glottal stop (letter) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
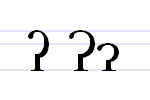 The character , called glottal stop, is an alphabetic letter in some
The character , called glottal stop, is an alphabetic letter in some
Latin alphabets
The lists and tables below summarize and compare the letter inventories of some of the Latin-script alphabets. In this article, the scope of the word "alphabet" is broadened to include letters with tone marks, and other diacritics used to repres ...
, most notably in several languages of Canada where it indicates a glottal stop sound. Such usage derives from phonetic transcription
Phonetic transcription (also known as phonetic script or phonetic notation) is the visual representation of speech sounds (or ''phones'') by means of symbols. The most common type of phonetic transcription uses a phonetic alphabet, such as the ...
, for example the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), that use this letter for the glottal stop sound. The letter derives graphically from use of the apostrophe
The apostrophe ( or ) is a punctuation mark, and sometimes a diacritical mark, in languages that use the Latin alphabet and some other alphabets. In English, the apostrophe is used for two basic purposes:
* The marking of the omission of one ...
or the symbol ĺ for glottal stop.
Graphic variants
Where is not available, not being in the basic Latin alphabet, it is sometimes replaced by aquestion mark
The question mark (also known as interrogation point, query, or eroteme in journalism) is a punctuation mark that indicates an interrogative clause or phrase in many languages.
History
In the fifth century, Syriac Bible manuscripts used ...
, which is its official representation in the SAMPA transcription scheme. In Skwomesh or Squamish, may be replaced by the digit (see image at right).
In Unicode, four graphic variants of the glottal stop letter are available.
* Unicase () is provided for the International Phonetic Alphabet and Americanist phonetic notation
Americanist phonetic notation, also known as the North American Phonetic Alphabet (NAPA), the Americanist Phonetic Alphabet or the American Phonetic Alphabet (APA), is a system of phonetic notation originally developed by European and American an ...
. It is found in a number of orthographies that use the IPA/APA symbol, such as those of several Salishan languages
The Salishan (also Salish) languages are a family of languages of the Pacific Northwest in North America (the Canadian province of British Columbia and the American states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana). They are characterised by a ...
.
* A case pair, uppercase () and lowercase (), is provided for the orthographies of several Athabaskan languages
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific C ...
. Uppercase may be slightly wider than unicase in fonts that distinguish them.
* Superscript () that is used in the IPA and the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet.
Other notations
Other common symbols for the glottal stop sound are variants of the punctuation mark apostrophe that was the historical basis of the glottal stop letters. These include the 9-shaped modifier letter apostrophe, , which is probably the most common (and the direct ancestor of ), the 6-shaped Ľokina of Hawaiian, , and the straight-apostrophe shaped saltillo of manylanguages of Mexico
Many languages are spoken in Mexico, though Spanish is the ''de facto'' national language spoken by the vast majority of the population, making Mexico the world's most populous Hispanophone country. The indigenous languages are from eleven lan ...
, which has the case forms .
Usage
Technical transcription
*Americanist phonetic notation
Americanist phonetic notation, also known as the North American Phonetic Alphabet (NAPA), the Americanist Phonetic Alphabet or the American Phonetic Alphabet (APA), is a system of phonetic notation originally developed by European and American an ...
and the International Phonetic Alphabet‚ÄĒunicase Ē or superscript ňÄ
* Transcription of Australian Aboriginal languages‚ÄĒoccasionally unicase Ē
* Uralic Phonetic Alphabet‚ÄĒsuperscript ňÄ only
Vernacular orthographies
* Languages of Canada ** Chipewyan‚ÄĒuppercase …Ā and lowercase …ā ** Dogrib‚ÄĒuppercase …Ā and lowercase …ā ** Kootenai‚ÄĒunicase Ē ** Musqueam language‚ÄĒunicase Ē ** Nootka‚ÄĒunicase Ē ** Slavey‚ÄĒuppercase …Ā and lowercase …ā ** Nitinaht‚ÄĒunicase Ē ** Thompson‚ÄĒunicase Ē **Lushootseed
Lushootseed (tx ∑…ôlŇ°ucid, dx ∑l…ôŇ°√ļcid), also Puget Salish, Puget Sound Salish or Skagit-Nisqually, is a language made up of a dialect continuum of several Salish tribes of modern-day Washington state. Lushootseed is one of the Coast Sali ...
‚ÄĒunicase Ē
** Squamish language, where it is sometimes represented with .
Computing codes
InUnicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, ...
1.0, only the unicase and superscript variants were included. In version 4.1 (2005), an uppercase character was added, and the existing unicase character was redefined as its lowercase. Then, in version 5.0 (2006), it was decided to separate the cased and caseless usages by adding a dedicated lowercase letter. The IPA character is first from left, while the extended Latin alphabet characters are third and fourth from left.
See also
* Glottal stop#Writing * ĺ (Modifier letter right half ring) * ē (Voiced pharyngeal fricative in IPA) * ° (Epiglottal stop in IPA) * Ę (Voiced epiglottal trill in IPA) * Ė and ∆ĺ ( Obsolete and nonstandard symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet) * ň§ (Pharyngealization in IPA) * ĽOkina *Aleph
Aleph (or alef or alif, transliterated ĺ) is the first letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Hebrew , Aramaic , Syriac , Arabic ĺ and North Arabian ūź™Ď. It also appears as South Arabian ūź©Ī and Ge'ez .
These let ...
* Apostrophe
The apostrophe ( or ) is a punctuation mark, and sometimes a diacritical mark, in languages that use the Latin alphabet and some other alphabets. In English, the apostrophe is used for two basic purposes:
* The marking of the omission of one ...
* Hamza
* Saltillo (letter)
* Sokuon
The is a Japanese symbol in the form of a small hiragana or katakana '' tsu''. In less formal language it is called or , meaning "small ''tsu''". It serves multiple purposes in Japanese writing.
Appearance
In both hiragana and katakana, ...
* Spiritus lenis
References
External links
* {{Latin script Glottal stop