Gold Bulletin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gold is a
 Gold is the most
Gold is the most
 Whereas most metals are gray or silvery white, gold is slightly reddish-yellow. This color is determined by the frequency of
Whereas most metals are gray or silvery white, gold is slightly reddish-yellow. This color is determined by the frequency of
 Although gold is the most noble of the
Although gold is the most noble of the 2 Au + 3 F2 ->[t] 2 AuF3
: 2 Au + 3 Cl2 ->[t] 2 AuCl3
: 2 Au + 2 Br2 ->[t] AuBr3 + AuBr
: 2 Au + I2 ->[t] 2 AuI
Gold does not react with sulfur directly, but gold(III) sulfide can be made by passing hydrogen sulfide through a dilute solution of gold(III) chloride or chlorauric acid.
Gold readily dissolves in 2 Au + 6 H2SeO4 ->[200^\circ C] Au2(SeO4)3 + 3 H2SeO3 + 3 H2O
: Au + 4HCl + HNO3 -> H[AuCl4] + NO\uparrow + 2H2O
Gold is similarly unaffected by most bases. It does not react with aqueous solution, aqueous, solid, or molten sodium hydroxide, sodium or potassium hydroxide. It does however, react with sodium cyanide, sodium or potassium cyanide under alkaline conditions when oxygen is present to form soluble complexes.
Common
 Gold is thought to have been produced in supernova nucleosynthesis, and from the Neutron star merger, collision of neutron stars, and to have been present in the solar nebula, dust from which the Solar System formed.
Traditionally, gold in the universe is thought to have formed by the r-process (rapid neutron capture) in supernova nucleosynthesis, but more recently it has been suggested that gold and other elements heavier than
Gold is thought to have been produced in supernova nucleosynthesis, and from the Neutron star merger, collision of neutron stars, and to have been present in the solar nebula, dust from which the Solar System formed.
Traditionally, gold in the universe is thought to have formed by the r-process (rapid neutron capture) in supernova nucleosynthesis, but more recently it has been suggested that gold and other elements heavier than
 The earliest recorded metal employed by humans appears to be gold, which can be found native metal, free or "native metal, native". Small amounts of natural gold have been found in Spanish caves used during the late Paleolithic period, c. 40,000 BC.
The oldest gold artifacts in the world are from Bulgaria and are dating back to the 5th millennium BC (4,600 BC to 4,200 BC), such as those found in the Varna Necropolis near Lake Varna and the Black Sea coast, thought to be the earliest "well-dated" finding of gold artifacts in history. Several prehistoric Bulgarian finds are considered no less old – the golden treasures of Hotnitsa, Durankulak, artifacts from the Kurgan settlement of Yunatsite near Pazardzhik, the golden treasure Sakar, as well as beads and gold jewelry found in the Kurgan settlement of Provadia – Solnitsata (“salt pit”). However, Varna gold is most often called the oldest since this treasure is the largest and most diverse.
Gold artifacts probably made their first appearance in Ancient Egypt at the very beginning of the pre-dynastic period, at the end of the fifth millennium BC and the start of the fourth, and smelting was developed during the course of the 4th millennium; gold artifacts appear in the archeology of Lower Mesopotamia during the early 4th millennium. As of 1990, gold artifacts found at the Wadi Qana cave cemetery of the 4th millennium BC in West Bank were the earliest from the Levant. Gold artifacts such as the golden hats and the Nebra disk appeared in Central Europe from the 2nd millennium BC European Bronze Age, Bronze Age.
The oldest known map of a gold mine was drawn in the 19th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt (1320–1200 BC), whereas the first written reference to gold was recorded in the 12th Dynasty around 1900 BC. Egyptian hieroglyphs from as early as 2600 BC describe gold, which King Tushratta of the Mitanni claimed was "more plentiful than dirt" in Egypt. Egypt and especially Nubia had the resources to make them major gold-producing areas for much of history. One of the earliest known maps, known as the Turin Papyrus Map, shows the plan of a gold mine in Nubia together with indications of the local geology. The primitive working methods are described by both Strabo and Diodorus Siculus, and included fire-setting. Large mines were also present across the Red Sea in what is now Saudi Arabia.
The earliest recorded metal employed by humans appears to be gold, which can be found native metal, free or "native metal, native". Small amounts of natural gold have been found in Spanish caves used during the late Paleolithic period, c. 40,000 BC.
The oldest gold artifacts in the world are from Bulgaria and are dating back to the 5th millennium BC (4,600 BC to 4,200 BC), such as those found in the Varna Necropolis near Lake Varna and the Black Sea coast, thought to be the earliest "well-dated" finding of gold artifacts in history. Several prehistoric Bulgarian finds are considered no less old – the golden treasures of Hotnitsa, Durankulak, artifacts from the Kurgan settlement of Yunatsite near Pazardzhik, the golden treasure Sakar, as well as beads and gold jewelry found in the Kurgan settlement of Provadia – Solnitsata (“salt pit”). However, Varna gold is most often called the oldest since this treasure is the largest and most diverse.
Gold artifacts probably made their first appearance in Ancient Egypt at the very beginning of the pre-dynastic period, at the end of the fifth millennium BC and the start of the fourth, and smelting was developed during the course of the 4th millennium; gold artifacts appear in the archeology of Lower Mesopotamia during the early 4th millennium. As of 1990, gold artifacts found at the Wadi Qana cave cemetery of the 4th millennium BC in West Bank were the earliest from the Levant. Gold artifacts such as the golden hats and the Nebra disk appeared in Central Europe from the 2nd millennium BC European Bronze Age, Bronze Age.
The oldest known map of a gold mine was drawn in the 19th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt (1320–1200 BC), whereas the first written reference to gold was recorded in the 12th Dynasty around 1900 BC. Egyptian hieroglyphs from as early as 2600 BC describe gold, which King Tushratta of the Mitanni claimed was "more plentiful than dirt" in Egypt. Egypt and especially Nubia had the resources to make them major gold-producing areas for much of history. One of the earliest known maps, known as the Turin Papyrus Map, shows the plan of a gold mine in Nubia together with indications of the local geology. The primitive working methods are described by both Strabo and Diodorus Siculus, and included fire-setting. Large mines were also present across the Red Sea in what is now Saudi Arabia.
 Gold is mentioned in the Amarna letters numbered Amarna letter EA 19, 19 and Amarna letter EA 26, 26 from around the 14th century BC.
Gold is mentioned frequently in the Old Testament, starting with Book of Genesis, Genesis 2:11 (at Havilah), the story of the golden calf, and many parts of the temple including the Menorah (Temple), Menorah and the golden altar. In the New Testament, it is included with the gifts of the magi in the first chapters of Matthew. The Book of Revelation 21:21 describes the city of New Jerusalem as having streets "made of pure gold, clear as crystal". Exploitation of gold in the south-east corner of the Black Sea is said to date from the time of Midas, and this gold was important in the establishment of what is probably the world's earliest coinage in Lydia around 610 BC. The legend of the golden fleece dating from eighth century BCE may refer to the use of fleeces to trap gold dust from placer deposits in the ancient world. From the 6th or 5th century BC, the Chu (state) circulated the Ying Yuan, one kind of square gold coin.
In Roman metallurgy, new methods for extracting gold on a large scale were developed by introducing hydraulic mining methods, especially in Hispania from 25 BC onwards and in Dacia from 106 AD onwards. One of their largest mines was at Las Medulas in León (province), León, where seven long aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts enabled them to sluice most of a large alluvial deposit. The mines at Roşia Montană in Transylvania were also very large, and until very recently, still mined by opencast methods. They also exploited smaller deposits in Roman Britain, Britain, such as placer and hard-rock deposits at Dolaucothi. The various methods they used are well described by Pliny the Elder in his encyclopedia ''Naturalis Historia'' written towards the end of the first century AD.
During Mansa Musa's (ruler of the Mali Empire from 1312 to 1337) hajj to Mecca in 1324, he passed through Cairo in July 1324, and was reportedly accompanied by a camel train that included thousands of people and nearly a hundred camels where he gave away so much gold that it depressed the price in Egypt for over a decade, causing high inflation. A contemporary Arab historian remarked:
Gold is mentioned in the Amarna letters numbered Amarna letter EA 19, 19 and Amarna letter EA 26, 26 from around the 14th century BC.
Gold is mentioned frequently in the Old Testament, starting with Book of Genesis, Genesis 2:11 (at Havilah), the story of the golden calf, and many parts of the temple including the Menorah (Temple), Menorah and the golden altar. In the New Testament, it is included with the gifts of the magi in the first chapters of Matthew. The Book of Revelation 21:21 describes the city of New Jerusalem as having streets "made of pure gold, clear as crystal". Exploitation of gold in the south-east corner of the Black Sea is said to date from the time of Midas, and this gold was important in the establishment of what is probably the world's earliest coinage in Lydia around 610 BC. The legend of the golden fleece dating from eighth century BCE may refer to the use of fleeces to trap gold dust from placer deposits in the ancient world. From the 6th or 5th century BC, the Chu (state) circulated the Ying Yuan, one kind of square gold coin.
In Roman metallurgy, new methods for extracting gold on a large scale were developed by introducing hydraulic mining methods, especially in Hispania from 25 BC onwards and in Dacia from 106 AD onwards. One of their largest mines was at Las Medulas in León (province), León, where seven long aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts enabled them to sluice most of a large alluvial deposit. The mines at Roşia Montană in Transylvania were also very large, and until very recently, still mined by opencast methods. They also exploited smaller deposits in Roman Britain, Britain, such as placer and hard-rock deposits at Dolaucothi. The various methods they used are well described by Pliny the Elder in his encyclopedia ''Naturalis Historia'' written towards the end of the first century AD.
During Mansa Musa's (ruler of the Mali Empire from 1312 to 1337) hajj to Mecca in 1324, he passed through Cairo in July 1324, and was reportedly accompanied by a camel train that included thousands of people and nearly a hundred camels where he gave away so much gold that it depressed the price in Egypt for over a decade, causing high inflation. A contemporary Arab historian remarked:
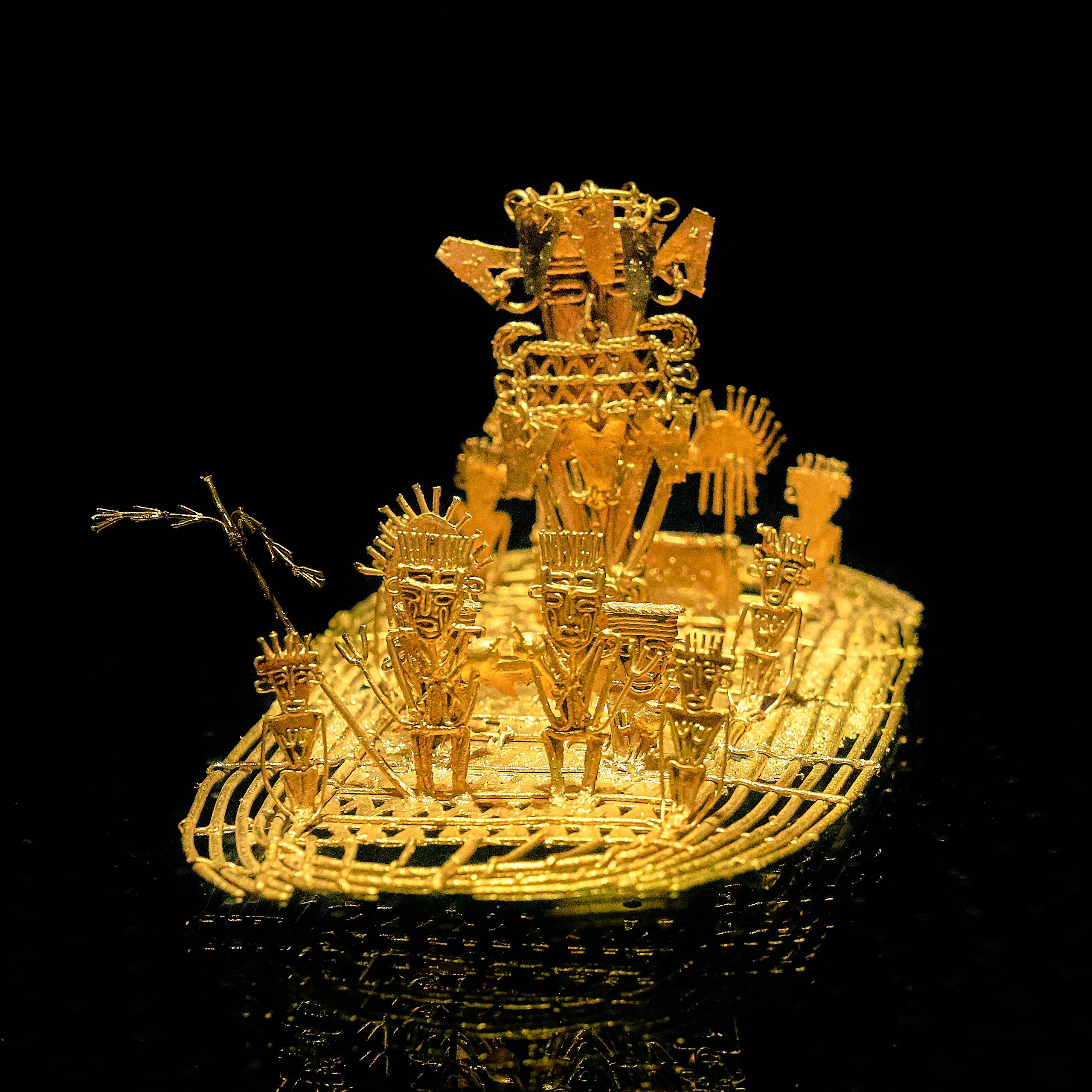
 The European exploration of the Americas was fueled in no small part by reports of the gold ornaments displayed in great profusion by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American peoples, especially in Mesoamerica, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia. The Aztecs regarded gold as the product of the gods, calling it literally "god excrement" (''teocuitlatl'' in Nahuatl), and after Moctezuma II was killed, most of this gold was shipped to Spain. However, for the indigenous peoples of North America gold was considered useless and they saw much greater value in other minerals which were directly related to their utility, such as obsidian, flint, and slate. El Dorado is applied to a legendary story in which precious stones were found in fabulous abundance along with gold coins. The concept of El Dorado underwent several transformations, and eventually accounts of the previous myth were also combined with those of a legendary lost city. El Dorado, was the term used by the Spanish Empire to describe a mythical tribal chief (zipa) of the Muisca native people in Colombia, who, as an initiation rite, covered himself with gold dust and submerged in Lake Guatavita. The legends surrounding El Dorado changed over time, as it went from being a man, to a city, to a kingdom, and then finally to an empire.
