Government of Japan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Government of Japan consists of legislative, executive and
 The is the head of the Imperial Family and the ceremonial
The is the head of the Imperial Family and the ceremonial
 The is designated by the National Diet and serves a term of four years or less; with no limits imposed on the number of terms the Prime Minister may hold. The Prime Minister heads the Cabinet and exercises "control and supervision" of the executive branch, and is the
The is designated by the National Diet and serves a term of four years or less; with no limits imposed on the number of terms the Prime Minister may hold. The Prime Minister heads the Cabinet and exercises "control and supervision" of the executive branch, and is the
 The consists of the Ministers of State and the Prime Minister. The members of the Cabinet are appointed by the Prime Minister, and under the Cabinet Law, the number of members of the Cabinet appointed, excluding the Prime Minister, must be fourteen or less, but may only be increased to nineteen should a special need arise. Article 68 of the Constitution states that all members of the Cabinet must be
The consists of the Ministers of State and the Prime Minister. The members of the Cabinet are appointed by the Prime Minister, and under the Cabinet Law, the number of members of the Cabinet appointed, excluding the Prime Minister, must be fourteen or less, but may only be increased to nineteen should a special need arise. Article 68 of the Constitution states that all members of the Cabinet must be

 The consist of eleven executive ministries and the Cabinet Office. Each ministry is headed by a Minister of State, which are mainly senior legislators, and are appointed from among the members of the Cabinet by the Prime Minister. The Cabinet Office, formally headed by the Prime Minister, is an agency that handles the day-to-day affairs of the Cabinet. The ministries are the most influential part of the daily-exercised executive power, and since few ministers serve for more than a year or so necessary to grab hold of the organisation, most of its power lies within the senior bureaucrats.
Below is a series of ministry-affiliated government agencies and bureaus responsible for government procedures and activities as of 23 August 2022.
* Cabinet Office
** National Public Safety Commission
** National Police Agency
** Consumer Affairs Agency
** Financial Services Agency
** Fair Trade Commission
** Food Safety Commission
** Personal Information Protection Commission
** Imperial Household Agency
** Gender Equality Bureau
** Council on Economic and Fiscal Policy
** Atomic Energy Commission
** International Peace Cooperation
** Council for Science, Technology and Innovation
** Headquarters for Ocean Policy
** Northern Territories Affairs Administration
** Public Relations Office of the Government of Japan
* Cabinet Secretariat
** National Information Security Centre
** National Personnel Authority
** Coordination Office of Measures on Emerging Infectious Diseases
** Headquarters for the Abduction Issue
** Cabinet Legislation Bureau
** Office of Policy Planning and Coordination on Territory and Sovereignty
*
