Grand Conjunction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A great conjunction is a conjunction of the planets Jupiter and
A great conjunction is a conjunction of the planets Jupiter and
 On average, great conjunction seasons occur once every 19.859 Julian years (each of which is 365.25 days). This number can be calculated by the synodic period formula
:
in which and are the orbital periods of Jupiter (4332.59 days) and Saturn (10759.22 days), respectively. This is about 52 days less than 20 years, but in practice, Earth's orbit size can cause great conjunctions to reoccur anytime between 18 years 10 months and 20 years 8 months after the previous one. (See table below.) Since the equivalent periods of other naked-eye planet pairs are all under 900 days, this makes great conjunctions the rarest.
Occasionally there is more than one great conjunction in a season, which happens whenever they're close enough to opposition: this is called a triple conjunction (which is not exclusive to great conjunctions). In this scenario, Jupiter and Saturn will occupy the same
On average, great conjunction seasons occur once every 19.859 Julian years (each of which is 365.25 days). This number can be calculated by the synodic period formula
:
in which and are the orbital periods of Jupiter (4332.59 days) and Saturn (10759.22 days), respectively. This is about 52 days less than 20 years, but in practice, Earth's orbit size can cause great conjunctions to reoccur anytime between 18 years 10 months and 20 years 8 months after the previous one. (See table below.) Since the equivalent periods of other naked-eye planet pairs are all under 900 days, this makes great conjunctions the rarest.
Occasionally there is more than one great conjunction in a season, which happens whenever they're close enough to opposition: this is called a triple conjunction (which is not exclusive to great conjunctions). In this scenario, Jupiter and Saturn will occupy the same
 When studying the great conjunction of 1603,
When studying the great conjunction of 1603,
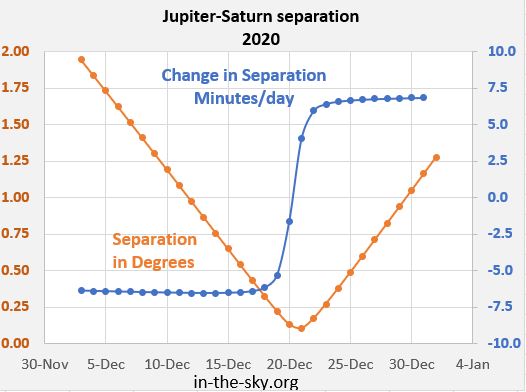 The great conjunction of 2020 was the closest since 1623 and eighth closest of the first three millennia AD, with a minimum separation between the two planets of 6.1
The great conjunction of 2020 was the closest since 1623 and eighth closest of the first three millennia AD, with a minimum separation between the two planets of 6.1
File:Grosse.Konjunktion.P1080051.jpg, Photograph taken two days before closest approach with a separation of approximately 15 arcminutes.
File:Great Conjunction image photographed on December 19, 2020.jpg, Great conjunction photographed on December 19, 2020, with a SCT telescope and color CCD.
File:2020 Great Conjunction simulation by NASA, labeled, 2020-12-21 2215UTC.jpg, Simulated best-case scenario view through a telescope.
File:CodysLab great conjunction clip.gif, Video created using photographs of the event taken over a span of 90 days.
File:Saturn—Jupiter—Conjunction.jpg, Photograph of the great conjunction of 2020 taken two days before closest approach with the four
Orbital Motion Simulation of Jupiter and Saturn
at GeoGebra
The December 21, 2020 Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn
The exceptional conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn on December 21, 2020!
Great Conjunctions
{{DEFAULTSORT:Great Conjunction Astrometry Astrological aspects Conjunctions (astronomy and astrology) Jupiter Saturn
 A great conjunction is a conjunction of the planets Jupiter and
A great conjunction is a conjunction of the planets Jupiter and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, when the two planets appear closest together in the sky. Great conjunctions occur approximately every 20 years when Jupiter "overtakes" Saturn in its orbit. They are named "great" for being by far the rarest of the conjunctions between naked-eye planets
In classical antiquity, the seven classical planets or seven luminaries are the seven moving astronomical objects in the sky visible to the naked eye: the Moon, Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, the Sun, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. The word ''pla ...
(i.e. excluding Uranus and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
).
