Greenland Sea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders
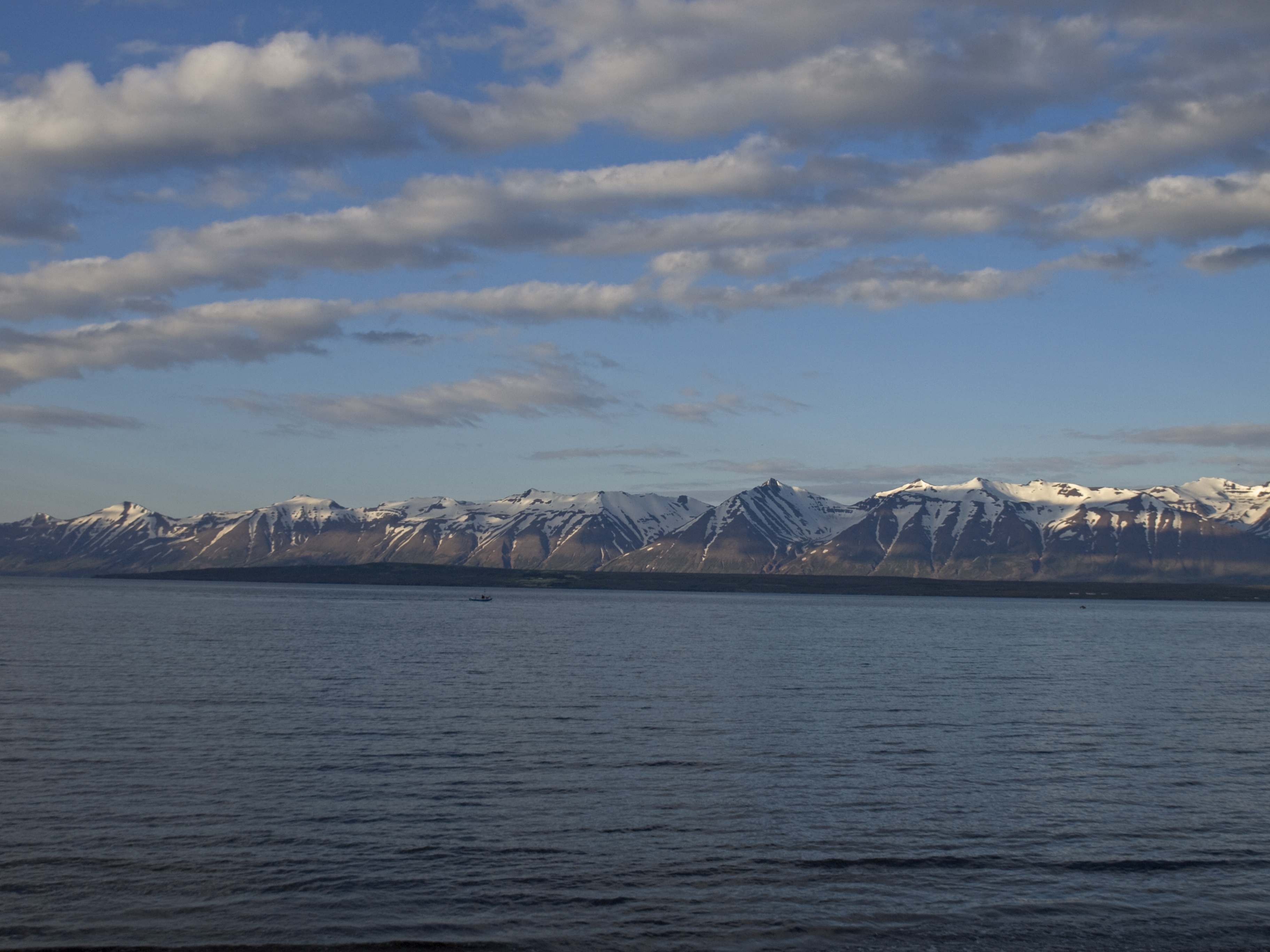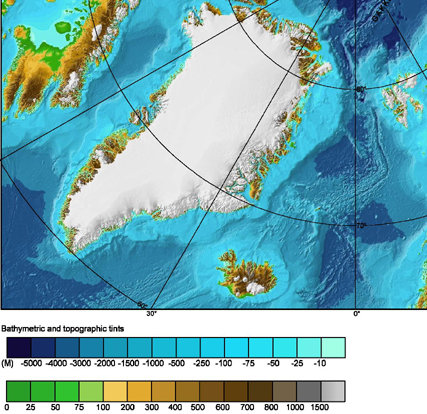
 The Greenland Sea is bounded to the west by the island of
The Greenland Sea is bounded to the west by the island of
 The climate is
The climate is
 In winter, a large area north of Iceland between
