Ground track on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A ground track or ground trace is the path on the surface of a planet directly below an
A ground track or ground trace is the path on the surface of a planet directly below an
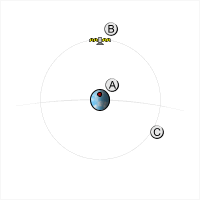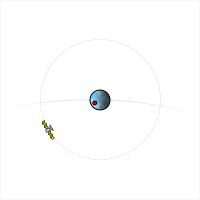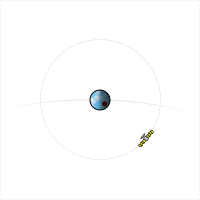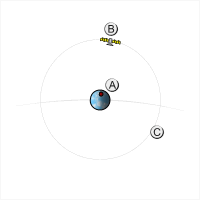 A satellite whose orbital period is an
A satellite whose orbital period is an
 As orbital operations are often required to monitor a specific location on Earth, orbits that cover the same ground track periodically are often used. On earth, these orbits are commonly referred to as Earth-repeat orbits, and are often designed with "frozen orbit" parameters to achieve a repeat ground track orbit with stable (minimally time-varying) orbit elements. These orbits use the
As orbital operations are often required to monitor a specific location on Earth, orbits that cover the same ground track periodically are often used. On earth, these orbits are commonly referred to as Earth-repeat orbits, and are often designed with "frozen orbit" parameters to achieve a repeat ground track orbit with stable (minimally time-varying) orbit elements. These orbits use the
''Satellites: Orbits and Missions''
Springer pp 175–264
Satellite Tracker
at eoPortal.org
satview.orgheavens-above.comhttps://isstracker.pl
ISS Tracker
satellite ground track
software code at smallsats.org
infosatellites.comn2yo.com
{{orbits Astrodynamics Curves Satellites Air navigation
aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. ...
's or satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
's trajectory. In the case of satellites, it is also known as a suborbital track, and is the vertical projection of the satellite's orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such a ...
onto the surface of the Earth (or whatever body the satellite is orbiting).
A satellite ground track may be thought of as a path along the Earth's surface that traces the movement of an imaginary line between the satellite and the center of the Earth. In other words, the ground track is the set of points at which the satellite will pass directly overhead, or cross the zenith
The zenith (, ) is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction ( plumb line) opposite to the gravity direction at that location ( nadir). The zenith is the "high ...
, in the frame of reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system whose origin, orientation, and scale are specified by a set of reference points― geometric points whose position is identified both mathem ...
of a ground observer..
Aircraft ground tracks
In air navigation, ground tracks typically approximate an arc of a great circle, this being the shortest distance between two points on the Earth's surface. In order to follow a specified ground track, a pilot must adjust their heading in order to compensate for the effect ofwind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
. Aircraft routes are planned to avoid restricted airspace and dangerous areas, and to pass near navigation beacons.
Satellite ground tracks
The ground track of a satellite can take a number of different forms, depending on the values of the orbital elements, parameters that define the size, shape, and orientation of the satellite's orbit. (This article discusses closed orbits, or orbits with eccentricity less than one, and thus excludes parabolic and hyperbolic trajectories.)Direct and retrograde motion
Typically, satellites have a roughly sinusoidal ground track. A satellite with an orbitalinclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a Plane of reference, reference plane and the orbital plane or Axis of rotation, axis of direction of the orbiting object ...
between zero and ninety degrees is said to be in what is called a ''direct'' or '' prograde orbit'', meaning that it orbits in the same direction as the planet's rotation. A satellite with an orbital inclination between 90° and 180° (or, equivalently, between 0° and −90°) is said to be in a '' retrograde orbit''. (Direct orbits are by far the most common for artificial satellites, as the initial velocity imparted by the Earth's rotation at launch reduces the delta-v needed to achieve orbit.)