Beginning in the early modern period, European Age of Discovery, exploration and Colonisation of Africa, colonization of West Africa was driven in large part by reports of gold deposits in the region, which was eventually referred to by Europeans as the "Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast". From the late 15th to early 19th centuries, European trade in the region was primarily focused in gold, along with ivory and Atlantic slave trade, slaves. The gold trade in West Africa was dominated by the Ashanti Empire, who initially traded with the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese before branching out and trading with British Empire, British, French colonial empire, French, Spanish Empire, Spanish and Danish colonial empire, Danish merchants. British desires to secure control of West African gold deposits played a role in the Anglo-Ashanti wars of the late 19th century, which saw the Ashanti Empire Gold Coast (British colony), annexed by Britain.
Gold played a role in western culture, as a cause for desire and of corruption, as told in children's fables such as Rumpelstiltskin—where Rumpelstiltskin turns hay into gold for the peasant's daughter in return for her child when she becomes a princess—and the stealing of the hen that lays golden eggs in Jack and the Beanstalk.
The top prize at the Olympic Games and many other sports competitions is the gold medal.
75% of the presently accounted for gold has been extracted since 1910, two-thirds since 1950.
One main goal of the alchemy, alchemists was to produce gold from other substances, such as
The European exploration of the Americas was fueled in no small part by reports of the gold ornaments displayed in great profusion by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American peoples, especially in Mesoamerica, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia. The Aztecs regarded gold as the product of the gods, calling it literally "god excrement" (''teocuitlatl'' in Nahuatl), and after Moctezuma II was killed, most of this gold was shipped to Spain. However, for the indigenous peoples of North America gold was considered useless and they saw much greater value in other minerals which were directly related to their utility, such as obsidian, flint, and slate. El Dorado is applied to a legendary story in which precious stones were found in fabulous abundance along with gold coins. The concept of El Dorado underwent several transformations, and eventually accounts of the previous myth were also combined with those of a legendary lost city. El Dorado, was the term used by the Spanish Empire to describe a mythical tribal chief (zipa) of the Muisca native people in Colombia, who, as an initiation rite, covered himself with gold dust and submerged in Lake Guatavita. The legends surrounding El Dorado changed over time, as it went from being a man, to a city, to a kingdom, and then finally to an empire.
Beginning in the early modern period, European Age of Discovery, exploration and Colonisation of Africa, colonization of West Africa was driven in large part by reports of gold deposits in the region, which was eventually referred to by Europeans as the "Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast". From the late 15th to early 19th centuries, European trade in the region was primarily focused in gold, along with ivory and Atlantic slave trade, slaves. The gold trade in West Africa was dominated by the Ashanti Empire, who initially traded with the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese before branching out and trading with British Empire, British, French colonial empire, French, Spanish Empire, Spanish and Danish colonial empire, Danish merchants. British desires to secure control of West African gold deposits played a role in the Anglo-Ashanti wars of the late 19th century, which saw the Ashanti Empire Gold Coast (British colony), annexed by Britain.
Gold played a role in western culture, as a cause for desire and of corruption, as told in children's fables such as Rumpelstiltskin—where Rumpelstiltskin turns hay into gold for the peasant's daughter in return for her child when she becomes a princess—and the stealing of the hen that lays golden eggs in Jack and the Beanstalk.
The top prize at the Olympic Games and many other sports competitions is the gold medal.
75% of the presently accounted for gold has been extracted since 1910, two-thirds since 1950.
One main goal of the alchemy, alchemists was to produce gold from other substances, such as
Gold leaf MET DP260372.jpg, Minoan civilization, Minoan jewellery; 2300–2100 BC; various sizes; Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City)
Earrings from Shulgi.JPG, Pair of Sumerian earrings with cuneiform inscriptions; 2093–2046 BC; Sulaymaniyah Museum (Sulaymaniyah, Iraq)
Statuette of Amun MET DT553.jpg, Ancient Egyptian statuette of Amun; 945–715 BC; gold; ; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Anillo de Sheshonq (46627183381).jpg, Ancient Egyptian signet ring; 664–525 BC; gold; diameter: ; British Museum (London)
Gold stater MET DP138743.jpg, Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek stater; 323–315 BC; ; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gold funerary wreath MET DP257471.jpg, Etruscans, Etruscan funerary wreath; 4th–3rd century BC; length: ; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gold aureus of Hadrian MET DP104782b.jpg, Roman Empire, Roman aureus of Hadrian; 134–138 AD; 7.4 g; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Lime Container (Poporo) MET DT1262.jpg, Quimbaya civilization, Quimbaya lime container; 5th–9th century; gold; height: ; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Byzantium, 11th century - Scyphate - 2001.25 - Cleveland Museum of Art.tif, Byzantine empire, Byzantine scyphate; 1059–1067; diameter: ; Cleveland Museum of Art (Cleveland, Ohio, USA)
Double Bat-Head Figure Pendant MET DT935.jpg, Pre-Columbian era, Pre-Columbian pendant with two bat-head warriors who carry spears; 11th–16th century; gold; overall: ; from the Chiriqui Province (Panama); Metropolitan Museum of Art
Box with scene depicting Roman hero Gaius Mucius Scaevola before the Etruscan king Lars Porsena MET DP170836 (cropped).jpg, English Neoclassicism, Neoclassical box; 1741; overall: ; Metropolitan Museum of Art
France, 18th century - Scent Bottle - 1916.315 - Cleveland Museum of Art.tif, French Rococo glass bottle mounted in gold; circa 1775; overall: ; Cleveland Museum of Art
 "Gold" is cognate with similar words in many Germanic languages, deriving via Proto-Germanic wikt:Appendix:Proto-Germanic/gulþą, *''gulþą'' from Proto-Indo-European wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/ǵʰelh₃-, *''ǵʰelh₃-'' ("to shine, to gleam; to be yellow or green").
The symbol ''Au'' is from the la, :wikt:aurum, aurum, the Latin word for "gold". The Proto-Indo-European ancestor of ''aurum'' was ''*h₂é-h₂us-o-'', meaning "glow". This word is derived from the same Root (linguistics), root (Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂u̯es-'' "to dawn") as wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/h₂éwsōs, ''*h₂éu̯sōs'', the ancestor of the Latin word Aurora, "dawn". This etymological relationship is presumably behind the frequent claim in scientific publications that ''aurum'' meant "shining dawn".Christie, A and Brathwaite, R. (Last updated 2 November 2011
"Gold" is cognate with similar words in many Germanic languages, deriving via Proto-Germanic wikt:Appendix:Proto-Germanic/gulþą, *''gulþą'' from Proto-Indo-European wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/ǵʰelh₃-, *''ǵʰelh₃-'' ("to shine, to gleam; to be yellow or green").
The symbol ''Au'' is from the la, :wikt:aurum, aurum, the Latin word for "gold". The Proto-Indo-European ancestor of ''aurum'' was ''*h₂é-h₂us-o-'', meaning "glow". This word is derived from the same Root (linguistics), root (Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂u̯es-'' "to dawn") as wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/h₂éwsōs, ''*h₂éu̯sōs'', the ancestor of the Latin word Aurora, "dawn". This etymological relationship is presumably behind the frequent claim in scientific publications that ''aurum'' meant "shining dawn".Christie, A and Brathwaite, R. (Last updated 2 November 2011
Mineral Commodity Report 14 — Gold
Institute of geological and Nuclear sciences Ltd – Retrieved 7 June 2012
 In popular culture gold is a high standard of excellence, often used in awards. Great achievements are frequently rewarded with gold, in the form of gold medals, gold trophy, trophies and other decorations. Winners of athletic events and other graded competitions are usually awarded a gold medal. Many awards such as the Nobel Prize are made from gold as well. Other award statues and prizes are depicted in gold or are gold plated (such as the Academy Awards, the Golden Globe Awards, the Emmy Awards, the Palme d'Or, and the British Academy Film Awards).
Aristotle in his Aristotelian ethics, ethics used gold symbolism when referring to what is now known as the golden mean (philosophy), golden mean. Similarly, gold is associated with perfect or divine principles, such as in the case of the golden ratio and the golden rule. Gold is further associated with the wisdom of aging and fruition. The fiftieth wedding anniversary is golden. A person's most valued or most successful latter years are sometimes considered "golden years". The height of a civilization is referred to as a golden age (metaphor), golden age.
In popular culture gold is a high standard of excellence, often used in awards. Great achievements are frequently rewarded with gold, in the form of gold medals, gold trophy, trophies and other decorations. Winners of athletic events and other graded competitions are usually awarded a gold medal. Many awards such as the Nobel Prize are made from gold as well. Other award statues and prizes are depicted in gold or are gold plated (such as the Academy Awards, the Golden Globe Awards, the Emmy Awards, the Palme d'Or, and the British Academy Film Awards).
Aristotle in his Aristotelian ethics, ethics used gold symbolism when referring to what is now known as the golden mean (philosophy), golden mean. Similarly, gold is associated with perfect or divine principles, such as in the case of the golden ratio and the golden rule. Gold is further associated with the wisdom of aging and fruition. The fiftieth wedding anniversary is golden. A person's most valued or most successful latter years are sometimes considered "golden years". The height of a civilization is referred to as a golden age (metaphor), golden age.
 According to the United States Geological Survey in 2016, about of gold has been accounted for, of which 85% remains in active use.
According to the United States Geological Survey in 2016, about of gold has been accounted for, of which 85% remains in active use.

 Since the 1880s, South Africa has been the source of a large proportion of the world's gold supply, and about 22% of the gold presently accounted is from South Africa. Production in 1970 accounted for 79% of the world supply, about 1,480 tonnes. In 2007 China (with 276 tonnes) overtook South Africa as the world's largest gold producer, the first time since 1905 that South Africa had not been the largest.
In 2020, Gold mining in China, China was the world's leading gold-mining country, followed in order by Russia, Australia, the United States, Canada, and Ghana.
Since the 1880s, South Africa has been the source of a large proportion of the world's gold supply, and about 22% of the gold presently accounted is from South Africa. Production in 1970 accounted for 79% of the world supply, about 1,480 tonnes. In 2007 China (with 276 tonnes) overtook South Africa as the world's largest gold producer, the first time since 1905 that South Africa had not been the largest.
In 2020, Gold mining in China, China was the world's leading gold-mining country, followed in order by Russia, Australia, the United States, Canada, and Ghana.
 In South America, the controversial project Pascua Lama aims at exploitation of rich fields in the high mountains of Atacama Desert, at the border between Chile and Argentina.
It has been estimated that up to one-quarter of the yearly global gold production originates from artisanal or small scale mining.
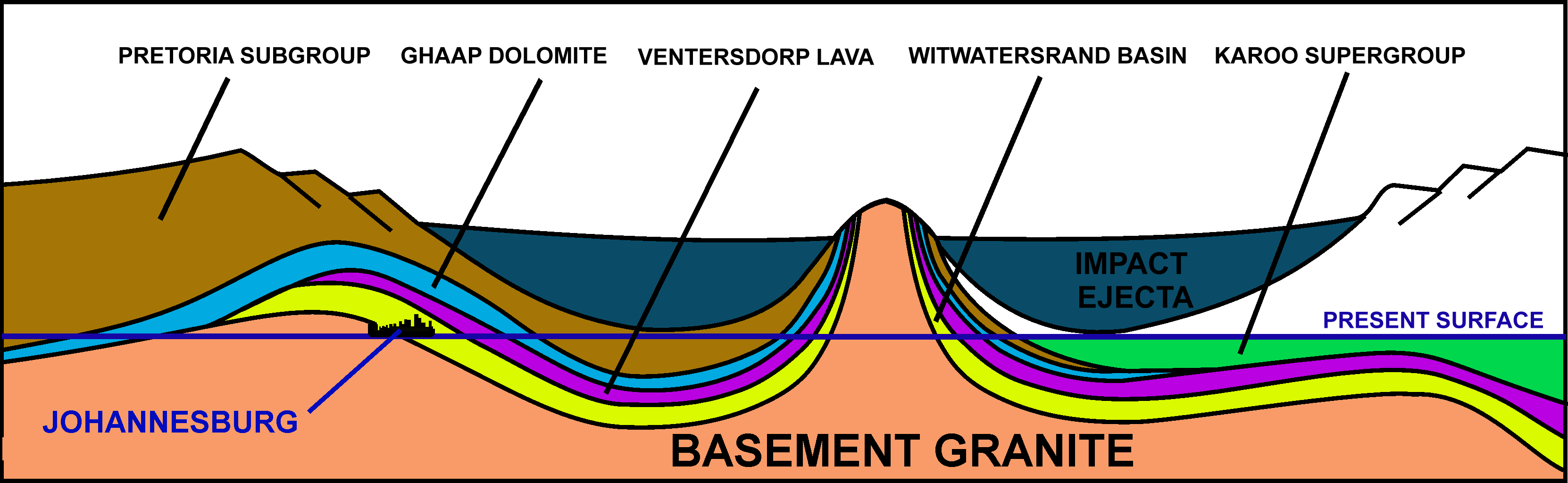
The city of Johannesburg located in South Africa was founded as a result of the Witwatersrand Gold Rush which resulted in the discovery of some of the largest natural gold deposits in recorded history. The gold fields are confined to the northern and north-western edges of the Witwatersrand basin, which is a thick layer of archean rocks located, in most places, deep under the Free State (South African province), Free State, Gauteng and surrounding provinces.Truswell, J.F. (1977). ''The Geological Evolution of South Africa''. pp. 21–28. Purnell, Cape Town. These Witwatersrand rocks are exposed at the surface on the Witwatersrand, in and around Johannesburg, but also in isolated patches to the south-east and south-west of Johannesburg, as well as in an arc around the Vredefort Dome which lies close to the center of the Witwatersrand basin. From these surface exposures the basin strike and dip, dips extensively, requiring some of the mining to occur at depths of nearly , making them, especially the Savuka Mine, Savuka and TauTona mines to the south-west of Johannesburg, the deepest mines on earth. The gold is found only in six areas where archean rivers from the north and north-west formed extensive pebbly Braided river deltas before draining into the "Witwatersrand sea" where the rest of the Witwatersrand sediments were deposited.
The Second Boer War of 1899–1901 between the British Empire and the Afrikaner Boers was at least partly over the rights of miners and possession of the gold wealth in South Africa.
In South America, the controversial project Pascua Lama aims at exploitation of rich fields in the high mountains of Atacama Desert, at the border between Chile and Argentina.
It has been estimated that up to one-quarter of the yearly global gold production originates from artisanal or small scale mining.