The spacing between the planets varies from conjunction to conjunction with most events being 0.5 to 1.3 degrees (30 to 78 arcminutes, or 1 to 2.5 times the width of a full moon). Very close conjunctions happen much less frequently (though the maximum of 1.3° is still close by inner planet standards): separations of less than 10 arcminutes have only happened four times since 1200, most recently in 2020.
In history
Great conjunctions attracted considerable attention in the past as omens. During the late Middle Ages and Renaissance they were a topic broached by the pre-scientific and transitional astronomer-astrologers of the period up to the time of Tycho Brahe andJohannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
, by scholastic thinkers such as Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiri ...
and Pierre d'Ailly, and they are mentioned in popular and literary works by authors such as Dante Lope de Vega
Félix Lope de Vega y Carpio ( , ; 25 November 156227 August 1635) was a Spanish playwright, poet, and novelist. He was one of the key figures in the Spanish Golden Age of Baroque literature. His reputation in the world of Spanish literature ...
and Shakespeare. This interest is traced back in Europe to translations of Arabic texts especially Albumasar's book on conjunctions.
Despite mathematical errors and some disagreement among astrologers about when trigons began, belief in the significance of such events generated a stream of publications that grew steadily until the end of the 16th century. As the great conjunction of 1583 was last in the water trigon it was widely supposed to herald apocalyptic changes; a papal bull against divination was issued in 1586 but as nothing significant happened by the feared event of 1603, public interest rapidly died. By the start of the next trigon, modern scientific consensus had long-established astrology as pseudoscience, and planetary alignments were no longer perceived as omens.Keith Thomas, ''Religion and the Decline of Magic: Studies in Popular Beliefs in Sixteenth and Seventeenth-Century England'' ( Oxford University Press, 1971) p. 414-415,
Celestial mechanics
 On average, great conjunction seasons occur once every 19.859 Julian years (each of which is 365.25 days). This number can be calculated by the synodic period formula
:
in which and are the orbital periods of Jupiter (4332.59 days) and Saturn (10759.22 days), respectively. This is about 52 days less than 20 years, but in practice, Earth's orbit size can cause great conjunctions to reoccur anytime between 18 years 10 months and 20 years 8 months after the previous one. (See table below.) Since the equivalent periods of other naked-eye planet pairs are all under 900 days, this makes great conjunctions the rarest.
Occasionally there is more than one great conjunction in a season, which happens whenever they're close enough to opposition: this is called a triple conjunction (which is not exclusive to great conjunctions). In this scenario, Jupiter and Saturn will occupy the same
On average, great conjunction seasons occur once every 19.859 Julian years (each of which is 365.25 days). This number can be calculated by the synodic period formula
:
in which and are the orbital periods of Jupiter (4332.59 days) and Saturn (10759.22 days), respectively. This is about 52 days less than 20 years, but in practice, Earth's orbit size can cause great conjunctions to reoccur anytime between 18 years 10 months and 20 years 8 months after the previous one. (See table below.) Since the equivalent periods of other naked-eye planet pairs are all under 900 days, this makes great conjunctions the rarest.
Occasionally there is more than one great conjunction in a season, which happens whenever they're close enough to opposition: this is called a triple conjunction (which is not exclusive to great conjunctions). In this scenario, Jupiter and Saturn will occupy the same right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When paired w ...
on three occasions or same ecliptic longitude on three occasions, depending on which definition of "conjunction" one uses (this is due to apparent retrograde motion
Apparent retrograde motion is the apparent motion of a planet in a direction opposite to that of other bodies within its system, as observed from a particular vantage point. Direct motion or prograde motion is motion in the same direction as ...
and happens within months). The most recent triple conjunction occurred in 1980–81 and the next will be in 2238–39.
The most recent great conjunction occurred on 21 December 2020, and the next will occur on 4 November 2040. During the 2020 great conjunction, the two planets were separated in the sky by 6 arcminutes
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
at their closest point, which was the closest distance between the two planets since 1623. The closeness is the result of the conjunction occurring in the vicinity of one of the two longitudes where the two orbits appear to intersect when viewed from the Sun (which has a point of view similar to Earth).