The consist of eleven executive ministries and the Cabinet Office. Each ministry is headed by a Minister of State, which are mainly senior legislators, and are appointed from among the members of the Cabinet by the Prime Minister. The Cabinet Office, formally headed by the Prime Minister, is an agency that handles the day-to-day affairs of the Cabinet. The ministries are the most influential part of the daily-exercised executive power, and since few ministers serve for more than a year or so necessary to grab hold of the organisation, most of its power lies within the senior bureaucrats.
Below is a series of ministry-affiliated government agencies and bureaus responsible for government procedures and activities as of 23 August 2022.
* Cabinet Office
** National Public Safety Commission
** National Police Agency
** Consumer Affairs Agency
** Financial Services Agency
** Fair Trade Commission
** Food Safety Commission
** Personal Information Protection Commission
** Imperial Household Agency
** Gender Equality Bureau
** Council on Economic and Fiscal Policy
** Atomic Energy Commission
** International Peace Cooperation
** Council for Science, Technology and Innovation
** Headquarters for Ocean Policy
** Northern Territories Affairs Administration
** Public Relations Office of the Government of Japan
* Cabinet Secretariat
** National Information Security Centre
** National Personnel Authority
** Coordination Office of Measures on Emerging Infectious Diseases
** Headquarters for the Abduction Issue
** Cabinet Legislation Bureau
** Office of Policy Planning and Coordination on Territory and Sovereignty
*
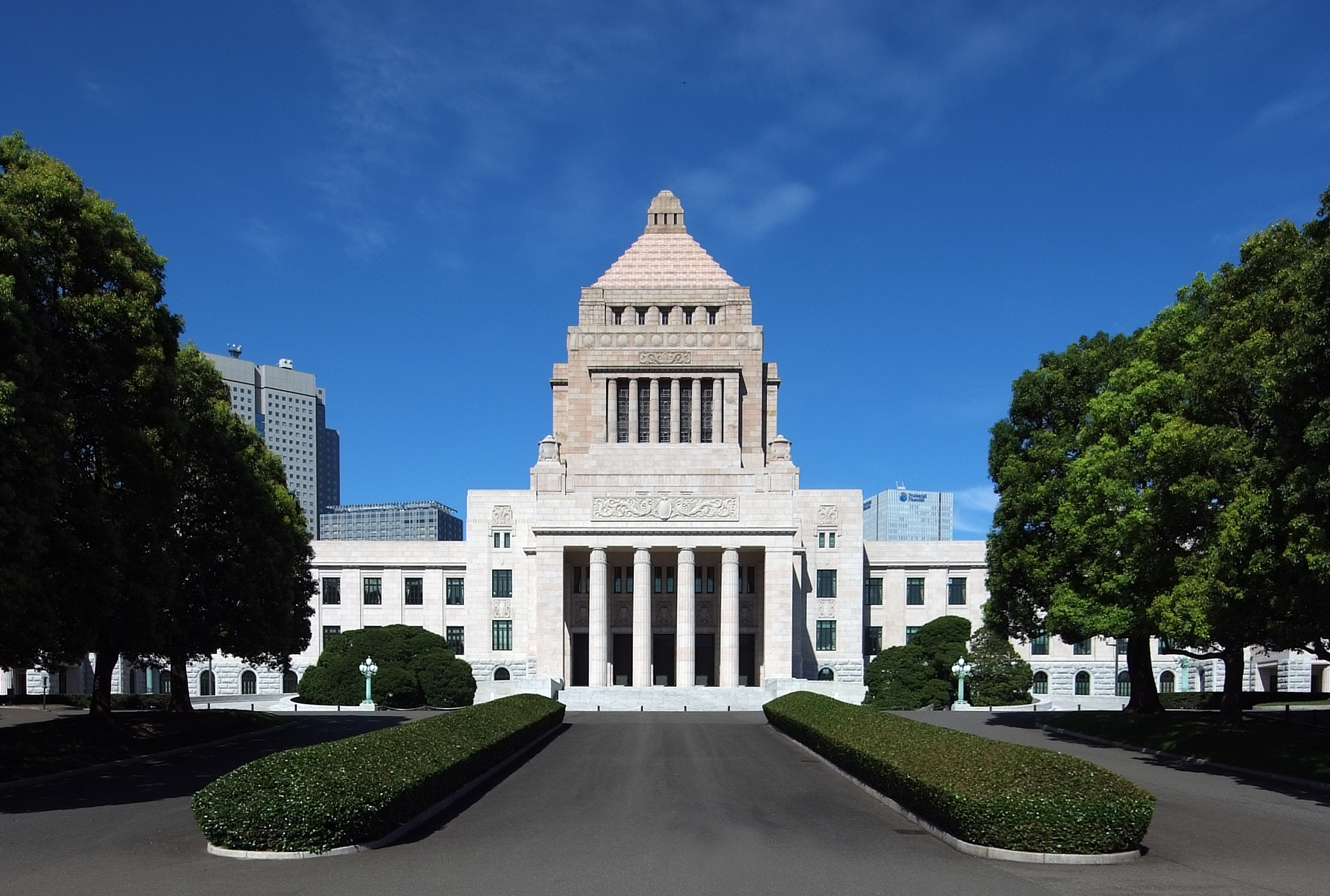 The Legislative branch organ of Japan is the . It is a bicameral legislature, composing of a lower house, the House of Representatives, and an upper house, the House of Councillors. Empowered by the
The Legislative branch organ of Japan is the . It is a bicameral legislature, composing of a lower house, the House of Representatives, and an upper house, the House of Councillors. Empowered by the
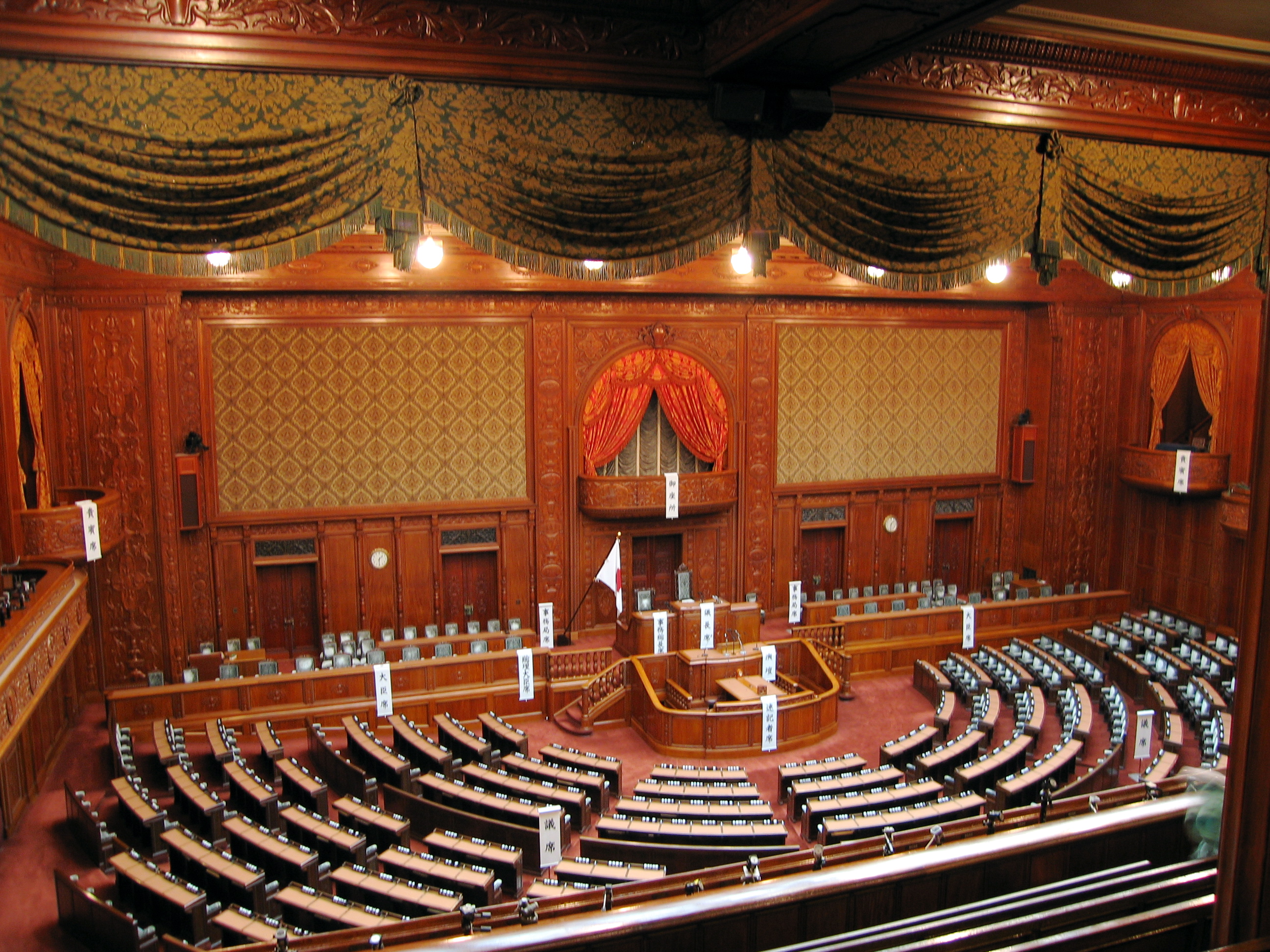 The is the Lower house, with the members of the house being elected once every four years, or when dissolved, for a four-year term. As of November 18, 2017, it has 465 members. Of these, 176 members are elected from 11 multi-member constituencies by a party-list system of
The is the Lower house, with the members of the house being elected once every four years, or when dissolved, for a four-year term. As of November 18, 2017, it has 465 members. Of these, 176 members are elected from 11 multi-member constituencies by a party-list system of
 The is the
The is the
 The Judicial branch of Japan consists of the Supreme Court, and four other lower courts; the High Courts, District Courts, Family Courts and Summary Courts. Divided into four basic tiers, the Court's independence from the executive and legislative branches are guaranteed by the
The Judicial branch of Japan consists of the Supreme Court, and four other lower courts; the High Courts, District Courts, Family Courts and Summary Courts. Divided into four basic tiers, the Court's independence from the executive and legislative branches are guaranteed by the
 The is the court of last resort and has the power of Judicial review; as defined by the Constitution to be "the court of last resort with power to determine the constitutionality of any law, order, regulation or official act". The Supreme Court is also responsible for nominating judges to lower courts and determining judicial procedures. It also oversees the judicial system, overseeing activities of public prosecutors, and disciplining judges and other judicial personnel.