A satellite in a direct orbit with an orbital period less than one day will tend to move from west to east along its ground track. This is called "apparent direct" motion. A satellite in a direct orbit with an orbital period ''greater'' than one day will tend to move from east to west along its ground track, in what is called "apparent retrograde" motion. This effect occurs because the satellite orbits more slowly than the speed at which the Earth rotates beneath it. Any satellite in a true retrograde orbit will always move from east to west along its ground track, regardless of the length of its orbital period.
Because a satellite in an eccentric orbit moves faster near perigee and slower near apogee, it is possible for a satellite to track eastward during part of its orbit and westward during another part. This phenomenon allows for ground tracks that cross over themselves in a single orbit, as in the geosynchronous and Molniya orbits discussed below.
Effect of orbital period
 A satellite whose orbital period is an
A satellite whose orbital period is an integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language ...
fraction of a day (e.g., 24 hours, 12 hours, 8 hours, etc.) will follow roughly the same ground track every day. This ground track is shifted east or west depending on the longitude of the ascending node, which can vary over time due to perturbations
Perturbation or perturb may refer to:
* Perturbation theory, mathematical methods that give approximate solutions to problems that cannot be solved exactly
* Perturbation (geology), changes in the nature of alluvial deposits over time
* Perturbatio ...
of the orbit. If the period of the satellite is slightly longer than an integer fraction of a day, the ground track will shift west over time; if it is slightly shorter, the ground track will shift east..
As the orbital period of a satellite increases, approaching the rotational period of the Earth (in other words, as its average orbital speed slows towards the rotational speed of the Earth), its sinusoidal ground track will become compressed longitudinally, meaning that the "nodes" (the points at which it crosses the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can al ...
) will become closer together until at geosynchronous orbit they lie directly on top of each other. For orbital periods ''longer'' than the Earth's rotational period, an increase in the orbital period corresponds to a longitudinal stretching out of the (apparent retrograde) ground track.
A satellite whose orbital period is ''equal'' to the rotational period of the Earth is said to be in a geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbit ...
. Its ground track will have a "figure eight" shape over a fixed location on the Earth, crossing the equator twice each day. It will track eastward when it is on the part of its orbit closest to perigee, and westward when it is closest to apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any el ...
.
A special case of the geosynchronous orbit, the geostationary orbit, has an eccentricity of zero (meaning the orbit is circular), and an inclination of zero in the Earth-Centered, Earth-Fixed coordinate system (meaning the orbital plane is not tilted relative to the Earth's equator). The "ground track" in this case consists of a single point on the Earth's equator, above which the satellite sits at all times. Note that the satellite is still orbiting the Earth — its apparent lack of motion is due to the fact that the Earth is rotating about its own center of mass at the same rate as the satellite is orbiting.
Effect of inclination
Orbitalinclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a Plane of reference, reference plane and the orbital plane or Axis of rotation, axis of direction of the orbiting object ...
is the angle formed between the plane of an orbit and the equatorial plane of the Earth. The geographic latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north po ...
s covered by the ground track will range from ''–i'' to ''i'', where ''i'' is the orbital inclination. In other words, the greater the inclination of a satellite's orbit, the further north and south its ground track will pass. A satellite with an inclination of exactly 90° is said to be in a polar orbit, meaning it passes over the Earth's north and south poles.
Launch sites at lower latitudes are often preferred partly for the flexibility they allow in orbital inclination; the initial inclination of an orbit is constrained to be greater than or equal to the launch latitude. Vehicles launched from Cape Canaveral, for instance, will have an initial orbital inclination of at least 28°27′, the latitude of the launch site—and to achieve this minimum requires launching with a due east azimuth
An azimuth (; from ar, اَلسُّمُوت, as-sumūt, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north.
Mathematicall ...
, which may not always be feasible given other launch constraints. At the extremes, a launch site located on the equator can launch directly into any desired inclination, while a hypothetical launch site at the north or south pole would only be able to launch into polar orbits. (While it is possible to perform an orbital inclination change maneuver once on orbit, such maneuvers are typically among the most costly, in terms of fuel, of all orbital maneuvers, and are typically avoided or minimized to the extent possible.)
