Golm Metabolome Database on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The Golm Metabolome Database (GMD) is a gas chromatography (GC) – mass spectrometry (MS) reference library dedicated to
The Golm Metabolome Database (GMD) is a gas chromatography (GC) – mass spectrometry (MS) reference library dedicated to
GMD website
Mass spectrometry software Organic compounds Chemical databases Metabolomic databases Biological databases



 The Golm Metabolome Database (GMD) is a gas chromatography (GC) – mass spectrometry (MS) reference library dedicated to
The Golm Metabolome Database (GMD) is a gas chromatography (GC) – mass spectrometry (MS) reference library dedicated to metabolite profiling
Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprin ...
experiments and comprises mass spectral and retention index (RI) information for non-annotated mass spectral tags (MSTs, mass spectral information with retention time attached indices) together with data of a multitude of already identified metabolites and reference substances. The GMD is hosted at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology in Golm district of Potsdam, Germany.
Background
Gas chromatography (GC) coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) is one of the most widespread routine technologies applied to the large scale screening and discovery of novel biomarkers in metabolomics. However, the majority of MSTs currently measured in plant metabolomic profiling experiments remains unidentified due to the lack of authenticated pure reference substances and the expensive and time-consuming effort to maintain mass spectral RI libraries required for compound identification by GC-MS. As the communication of analytical results and other approach-related details such as mass spectral and RI reference information within the scientific community is becoming increasingly popular, open access platforms for information exchange, such as the GMD, are obligatory. Due to the lack of mandatory standards it remains difficult to compare individual mass spectrums. While the different mass detector technologies, namely quadrupole, ion trap and time of flight, can be deemed irrelevant, the chromatography settings such as temperature programming, type of capillary column and choice of column manufacturer heavily affect the empirically determined RI properties. Procedures for the transfer of RI properties between chromatography variants are, therefore, highly relevant for a shared library use. The GMD assesses the accuracy of RI transfer between chromatography variants and implements means to transfer empirically determined RI properties. Aiming at the classification and identification of un-identified MSTs, the GMD accesses the information on available reference compounds. These compounds serve as training set of data to apply decision trees (DT) as a supervised machine learning approach. Structural feature extraction was applied to classify the metabolite space of the GMD prior to DT training. DT-based predictions of the most frequent substructures classify low resolution GC-MS mass spectra of the linked (potentially unknown) metabolite with respect to the presence or absence of the chemical moieties. The web-based frontend supports conventional mass spectral and RI comparison by ranked hit lists as well as advanced DT supported substructure prediction. Batch processing is enabled via Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)-based web services while web-based data access services expose particular data base entities adapting Representational State Transfer (ReST) principles and mass spectral standards such asNIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...
-MSP and JCAMP The Joint Committee on Atomic and Molecular Physical Data (JCAMP) defined several JCAMP-DX (JCAMP-data exchange) file formats in chemistry. IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of ...
-DX.
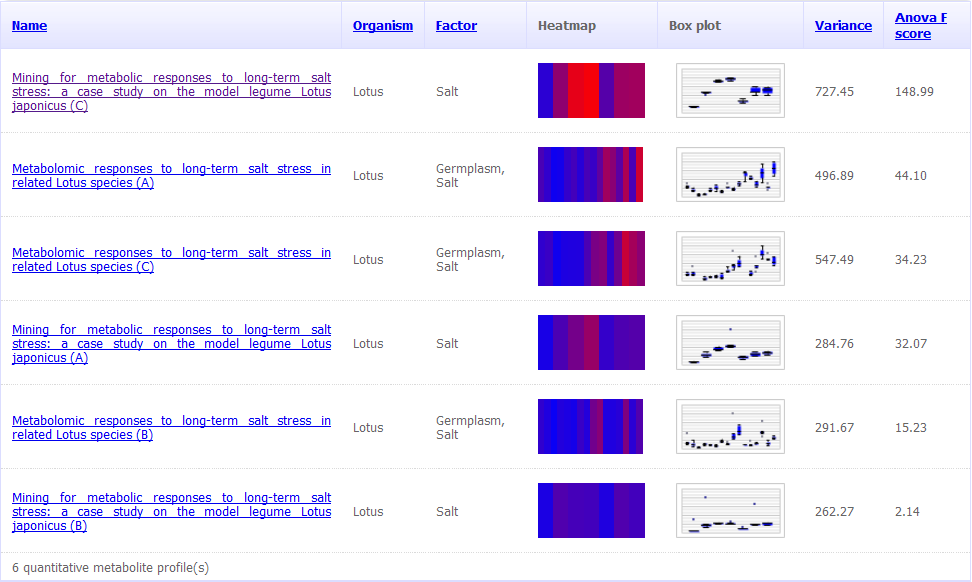
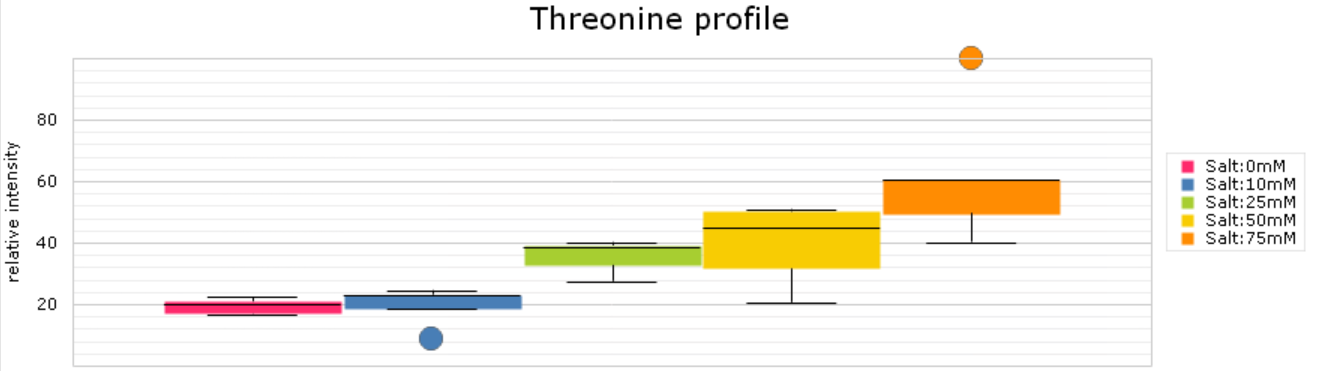
The GMD visualise quantitative metabolite pool size changes data.
See also
*Human Metabolome Database
The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a comprehensive, high-quality, freely accessible, online database of small molecule metabolites found in the human body. Created by the Human Metabolome Project funded by Genome Canada. One of the fir ...
* MassBank
References
{{reflistExternal links
GMD website
Mass spectrometry software Organic compounds Chemical databases Metabolomic databases Biological databases