Guanosine Monophosphate Kinase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
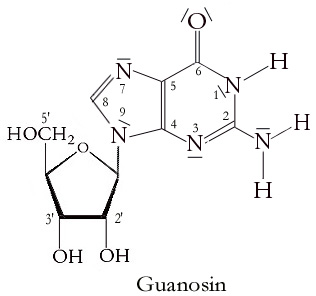
Guanosine (
Splicing (JPG)
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose ( ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine.
Physical and chemical properties
Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste. It is very soluble inacetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene and chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, HChlorine, Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to ...
.
Functions
Guanosine is required for anRNA splicing
RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). It works by removing all the introns (non-coding regions of RNA) and ''splicing'' b ...
reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene. ...
removes itself from the mRNA message by cutting at both ends, re-ligating, and leaving just the exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequen ...
s on either side to be translated into protein.
Uses
The antiviral drug acyclovir, often used in herpes treatment, and the anti-HIV drugabacavir
Abacavir, sold under the brand name Ziagen among others, is a medication used to treat HIV/AIDS. Similar to other nucleoside analog reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), abacavir is used together with other HIV medications, and is not recom ...
, are structurally similar to guanosine.Product Information: ZIAGEN(R) oral tablets, oral solution, abacavir sulfate oral tablets, oral solution. ViiV Healthcare (per Manufacturer), Research Triangle Park, NC, 2015. Guanosine was also used to make regadenoson.
Sources
Guanosine can be found in pancreas, clover, coffee plant, and pollen of pines.References
{{Purinergics Nucleosides Purines Hydroxymethyl compounds