The is the court of last resort and has the power of Judicial review; as defined by the Constitution to be "the court of last resort with power to determine the constitutionality of any law, order, regulation or official act". The Supreme Court is also responsible for nominating judges to lower courts and determining judicial procedures. It also oversees the judicial system, overseeing activities of public prosecutors, and disciplining judges and other judicial personnel.
 The Cabinet Public Affairs Office's Government Directory also listed a number of government agencies that are more independent from executive ministries. The list for these types of agencies can be seen below.
* Japan National Tourism Organisation (JNTO)
* Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA)
* Japan External Trade Organisation (JETRO)
* The Japan Foundation
*
The Cabinet Public Affairs Office's Government Directory also listed a number of government agencies that are more independent from executive ministries. The list for these types of agencies can be seen below.
* Japan National Tourism Organisation (JNTO)
* Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA)
* Japan External Trade Organisation (JETRO)
* The Japan Foundation
*
 According to Article 92 of the Constitution, the are local public entities whose body and functions are defined by law in accordance with the principle of local autonomy. The main law that defines them is the Local Autonomy Law. They are given limited executive and legislative powers by the Constitution. Governors, mayors and members of assemblies are constitutionally elected by the residents.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications intervenes significantly in local government, as do other ministries. This is done chiefly financially because many local government jobs need funding initiated by national ministries. This is dubbed as the "thirty-percent autonomy".三割自治
The result of this power is a high level of organizational and policy standardization among the different local jurisdictions allowing them to preserve the uniqueness of their prefecture, city, or town. Some of the more collectivist jurisdictions, such as
According to Article 92 of the Constitution, the are local public entities whose body and functions are defined by law in accordance with the principle of local autonomy. The main law that defines them is the Local Autonomy Law. They are given limited executive and legislative powers by the Constitution. Governors, mayors and members of assemblies are constitutionally elected by the residents.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications intervenes significantly in local government, as do other ministries. This is done chiefly financially because many local government jobs need funding initiated by national ministries. This is dubbed as the "thirty-percent autonomy".三割自治
The result of this power is a high level of organizational and policy standardization among the different local jurisdictions allowing them to preserve the uniqueness of their prefecture, city, or town. Some of the more collectivist jurisdictions, such as
Background notes of the US Department of State, Japan's Government
Facts about Japan by CIA's The World Factbook
Video of the Enthronement Ceremony of the Emperor
Video of the National Diet Convocation Ceremony
Video of the House of Representatives Dissolution Ceremony
* {{Asia topic, Government of, title=Governments of Asia, TW=Government of the Republic of China
judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
branches and is based on popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
. The Government runs under the framework established by the Constitution of Japan, adopted in 1947. It is a unitary state
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only th ...
, containing forty-seven administrative divisions, with the Emperor as its Head of State
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state (polity), state#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international p ...
. His role is ceremonial and he has no powers related to Government. Instead, it is the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, comprising the Ministers of State and the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
, that directs and controls the Government and the civil service
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil servants hired on professional merit rather than appointed or elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leaders ...
. The Cabinet has the executive power and is formed by the Prime Minister, who is the Head of Government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
. The Prime Minister is nominated by the National Diet and appointed to office by the Emperor.
The National Diet is the legislature
A legislature is an deliberative assembly, assembly with the authority to make laws for a Polity, political entity such as a Sovereign state, country or city. They are often contrasted with the Executive (government), executive and Judiciary, ...
, the organ of the Legislative branch. It is bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single gro ...
, consisting of two houses with the House of Councilors being the upper house
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restric ...
, and the House of Representatives being the lower house. Its members are directly elected by the people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of proper ...
, who are the source of sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
. It is defined as the supreme organ of sovereignty in the Constitution. The Supreme Court and other inferior courts make up the Judicial branch and have all the judicial powers in the state. It has ultimate judicial authority to interpret the Japanese constitution
The Constitution of Japan ( Shinjitai: , Kyūjitai: , Hepburn: ) is the constitution of Japan and the supreme law in the state. Written primarily by American civilian officials working under the Allied occupation of Japan, the constitution ...
and the power of judicial review. They are independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independe ...
from the executive and the legislative branches. Judges are nominated or appointed by the Cabinet and never removed by the executive or the legislature except during impeachment.