In winter, a large area north of Iceland between
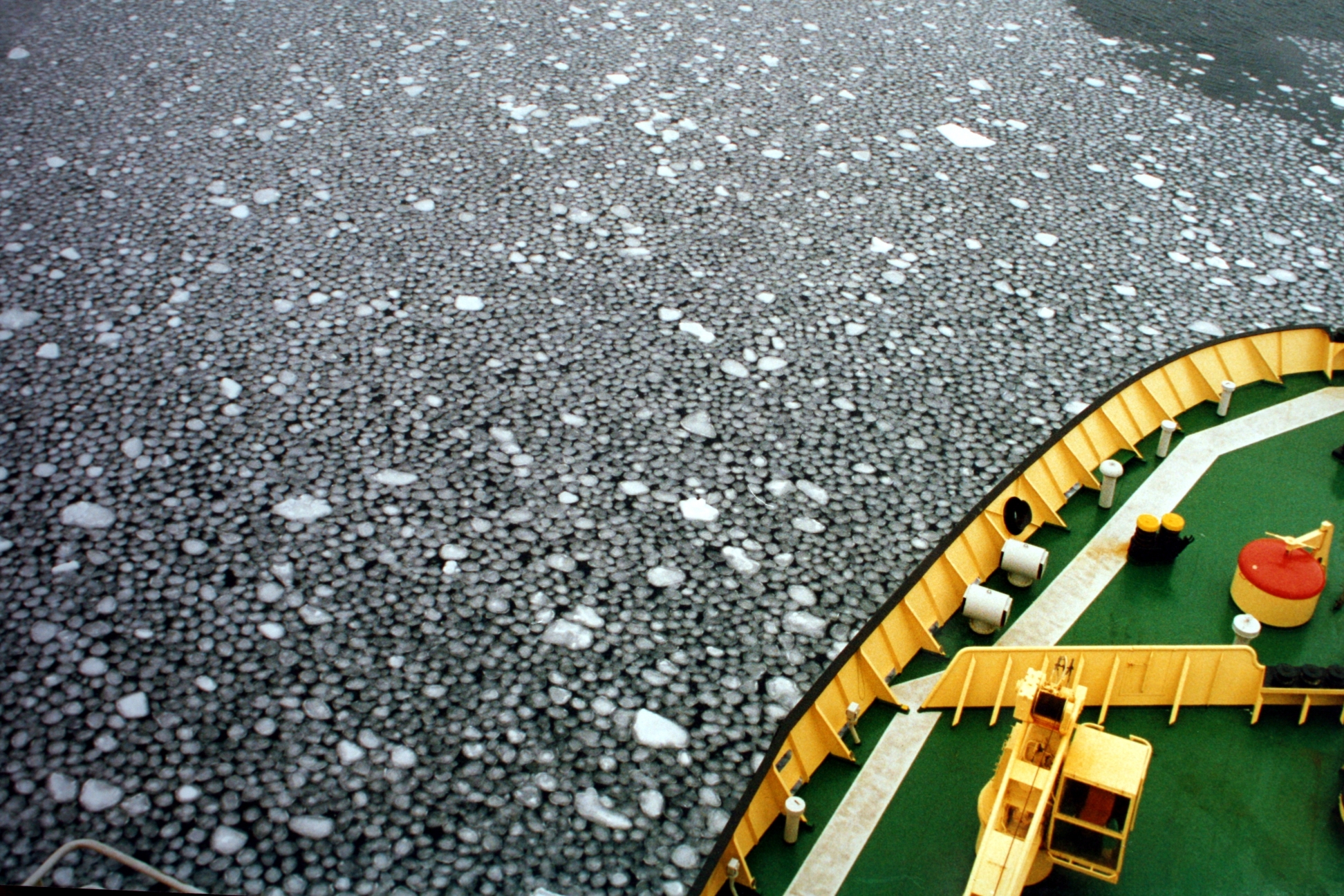 The Odden ice tongue or simply the Odden (Odden is Norwegian word for ''headland'') was a key winter ice formation area in the Arctic. It was known for a long time and was encountered by Fridtjof Nansen but was only fully understood with the advent of satellite imagery.
