Graduated (measurement) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
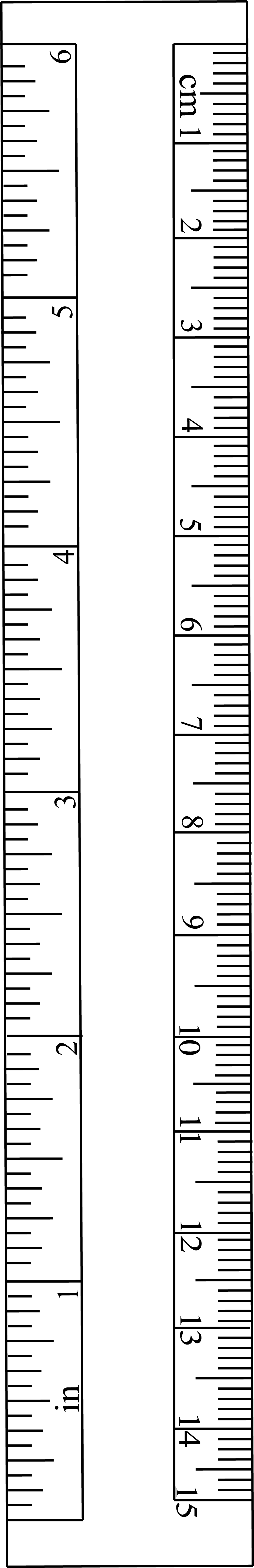 A graduation is a marking used to indicate points on a visual
A graduation is a marking used to indicate points on a visual

 A graduation is a marking used to indicate points on a visual
A graduation is a marking used to indicate points on a visual scale
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
, which can be present on a container, a measuring device, or the axes of a line plot, usually one of many along a line or curve, each in the form of short line segments perpendicular to the line or curve. Often, some of these line segments are longer and marked with a numeral, such as every fifth or tenth graduation. The scale itself can be linear (the graduations are spaced at a constant distance apart) or nonlinear.
Linear graduation of a scale occurs mainly (but not exclusively) on straight measuring devices, such as a rule
Rule or ruling may refer to:
Education
* Royal University of Law and Economics (RULE), a university in Cambodia
Human activity
* The exercise of political or personal control by someone with authority or power
* Business rule, a rule perta ...
or measuring tape, using units such as inch
Measuring tape with inches
The inch (symbol: in or ″) is a unit of length in the British imperial and the United States customary systems of measurement. It is equal to yard or of a foot. Derived from the Roman uncia ("twelfth") ...
es or millimetre
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the electromagnetic spectrum, measured by the metre and its derived scales. The microwave is between 1 meter to 1 millimeter.
The millimetre (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, ...
s.
Graduations can also be spaced at varying spatial intervals, such as when using a logarithmic Logarithmic can refer to:
* Logarithm, a transcendental function in mathematics
* Logarithmic scale, the use of the logarithmic function to describe measurements
* Logarithmic spiral,
* Logarithmic growth
* Logarithmic distribution, a discrete pr ...
, for instance on a measuring cup, can vary in scale due to the container's non-cylindrical
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infini ...
shape.
Graduations along a curve
Circular graduations of a scale occur on a circular arc orlimb
Limb may refer to:
Science and technology
* Limb (anatomy), an appendage of a human or animal
*Limb, a large or main branch of a tree
*Limb, in astronomy, the curved edge of the apparent disk of a celestial body, e.g. lunar limb
*Limb, in botany, ...
of an instrument. In some cases, non-circular curves are graduated in instruments. A typical circular arc graduation is the division into angular measurements, such as degrees, minutes and seconds. These types of graduated markings are traditionally seen on devices ranging from compasses and clock faces to alidades found on such instruments as telescopes, theodolites, inclinometers, astrolabes, armillary spheres
An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (on the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centered on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of ...
, and celestial spheres.
There can also be non-uniform graduations such as logarithmic or other scales such as seen on circular slide rules and graduated cylinders
A graduated cylinder, also known as a measuring cylinder or mixing cylinder, is a common piece of laboratory equipment used to measure the volume of a liquid. It has a narrow cylindrical shape. Each marked line on the graduated cylinder represent ...
.

Manufacture of graduations
Graduations can be placed on an instrument by etching, scribing or engraving, painting, printing or other means. For durability and accuracy, etched or scribed marks are usually preferable to surface coatings such as paints and inks. Markings can be a combination of both physical marks such as a scribed line and a paint or other marking material. For example, it is common for black ink or paint to fill the grooves cut in a scribed rule. Inexpensive plastic devices can be molded and painted or molded with two or more colors of plastic used. Some rather high-quality devices can be manufactured with plastic and reveal high-precision graduations. Graduations traditionally have been scribed into an instrument by hand with a sharp, hard tool.Daumas, Maurice, ''Scientific Instruments of the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries and Their Makers'', Portman Books, London 1989 Later developments in devices such as dividing engines allowed the process to be automated with greater precision. Modern devices can be stamped, cut on a milling machine or with a CNC machine. In the case of stamping, the master has the precision built into itself and the stamped device is as accurate as the stamping process allows. Similarly, molding of plastic can be as precise as the mold process. With proper concern for such effects as thermal expansion or contraction and shrinkage, the precision can be very high.US graduation style
The US graduation style of an instrument was a Federal standard for codes used by manufacturers to quickly determine which types of scales are marked on the instrument. Other commonly recognized styles are:{{Citation needed, date=February 2019 * 30–1 mm, 0.5 mm *31–1 mm, 0.5 mm, 1/32″, 1/64″ *34–1 mm, 0.5 mm, 1/10″, 1/50″ *35–1 mm, 0.5 mm on both sides *35E—1 mm, 0.5 mm on both sides, plus mm on both ends on one side *36—1/32″ and 1 mm on one side; 1/64″ and 1 mm on other side *37–1 mm, 0.5 mm *37E—1 mm, 0.5 mm on both sides, plus mm on both ends on one side, Single row inch figure *E/M—edge 1: 1/10″, edge 2: 1/100″, edge 3: 1.0 mm, edge 4: 0.5 mm *3R—1/64″, 1/50″, 1/32″, 1/10″ * 4R—1/64″, 1/32″, 1/16″, 1/8″ * 5R—1/100″, 1/64″, 1/32″, 1/10″ * 6R—1/32″, 1/64″, 1/10″, 1/100″ * 7R—1/100″,1/64″, 1/32″, 1/16″ *9R—1/16″, 1/32″, 1/64″ *10R—1/32″, 1/64″ (quick-reading) *10R/D—1/64″, 1/32″, Decimal Equivalency Table Graduation * 12R—1/100″, 1/64″, 1/50″, 1/32″ * 16R—1/100″, 1/64″, 1/50″, 1/32″ Suffix key: * R = Rapid Read (32nd & 64th graduations marked with number values) * E = End Graduations (Graduations appear on end edge/edges) * ME = Metric/English (Metric units in preferred position) * E/M = English/Metric (English units in preferred position)See also
* Level staff * Monochord * Volumetric flaskReferences