The city of Johannesburg located in South Africa was founded as a result of the Witwatersrand Gold Rush which resulted in the discovery of some of the largest natural gold deposits in recorded history. The gold fields are confined to the northern and north-western edges of the Witwatersrand basin, which is a thick layer of archean rocks located, in most places, deep under the Free State (South African province), Free State, Gauteng and surrounding provinces.Truswell, J.F. (1977). ''The Geological Evolution of South Africa''. pp. 21–28. Purnell, Cape Town. These Witwatersrand rocks are exposed at the surface on the Witwatersrand, in and around Johannesburg, but also in isolated patches to the south-east and south-west of Johannesburg, as well as in an arc around the Vredefort Dome which lies close to the center of the Witwatersrand basin. From these surface exposures the basin strike and dip, dips extensively, requiring some of the mining to occur at depths of nearly , making them, especially the Savuka Mine, Savuka and TauTona mines to the south-west of Johannesburg, the deepest mines on earth. The gold is found only in six areas where archean rivers from the north and north-west formed extensive pebbly Braided river deltas before draining into the "Witwatersrand sea" where the rest of the Witwatersrand sediments were deposited.
The Second Boer War of 1899–1901 between the British Empire and the Afrikaner Boers was at least partly over the rights of miners and possession of the gold wealth in South Africa.
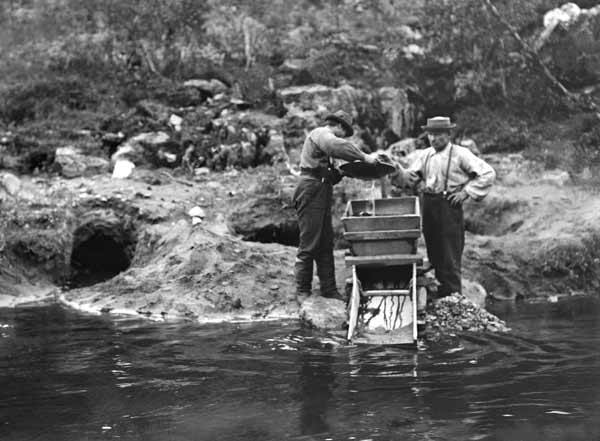 During the 19th century, gold rushes occurred whenever large gold deposits were discovered. The first documented discovery of gold in the United States was at the Reed Gold Mine near Georgeville, North Carolina in 1803. The first major gold strike in the United States occurred in a small north Georgia town called Dahlonega, Georgia, Dahlonega. Further gold rushes occurred in California Gold Rush, California, Pike's Peak Gold Rush, Colorado, the Black Hills Gold Rush, Black Hills, Central Otago Gold Rush, Otago in New Zealand, a number of locations across Australian gold rushes, Australia, Witwatersrand Gold Rush, Witwatersrand in South Africa, and the Klondike Gold Rush, Klondike in Canada.
Grasberg mine located in Papua (province), Papua, Indonesia is the largest gold mining, gold mine in the world.
During the 19th century, gold rushes occurred whenever large gold deposits were discovered. The first documented discovery of gold in the United States was at the Reed Gold Mine near Georgeville, North Carolina in 1803. The first major gold strike in the United States occurred in a small north Georgia town called Dahlonega, Georgia, Dahlonega. Further gold rushes occurred in California Gold Rush, California, Pike's Peak Gold Rush, Colorado, the Black Hills Gold Rush, Black Hills, Central Otago Gold Rush, Otago in New Zealand, a number of locations across Australian gold rushes, Australia, Witwatersrand Gold Rush, Witwatersrand in South Africa, and the Klondike Gold Rush, Klondike in Canada.
Grasberg mine located in Papua (province), Papua, Indonesia is the largest gold mining, gold mine in the world.
, ''The New York Times'', 24 October 2005 Gold ore dumps are the source of many heavy elements such as cadmium, lead, zinc, copper, arsenic, selenium and mercury. When sulfide-bearing minerals in these ore dumps are exposed to air and water, the sulfide transforms into sulfuric acid which in turn dissolves these heavy metals facilitating their passage into surface water and ground water. This process is called acid mine drainage. These gold ore dumps are long-term, highly hazardous wastes second only to nuclear waste dumps. It was once common to use mercury to recover gold from ore, but today the use of mercury is largely limited to small-scale individual miners. Minute quantities of mercury compounds can reach water bodies, causing heavy metal contamination. Mercury can then enter into the human food chain in the form of methylmercury. Mercury poisoning in humans causes incurable brain function damage and severe retardation. Gold extraction is also a highly energy-intensive industry, extracting ore from deep mines and grinding the large quantity of ore for further chemical extraction requires nearly 25 Kilowatt-hour, kWh of electricity per gram of gold produced.
 Gold has been History of money, widely used throughout the world as money, for efficient indirect exchange (versus barter), and to store wealth in hoards. For exchange purposes, Mint (coin), mints produce standardized bullion, gold bullion coins, gold bar, bars and Good delivery, other units of fixed weight and purity.
The first known coins containing gold were struck in Lydia, Asia Minor, around 600 BC. The ''talent (measurement), talent'' coin of gold in use during the periods of Grecian history both before and during the time of the life of Homer weighed between 8.42 and 8.75 grams. From an earlier preference in using silver, European economies re-established the minting of gold as coinage during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries.
Real bills doctrine, Bills (that mature into gold coin) and gold certificates (convertible into gold coin at the issuing bank) added to the circulating stock of
Gold has been History of money, widely used throughout the world as money, for efficient indirect exchange (versus barter), and to store wealth in hoards. For exchange purposes, Mint (coin), mints produce standardized bullion, gold bullion coins, gold bar, bars and Good delivery, other units of fixed weight and purity.
The first known coins containing gold were struck in Lydia, Asia Minor, around 600 BC. The ''talent (measurement), talent'' coin of gold in use during the periods of Grecian history both before and during the time of the life of Homer weighed between 8.42 and 8.75 grams. From an earlier preference in using silver, European economies re-established the minting of gold as coinage during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries.
Real bills doctrine, Bills (that mature into gold coin) and gold certificates (convertible into gold coin at the issuing bank) added to the circulating stock of
 , gold is valued at around $42 per gram ($1,300 per troy ounce).
Like other precious metals, gold is measured by troy weight and by grams. The proportion of gold in the alloy is measured by ''karat'' (k), with 24 karat (24k) being pure gold (100%), and lower karat numbers proportionally less (18k = 75%). The purity of a
, gold is valued at around $42 per gram ($1,300 per troy ounce).
Like other precious metals, gold is measured by troy weight and by grams. The proportion of gold in the alloy is measured by ''karat'' (k), with 24 karat (24k) being pure gold (100%), and lower karat numbers proportionally less (18k = 75%). The purity of a

 Because of the softness of pure (24k) gold, it is usually
Because of the softness of pure (24k) gold, it is usually
World Gold Council Nickel is toxic, and its release from nickel white gold is controlled by legislation in Europe. Palladium-gold alloys are more expensive than those using nickel. High-karat white gold alloys are more resistant to corrosion than are either pure silver or sterling silver. The Japanese craft of Mokume-gane exploits the color contrasts between laminated colored gold alloys to produce decorative wood-grain effects. By 2014, the gold jewelry industry was escalating despite a dip in gold prices. Demand in the first quarter of 2014 pushed turnover to $23.7 billion according to a World Gold Council report. Gold solder is used for joining the components of gold jewelry by high-temperature hard soldering or brazing. If the work is to be of hallmarking quality, the gold solder alloy must match the Karat, fineness (purity) of the work, and alloy formulas are manufactured to color-match yellow and white gold. Gold solder is usually made in at least three melting-point ranges referred to as Easy, Medium and Hard. By using the hard, high-melting point solder first, followed by solders with progressively lower melting points, goldsmiths can assemble complex items with several separate soldered joints. Gold can also be made into gold thread, thread and used in embroidery.
 * Gold produces a deep, intense red color when used as a coloring agent in cranberry glass.
* In photography, gold toners are used to shift the color of silver bromide black-and-white prints towards brown or blue tones, or to increase their stability. Used on sepia tone, sepia-toned prints, gold toners produce red tones. Kodak published formulas for several types of gold toners, which use gold as the chloride.
* Gold is a good reflector of electromagnetic radiation such as
* Gold produces a deep, intense red color when used as a coloring agent in cranberry glass.
* In photography, gold toners are used to shift the color of silver bromide black-and-white prints towards brown or blue tones, or to increase their stability. Used on sepia tone, sepia-toned prints, gold toners produce red tones. Kodak published formulas for several types of gold toners, which use gold as the chloride.
* Gold is a good reflector of electromagnetic radiation such as
 * Bulk leach extractable gold, for sampling ores
* Chrysiasis (dermatological condition)
* Digital gold currency, form of electronic currency
* GFMS business consultancy
* Gold fingerprinting, use impurities to identify an alloy
* Gold standard in banking
* List of countries by gold production
* Tumbaga, alloy of gold and copper
* Iron pyrite, fool's gold
* Nordic gold, non-gold copper alloy
* Bulk leach extractable gold, for sampling ores
* Chrysiasis (dermatological condition)
* Digital gold currency, form of electronic currency
* GFMS business consultancy
* Gold fingerprinting, use impurities to identify an alloy
* Gold standard in banking
* List of countries by gold production
* Tumbaga, alloy of gold and copper
* Iron pyrite, fool's gold
* Nordic gold, non-gold copper alloy
online
* Bernstein, Peter L. ''The Power of Gold: The History of an Obsession'' (2000
online
* Brands, H.W. ''The Age of Gold: The California Gold Rush and the New American Dream'' (2003
excerpt
* Buranelli, Vincent. ''Gold : an illustrated history'' (1979
online
wide-ranging popular history * Cassel, Gustav. "The restoration of the gold standard." ''Economica'' 9 (1923): 171–185
online
* Eichengreen, Barry. ''Golden Fetters: The Gold Standard and the Great Depression, 1919–1939'' (Oxford UP, 1992). * Ferguson, Niall. ''The Ascent of Money - Financial History of the World'' (2009
online
* Hart, Matthew
Gold: The Race for the World's Most Seductive Metal
''Gold : the race for the world's most seductive metal"], New York: Simon & Schuster, 2013. '' * Johnson, Harry G. "The gold rush of 1968 in retrospect and prospect." ''American Economic Review'' 59.2 (1969): 344–348
online
* Kwarteng, Kwasi. ''War and Gold: A Five-Hundred-Year History of Empires, Adventures, and Debt'' (2014
online
* Vilar, Pierre. '' A History of Gold and Money, 1450 to 1920'' (1960)
online
* Vilches, Elvira. ''New World Gold: Cultural Anxiety and Monetary Disorder in Early Modern Spain'' (2010).
Chemistry in its element podcast
(MP3) from the Royal Society of Chemistry's Chemistry World
Gold
www.rsc.org
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
''Getting Gold'' 1898 book
www.lateralscience.co.uk * , www.epa.gov
Gold element information
- rsc.org {{Authority control Gold, Chemical elements Transition metals Noble metals Precious metals Cubic minerals Minerals in space group 225 Dental materials Electrical conductors Native element minerals E-number additives Symbols of Alaska Symbols of California Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
with the symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright
Bright may refer to:
Common meanings
*Bright, an adjective meaning giving off or reflecting illumination; see Brightness
*Bright, an adjective meaning someone with intelligence
People
* Bright (surname)
* Bright (given name)
*Bright, the stage na ...
, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
, and ductile
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
and a group 11 element
Group 11, by modern IUPAC numbering, is a group of chemical elements in the periodic table, consisting of copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au), and roentgenium (Rg), although no chemical experiments have yet been carried out to confirm that ...
. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements to be established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union ...
. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets
Nuggets may refer to:
Music
* ''Nuggets'' (series), a series of compilation albums by Elektra Records, continued by Rhino
* '' Nuggets: Original Artyfacts from the First Psychedelic Era, 1965–1968''
* '' Nuggets II: Original Artyfacts from ...
or grains, in rocks
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's ...
, veins
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated b ...
, and alluvial deposit
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
s. It occurs in a solid solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word ...
series with the native element silver (as electrum
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially, and ...
), naturally alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
ed with other metals like copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
and palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself na ...
, and mineral inclusion
In mineralogy, an inclusion is any material that is trapped inside a mineral during its formation. In gemology, an inclusion is a characteristic enclosed within a gemstone, or reaching its surface from the interior.
According to James Hutton, ...
s such as within pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally fou ...
(gold telluride Gold chalcogenides are compounds formed between gold and one of the chalcogens, elements from group 16 of the periodic table: oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium.
* Gold(III) oxide, Au2O3. Decomposes into gold and oxygen above 160 °C, and ...
s).
Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
and hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate
Chloroauric acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates . Both the trihydrate and tetrahydrate are known. Both are orange-yellow solids consisting of the planar anion. Often chloroauric acid is handled as a solutio ...
anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
. Gold is insoluble in nitric acid alone, which dissolves silver and base metal
A base metal is a common and inexpensive metal, as opposed to a precious metal such as gold or silver. In numismatics, coins often derived their value from the precious metal content; however, base metals have also been used in coins in the past ...
s, a property long used to refine
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
Refining (also perhaps called by the mathematical term affining) is the process of purification of a (1) substance or a (2) form. The term is usually used of a natural resource that is almost in a usable form, b ...
gold and confirm the presence of gold in metallic substances, giving rise to the term ' acid test'. Gold dissolves in alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a base (chemistry), basic, ionic compound, ionic salt (chemistry), salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as ...
solutions of cyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
, which are used in mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
and electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
. Gold also dissolves in mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, forming amalgam
Amalgam most commonly refers to:
* Amalgam (chemistry), mercury alloy
* Amalgam (dentistry), material of silver tooth fillings
** Bonded amalgam, used in dentistry
Amalgam may also refer to:
* Amalgam Comics, a publisher
* Amalgam Digital
...
alloys, and as the gold acts simply as a solute, this is not a chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
.
A relatively rare element, gold is a precious metal
Precious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements of high economic value.
Chemically, the precious metals tend to be less reactive than most elements (see noble metal). They are usually ductile and have a high lustre. ...
that has been used for coinage
Coinage may refer to:
* Coins, standardized as currency
* Neologism, coinage of a new word
* '' COINage'', numismatics magazine
* Tin coinage, a tax on refined tin
* Protologism
''Protologism'' is a term coined in 2003 by the American literary ...
, jewelry
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry (U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a western ...
, and other arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both hi ...
throughout recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world hist ...
