Great Bustard on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The great bustard (''Otis tarda'') is a bird in the

 The adult male great bustard is amongst the heaviest living flying animals. A male is typically tall, with a length of around and has a wingspan. The male can range in weight from . The heaviest verified specimen, collected in
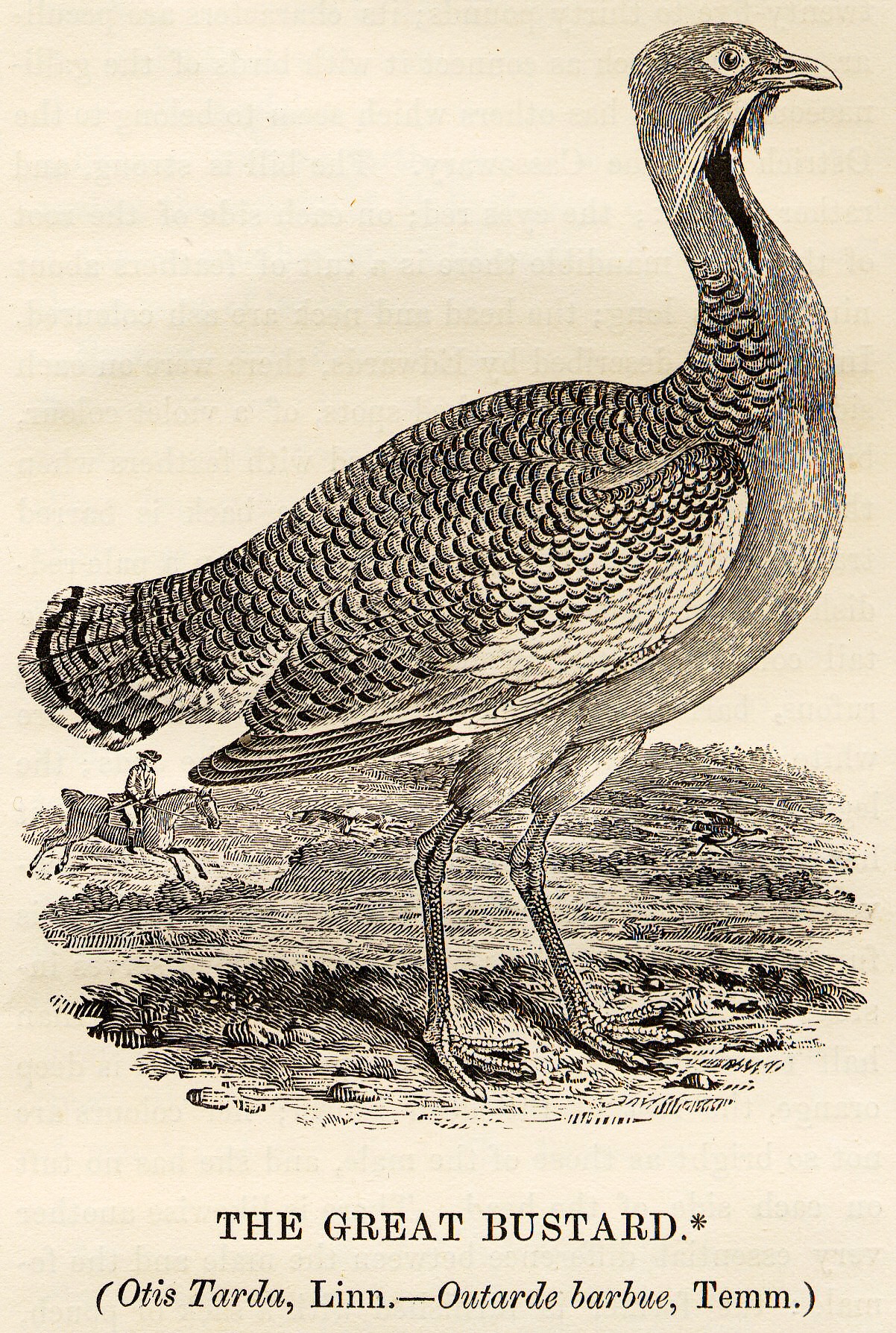
The adult male great bustard is amongst the heaviest living flying animals. A male is typically tall, with a length of around and has a wingspan. The male can range in weight from . The heaviest verified specimen, collected in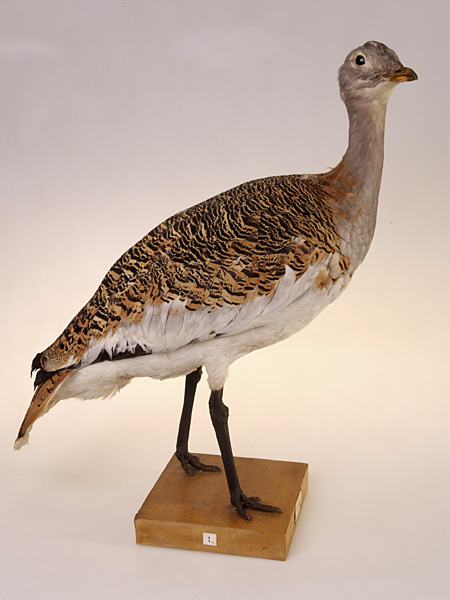  An adult male is brown above, barred with blackish colouration, and white below, with a long grey neck and head. His breast and lower neck sides are chestnut and there is a golden wash to the back and the extent of these bright colours tending to increase as the male ages. In the breeding season, the male has long white neck bristles, which measure up to in length, continually growing from the third to the sixth year of life. In flight, the long wings are predominantly white with brown showing along the edges of the lower primary and secondary feathers and a dark brown streak along the upper-edge of the wing. The breast and neck of the female are buff, with brown and pale colouration over the rest of the plumage rendering it well camouflaged in open habitats. Immature birds resemble the female. The eastern subspecies (''O. t. dybowskii'') is more extensively grey in colour in both sexes, with more extensive barring on the back. The great bustard has long legs, a long neck and a heavy, barrel-chested body. It is fairly typical of the family in its overall shape and habitat preferences. Three other bustard species overlap in range with this species: the Macqueen's (''Chlamydotis macqueenii''), houbara (''Chlamydotis undulata'') and
An adult male is brown above, barred with blackish colouration, and white below, with a long grey neck and head. His breast and lower neck sides are chestnut and there is a golden wash to the back and the extent of these bright colours tending to increase as the male ages. In the breeding season, the male has long white neck bristles, which measure up to in length, continually growing from the third to the sixth year of life. In flight, the long wings are predominantly white with brown showing along the edges of the lower primary and secondary feathers and a dark brown streak along the upper-edge of the wing. The breast and neck of the female are buff, with brown and pale colouration over the rest of the plumage rendering it well camouflaged in open habitats. Immature birds resemble the female. The eastern subspecies (''O. t. dybowskii'') is more extensively grey in colour in both sexes, with more extensive barring on the back. The great bustard has long legs, a long neck and a heavy, barrel-chested body. It is fairly typical of the family in its overall shape and habitat preferences. Three other bustard species overlap in range with this species: the Macqueen's (''Chlamydotis macqueenii''), houbara (''Chlamydotis undulata'') and