In addition to providing for a wider range of initial orbit inclinations, low-latitude launch sites offer the benefit of requiring less energy to make orbit (at least for prograde orbits, which comprise the vast majority of launches), due to the initial velocity provided by the Earth's rotation. The desire for equatorial launch sites, coupled with geopolitical and logistical realities, has fostered the development of floating launch platforms, most notably Sea Launch.
Effect of argument of perigee
If the argument of perigee is zero, meaning that perigee and apogee lie in the equatorial plane, then the ground track of the satellite will appear the same above and below the equator (i.e., it will exhibit 180° rotational symmetry about the orbital nodes.) If the argument of perigee is non-zero, however, the satellite will behave differently in the northern and southern hemispheres. The Molniya orbit, with an argument of perigee near −90°, is an example of such a case. In a Molniya orbit, apogee occurs at a highlatitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north po ...
(63°), and the orbit is highly eccentric (''e'' = 0.72). This causes the satellite to "hover" over a region of the northern hemisphere for a long time, while spending very little time over the southern hemisphere. This phenomenon is known as "apogee dwell", and is desirable for communications for high latitude regions.
Repeat orbits
 As orbital operations are often required to monitor a specific location on Earth, orbits that cover the same ground track periodically are often used. On earth, these orbits are commonly referred to as Earth-repeat orbits, and are often designed with "frozen orbit" parameters to achieve a repeat ground track orbit with stable (minimally time-varying) orbit elements. These orbits use the
As orbital operations are often required to monitor a specific location on Earth, orbits that cover the same ground track periodically are often used. On earth, these orbits are commonly referred to as Earth-repeat orbits, and are often designed with "frozen orbit" parameters to achieve a repeat ground track orbit with stable (minimally time-varying) orbit elements. These orbits use the nodal precession Nodal precession is the precession of the orbital plane of a satellite around the rotational axis of an astronomical body such as Earth. This precession is due to the non-spherical nature of a rotating body, which creates a non-uniform gravitational ...
effect to shift the orbit so the ground track coincides with that of a previous orbit, so that this essentially balances out the offset in the revolution of the orbited body. The longitudinal rotation after a certain period of time of a planet is given by:
:
where
* is the time elapsed
* is the time for a full revolution of the orbiting body, in the case of Earth one sidereal day
The effect of the nodal precession Nodal precession is the precession of the orbital plane of a satellite around the rotational axis of an astronomical body such as Earth. This precession is due to the non-spherical nature of a rotating body, which creates a non-uniform gravitational ...
can be quantified as:
:
where
* is the body's second dynamic form factor
* is the body's radius
* is the orbital inclination
* is the orbit's semi-major axis
* is the orbital eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values b ...
These two effects must cancel out after a set orbital revolutions and (sidereal) days. Hence, equating the elapsed time to the orbital period of the satellite and combining the above two equations yields an equation which holds for any orbit that is a repeat orbit:
:
where
* is the standard gravitational parameter for the body being orbited
* is the number of orbital revolutions after which the same ground track is covered
* is the number of sidereal days after which the same ground track is covered
See also
* Course (navigation) *Ground tracking station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves fro ...
* Pass (spaceflight), the period in which a spacecraft is visible above the local horizon
*Satellite revisit period
The satellite revisit period is the time elapsed between observations of the same point on Earth by a satellite. It depends on the satellite's orbit, target location, and swath of the sensor.
"Revisit" is related to the same ground trace, a proj ...
, the time elapsed between observations of the same point on Earth by a satellite
* Satellite watching, as a hobby
* Terminator (solar), the moving line that separates the illuminated day side and the dark night side of a planetary body
References
''Satellites: Orbits and Missions''
Springer pp 175–264
External links
Satellite Tracker
at eoPortal.org
satview.org
ISS Tracker
satellite ground track
software code at smallsats.org
infosatellites.com
{{orbits Astrodynamics Curves Satellites Air navigation