. In the past, a gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the la ...
was often implemented as a monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to control either the interest rate payable for very short-term borrowing (borrowing by banks from each other to meet their short-term needs) or the money supply, often a ...
. Gold coins ceased to be minted as a circulating currency in the 1930s, and the world gold standard was abandoned for a fiat currency
Fiat money (from la, fiat, "let it be done") is a type of currency that is not backed by any commodity such as gold or silver. It is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tender. Throughout history, fiat money was sometime ...
system after the Nixon shock measures of 1971.
In 2020, the world's largest gold producer was China, followed by Russia and Australia. A total of around 201,296 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s of gold exists above ground, . This is equal to a cube with each side measuring roughly . The world consumption of new gold produced is about 50% in jewelry, 40% in investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing i ...
s and 10% in industry
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial sector ...
. Gold's high malleability, ductility, resistance to corrosion and most other chemical reactions, and conductivity of electricity have led to its continued use in corrosion-resistant electrical connector
Components of an electrical circuit are electrically connected if an electric current can run between them through an electrical conductor. An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to create an electrical connection between ...
s in all types of computerized devices (its chief industrial use). Gold is also used in infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
shielding, production of colored glass
Glass coloring and color marking may be obtained in several ways.
# by the addition of ''coloring ions'',Bernard H. W. S. De Jong, Ruud G. C. Beerkens, Peter A. van Nijnatten: "Glass", in: "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry"; Wiley-VC ...
, gold leaf
Gold leaf is gold that has been hammered into thin sheets (usually around 0.1 µm thick) by goldbeating and is often used for gilding. Gold leaf is available in a wide variety of karats and shades. The most commonly used gold is 22-kara ...
ing, and tooth restoration
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure sup ...
. Certain gold salts
Gold-containing drugs are pharmaceuticals that contain gold. Sometimes these species are referred to as "gold salts". "Chrysotherapy" and "aurotherapy" are the applications of gold compounds to medicine. Research on the medicinal effects of g ...
are still used as anti-inflammatories in medicine.
Characteristics

 Gold is the most
Gold is the most malleable
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
of all metals. It can be drawn into a wire of single-atom width, and then stretched considerably before it breaks. Such nanowires distort via formation, reorientation and migration of dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sl ...
s and crystal twins without noticeable hardening. A single gram of gold can be beaten into a sheet of , and an avoirdupois ounce
The ounce () is any of several different units of mass, weight or volume and is derived almost unchanged from the , an Ancient Roman unit of measurement.
The avoirdupois ounce (exactly ) is avoirdupois pound; this is the United States custom ...
into . Gold leaf can be beaten thin enough to become semi-transparent. The transmitted light appears greenish-blue, because gold strongly reflects yellow and red. Such semi-transparent sheets also strongly reflect infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
light, making them useful as infrared (radiant heat) shields in visors of heat-resistant suits, and in sun-visors for spacesuit
A space suit or spacesuit is a garment worn to keep a human alive in the harsh environment of outer space, vacuum and temperature extremes. Space suits are often worn inside spacecraft as a safety precaution in case of loss of cabin pressure, ...
s. Gold is a good conductor of heat and electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
.
Gold has a density of 19.3 g/cm3, almost identical to that of tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolat ...
at 19.25 g/cm3; as such, tungsten has been used in counterfeiting of gold bar
A gold bar, also called gold bullion or gold ingot, is a quantity of refined metallic gold of any shape that is made by a bar producer meeting standard conditions of manufacture, labeling, and record keeping. Larger gold bars that are produced ...
s, such as by plating a tungsten bar with gold, or taking an existing gold bar, drilling holes, and replacing the removed gold with tungsten rods. By comparison, the density of lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
is 11.34 g/cm3, and that of the densest element, osmium, is .
Color
plasma oscillation Plasma oscillations, also known as Langmuir waves (after Irving Langmuir), are rapid oscillations of the electron density in conducting media such as plasmas or metals in the ultraviolet region. The oscillations can be described as an instability i ...
s among the metal's valence electrons, in the ultraviolet range for most metals but in the visible range for gold due to relativistic effects
Relativistic quantum chemistry combines relativistic mechanics with quantum chemistry to calculate elemental properties and structure, especially for the heavier elements of the periodic table. A prominent example is an explanation for the color of ...
affecting the orbitals around gold atoms. Similar effects impart a golden hue to metallic caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
.
Common colored gold alloys include the distinctive eighteen-karat rose gold
Pure gold is slightly reddish yellow in color, but colored gold in various other colors can be produced by alloying gold with other elements.
Colored golds can be classified in three groups:
* Alloys with silver and copper in various proportion ...
created by the addition of copper. Alloys containing palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself na ...
or nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
are also important in commercial jewelry as these produce white gold alloys. Fourteen-karat gold-copper alloy is nearly identical in color to certain bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
alloys, and both may be used to produce police and other badge
A badge is a device or accessory, often containing the insignia of an organization, which is presented or displayed to indicate some feat of service, a special accomplishment, a symbol of authority granted by taking an oath (e.g., police and fi ...
s. Fourteen- and eighteen-karat gold alloys with silver alone appear greenish-yellow and are referred to as green gold
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially, and ...
. Blue gold can be made by alloying with iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
, and purple gold can be made by alloying with aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
. Less commonly, addition of manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
, indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts p ...
, and other elements can produce more unusual colors of gold for various applications.
Colloidal gold
Colloidal gold is a sol or colloidal suspension of nanoparticles of gold in a fluid, usually water. The colloid is usually either wine-red coloured (for spherical particles less than 100 nm) or blue/purple (for larger spherical particl ...
, used by electron-microscopists, is red if the particles are small; larger particles of colloidal gold are blue.
Isotopes
Gold has only one stableisotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
, , which is also its only naturally occurring isotope, so gold is both a mononuclidic and monoisotopic element
A monoisotopic element is an element which has only a single stable isotope (nuclide). There are only 26 elements that have this property. A list is given in a following section.
Stability is experimentally defined for chemical elements, as ther ...
. Thirty-six radioisotopes
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
have been synthesized, ranging in atomic mass
The atomic mass (''m''a or ''m'') is the mass of an atom. Although the SI unit of mass is the kilogram (symbol: kg), atomic mass is often expressed in the non-SI unit dalton (symbol: Da) – equivalently, unified atomic mass unit (u). 1&nbs ...
from 169 to 205. The most stable of these is with a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
of 186.1 days. The least stable is , which decays by proton emission
Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay, in which case t ...
with a half-life of 30 µs. Most of gold's radioisotopes with atomic masses below 197 decay by some combination of proton emission
Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay, in which case t ...
, α decay, and β+ decay. The exceptions are , which decays by electron capture, and , which decays most often by electron capture (93%) with a minor β− decay path (7%). All of gold's radioisotopes with atomic masses above 197 decay by β− decay.
At least 32 nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state, higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited ...
s have also been characterized, ranging in atomic mass from 170 to 200. Within that range, only , , , , and do not have isomers. Gold's most stable isomer is with a half-life of 2.27 days. Gold's least stable isomer is with a half-life of only 7 ns. has three decay paths: β+ decay, isomeric transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have ha ...
, and alpha decay. No other isomer or isotope of gold has three decay paths.
Synthesis
The possible production of gold from a more common element, such aslead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, has long been a subject of human inquiry, and the ancient and medieval discipline of alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
often focused on it; however, the transmutation of the chemical elements did not become possible until the understanding of nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the ...
in the 20th century. The first synthesis of gold was conducted by Japanese physicist Hantaro Nagaoka
was a Japanese physicist and a pioneer of Japanese physics during the Meiji period.
Life
Nagaoka was born in Nagasaki, Japan on August 19, 1865 and educated at the University of Tokyo. After graduating with a degree in physics in 1887, Naga ...
, who synthesized gold from mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
in 1924 by neutron bombardment. An American team, working without knowledge of Nagaoka's prior study, conducted the same experiment in 1941, achieving the same result and showing that the isotopes of gold
Gold (79Au) has one stable isotope, 197Au, and 36 radioisotopes, with 195Au being the most stable with a half-life of 186 days. Gold is currently considered the heaviest monoisotopic element. Bismuth formerly held that distinction until alpha-deca ...
produced by it were all radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
. In 1980, Glenn Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg (; April 19, 1912February 25, 1999) was an American chemist whose involvement in the synthesis, discovery and investigation of ten transuranium elements earned him a share of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. His work i ...
transmuted several thousand atoms of bismuth into gold at the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory. Gold can be manufactured in a nuclear reactor, but doing so is highly impractical and would cost far more than the value of the gold that is produced.
Chemistry
 Although gold is the most noble of the
Although gold is the most noble of the noble metal
A noble metal is ordinarily regarded as a metallic chemical element that is generally resistant to corrosion and is usually found in nature in its raw form. Gold, platinum, and the other platinum group metals (ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, o ...
s, it still forms many diverse compounds. The oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
of gold in its compounds ranges from −1 to +5, but Au(I) and Au(III) dominate its chemistry. Au(I), referred to as the aurous ion, is the most common oxidation state with soft ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
s such as thioether
In organic chemistry, an organic sulfide (British English sulphide) or thioether is an organosulfur functional group with the connectivity as shown on right. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile sulfides have foul odors. A sul ...
s, thiolate
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl grou ...
s, and organophosphine Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PR''n''H3−''n'', where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of ''n'': primary phosphines (''n'' = 1), secondary phosphines ...
s. Au(I) compounds are typically linear. A good example is , which is the soluble form of gold encountered in mining. The binary gold halide
Gold halides are compounds of gold with the halogens.
Monohalides
AuCl, AuBr, and AuI are all crystalline solids with a structure containing alternating linear chains: ..-X-Au-X-Au-X-Au-X-... The X-Au-X angle is less than 180°.
The monomer ...
s, such as AuCl, form zigzag polymeric chains, again featuring linear coordination at Au. Most drugs based on gold are Au(I) derivatives.
Au(III) (referred to as the auric) is a common oxidation state, and is illustrated by gold(III) chloride
Gold(III) chloride, traditionally called auric chloride, is a compound of gold and chlorine with the molecular formula . The "III" in the name indicates that the gold has an oxidation state of +3, typical for many gold compounds. Gold(III) c ...
, . The gold atom centers in Au(III) complexes, like other d8 compounds, are typically square planar
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corne ...
, with chemical bond
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of ...
s that have both covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
and ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
ic character. Gold(I,III) chloride
Gold(I,III) chloride is a black solid with the chemical formula Au4 Cl8. It is an example of a mixed valence compound as it contains gold in two different oxidation states; square-planar gold(III) and almost linear gold(I). The compound is photo ...
is also known, an example of a mixed-valence complex
Mixed valence complexes contain an element which is present in more than one oxidation state. Well-known mixed valence compounds include the Creutz–Taube complex, Prussian blue, and molybdenum blue. Many solids are mixed-valency including ...
.
Gold does not react with oxygen at any temperature and, up to 100 °C, is resistant to attack from ozone.
:
:
Some free halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
s react with gold. Gold is strongly attacked by fluorine at dull-red heat to form gold(III) fluoride
Gold(III) fluoride, , is an orange solid that sublimes at 300 °C. It is a powerful fluorinating agent.
Preparation
AuF3 can be prepared by reacting AuCl3 with F2 or BrF3.
Structure
The crystal structure of AuF3 consists of spirals ...
. Powdered gold reacts with chlorine at 180 °C to form gold(III) chloride
Gold(III) chloride, traditionally called auric chloride, is a compound of gold and chlorine with the molecular formula . The "III" in the name indicates that the gold has an oxidation state of +3, typical for many gold compounds. Gold(III) c ...
. Gold reacts with bromine at 140 °C to form gold(III) bromide , but reacts only very slowly with iodine to form gold(I) iodide AuI.
: mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
at room temperature to form an amalgam (chemistry), amalgam, and forms alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
s with many other metals at higher temperatures. These alloys can be produced to modify the hardness and other metallurgical properties, to control melting point or to create exotic colors.
Gold is unaffected by most acids. It does not react with hydrofluoric acid, hydrofluoric, hydrochloric acid, hydrochloric, hydrobromic acid, hydrobromic, hydriodic acid, hydriodic, sulfuric acid, sulfuric, or nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
. It does react with selenic acid, and is dissolved by aqua regia, a 1:3 mixture of nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
and hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
. Nitric acid oxidizes the metal to +3 ions, but only in minute amounts, typically undetectable in the pure acid because of the chemical equilibrium of the reaction. However, the ions are removed from the equilibrium by hydrochloric acid, forming ions, or chloroauric acid, thereby enabling further oxidation.
: oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
s of gold include +1 (gold(I) or aurous compounds) and +3 (gold(III) or auric compounds). Gold ions in solution are readily reduction (chemistry), reduced and precipitation (chemistry), precipitated as metal by adding any other metal as the reducing agent. The added metal is oxidation, oxidized and dissolves, allowing the gold to be displaced from solution and be recovered as a solid precipitate.
Rare oxidation states
Less common oxidation states of gold include −1, +2, and +5. The −1 oxidation state occurs in aurides, compounds containing theanion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
. Caesium auride (CsAu), for example, crystallizes in the caesium chloride motif; rubidium, potassium, and tetramethylammonium aurides are also known. Gold has the highest electron affinity of any metal, at 222.8 kJ/mol, making a stable species, analogous to the halides.
Gold also has a –1 oxidation state in covalent complexes with the Group 4 element, group 4 transition metals, such as in titanium tetraauride and the analogous zirconium and hafnium compounds. These chemicals are expected to form gold-bridged dimer (chemistry), dimers in a manner similar to titanium(IV) hydride.
Gold(II) compounds are usually diamagnetic with Au–Au bonds such as [. The evaporation of a solution of in concentrated produces red crystals of gold(II) sulfate, . Originally thought to be a mixed-valence compound, it has been shown to contain cations, analogous to the better-known mercury(I) ion, . A gold(II) complex, the tetraxenonogold(II) cation, which contains xenon as a ligand, occurs in .
Gold pentafluoride, along with its derivative anion, , and its difluorine complex, gold heptafluoride, is the sole example of gold(V), the highest verified oxidation state.
Some gold compounds exhibit ''aurophilicity, aurophilic bonding'', which describes the tendency of gold ions to interact at distances that are too long to be a conventional Au–Au bond but shorter than Van der Waals force, van der Waals bonding. The interaction is estimated to be comparable in strength to that of a hydrogen bond.
Well-defined cluster compounds are numerous. In some cases, gold has a fractional oxidation state. A representative example is the octahedral species .