 These birds'
These birds'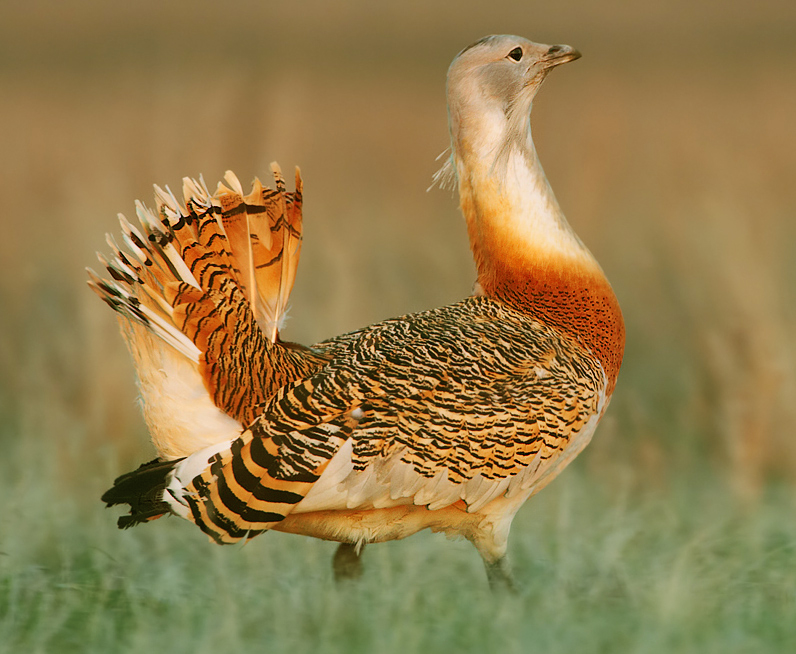 
 As of 2008, the global population numbered between 44,000 and 51,000 birds (Palacin & Alonso 2008), about 38,000 to 47,000 in Europe, with 30,000 or more than half in Spain. Hungary had the next largest Great Bustard population with about 1,555 in the year 2012, followed by Ukraine and Austria. Between 4,200 and 4,500 were found in east Asia. In recent times, there have been steep declines throughout eastern and central Europe and in Asia, particularly in Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Sizeable populations exist in
As of 2008, the global population numbered between 44,000 and 51,000 birds (Palacin & Alonso 2008), about 38,000 to 47,000 in Europe, with 30,000 or more than half in Spain. Hungary had the next largest Great Bustard population with about 1,555 in the year 2012, followed by Ukraine and Austria. Between 4,200 and 4,500 were found in east Asia. In recent times, there have been steep declines throughout eastern and central Europe and in Asia, particularly in Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Sizeable populations exist in
 The great bustard is classified as vulnerable at the species level. There are myriad threats faced by great bustards. Increasing human disturbance could lead to habitat loss caused by the ploughing of grasslands, intensive agriculture, afforestation, increased development of irrigation schemes, and the construction of roads, power lines, fencing and ditches. Mechanisation, chemical fertilizers and pesticides, fire and predation by dogs are serious threats for chicks and juveniles, and hunting of adults contributes to high mortality in some of their range countries. Agricultural activity is a major disturbance at nest and, in Hungary, few successful nests are found outside of protected areas.
Bustards, despite their large size, are able to fly at high speed and are often mutilated or killed by overhead electricity cables, which are placed in the West Pannonia region of Eastern Austria and Western Hungary just at their flying height. The electricity companies affected have buried part of the dangerous cables, and have marked remaining aerial parts with fluorescent markers to warn off the birds. These measures have rapidly reduced bustard mortality. Bustards are also occasionally killed by collisions with automobiles or by entanglement in wires.
The great bustard is classified as vulnerable at the species level. There are myriad threats faced by great bustards. Increasing human disturbance could lead to habitat loss caused by the ploughing of grasslands, intensive agriculture, afforestation, increased development of irrigation schemes, and the construction of roads, power lines, fencing and ditches. Mechanisation, chemical fertilizers and pesticides, fire and predation by dogs are serious threats for chicks and juveniles, and hunting of adults contributes to high mortality in some of their range countries. Agricultural activity is a major disturbance at nest and, in Hungary, few successful nests are found outside of protected areas.