History
Prior to the Meiji Restoration, Japan was ruled by the government of a successive military ''shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakur ...
''. During this period, effective power of the government resided in the Shōgun, who officially ruled the country in the name of the Emperor. The Shōgun were the hereditary military governors, with their modern rank equivalent to a generalissimo. Although the Emperor was the sovereign who appointed the Shōgun, his roles were ceremonial and he took no part in governing the country. This is often compared to the present role of the Emperor, whose official role is to appoint the Prime Minister.
The Meiji Restoration in 1872 led to the resignation of Shōgun Tokugawa Yoshinobu
Prince was the 15th and last ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan. He was part of a movement which aimed to reform the aging shogunate, but was ultimately unsuccessful. He resigned of his position as shogun in late 1867, while aiming ...
, agreeing to "be the instrument for carrying out" the Emperor's orders. This event restored the country to Imperial rule and the proclamation of the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent for ...
. In 1889, the Meiji Constitution was adopted in a move to strengthen Japan to the level of western nations, resulting in the first parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance
Governance is the process of interactions through the laws, norms, power or language of an organized society over a social system ( family, t ...
in Asia. It provided a form of mixed constitutional-absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constituti ...
, with an independent judiciary, based on the Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n model of the time.
A new aristocracy known as the '' kazoku'' was established. It merged the ancient court nobility of the Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese ...
, the '' kuge'', and the former ''daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominall ...
'', feudal lords subordinate to the ''shōgun''. It also established the Imperial Diet, consisting of the House of Representatives and the House of Peers. Members of the House of Peers were made up of the Imperial Family, the Kazoku, and those nominated by the Emperor, while members of the House of Representatives were elected by direct male suffrage. Despite clear distinctions between powers of the executive branch and the Emperor in the Meiji Constitution, ambiguity and contradictions in the Constitution eventually led to a political crisis
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
. It also devalued the notion of civilian control over the military, which meant that the military could develop and exercise a great influence on politics.
Following the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the present Constitution of Japan was adopted. It replaced the previous Imperial rule with a form of Western-style liberal democracy
Liberal democracy is the combination of a liberal political ideology that operates under an indirect democratic form of government. It is characterized by elections between multiple distinct political parties, a separation of powers into ...
.
As of 2020, the Japan Research Institute found the national government is mostly analog, because only 7.5% (4,000 of the 55,000) administrative procedures can be completed entirely online. The rate is 7.8% at the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, 8% at the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, and only 1.3% at the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.
On 12 February, 2021, Tetsushi Sakamoto was appointed as the Minister of Loneliness to alleviate social isolation and loneliness across different age groups and genders.
The Emperor
head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state (polity), state#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international p ...
. He is defined by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
to be "the symbol of the State and of the unity of the people". However, his role is entirely ceremonial and representative in nature. As explicitly stated in article 4 of the Constitution, he has no powers related to government.
Article 6 of the Constitution of Japan delegates the Emperor the following ceremonial roles:
# Appointment of the Prime Minister as designated by the Diet.
# Appointment of the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court as designated by the Cabinet.
While the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
is the source of executive power and most of its power is exercised directly by the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
, several of its powers are exercised through the Emperor. The powers exercised via the Emperor, as stipulated by Article 7 of the Constitution, are:
# Promulgation of amendments of the constitution, laws, cabinet orders and treaties.
# Dissolution of the House of Representatives.
# Proclamation of general election of members of the Diet.
# Attestation of the appointment and dismissal of Ministers of State and other officials as provided for by law, and of full powers and credentials of Ambassadors and Ministers.
# Attestation of general and special amnesty, commutation of punishment, reprieve, and restoration of rights.
# Awarding of honors.
# Attestation of instruments of ratification and other diplomatic documents as provided for by law.
# Receiving foreign ambassadors and ministers.
# Performance of ceremonial functions.
These powers are exercised in accordance with the binding advice of the Cabinet.
The Emperor is known to hold the nominal ceremonial authority. For example, he is the only person that has the authority to appoint the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
, even though the Diet has the power to designate the person fitted for the position. One such example can be prominently seen in the 2009 Dissolution of the House of Representatives. The House was expected to be dissolved on the advice of the Prime Minister, but was temporarily unable to do so for the next general election, as both the Emperor and Empress were visiting Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
.
In this manner, the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
's modern role is often compared to those of the Shogunate period and much of Japan's history, whereby the Emperor held great symbolic authority but had little political power; which is often held by others nominally appointed by the Emperor himself. Today, a legacy has somewhat continued for a retired Prime Minister who still wields considerable power, to be called a .
Unlike his European counterparts, the Emperor is not the source of sovereign power and the government does not act under his name. Instead, the Emperor represents the State and appoints other high officials in the name of the State, in which the Japanese people
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Ja ...
hold sovereignty. Article 5 of the Constitution, in accordance with the Imperial Household Law, allows a regency to be established in the Emperor's name, should the Emperor be unable to perform his duties.
On November 20, 1989, the Supreme Court ruled it doesn't have judicial power over the Emperor.
The Imperial House of Japan is said to be the oldest continuing hereditary monarchy in the world. According to the Kojiki and Nihon Shoki, Japan was founded by the Imperial House in 660 BC by . Emperor Jimmu was the first Emperor of Japan and the ancestor of all of the Emperors that followed. He is, according to Japanese mythology, the direct descendant of , the sun goddess of the native Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoist ...
religion, through Ninigi, his great-grandfather.
The is Naruhito. He was officially enthroned on May 1, 2019, following the abdication of his father. He is styled as , and his reign bears the era name of . Fumihito is the heir presumptive to the Chrysanthemum Throne.