Origin
Gold production in the universe
 Gold is thought to have been produced in supernova nucleosynthesis, and from the Neutron star merger, collision of neutron stars, and to have been present in the solar nebula, dust from which the Solar System formed.
Traditionally, gold in the universe is thought to have formed by the r-process (rapid neutron capture) in supernova nucleosynthesis, but more recently it has been suggested that gold and other elements heavier than
Gold is thought to have been produced in supernova nucleosynthesis, and from the Neutron star merger, collision of neutron stars, and to have been present in the solar nebula, dust from which the Solar System formed.
Traditionally, gold in the universe is thought to have formed by the r-process (rapid neutron capture) in supernova nucleosynthesis, but more recently it has been suggested that gold and other elements heavier than iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
may also be produced in quantity by the r-process in the neutron star merger, collision of neutron stars. In both cases, satellite spectrometers at first only indirectly detected the resulting gold. However, in August 2017, the spectroscopic signatures of heavy elements, including gold, were observed by electromagnetic observatories in the GW170817 neutron star merger event, after gravitational wave detectors confirmed the event as a neutron star merger. Current astrophysical models suggest that this single neutron star merger event generated between 3 and 13 Earth masses of gold. This amount, along with estimations of the rate of occurrence of these neutron star merger events, suggests that such mergers may produce enough gold to account for most of the abundance of this element in the universe.
Asteroid origin theories
Because the Earth was molten History of Earth, when it was formed, almost all of the gold present in the early Earth probably sank into the core (geology), planetary core. Therefore, most of the gold that is in the Earth's crust (geology), crust and mantle (geology), mantle has in one model thought to have been delivered to Earth later, by asteroid impacts during the Late Heavy Bombardment, about 4 billion years ago. Gold which is reachable by humans has, in one case, been associated with a particular asteroid impact. The asteroid that formed Vredefort impact structure 2.020 billion years ago is often credited with seeding the Witwatersrand basin in South Africa with the richest gold deposits on earth. However, this scenario is now questioned. The gold-bearing Witwatersrand rocks were laid down between 700 and 950 million years before the Vredefort impact.McCarthy, T., Rubridge, B. (2005). ''The Story of Earth and Life''. Struik Publishers, Cape Town. pp. 89–90, 102–107, 134–136. Norman, N., Whitfield, G. (2006) ''Geological Journeys''. Struik Publishers, Cape Town. pp. 38–49, 60–61. These gold-bearing rocks had furthermore been covered by a thick layer of Ventersdorp lavas and the Transvaal Basin, Transvaal Supergroup of rocks before the meteor struck, and thus the gold did not actually arrive in the asteroid/meteorite. What the Vredefort impact achieved, however, was to distort the Witwatersrand basin in such a way that the gold-bearing rocks were brought to the present erosion surface in Johannesburg, on the Witwatersrand, just inside the rim of the original diameter crater caused by the meteor strike. The discovery of the deposit in 1886 launched the Witwatersrand Gold Rush. Some 22% of all the gold that is ascertained to exist today on Earth has been extracted from these Witwatersrand rocks.Mantle return theories
Notwithstanding the impact above, much of the rest of the gold on Earth is thought to have been incorporated into the planet since its very beginning, as planetesimals formed the planet's mantle, early in Earth's creation. In 2017, an international group of scientists, established that gold "came to the Earth's surface from the deepest regions of our planet", the Mantle (geology), mantle, evidenced by their findings at Deseado Massif in the Argentinian Patagonia.Occurrence
On Earth, gold is found in ores in rock formed from the Precambrian time onward. It most often occurs as a native metal, typically in a metalsolid solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word ...
with silver (i.e. as a gold/silver alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
). Such alloys usually have a silver content of 8–10%. Electrum is elemental gold with more than 20% silver, and is commonly known as white gold. Electrum's color runs from golden-silvery to silvery, dependent upon the silver content. The more silver, the lower the specific gravity.
Native gold occurs as very small to microscopic particles embedded in rock, often together with quartz or sulfide minerals such as "fool's gold", which is a pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
. These are called lode deposits. The metal in a native state is also found in the form of free flakes, grains or larger nuggets
Nuggets may refer to:
Music
* ''Nuggets'' (series), a series of compilation albums by Elektra Records, continued by Rhino
* '' Nuggets: Original Artyfacts from the First Psychedelic Era, 1965–1968''
* '' Nuggets II: Original Artyfacts from ...
that have been eroded from rocks and end up in alluvial deposits called placer deposits. Such free gold is always richer at the exposed surface of gold-bearing veins, owing to the oxidation of accompanying minerals followed by weathering; and by washing of the dust into streams and rivers, where it collects and can be welded by water action to form nuggets.
Gold sometimes occurs combined with tellurium
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally fou ...
as the minerals calaverite, krennerite, nagyagite, petzite and sylvanite (see telluride minerals), and as the rare bismuthide maldonite () and antimonide aurostibite (). Gold also occurs in rare alloys with copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, and mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
: the minerals auricupride (), novodneprite () and weishanite ().
Recent research suggests that microbes can sometimes play an important role in forming gold deposits, transporting and precipitating gold to form grains and nuggets that collect in alluvial deposits.
Another recent study has claimed water in faults vaporizes during an earthquake, depositing gold. When an earthquake strikes, it moves along a fault (geology), fault. Water often lubricates faults, filling in fractures and jogs. About below the surface, under very high temperatures and pressures, the water carries high concentrations of carbon dioxide, silica, and gold. During an earthquake, the fault jog suddenly opens wider. The water inside the void instantly vaporizes, flashing to steam and forcing silica, which forms the mineral quartz, and gold out of the fluids and onto nearby surfaces.
Seawater
The world's oceans contain gold. Measured concentrations of gold in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific are 50–150 femtomolar, femtomol/L or 10–30 parts per quadrillion (about 10–30 g/km3). In general, gold concentrations for south Atlantic and central Pacific samples are the same (~50 femtomol/L) but less certain. Mediterranean deep waters contain slightly higher concentrations of gold (100–150 femtomol/L) attributed to wind-blown dust and/or rivers. At 10 parts per quadrillion the Earth's oceans would hold 15,000 tonnes of gold. These figures are three orders of magnitude less than reported in the literature prior to 1988, indicating contamination problems with the earlier data. A number of people have claimed to be able to economically recover gold from sea water, but they were either mistaken or acted in an intentional deception. Prescott Jernegan ran a gold-from-seawater swindle in the United States in the 1890s, as did an English fraudster in the early 1900s. Fritz Haber did research on the extraction of gold from sea water in an effort to help pay Germany's reparations following World War I. Based on the published values of 2 to 64 ppb of gold in seawater a commercially successful extraction seemed possible. After analysis of 4,000 water samples yielding an average of 0.004 ppb it became clear that extraction would not be possible and he ended the project.History

 The earliest recorded metal employed by humans appears to be gold, which can be found native metal, free or "native metal, native". Small amounts of natural gold have been found in Spanish caves used during the late Paleolithic period, c. 40,000 BC.
The oldest gold artifacts in the world are from Bulgaria and are dating back to the 5th millennium BC (4,600 BC to 4,200 BC), such as those found in the Varna Necropolis near Lake Varna and the Black Sea coast, thought to be the earliest "well-dated" finding of gold artifacts in history. Several prehistoric Bulgarian finds are considered no less old – the golden treasures of Hotnitsa, Durankulak, artifacts from the Kurgan settlement of Yunatsite near Pazardzhik, the golden treasure Sakar, as well as beads and gold jewelry found in the Kurgan settlement of Provadia – Solnitsata (“salt pit”). However, Varna gold is most often called the oldest since this treasure is the largest and most diverse.
Gold artifacts probably made their first appearance in Ancient Egypt at the very beginning of the pre-dynastic period, at the end of the fifth millennium BC and the start of the fourth, and smelting was developed during the course of the 4th millennium; gold artifacts appear in the archeology of Lower Mesopotamia during the early 4th millennium. As of 1990, gold artifacts found at the Wadi Qana cave cemetery of the 4th millennium BC in West Bank were the earliest from the Levant. Gold artifacts such as the golden hats and the Nebra disk appeared in Central Europe from the 2nd millennium BC European Bronze Age, Bronze Age.
The oldest known map of a gold mine was drawn in the 19th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt (1320–1200 BC), whereas the first written reference to gold was recorded in the 12th Dynasty around 1900 BC. Egyptian hieroglyphs from as early as 2600 BC describe gold, which King Tushratta of the Mitanni claimed was "more plentiful than dirt" in Egypt. Egypt and especially Nubia had the resources to make them major gold-producing areas for much of history. One of the earliest known maps, known as the Turin Papyrus Map, shows the plan of a gold mine in Nubia together with indications of the local geology. The primitive working methods are described by both Strabo and Diodorus Siculus, and included fire-setting. Large mines were also present across the Red Sea in what is now Saudi Arabia.
The earliest recorded metal employed by humans appears to be gold, which can be found native metal, free or "native metal, native". Small amounts of natural gold have been found in Spanish caves used during the late Paleolithic period, c. 40,000 BC.
The oldest gold artifacts in the world are from Bulgaria and are dating back to the 5th millennium BC (4,600 BC to 4,200 BC), such as those found in the Varna Necropolis near Lake Varna and the Black Sea coast, thought to be the earliest "well-dated" finding of gold artifacts in history. Several prehistoric Bulgarian finds are considered no less old – the golden treasures of Hotnitsa, Durankulak, artifacts from the Kurgan settlement of Yunatsite near Pazardzhik, the golden treasure Sakar, as well as beads and gold jewelry found in the Kurgan settlement of Provadia – Solnitsata (“salt pit”). However, Varna gold is most often called the oldest since this treasure is the largest and most diverse.
Gold artifacts probably made their first appearance in Ancient Egypt at the very beginning of the pre-dynastic period, at the end of the fifth millennium BC and the start of the fourth, and smelting was developed during the course of the 4th millennium; gold artifacts appear in the archeology of Lower Mesopotamia during the early 4th millennium. As of 1990, gold artifacts found at the Wadi Qana cave cemetery of the 4th millennium BC in West Bank were the earliest from the Levant. Gold artifacts such as the golden hats and the Nebra disk appeared in Central Europe from the 2nd millennium BC European Bronze Age, Bronze Age.
The oldest known map of a gold mine was drawn in the 19th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt (1320–1200 BC), whereas the first written reference to gold was recorded in the 12th Dynasty around 1900 BC. Egyptian hieroglyphs from as early as 2600 BC describe gold, which King Tushratta of the Mitanni claimed was "more plentiful than dirt" in Egypt. Egypt and especially Nubia had the resources to make them major gold-producing areas for much of history. One of the earliest known maps, known as the Turin Papyrus Map, shows the plan of a gold mine in Nubia together with indications of the local geology. The primitive working methods are described by both Strabo and Diodorus Siculus, and included fire-setting. Large mines were also present across the Red Sea in what is now Saudi Arabia.
 Gold is mentioned in the Amarna letters numbered Amarna letter EA 19, 19 and Amarna letter EA 26, 26 from around the 14th century BC.
Gold is mentioned frequently in the Old Testament, starting with Book of Genesis, Genesis 2:11 (at Havilah), the story of the golden calf, and many parts of the temple including the Menorah (Temple), Menorah and the golden altar. In the New Testament, it is included with the gifts of the magi in the first chapters of Matthew. The Book of Revelation 21:21 describes the city of New Jerusalem as having streets "made of pure gold, clear as crystal". Exploitation of gold in the south-east corner of the Black Sea is said to date from the time of Midas, and this gold was important in the establishment of what is probably the world's earliest coinage in Lydia around 610 BC. The legend of the golden fleece dating from eighth century BCE may refer to the use of fleeces to trap gold dust from placer deposits in the ancient world. From the 6th or 5th century BC, the Chu (state) circulated the Ying Yuan, one kind of square gold coin.
In Roman metallurgy, new methods for extracting gold on a large scale were developed by introducing hydraulic mining methods, especially in Hispania from 25 BC onwards and in Dacia from 106 AD onwards. One of their largest mines was at Las Medulas in León (province), León, where seven long aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts enabled them to sluice most of a large alluvial deposit. The mines at Roşia Montană in Transylvania were also very large, and until very recently, still mined by opencast methods. They also exploited smaller deposits in Roman Britain, Britain, such as placer and hard-rock deposits at Dolaucothi. The various methods they used are well described by Pliny the Elder in his encyclopedia ''Naturalis Historia'' written towards the end of the first century AD.
During Mansa Musa's (ruler of the Mali Empire from 1312 to 1337) hajj to Mecca in 1324, he passed through Cairo in July 1324, and was reportedly accompanied by a camel train that included thousands of people and nearly a hundred camels where he gave away so much gold that it depressed the price in Egypt for over a decade, causing high inflation. A contemporary Arab historian remarked:
Gold is mentioned in the Amarna letters numbered Amarna letter EA 19, 19 and Amarna letter EA 26, 26 from around the 14th century BC.
Gold is mentioned frequently in the Old Testament, starting with Book of Genesis, Genesis 2:11 (at Havilah), the story of the golden calf, and many parts of the temple including the Menorah (Temple), Menorah and the golden altar. In the New Testament, it is included with the gifts of the magi in the first chapters of Matthew. The Book of Revelation 21:21 describes the city of New Jerusalem as having streets "made of pure gold, clear as crystal". Exploitation of gold in the south-east corner of the Black Sea is said to date from the time of Midas, and this gold was important in the establishment of what is probably the world's earliest coinage in Lydia around 610 BC. The legend of the golden fleece dating from eighth century BCE may refer to the use of fleeces to trap gold dust from placer deposits in the ancient world. From the 6th or 5th century BC, the Chu (state) circulated the Ying Yuan, one kind of square gold coin.
In Roman metallurgy, new methods for extracting gold on a large scale were developed by introducing hydraulic mining methods, especially in Hispania from 25 BC onwards and in Dacia from 106 AD onwards. One of their largest mines was at Las Medulas in León (province), León, where seven long aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts enabled them to sluice most of a large alluvial deposit. The mines at Roşia Montană in Transylvania were also very large, and until very recently, still mined by opencast methods. They also exploited smaller deposits in Roman Britain, Britain, such as placer and hard-rock deposits at Dolaucothi. The various methods they used are well described by Pliny the Elder in his encyclopedia ''Naturalis Historia'' written towards the end of the first century AD.