Bustards, despite their large size, are able to fly at high speed and are often mutilated or killed by overhead electricity cables, which are placed in the West Pannonia region of Eastern Austria and Western Hungary just at their flying height. The electricity companies affected have buried part of the dangerous cables, and have marked remaining aerial parts with fluorescent markers to warn off the birds. These measures have rapidly reduced bustard mortality. Bustards are also occasionally killed by collisions with automobiles or by entanglement in wires.
 The great bustard was formerly native in
The great bustard was formerly native in
CMS Great Bustard Memorandum of Understanding
*
Field Guide Page on Flickr
* * {{Taxonbar, from=Q171655 Otididae, great bustard Birds of Eurasia Birds described in 1758, great bustard Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus, great bustard
bustard
Bustards, including floricans and korhaans, are large, terrestrial birds living mainly in dry grassland areas and on the steppes of the Old World. They range in length from . They make up the family Otididae (, formerly known as Otidae). Bustards ...
family, and it is the only living member of the genus ''Otis
Otis may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Characters
* Otis (Superman), in the films ''Superman'' and ''Superman II'' and related DC Comics media
** Otis Graves, in the TV series ''Supergirl''
* Otis (The Walking Dead), Otis (''The Walking Dead' ...
''. It breeds in open grasslands and farmland from northern Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
, South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
and Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area' ...
, to temperate Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and ...
. European populations are mainly resident, but Asian populations migrate
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
farther south in winter. It has been listed as a Vulnerable species
A vulnerable species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being threatened species, threatened with extinction unless the circumstances that are threatened species, ...
on the IUCN Red List since 1996.
Portugal and Spain now have about 60% of the world's population. It was driven to extinction in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, when the last bird was shot in 1832. Recent attempts to reintroduce it into England have met with some success, and there is a population of about 40 birds on Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain is a chalk plateau in the south western part of central southern England covering . It is part of a system of chalk downlands throughout eastern and southern England formed by the rocks of the Chalk Group and largely lies wi ...
