Government Spending In The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Government spending in the United States is the spending of the
Government spending in the United States is the spending of the
 For most governments around the world, the majority of government spending takes place at the federal/national level. As of 2019, in the United States, approximately 55% of government spending is spent by the
For most governments around the world, the majority of government spending takes place at the federal/national level. As of 2019, in the United States, approximately 55% of government spending is spent by the

 Mandatory/entitlement spending is spending for programs with funding levels that are automatically determined by the number of eligible recipients in those programs. Mandatory programs are created under authorization laws, meaning that
Mandatory/entitlement spending is spending for programs with funding levels that are automatically determined by the number of eligible recipients in those programs. Mandatory programs are created under authorization laws, meaning that

 Discretionary spending is optional spending that is determined by Congress each year through an annual appropriations process. After
Discretionary spending is optional spending that is determined by Congress each year through an annual appropriations process. After
 National defense spending is any government spending attributable to the maintenance and strengthening of the United States Armed Forces, including the
National defense spending is any government spending attributable to the maintenance and strengthening of the United States Armed Forces, including the
 The Census of Governments for 2017 shows $3.7 trillion total of state ($2.3) and local ($1.9) government expenditures. The total is less than the parts, to exclude duplicative inter-governmental transactions. The data are available for detailed categories of revenue and expenditure for each state, and for the total of local governments in each state.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the majority of government spending in the United States took place at the local level. However, federal spending increased relative to state and local spending as a result of
The Census of Governments for 2017 shows $3.7 trillion total of state ($2.3) and local ($1.9) government expenditures. The total is less than the parts, to exclude duplicative inter-governmental transactions. The data are available for detailed categories of revenue and expenditure for each state, and for the total of local governments in each state.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the majority of government spending in the United States took place at the local level. However, federal spending increased relative to state and local spending as a result of

 Government spending in the United States is the spending of the
Government spending in the United States is the spending of the federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fede ...
, and the spending of its state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
and local governments
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
.
Total government spending
The US government'sBureau of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official economy of the United States, macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic ...
for 2019 estimates $7.3 trillion in total government expenditure and $21.4 trillion total GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
which is 34%.Tables 3.1 and 1.1.5,
This government total excludes spending by "government enterprises" which sell goods and services "to households and businesses in a market transaction." These "government enterprises" include the U.S. Postal Service, Federal Housing Administration, flood insurance, housing authorities, transit systems, airports, water ports, and utilities. However "their investment, interest payments, and operating surplus (or deficit) are recorded as government transactions."
BEA also shows $3.8 trillion government consumption expenditures and gross investment, which excludes transfer payments (like social security), subsidies and interest. BEA describes its different totals.
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
for 2015 shows general government spending at 37.9% of GDP, or $21,536 per capita.
BEA's 34% is smaller because it just includes government spending. OECD's total is larger because it also includes fees, e.g. tuition payments at public colleges.
IMF for 2018 shows general government at 35% of GDP.
Components of federal government spending
 For most governments around the world, the majority of government spending takes place at the federal/national level. As of 2019, in the United States, approximately 55% of government spending is spent by the
For most governments around the world, the majority of government spending takes place at the federal/national level. As of 2019, in the United States, approximately 55% of government spending is spent by the federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
, while the remaining 45% of government spending is spent by state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
and local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
. Federal government spending in the United States can be broken down into three general categories: mandatory/entitlement spending, discretionary spending, and interest on government debt.
Mandatory/entitlement spending

 Mandatory/entitlement spending is spending for programs with funding levels that are automatically determined by the number of eligible recipients in those programs. Mandatory programs are created under authorization laws, meaning that
Mandatory/entitlement spending is spending for programs with funding levels that are automatically determined by the number of eligible recipients in those programs. Mandatory programs are created under authorization laws, meaning that Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
must provide whatever funds are necessary to keep these programs functional. Funding for these programs cannot be adjusted in the annual budget process; on the contrary, the only way Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
can change funding levels for these programs is by amending the authorization laws directly. Each year, the Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, pol ...
provides an estimate of required funds for these programs, which is included in the annual budget.
Mandatory programs include:
* Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
: Financial support for the elderly.
* Healthcare: Medicare (health insurance for the elderly) and Medicaid
Medicaid in the United States is a federal and state program that helps with healthcare costs for some people with limited income and resources. Medicaid also offers benefits not normally covered by Medicare, including nursing home care and pers ...
(health insurance for low-income individuals).
* Income Security: Disability Assistance, Food and Nutrition Assistance, Supplemental Security Income
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is a means-tested program that provides cash payments to disabled children, disabled adults, and individuals aged 65 or older who are citizens or nationals of the United States. SSI was created by the Social Se ...