Because 19.859 years is equal to 1.674 Jupiter orbits and 0.674 Saturn orbits, three of these periods come close to a whole number of revolutions. This is why the longitude cycle, as shown in the diagram to the right, has a triangular pattern. The three points of the triangle revolve in the same direction as the planets at the rate of approximately one-sixth of a revolution per four centuries thus creating especially close conjunctions on an approximately four-century cycle. Currently the longitudes of close great conjunctions are about 307.4 and 127.4 degrees, in the constellations Capricornus and Cancer respectively. The position of Earth in its orbit, however, can make the planets appear up to about 10 degrees ahead of or behind their heliocentric longitude.
Saturn's orbit plane is inclined 2.485 degrees relative to Earth's, and Jupiter's is inclined 1.303 degrees. The ascending nodes of both planets are similar (100.6 degrees for Jupiter and 113.7 degrees for Saturn), meaning if Saturn is above or below Earth's orbital plane Jupiter usually is too. Because these nodes align so well it would be expected that no closest approach will ever be much worse than the difference between the two inclinations. Indeed, between year 1 and 3000, the maximum conjunction distances were 1.3 degrees in 1306 and 1940. Conjunctions in both years occurred when the planets were tilted most out of the plane: longitude 206 degrees (therefore above the plane) in 1306, and longitude 39 degrees (therefore below the plane) in 1940.
List of great conjunctions (1200 to 2400)
The following table details great conjunctions in between 1200 and 2400. The dates are given for the conjunctions inright ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When paired w ...
(the dates for conjunctions in ecliptic longitude can differ by several days). Dates before 1582 are in the Julian calendar while dates after 1582 are in the Gregorian calendar.
Longitude is measured counterclockwise from the location of the First Point of Aries (the location of the March equinox) at epoch J2000. This non-rotating coordinate system doesn't move with the precession of Earth's axes, thus being suited for calculations of the locations of stars. (In astrometry
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, the Milky Way.
His ...
latitude and longitude are based on the ecliptic which is Earth's orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time Earth ...
extended sunward and anti-sunward indefinitely.) The other common conjunction coordinate system is measured counterclockwise in right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When paired w ...
from the First Point of Aries and is based on Earth's equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
and the meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
of the equinox point both extended upwards indefinitely; ecliptic separations are usually smaller.
Distance is the angular separation between the planets in sixtieths of a degree ( minutes of arc) and elongation is the angular distance from the Sun in degrees. An elongation between around −20 and +20 degrees indicates that the Sun is close enough to the conjunction to make it difficult or impossible to see, sometimes more difficult at some geographic latitudes and less difficult elsewhere. Note that the exact moment of conjunction cannot be seen everywhere as it is below the horizon or it is daytime in some places, but a place on Earth affects minimum separation less than it would if an inner planet was involved. Negative elongations indicate the planet is west of the Sun (visible in the morning sky), whereas positive elongations indicate the planet is east of the Sun (visible in the evening sky).
The great conjunction series is roughly analogous to the Saros series
The saros () is a period of exactly 223 synodic months, approximately 6585.3211 days, or 18 years, 10, 11, or 12 days (depending on the number of leap years), and 8 hours, that can be used to predict eclipses of the Sun and Moon. One saros period a ...
for solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six month ...
s (which are Sun–Moon conjunctions). Conjunctions in a particular series occur about 119.16 years apart. The reason it is every six conjunctions instead of every three is that 119.16 years is closer to a whole number of years than = 59.58 is, so Earth will be closer to the same position in its orbit and conjunctions will appear more similar. All series will have progressions where conjunctions gradually shift from only visible before sunrise to visible throughout the night to only visible after sunset and finally back to the morning sky again. The location in the sky of each conjunction in a series should increase in longitude by 16.3 degrees on average, making one full cycle relative to the stars on average once every 2,634 years. If instead we use the convention of measuring longitude eastward from the First Point of Aries, we have to keep in mind that the equinox circulates once every c. 25,772 years, so longitudes measured that way increase slightly faster and those numbers become 17.95 degrees and 2,390 years.
A conjunction can be a member of a triple conjunction. In a triple conjunction, the series does not advance by one each event as the constellation and year is the same or close to it, this is the only time great conjunctions can be less than about 20 years apart.