, a British Army training area. Here, the lack of public access and disturbance allows them the seclusion they (and other animals) desire, especially as a large, ground-nesting bird.
Taxonomy
Thegenus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
''Otis
Otis may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Characters
* Otis (Superman), in the films ''Superman'' and ''Superman II'' and related DC Comics media
** Otis Graves, in the TV series ''Supergirl''
* Otis (The Walking Dead), Otis (''The Walking Dead' ...
'' was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
''; it came from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
name ''ōtis'' used for this species taken from '' Natural History'' by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
published around 77 AD which briefly mentions a bird like it, it was also given the name ''ōtidos'' and the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''aves tardas'' mentioned by the Pierre Belon
Pierre Belon (1517–1564) was a French traveller, naturalist, writer and diplomat. Like many others of the Renaissance period, he studied and wrote on a range of topics including ichthyology, ornithology, botany, comparative anatomy, architectur ...
in 1555 and Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi (11 September 1522 – 4 May 1605) was an Italian naturalist, the moving force behind Bologna's botanical garden, one of the first in Europe. Carl Linnaeus and the comte de Buffon reckoned him the father of natural history st ...
in 1600.
The specific epithet ''tarda'' comes from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word ''tardus'' for "slow" and "deliberate", which is apt to describe the typical walking style of the species. The Latin phrase ''avis tarda'' "slow bird" is where the word ''bustard
Bustards, including floricans and korhaans, are large, terrestrial birds living mainly in dry grassland areas and on the steppes of the Old World. They range in length from . They make up the family Otididae (, formerly known as Otidae). Bustards ...
'' comes from borrowing Old French ''bistarda''.

Description
 The adult male great bustard is amongst the heaviest living flying animals. A male is typically tall, with a length of around and has a wingspan. The male can range in weight from . The heaviest verified specimen, collected in
The adult male great bustard is amongst the heaviest living flying animals. A male is typically tall, with a length of around and has a wingspan. The male can range in weight from . The heaviest verified specimen, collected in Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer Manc ...
, was about , a world record for heaviest flying bird. In a study in Spain, one male weighed as much as . Larger specimens have been reported but remain unverified. Average male weights as reported have been fairly variable: in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, males weighed a median of ; in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, males weighed a mean of during breeding season and during non-breeding; in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, males weighed a mean of ; and the Guinness World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world ...
has indicated that male bustards in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
weighed an average of . Average weight of males is almost an exact match to that of male Kori bustards. Among all flying animals and land birds, male Andean condor
The Andean condor (''Vultur gryphus'') is a giant South American Cathartid vulture and is the only member of the genus ''Vultur''. Found in the Andes mountains and adjacent Pacific coasts of western South America, the Andean condor is the larg ...
s (''Vultur gryphus'') may match or exceed the mean body masses of these male bustards but not their maximum weights. Furthermore, male swan
Swans are birds of the family (biology), family Anatidae within the genus ''Cygnus''. The swans' closest relatives include the goose, geese and ducks. Swans are grouped with the closely related geese in the subfamily Anserinae where they form t ...
s of the two largest species (trumpeter
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B ...
and mute
Muteness is a speech disorder in which a person lacks the ability to speak.
Mute or the Mute may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Mute'' (2005 film), a short film by Melissa Joan Hart
* ''Mute'' (2018 film), a scien ...
) may attain a similar average mass depending on season and region. Among both bustards and all living birds, the upper reported mass of this species is rivaled by that of the kori bustard
The kori bustard (''Ardeotis kori'') is the largest flying bird native to Africa. It is a member of the bustard family, which all belong to the order Otidiformes and are restricted in distribution to the Old World. It is one of the four species ( ...
(''Ardeotis kori''), which, due to its relatively longer tarsi and tail, is both longer and taller on average and is less sexually dimorphic. In terms of weight ranges reported, the great Indian bustard
The great Indian bustard (''Ardeotis nigriceps'') or Indian bustard, is a bustard found on the Indian subcontinent. A large bird with a horizontal body and long bare legs, giving it an ostrich like appearance, this bird is among the heaviest of t ...
(''Ardeotis nigriceps'') also only lags slightly behind these species.