Executive
The Executive branch of Japan is headed by thePrime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
. The Prime Minister is the head of the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, and is designated by the legislative organ, the National Diet. The Cabinet consists of the Ministers of State and may be appointed or dismissed by the Prime Minister at any time. Explicitly defined to be the source of executive power, it is in practice, however, mainly exercised by the Prime Minister. The practice of its powers is responsible to the Diet, and as a whole, should the Cabinet lose confidence and support to be in office by the Diet, the Diet may dismiss the Cabinet ''en masse'' with a motion of no confidence
A motion of no confidence, also variously called a vote of no confidence, no-confidence motion, motion of confidence, or vote of confidence, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility like in government or mana ...
.
Prime Minister
head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
and commander-in-chief of the Japan Self-Defense Forces
The Japan Self-Defense Forces ( ja, 自衛隊, Jieitai; abbreviated JSDF), also informally known as the Japanese Armed Forces, are the unified ''de facto''Since Article 9 of the Japanese Constitution outlaws the formation of Military, armed f ...
. The prime minister is vested with the power to present bills to the Diet, to sign laws, to declare a state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
, and may also dissolve the Diet's House of Representatives at will. The prime minister presides over the Cabinet and appoints, or dismisses, the other Cabinet ministers.
Both houses of the National Diet designates the Prime Minister with a ballot cast under the run-off system. Under the Constitution, should both houses not agree on a common candidate, then a joint committee is allowed to be established to agree on the matter; specifically within a period of ten days, exclusive of the period of recess. However, if both houses still do not agree to each other, the decision made by the House of Representatives is deemed to be that of the National Diet. Upon designation, the Prime Minister is presented with their commission, and then formally appointed to office by the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
.
As a candidate designated by the Diet, the prime minister is required to report to the Diet whenever demanded. The prime minister must also be both a civilian
Civilians under international humanitarian law are "persons who are not members of the armed forces" and they are not " combatants if they carry arms openly and respect the laws and customs of war". It is slightly different from a non-combatan ...
and a member of either house of the Diet.
The Cabinet

 The consists of the Ministers of State and the Prime Minister. The members of the Cabinet are appointed by the Prime Minister, and under the Cabinet Law, the number of members of the Cabinet appointed, excluding the Prime Minister, must be fourteen or less, but may only be increased to nineteen should a special need arise. Article 68 of the Constitution states that all members of the Cabinet must be
The consists of the Ministers of State and the Prime Minister. The members of the Cabinet are appointed by the Prime Minister, and under the Cabinet Law, the number of members of the Cabinet appointed, excluding the Prime Minister, must be fourteen or less, but may only be increased to nineteen should a special need arise. Article 68 of the Constitution states that all members of the Cabinet must be civilian
Civilians under international humanitarian law are "persons who are not members of the armed forces" and they are not " combatants if they carry arms openly and respect the laws and customs of war". It is slightly different from a non-combatan ...
s and the majority of them must be chosen from among the members of either house of the National Diet. The precise wording leaves an opportunity for the Prime Minister to appoint some non-elected Diet officials. The Cabinet is required to resign ''en masse'' while still continuing its functions, till the appointment of a new Prime Minister, when the following situation arises:
# The Diet's House of Representatives passes a non-confidence resolution, or rejects a confidence resolution, unless the House of Representatives is dissolved within the next ten days.
# When there is a vacancy in the post of the Prime Minister, or upon the first convocation of the Diet after a general election of the members of the House of Representatives.
Conceptually deriving legitimacy from the Diet, whom it is responsible to, the Cabinet exercises its power in two different ways. In practice, much of its power is exercised by the Prime Minister, while others are exercised nominally by the Emperor.
Article 73 of the Constitution of Japan expects the Cabinet to perform the following functions, in addition to general administration:
# Administer the law faithfully; conduct affairs of state.
# Manage foreign affairs.
# Conclude treaties. However, it shall obtain prior or, depending on circumstances, subsequent approval of the Diet.
# Administer the civil service
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil servants hired on professional merit rather than appointed or elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leaders ...
, in accordance with standards established by law.
# Prepare the budget, and present it to the Diet.
# Enact cabinet orders in order to execute the provisions of this Constitution and of the law. However, it cannot include penal provisions in such cabinet orders unless authorized by such law.
# Decide on general amnesty, special amnesty, commutation of punishment, reprieve, and restoration of rights.
Under the Constitution, all laws and cabinet orders must be signed by the competent Minister and countersigned by the Prime Minister, before being formally promulgated by the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
. Also, all members of the Cabinet cannot be subject to legal action without the consent of the Prime Minister; however, without impairing the right to take legal action.
Ministries and agencies

Reconstruction Agency
The is an agency of the Japanese government established on February 10, 2012 to coordinate reconstruction activities related to the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.
Mission
According to "Role of the Re ...
* Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
** Environmental Dispute Coordination Commission
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
** Fire and Disaster Management Agency
* Ministry of Justice A Ministry of Justice is a common type of government department that serves as a justice ministry.
Lists of current ministries of justice
Named "Ministry"
* Ministry of Justice (Abkhazia)
* Ministry of Justice (Afghanistan)
* Ministry of Just ...
** Public Security Examination Commission
** Public Security Intelligence Agency
** Public Prosecutors Office
The is the agency for conducting prosecution in Japan. It is an under the . It consists of four tiers of offices: the Supreme Public Prosecutors Office; the High Public Prosecutors Offices (8), the District Public Prosecutors Offices (50); and ...
** Immigration Services Agency
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs
* Ministry of Finance
** National Tax Agency
** Japan Customs
* Ministry of Defense
** Acquisition, Technology and Logistics Agency
** Japan Self-Defence Forces
The Japan Self-Defense Forces ( ja, 自衛隊, Jieitai; abbreviated JSDF), also informally known as the Japanese Armed Forces, are the unified ''de facto''Since Article 9 of the Japanese Constitution outlaws the formation of armed forces, the ...
(Ground
Ground may refer to:
Geology
* Land, the surface of the Earth not covered by water
* Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth
Electricity
* Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical c ...
