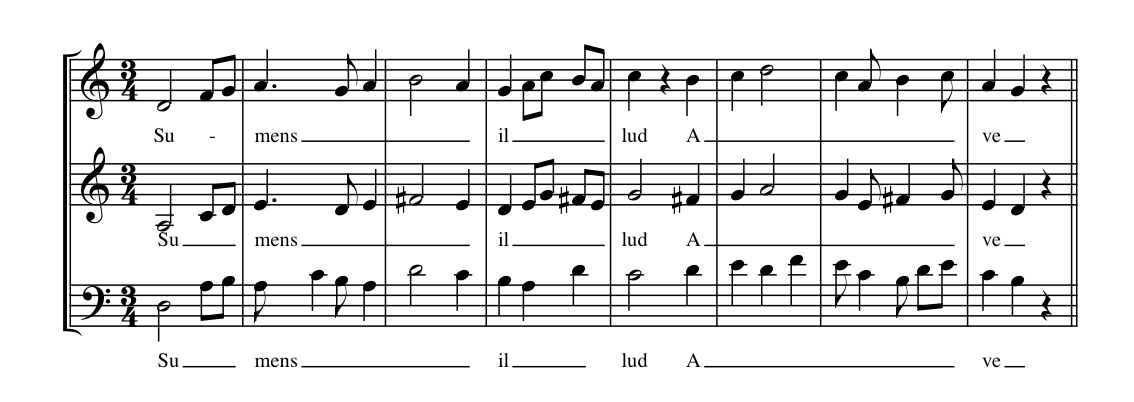
Many of Du Fay's compositions were simple settings of chant, obviously designed for liturgical use, probably as substitutes for the unadorned chant, and can be seen as chant harmonizations. Often the harmonization used a technique of parallel writing known asfauxbourdon
Fauxbourdon (also fauxbordon, and also commonly two words: faux bourdon or faulx bourdon, and in Italian falso bordone) – French for ''false drone'' – is a technique of musical harmonisation used in the late Middle Ages and early Renaissance, ...
, as in the following example, a setting of the Marian antiphon ''Ave maris stella
"Ave maris stella" (Latin for 'Hail, star of the sea') is a medieval Marian hymn, usually sung at Vespers. It was especially popular in the Middle Ages and has been used by many composers as the basis of other compositions.
Background
Authorship ...
'':
 Du Fay may have been the first composer to use the term "fauxbourdon" for this simpler compositional style, prominent in 15th century liturgical music in general and that of the Burgundian school in particular.
Du Fay may have been the first composer to use the term "fauxbourdon" for this simpler compositional style, prominent in 15th century liturgical music in general and that of the Burgundian school in particular.
Secular music
Most of Du Fay's secular songs follow theformes fixes
The ''formes fixes'' (; singular: ''forme fixe'', "fixed form") are the three 14th- and 15th-century French poetic forms: the ''ballade'', '' rondeau'', and ''virelai''. Each was also a musical form, generally a ''chanson'', and all consisted of ...
( rondeau, ballade, and virelai), which dominated secular European music of the 14th and 15th centuries. He also wrote a handful of Italian ballate
The ''ballata'' (plural: ''ballate'') is an Italian poetic and musical form in use from the late 13th to the 15th century. It has the musicapenim
AbbaA, with the first and last stanzas having the same texts. It is thus most similar to the Fre ...
, almost certainly while he was in Italy. As is the case with his motets, many of the songs were written for specific occasions, and many are datable, thus supplying useful biographical information.
Most of his songs are for three voices, using a texture dominated by the highest voice; the other two voices, unsupplied with text, were probably played by instruments. Occasionally Du Fay used four voices, but in a number of these songs the fourth voice was supplied by a later, usually anonymous, composer. Typically he used the rondeau form when writing love songs. His latest secular songs show influence from Busnois and Ockeghem, and the rhythmic and melodic differentiation between the voices is less; as in the work of other composers of the mid-15th century, he was beginning to tend towards the smooth polyphony which was to become the predominant style fifty years later.
A typical ballade is ''Resvellies vous et faites chiere lye'', which was written in 1423 for the marriage of Carlo Malatesta
Carlo I Malatesta (June 1368 – 13 September 1429) (also Carlo of Rimini) was an Italian condottiero during the Wars in Lombardy and lord of Rimini, Fano, Cesena and Pesaro. He was a member of the powerful House of Malatesta. Carlo's wife ...
and Vittoria di Lorenzo Colonna The musical form is ''aabC'' for each stanza, with ''C'' being the refrain. The musical setting emphasizes passages in the text which specifically refer to the couple being married.
Music theory writings
Two written works on music theory by Du Fay have been documented, but neither has survived. The first of these is known from the theorist Gaffurius, who wrote in the margins of both his ''Ext, uetus parvus musicae'' and ''Tractatus brevis cantus plani'' references to a ''Musica'' by Du Fay. The citations, however, are very brief and reveal nothing more than information which might be found in any music treatise of the period. Given the supposed unimportance of the treatise, the biographer Francesco Rocco Rossi questions why Gaffurius would even include the citations, and suggests that perhaps he was relying on the elder composer's authority. He concludes that "the chronological proximity between the two musicians leads us to consider this testimony faithful." The second derives from the nineteenth-century musicologistFrançois-Joseph Fétis
François-Joseph Fétis (; 25 March 1784 – 26 March 1871) was a Belgian musicologist, composer, teacher, and one of the most influential music critics of the 19th century. His enormous compilation of biographical data in the ''Biographie univer ...
, who claimed to have seen a sixteenth-century copy of a treatise ascribed to Du Fay, entitled ''Tractatus de musica mensurata et de proportionibus'' ('A Treatise on Measured Music and Proportions'). It was last documented as having been sold to a London book dealer in 1824. The testimony from Fétis remains problematic, as nothing of it is known aside from its name, making it impossible reconstruct.