The Odden had a length of about and covered an area of up to in most years. It extended eastward from the main East Greenland ice edge in the vicinity of 72–74°N during the winter because of the presence of very cold polar surface water in the Jan Mayen Current, which diverts some water eastward from the East Greenland Current at that latitude. Most of the already formed ice continued floating south, driven by the wind, so a cold open water surface was exposed on which new ice formed as frazil ice and pancake ice in the rough seas, producing a giant tongue shape. The salt rejected back into the ocean from this ice formation caused the surface water to become denser and sink, sometimes to great depths ( or more), making this one of the few regions of the ocean where winter convection occurred, which helped drive the entire worldwide system of surface and deep currents known as the thermohaline circulation. Since the 1990s, the Odden ice tongue rarely develops.
The Odden ice tongue or simply the Odden (Odden is Norwegian word for ''headland'') was a key winter ice formation area in the Arctic. It was known for a long time and was encountered by Fridtjof Nansen but was only fully understood with the advent of satellite imagery.
The Odden had a length of about and covered an area of up to in most years. It extended eastward from the main East Greenland ice edge in the vicinity of 72–74°N during the winter because of the presence of very cold polar surface water in the Jan Mayen Current, which diverts some water eastward from the East Greenland Current at that latitude. Most of the already formed ice continued floating south, driven by the wind, so a cold open water surface was exposed on which new ice formed as frazil ice and pancake ice in the rough seas, producing a giant tongue shape. The salt rejected back into the ocean from this ice formation caused the surface water to become denser and sink, sometimes to great depths ( or more), making this one of the few regions of the ocean where winter convection occurred, which helped drive the entire worldwide system of surface and deep currents known as the thermohaline circulation. Since the 1990s, the Odden ice tongue rarely develops.
Measurements of the Greenland Sea ice extent
– University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
– Technical University of Denmark (DTU) {{Authority control Seas of the Arctic Ocean Seas of the Atlantic Ocean Seas of Greenland Seas of Norway Greenland–Iceland border Geography of North America Geography of Northern Europe
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...
to the west, the Svalbard archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
to the north, and the Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
and Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
, sometimes as part of the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
. However, definitions of the Arctic Ocean and its seas tend to be imprecise or arbitrary. In general usage the term "Arctic Ocean" would exclude the Greenland Sea. In oceanographic studies the Greenland Sea is considered part of the Nordic Seas, along with the Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
. The Nordic Seas are the main connection between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans and, as such, could be of great significance in a possible shutdown of thermohaline circulation
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is part of a global thermohaline circulation in the oceans and is the zonally integrated component of surface and deep currents in the Atlantic Ocean. It is characterized by a northward fl ...
. In oceanography the Arctic Ocean and Nordic Seas are often referred to collectively as the "Arctic Mediterranean Sea", a marginal sea
This is a list of seas of the World Ocean, including marginal seas, areas of water, various gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.
Terminology
* Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Oce ...
of the Atlantic.
The sea has Arctic climate
The climate of the Arctic is characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. There is a large amount of variability in climate across the Arctic, but all regions experience extremes of solar radiation in both summer and winter. ...
with regular northern winds and temperatures rarely rising above . It previously contained the Odden ice tongue (or Odden) area, which extended eastward from the main East Greenland ice edge in the vicinity of 72– 74°N during the winter and acted as a key winter ice formation area in the Arctic. The West Ice forms in winter in the Greenland Sea, north of Iceland, between Greenland and Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...
island. It is a major breeding ground of harp seal and hooded seal that has been used for seal hunting for more than 200 years.