The great bustard is also arguably the most sexual dimorphic extant bird species, in terms of the size difference between males and females. Adult male great bustards measured in Spain weighed on average 2.48 times more than females. Going on mass, the only known bird with a higher dimorphism is the green peafowl
The green peafowl or Indonesian peafowl (''Pavo muticus'') is a peafowl species native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. It has been listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List since 2009 because the global population has been declining r ...
(''Pavo muticus'') as the males are apparently near four times as heavy as females. The female is about a third smaller in linear dimensions, typically measuring in height, about in length and across the wings. Overall, the female's weight can range from . Like male weights, females weights are quite variable as reported: in Germany, females had a mean weight of , in Spain, females had a mean weight of and in Russia, females reportedly had a median weight of . The latter figure indicates that eastern birds (presumably ''O. t. dybowskii'') are considerably less sexually dimorphic in body mass than in other populations. Perhaps because of this physical sexual dimorphism, there is a skewed sex ratio of about 1.5:1 female to male.
 An adult male is brown above, barred with blackish colouration, and white below, with a long grey neck and head. His breast and lower neck sides are chestnut and there is a golden wash to the back and the extent of these bright colours tending to increase as the male ages. In the breeding season, the male has long white neck bristles, which measure up to in length, continually growing from the third to the sixth year of life. In flight, the long wings are predominantly white with brown showing along the edges of the lower primary and secondary feathers and a dark brown streak along the upper-edge of the wing. The breast and neck of the female are buff, with brown and pale colouration over the rest of the plumage rendering it well camouflaged in open habitats. Immature birds resemble the female. The eastern subspecies (''O. t. dybowskii'') is more extensively grey in colour in both sexes, with more extensive barring on the back. The great bustard has long legs, a long neck and a heavy, barrel-chested body. It is fairly typical of the family in its overall shape and habitat preferences. Three other bustard species overlap in range with this species: the Macqueen's (''Chlamydotis macqueenii''), houbara (''Chlamydotis undulata'') and
An adult male is brown above, barred with blackish colouration, and white below, with a long grey neck and head. His breast and lower neck sides are chestnut and there is a golden wash to the back and the extent of these bright colours tending to increase as the male ages. In the breeding season, the male has long white neck bristles, which measure up to in length, continually growing from the third to the sixth year of life. In flight, the long wings are predominantly white with brown showing along the edges of the lower primary and secondary feathers and a dark brown streak along the upper-edge of the wing. The breast and neck of the female are buff, with brown and pale colouration over the rest of the plumage rendering it well camouflaged in open habitats. Immature birds resemble the female. The eastern subspecies (''O. t. dybowskii'') is more extensively grey in colour in both sexes, with more extensive barring on the back. The great bustard has long legs, a long neck and a heavy, barrel-chested body. It is fairly typical of the family in its overall shape and habitat preferences. Three other bustard species overlap in range with this species: the Macqueen's (''Chlamydotis macqueenii''), houbara (''Chlamydotis undulata'') and little bustard
The little bustard (''Tetrax tetrax'') is a bird in the bustard family, the only member of the genus ''Tetrax''. The genus name is from Ancient Greek and refers to a gamebird mentioned by Aristophanes and others. Distribution
It breeds in Southe ...
s (''Tetrax tetrax''). However, none of these attains the plumage coloration nor approach the body sizes of this species. Thus, the great bustard is essentially unmistakable.
Habitat
 These birds'
These birds' habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
is grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
or steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
defined by open, flat or somewhat rolling landscapes. They can be found on undisturbed cultivation and seem to prefer areas with wild or cultivated crops such as cereals, vineyards and fodder plants. However, during the breeding season, they actively avoid areas with regular human activity and can be disturbed by agricultural practices. Great bustards are often attracted to areas with considerable insect activity.
The breeding range of the great bustard currently stretches from Portugal to Manchuria, though previously the species bred even further east in Russian Primorsky Krai. Due to population declines across much of the range, more than half of the global population is now found in central Spain with around 30,000 individuals. Smaller populations are in southern Russia and the Great Hungarian Plain.

Behaviour
The species is gregarious, especially in winter when gatherings of several dozen birds may occur. Male and female groups do not mix outside of the breeding season. The great bustard has a stately slow walk but tends to run when disturbed rather than fly. Running speeds have not been measured but adult females have been known to outrunred fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
es (''Vulpes vulpes''), which can reach a trotting speed of . Both sexes are usually silent but can engage in deep grunts when alarmed or angered. The displaying adult male may produce some booming, grunting and raucous noises. The female may utter some guttural calls at the nest and brooded young make a soft, trilling call in communication with their mothers.