/ Maritime / Air)
** Joint Staff
* Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
** Education Policy Bureau
** Elementary and Secondary Education Bureau
** Higher Education Bureau
** Science and Technology Policy Bureau
** Research Promotion Bureau
** Agency for Cultural Affairs
The is a special body of the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). It was set up in 1968 to promote Japanese arts and culture.
The agency's budget for FY 2018 rose to ¥107.7 billion.
Overview
The ...
** Japan Sports Agency
** The Japan Art Academy
** National Institute for Educational Policy Research
** National Institute of Science and Technology Policy
** The Japan Academy
The Japan Academy ( Japanese: 日本学士院, ''Nihon Gakushiin'') is an honorary organisation and science academy founded in 1879 to bring together leading Japanese scholars with distinguished records of scientific achievements. The Academy is ...
** Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion
** Japanese National Commission for UNESCO
* Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare
** Pension Service
** Central Labour Relations Commission
* Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries may refer to:
* Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (Cambodia)
* Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (Japan)
* Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (Niue)
* Dep ...
** Fisheries Agency
** Forestry Agency
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. Th ...
* Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI)
** Agency for Natural Resources and Energy
** Small and Medium Enterprise Agency
** Japan Patent Office
* Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT)
** Japan Transport Safety Board
** Japan Tourism Agency
** Japan Meteorological Agency
The , abbreviated JMA, is an agency of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. It is charged with gathering and providing results for the public in Japan that are obtained from data based on daily scientific observation an ...
** Japan Coast Guard
* Ministry of the Environment
** Nuclear Regulation Authority
*Board of Audit
The reviews government expenditures and submits an annual report to the Diet. Article 90 of the Constitution of Japan and the Board of Audit Act of 1947 give this body substantial independence from both cabinet and Diet control.
In 1968, it hos ...
Legislative
 The Legislative branch organ of Japan is the . It is a bicameral legislature, composing of a lower house, the House of Representatives, and an upper house, the House of Councillors. Empowered by the
The Legislative branch organ of Japan is the . It is a bicameral legislature, composing of a lower house, the House of Representatives, and an upper house, the House of Councillors. Empowered by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
to be "the highest organ of State power" and the only "sole law-making organ of the State", its houses are both directly elected under a parallel voting system and is ensured by the Constitution to have no discrimination on the qualifications of each members; whether be it based on "race, creed, sex, social status, family origin, education, property or income". The National Diet, therefore, reflects the sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
of the people; a principle of popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
whereby the supreme power lies within, in this case, the Japanese people
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Ja ...
.
The Diet responsibilities includes the making of laws, the approval of the annual national budget, the approval of the conclusion of treaties and the selection of the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
. In addition, it has the power to initiate draft constitutional amendments, which, if approved, are to be presented to the people for ratification in a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
before being promulgated by the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
, in the name of the people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of proper ...
. The Constitution also enables both houses to conduct investigations in relation to government, demand the presence and testimony of witnesses, and the production of records, as well as allowing either house of the Diet to demand the presence of the Prime Minister or the other Minister of State, in order to give answers or explanations whenever so required. The Diet is also able to impeach Court judges convicted of criminal or irregular conduct. The Constitution, however, does not specify the voting methods, the number of members of each house, and all other matters pertaining to the method of election of the each members, and are thus, allowed to be determined for by law.
Under the provisions of the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
and by law, all adults aged over 18 are eligible to vote, with a secret ballot and a universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political sta ...
, and those elected have certain protections from apprehension while the Diet is in session. Speeches, debates, and votes cast in the Diet also enjoy parliamentary privilege
Parliamentary privilege is a legal immunity enjoyed by members of certain legislatures, in which legislators are granted protection against civil or criminal liability for actions done or statements made in the course of their legislative duties ...
s. Each house is responsible for disciplining its own members, and all deliberations are public unless two-thirds or more of those members present passes a resolution agreeing it otherwise. The Diet also requires the presence of at least one-third of the membership of either house in order to constitute a quorum. All decisions are decided by a majority of those present, unless otherwise stated by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
, and in the case of a tie, the presiding officer has the right to decide the issue. A member cannot be expelled, however, unless a majority of two-thirds or more of those members present passes a resolution therefor.
Under the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
, at least one session of the Diet must be convened each year. The Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
can also, at will, convoke extraordinary sessions of the Diet and is required to, when a quarter or more of the total members of either house demands it. During an election, only the House of Representatives is dissolved. The House of Councillors is however, not dissolved but only closed, and may, in times of national emergency, be convoked for an emergency session. The Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
both convokes the Diet and dissolves the House of Representatives, but only does so on the advice of the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
.
For bills to become Law, they are to be first passed by both houses of the National Diet, signed by the Ministers of State, countersigned by the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
, and then finally promulgated by the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
; however, without specifically giving the Emperor the power to oppose legislation.
House of Representatives
 The is the Lower house, with the members of the house being elected once every four years, or when dissolved, for a four-year term. As of November 18, 2017, it has 465 members. Of these, 176 members are elected from 11 multi-member constituencies by a party-list system of
The is the Lower house, with the members of the house being elected once every four years, or when dissolved, for a four-year term. As of November 18, 2017, it has 465 members. Of these, 176 members are elected from 11 multi-member constituencies by a party-list system of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
, and 289 are elected from single-member constituencies. 233 seats are required for majority. The House of Representatives is the more powerful house out of the two, it is able to override veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto ...
es on bills imposed by the House of Councillors with a two-thirds majority. It can, however, be dissolved by the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
at will. Members of the house must be of Japanese nationality; those aged 18 years and older may vote, while those aged 25 years and older may run for office in the lower house.