, Earned Income Tax Credits, and Child Tax Credits.
* Veterans Benefits
The US Department of Veterans Affairs provides a wide variety of benefits, e.g., educational assistance (GI Bill), healthcare, assisted living, home loans, insurance, and burial and memorial services, for retired or separated United States armed f ...
: Income Security for Veterans and Healthcare Assistance.
* Other: Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
, General Government Services, and International Affairs.
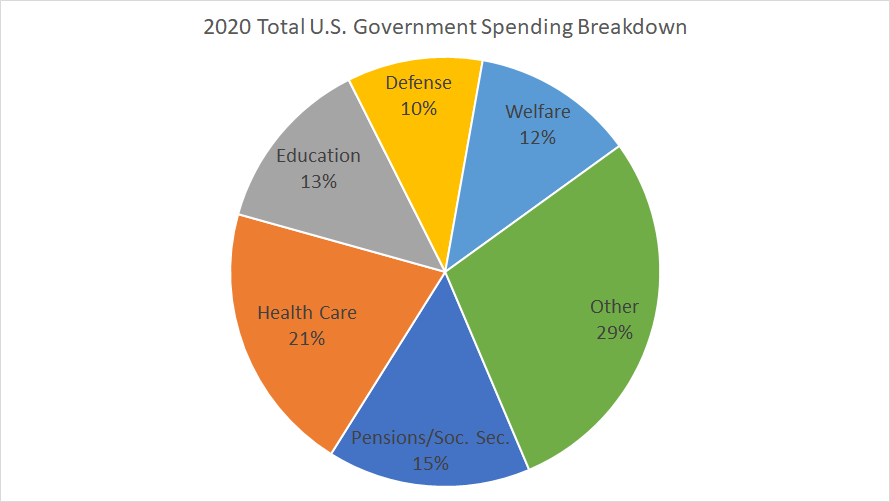
''Figure A'' provides a breakdown of the major mandatory government spending categories as of the fiscal year 2019 budget approved by Congress. As ''Figure A'' suggests, Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
is the single largest mandatory spending
The United States federal budget is divided into three categories: mandatory spending, discretionary spending, and interest on debt. Also known as entitlement spending, in US fiscal policy, mandatory spending is government spending on certain p ...
item, taking up 38% or nearly $1,050 billion of the $2,736 billion total. The next largest expenditures are Medicare and Income Security, with the remaining amount going to Medicaid
Medicaid in the United States is a federal and state program that helps with healthcare costs for some people with limited income and resources. Medicaid also offers benefits not normally covered by Medicare, including nursing home care and pers ...
, Veterans Benefits, and other programs.
Discretionary spending

 Discretionary spending is optional spending that is determined by Congress each year through an annual appropriations process. After
Discretionary spending is optional spending that is determined by Congress each year through an annual appropriations process. After mandatory spending
The United States federal budget is divided into three categories: mandatory spending, discretionary spending, and interest on debt. Also known as entitlement spending, in US fiscal policy, mandatory spending is government spending on certain p ...
levels have been estimated by the Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, pol ...
, discretionary spending is determined by both chambers of Congress and usually includes input from the incumbent president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
. Subcommittee
A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly. A committee is not itself considered to be a form of assembly. Usually, the assembly sends matters into a committee as a way to explore them more ...
s in both the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
and the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
appropriate discretionary funds for their respective areas, and the two chambers reconcile their differences. Once a final spending bill has been created, passed and signed by the president, the bill becomes law.
Discretionary spending includes:
* Defense: Spending attributable to the maintenance and strengthening of the United States Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
.
* Non-defense:
** Transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
: Road improvements and repairs, air traffic control, Amtrak and other infrastructure investments.
** Education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...
: K-12
K-1 is a professional kickboxing promotion established in 1993, well known worldwide mainly for its heavyweight division fights and Grand Prix tournaments. In January 2012, K-1 Global Holdings Limited, a company registered in Hong Kong, acquired ...
education grants, school choice programs, disability and special education
Special education (known as special-needs education, aided education, exceptional education, alternative provision, exceptional student education, special ed., SDC, or SPED) is the practice of educating students in a way that accommodates th ...
programs, and lunch assistance.
** Other veterans' benefits
The US Department of Veterans Affairs provides a wide variety of benefits, e.g., educational assistance (GI Bill), healthcare, assisted living, home loans, insurance, and burial and memorial services, for retired or separated United States armed ...
.
** Public health, law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of government who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by discovering, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms governing that society. The term en ...
, natural resources, and science.