Migration
Some individuals in Iberian populations make short seasonal movements of 5 – 200 km, particularly males which appear to move in response to higher summer temperatures. European populations are sedentary or make irregular movements in response to severe winter weather. Populations breeding along the Volga River in Russia migrate 1000 km to overwinter in Crimea and Kherson Oblast. Populations breeding in northern Mongolia migrate over 2000 km to overwinter in Shaanxi Province of China. In migratory populations, great bustards often gather in larger numbers at pre-migratory sites in order to move collectively to winter grounds. In theIberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, bustards that engage in migration seem to choose different periods for movements based on sex. No population is known to use the same grounds for wintering and summering. Great Bustards are strong fliers and reach speeds of 48 km/hr (30 mph) to 98 km/hr (60 miles/hr)during migration.
Reproduction
The great bustard breeds in March, and a single male may mate with up to five females. Before mating, the males moult into their breeding plumage around January. Males establish dominance in their groups during winter, clashing violently by ramming into and hitting each other with their bills. Like other bustards, the male great bustard displays and competes for the attention of females on what is known as alek
Lek or LEK may refer to:
* Lek mating, mating in a lek, a type of animal territory in which males of a species gather
* Albanian lek, the currency of Albania
* Lek (magazine), a Norwegian softcore pornographic magazine
* Lek (pharmaceutical comp ...
. In this species, the male has a flamboyant display beginning with the strutting male puffing up his throat to the size of a football. He then tilts forwards and pulls his head in so that the long whiskery chin feathers point upwards and the head is no longer visible. He next cocks his tail flat along his back, exposing the normally hidden bright white plumage then he lowers his wings, with the primary flight feathers folded but with the white secondaries fanning out. The displaying males, who may walk around for several minutes at a time with feathers flared and head buried waiting for hens to arrive, have been described as a "foam-bath" because of their appearance. All breeding great bustards also moult again from June to September.
One to three olive or tan coloured, glossy eggs (two eggs being the average) are laid by the female in May or June. The nests, which are shallow scrapes made by the female on dry, soft slopes and plains, are usually situated close to the prior lek location. Nests are situated in sparse clusters, with a study in Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
finding nests at a minimal apart from each other. In the same study, nests were placed at mid-elevation on a hill, at about . Nesting sites are typically in dense grassy vegetation about , likely for protection against predation, with extensive exposure to sunlight. Eggs weigh about and are on average tall by wide. The female incubates the eggs alone for 21 to 28 days. The chicks almost immediately leave the nest after they hatch, although they do not move very far from their mother until they are at least 1 year old. Young great bustards begin developing their adult plumage at about 2 months, and begin to develop flying skills at the same time. They practice by stretching, running, flapping, and making small hops and jumps to get airborne. By three months they are able to fly reasonable distances. If threatened, the young stand still, using their downy plumage, mainly sepia in colour with paler buffy streaks, as camouflage. Juveniles are independent by their first winter, but normally stay with their mother until the next breeding season. Males usually start to mate from 5 to 6 years of age, although may engage in breeding display behaviour at a younger age. Females usually first breed at 2 to 3 years old.
Diet
The species isomnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutri ...
, taking different foods in differing seasons. In northwestern Spain in August, 48.4% of the diet of adult birds was green plant material, 40.9% was invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s and 10.6% was seeds. In the same population during winter, seeds and green plant material constituted almost the entirety of the diet. Alfalfa
Alfalfa () (''Medicago sativa''), also called lucerne, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as w ...
is seemingly preferred in the diet of birds from Spain. Other favoured plant life in the diet can including legumes, Brassicaceae, crucifers, Taraxacum officinale, common dandelion and grapes and the dry seeds of wheat and barley. Among animal prey, insects are generally eaten and are the main food for young bustards in their first summer, though they then switch to the seasonal herbivorous preferences of adults by winter. Coleoptera (including beetles), Hymenoptera (including bees, wasps and ants) and Orthoptera (including cricket (insect), crickets, grasshoppers and locusts) are mainly taken, largely based on availability and abundance. Small vertebrates, including small rodents, frogs, lizards and chicks of other birds, may supplement the diet when the opportunity arises. Great bustards may eat toxic blister beetles of the genus ''Meloe'' to self-medicate (Zoopharmacognosy) increasing sexual arousal of males. Some plants selected in the mating season showed in-vitro activity against laboratory models of parasites and pathogens.