The legislative powers of the House of Representatives is considered to be more powerful than that of the House of Councillors. While the House of Councillors has the ability to veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto ...
most decisions made by the House of Representatives, some however, can only be delayed. This includes the legislation of treaties, the budget, and the selection of the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
. The Prime Minister, and collectively his Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, can in turn, however, dissolve the House of Representatives whenever intended. While the House of Representatives is considered to be officially dissolved upon the preparation of the document, the House is only formally dissolved by the dissolution ceremony. The dissolution ceremony of the House is as follows:
# The document is rubber stamped by the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
, and wrapped in a purple silk cloth; an indication of a document of state act, done on behalf of the people.
# The document is passed on to the Chief Cabinet Secretary
The is a member of the cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transp ...
at the House of Representatives President's reception room.
# The document is taken to the Chamber for preparation by the General-Secretary.
# The General-Secretary prepares the document for reading by the Speaker.
# The Speaker of the House of Representatives promptly declares the dissolution of the House.
# The House of Representatives is formally dissolved.
It is customary that, upon the dissolution of the House, members will shout the Three Cheers of Banzai (萬歲).
House of Councillors
 The is the
The is the Upper house
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restric ...
, with half the members of the house being elected once every three years, for a six-year term. As of November 18, 2017, it has 242 members. Of these, 73 are elected from the 47 prefectural districts, by single non-transferable vote
Single non-transferable vote or SNTV is an electoral system used to elect multiple winners. It is a generalization of first-past-the-post, applied to multi-member districts with each voter casting just one vote. Unlike FPTP, which is a single-win ...
s, and 48 are elected from a nationwide list by proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
with open lists. The House of Councillors cannot be dissolved by the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
. Members of the house must be of Japanese nationality; those aged 18 years and older may vote, while those aged 30 years and older may run for office in the upper house.
As the House of Councillors can veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto ...
a decision made by the House of Representatives, the House of Councillors can cause the House of Representatives to reconsider its decision. The House of Representatives however, can still insist on its decision by overriding the veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto ...
by the House of Councillors with a two-thirds majority of its members present. Each year, and when required, the National Diet is convoked at the House of Councillors, on the advice of the Cabinet, for an extra or an ordinary session, by the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
. A short speech is, however, usually first made by the Speaker of the House of Representatives before the Emperor proceeds to convoke the Diet with his Speech from the throne.
Judicial

 The Judicial branch of Japan consists of the Supreme Court, and four other lower courts; the High Courts, District Courts, Family Courts and Summary Courts. Divided into four basic tiers, the Court's independence from the executive and legislative branches are guaranteed by the
The Judicial branch of Japan consists of the Supreme Court, and four other lower courts; the High Courts, District Courts, Family Courts and Summary Courts. Divided into four basic tiers, the Court's independence from the executive and legislative branches are guaranteed by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
, and is stated as: "no extraordinary tribunal shall be established, nor shall any organ or agency of the Executive be given final judicial power"; a feature known as the Separation of Powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typica ...
. Article 76 of the Constitution states that all the Court judges are independent in the exercise of their own conscience and that they are only bounded by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
and the laws. Court judges are removable only by public impeachment, and can only be removed, without impeachment, when they are judicially declared mentally or physically incompetent to perform their duties. The Constitution also explicitly denies any power for executive organs or agencies to administer disciplinary actions against judges. However, a Supreme Court judge may be dismissed by a majority in a referendum; of which, must occur during the first general election of the National Diet's House of Representatives following the judge's appointment, and also the first general election for every ten years lapse thereafter. Trials must be conducted, with judgment declared, publicly, unless the Court "unanimously determines publicity to be dangerous to public order or morals"; with the exception for trials of political offenses, offenses involving the press, and cases wherein the rights of people as guaranteed by the Constitution, which cannot be deemed and conducted privately. Court judges are appointed by the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, in attestation of the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
, while the Chief Justice is appointed by the Emperor, after being nominated by the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
; which in practice, known to be under the recommendation of the former Chief Justice.
The Legal system
The contemporary national legal systems are generally based on one of four basic systems: civil law, common law, statutory law, religious law or combinations of these. However, the legal system of each country is shaped by its unique history an ...
in Japan has been historically influenced by Chinese law; developing independently during the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional ''daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was character ...
through texts such as ''Kujikata Osadamegaki ''Kujikata Osadamegaki'' (公事方御定書, "book of rules for public officials") was a two-volume rulebook for Japanese judicial bureaucrats during the Edo period (江戸時代). It was enacted by Shōgun Tokugawa Yoshimune in 1742.
The book was ...
''. It has, however, changed during the Meiji Restoration, and is now largely based on the Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
an civil law
Civil law may refer to:
* Civil law (common law), the part of law that concerns private citizens and legal persons
* Civil law (legal system), or continental law, a legal system originating in continental Europe and based on Roman law
** Private la ...
; notably, the civil code based on the German model still remains in effect. A quasi-jury system has recently came into use, and the legal system also includes a bill of rights since May 3, 1947. The collection of Six Codes makes up the main body of the Japanese statutory law.
All Statutory Laws in Japan are required to be rubber stamped by the Emperor with the , and no Law can take effect without the Cabinet's signature, the Prime Minister's countersignature and the Emperor's promulgation.
Supreme Court
 The is the court of last resort and has the power of Judicial review; as defined by the Constitution to be "the court of last resort with power to determine the constitutionality of any law, order, regulation or official act". The Supreme Court is also responsible for nominating judges to lower courts and determining judicial procedures. It also oversees the judicial system, overseeing activities of public prosecutors, and disciplining judges and other judicial personnel.
The is the court of last resort and has the power of Judicial review; as defined by the Constitution to be "the court of last resort with power to determine the constitutionality of any law, order, regulation or official act". The Supreme Court is also responsible for nominating judges to lower courts and determining judicial procedures. It also oversees the judicial system, overseeing activities of public prosecutors, and disciplining judges and other judicial personnel.