** Housing assistance and community services.
** Foreign affairs and other expenditures.
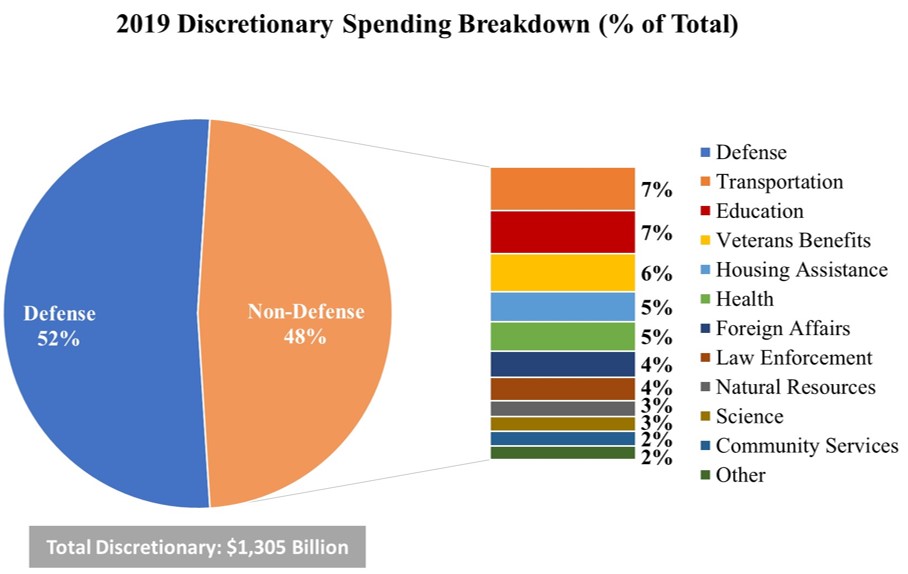
''Figure B'' provides a snapshot of the major discretionary government spending categories as of the fiscal year 2019 budget approved by Congress. As the figure suggests, over 50% of discretionary spending is attributed to national defense
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military attac ...
. The remaining 48% of funds is divided among non-defense items such as transportation and education. Total discretionary spending approved for the fiscal year 2019 is $1,305 billion, just 28% of total spending.
National defense spending
 National defense spending is any government spending attributable to the maintenance and strengthening of the United States Armed Forces, including the
National defense spending is any government spending attributable to the maintenance and strengthening of the United States Armed Forces, including the Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
, Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and ...
, Marines
Marines, or naval infantry, are typically a military force trained to operate in littoral zones in support of naval operations. Historically, tasks undertaken by marines have included helping maintain discipline and order aboard the ship (refle ...
, and the Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an a ...
. As of the fiscal year
A fiscal year (or financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many ...
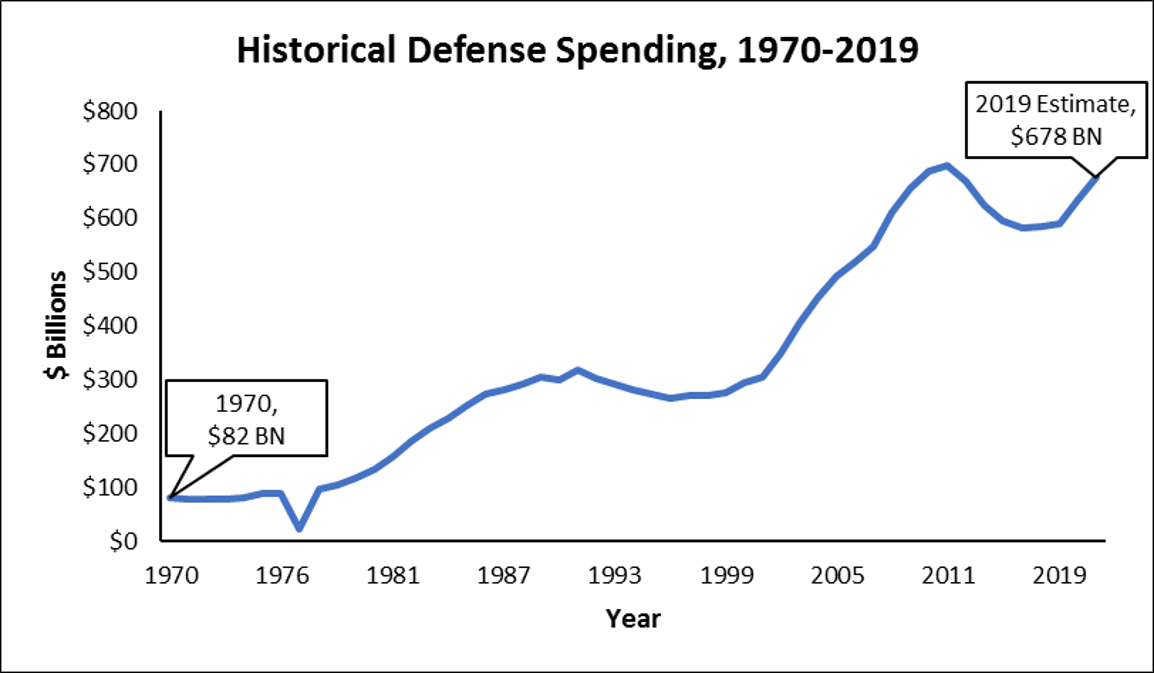
2019 budget approved by Congress, national defense is the largest discretionary expenditure in the federal budget. ''Figure C'' provides a historical picture of military spending
A military budget (or military expenditure), also known as a defense budget, is the amount of financial resources dedicated by a state to raising and maintaining an armed forces or other methods essential for defense purposes.