Extent
TheInternational Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) is an intergovernmental organisation representing hydrography. , the IHO comprised 98 Member States.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ensure that the world's seas, oceans and navigable waters ...
defines the limits of the Greenland Sea as follows:
''On the North.'' A line joining the Northernmost point of SpitzbergenSvalbard">/nowiki> Svalbardto the Northernmost point of Greenland Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is .... ''On the East.'' The West coast of West Spitzbergen sland of Spitsbergen">Spitsbergen.html" ;"title="sland of Spitsbergen">sland of Spitsbergen /nowiki>. ''On the Southeast.'' A line joining the Southernmost point of West Spitzbergen to the Northern point of Jan Mayen Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...Island, down the West coast of that island to its Southern extreme, thence a Line to the Eastern extreme of Gerpir (67°05′N, 13°30′W) [''sic'', actually at ] inIceland Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its .... ''On the Southwest.'' A line joiningStraumnes Straumnes is a village in the municipality of Vågan in Nordland county, Norway. It is located just east of the village of Laukvika along the Vesterålsfjorden (a part of the Norwegian Sea) on the northwestern side of the island of Austvågøya ...(NW extreme of Iceland) to Cape Nansen () in Greenland. ''On the West.'' The East and Northeast coast of Greenland between Cape Nansen and the northernmost point.
History
While the sea has been known for millennia, the first scientific investigations were carried out in 1876–1878 as part of the Norwegian North-Atlantic Expedition. Since then, many countries, mostly Norway, Iceland and Russia have sent scientific expeditions to the area. The complex water current system in the Greenland Sea was described in 1909 by Fridtjof Nansen. The Greenland Sea was a popular hunting ground for thewhaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industry ...
industry for 300 years, until 1911, primarily based in Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern N ...
. At that point, the formerly rich whale population here, was so depleted that the industry was no longer profitable. The remaining whales of the Greenland Sea has been protected ever since, but the populations have not shown any proof of significant regeneration. Since the late 1990s, polar biologists reports an increase in the local bowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus'') is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena''. They are the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, ...
population and in 2015, arctic scientists discovered a surprising abundance of them in a small area. These results may be interpreted as an early sign of a beginning recovery for this particular species, that once formed the largest bowhead population in the world, at an estimated 52,000 whales.
The Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, ...
hunted whales on a non-industrial scale in the Greenland Sea since the 15th century, as evidenced by archaeology.
The first complete man-powered crossing of the Greenland Sea was achieved in 2017 by rowing expedition, Polar Row led by Fiann Paul.

Geography and geology
 The Greenland Sea is bounded to the west by the island of
The Greenland Sea is bounded to the west by the island of Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...
, and to the south by the Denmark Strait and Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
. To the southeast, behind the Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...
island (Norway) lies the vast expanse of the Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
, of which Greenland Sea may be considered an extension. Across the Fram Strait to the northeast, the sea is delimited by the Svalbard archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
(Norway). The southern part of the Greenland Sea, roughly the area south of the Jan Mayen Francture Zone or the line Cape Brewster – Jan Mayen is sometimes referred to as Iceland Sea
The Iceland Sea is a small body of water delimited by the Jan Mayen fracture zone to the north, Greenland to the west, the Denmark Strait to the south, and the Jan Mayen Ridge to the east. Depths usually range from 500 to 2,000 meters but can be ...
.
The bottom of the Greenland Sea is a depression bounded to the south by the underwater Greenland-Iceland ridge and to the east by the Mohns Ridge and Knipovich Ridge (parts of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge). To the west, the bottom rises first slowly, but then rapidly toward the wide Greenland coastal strip. Silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel wh ...
s fill the submarine hollows and gorges; silty sands, gravel, boulders, and other products of erosion coat the shelves and ridges.
Although the deepest point inside of the sea is , depths down to have been measured in the Molloy Deep of the Fram Strait which connects the sea to the Arctic Ocean on the north. The Greenland ice sheet
The Greenland ice sheet ( da, Grønlands indlandsis, kl, Sermersuaq) is a vast body of ice covering , roughly near 80% of the surface of Greenland. It is sometimes referred to as an ice cap, or under the term ''inland ice'', or its Danish equ ...
reaches down to the sea at Jokel Bay.
Major islands of the Greenland Sea include the Svalbard archipelago, Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...
as well as coastal islands off the NE Greenland shores, such as Hovgaard, Ella, Godfred Hansen
Gudfred was a ninth century Danish king who reigned from at least 804 to 810. Alternate spellings include ''Godfred'' (Danish), ''Göttrick'' (German), ''Gøtrik'' (Danish), ''Gudrød'' (Danish), and ''Godofredus'' (Latin). He stands at the thres ...