During Mansa Musa's (ruler of the Mali Empire from 1312 to 1337) hajj to Mecca in 1324, he passed through Cairo in July 1324, and was reportedly accompanied by a camel train that included thousands of people and nearly a hundred camels where he gave away so much gold that it depressed the price in Egypt for over a decade, causing high inflation. A contemporary Arab historian remarked:
 The European exploration of the Americas was fueled in no small part by reports of the gold ornaments displayed in great profusion by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American peoples, especially in Mesoamerica, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia. The Aztecs regarded gold as the product of the gods, calling it literally "god excrement" (''teocuitlatl'' in Nahuatl), and after Moctezuma II was killed, most of this gold was shipped to Spain. However, for the indigenous peoples of North America gold was considered useless and they saw much greater value in other minerals which were directly related to their utility, such as obsidian, flint, and slate. El Dorado is applied to a legendary story in which precious stones were found in fabulous abundance along with gold coins. The concept of El Dorado underwent several transformations, and eventually accounts of the previous myth were also combined with those of a legendary lost city. El Dorado, was the term used by the Spanish Empire to describe a mythical tribal chief (zipa) of the Muisca native people in Colombia, who, as an initiation rite, covered himself with gold dust and submerged in Lake Guatavita. The legends surrounding El Dorado changed over time, as it went from being a man, to a city, to a kingdom, and then finally to an empire.
Beginning in the early modern period, European Age of Discovery, exploration and Colonisation of Africa, colonization of West Africa was driven in large part by reports of gold deposits in the region, which was eventually referred to by Europeans as the "Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast". From the late 15th to early 19th centuries, European trade in the region was primarily focused in gold, along with ivory and Atlantic slave trade, slaves. The gold trade in West Africa was dominated by the Ashanti Empire, who initially traded with the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese before branching out and trading with British Empire, British, French colonial empire, French, Spanish Empire, Spanish and Danish colonial empire, Danish merchants. British desires to secure control of West African gold deposits played a role in the Anglo-Ashanti wars of the late 19th century, which saw the Ashanti Empire Gold Coast (British colony), annexed by Britain.
Gold played a role in western culture, as a cause for desire and of corruption, as told in children's fables such as Rumpelstiltskin—where Rumpelstiltskin turns hay into gold for the peasant's daughter in return for her child when she becomes a princess—and the stealing of the hen that lays golden eggs in Jack and the Beanstalk.
The top prize at the Olympic Games and many other sports competitions is the gold medal.
75% of the presently accounted for gold has been extracted since 1910, two-thirds since 1950.
One main goal of the alchemy, alchemists was to produce gold from other substances, such as
The European exploration of the Americas was fueled in no small part by reports of the gold ornaments displayed in great profusion by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American peoples, especially in Mesoamerica, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia. The Aztecs regarded gold as the product of the gods, calling it literally "god excrement" (''teocuitlatl'' in Nahuatl), and after Moctezuma II was killed, most of this gold was shipped to Spain. However, for the indigenous peoples of North America gold was considered useless and they saw much greater value in other minerals which were directly related to their utility, such as obsidian, flint, and slate. El Dorado is applied to a legendary story in which precious stones were found in fabulous abundance along with gold coins. The concept of El Dorado underwent several transformations, and eventually accounts of the previous myth were also combined with those of a legendary lost city. El Dorado, was the term used by the Spanish Empire to describe a mythical tribal chief (zipa) of the Muisca native people in Colombia, who, as an initiation rite, covered himself with gold dust and submerged in Lake Guatavita. The legends surrounding El Dorado changed over time, as it went from being a man, to a city, to a kingdom, and then finally to an empire.
Beginning in the early modern period, European Age of Discovery, exploration and Colonisation of Africa, colonization of West Africa was driven in large part by reports of gold deposits in the region, which was eventually referred to by Europeans as the "Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast". From the late 15th to early 19th centuries, European trade in the region was primarily focused in gold, along with ivory and Atlantic slave trade, slaves. The gold trade in West Africa was dominated by the Ashanti Empire, who initially traded with the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese before branching out and trading with British Empire, British, French colonial empire, French, Spanish Empire, Spanish and Danish colonial empire, Danish merchants. British desires to secure control of West African gold deposits played a role in the Anglo-Ashanti wars of the late 19th century, which saw the Ashanti Empire Gold Coast (British colony), annexed by Britain.
Gold played a role in western culture, as a cause for desire and of corruption, as told in children's fables such as Rumpelstiltskin—where Rumpelstiltskin turns hay into gold for the peasant's daughter in return for her child when she becomes a princess—and the stealing of the hen that lays golden eggs in Jack and the Beanstalk.
The top prize at the Olympic Games and many other sports competitions is the gold medal.
75% of the presently accounted for gold has been extracted since 1910, two-thirds since 1950.
One main goal of the alchemy, alchemists was to produce gold from other substances, such as lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
— presumably by the interaction with a mythical substance called the philosopher's stone. Trying to produce gold led the alchemists to systematically find out what can be done with substances, and this laid the foundation for today's chemistry, which can produce gold (albeit uneconomically) by using nuclear transmutation. Their symbol for gold was the circle with a point at its center (☉), which was also the astrology, astrological symbol and the ancient Chinese character for the Sun.
The Dome of the Rock is covered with an ultra-thin golden glassier. The Sikh Golden temple, the Harmandir Sahib, is a building covered with gold. Similarly the Wat Phra Kaew emerald Buddhism, Buddhist temple (wat) in Thailand has ornamental gold-leafed statues and roofs. Some European king and queen's crown (headgear), crowns were made of gold, and gold was used for the bridal crown since antiquity. An ancient Talmudic text circa 100 AD describes Rachel, wife of Rabbi Akiva, receiving a "Jerusalem of Gold" (diadem). A Greek burial crown made of gold was found in a grave circa 370 BC.
Etymology
 "Gold" is cognate with similar words in many Germanic languages, deriving via Proto-Germanic wikt:Appendix:Proto-Germanic/gulþą, *''gulþą'' from Proto-Indo-European wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/ǵʰelh₃-, *''ǵʰelh₃-'' ("to shine, to gleam; to be yellow or green").
The symbol ''Au'' is from the la, :wikt:aurum, aurum, the Latin word for "gold". The Proto-Indo-European ancestor of ''aurum'' was ''*h₂é-h₂us-o-'', meaning "glow". This word is derived from the same Root (linguistics), root (Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂u̯es-'' "to dawn") as wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/h₂éwsōs, ''*h₂éu̯sōs'', the ancestor of the Latin word Aurora, "dawn". This etymological relationship is presumably behind the frequent claim in scientific publications that ''aurum'' meant "shining dawn".Christie, A and Brathwaite, R. (Last updated 2 November 2011
"Gold" is cognate with similar words in many Germanic languages, deriving via Proto-Germanic wikt:Appendix:Proto-Germanic/gulþą, *''gulþą'' from Proto-Indo-European wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/ǵʰelh₃-, *''ǵʰelh₃-'' ("to shine, to gleam; to be yellow or green").
The symbol ''Au'' is from the la, :wikt:aurum, aurum, the Latin word for "gold". The Proto-Indo-European ancestor of ''aurum'' was ''*h₂é-h₂us-o-'', meaning "glow". This word is derived from the same Root (linguistics), root (Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂u̯es-'' "to dawn") as wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/h₂éwsōs, ''*h₂éu̯sōs'', the ancestor of the Latin word Aurora, "dawn". This etymological relationship is presumably behind the frequent claim in scientific publications that ''aurum'' meant "shining dawn".Christie, A and Brathwaite, R. (Last updated 2 November 2011Mineral Commodity Report 14 — Gold
Institute of geological and Nuclear sciences Ltd – Retrieved 7 June 2012
Culture
 In popular culture gold is a high standard of excellence, often used in awards. Great achievements are frequently rewarded with gold, in the form of gold medals, gold trophy, trophies and other decorations. Winners of athletic events and other graded competitions are usually awarded a gold medal. Many awards such as the Nobel Prize are made from gold as well. Other award statues and prizes are depicted in gold or are gold plated (such as the Academy Awards, the Golden Globe Awards, the Emmy Awards, the Palme d'Or, and the British Academy Film Awards).
Aristotle in his Aristotelian ethics, ethics used gold symbolism when referring to what is now known as the golden mean (philosophy), golden mean. Similarly, gold is associated with perfect or divine principles, such as in the case of the golden ratio and the golden rule. Gold is further associated with the wisdom of aging and fruition. The fiftieth wedding anniversary is golden. A person's most valued or most successful latter years are sometimes considered "golden years". The height of a civilization is referred to as a golden age (metaphor), golden age.
In popular culture gold is a high standard of excellence, often used in awards. Great achievements are frequently rewarded with gold, in the form of gold medals, gold trophy, trophies and other decorations. Winners of athletic events and other graded competitions are usually awarded a gold medal. Many awards such as the Nobel Prize are made from gold as well. Other award statues and prizes are depicted in gold or are gold plated (such as the Academy Awards, the Golden Globe Awards, the Emmy Awards, the Palme d'Or, and the British Academy Film Awards).
Aristotle in his Aristotelian ethics, ethics used gold symbolism when referring to what is now known as the golden mean (philosophy), golden mean. Similarly, gold is associated with perfect or divine principles, such as in the case of the golden ratio and the golden rule. Gold is further associated with the wisdom of aging and fruition. The fiftieth wedding anniversary is golden. A person's most valued or most successful latter years are sometimes considered "golden years". The height of a civilization is referred to as a golden age (metaphor), golden age.
Religion
In some forms of Christianity and Judaism, gold has been associated both with the sacred and evil. In the Book of Exodus, the Golden Calf is a symbol of idolatry, while in the Book of Genesis, Abraham was said to be rich in gold and silver, and Moses was instructed to cover the Mercy Seat of Ark of the Covenant, the Ark of the Covenant with pure gold. In Eastern Christianity, Byzantine iconography the Halo (religious iconography), halos of Christ, Virgin Mary and the saints are often golden. In Islam, gold (along with silk) is often cited as being forbidden for men to wear. Abu Bakr al-Jazaeri, quoting a hadith, said that "[t]he wearing of silk and gold are forbidden on the males of my nation, and they are lawful to their women". This, however, has not been enforced consistently throughout history, e.g. in the Ottoman Empire. Further, small gold accents on clothing, such as in embroidery, may be permitted. In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Theia was seen as the goddess of gold, silver and other gems. According to Christopher Columbus, those who had something of gold were in possession of something of great value on Earth and a substance to even help souls to paradise. Wedding rings are typically made of gold. It is long lasting and unaffected by the passage of time and may aid in the ring symbolism of eternal vows before God and the perfection the marriage signifies. In Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christian wedding ceremonies, the wedded couple is adorned with a golden crown (though some opt for wreaths, instead) during the ceremony, an amalgamation of symbolic rites. On 24 August 2020, Israeli archaeologists discovered a trove of early Islamic gold coins near the central city of Yavne. Analysis of the extremely rare collection of 425 gold coins indicated that they were from the late 9th century. Dating to around 1,100 years back, the gold coins were from the Abbasid Caliphate.Production
Mining and prospecting

 Since the 1880s, South Africa has been the source of a large proportion of the world's gold supply, and about 22% of the gold presently accounted is from South Africa. Production in 1970 accounted for 79% of the world supply, about 1,480 tonnes. In 2007 China (with 276 tonnes) overtook South Africa as the world's largest gold producer, the first time since 1905 that South Africa had not been the largest.
In 2020, Gold mining in China, China was the world's leading gold-mining country, followed in order by Russia, Australia, the United States, Canada, and Ghana.
Since the 1880s, South Africa has been the source of a large proportion of the world's gold supply, and about 22% of the gold presently accounted is from South Africa. Production in 1970 accounted for 79% of the world supply, about 1,480 tonnes. In 2007 China (with 276 tonnes) overtook South Africa as the world's largest gold producer, the first time since 1905 that South Africa had not been the largest.
In 2020, Gold mining in China, China was the world's leading gold-mining country, followed in order by Russia, Australia, the United States, Canada, and Ghana.
 In South America, the controversial project Pascua Lama aims at exploitation of rich fields in the high mountains of Atacama Desert, at the border between Chile and Argentina.
It has been estimated that up to one-quarter of the yearly global gold production originates from artisanal or small scale mining.
The city of Johannesburg located in South Africa was founded as a result of the Witwatersrand Gold Rush which resulted in the discovery of some of the largest natural gold deposits in recorded history. The gold fields are confined to the northern and north-western edges of the Witwatersrand basin, which is a thick layer of archean rocks located, in most places, deep under the Free State (South African province), Free State, Gauteng and surrounding provinces.Truswell, J.F. (1977). ''The Geological Evolution of South Africa''. pp. 21–28. Purnell, Cape Town. These Witwatersrand rocks are exposed at the surface on the Witwatersrand, in and around Johannesburg, but also in isolated patches to the south-east and south-west of Johannesburg, as well as in an arc around the Vredefort Dome which lies close to the center of the Witwatersrand basin. From these surface exposures the basin strike and dip, dips extensively, requiring some of the mining to occur at depths of nearly , making them, especially the Savuka Mine, Savuka and TauTona mines to the south-west of Johannesburg, the deepest mines on earth. The gold is found only in six areas where archean rivers from the north and north-west formed extensive pebbly Braided river deltas before draining into the "Witwatersrand sea" where the rest of the Witwatersrand sediments were deposited.
The Second Boer War of 1899–1901 between the British Empire and the Afrikaner Boers was at least partly over the rights of miners and possession of the gold wealth in South Africa.
In South America, the controversial project Pascua Lama aims at exploitation of rich fields in the high mountains of Atacama Desert, at the border between Chile and Argentina.
It has been estimated that up to one-quarter of the yearly global gold production originates from artisanal or small scale mining.
The city of Johannesburg located in South Africa was founded as a result of the Witwatersrand Gold Rush which resulted in the discovery of some of the largest natural gold deposits in recorded history. The gold fields are confined to the northern and north-western edges of the Witwatersrand basin, which is a thick layer of archean rocks located, in most places, deep under the Free State (South African province), Free State, Gauteng and surrounding provinces.Truswell, J.F. (1977). ''The Geological Evolution of South Africa''. pp. 21–28. Purnell, Cape Town. These Witwatersrand rocks are exposed at the surface on the Witwatersrand, in and around Johannesburg, but also in isolated patches to the south-east and south-west of Johannesburg, as well as in an arc around the Vredefort Dome which lies close to the center of the Witwatersrand basin. From these surface exposures the basin strike and dip, dips extensively, requiring some of the mining to occur at depths of nearly , making them, especially the Savuka Mine, Savuka and TauTona mines to the south-west of Johannesburg, the deepest mines on earth. The gold is found only in six areas where archean rivers from the north and north-west formed extensive pebbly Braided river deltas before draining into the "Witwatersrand sea" where the rest of the Witwatersrand sediments were deposited.