Financing milit ...
over the last few decades. In 1970, the United States government spent just over $80 billion on national defense. Over the next two decades, national defense spending increased steadily to around $300 billion per year. Military spending fell in the 1990s, but increased markedly in the 2000s as a result of the War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
*Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see als ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
. Military spending was cut slightly during the Obama Administration
Barack Obama's tenure as the 44th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 2009, and ended on January 20, 2017. A Democrat from Illinois, Obama took office following a decisive victory over Republican ...
, but the Trump Administration
Donald Trump's tenure as the List of presidents of the United States, 45th president of the United States began with Inauguration of Donald Trump, his inauguration on January 20, 2017, and ended on January 20, 2021. Trump, a Republican Party ...
plans to ramp up military spending to combat ISIL
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
. National defense spending is expected to be $678 billion in 2019, an amount greater than the military expenditures of the next 9 countries combined.
Key defense expenditures typically include:
* Power Projection: Spending on sea power
Command of the sea (also called control of the sea or sea control) is a naval military concept regarding the strength of a particular navy to a specific naval area it controls. A navy has command of the sea when it is so strong that its rivals ...
and air power
Airpower or air power consists of the application of military aviation, military strategy and strategic theory to the realm of aerial warfare and close air support. Airpower began in the advent of powered flight early in the 20th century. Airpo ...
, including nuclear submarine
A nuclear submarine is a submarine powered by a nuclear reactor, but not necessarily nuclear-armed. Nuclear submarines have considerable performance advantages over "conventional" (typically diesel-electric) submarines. Nuclear propulsion, ...
s, aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
, and aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a ...
s.
* Munitions
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other weap ...
: Maintenance of existing ammunition inventory, as well as procurement of new ammunition.
* Nuclear Deterrence: Maintaining and expanding all nuclear systems.
* Overseas Contingency Operations: Funds available for unexpected warfare abroad. For example, these funds were used to pay for the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan.
* Missile Defense: Improvements in missile defense technology and integration of current technology at home and abroad.
* Space Systems and Cyberspace Operations: Communication control and radar technology.
Interest on government debt
Oftentimes, federal governments spend more money than they collect intax revenue
Tax revenue is the income that is collected by governments through taxation. Taxation is the primary source of government revenue. Revenue may be extracted from sources such as individuals, public enterprises, trade, royalties on natural resou ...
in a given year. When the government spends more than it brings in, it runs a Budget Deficit that year. In order to pay for the extra spending, governments issue debt. Government debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
is the amount of money credited from individuals, firms, foreign entities as well as the federal government itself through the federal reserve system. Debt accrues over time. Most public debt is held in the form of treasury bills
United States Treasury securities, also called Treasuries or Treasurys, are government debt instruments issued by the United States Department of the Treasury to finance government spending as an alternative to taxation. Since 2012, U.S. gov ...
and bonds, and the government has to repay debt over time. In order to provide an incentive for individuals, businesses and other entities to lend money, the government must also pay these parties interest
In finance and economics, interest is payment from a borrower or deposit-taking financial institution to a lender or depositor of an amount above repayment of the principal sum (that is, the amount borrowed), at a particular rate. It is distinct ...
on the debt. The interest expense
Interest expense relates to the cost of borrowing money. It is the price that a lender charges a borrower for the use of the lender's money. On the income statement, interest expense can represent the cost of borrowing money from banks, bond inve ...
for fiscal year 2019 is $363 billion, or 7.9% of the total budget. According to estimates from the Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, pol ...
, interest on government debt is expected to more than double by 2028 and account for a larger percentage of total expenditures.