Foraging
In winter the feeding intensity increased and then decreased through the morning in both sexes, and was lower in flocks of males than in flocks of females. This sexual difference is greater where legume availability was smaller in central Spain. Males that foraged slightly less intensively than females could compensate with longer periods of foraging and bigger bite size that would allow them to obtain enough food relative to their absolute daily energy requirements. The size of morning foraging area is smaller in sites with more legume availability, likely because legumes are the most preferred substrate type.Mortality
Great bustards typically live for around 10 years, but some have been known to live up to 15 years or more. The maximum known life span for the species was 28 years. Adult males seem to have a higher mortality rate than females due mainly to fierce intraspecies fighting with other males during the breeding season. Many males may perish in their first couple of years of maturity due to this cause. Although little detailed information has been obtained of predators, over 80% of great bustards die in the first year of life and many are victims of predation. Chicks are subject to predation by the fact that they are ground-dwelling birds which are reluctant to fly. Predators of bird egg, eggs and hatchlings include Bird of prey, raptors, corvids, hedgehogs, foxes, weasels, badgers (''Meles'' ssp.), martens (''Martes'' ssp.), rats (''Rattus'' ssp.) and wild boars (''Sus scrofa''). The most serious natural predators of nests are perhapsred fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
es and hooded crows (''Corvus cornix''). Chicks grow very quickly, by 6 months being nearly two-thirds of their adult size, and are predated by foxes, lynxes, gray wolf, wolves (''Canis lupus''), dogs, jackals and eagles. Predation on adult male great bustards has been reportedly committed by white-tailed eagles (''Haliaeetus albicilla'') while golden eagles (''Aquila chrysaetos'') are potential predators and eastern imperial eagles (''Aquila heliaca'') have been known to prey on great bustards (but not likely to include adult males).Love, J.A. (1983). ''The return of the Sea Eagle''. Cambridge University Press, . Great bustards of unspecified age and sex have been found amongst Eurasian eagle-owl (''Bubo bubo'') prey remains in Bulgaria. A possible act of predation on a great bustard was observed to be committed by a much smaller raptor, the western marsh harrier (''Circus aeruginosus''), though it was likely that this bustard was "weak or injured" if it was taken alive. The bold, conspicuous behaviour of the breeding adult male bustard may attract the same large mammalian predators that predate chicks, such as wolves and lynx, while the more inconspicuous female may sometimes be attacked by various predators. However, predation is generally fairly rare for adults due to their size, nimbleness and safety in numbers due to their social behaviour.
Occasionally, other natural causes may contribute to mortality in the species, especially starvation in harsh winter months. However, major causes of mortality in recent centuries have been largely linked to human activity, as described below.
Population distribution
 As of 2008, the global population numbered between 44,000 and 51,000 birds (Palacin & Alonso 2008), about 38,000 to 47,000 in Europe, with 30,000 or more than half in Spain. Hungary had the next largest Great Bustard population with about 1,555 in the year 2012, followed by Ukraine and Austria. Between 4,200 and 4,500 were found in east Asia. In recent times, there have been steep declines throughout eastern and central Europe and in Asia, particularly in Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Sizeable populations exist in
As of 2008, the global population numbered between 44,000 and 51,000 birds (Palacin & Alonso 2008), about 38,000 to 47,000 in Europe, with 30,000 or more than half in Spain. Hungary had the next largest Great Bustard population with about 1,555 in the year 2012, followed by Ukraine and Austria. Between 4,200 and 4,500 were found in east Asia. In recent times, there have been steep declines throughout eastern and central Europe and in Asia, particularly in Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Sizeable populations exist in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
(23,055 birds), Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
(8,000 birds), Turkey (800–3,000 birds), Portugal (1,435 birds) and Mongolia (1,000 birds). In Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Austria the populations are small (Germany 2016: 232 birds; Austria 2012: 335 birds) but steadily growing for about two decades. Elsewhere, the populations are declining due to habitat loss throughout its range. A sizeable population also exists in Hungary (1,100–1,300 birds) where the Eastern European steppe zone ends, near Dévaványa town and also in the Hortobágy National Park, Nagykunság and Nagy-Sárrét regions. The population is down from a population of 10,000–12,000 before the Second World War.
Agrienvironment schemes as unirrigated legumes fostered a population increase of great bustards in Castilla y Leon, central Spain.
