Gonococcemia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gonococcemia (also known as "Disseminated gonococcal infection") is a rare complication of mucosal ''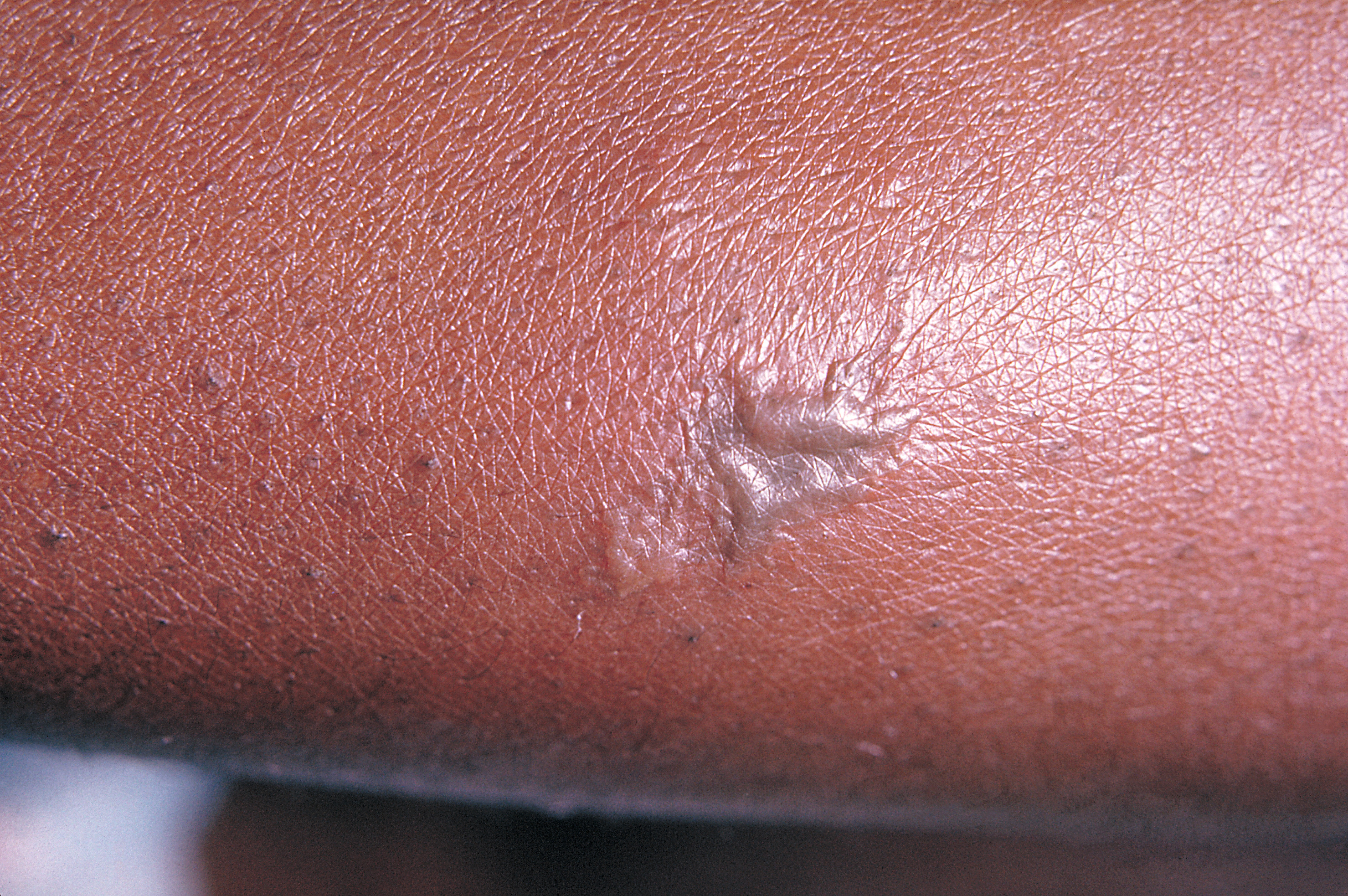
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', also known as ''gonococcus'' (singular), or ''gonococci'' (plural), is a species of Gram-negative diplococci bacteria isolated by Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser, Albert Neisser in 1879. It causes the sexually transmit ...
'' infection, or Gonorrhea, that occurs when the bacteria invade the bloodstream. It is characterized by fever, tender hemorrhagic pustules on the extremities or the trunk, migratory polyarthritis, and tenosynovitis. It also rarely leads to endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
and meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
. This condition occurs in 0.5-3% of individuals with gonorrhea, and it usually presents 2–3 weeks after acquiring the infection. Risk factors include female sex, sexual promiscuity, and infection with resistant strains of ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. This condition is treated with cephalosporin and fluoroquinolone antibiotics.

Epidemiology
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', also known as ''gonococcus'' (singular), or ''gonococci'' (plural), is a species of Gram-negative diplococci bacteria isolated by Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser, Albert Neisser in 1879. It causes the sexually transmit ...
'' is a gram negative diplococcus (also referred to as "Gonococcus") and a pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
ic bacteria. In 2019, there were 616,392 reported cases of gonorrhea in the United States, with an overall increased rate 5.7% from 2018 to 2019. Among those approximately 600,000 cases, it is estimated that 0.5-3% of gonorrheal infections result in gonococcemia. This condition is more common in women, affecting approximately 2.3-3% of women with gonorrhea and 0.4-0.7% of men. This discrepancy is explained by increased incidence of silent gonorrheal infections in females and an increased rate of transmission to females that have sexual intercourse with infected males. Gonococcemia also occurs more frequently in pregnant women, those with recent menstruation, and those with IUDs.
Risk Factors
* Infection with certain strains of ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' * Prolonged infection * Female sex (due to asymptomatic infection, and therefore prolonged infection) * Sexual promiscuity * Immune system deficiencies * Infection duringmenstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of hor ...
, pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
, or in the puerperium
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within 6 weeks as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium, puerperal perio ...
period
Symptoms
* Fever * Migratory arthralgias * Hemorrhagic pustules * Tenosynovitis * Rarely headache, neck stiffness, and visual changes (associated with meningitis)Treatment
Treatment typically consists ofcephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics ...
and fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Gonococcemia is typically treated with intravenous or intramuscular cephalosporin antibiotics. Approximately 10-30% of gonorrheal infections present with a co-infection of chlamydia, so it is common to add a one-time dose of oral azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneumon ...
or doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, an ...
for coverage of '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Bacterial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. P ...
to antibiotics is increasingly common in ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', so it is often advised to check susceptibility of the bacterial culture and then adjust the antibiotic therapy as needed.
Pathogenesis
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' is transmitted during sexual contact with an infected individual. The bacteria invade the non-ciliated columnar epithelium of the urogenital tract, oral mucosa, or anal mucosa following exposure. Invasion of the host cells is made possible due to virulence factors such as Pili, LOS, Opa, and others. Similarly, these virulence factors can be used for avoiding the host immune system, which may explain prolonged infection, bacterial resistance, and gonococcemia.See also
* Primary gonococcal dermatitis *List of cutaneous conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against t ...
References
{{Bacterial cutaneous infections Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions Medical triads