Grenzmark Posen-Westpreußen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Frontier March of Posen-West Prussia (german: Grenzmark Posen-Westpreußen, pl, Marchia Graniczna Poznańsko-Zachodniopruska) was a
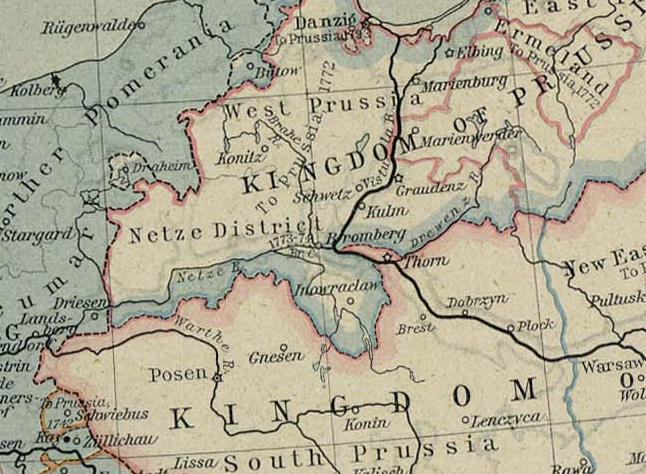 Until the late 18th century partitions of Poland, the lands which made up Posen-West Prussia had been part of the Greater Poland and East
Until the late 18th century partitions of Poland, the lands which made up Posen-West Prussia had been part of the Greater Poland and East  In 1807, during the
In 1807, during the
 Despite the name, the city of Posen, Polish:
Despite the name, the city of Posen, Polish:
 The office of an ''
The office of an ''
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
from 1922 to 1938. Posen-West Prussia was established in 1922 as a province of the Free State of Prussia
The Free State of Prussia (german: Freistaat Preußen, ) was one of the constituent states of Germany from 1918 to 1947. The successor to the Kingdom of Prussia after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, it continued to be the domina ...
within Weimar Germany
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is als ...
, formed from merging three remaining non-contiguous territories of Posen and West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 177 ...
, which had lost the majority of their territory to the Second Polish Republic and Free City of Danzig in the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
. From 1934, Posen-West Prussia was ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' ruled by Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
until it was dissolved by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, effective 1 October 1938 and its territory divided between the Prussian provinces of Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
and Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
. Schneidemühl (present-day Piła) was the provincial capital. Today, the province is entirely contained within the modern state of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
.
Background
 Until the late 18th century partitions of Poland, the lands which made up Posen-West Prussia had been part of the Greater Poland and East
Until the late 18th century partitions of Poland, the lands which made up Posen-West Prussia had been part of the Greater Poland and East Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
n (Pomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
n) regions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
and were administratively parts of the Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
, Gniezno
Gniezno (; german: Gnesen; la, Gnesna) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, ...
(Kalisz
(The oldest city of Poland)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = ''Top:'' Town Hall, Former "Calisia" Piano Factory''Middle:'' Courthouse, "Gołębnik" tenement''Bottom:'' Aerial view of the Kalisz Old Town
, image_flag = POL Kalisz flag.svg ...
before 1768) and Pomeranian Voivodeships. Following the First Partition in 1772 the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
established the West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 177 ...
n province and the Netze District
The Netze District or District of the Netze (german: link=no, Netzedistrikt or '; pl, Obwód Nadnotecki) was a territory in the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 until 1807. It included the urban centers of Bydgoszcz (''Bromberg''), Inowrocław (''In ...
on annexed Pomerelian and Greater Polish (and Kuyavia
Kuyavia ( pl, Kujawy; german: Kujawien; la, Cuiavia), also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three ...
n) territories respectively. The South Prussia
South Prussia (german: Südpreußen; pl, Prusy Południowe) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1793 to 1807.
History
South Prussia was created out of territory annexed in the Second Partition of Poland, Second P ...
n province was established following the Second Partition of 1793 and included the remainder of Greater Poland among other territories; the Third Partition in 1795 ended the existence of the Polish state entirely.
 In 1807, during the
In 1807, during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, South Prussia, the Kulmerland (part of West Prussia) and part of the Netze District, along with New Silesia
New Silesia (german: Neuschlesien or ''Neu-Schlesien'') was a small province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1795 to 1807, created after the Third Partition of Poland. It was located northwest of Kraków and southeast of Częstochowa, in the lands ...
and New East Prussia
New East Prussia (german: Neuostpreußen; pl, Prusy Nowowschodnie; lt, Naujieji Rytprūsiai) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1795 to 1807. It was created out of territory annexed in the Third Partition of the Polish–Lithuanian C ...
