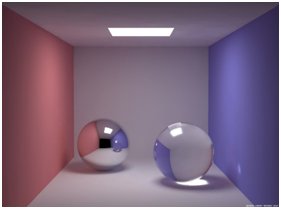
Gloss is an
optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviole ...
property which indicates how well a surface reflects light in a
specular
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface.
The law of reflection states that a reflected ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surfac ...
(mirror-like) direction. It is one of the important parameters that are used to describe the
visual appearance
The visual appearance of objects is given by the way in which they reflect and transmit light. The color of objects is determined by the parts of the spectrum of (incident white) light that are reflected or transmitted without being absorbed. Ad ...
of an object. The factors that affect gloss are the refractive index of the material, the angle of incident light and the
surface topography
Surface finish, also known as surface texture or surface topography, is the nature of a surface as defined by the three characteristics of lay, surface roughness, and waviness.. It comprises the small, local deviations of a surface from the per ...
.
Apparent gloss depends on the amount of ''specular'' reflection – light reflected from the surface in an equal amount and the symmetrical angle to the one of incoming light – in comparison with
''diffuse'' reflection – the amount of light scattered into other directions.
Theory

When light illuminates an object, it interacts with it in a number of ways:
* Absorbed within it (largely responsible for colour)
* Transmitted through it (dependent on the surface transparency and opacity)
* Scattered from or within it (diffuse reflection, haze and transmission)
* Specularly reflected from it (gloss)
Variations in surface texture directly influence the level of specular reflection. Objects with a smooth surface, i.e. highly polished or containing coatings with finely dispersed pigments, appear shiny to the eye due to a large amount of light being reflected in a specular direction whilst rough surfaces reflect no specular light as the light is scattered in other directions and therefore appears dull. The image forming qualities of these surfaces are much lower making any reflections appear blurred and distorted.
Substrate material type also influences the gloss of a surface. Non-metallic materials, i.e. plastics etc. produce a higher level of reflected light when illuminated at a greater illumination angle due to light being absorbed into the material or being diffusely scattered depending on the colour of the material. Metals do not suffer from this effect producing higher amounts of reflection at any angle.
The Fresnel formula gives the specular reflectance,
, for an unpolarized light of
intensity , at angle of incidence
, giving the intensity of specularly reflected beam of intensity
, while the refractive index of the surface specimen is
.
The
Fresnel equation
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresne ...
is given as follows :
:
 Gloss is an
Gloss is an  When light illuminates an object, it interacts with it in a number of ways:
* Absorbed within it (largely responsible for colour)
* Transmitted through it (dependent on the surface transparency and opacity)
* Scattered from or within it (diffuse reflection, haze and transmission)
* Specularly reflected from it (gloss)
Variations in surface texture directly influence the level of specular reflection. Objects with a smooth surface, i.e. highly polished or containing coatings with finely dispersed pigments, appear shiny to the eye due to a large amount of light being reflected in a specular direction whilst rough surfaces reflect no specular light as the light is scattered in other directions and therefore appears dull. The image forming qualities of these surfaces are much lower making any reflections appear blurred and distorted.
Substrate material type also influences the gloss of a surface. Non-metallic materials, i.e. plastics etc. produce a higher level of reflected light when illuminated at a greater illumination angle due to light being absorbed into the material or being diffusely scattered depending on the colour of the material. Metals do not suffer from this effect producing higher amounts of reflection at any angle.
The Fresnel formula gives the specular reflectance, , for an unpolarized light of intensity , at angle of incidence , giving the intensity of specularly reflected beam of intensity , while the refractive index of the surface specimen is .
The
When light illuminates an object, it interacts with it in a number of ways:
* Absorbed within it (largely responsible for colour)
* Transmitted through it (dependent on the surface transparency and opacity)
* Scattered from or within it (diffuse reflection, haze and transmission)
* Specularly reflected from it (gloss)
Variations in surface texture directly influence the level of specular reflection. Objects with a smooth surface, i.e. highly polished or containing coatings with finely dispersed pigments, appear shiny to the eye due to a large amount of light being reflected in a specular direction whilst rough surfaces reflect no specular light as the light is scattered in other directions and therefore appears dull. The image forming qualities of these surfaces are much lower making any reflections appear blurred and distorted.
Substrate material type also influences the gloss of a surface. Non-metallic materials, i.e. plastics etc. produce a higher level of reflected light when illuminated at a greater illumination angle due to light being absorbed into the material or being diffusely scattered depending on the colour of the material. Metals do not suffer from this effect producing higher amounts of reflection at any angle.
The Fresnel formula gives the specular reflectance, , for an unpolarized light of intensity , at angle of incidence , giving the intensity of specularly reflected beam of intensity , while the refractive index of the surface specimen is .
The
 Gloss is an
Gloss is an  When light illuminates an object, it interacts with it in a number of ways:
* Absorbed within it (largely responsible for colour)
* Transmitted through it (dependent on the surface transparency and opacity)
* Scattered from or within it (diffuse reflection, haze and transmission)
* Specularly reflected from it (gloss)
Variations in surface texture directly influence the level of specular reflection. Objects with a smooth surface, i.e. highly polished or containing coatings with finely dispersed pigments, appear shiny to the eye due to a large amount of light being reflected in a specular direction whilst rough surfaces reflect no specular light as the light is scattered in other directions and therefore appears dull. The image forming qualities of these surfaces are much lower making any reflections appear blurred and distorted.
Substrate material type also influences the gloss of a surface. Non-metallic materials, i.e. plastics etc. produce a higher level of reflected light when illuminated at a greater illumination angle due to light being absorbed into the material or being diffusely scattered depending on the colour of the material. Metals do not suffer from this effect producing higher amounts of reflection at any angle.
The Fresnel formula gives the specular reflectance, , for an unpolarized light of intensity , at angle of incidence , giving the intensity of specularly reflected beam of intensity , while the refractive index of the surface specimen is .
The
When light illuminates an object, it interacts with it in a number of ways:
* Absorbed within it (largely responsible for colour)
* Transmitted through it (dependent on the surface transparency and opacity)
* Scattered from or within it (diffuse reflection, haze and transmission)
* Specularly reflected from it (gloss)
Variations in surface texture directly influence the level of specular reflection. Objects with a smooth surface, i.e. highly polished or containing coatings with finely dispersed pigments, appear shiny to the eye due to a large amount of light being reflected in a specular direction whilst rough surfaces reflect no specular light as the light is scattered in other directions and therefore appears dull. The image forming qualities of these surfaces are much lower making any reflections appear blurred and distorted.
Substrate material type also influences the gloss of a surface. Non-metallic materials, i.e. plastics etc. produce a higher level of reflected light when illuminated at a greater illumination angle due to light being absorbed into the material or being diffusely scattered depending on the colour of the material. Metals do not suffer from this effect producing higher amounts of reflection at any angle.
The Fresnel formula gives the specular reflectance, , for an unpolarized light of intensity , at angle of incidence , giving the intensity of specularly reflected beam of intensity , while the refractive index of the surface specimen is .
The