, Île-de-France
The Île-de-France (, ; literally "Isle of France") is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France. Centred on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the country and often called the ''Région parisienne'' (; en, Pa ...
, Lynn
Lynn may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Lynn (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Lynn (surname)
* The Lynns, a 1990s American country music duo consisting of twin sisters Peggy and Patsy Lynn
* Lynn ( ...
, Norske, Gamma and Schnauder islands. Of those, only the Svalbard islands are inhabited, and Jan Mayen has only temporal military staff. After the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
gave Norway jurisdiction over the island, in 1921 Norway opened the first meteorological station there, which was a subject of contention between Germany and United Kingdom during World War II.Rigge, Simon (1980), ''War in the Outposts'', pp. 24–25. Alexandria, Virginia: Time-Life Books, . Several radio and meteorological stations operate on the island nowadays.
Hydrology, climate, and ice
 The climate is
The climate is Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada ( Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm ( Greenland), Finland, Iceland ...
and varies significantly across the vast sea area.
Air temperatures fluctuate between near Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern N ...
in winter and off Greenland in summer. Averages are in the south and in the north in February, which is the coldest month. The corresponding values for the warmest month, August, are in the south and in the north. The summer is very short: The number of days per year when the temperature rises above varies between 225 in the north to 334 in the south. The annual precipitation is in the north, but in the south.
Northern winds continue through the whole year, cooling the surface water and bringing ice to the south. The average surface water temperature is about or lower in the north and in the south; the corresponding summer temperatures are about respectively. The bottom water temperatures are below . The surface water salinity is 3.30–3.45% in the eastern and below 3.20% in the western parts, increasing to 3.49% toward the bottom. The water is green. Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables can ...
s are semidiurnal with the average height of . Together with the water currents, they break up the floating ice sheets and mix various water layers both laterally and along the depth.
The progressively colder waters of North Atlantic Current
The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five ocean ...
sink in the Arctic Ocean, returning south in the form of cold East Greenland Current, an important part of the Atlantic conveyor belt, which flows along the western part of the sea. Along the eastern part flows the warm Spitsbergen Current
The West Spitsbergen Current (WSC) is a warm, salty current that runs poleward just west of Spitsbergen, (formerly called West Spitsbergen), in the Arctic Ocean. The WSC branches off the Norwegian Atlantic Current in the Norwegian Sea. The WSC i ...
, a part of Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Uni ...
. Mixtures of cold, freshwater ice melt and the warm, salty Spitsbergen Current may experience cabbeling, which might contribute to thermohaline circulation. The combination of those currents creates a counter-clockwise water flow in the central part of the sea.
Because of frequent fogs, winds, and currents, which continuously transport ice and icebergs through the Greenland Sea to the south, the Greenland Sea has a narrow window for commercial navigation: The ice season starts in October and ends in August. Three types of floating ice are distinguished: Arctic pack ice (several meters thick), sea ice (about a meter thick), and freshwater icebergs.
West Ice
 In winter, a large area north of Iceland between
In winter, a large area north of Iceland between Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...
and Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...
, called West Ice, is covered by continuous ice. It is a major breeding ground for seals, including harp seal, hooded seal, and gray seal. It was discovered in the early 18th century by British whalers and since late 1750s was used for seal hunting. The hunting was especially intensive in the 19th century, but declined in the 20th century because of hunting restrictions and lower market demand. Around 5 April 1952, a major storm resulted in disappearance of ships with 79 Norwegian seal hunters on board. Seven other Norwegian seal hunting vessels shipwrecked the same month.
Odden ice tongue
 The Odden ice tongue or simply the Odden (Odden is Norwegian word for ''headland'') was a key winter ice formation area in the Arctic. It was known for a long time and was encountered by Fridtjof Nansen but was only fully understood with the advent of satellite imagery.
The Odden had a length of about and covered an area of up to in most years. It extended eastward from the main East Greenland ice edge in the vicinity of 72–74°N during the winter because of the presence of very cold polar surface water in the Jan Mayen Current, which diverts some water eastward from the East Greenland Current at that latitude. Most of the already formed ice continued floating south, driven by the wind, so a cold open water surface was exposed on which new ice formed as frazil ice and pancake ice in the rough seas, producing a giant tongue shape. The salt rejected back into the ocean from this ice formation caused the surface water to become denser and sink, sometimes to great depths ( or more), making this one of the few regions of the ocean where winter convection occurred, which helped drive the entire worldwide system of surface and deep currents known as the thermohaline circulation. Since the 1990s, the Odden ice tongue rarely develops.