State and local government spending
 The Census of Governments for 2017 shows $3.7 trillion total of state ($2.3) and local ($1.9) government expenditures. The total is less than the parts, to exclude duplicative inter-governmental transactions. The data are available for detailed categories of revenue and expenditure for each state, and for the total of local governments in each state.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the majority of government spending in the United States took place at the local level. However, federal spending increased relative to state and local spending as a result of
The Census of Governments for 2017 shows $3.7 trillion total of state ($2.3) and local ($1.9) government expenditures. The total is less than the parts, to exclude duplicative inter-governmental transactions. The data are available for detailed categories of revenue and expenditure for each state, and for the total of local governments in each state.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the majority of government spending in the United States took place at the local level. However, federal spending increased relative to state and local spending as a result of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, and by the 1930s, state and local government spending accounted for less than one half of government spending. By 2019, federal spending was more than 20% of GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
, while state and local spending hovered around 17% of GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
. As a result, in recent years, state and local governments account for approximately 45% of total government expenditures. State and local government spending is typically spent in 6 broad categories: elementary
Elementary may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''Elementary'' (Cindy Morgan album), 2001
* ''Elementary'' (The End album), 2007
* ''Elementary'', a Melvin "Wah-Wah Watson" Ragin album, 1977
Other uses in arts, entertainment, an ...
and secondary education
Secondary education or post-primary education covers two phases on the International Standard Classification of Education scale. Level 2 or lower secondary education (less commonly junior secondary education) is considered the second and final pha ...
, higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completi ...
, health, welfare
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
, police and safety, and transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
. Over the last few decades, funding for education at the state level has fallen, while funding for health has more than doubled.
While federal governments often run budget deficits (where government spending exceeds government tax revenue), state governments
A state government is the government that controls a subdivision of a country in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonomy, or ...
usually have balanced budget
A balanced budget (particularly that of a government) is a budget in which revenues are equal to expenditures. Thus, neither a budget deficit nor a budget surplus exists (the accounts "balance"). More generally, it is a budget that has no budge ...
s. A balanced budget
A balanced budget (particularly that of a government) is a budget in which revenues are equal to expenditures. Thus, neither a budget deficit nor a budget surplus exists (the accounts "balance"). More generally, it is a budget that has no budge ...
is when government spending in a given year equals government revenue
Government revenue or national revenue is money received by a government from taxes and non-tax sources to enable it to undertake public expenditure. Government revenue as well as government spending are components of the government budget and ...
in that year. This high degree of fiscal balancing is a result of most states in the U.S. having balanced budget requirements. A balanced budget requirement is a law that requires a government to balance its budget annually, such that government spending equals government revenue
Government revenue or national revenue is money received by a government from taxes and non-tax sources to enable it to undertake public expenditure. Government revenue as well as government spending are components of the government budget and ...
. There are two types of balanced budget requirements: ex-post balanced budget requirements, and ex-ante balanced budget requirements. An ex-post balanced budget requirement stipulates that a government must balance their budget by the end of each fiscal year, while an ex-ante balanced budget requirement dictates that a state must adopt a balanced budget at the beginning of each fiscal year. Ex-ante balanced budget requirements rely on estimates and assumptions about future costs and revenue growth, so they are more easily manipulated.
California
With a population of nearly 40 million as of 2018,California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
has by far the largest annual state expenditures. California receives a significant amount of money from the federal government, especially for healthcare and welfare program
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
s, but also has large in-state expenditures. According to California's Department of Finance, the state's 2017-2018 enacted state budget includes over $180 billion in state funds. As can be seen below, ''Table 1'' gives an overview of California's 2017-2018 enacted state budget. As the table suggests, health care and K12 education represent California's largest expenditures of state funds. The largest health care expenditure is for California's Medi-Cal The California Medical Assistance Program (Medi-Cal or MediCal) is California's Medicaid program serving low-income individuals, including families, seniors, persons with disabilities, children in foster care, pregnant women, and childless adults wi ...
program, a health insurance program for low-income families in California. In addition, health care spending is focused on women's health services, treatment for addiction, and dentistry. As ''Table 1'' suggests, California also spends significantly on higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completi ...
, police
The police are a constituted body of persons empowered by a state, with the aim to enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citizens, and to prevent crime and civil disorder. Their lawful powers include arrest and t ...
, and transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
, with smaller portions of funding attributable to environmental protection
Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment by individuals, organizations and governments. Its objectives are to conserve natural resources and the existing natural environment and, where possible, to repair dam ...
and other activities.
References
{{reflist Government finances in the United States Government spending