(excluding the area around Białystok which was ceded to Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
) were ceded to the Napoleonic client
Client(s) or The Client may refer to:
* Client (business)
* Client (computing), hardware or software that accesses a remote service on another computer
* Customer or client, a recipient of goods or services in return for monetary or other valuabl ...
Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
; Danzig was also detached from West Prussia as the Free City of Danzig. The parts of the Netze District which remained within the Kingdom of Prussia were incorporated into West Prussia. After the Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
in 1815, the Duchy of Warsaw was re-partitioned between the Grand Duchy of Posen
The Grand Duchy of Posen (german: Großherzogtum Posen; pl, Wielkie Księstwo Poznańskie) was part of the Kingdom of Prussia, created from territories annexed by Prussia after the Partitions of Poland, and formally established following the ...
under Prussia, the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
under Russia and the Free City of Cracow
The Free, Independent, and Strictly Neutral City of Cracow with its Territory, more commonly known as the Free City of Cracow, and the Republic of Cracow, was a city republic created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815, which included the Polish ...
(a joint protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its int ...
of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Prussia, and Russia); Danzig returned to West Prussia. The Grand Duchy of Posen was mostly made up of former parts of South Prussia and the Netze District, but also included the Kulmerland which had been part of West Prussia before 1807; the Kulmerland was restored to West Prussia in 1817.
In 1829 West Prussia and East Prussia were merged to form the Province of Prussia
The Province of Prussia (; ; pl, Prowincja Prusy; csb, Prowincjô Prësë) was a province of Prussia from 1829 to 1878. Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1829 from the provinces of East Prussia and West Prussia ...
, but they were restored in 1878.
Both Posen and West Prussia lay beyond the borders of the German Confederation
The German Confederation (german: Deutscher Bund, ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, w ...
and Posen was, at least nominally, semi-autonomous. Their population was predominantly Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
-speaking, while a sizable Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
German minority settled mainly in the western parts. Posen lost its semi-autonomous status after the failed Greater Poland Uprising of 1848, becoming the Province of Posen. With Prussia, these provinces became part of the North German Confederation
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated st ...
in 1867 and the unified German Empire in 1871. Ethnic tensions were exacerbated by the Germanisation policies of the Berlin government and the anti-Catholic measures enacted by Chancellor Otto von Bismarck.
History
Upon the German defeat in World War I, another Greater Poland Uprising broke out in 1918, which aimed to incorporate the lands once annexed by Prussia into a re-established Polish state. The forces of thePolish Military Organisation
The Polish Military Organisation, PMO ( pl, Polska Organizacja Wojskowa, POW) was a secret military organization which formed during World War I (1914-1918). Józef Piłsudski founded the group in August 1914; it adopted the name ''POW'' in Novem ...
were able to oust the German administration from the bulk of the Greater Polish lands, whereafter the Posen governor ('' Landeshauptmann'') Ernst von Heyking was forced to retire to Meseritz (Międzyrzecz) and ''de facto'' only ruled over the far western, predominantly German settled districts at the border with the adjacent Prussian provinces of Pomerania, Brandenburg and Silesia.
The Polish advance was halted, after the German forces had re-organised in several ''Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European military volunteer units, or paramilitary, that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenary or private armies, rega ...
'' units and the demarcation line became the basis of the ruling by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, adjudicating the parts occupied by Polish forces ''uti possidetis
''Uti possidetis'' is an expression that originated in Roman private law, where it was the name of a procedure used in litigation about land. It came from a praetorial edict that could be abbreviated "As you possess, so shall you possess". La ...
'' to the Second Polish Republic. The governmental power of the German administration was confined to the smaller western parts of Posen and West Prussia, the Prussian state government was represented by the former Bromberg supervisor (''Regierungspräsident'') Friedrich von Bülow, who relocated his administrative seat to Schneidemühl. With the entry into force of the German ''Ostmark
Ostmark is a German term meaning either Eastern march when applied to territories or Eastern Mark when applied to currencies.
Ostmark may refer to:
*the medieval March of Austria and its predecessors ''Bavarian Eastern March'' and ''March of Pann ...
'' law on 1 July 1922, the province was created out of those smaller western parts of former Posen and West Prussia that remained with the Weimar Republic.
In view of the previous clashes of arms and the "lost" territories, the remaining German population from the beginning had a strong nationalistic
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: T ...
attitude, with the national conservative German National People's Party
The German National People's Party (german: Deutschnationale Volkspartei, DNVP) was a national-conservative party in Germany during the Weimar Republic. Before the rise of the Nazi Party, it was the major conservative and nationalist party in Wei ...
(DNVP) emerging as the strongest political power in the provincial elections. Friedrich von Bülow, himself a member of the national liberal German People's Party
The German People's Party (German: , or DVP) was a liberal party during the Weimar Republic that was the successor to the National Liberal Party of the German Empire. A right-liberal, or conservative-liberal political party, it represented politi ...