The Odden ice tongue or simply the Odden (Odden is Norwegian word for ''headland'') was a key winter ice formation area in the Arctic. It was known for a long time and was encountered by Fridtjof Nansen but was only fully understood with the advent of satellite imagery.
The Odden had a length of about and covered an area of up to in most years. It extended eastward from the main East Greenland ice edge in the vicinity of 72–74°N during the winter because of the presence of very cold polar surface water in the Jan Mayen Current, which diverts some water eastward from the East Greenland Current at that latitude. Most of the already formed ice continued floating south, driven by the wind, so a cold open water surface was exposed on which new ice formed as frazil ice and pancake ice in the rough seas, producing a giant tongue shape. The salt rejected back into the ocean from this ice formation caused the surface water to become denser and sink, sometimes to great depths ( or more), making this one of the few regions of the ocean where winter convection occurred, which helped drive the entire worldwide system of surface and deep currents known as the thermohaline circulation. Since the 1990s, the Odden ice tongue rarely develops.
Fauna
The Greenland Sea is densely inhabited by the organisms that form the base of the oceanic food chain. Largeinvertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
(such as cod, herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Ocea ...
, redfish, halibut, and plaice), birds, and mammals (including various species of seals, whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s, and dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s) all feed on the smaller invertebrates and small organism
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
s. Mosses, lichens, and scanty bushes around the coasts serve as food to the deer and musk oxen, which in turn are hunted by the polar bear.
The Greenland Sea was formerly home to a large population of various whale species, especially bowhead whales, but the whaling industry decimated them greatly from the beginning of the 1600s till 1911. In the last few decades there have been a few signs indicating a beginning recovery.
Oil and gas
US Geological Survey has estimated that at least 13% of the world's undiscovered oil deposits and 30% of the world's undiscovered gas pockets are located in the Arctic, with the Greenland Sea potentially holding large amounts ofnatural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
and lesser amounts of natural gas liquids and crude oil. This has led the Greenland's minister and provincial council to offer a large number of off-shore concessions to potential hydrocarbon (oil and gas) extraction. The majority of the concessions are located in seas west of Greenland (primarily the Davis Strait and Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay (Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; kl, Avannaata Imaa; french: Baie de Baffin), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Ar ...
), but with 19 concessions in the Greenland Sea.
In late 2013, a total of three consortia obtained hydrocarbon extraction rights to four large areas of the Greenland Sea from the Greenland Bureau of Mineral and Petroleum. The consortia are led by the oil companies of Statoil, Chevron, and Eni
Eni S.p.A. () is an Italian multinational energy company headquartered in Rome. Considered one of the seven "supermajor" oil companies in the world, it has operations in 69 countries with a market capitalization of US$54.08 billion, as of 11 Ap ...
, but includes several other smaller companies such as Shell, British Petroleum, DONG Energy
Dong or DONG may refer to:
Places
* Dong Lake, or East Lake, a lake in China
* Dong, Arunachal Pradesh, a village in India
* Dong (administrative division) (동 or 洞), a neighborhood division in Korea
Persons
* Queen Dong (1623–1681), pri ...
and Nunaoil. Since then, a fifth hydrocarbon concession has been sold. Exxon Mobil, the largest oil company in the world and with a lot of experience in the Arctic, was also applying for oil extraction rights in the Greenland Sea initially, but pulled out in December 2013 for unexplained reasons, concentrating efforts on shale gas and the American market instead.
Drilling for oil in deep waters in an ice-filled Arctic environment is a potential new undertaking for the oil industry, and poses many risks and dangers. Because of these difficulties, the Greenland Minister Council expects the first exploratory drills to take place no sooner than the mid 2020s. They estimate that a full preliminary program with seismic surveys, exploratory drills, and proper safety measures will take about 16 years and an investment of about US$500 million in each concession.
See also
* List of seasReferences
Further reading
Measurements of the Greenland Sea ice extent
– University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
– Technical University of Denmark (DTU) {{Authority control Seas of the Arctic Ocean Seas of the Atlantic Ocean Seas of Greenland Seas of Norway Greenland–Iceland border Geography of North America Geography of Northern Europe