High Courts
The has the jurisdiction to hear appeals to judgments rendered by District Courts and Family Courts, excluding cases under the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court. Criminal appeals are directly handled by the High Courts, but Civil cases are first handled by District Courts. There are eight High Courts in Japan: the Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya, Hiroshima, Fukuoka, Sendai, Sapporo, and Takamatsu High Courts.Penal system
The is operated by theMinistry of Justice A Ministry of Justice is a common type of government department that serves as a justice ministry.
Lists of current ministries of justice
Named "Ministry"
* Ministry of Justice (Abkhazia)
* Ministry of Justice (Afghanistan)
* Ministry of Just ...
. It is part of the criminal justice system, and is intended to resocialize, reform
Reform ( lat, reformo) means the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The use of the word in this way emerges in the late 18th century and is believed to originate from Christopher Wyvill's Association movement ...
, and rehabilitate offenders. The ministry's Correctional Bureau administers the adult prison system, the juvenile correctional system, and three of the women's guidance homes, while the Rehabilitation Bureau operates the probation and the parole
Parole (also known as provisional release or supervised release) is a form of early release of a prison inmate where the prisoner agrees to abide by certain behavioral conditions, including checking-in with their designated parole officers, or ...
systems.
Other government agencies
 The Cabinet Public Affairs Office's Government Directory also listed a number of government agencies that are more independent from executive ministries. The list for these types of agencies can be seen below.
* Japan National Tourism Organisation (JNTO)
* Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA)
* Japan External Trade Organisation (JETRO)
* The Japan Foundation
*
The Cabinet Public Affairs Office's Government Directory also listed a number of government agencies that are more independent from executive ministries. The list for these types of agencies can be seen below.
* Japan National Tourism Organisation (JNTO)
* Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA)
* Japan External Trade Organisation (JETRO)
* The Japan Foundation
* Bank of Japan
The is the central bank of Japan. Nussbaum, Louis Frédéric. (2005). "Nihon Ginkō" in The bank is often called for short. It has its headquarters in Chūō, Tokyo.
History
Like most modern Japanese institutions, the Bank of Japan was fou ...
* Japan Mint
* National Research Bureau of Brewing (NRIB)
* State Guest Houses ( Akasaka Palace, Kyoto State Guest House
is one of the two state guest houses of the Government of Japan. The other state guesthouse is the Akasaka Palace.
History
During the Edo period (1603 – 1868) a Garden House and multiple mansions of aristocrats stood in the northeastern part ...
)
* National Archives of Japan
* National Women's Education Centre
* Japan Broadcasting Corporation (NHK)
* National Institutes for Cultural Heritage
* Japan Arts Council
* Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
* Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
* Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)
* Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC)
* National Institute for Materials Science (JIMS)
* Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA)
* New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO)
* National Institute of Infectious Diseases (NIID)
* The Japan Institute for Labour Policy and Training
Local government
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
and Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
, have experimented with policies in such areas as social welfare that later were adopted by the national government.
Local authorities
Japan is divided into forty-seven administrative divisions, the prefectures are: one metropolitan district (Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
), two urban prefectures (Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
and Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
), forty-three rural prefectures, and one "district", Hokkaidō. Large cities are subdivided into wards, and further split into towns, or precincts, or subprefectures and counties.
Cities are self-governing units administered independently of the larger jurisdictions within which they are located. In order to attain city status, a jurisdiction must have at least 500,000 inhabitants, 60 percent of whom are engaged in urban occupations. There are self-governing towns outside the cities as well as precincts of urban wards. Like the cities, each has its own elected mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as ...
and assembly. Villages are the smallest self-governing entities in rural areas. They often consist of a number of rural hamlets containing several thousand people connected to one another through the formally imposed framework of village administration. Villages have mayors and councils elected to four-year terms.
Structure
Each jurisdiction has a chief executive, called a in prefectures and a in municipalities. Most jurisdictions also have a unicameral , although towns and villages may opt for direct governance by citizens in a . Both the executive and assembly are elected by popular vote every four years. Local governments follow a modified version of theseparation of powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typica ...
used in the national government. An assembly may pass a vote of no confidence in the executive, in which case the executive must either dissolve the assembly within ten days or automatically lose their office. Following the next election, however, the executive remains in office unless the new assembly again passes a no confidence resolution.
The primary methods of local lawmaking are and . Ordinances, similar to statutes in the national system, are passed by the assembly and may impose limited criminal penalties for violations (up to 2 years in prison and/or 1 million yen in fines). Regulations, similar to cabinet orders in the national system, are passed by the executive unilaterally, are superseded by any conflicting ordinances, and may only impose a fine of up to 50,000 yen.
Local governments also generally have multiple committee
A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly. A committee is not itself considered to be a form of assembly. Usually, the assembly sends matters into a committee as a way to explore them more ...
s such as school boards, public safety committees (responsible for overseeing the police
The police are a constituted body of persons empowered by a state, with the aim to enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citizens, and to prevent crime and civil disorder. Their lawful powers include arrest a ...
), personnel committees, election committees and auditing committees. These may be directly elected or chosen by the assembly, executive or both.
All prefectures are required to maintain departments of general affairs, finance, welfare, health, and labor. Departments of agriculture, fisheries, forestry, commerce, and industry are optional, depending on local needs. The Governor is responsible for all activities supported through local taxation or the national government.
See also
* Japanese honours system *Politics of Japan
Politics of Japan are conducted in a framework of a dominant-party bicameral parliamentary constitutional monarchy, in which the Emperor is the head of state and the Prime Minister is the head of government and the head of the Cabinet, w ...
References
External links
Background notes of the US Department of State, Japan's Government
Facts about Japan by CIA's The World Factbook
Video of the Enthronement Ceremony of the Emperor
Video of the National Diet Convocation Ceremony
Video of the House of Representatives Dissolution Ceremony
* {{Asia topic, Government of, title=Governments of Asia, TW=Government of the Republic of China