, remained ''Oberpräsident'' until his retirement in 1933, whereafter he was succeeded by the Meseritz DNVP politician Hans von Meibom. After the DNVP dissolved in the course of the Nazi '' Gleichschaltung'' process, von Meibom was disempowered and replaced by the Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
''Oberpräsident'' of neighbouring Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
, Wilhelm Kube
Wilhelm Kube (13 November 1887 – 22 September 1943) was a Nazi official and German politician. He was an important figure in the German Christian movement during the early years of Nazi rule. During the war he became a senior official in the o ...
. Kube, notorious for his corruption, ruled over both provinces until he was deposed after entering into a conflict with the Nazi jurist Walter Buch
Walter Buch (24 October 1883 – 12 September 1949) was a German jurist as well as an SA and SS official during the Nazi era. He was Martin Bormann's father-in-law. As head of the Supreme Party Court, he was an important Party official. ...
, father-in-law of mighty Martin Bormann. Posen-West Prussia was further on ruled with Brandenburg under Nazi ''Oberpräsident'' Emil Stürtz until it was dissolved in 1938, when its territory was divided between the adjacent provinces of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
, Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
and Brandenburg.
Subdivision
 Despite the name, the city of Posen, Polish:
Despite the name, the city of Posen, Polish: Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
, was no longer part of the province, as it had become the capital of the re-established Greater Polish Poznań Voivodeship
Poznań Voivodeship was the name of several former administrative regions (''województwo'', rendered as ''voivodeship'' and usually translated as "province") in Poland, centered on the city of Poznań, although the exact boundaries changed over t ...
of the Second Polish Republic. The capital of the Prussian Posen-Westpreußen province and seat of the ''Oberpräsident'' supervisor was Schneidemühl. The seat of the province's '' Landeshauptmann'' elected by the ''Landtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non ...
'' assembly remained at Meseritz.
Regierungsbezirk Schneidemühl
*former Province of Posen: ;Urbandistrict
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
()
# Schneidemühl (formerly Bromberg Region)
;Rural districts ()
# Bomst (formerly Posen Region), seat at Bomst (now Babimost
Babimost (german: Bomst) is a small town in western Poland in Zielona Góra County, Lubusz Voivodeship. It is the administrative seat of Gmina Babimost. As of December 2021, it has a population of 3,847.
Geography
The town is situated on the Le ...
)
# Fraustadt (formerly Posen Region), seat at Fraustadt (now Wschowa
Wschowa (pronounced , german: Fraustadt) is a town in the Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland with 13,875 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Wschowa County and a significant tourist site containing many important historical monuments.
Hi ...
)
# Meseritz (formerly Posen Region), seat at Meseritz (now Międzyrzecz
Międzyrzecz (; la, Meserici, german: link=no, Meseritz) is a town in western Poland, on the Obra and Paklica river, with 17,667 inhabitants (2020). The capital of Gmina Międzyrzecz and Międzyrzecz County. Since the Local Government Reorganiz ...
)
# Netzekreis (formerly parts of the Czarnikau, Filehne and Kolmar districts in Bromberg Region), seat at Schönlanke (now Trzcianka
Trzcianka (; german: Schönlanke) is a town in the Greater Poland region in northwestern Poland. Since 1999, it has been part of the Greater Poland Voivodeship and Czarnków-Trzcianka County. From 1975 to 1998, it was located in the Piła Voivod ...
)
# Schwerin an der Warthe (formerly Posen Region), seat at Schwerin an der Warthe (now Skwierzyna
Skwierzyna (german: Schwerin an der Warthe) is a town of 9,671 inhabitants (2019) in Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland, the administrative seat of the Gmina Skwierzyna. It is located at the confluence of the Obra and Warta rivers, about nor ...
)
*former West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 177 ...
:
Rural districts ()
# Deutsch Krone
Deutsch or Deutsche may refer to:
*''Deutsch'' or ''(das) Deutsche'': the German language, in Germany and other places
*''Deutsche'': Germans, as a weak masculine, feminine or plural demonym
*Deutsch (word), originally referring to the Germanic ve ...
(formerly Marienwerder Region), seat at Deutsch Krone (now Wałcz
Wałcz (pronounced ; german: Deutsch Krone) is a county town in Wałcz County of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. During the years 1975 to 1998, the city was administratively part of the Piła Voivodeship.
Granted city r ...
)
# Flatow (formerly Marienwerder Region), seat at Flatow (now Złotów
Złotów (german: Flatow) is a town in northwestern Poland, with a population of 18,303 inhabitants (2011). Today it is part of Greater Poland Voivodeship (province), previously being in Piła Voivodeship (1975–1998). Since 1999 Złotów has b ...