Notable great conjunctions
7 BC
 When studying the great conjunction of 1603,
When studying the great conjunction of 1603, Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
thought that the Star of Bethlehem might have been the occurrence of a great conjunction. He calculated that a triple conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn occurred in 7 BC (−6 using astronomical year numbering);
1563
The astronomers from theCracow Academy
The Jagiellonian University (Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
(Jan Muscenius Jan Muscenius, (Jan Muszczeński alias Jan Mucha, 1532 – 21 July 1602) was a Polish astronomer, theologian, and the rector of Kraków Academy (now Jagiellonian University).
Life
Jan Muscenius was born in Kurzelów, Sandomierz Province, and l ...
, Stanisław Jakobejusz, Nicolaus Schadeck, Petrus Probosczowicze, and others) observed the great conjunction of 1563 to compare Alfonsine tables (based on a geocentric model
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, an ...
) with the Prutenic Tables (based on Copernican heliocentrism). In the Prutenic Tables the astronomers found Jupiter and Saturn so close to each other that Jupiter covered Saturn (actual angular separation was 6.8 minutes on 25 August 1563). The Alfonsine tables suggested that the conjunction should be observed on another day but on the day indicated by the Alfonsine tables the angular separation was a full 141 minutes. The Cracow professors suggested following the more accurate Copernican predictions and between 1578 and 1580 Copernican heliocentrism was lectured on three times by Valentin Fontani.
This conjunction was also observed by Tycho Brahe, who noticed that the Copernican and Ptolemaic tables used to predict the conjunction were inaccurate. This led him to realise that progress in astronomy required systematic, rigorous observation, night after night, using the most accurate instruments obtainable.
2020
 The great conjunction of 2020 was the closest since 1623 and eighth closest of the first three millennia AD, with a minimum separation between the two planets of 6.1
The great conjunction of 2020 was the closest since 1623 and eighth closest of the first three millennia AD, with a minimum separation between the two planets of 6.1 arcminutes
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
. This great conjunction was also the most easily visible close conjunction since 1226 (as the previous close conjunctions in 1563 and 1623 were closer to the Sun and therefore more difficult to see). It occurred seven weeks after the heliocentric conjunction, when Jupiter and Saturn shared the same heliocentric longitude.
The closest separation occurred on 21 December at 18:20 UTC, when Jupiter was 0.1° south of Saturn and 30° east of the Sun. This meant both planets appeared together in the field of view of most small- and medium-sized telescopes (though they were distinguishable from each other without optical aid). During the closest approach, both planets appeared to be a binary object to the naked eye. From mid-northern latitudes, the planets were visible one hour after sunset at less than 15° in altitude above the southwestern horizon in the constellation of Capricornus.
The conjunction attracted considerable media attention, with news sources calling it the "Christmas Star" due to the proximity of the date of the conjunction to Christmas, and for a great conjunction being one of the hypothesized explanations for the biblical Star of Bethlehem.
Gallery
Galilean moons
The Galilean moons (), or Galilean satellites, are the four largest moons of Jupiter: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. They were first seen by Galileo Galilei in December 1609 or January 1610, and recognized by him as satellites of Jupiter ...
visible around Jupiter. (Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
can also be seen to the right of Saturn.)
File:KoniunkcjaJS.gif, December 21, 2020, Jupiter and Saturn, 130mm Bresser Messier
File:Grande congiunzione Giove Saturno 22 dicembre 2020ok.jpg, Photograph depicting the great conjunction, taken from Syracuse, Italy.
File:Great conjunction.jpg, Photograph of Jupiter and Saturn with the Moon on 16 December 2020
7541
As well as being a triple conjunction, the great conjunction of 7541 is expected to feature two occultations: one partial on 16 February, and one total on 17 June. However, the accuracy of planetary positions this far into the future is highly uncertain, so some calculations of planetary positions predict very close conjunctions in 7541 instead of occultations. This will be the first occultation between the two planets since 6857 BC; superimposition requires a separation of less than approximately 0.4 arcminutes.See also
*Positional astronomy
Spherical astronomy, or positional astronomy, is a branch of observational astronomy used to locate astronomical objects on the celestial sphere, as seen at a particular date, time, and location on Earth. It relies on the mathematical methods of ...
Notes
References
External links
Orbital Motion Simulation of Jupiter and Saturn
at GeoGebra
The December 21, 2020 Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn
The exceptional conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn on December 21, 2020!
Great Conjunctions
{{DEFAULTSORT:Great Conjunction Astrometry Astrological aspects Conjunctions (astronomy and astrology) Jupiter Saturn