Threats and conservation status
 The great bustard is classified as vulnerable at the species level. There are myriad threats faced by great bustards. Increasing human disturbance could lead to habitat loss caused by the ploughing of grasslands, intensive agriculture, afforestation, increased development of irrigation schemes, and the construction of roads, power lines, fencing and ditches. Mechanisation, chemical fertilizers and pesticides, fire and predation by dogs are serious threats for chicks and juveniles, and hunting of adults contributes to high mortality in some of their range countries. Agricultural activity is a major disturbance at nest and, in Hungary, few successful nests are found outside of protected areas.
Bustards, despite their large size, are able to fly at high speed and are often mutilated or killed by overhead electricity cables, which are placed in the West Pannonia region of Eastern Austria and Western Hungary just at their flying height. The electricity companies affected have buried part of the dangerous cables, and have marked remaining aerial parts with fluorescent markers to warn off the birds. These measures have rapidly reduced bustard mortality. Bustards are also occasionally killed by collisions with automobiles or by entanglement in wires.
The great bustard is classified as vulnerable at the species level. There are myriad threats faced by great bustards. Increasing human disturbance could lead to habitat loss caused by the ploughing of grasslands, intensive agriculture, afforestation, increased development of irrigation schemes, and the construction of roads, power lines, fencing and ditches. Mechanisation, chemical fertilizers and pesticides, fire and predation by dogs are serious threats for chicks and juveniles, and hunting of adults contributes to high mortality in some of their range countries. Agricultural activity is a major disturbance at nest and, in Hungary, few successful nests are found outside of protected areas.
Bustards, despite their large size, are able to fly at high speed and are often mutilated or killed by overhead electricity cables, which are placed in the West Pannonia region of Eastern Austria and Western Hungary just at their flying height. The electricity companies affected have buried part of the dangerous cables, and have marked remaining aerial parts with fluorescent markers to warn off the birds. These measures have rapidly reduced bustard mortality. Bustards are also occasionally killed by collisions with automobiles or by entanglement in wires.
 The great bustard was formerly native in
The great bustard was formerly native in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
and a bustard forms part of the design of the Wiltshire Coat of arms, Coat of Arms and as supporters for the Cambridgeshire arms. As early as 1797, the naturalist and wood engraver Thomas Bewick commented in his ''A History of British Birds'' that "Both this [the little bustard] and the Great Bustard are excellent eating, and would well repay the trouble of domestication; indeed, it seems surprising, that we should suffer these fine birds to be in danger of total extinction, although, if properly cultivated, they might afford as excellent a repast as our own domestic poultry, or even as the Turkey, for which we are indebted to distant countries." Bewick's prediction was correct; the great bustard was hunted out of existence in Britain by the 1840s.
In 2004, a project overseeing the reintroduction to Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain is a chalk plateau in the south western part of central southern England covering . It is part of a system of chalk downlands throughout eastern and southern England formed by the rocks of the Chalk Group and largely lies wi ...
in Wiltshire using eggs taken from Saratov Oblast, Saratov in Russia was undertaken by The Great Bustard Group, a UK Registered Charity that aims to establish a self-sustaining population of great bustards in the UK. The reintroduced birds have laid eggs and raised chicks in Britain in 2009 and 2010. Although the great bustard was once native to Britain, great bustards are considered an alien species under English law. The reintroduction of the great bustard to the UK by the Great Bustard Group is being carried out in parallel with researchers from the University of Bath who are providing insight into the habitat of native great bustard populations in Russia and Hungary. On January 19, 2011, it was announced that the Great Bustard Project had been awarded EU The LIFE Programme, LIFE+ funding, reportedly to the tune of £1.8 million. By 2020 the population in Wiltshire exceeded 100 birds. In Hungary, where the species is the List of national birds, national bird, great bustards are actively protected. The Hungarian authorities are seeking to preserve the long-term future of the population by active protection measures; the area affected by the special ecological treatment had grown to by the summer of 2006.
Under the auspices of the Bonn Convention, Convention on Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), also known as the Bonn Convention, Great Bustard Memorandum of Understanding, the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on the Conservation and Management of Middle-European Populations of the Great Bustard was concluded and came into effect on June 1, 2001. The MoU provides a framework for governments, scientists, conservation bodies and others to monitor and coordinate conservation efforts in order to protect the middle-European populations of the great bustard.
Notes
References
Further reading
* *External links
*CMS Great Bustard Memorandum of Understanding
*
Field Guide Page on Flickr
* * {{Taxonbar, from=Q171655 Otididae, great bustard Birds of Eurasia Birds described in 1758, great bustard Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus, great bustard