If Du Fay did indeed write these works, he would be among a large tradition of 'composer-theorists', including Johannes Ciconia
Johannes Ciconia ( – between 10 June and 13 July 1412) was an important Flemish composer and music theorist of trecento music during the late Medieval era. He was born in Liège, but worked most of his adult life in Italy, particularly ...
, Franchinus Gaffurius
Franchinus Gaffurius (Franchino Gaffurio; 14 January 1451 – 25 June 1522) was an Italian music theorist and composer of the Renaissance. He was an almost exact contemporary of Josquin des Prez and Leonardo da Vinci, both of whom were his per ...
and Tinctoris, among others. It is possible that these documents are the same treatise, and the references to ''Musica'' were shorthand for the work seen by Fétis. Alternatively, Rossi notes that Fétis spoke specifically of a treatise influenced by Du Fay, which may not necessarily mean he was its author. Rossi, however, contends that the works are the same, while Planchart and Laurenz Lütteken list them separately in their catalogues.
Portraits
miniature
A miniature is a small-scale reproduction, or a small version. It may refer to:
* Portrait miniature, a miniature portrait painting
* Miniature art, miniature painting, engraving and sculpture
* Miniature (chess), a masterful chess game or probl ...
of him and Binchois from a manuscript of the poet Martin le Franc's ''Le champion des dames'', dated sometime before 1451. The illustration depicts Du Fay on the left beside a portative organ
A portative organ (from the Latin verb , "to carry"), also known during Italian Trecento as the , is a small pipe organ that consists of one rank of flue pipes, sometimes arranged in two rows, to be played while strapped to the performer at a ri ...
, with Binchois on the right holding a small harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orche ...
. It is folio 98 recto
''Recto'' is the "right" or "front" side and ''verso'' is the "left" or "back" side when text is written or printed on a leaf of paper () in a bound item such as a codex, book, broadsheet, or pamphlet.
Etymology
The terms are shortened from ...
of the manuscript, which is kept in Bibliothèque nationale de France
The Bibliothèque nationale de France (, 'National Library of France'; BnF) is the national library of France, located in Paris on two main sites known respectively as ''Richelieu'' and ''François-Mitterrand''. It is the national repository ...
( 12476). In comparison to the later depiction, Fallows characterizes the miniature as "more general in its iconography". The image's illuminator is unknown, though it was likely Barthélemy Poignare, who was the manuscript's scribe
A scribe is a person who serves as a professional copyist, especially one who made copies of manuscripts before the invention of automatic printing.
The profession of the scribe, previously widespread across cultures, lost most of its promi ...
. Regardless of the illuminator's identity, the artist probably knew Du Fay personally, as their work has been identified in other manuscripts originating in Cambrai.
The other is carving on Du Fay's funeral monument where he is kneeling in the bottom left corner. Standing behind him is Saint Waltrude
Saint Waltrude (french: Waudru; nl, Waldetrudis; german: Waltraud; la, Valdetrudis, Valtrudis, Waltrudis; died April 9, 688 AD) is the patron saint of Mons, Belgium, where she is known in French as Sainte Waudru, and of Herentals, Belgium, wher ...
of Mons, the eponymous saint of the church in Mons where he also held a benefice. To his right, three soldiers and an angel observe the resurrected Christ. The art historian Ludovic Nys has suggested it was based on a woodcut from Florence, though the art historian Douglas Brine has not found his convincing.
Legacy
Before Du Fay's time, the concept of a 'composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and Defi ...
'—that is, a musician whose primary occupation is composition
Composition or Compositions may refer to:
Arts and literature
*Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography
*Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include v ...
—was largely unfamiliar in Europe. The emergence of musicians who focused on composition above other musical endeavors arose in the 15th century, and was exemplified by Du Fay.
Du Fay was one of the last composers to make use of late-medieval polyphonic structural techniques such as isorhythm
Isorhythm (from the Greek for "the same rhythm") is a musical technique using a repeating rhythmic pattern, called a ''talea'', in at least one voice part throughout a composition. ''Taleae'' are typically applied to one or more melodic patterns o ...
, and one of the first to employ the more mellifluous harmonies, phrasing and melodies characteristic of the early Renaissance. His compositions within the larger genres (masses, motets and chansons) are mostly similar to each other; his renown is largely due to what was perceived as his perfect control of the forms in which he worked, as well as his gift for memorable and singable melody. During the 15th century he was universally regarded as the greatest composer of his time, an opinion that has largely survived to the present day.
Du Fay is the namesake of the Dufay Collective
The Dufay Collective is an Early music, early-music ensemble from the United Kingdom, specializing in Medieval music, Medieval and Renaissance music. Founded in 1987, it was named after the Renaissance composer Guillaume Dufay. The group is direc ...
, an early music
Early music generally comprises Medieval music (500–1400) and Renaissance music (1400–1600), but can also include Baroque music (1600–1750). Originating in Europe, early music is a broad musical era for the beginning of Western classical m ...
ensemble of historically informed performance
Historically informed performance (also referred to as period performance, authentic performance, or HIP) is an approach to the performance of Western classical music, classical music, which aims to be faithful to the approach, manner and style of ...
s.
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
:Books * * * * :Journal and encyclopedia articles * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * * * Free pdfs oNew Du Fay edition by Alejandro Planchart
downloadable from Digital Image Archive of Medieval Music {{DEFAULTSORT:Du Fay, Guillaume 1390s births 1397 births 1474 deaths 15th-century Franco-Flemish composers French classical composers French male classical composers People from Beersel