)
# Schlochau (formerly Marienwerder Region), seat at Schlochau (now Człuchów
Człuchów (, ''Człochòwo'', or ''Człëchòwò''; formerly ) is a town in the region of Gdańsk Pomerania, northwestern Poland, with 13,350 inhabitants as of December 2021.
Człuchów has been the capital of Człuchów County in the Pomerani ...
)
Administration
Oberpräsident
The ''german: Oberpräsident, label=none'' (Supreme President) was the highest administrative official in the Prussian provinces.
History
The Oberpräsident of a Prussian province was the supreme representative of the Prussian crown, until its ...
'' (i.e. upper president) appointed by the Prussian state government had to carry out central prerogatives on the provincial level and to supervise the implementation of central policy on the lower levels of administration.
As to common interests and tasks to be fulfilled on the provincial level, such as schools, traffic installations, hospitals, cultural institutions, sanitary premises, jails etc., the urban and rural districts (''Kreise'') within each province (sometimes within each government region) formed a corporation with common assets to these ends, called Provinzialverband (provincial association, or – within government regions or smaller entities – Bezirksverband or Kommunalverband, i.e. municipal or regional association). Since 1875 all provinces had this double identity, being based on central Prussian prerogatives from above, on the one hand, and being bottom-up corporations of province-wide or region-wide self-rule, on the other hand. Initially, the assemblies of the urban and rural districts elected representatives for the provincial diets (''Provinziallandtag
The Provinces of Prussia (german: Provinzen Preußens) were the main administrative divisions of Prussia from 1815 to 1946. Prussia's province system was introduced in the Stein-Hardenberg Reforms in 1815, and were mostly organized from duchies a ...
e''; or as to regional diets, the so-called Kommunallandtage), which were thus indirectly elected.
After the end of the Prussian monarchy, the provincial or regional diets were all directly elected by the citizens of the provinces (or regions, respectively), with direct elections first held in 1921 and 1922. These parliaments legislated within the competences transferred to the provincial or regional associations. Before the formal establishment of the new Province, the rural and urban district assemblies elected representatives for the Kommunallandtag Posen-West Prussia, legislating within the competences of the former Posen and West Prussia provincial associations and its premises within the territory of the future Posen-West Prussia. After the formal formation of the province, its parliament was called the provincial diet of Posen-West Prussia which elected a provincial executive body (government), the provincial committee (''Provinzialausschuss''), and a head of province, the '' Landeshauptmann'' ("Land Captain").
Oberpräsident
* 1922–1933: Friedrich von Bülow,DVP DVP may refer to:
* ''decessit vita patris'', "died in the lifetime of his father", term used by genealogists to denote a child who pre-deceased his or her father and did not live long enough to inherit the father's title or estate.
* Delivery versu ...
* 1933–1934: Hans von Meibom, DNVP
The German National People's Party (german: Deutschnationale Volkspartei, DNVP) was a national-conservative party in Germany during the Weimar Republic. Before the rise of the Nazi Party, it was the major conservative and nationalist party in Wei ...
* 1934–1936: Wilhelm Kube
Wilhelm Kube (13 November 1887 – 22 September 1943) was a Nazi official and German politician. He was an important figure in the German Christian movement during the early years of Nazi rule. During the war he became a senior official in the o ...
, NSDAP
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
(acting), ''Oberpräsident'' of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
* 1936–1938: Emil Stürtz, NSDAP, ''Oberpräsident'' of Brandenburg
Landeshauptmann
* 1922–1933: Johannes Caspari,SPD
The Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, ; SPD, ) is a centre-left social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany.
Saskia Esken has been t ...
* 1933–1938: Hermann Fiebing, NSDAP
Population
*1910: 309,200 (in areas which later became parts of this province) *1919: 326,900 *1925: 332,400 *1933: 470,600Polish minority
After theTreaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
came into force, some members of the local Polish minority emigrated to Poland. In 1925, 13,284 people declared themselves to be either Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
-speaking or bilingual German/Polish. This corresponded to a population share of 4.3%. The share of the vote of the Polish-Catholic People's Party was stable at around 3% in all state and Reichstag elections in the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is ...
. The settlement centers of the Polish minority were unevenly distributed. According to the census of 1925, the districts of Bomst (20.6%), Flatow (16.8%) and Meseritz (5.8%) had the highest proportions of Polish speakers (including bilinguals). A special achievement of the Polish minority was the establishment of a network of Polish private schools.
See also
* Roman Catholic Territorial Prelature of SchneidemühlReferences
{{Authority control Provinces of Prussia Former administrative regions of Greater Poland 1922 establishments in Germany 1938 disestablishments in Germany Former exclaves