The Second Boer War of 1899–1901 between the British Empire and the Afrikaner Boers was at least partly over the rights of miners and possession of the gold wealth in South Africa.
 During the 19th century, gold rushes occurred whenever large gold deposits were discovered. The first documented discovery of gold in the United States was at the Reed Gold Mine near Georgeville, North Carolina in 1803. The first major gold strike in the United States occurred in a small north Georgia town called Dahlonega, Georgia, Dahlonega. Further gold rushes occurred in California Gold Rush, California, Pike's Peak Gold Rush, Colorado, the Black Hills Gold Rush, Black Hills, Central Otago Gold Rush, Otago in New Zealand, a number of locations across Australian gold rushes, Australia, Witwatersrand Gold Rush, Witwatersrand in South Africa, and the Klondike Gold Rush, Klondike in Canada.
Grasberg mine located in Papua (province), Papua, Indonesia is the largest gold mining, gold mine in the world.
During the 19th century, gold rushes occurred whenever large gold deposits were discovered. The first documented discovery of gold in the United States was at the Reed Gold Mine near Georgeville, North Carolina in 1803. The first major gold strike in the United States occurred in a small north Georgia town called Dahlonega, Georgia, Dahlonega. Further gold rushes occurred in California Gold Rush, California, Pike's Peak Gold Rush, Colorado, the Black Hills Gold Rush, Black Hills, Central Otago Gold Rush, Otago in New Zealand, a number of locations across Australian gold rushes, Australia, Witwatersrand Gold Rush, Witwatersrand in South Africa, and the Klondike Gold Rush, Klondike in Canada.
Grasberg mine located in Papua (province), Papua, Indonesia is the largest gold mining, gold mine in the world.
Extraction and refining
Gold extraction is most economical in large, easily mined deposits. Ore grades as little as 0.5 parts per million (ppm) can be economical. Typical ore grades in open-pit mining, open-pit mines are 1–5 ppm; ore grades in underground or Underground mining (hard rock), hard rock mines are usually at least 3 ppm. Because ore grades of 30 ppm are usually needed before gold is visible to the naked eye, in most gold mines the gold is invisible. The average gold mining and extraction costs were about $317 per troy ounce in 2007, but these can vary widely depending on mining type and ore quality; global mine production amounted to 2,471.1 tonnes. After initial production, gold is often subsequently refined industrially by the Wohlwill process which is based on electrolysis or by the Miller process, that is chlorination in the melt. The Wohlwill process results in higher purity, but is more complex and is only applied in small-scale installations. Other methods of assaying and purifying smaller amounts of gold include parting and inquartation as well as cupellation, or refining methods based on the dissolution of gold in aqua regia. As of 2020, the amount of carbon dioxide produced in mining a kilogram of gold is 16 tonnes, while recycling a kilogram of gold produces 53 kilograms of equivalent. Approximately 30 percent of the global gold supply is recycled and not mined as of 2020. Corporations are starting to adopt gold recycling including jewelry companies such as Generation Collection and computer companies including Dell.Consumption
The consumption of gold produced in the world is about 50% in jewelry, 40% in investments, and 10% in industry. According to the World Gold Council, China was the world's largest single consumer of gold in 2013, overtaking India.Pollution
Gold production is associated with contribution to hazardous pollution. Low-grade gold ore may contain less than one Parts per million, ppm gold metal; such ore is Milling (grinding), ground and mixed with sodium cyanide to dissolve the gold. Cyanide is a highly poisonous chemical, which can kill living creatures when exposed in minute quantities. Many List of gold mining disasters, cyanide spills from gold mines have occurred in both developed and developing countries which killed aquatic life in long stretches of affected rivers. Environmentalists consider these events major environmental disasters. Up to thirty tons of used ore can dumped as waste for producing one troy ounce of gold.Behind gold's glitter, torn lands and pointed questions, ''The New York Times'', 24 October 2005 Gold ore dumps are the source of many heavy elements such as cadmium, lead, zinc, copper, arsenic, selenium and mercury. When sulfide-bearing minerals in these ore dumps are exposed to air and water, the sulfide transforms into sulfuric acid which in turn dissolves these heavy metals facilitating their passage into surface water and ground water. This process is called acid mine drainage. These gold ore dumps are long-term, highly hazardous wastes second only to nuclear waste dumps. It was once common to use mercury to recover gold from ore, but today the use of mercury is largely limited to small-scale individual miners. Minute quantities of mercury compounds can reach water bodies, causing heavy metal contamination. Mercury can then enter into the human food chain in the form of methylmercury. Mercury poisoning in humans causes incurable brain function damage and severe retardation. Gold extraction is also a highly energy-intensive industry, extracting ore from deep mines and grinding the large quantity of ore for further chemical extraction requires nearly 25 Kilowatt-hour, kWh of electricity per gram of gold produced.
Monetary use
 Gold has been History of money, widely used throughout the world as money, for efficient indirect exchange (versus barter), and to store wealth in hoards. For exchange purposes, Mint (coin), mints produce standardized bullion, gold bullion coins, gold bar, bars and Good delivery, other units of fixed weight and purity.
The first known coins containing gold were struck in Lydia, Asia Minor, around 600 BC. The ''talent (measurement), talent'' coin of gold in use during the periods of Grecian history both before and during the time of the life of Homer weighed between 8.42 and 8.75 grams. From an earlier preference in using silver, European economies re-established the minting of gold as coinage during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries.
Real bills doctrine, Bills (that mature into gold coin) and gold certificates (convertible into gold coin at the issuing bank) added to the circulating stock of
Gold has been History of money, widely used throughout the world as money, for efficient indirect exchange (versus barter), and to store wealth in hoards. For exchange purposes, Mint (coin), mints produce standardized bullion, gold bullion coins, gold bar, bars and Good delivery, other units of fixed weight and purity.
The first known coins containing gold were struck in Lydia, Asia Minor, around 600 BC. The ''talent (measurement), talent'' coin of gold in use during the periods of Grecian history both before and during the time of the life of Homer weighed between 8.42 and 8.75 grams. From an earlier preference in using silver, European economies re-established the minting of gold as coinage during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries.
Real bills doctrine, Bills (that mature into gold coin) and gold certificates (convertible into gold coin at the issuing bank) added to the circulating stock of gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the la ...
money in most 19th century industrial economies.
In preparation for World War I the warring nations moved to fractional gold standards, inflating their currencies to finance the war effort.
Post-war, the victorious countries, most notably Britain, gradually restored gold-convertibility, but international flows of gold via bills of exchange remained embargoed; international shipments were made exclusively for bilateral trades or to pay war reparations.
After World War II gold was replaced by a system of nominally convertible currency, convertible currencies related by fixed exchange rates following the Bretton Woods system. Gold standards and the direct convertibility of currencies to gold have been abandoned by world governments, led in 1971 by the United States' refusal to redeem its dollars in gold. Fiat currency now fills most monetary roles. Switzerland was the last country to tie its currency to gold; this was ended by a referendum in 1999.
Central banks continue to keep a portion of their liquid reserves as gold in some form, and metals exchanges such as the London Bullion Market Association still clear transactions denominated in gold, including future delivery contracts. Today, gold mining output is declining. With the sharp growth of economies in the 20th century, and increasing foreign exchange, the world's gold reserves and their trading market have become a small fraction of all markets and fixed exchange rates of currencies to gold have been replaced by floating prices for gold and gold Futures contract, future contract. Though the gold stock grows by only 1% or 2% per year, very little metal is irretrievably consumed. Inventory above ground would satisfy many decades of industrial and even artisan uses at current prices.
The gold proportion (fineness) of alloys is measured by karat (k). Pure gold (commercially termed ''fine'' gold) is designated as 24 karat, abbreviated 24k. English gold coins intended for circulation from 1526 into the 1930s were typically a standard 22k alloy called crown gold, for hardness (American gold coins for circulation after 1837 contain an alloy of 0.900 fine gold, or 21.6 kt).
Although the prices of some platinum group metals can be much higher, gold has long been considered the most desirable of precious metal
Precious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements of high economic value.
Chemically, the precious metals tend to be less reactive than most elements (see noble metal). They are usually ductile and have a high lustre. ...
s, and its value has been used as the standard for many currency, currencies. Gold has been used as a symbol for purity, value, royalty, and particularly roles that combine these properties. Gold as a sign of wealth and prestige was ridiculed by Thomas More in his treatise ''Utopia (book), Utopia''. On that imaginary island, gold is so abundant that it is used to make chains for slaves, tableware, and lavatory seats. When ambassadors from other countries arrive, dressed in ostentatious gold jewels and badges, the Utopians mistake them for menial servants, paying homage instead to the most modestly dressed of their party.
The ISO 4217 currency code of gold is XAU. Many holders of gold store it in form of bullion coins or gold bar, bars as a hedge against inflation or other economic disruptions, though its efficacy as such has been questioned; historically, it has not proven itself reliable as a hedging instrument. Modern bullion coins for investment or collector purposes do not require good mechanical wear properties; they are typically fine gold at 24k, although the American Gold Eagle and the British Sovereign (British coin), gold sovereign continue to be minted in 22k (0.92) metal in historical tradition, and the South African Krugerrand, first released in 1967, is also 22k (0.92).
The ''special issue'' Canadian Gold Maple Leaf coin contains the highest purity gold of any bullion coin, at 99.999% or 0.99999, while the ''popular issue'' Canadian Gold Maple Leaf coin has a purity of 99.99%. In 2006, the United States Mint began producing the American Buffalo (coin), American Buffalo gold bullion coin with a purity of 99.99%. The Australian Gold Kangaroos were first coined in 1986 as the Australian Gold Nugget but changed the reverse design in 1989. Other modern coins include the Austrian Vienna Philharmonic (coin), Vienna Philharmonic bullion coin and the Chinese Gold Panda.
Price
 , gold is valued at around $42 per gram ($1,300 per troy ounce).
Like other precious metals, gold is measured by troy weight and by grams. The proportion of gold in the alloy is measured by ''karat'' (k), with 24 karat (24k) being pure gold (100%), and lower karat numbers proportionally less (18k = 75%). The purity of a
, gold is valued at around $42 per gram ($1,300 per troy ounce).
Like other precious metals, gold is measured by troy weight and by grams. The proportion of gold in the alloy is measured by ''karat'' (k), with 24 karat (24k) being pure gold (100%), and lower karat numbers proportionally less (18k = 75%). The purity of a gold bar
A gold bar, also called gold bullion or gold ingot, is a quantity of refined metallic gold of any shape that is made by a bar producer meeting standard conditions of manufacture, labeling, and record keeping. Larger gold bars that are produced ...
or coin can also be expressed as a decimal figure ranging from 0 to 1, known as the millesimal fineness, such as 0.995 being nearly pure.
The price of gold is determined through trading in the gold and derivative (finance), derivatives markets, but a procedure known as the Gold Fixing in London, originating in September 1919, provides a daily benchmark price to the industry. The afternoon fixing was introduced in 1968 to provide a price when US markets are open.
History
Historically gold Mint (coin), coinage was widely used as currency; when paper money was introduced, it typically was a receipt redeemable for gold coin or bullion. In a monetary system known as thegold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the la ...
, a certain weight of gold was given the name of a unit of currency. For a long period, the United States government set the value of the US dollar so that one troy ounce was equal to $20.67 ($0.665 per gram), but in 1934 the dollar was devalued to $35.00 per troy ounce ($0.889/g). By 1961, it was becoming hard to maintain this price, and London Gold Pool, a pool of US and European banks agreed to manipulate the market to prevent further devaluation, currency devaluation against increased gold demand.
On 17 March 1968, economic circumstances caused the collapse of the gold pool, and a two-tiered pricing scheme was established whereby gold was still used to settle international accounts at the old $35.00 per troy ounce ($1.13/g) but the price of gold on the private market was allowed to fluctuate; this two-tiered pricing system was abandoned in 1975 when the price of gold was left to find its free-market level. Central banks still hold historical official gold reserves, gold reserves as a store of value although the level has generally been declining. The largest gold depository in the world is that of the Federal Reserve System, U.S. Federal Reserve Bank in New York City, New York, which holds about 3% of the gold known to exist and accounted for today, as does the similarly laden United States Bullion Depository, U.S. Bullion Depository at Fort Knox.
In 2005 the World Gold Council estimated total global gold supply to be 3,859 tonnes and demand to be 3,754 tonnes, giving a surplus of 105 tonnes.
After 15 August 1971 Nixon shock, the price began to greatly increase, and between 1968 and 2000 the price of gold ranged widely, from a high of $850 per troy ounce ($27.33/g) on 21 January 1980, to a low of $252.90 per troy ounce ($8.13/g) on 21 June 1999 (London Gold Fixing). Prices increased rapidly from 2001, but the 1980 high was not exceeded until 3 January 2008, when a new maximum of $865.35 per troy weight, troy ounce was set. Another record price was set on 17 March 2008, at $1023.50 per troy ounce ($32.91/g).
In late 2009, gold markets experienced renewed momentum upwards due to increased demand and a weakening US dollar. On 2 December 2009, gold reached a new high closing at $1,217.23. Gold further rallied hitting new highs in May 2010 after the European Union debt crisis prompted further purchase of gold as a safe asset. On 1 March 2011, gold hit a new all-time high of $1432.57, based on Gold as an investment, investor concerns regarding ongoing Arab Spring, unrest in North Africa as well as in the Middle East.
From April 2001 to August 2011, spot gold prices more than quintupled in value against the US dollar, hitting a new all-time high of $1,913.50 on 23 August 2011, prompting speculation that the long secular bear market had ended and a bull market had returned. However, the price then began a slow decline towards $1200 per troy ounce in late 2014 and 2015.
In August 2020, the gold price picked up to US$2060 per ounce after a complexive growth of 59% from August 2018 to October 2020, a period during which it outplaced the Nasdaq total return of 54%.
Gold futures are traded on the COMEX exchange. These contacts are priced in USD per troy ounce (1 troy ounce = 31.1034768 grams). Below are the CQG contract specifications outlining the futures contracts:
Medicinal uses
Medicinal applications of gold and its complexes have a long history dating back thousands of years. Several gold complexes have been applied to treat rheumatoid arthritis, the most frequently used being aurothiomalate, aurothioglucose, and auranofin. Both gold(I) and gold(III) compounds have been investigated as possible anti-cancer drugs. For gold(III) complexes, reduction to gold(0/I) under physiological conditions has to be considered. Stable complexes can be generated using different types of bi-, tri-, and tetradentate ligand systems, and their efficacy has been demonstrated in vitro and in vivo.Other applications
Jewelry

 Because of the softness of pure (24k) gold, it is usually
Because of the softness of pure (24k) gold, it is usually alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
ed with base metals for use in jewelry, altering its hardness and ductility, melting point, color and other properties. Alloys with lower Fineness, karat rating, typically 22k, 18k, 14k or 10k, contain higher percentages of copper or other base metals or silver or palladium in the alloy.Jewellery AlloysWorld Gold Council Nickel is toxic, and its release from nickel white gold is controlled by legislation in Europe. Palladium-gold alloys are more expensive than those using nickel. High-karat white gold alloys are more resistant to corrosion than are either pure silver or sterling silver. The Japanese craft of Mokume-gane exploits the color contrasts between laminated colored gold alloys to produce decorative wood-grain effects. By 2014, the gold jewelry industry was escalating despite a dip in gold prices. Demand in the first quarter of 2014 pushed turnover to $23.7 billion according to a World Gold Council report. Gold solder is used for joining the components of gold jewelry by high-temperature hard soldering or brazing. If the work is to be of hallmarking quality, the gold solder alloy must match the Karat, fineness (purity) of the work, and alloy formulas are manufactured to color-match yellow and white gold. Gold solder is usually made in at least three melting-point ranges referred to as Easy, Medium and Hard. By using the hard, high-melting point solder first, followed by solders with progressively lower melting points, goldsmiths can assemble complex items with several separate soldered joints. Gold can also be made into gold thread, thread and used in embroidery.
Electronics
Only 10% of the world consumption of new gold produced goes to industry, but by far the most important industrial use for new gold is in fabrication of corrosion-free electrical connectors in computers and other electrical devices. For example, according to the World Gold Council, a typical cell phone may contain 50 mg of gold, worth about 2 dollars 82 cents. But since nearly one billion cell phones are produced each year, a gold value of US$2.82 in each phone adds to US$2.82 billion in gold from just this application. (Prices updated to November 2022) Though gold is attacked by free chlorine, its good conductivity and general resistance to oxidation and corrosion in other environments (including resistance to non-chlorinated acids) has led to its widespread industrial use in the electronic era as a thin-layer coating onelectrical connector
Components of an electrical circuit are electrically connected if an electric current can run between them through an electrical conductor. An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to create an electrical connection between ...
s, thereby ensuring good connection. For example, gold is used in the connectors of the more expensive electronics cables, such as audio, video and USB cables. The benefit of using gold over other connector metals such as tin in these applications has been debated; gold connectors are often criticized by audio-visual experts as unnecessary for most consumers and seen as simply a marketing ploy. However, the use of gold in other applications in electronic sliding contacts in highly humid or corrosive atmospheres, and in use for contacts with a very high failure cost (certain computers, communications equipment, spacecraft, jet aircraft engines) remains very common.
Besides sliding electrical contacts, gold is also used in electrical contacts because of its resistance to corrosion, electrical conductivity, ductile, ductility and lack of toxicity. Switch contacts are generally subjected to more intense corrosion stress than are sliding contacts. Fine gold wires are used to connect semiconductor devices to their packages through a process known as wire bonding.
The concentration of free electrons in gold metal is 5.91×1022 cm−3. Gold is highly electrical conductivity, conductive to electricity, and has been used for electrical wiring in some high-energy applications (only silver and copper are more conductive per volume, but gold has the advantage of corrosion resistance). For example, gold electrical wires were used during some of the Manhattan Project's atomic experiments, but large high-current silver wires were used in the calutron isotope separator magnets in the project.
It is estimated that 16% of the world's presently-accounted-for gold and 22% of the world's silver is contained in electronic technology in Japan.
Medicine
Metallic and gold compounds have long been used for medicinal purposes. Gold, usually as the metal, is perhaps the most anciently administered medicine (apparently by shamanic practitioners) and known to Dioscorides. In medieval times, gold was often seen as beneficial for the health, in the belief that something so rare and beautiful could not be anything but healthy. Even some modern esotericism, esotericists and forms of alternative medicine assign metallic gold a healing power. In the 19th century gold had a reputation as an anxiolytic, a therapy for nervous disorders. Depression (mood), Depression, epilepsy, migraine, and glandular problems such as amenorrhea and impotence were treated, and most notably alcoholism (Keeley, 1897). The apparent paradox of the actual toxicology of the substance suggests the possibility of serious gaps in the understanding of the action of gold in physiology. Only salts and radioisotopes of gold are of pharmacological value, since elemental (metallic) gold is inert to all chemicals it encounters inside the body (e.g., ingested gold cannot be attacked by stomach acid). Some gold salts do have anti-inflammatory properties and at present two are still used as pharmaceuticals in the treatment of arthritis and other similar conditions in the US (sodium aurothiomalate and auranofin). These drugs have been explored as a means to help to reduce the pain and swelling of rheumatoid arthritis, and also (historically) against tuberculosis and some parasites. Gold alloys are used in restorative dentistry, especially in tooth restorations, such as crown (dentistry), crowns and permanent bridge (dentistry), bridges. The gold alloys' slight malleability facilitates the creation of a superior molar mating surface with other teeth and produces results that are generally more satisfactory than those produced by the creation of porcelain crowns. The use of gold crowns in more prominent teeth such as incisors is favored in some cultures and discouraged in others.Colloidal gold
Colloidal gold is a sol or colloidal suspension of nanoparticles of gold in a fluid, usually water. The colloid is usually either wine-red coloured (for spherical particles less than 100 nm) or blue/purple (for larger spherical particl ...
preparations (suspensions of gold nanoparticles) in water are intensely red-colored, and can be made with tightly controlled particle sizes up to a few tens of nanometers across by reduction of gold chloride with citrate or ascorbate ions. Colloidal gold is used in research applications in medicine, biology and materials science. The technique of immunogold labeling exploits the ability of the gold particles to adsorb protein molecules onto their surfaces. Colloidal gold particles coated with specific antibodies can be used as probes for the presence and position of antigens on the surfaces of cells. In ultrathin sections of tissues viewed by electron microscope, electron microscopy, the immunogold labels appear as extremely dense round spots at the position of the antigen.
Gold, or alloys of gold and palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself na ...
, are applied as conductive coating to biological specimens and other non-conducting materials such as plastics and glass to be viewed in a scanning electron microscope. The coating, which is usually applied by sputtering with an argon plasma (physics), plasma, has a triple role in this application. Gold's very high electrical conductivity drains electric charge, electrical charge to earth, and its very high density provides stopping power for electrons in the electron beam, helping to limit the depth to which the electron beam penetrates the specimen. This improves definition of the position and topography of the specimen surface and increases the Angular resolution, spatial resolution of the image. Gold also produces a high output of secondary emission, secondary electrons when irradiated by an electron beam, and these low-energy electrons are the most commonly used signal source used in the scanning electron microscope.
The isotope gold-198 (half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
2.7 days) is used in nuclear medicine, in some cancer treatments and for treating other diseases.
Cuisine
* Gold can be used in food and has the E number 175. In 2016, the European Food Safety Authority published an opinion on the re-evaluation of gold as a food additive. Concerns included the possible presence of minute amounts of gold nanoparticles in the food additive, and that gold nanoparticles have been shown to be genotoxic in mammalian cells in vitro. * Gold leaf, flake or dust is used on and in some gourmet foods, notably sweets and drinks as decorative ingredient. Gold flake was used by the nobility in medieval Europe as a decoration in food and drinks, in the form of leaf, flakes or dust, either to demonstrate the host's wealth or in the belief that something that valuable and rare must be beneficial for one's health. * Danziger Goldwasser (German: Gold water of Danzig) or Goldwasser ( en, Goldwater) is a traditional German herbal liqueur produced in what is today Gdańsk, Poland, and Schwabach, Germany, and contains flakes of gold leaf. There are also some expensive (c. $1000) cocktails which contain flakes of gold leaf. However, since metallic gold is inert to all body chemistry, it has no taste, it provides no nutrition, and it leaves the body unaltered. * Vark is a Metal leaf, foil composed of a pure metal that is sometimes gold, and is used for Garnish (food), garnishing sweets in South Asian cuisine.Miscellanea

 * Gold produces a deep, intense red color when used as a coloring agent in cranberry glass.
* In photography, gold toners are used to shift the color of silver bromide black-and-white prints towards brown or blue tones, or to increase their stability. Used on sepia tone, sepia-toned prints, gold toners produce red tones. Kodak published formulas for several types of gold toners, which use gold as the chloride.
* Gold is a good reflector of electromagnetic radiation such as
* Gold produces a deep, intense red color when used as a coloring agent in cranberry glass.
* In photography, gold toners are used to shift the color of silver bromide black-and-white prints towards brown or blue tones, or to increase their stability. Used on sepia tone, sepia-toned prints, gold toners produce red tones. Kodak published formulas for several types of gold toners, which use gold as the chloride.
* Gold is a good reflector of electromagnetic radiation such as infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
and visible spectrum, visible light, as well as radio frequency, radio waves. It is used for the protective coatings on many artificial satellites, in infrared protective faceplates in thermal-protection suits and astronauts' helmets, and in electronic warfare planes such as the EA-6B Prowler.
* Gold is used as the reflective layer on some Gold CD, high-end CDs.
* Automobiles may use gold for heat shielding. McLaren uses gold foil in the engine compartment of its McLaren F1, F1 model.
* Gold can be manufactured so thin that it appears semi-transparent. It is used in some aircraft cockpit windows for Deicing, de-icing or anti-icing by passing electricity through it. The heat produced by the resistance of the gold is enough to prevent ice from forming.
* Gold is attacked by and dissolves in alkaline solutions of potassium or sodium cyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
, to form the salt gold cyanide—a technique that has been used in extracting metallic gold from ores in the cyanide process. Gold cyanide is the electrolyte used in commercial electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
of gold onto base metals and electroforming.
* Gold chloride (chloroauric acid) solutions are used to make colloidal gold by reduction with citrate or ascorbate ions. Gold chloride and gold oxide are used to make cranberry or red-colored glass, which, like colloidal gold suspensions, contains evenly sized spherical gold nanoparticles.
* Gold, when dispersed in nanoparticles, can act as a Heterogeneous gold catalysis, heterogeneous catalyst of chemical reactions.
Toxicity
Pure metallic (elemental) gold is non-toxic and non-irritating when ingested and is sometimes used as a food decoration in the form ofgold leaf
Gold leaf is gold that has been hammered into thin sheets (usually around 0.1 µm thick) by goldbeating and is often used for gilding. Gold leaf is available in a wide variety of karats and shades. The most commonly used gold is 22-kara ...
. Metallic gold is also a component of the alcoholic drinks Goldschläger, Gold Strike (drink), Gold Strike, and Goldwasser. Metallic gold is approved as a food additive in the EU (E number, E175 in the Codex Alimentarius). Although the gold ion is toxic, the acceptance of metallic gold as a food additive is due to its relative chemical inertness, and resistance to being corroded or transformed into soluble salts (gold compounds) by any known chemical process which would be encountered in the human body.
Soluble compounds (gold salts
Gold-containing drugs are pharmaceuticals that contain gold. Sometimes these species are referred to as "gold salts". "Chrysotherapy" and "aurotherapy" are the applications of gold compounds to medicine. Research on the medicinal effects of g ...
) such as gold(I,III) chloride, gold chloride are toxic to the liver and kidneys. Common cyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
salts of gold such as potassium gold cyanide, used in gold electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
, are toxic by virtue of both their cyanide and gold content. There are rare cases of lethal gold poisoning from potassium gold cyanide. Gold toxicity can be ameliorated with chelation therapy with an agent such as dimercaprol.
Gold metal was voted Allergen of the Year in 2001 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society; gold contact allergies affect mostly women. Despite this, gold is a relatively non-potent contact allergen, in comparison with metals like nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
.
A sample of the fungus ''Aspergillus niger'' was found growing from gold mining solution; and was found to contain cyano metal complexes, such as gold, silver, copper, iron and zinc. The fungus also plays a role in the solubilization of heavy metal sulfides.
See also
 * Bulk leach extractable gold, for sampling ores
* Chrysiasis (dermatological condition)
* Digital gold currency, form of electronic currency
* GFMS business consultancy
* Gold fingerprinting, use impurities to identify an alloy
* Gold standard in banking
* List of countries by gold production
* Tumbaga, alloy of gold and copper
* Iron pyrite, fool's gold
* Nordic gold, non-gold copper alloy
* Bulk leach extractable gold, for sampling ores
* Chrysiasis (dermatological condition)
* Digital gold currency, form of electronic currency
* GFMS business consultancy
* Gold fingerprinting, use impurities to identify an alloy
* Gold standard in banking
* List of countries by gold production
* Tumbaga, alloy of gold and copper
* Iron pyrite, fool's gold
* Nordic gold, non-gold copper alloy
References
Further reading
* Bachmann, H. G. ''The lure of gold : an artistic and cultural history'' (2006online
* Bernstein, Peter L. ''The Power of Gold: The History of an Obsession'' (2000
online
* Brands, H.W. ''The Age of Gold: The California Gold Rush and the New American Dream'' (2003
excerpt
* Buranelli, Vincent. ''Gold : an illustrated history'' (1979
online
wide-ranging popular history * Cassel, Gustav. "The restoration of the gold standard." ''Economica'' 9 (1923): 171–185
online
* Eichengreen, Barry. ''Golden Fetters: The Gold Standard and the Great Depression, 1919–1939'' (Oxford UP, 1992). * Ferguson, Niall. ''The Ascent of Money - Financial History of the World'' (2009
online
* Hart, Matthew
Gold: The Race for the World's Most Seductive Metal
''Gold : the race for the world's most seductive metal"], New York: Simon & Schuster, 2013. '' * Johnson, Harry G. "The gold rush of 1968 in retrospect and prospect." ''American Economic Review'' 59.2 (1969): 344–348
online
* Kwarteng, Kwasi. ''War and Gold: A Five-Hundred-Year History of Empires, Adventures, and Debt'' (2014
online
* Vilar, Pierre. '' A History of Gold and Money, 1450 to 1920'' (1960)
online
* Vilches, Elvira. ''New World Gold: Cultural Anxiety and Monetary Disorder in Early Modern Spain'' (2010).
External links
*Chemistry in its element podcast
(MP3) from the Royal Society of Chemistry's Chemistry World
Gold
www.rsc.org
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
''Getting Gold'' 1898 book
www.lateralscience.co.uk * , www.epa.gov
Gold element information
- rsc.org {{Authority control Gold, Chemical elements Transition metals Noble metals Precious metals Cubic minerals Minerals in space group 225 Dental materials Electrical conductors Native element minerals E-number additives Symbols of Alaska Symbols of California Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure