William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and
Liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as
Prime Minister of the United Kingdom
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern pr ...
, spread over four non-consecutive terms (the most of any British prime minister) beginning in 1868 and ending in 1894. He also served as
Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is ...
four times, serving over 12 years.
Gladstone was born in
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
to Scottish parents. He first entered the
House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
in 1832, beginning his political career as a
High Tory
In the United Kingdom and elsewhere, High Toryism is the old traditionalist conservatism which is in line with the Toryism originating in the 17th century. High Tories and their worldview are sometimes at odds with the modernising elements of the ...
, a grouping which became the
Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
under
Robert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet, (5 February 1788 – 2 July 1850) was a British Conservative statesman who served twice as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (1834–1835 and 1841–1846) simultaneously serving as Chancellor of the Exchequer ...
in 1834. Gladstone served as a minister in both of Peel's governments, and in 1846 joined the breakaway
Peelite
The Peelites were a breakaway dissident political faction of the British Conservative Party from 1846 to 1859. Initially led by Robert Peel, the former Prime Minister and Conservative Party leader in 1846, the Peelites supported free trade whilst ...
faction, which eventually merged into the new
Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world. The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left.
__TOC__ Active liberal parties
This is a li ...
in 1859. He was chancellor under
Lord Aberdeen
George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen, (28 January 178414 December 1860), styled Lord Haddo from 1791 to 1801, was a British statesman, diplomat and landowner, successively a Tory, Conservative and Peelite politician and specialist in ...
(1852–1855),
Lord Palmerston
Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, (20 October 1784 – 18 October 1865) was a British statesman who was twice Prime Minister of the United Kingdom in the mid-19th century. Palmerston dominated British foreign policy during the period ...
(1859–1865) and
Lord Russell (1865–1866). Gladstone's own political doctrine—which emphasised
equality of opportunity
Equal opportunity is a state of fairness in which individuals are treated similarly, unhampered by artificial barriers, prejudices, or preferences, except when particular distinctions can be explicitly justified. The intent is that the important ...
and opposition to trade
protectionism
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. ...
—came to be known as
Gladstonian liberalism. His popularity amongst the
working-class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
earned him the sobriquet "The People's William".
In 1868, Gladstone became prime minister for the first time. Many reforms were passed during his first ministry, including the disestablishment of the
Church of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the second ...
and the introduction of
secret voting. After electoral defeat in
1874
Events
January–March
* January 1 – New York City annexes The Bronx.
* January 2 – Ignacio María González becomes head of state of the Dominican Republic for the first time.
* January 3 – Third Carlist War &ndas ...
, Gladstone resigned as leader of the Liberal Party. From 1876 he began a comeback based on opposition to the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
's reaction to the
Bulgarian April Uprising. His
Midlothian Campaign
The Midlothian campaign of 1878–80 was a series of foreign policy speeches given by William Gladstone, leader of Britain's Liberal Party. It is often cited as the first modern political campaign. It also set the stage for Gladstone's comeback ...
of 1879–1880 was an early example of many modern political campaigning techniques.
After the
1880 general election, Gladstone formed his second ministry (1880–1885), which saw the passage of the
Third Reform Act
In the United Kingdom under the premiership of William Gladstone, the Representation of the People Act 1884 (48 & 49 Vict. c. 3, also known informally as the Third Reform Act) and the Redistribution Act of the following year were laws which ...
as well as crises in Egypt (culminating in the
Fall of Khartoum) and Ireland, where his government passed repressive measures but also improved the legal rights of Irish tenant farmers.
Back in office in early 1886, Gladstone proposed
home rule for Ireland
The Irish Home Rule movement was a movement that campaigned for Devolution, self-government (or "home rule") for Ireland within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was the dominant political movement of Irish nationalism from 1 ...
but was defeated in the House of Commons. The resulting split in the Liberal Party helped keep them out of office—with one short break—for 20 years. Gladstone formed his last government in
1892
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Ellis Island begins accommodating immigrants to the United States.
* February 1 - The historic Enterprise Bar and Grill was established in Rico, Colorado.
* February 27 – Rudolf Diesel applies for ...
, at the age of 82. The
Government of Ireland Bill 1893
The Government of Ireland Bill 1893 (known generally as the Second Home Rule Bill) was the second attempt made by Liberal Party leader William Ewart Gladstone, as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, to enact a system of home rule for Ireland. ...
passed through the Commons but was defeated in the
House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
in 1893, after which Irish Home Rule became a lesser part of his party's agenda. Gladstone left office in March 1894, aged 84, as both the oldest person to serve as Prime Minister and the only prime minister to have served four non-consecutive terms. He left Parliament in
1895
Events
January–March
* January 5 – Dreyfus affair: French officer Alfred Dreyfus is stripped of his army rank, and sentenced to life imprisonment on Devil's Island.
* January 12 – The National Trust for Places of Histor ...
and died three years later.
Gladstone was known affectionately by his supporters as "The People's William" or the "G.O.M." ("Grand Old Man", or, to political rivals "God's Only Mistake"). Historians often call him one of Britain's greatest leaders.
Early life
Born in 1809 in
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
, at 62
Rodney Street, William Ewart Gladstone was the fourth son of the wealthy slaveowner
John Gladstone, and his second wife, Anne MacKenzie Robertson.
He was named after a close friend of his father, William Ewart, another Liverpool merchant and the father of
William Ewart, later a Liberal politician. In 1835, the family name was changed from Gladstones to Gladstone by royal licence. His father was made a
baronet
A baronet ( or ; abbreviated Bart or Bt) or the female equivalent, a baronetess (, , or ; abbreviation Btss), is the holder of a baronetcy, a hereditary title awarded by the British Crown. The title of baronet is mentioned as early as the 14th ...
, of Fasque and Balfour, in 1846.
Although born and raised in Liverpool, William Gladstone was of purely
Scottish ancestry.
[Shannon, 1985] His grandfather
Thomas Gladstones
Thomas Gladstones (3 June 1732 – 12 May 1809) was a Scottish flour merchant and philanthropist. He was the father of Sir John Gladstone and the grandfather of the British prime minister William Ewart Gladstone.
Early life
Born at the farm of ...
(1732–1809) was a prominent merchant from
Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
, and his maternal grandfather, Andrew Robertson, was Provost of Dingwall and a Sheriff-Substitute of
Ross-shire
Ross-shire (; gd, Siorrachd Rois) is a historic county in the Scottish Highlands. The county borders Sutherland to the north and Inverness-shire to the south, as well as having a complex border with Cromartyshire – a county consisting of ...
.
His biographer
John Morley
John Morley, 1st Viscount Morley of Blackburn, (24 December 1838 – 23 September 1923) was a British Liberal statesman, writer and newspaper editor.
Initially, a journalist in the North of England and then editor of the newly Liberal-leani ...
described him as "a highlander in the custody of a lowlander", and an adversary as "an ardent Italian in the custody of a Scotsman". One of his earliest childhood memories was being made to stand on a table and say "Ladies and gentlemen" to the assembled audience, probably at a gathering to promote the election of
George Canning
George Canning (11 April 17708 August 1827) was a British Tory statesman. He held various senior cabinet positions under numerous prime ministers, including two important terms as Foreign Secretary, finally becoming Prime Minister of the Unit ...
as MP for Liverpool in 1812. In 1814, young "Willy" visited
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
for the first time, as he and his brother
John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
travelled with their father to
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
,
Biggar and
Dingwall
Dingwall ( sco, Dingwal, gd, Inbhir Pheofharain ) is a town and a royal burgh in the Highland council area of Scotland. It has a population of 5,491. It was an east-coast harbour that now lies inland. Dingwall Castle was once the biggest cast ...
to visit their relatives. Willy and his brother were both made
freemen of the burgh of Dingwall. In 1815, Gladstone also travelled to
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
and
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
for the first time with his parents. Whilst in London, he attended a service of thanksgiving with his family at
St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral in London and is the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London. It is on Ludgate Hill at the highest point of the City of London and is a Grad ...
following the
Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
, where he saw the
Prince Regent
A prince regent or princess regent is a prince or princess who, due to their position in the line of succession, rules a monarchy as regent in the stead of a monarch regnant, e.g., as a result of the sovereign's incapacity (minority or illness ...
.
William Gladstone was educated from 1816 to 1821 at a
preparatory school at the vicarage of St. Thomas' Church at
Seaforth, close to his family's residence,
Seaforth House
Seaforth House was a mansion in Seaforth, Merseyside England built in 1813 for Sir John Gladstone, father of William Ewart Gladstone who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom four times.
Sir John had lived on Rodney Street, Liverpool and de ...
.
In 1821, William followed in the footsteps of his elder brothers and attended
Eton College
Eton College () is a public school in Eton, Berkshire, England. It was founded in 1440 by Henry VI under the name ''Kynge's College of Our Ladye of Eton besyde Windesore'',Nevill, p. 3 ff. intended as a sister institution to King's College, C ...
before
matriculating
Matriculation is the formal process of entering a university, or of becoming eligible to enter by fulfilling certain academic requirements such as a matriculation examination.
Australia
In Australia, the term "matriculation" is seldom used now. ...
in 1828 at
Christ Church, Oxford
Christ Church ( la, Ædes Christi, the temple or house, '' ædēs'', of Christ, and thus sometimes known as "The House") is a constituent college of the University of Oxford in England. Founded in 1546 by King Henry VIII, the college is uniqu ...
, where he read
Classics
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics ...
and
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, although he had no great interest in the latter subject. In December 1831, he achieved the
double first-class degree he had long desired. Gladstone served as President of the
Oxford Union
The Oxford Union Society, commonly referred to simply as the Oxford Union, is a debating society in the city of Oxford England, whose membership is drawn primarily from the University of Oxford. Founded in 1823, it is one of Britain's oldest ...
, where he developed a reputation as an orator, which followed him into the
House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
. At university, Gladstone was a
Tory
A Tory () is a person who holds a political philosophy known as Toryism, based on a British version of traditionalism and conservatism, which upholds the supremacy of social order as it has evolved in the English culture throughout history. Th ...
and denounced
Whig proposals for parliamentary reform.

Following the success of his double first, William travelled with his brother
John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
on a
Grand Tour
The Grand Tour was the principally 17th- to early 19th-century custom of a traditional trip through Europe, with Italy as a key destination, undertaken by upper-class young European men of sufficient means and rank (typically accompanied by a tuto ...
of western Europe.
Although Gladstone entered
Lincoln's Inn
The Honourable Society of Lincoln's Inn is one of the four Inns of Court in London to which barristers of England and Wales belong and where they are called to the Bar. (The other three are Middle Temple, Inner Temple and Gray's Inn.) Lincoln ...
in 1833, with intentions of becoming a
barrister
A barrister is a type of lawyer in common law jurisdictions. Barristers mostly specialise in courtroom advocacy and litigation. Their tasks include taking cases in superior courts and tribunals, drafting legal pleadings, researching law and ...
, by 1839 he had requested that his name should be removed from the list because he no longer intended to be called to
the Bar.
In September 1842 he lost the
forefinger
The index finger (also referred to as forefinger, first finger, second finger, pointer finger, trigger finger, digitus secundus, digitus II, and many other terms) is the second digit of a human hand. It is located between the thumb and the mid ...
of his left hand in an accident while reloading a gun. Thereafter he wore a glove or finger sheath (stall).
House of Commons
First term
When Gladstone was 22 the
Duke of Newcastle
Duke of Newcastle upon Tyne was a title that was created three times, once in the Peerage of England and twice in the Peerage of Great Britain. The first grant of the title was made in 1665 to William Cavendish, 1st Marquess of Newcastle u ...
, a Conservative party activist, provided him with one of two seats at
Newark
Newark most commonly refers to:
* Newark, New Jersey, city in the United States
* Newark Liberty International Airport, New Jersey; a major air hub in the New York metropolitan area
Newark may also refer to:
Places Canada
* Niagara-on-the ...
where he controlled about a fourth of the very small electorate. The Duke spent thousands of pounds entertaining the voters. Gladstone displayed remarkably strong technique as a campaigner and stump speaker. He won his seat at the
1832 United Kingdom general election
The 1832 United Kingdom general election, the first after the Reform Act, saw the Whigs win a large majority, with the Tories winning less than 30% of the vote.
Political situation
The Earl Grey had been Prime Minister since November 1830. H ...
with 887 votes. Initially a disciple of
High Toryism
In the United Kingdom and elsewhere, High Toryism is the old traditionalist conservatism which is in line with the Toryism originating in the 17th century. High Tories and their worldview are sometimes at odds with the modernising elements of the ...
, Gladstone's maiden speech as a young
Tory
A Tory () is a person who holds a political philosophy known as Toryism, based on a British version of traditionalism and conservatism, which upholds the supremacy of social order as it has evolved in the English culture throughout history. Th ...
was a defence of the rights of West Indian sugar plantation magnates—slave-owners—among whom his father was prominent. He immediately came under attack from anti-slavery elements. He also surprised the duke by urging the need to increase pay for unskilled factory workers.; After new bills to protect child workers were proposed following the publication of the
Sadler report
:''This is an article about a 19th century British report. It should not be confused with the Sadler Commission, an investigation into Indian University education at the end of the First World War.''
The Sadler Report, also known as the Report of ...
, he voted against the 1833
Factory Acts
The Factory Acts were a series of acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom to regulate the conditions of industrial employment.
The early Acts concentrated on regulating the hours of work and moral welfare of young children employed ...
that would regulate the hours of work and welfare of minors employed in cotton mills.
Attitude towards slavery
Gladstone's early attitude towards slavery was highly shaped by his father,
Sir John Gladstone, one of the largest slave owners in the British Empire. Gladstone wanted gradual rather than immediate emancipation, and proposed that slaves should serve a period of apprenticeship after being freed. They also opposed the international slave trade (which lowered the value of the slaves the father already owned). The antislavery movement demanded the immediate abolition of slavery. Gladstone opposed this and said in 1832 that emancipation should come after moral emancipation through the adoption of an education and the inculcation of "honest and industrious habits" among the slaves. Then "with the utmost speed that prudence will permit, we shall arrive at that exceedingly desired consummation, the utter extinction of slavery." In 1831, when the Oxford Union considered a motion in favour of the immediate emancipation of the slaves in the West Indies, Gladstone moved an amendment in favour of gradual manumission along with better protection for the personal and civil rights of the slaves and better provision for their Christian education. His early Parliamentary speeches followed a similar line: in June 1833, Gladstone concluded his speech on the ‘slavery question’ by declaring that though he had dwelt on "the dark side" of the issue, he looked forward to "a safe and gradual emancipation".
In 1834, when slavery was abolished across the British Empire, the owners were paid full value for the slaves. Gladstone helped his father obtain £106,769 in official reimbursement by the government for the 2,508 slaves he owned across nine plantations in the Caribbean.
In later years Gladstone's attitude towards slavery became more critical as his father's influence over his politics diminished. In 1844 Gladstone broke with his father when, as
President of the Board of Trade
The president of the Board of Trade is head of the Board of Trade. This is a committee of the His Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council, Privy Council of the United Kingdom, first established as a temporary committee of inquiry in the 17th centu ...
, he advanced proposals to halve duties on foreign sugar not produced by slave labour, in order to "secure the effectual exclusion of slave-grown sugar" and to encourage Brazil and Spain to end slavery. Sir John Gladstone, who opposed any reduction in duties on foreign sugar, wrote a letter to ''The Times'' criticizing the measure. Looking back late in life, Gladstone named the abolition of slavery as one of ten great achievements of the previous sixty years where the masses had been right and the upper classes had been wrong.
[''The Times'' (29 June 1886), p. 11.]
Opposition to the opium trade
Gladstone was an intense opponent of the
opium trade
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid m ...
.
Referring to the opium trade between
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and
Qing China
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu people, Manchu-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin (1616–1636), La ...
, Gladstone described it as "infamous and atrocious".
Gladstone emerged as a fierce critic of the
Opium Wars
The Opium Wars () were two conflicts waged between China and Western powers during the mid-19th century. The First Opium War was fought from 1839 to 1842 between China and the United Kingdom, and was triggered by the Chinese government's cam ...
, which Britain waged to re-legalise the British opium trade into China, which had been made illegal by the Chinese government.
He publicly lambasted the wars as "
Palmerston's Opium War" and said that he felt "in dread of the judgements of God upon England for our national iniquity towards China" in May 1840.
A famous speech was made by Gladstone in Parliament against the
First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
.
Gladstone criticised it as "a war more unjust in its origin, a war more calculated in its progress to cover this country with permanent disgrace".
His hostility to opium stemmed from the effects of opium upon his sister Helen.
Before 1841, Gladstone was reluctant to join the Peel government because of the First Opium War, which Palmerston had brought on.
Minister under Peel (1841–1846)
Gladstone was re-elected in 1841. In the second ministry of Robert Peel, he served as
President of the Board of Trade
The president of the Board of Trade is head of the Board of Trade. This is a committee of the His Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council, Privy Council of the United Kingdom, first established as a temporary committee of inquiry in the 17th centu ...
(1843–1845).
Gladstone was responsible for the
Railways Act 1844, regarded by historians as the birth of the
regulatory state, of network industry regulation, of rate of return regulation, and telegraph regulation. Examples of its foresight are the clauses empowering government to take control of railway in time of war, the concept of
Parliamentary train
A parliamentary train was a passenger service operated in the United Kingdom to comply with the Railway Regulation Act 1844 that required train companies to provide inexpensive and basic rail transport for less affluent passengers. The act requ ...
s, limited in cost to a penny a mile, of universal service, and of control of the recently invented electric telegraph which ran alongside railway lines. Railways were the largest investment (as a percentage of GNP) in human history and this Bill the most heavily lobbied in Parliamentary history. Gladstone succeeded in guiding the Act through Parliament at the height of the
railway bubble.
Gladstone became concerned with the situation of "coal whippers". These were the men who worked on London docks, "whipping" in baskets from ships to barges or wharves all incoming coal from the sea. They were called up and relieved through public houses, so a man could not get this job unless he had the favourable opinion of the publican, who looked most favourably upon those who drank. The man's name was written down and the "score" followed. Publicans issued employment solely on the capacity of the man to pay, and men were often drunk when they left the pub to work. They spent their savings on drink to secure the favourable opinion of publicans and further employment.
Gladstone initiated the Coal Vendors Act 1843, which set up a central office for employment. When that Act expired in 1856, a Select Committee was appointed by the Lords in 1857 to look into the question. Gladstone gave evidence to the committee, stating: "I approached the subject in the first instance as I think everyone in Parliament of necessity did, with the strongest possible prejudice against the proposal
o interfere
O, or o, is the fifteenth letter and the fourth vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''o'' (pronounced ), pl ...
but the facts stated were of so extraordinary and deplorable a character, that it was impossible to withhold attention from them. Then the question being whether legislative interference was required I was at length induced to look at a remedy of an extraordinary character as the only one I thought applicable to the case ... it was a great innovation". Looking back in 1883, Gladstone wrote that "In principle, perhaps my Coalwhippers Act of 1843 was the most Socialistic measure of the last half century".
He resigned in 1845 over the
Maynooth Grant
The Maynooth Grant was a cash grant from the British government to a Catholic seminary in Ireland. In 1845, the Conservative Prime Minister, Sir Robert Peel, sought to improve the relationship between Catholic Ireland and Protestant Britain by in ...
issue, which was a matter of conscience for him. To improve relations with the Catholic Church, Peel's government proposed increasing the annual grant paid to the
Maynooth Seminary for training Catholic priests in Ireland. Gladstone, who had previously argued in a book that a Protestant country should not pay money to other churches, nevertheless supported the increase in the Maynooth grant and voted for it in Commons, but resigned rather than face charges that he had compromised his principles to remain in office. After accepting Gladstone's resignation, Peel confessed to a friend, "I really have great difficulty sometimes in exactly comprehending what he means". In December 1845, Gladstone returned to Peel's government as
Colonial Secretary. The ''
Dictionary of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September ...
'' notes: "As such, he had to stand for re-election, but the strong protectionism of the Duke of Newcastle, his patron in Newark, meant that he could not stand there and no other seat was available. Throughout the corn law crisis of 1846, therefore, Gladstone was in the highly anomalous and possibly unique position of being a secretary of state without a seat in either house and thus unanswerable to parliament."
Return to the backbenches (1846–1851)
When Peel's government fell in 1846, Gladstone and other Peel loyalists followed their leader in separating from the protectionist Conservatives; instead offering tentative support to the new Whig prime minister
Lord John Russell
John Russell, 1st Earl Russell, (18 August 1792 – 28 May 1878), known by his courtesy title Lord John Russell before 1861, was a British Whig and Liberal statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1852 and ag ...
, with whom Peel had cooperated over the repeal of the
Corn Laws
The Corn Laws were tariffs and other trade restrictions on imported food and corn enforced in the United Kingdom between 1815 and 1846. The word ''corn'' in British English denotes all cereal grains, including wheat, oats and barley. They were ...
. After Peel's death in 1850, Gladstone emerged as the leader of the
Peelites
The Peelites were a breakaway dissident political faction of the British Conservative Party from 1846 to 1859. Initially led by Robert Peel, the former Prime Minister and Conservative Party leader in 1846, the Peelites supported free trade whilst ...
in the House of Commons. He was re-elected for the
University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
(i.e. representing the MA graduates of the university) at the General Election in 1847—Peel had once held this seat but had lost it because of his espousal of Catholic Emancipation in 1829. Gladstone became a constant critic of
Lord Palmerston
Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, (20 October 1784 – 18 October 1865) was a British statesman who was twice Prime Minister of the United Kingdom in the mid-19th century. Palmerston dominated British foreign policy during the period ...
.
In 1847 Gladstone helped to establish
Glenalmond College
Glenalmond College is a co-educational independent boarding school in Perth and Kinross, Scotland, for children aged between 12 and 18 years. It is situated on the River Almond near the village of Methven, about west of the city of Perth. T ...
, then The Holy and Undivided Trinity College at Glenalmond. The school was set up as an episcopal foundation to spread the ideas of
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
in Scotland, and to educate the sons of the gentry.
As a young man Gladstone had treated his father's estate, Fasque, in
Forfarshire, southwest of Aberdeen, as home, but as a younger son he would not inherit it. Instead, from the time of his marriage, he lived at his wife's family's estate at
Hawarden
Hawarden (; cy, Penarlâg) is a village, community (Wales), community and Wards and electoral divisions of the United Kingdom, electoral ward in Flintshire, Wales. It is part of the Deeside conurbation on the Wales-England border and is home ...
in Flintshire, Wales. He never actually owned Hawarden, which belonged first to his brother-in-law
Sir Stephen Glynne, and was then inherited by Gladstone's eldest son in 1874. During the late 1840s, when he was out of office, he worked extensively to turn Hawarden into a viable business.
In 1848 he founded the
Church Penitentiary Association for the Reclamation of
Fallen Women
"Fallen woman" is an archaic term which was used to describe a woman who has "lost her innocence", and fallen from the grace of God. In 19th-century Britain especially, the meaning came to be closely associated with the loss or surrender of a w ...
. In May 1849 he began his most active "rescue work" and met prostitutes late at night on the street, in his house or in their houses, writing their names in a private notebook. He aided the
House of Mercy
Houses of Mercy were Anglican institutions that operated from the mid 19th century to the mid 20th.
They were to house " fallen women", a term used to imply female sexual promiscuity or work in prostitution. Many women entering were unmarried ...
at
Clewer
Clewer (also known as Clewer Village) is an ecclesiastical parish and an area of Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor in the county of Berkshire, England. Clewer makes up three Ward (electoral subdivision), wards of the Royal Borough of Windsor and Maid ...
near
Windsor
Windsor may refer to:
Places Australia
* Windsor, New South Wales
** Municipality of Windsor, a former local government area
* Windsor, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane, Queensland
**Shire of Windsor, a former local government authority around Wi ...
(which exercised extreme in-house discipline) and spent much time arranging employment for ex-prostitutes. In a "Declaration" signed on 7 December 1896 and only to be opened after his death, Gladstone wrote, "I desire to record my solemn declaration and assurance, as in the sight of God and before His Judgement Seat, that at no period of my life have I been guilty of the act which is known as that of infidelity to the marriage bed."
In 1850–51 Gladstone visited
Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
. Italy, for the benefit of his daughter Mary's eyesight. Giacomo Lacaita, legal adviser to the British embassy, was at the time imprisoned by the Neapolitan government, as were other political dissidents. Gladstone became concerned at the political situation in Naples and the arrest and imprisonment of Neapolitan liberals. In February 1851 Gladstone visited the prisons where thousands of them were held and was extremely outraged. In April and July he published two ''Letters to the Earl of Aberdeen'' against the Neapolitan government and responded to his critics in ''An Examination of the Official Reply of the Neapolitan Government'' in 1852. Gladstone's first letter described what he saw in Naples as "the negation of God erected into a system of government".
Chancellor of the Exchequer (1852–1855)

In 1852, following the appointment of
Lord Aberdeen
George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen, (28 January 178414 December 1860), styled Lord Haddo from 1791 to 1801, was a British statesman, diplomat and landowner, successively a Tory, Conservative and Peelite politician and specialist in ...
as Prime Minister, head of a coalition of
Whigs and Peelites, Gladstone became
Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is ...
. The Whig Sir
Charles Wood and the Tory Disraeli had both been perceived to have failed in the office and so this provided Gladstone with a great political opportunity.
His first budget in 1853 almost completed the work begun by Peel eleven years before in simplifying Britain's tariff of duties and customs. 123 duties were abolished and 133 duties were reduced. The income tax had legally expired but Gladstone proposed to extend it for seven years to fund tariff reductions:
We propose, then, to re-enact it for two years, from April, 1853, to April, 1855, at the rate of 7d. in the £; from April, 1855, to enact it for two more years at 6d. in the £; and then for three years more ... from April, 1857, at 5d. Under this proposal, on 5 April 1860, the income-tax will by law expire.
Gladstone wanted to maintain a balance between direct and indirect taxation and to abolish income tax. He knew that its abolition depended on a considerable retrenchment in government expenditure. He therefore increased the number of people eligible to pay it by lowering the threshold from £150 to £100. The more people that paid income tax, Gladstone believed, the more the public would pressure the government into abolishing it.
[Matthew, ''Gladstone, 1809–1874'', p. 127.] Gladstone argued that the £100 line was "the dividing line ... between the educated and the labouring part of the community" and that therefore the income tax payers and the electorate were to be the same people, who would then vote to cut government expenditure.
The budget speech (delivered on 18 April), nearly five hours long, raised Gladstone "at once to the front rank of financiers as of orators".
H.C.G. Matthew has written that Gladstone "made finance and figures exciting, and succeeded in constructing budget speeches epic in form and performance, often with lyrical interludes to vary the tension in the Commons as the careful exposition of figures and argument was brought to a climax". The contemporary diarist
Charles Greville wrote of Gladstone's speech:
... by universal consent it was one of the grandest displays and most able financial statement that ever was heard in the House of Commons; a great scheme, boldly, skilfully, and honestly devised, disdaining popular clamour and pressure from without, and the execution of it absolute perfection. Even those who do not admire the Budget, or who are injured by it, admit the merit of the performance. It has raised Gladstone to a great political elevation, and, what is of far greater consequence than the measure itself, has given the country assurance of a man equal to great political necessities, and fit to lead parties and direct governments.
During wartime, he insisted on raising taxes and not borrowing funds to pay for the war. The goal was to turn wealthy Britons against expensive wars. Britain entered the
Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
in February 1854, and Gladstone introduced his budget on 6 March. He had to increase expenditure on the military and a vote of credit of £1,250,000 was taken to send a force of 25,000 to the front. The deficit for the year would be £2,840,000 (estimated revenue £56,680,000; estimated expenditure £59,420,000). Gladstone refused to borrow the money needed to rectify this deficit and instead increased income tax by half, from sevenpence to tenpence-halfpenny in the pound (from 2.92% to 4.38%). By May another £6,870,000 was needed for the war and Gladstone raised the income tax from tenpence halfpenny to fourteen pence in the pound to raise £3,250,000. Spirits, malt, and sugar were taxed to raise the rest of the money needed. He proclaimed:
:The expenses of a war are the moral check which it has pleased the Almighty to impose upon the ambition and lust of conquest that are inherent in so many nations ... The necessity of meeting from year to year the expenditure which it entails is a salutary and wholesome check, making them feel what they are about, and making them measure the cost of the benefit upon which they may calculate
He served until 1855, a few weeks into Lord Palmerston's first premiership, and resigned along with the rest of the Peelites after a motion was passed to appoint a committee of inquiry into the conduct of the war.
Opposition (1855–1859)

The Conservative Leader
Lord Derby
Edward George Geoffrey Smith-Stanley, 14th Earl of Derby, (29 March 1799 – 23 October 1869, known before 1834 as Edward Stanley, and from 1834 to 1851 as Lord Stanley) was a British statesman, three-time Prime Minister of the United Kingdom ...
became Prime Minister in 1858, but Gladstone—who like the other Peelites was still nominally a Conservative—declined a position in his government, opting not to sacrifice his free trade principles.
Between November 1858 and February 1859, Gladstone, on behalf of Lord Derby's government, was made Extraordinary
Lord High Commissioner of the Ionian Islands
The Lord High Commissioner of the Ionian Islands was the local representative of the British government in the United States of the Ionian Islands between 1816 and 1864, succeeding the earlier office of the Civil Commissioner of the Ionian Island ...
embarking via Vienna and Trieste on a twelve-week mission to the southern Adriatic entrusted with complex challenges that had arisen in connection with the future of the British protectorate of the
United States of the Ionian Islands
The United States of the Ionian Islands ( el, Ἡνωμένον Κράτος τῶν Ἰονίων Νήσων, Inoménon-Krátos ton Ioníon Níson, United State of the Ionian Islands; it, Stati Uniti delle Isole Ionie) was a Greek state and am ...
.
In 1858, Gladstone took up the hobby of tree felling, mostly of oak trees, an exercise he continued with enthusiasm until he was 81 in 1891. Eventually, he became notorious for this activity, prompting
Lord Randolph Churchill
Lord Randolph Henry Spencer-Churchill (13 February 1849 – 24 January 1895) was a British statesman. Churchill was a Tory radical and coined the term 'Tory democracy'. He inspired a generation of party managers, created the National Union of ...
to observe: "For the purposes of recreation he has selected the felling of trees; and we may usefully remark that his amusements, like his politics, are essentially destructive. Every afternoon the whole world is invited to assist at the crashing fall of some beech or elm or oak. The forest laments in order that Mr Gladstone may perspire." Less noticed at the time was his practice of replacing the trees felled by planting new saplings.
Gladstone was a lifelong
bibliophile
Bibliophilia or bibliophilism is the love of books. A bibliophile or bookworm is an individual who loves and frequently reads and/or collects books.
Profile
The classic bibliophile is one who loves to read, admire and collect books, often ama ...
. In his lifetime, he read around 20,000 books, and eventually owned a library of over 32,000.
Chancellor of the Exchequer (1859–1866)

In 1859, Lord Palmerston formed a new mixed government with Radicals included, and Gladstone again joined the government (with most of the other remaining Peelites) as Chancellor of the Exchequer, to become part of the new
Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world. The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left.
__TOC__ Active liberal parties
This is a li ...
.
Gladstone inherited a deficit of nearly £5,000,000, with income tax now set at 5d (fivepence). Like Peel, Gladstone dismissed the idea of borrowing to cover the deficit. Gladstone argued that "In time of peace nothing but dire necessity should induce us to borrow". Most of the money needed was acquired through raising the income tax to 9d. Usually not more than two-thirds of a tax imposed could be collected in a financial year so Gladstone therefore imposed the extra four pence at a rate of 8d. during the first half of the year so that he could obtain the additional revenue in one year. Gladstone's dividing line set up in 1853 had been abolished in 1858 but Gladstone revived it, with lower incomes to pay 6½d. instead of 9d. For the first half of the year the lower incomes paid 8d. and the higher incomes paid 13d. in income tax.
On 12 September 1859 the Radical MP
Richard Cobden
Richard Cobden (3 June 1804 – 2 April 1865) was an English Radical and Liberal politician, manufacturer, and a campaigner for free trade and peace. He was associated with the Anti-Corn Law League and the Cobden–Chevalier Treaty.
As a young ...
visited Gladstone, who recorded it in his diary: "... further conv. with Mr. Cobden on Tariffs & relations with France. We are closely & warmly agreed". Cobden was sent as Britain's representative to the negotiations with France's
Michel Chevalier
Michel Chevalier (; 13 January 1806 – 18 November 1879) was a French engineer, statesman, economist and free market liberal.
Biography
Born in Limoges, Haute-Vienne, Chevalier studied at the ''École Polytechnique'', obtaining an engineering d ...
for a free trade treaty between the two countries. Gladstone wrote to Cobden: "... the great aim—the moral and political significance of the act, and its probable and desired fruit in binding the two countries together by interest and affection. Neither you nor I attach for the moment any superlative value to this Treaty for the sake of the extension of British trade. ... What I look to is the social good, the benefit to the relations of the two countries, and the effect on the peace of Europe".
Gladstone's budget of 1860 was introduced on 10 February along with the
Cobden–Chevalier Treaty
The Cobden–Chevalier Treaty was an Anglo-French free trade agreement signed between Great Britain and France on 23 January 1860. After Britain began free trade policies in 1846, there remained tariffs with France. The 1860 treaty ended tariffs o ...
between Britain and France that would reduce tariffs between the two countries. This budget "marked the final adoption of the Free Trade principle, that taxation should be levied for Revenue purposes alone, and that every protective, differential, or discriminating duty ... should be dislodged". At the beginning of 1859, there were 419 duties in existence. The 1860 budget reduced the number of duties to 48, with 15 duties constituting the majority of the revenue. To finance these reductions in indirect taxation, the income tax, instead of being abolished, was raised to 10d. for incomes above £150 and at 7d. for incomes above £100.
In 1860 Gladstone intended to abolish the duty on paper—a controversial policy—because the duty traditionally inflated the cost of publishing and hindered the dissemination of radical working-class ideas. Although Palmerston supported continuation of the duty, using it and income tax revenue to buy arms, a majority of his Cabinet supported Gladstone. The Bill to abolish duties on paper narrowly passed Commons but was rejected by the House of Lords. No
money bill
In the Westminster system (and, colloquially, in the United States), a money bill or supply bill is a bill that solely concerns taxation or government spending (also known as appropriation of money), as opposed to changes in public law.
Conv ...
had been rejected by Lords for over 200 years, and a furore arose over this vote. The next year, Gladstone included the abolition of paper duty in a consolidated
Finance Bill
A government budget is a document prepared by the government and/or other political entity presenting its anticipated tax revenues (Inheritance tax, income tax, corporation tax, import taxes) and proposed spending/expenditure (Healthcare, Educat ...
(the first ever) to force the Lords to accept it, and accept it they did. The proposal in the Commons of one bill only per session for the national finances was a precedent uniformly followed from that date until 1910, and it has been ever since the rule.
Gladstone steadily reduced Income tax over the course of his tenure as Chancellor. In 1861 the tax was reduced to ninepence (£0–0s–9d), in 1863 to sevenpence, in 1864 to fivepence and in 1865 to fourpence. Gladstone believed that government was extravagant and wasteful with taxpayers' money and so sought to let money "fructify in the pockets of the people" by keeping taxation levels down through "peace and retrenchment". In 1859 he wrote to his brother, who was a member of the Financial Reform Association at Liverpool: "Economy is the first and great article (economy such as I understand it) in my financial creed. The controversy between direct and indirect taxation holds a minor, though important place". He wrote to his wife on 14 January 1860: "I am ''certain'', from experience, of the immense advantage of strict account-keeping in early life. It is just like learning the grammar then, which when once learned need not be referred to afterwards".
Due to his actions as Chancellor, Gladstone earned the reputation as the liberator of British trade and the working man's breakfast table, the man responsible for the emancipation of the popular press from "taxes upon knowledge" and for placing a duty on the succession of the estates of the rich. Gladstone's popularity rested on his taxation policies which meant to his supporters balance, social equity and political justice. The most significant expression of working-class opinion was at Northumberland in 1862 when Gladstone visited.
George Holyoake
George Jacob Holyoake (13 April 1817 – 22 January 1906) was an English secularist, co-operator and newspaper editor. He coined the terms secularism in 1851 and "jingoism" in 1878. He edited a secularist paper, the ''Reasoner'', from 1846 to Ju ...
recalled in 1865:
When Mr Gladstone visited the North, you well remember when word passed from the newspaper to the workman that it circulated through mines and mills, factories and workshops, and they came out to greet the only British minister who ever gave the English people a right because it was just they should have it ... and when he went down the Tyne, all the country heard how twenty miles of banks were lined with people who came to greet him. Men stood in the blaze of chimneys; the roofs of factories were crowded; colliers came up from the mines; women held up their children on the banks that it might be said in after life that they had seen the Chancellor of the People go by. The river was covered like the land. Every man who could ply an oar pulled up to give Mr Gladstone a cheer. When Lord Palmerston went to Bradford the streets were still, and working men imposed silence upon themselves. When Mr Gladstone appeared on the Tyne he heard cheer no other English minister ever heard ... the people were grateful to him, and rough pitmen who never approached a public man before, pressed round his carriage by thousands ... and thousands of arms were stretched out at once, to shake hands with Mr Gladstone as one of themselves.
When Gladstone first joined Palmerston's government in 1859, he had opposed further electoral reform, but he changed his position during Palmerston's last premiership, and by 1865 he was firmly in favour of enfranchising the working classes in towns. The policy caused friction with Palmerston, who strongly opposed enfranchisement. At the beginning of each
session, Gladstone would passionately urge the Cabinet to adopt new policies, while Palmerston would fixedly stare at a paper before him. At a lull in Gladstone's speech, Palmerston would smile, rap the table with his knuckles, and interject pointedly, "Now, my Lords and gentlemen, let us go to business". Although he personally was not a Nonconformist, and rather disliked them in person, he formed a coalition with the Nonconformists that gave the Liberals a powerful base of support.
American Civil War
Shortly after the outbreak of the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
Gladstone wrote to his friend the
Duchess of Sutherland
{{Unreferenced, date=June 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
The Duchess of Sutherland is the wife of the Duke of Sutherland, an extant title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom which was created by William IV in 1833.
Duchesses of Sutherland
* Elizab ...
that "the
principle announced by the
vice-president of the South...which asserts the superiority of the white man, and therewith founds on it his right to hold the black in slavery, I think that principle detestable, and I am wholly with the opponents of it" but that he felt that the North was wrong to try to restore the Union by military force, which he believed would end in failure.
[Morley, ''Life of Gladstone: II'', p. 82.] Palmerston's government adopted a position of British neutrality throughout the war, while declining to recognise the independence of the
Confederacy. In October 1862 Gladstone made a speech in
Newcastle Newcastle usually refers to:
*Newcastle upon Tyne, a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England
*Newcastle-under-Lyme, a town in Staffordshire, England
*Newcastle, New South Wales, a metropolitan area in Australia, named after Newcastle ...
in which he said that
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as a ...
and the other Confederate leaders had "made a nation", that the Confederacy seemed certain to succeed in asserting its independence from the North, and that the time might come when it would be the duty of the European powers to "offer friendly aid in compromising the quarrel." The speech caused consternation on both sides of the Atlantic and led to speculation that the Britain might be about to recognise the Confederacy."
[''The Times'' (20 October 1862), p. 7.] Gladstone was accused of sympathising with the South, a charge he rejected.
Gladstone was forced to clarify in the press that his comments in Newcastle had not been intended to signal a change in Government policy, but to express his belief that the North's efforts to defeat the South would fail, due to the strength of Southern resistance.
In a memorandum to the Cabinet later that month Gladstone wrote that, although he believed the Confederacy would probably win the war, it was "seriously tainted by its connection with slavery" and argued that the European powers should use their influence on the South to effect the "mitigation or removal of slavery."
Electoral reform
In May 1864 Gladstone said that he saw no reason in principle why all mentally able men could not be enfranchised, but admitted that this would only come about once the working classes themselves showed more interest in the subject. Queen Victoria was not pleased with this statement, and an outraged Palmerston considered it a seditious incitement to agitation.
Gladstone's support for electoral reform and disestablishment of the (Anglican)
Church of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the second ...
won support from Nonconformists but alienated him from constituents in his Oxford University seat, and he lost it in the
1865 general election. A month later he stood as a candidate in
South Lancashire
South Lancashire is a geographical county area, used to indicate the southern part of the historic county of Lancashire, today without any administrative purpose. The county region has no exact boundaries but generally includes areas that form t ...
, where he was elected third MP (South Lancashire at this time elected three MPs). Palmerston campaigned for Gladstone in Oxford because he believed that his constituents would keep him "partially muzzled"; many Oxford graduates were Anglican clergymen at that time. A victorious Gladstone told his new constituency, "At last, my friends, I am come among you; and I am come—to use an expression which has become very famous and is not likely to be forgotten—I am come 'unmuzzled'."
On Palmerston's death in October, Earl Russell formed his second ministry. Russell and Gladstone (now the senior Liberal in the House of Commons) attempted to pass a reform bill, which was defeated in the Commons because the "
Adullamite" Whigs, led by
Robert Lowe
Robert Lowe, 1st Viscount Sherbrooke, GCB, PC (4 December 1811 – 27 July 1892), British statesman, was a pivotal conservative spokesman who helped shape British politics in the latter half of the 19th century. He held office under William E ...
, refused to support it. The Conservatives then formed a ministry, in which after long Parliamentary debate Disraeli passed the
Second Reform Act of 1867; Gladstone's proposed bill had been totally outmanoeuvred; he stormed into the Chamber, but too late to see his arch-enemy pass the bill. Gladstone was furious; his animus commenced a long rivalry that would only end on Disraeli's death and Gladstone's encomium in the Commons in 1881.
Leader of the Liberal Party, from 1867
Lord Russell retired in 1867 and Gladstone became leader of the Liberal Party.
[ In 1868 the Irish Church Resolutions was proposed as a measure to reunite the Liberal Party in government (on the issue of disestablishment of the ]Church of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the second ...
—this would be done during Gladstone's First Government in 1869 and meant that Irish Roman Catholics did not need to pay their tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques or more r ...
s to the Anglican Church of Ireland). When it was passed Disraeli took the hint and called a General Election.
First premiership (1868–1874)
In the next general election in 1868, the South Lancashire constituency had been broken up by the Second Reform Act
The Representation of the People Act 1867, 30 & 31 Vict. c. 102 (known as the Reform Act 1867 or the Second Reform Act) was a piece of British legislation that enfranchised part of the urban male working class in England and Wales for the first ...
into two: South East Lancashire and South West Lancashire. Gladstone stood for South West Lancashire and for Greenwich
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross.
Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich ...
, it being quite common then for candidates to stand in two constituencies
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other polity ...
simultaneously.The only means which have been placed in my power of 'raising the wages of colliers' has been by endeavouring to beat down all those restrictions upon trade which tend to reduce the price to be obtained for the product of their labour, & to lower as much as may be the taxes on the commodities which they may require for use or for consumption. Beyond this I look to the forethought not yet so widely diffused in this country as in Scotland, & in some foreign lands; & I need not remind you that in order to facilitate its exercise the Government have been empowered by Legislation to become through the Dept. of the P.O. the receivers & guardians of savings.
Gladstone's first premiership instituted reforms in the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
, civil service, and local government to cut restrictions on individual advancement. The Local Government Board Act 1871
The Local Government Board (LGB) was a British Government supervisory body overseeing local administration in England and Wales from 1871 to 1919.
The LGB was created by the Local Government Board Act 1871 (C. 70) and took over the public health ...
put the supervision of the Poor Law under the Local Government Board (headed by G.J. Goschen) and Gladstone's "administration could claim spectacular success in enforcing a dramatic reduction in supposedly sentimental and unsystematic outdoor poor relief, and in making, in co-operation with the Charity Organization Society
The Charity Organisation Societies were founded in England in 1869 following the ' Goschen Minute' that sought to severely restrict outdoor relief distributed by the Poor Law Guardians. In the early 1870s a handful of local societies were formed w ...
(1869), the most sustained attempt of the century to impose upon the working classes the Victorian values of providence, self-reliance, foresight, and self-discipline". Gladstone was associated with the Charity Organization Society's first annual report in 1870. Some leading Conservatives at this time were contemplating an alliance between the aristocracy and the working class against the capitalist class, an idea called the New Social Alliance. At a speech at Blackheath on 28 October 1871, he warned his constituents against these social reformers:
... they are not your friends, but they are your enemies in fact, though not in intention, who teach you to look to the Legislature for the radical removal of the evils that afflict human life. ... It is the individual mind and conscience, it is the individual character, on which mainly human happiness or misery depends. (Cheers.) The social problems that confront us are many and formidable. Let the Government labour to its utmost, let the Legislature labour days and nights in your service; but, after the very best has been attained and achieved, the question whether the English father is to be the father of a happy family and the centre of a united home is a question which must depend mainly upon himself. (Cheers.) And those who ... promise to the dwellers in towns that every one of them shall have a house and garden in free air, with ample space; those who tell you that there shall be markets for selling at wholesale prices retail quantities—I won't say are impostors, because I have no doubt they are sincere; but I will say they are quacks (cheers); they are deluded and beguiled by a spurious philanthropy, and when they ought to give you substantial, even if they are humble and modest boons, they are endeavouring, perhaps without their own consciousness, to delude you with fanaticism, and offering to you a fruit which, when you attempt to taste it, will prove to be but ashes in your mouths. (Cheers.)
 Gladstone instituted abolition of the
Gladstone instituted abolition of the sale of commissions
The purchase of officer commissions in the British Army was the practice of paying money to the Army to be made an officer of a cavalry or infantry regiment of the English and later British Army. By payment, a commission as an officer could be sec ...
in the army: he also instituted the Cardwell Reforms
The Cardwell Reforms were a series of reforms of the British Army undertaken by Secretary of State for War Edward Cardwell between 1868 and 1874 with the support of Liberal prime minister William Ewart Gladstone. Gladstone paid little attention ...
in 1869 that made peacetime flogging
Flagellation (Latin , 'whip'), flogging or whipping is the act of beating the human body with special implements such as whips, rods, switches, the cat o' nine tails, the sjambok, the knout, etc. Typically, flogging has been imposed on ...
illegal. In 1870, his government passed the Irish Land Act
The Land Acts (officially Land Law (Ireland) Acts) were a series of measures to deal with the question of tenancy contracts and peasant proprietorship of land in Ireland in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Five such acts were introduced by ...
and Forster's Education Act. In 1871 his government passed the Trade Union Act allowing trade unions to organise and operate legally for the first time (although picketing remained illegal). Gladstone later counted this reform as one of the most significant of the previous half century, saying that prior to its passage the law had effectively "compelled the British workman to work...in chains."Universities Tests Act
The Universities Tests Act 1871 was an Act of Parliament, Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It abolished religious "Tests" and allowed Roman Catholics, Nonconformist (Protestantism), non-conformists and non-Christians to take up profe ...
. He secured passage of the Ballot Act for secret ballots, and the Licensing Act 1872
The Licensing Act 1872 (35 & 36 Vict c 94) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is one of the Licensing Acts 1828 to 1886 and was one of the Licensing (Ireland) Acts 1833 to 1886. It enacted various regulations and offences r ...
. In foreign affairs his over-riding aim was to promote peace and understanding, characterised by his settlement of the ''Alabama'' Claims in 1872 in favour of the Americans. During this time, his government gave approval to launch the expedition of HMS Challenger at a time when public interest had turned away from scientific explorations. His leadership also led to the passage of the Supreme Court of Judicature Act 1873
The Supreme Court of Judicature Act 1873 (sometimes known as the Judicature Act 1873) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom in 1873. It reorganised the English court system to establish the High Court and the Court of Appeal, and ...
restructuring the courts to create the modern High Court and Court of Appeal
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much of t ...
.
Gladstone unexpectedly dissolved Parliament in January 1874 and called a general election.
Gladstone's proposals went some way to meet working-class demands, such as the realisation of the free breakfast table through repealing duties on tea and sugar, and reform of local taxation which was increasing for the poorer ratepayers. According to the working-class financial reformer Thomas Briggs, writing in the trade unionist newspaper '' The Bee-Hive'', the manifesto relied on "a much higher authority than Mr. Gladstone...viz., the late Richard Cobden". The dissolution itself was reported in ''The Times'' on 24 January. On 30 January, the names of the first fourteen MPs for uncontested seats were published. By 9 February a Conservative victory was apparent. In contrast to 1868 and 1880 when the Liberal campaign lasted several months, only three weeks separated the news of the dissolution and the election. The working-class newspapers were so taken by surprise they had little time to express an opinion on Gladstone's manifesto before the election was over. Unlike the efforts of the Conservatives, the organisation of the Liberal Party had declined since 1868 and they had also failed to retain Liberal voters on the electoral register. George Howell wrote to Gladstone on 12 February: "There is one lesson to be learned from this Election, that is Organization. ... We have lost not by a change of sentiment so much as by want of organised power". The Liberals received a majority of the vote in each of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom and 189,000 more votes nationally than the Conservatives. However, they obtained a minority of seats in the House of Commons.
Opposition (1874–1880)
 In the wake of
In the wake of Benjamin Disraeli
Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield, (21 December 1804 – 19 April 1881) was a British statesman and Conservative politician who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a central role in the creation o ...
's victory, Gladstone retired from the leadership of the Liberal party, although he retained his seat in the House.
Anti-Catholicism
Gladstone had a complex ambivalence about Catholicism. He was attracted by its international success in majestic traditions. More important, he was strongly opposed to the authoritarianism of its pope and bishops, its profound public opposition to liberalism, and its refusal to distinguish between secular allegiance on the one hand and spiritual obedience on the other. The danger came when the pope or bishops attempted to exert temporal power, as in the Vatican decrees of 1870 as the climax of the papal attempt to control churches in different nations, despite their independent nationalism. On the other hand, when ritual practices in the Church of England—such as vestments and incense—came under attack as too ritualistic and too much akin to Catholicism, Gladstone strongly opposed passage of the Public Worship Regulation Act
The Public Worship Regulation Act 1874 (37 & 38 Vict c 85) was an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom, introduced as a Private Member's Bill by Archbishop of Canterbury Archibald Campbell Tait, to limit what he perceived as the growing ritual ...
in 1874.
In November 1874, he published the pamphlet '' The Vatican Decrees in their Bearing on Civil Allegiance'', directed at the First Vatican Council
The First Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the First Vatican Council or Vatican I was convoked by Pope Pius IX on 29 June 1868, after a period of planning and preparation that began on 6 December 1864. This, the twentieth ecu ...
's dogmatising Papal Infallibility
Papal infallibility is a dogma of the Catholic Church which states that, in virtue of the promise of Jesus to Peter, the Pope when he speaks ''ex cathedra'' is preserved from the possibility of error on doctrine "initially given to the aposto ...
in 1870, which had outraged him. Gladstone claimed that this decree had placed British Catholics in a dilemma over conflicts of loyalty to the Crown. He urged them to reject papal infallibility as they had opposed the Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aris ...
of 1588. The pamphlet sold 150,000 copies by the end of 1874. Cardinal Manning denied that the council had changed the relation of Catholics to their civil governments, and Archbishop James Roosevelt Bayley
James Roosevelt Bayley (August 23, 1814 – October 3, 1877) was an American prelate of the Catholic Church. He served as the first Bishop of Newark (1853–1872) and the eighth Archbishop of Baltimore (1872–1877).
Early life and educat ...
, in a letter which was obtained by the ''New York Herald
The ''New York Herald'' was a large-distribution newspaper based in New York City that existed between 1835 and 1924. At that point it was acquired by its smaller rival the ''New-York Tribune'' to form the '' New York Herald Tribune''.
His ...
'' and published without Bayley's express permission, called Gladstone's declaration "a shameful calumny" and attributed his "monomania" to the "political hari-kari" he had committed by dissolving Parliament, accusing him of "putting on 'the cap and bells
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. Caps typically have a visor, or no brim at all. They are popular in casual and informal se ...
' and attempting to play the part of Lord George Gordon
Lord George Gordon (26 December 1751 – 1 November 1793) was a British politician best known for lending his name to the Gordon Riots of 1780.
An eccentric and flighty personality, he was born into the Scottish nobility and sat in the Hous ...
" in order to restore his political fortunes.John Henry Newman
John Henry Newman (21 February 1801 – 11 August 1890) was an English theologian, academic, intellectual, philosopher, polymath, historian, writer, scholar and poet, first as an Anglican ministry, Anglican priest and later as a Catholi ...
wrote the ''Letter to the Duke of Norfolk
''Letter to the Duke of Norfolk'' is a book written in 1875 by St John Henry Newman. Consisting of about 150 pages, it was meant as a response to Protestant-Catholic polemics that had emerged in the era of the First Vatican Council. In the book, ...
'' in reply to Gladstone's charges that Catholics have "no mental freedom" and cannot be good citizens.
A second pamphlet followed in Feb 1875, a defence of the earlier pamphlet and a reply to his critics, entitled ''Vaticanism: an Answer to Reproofs and Replies''. He described the Catholic Church as "an Asian monarchy: nothing but one giddy height of despotism, and one dead level of religious subservience". He further claimed that the Pope wanted to destroy the rule of law and replace it with arbitrary tyranny, and then to hide these "crimes against liberty beneath a suffocating cloud of incense".

Opposition to socialism
Gladstone was opposed to socialism after 1842, when he heard a socialist lecturer. Lord Kilbracken, one of Gladstone's secretaries commented:
The Liberal doctrines of that time, with their violent anti-socialist spirit and their strong insistence on the gospel of thrift, self-help, settlement of wages by the higgling of the market, and non-interference by the State.... I think that Mr. Gladstone was the strongest anti-socialist that I have ever known....It is quite true, as has been often said, that “we are all socialists up to a certain point”; but Mr. Gladstone fixed that point lower, and was more vehement against those who went above it, than any other politician or official of my acquaintance. I remember his speaking indignantly to me of the budget of 1874 as “That socialistic budget of Northcote's,” merely because of the special relief which it gave to the poorer class of income-tax payers. His strong belief in Free Trade was only one of the results of his deep-rooted conviction that the Government's interference with the free action of the individual, whether by taxation or otherwise, should be kept at an irreducible minimum. It is, indeed, not too much to say that his conception of Liberalism was the negation of Socialism.
Bulgarian Horrors
A pamphlet Gladstone published on 6 September 1876, ''Bulgarian Horrors and the Question of the East'', attacked the Disraeli government for its indifference to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
's violent repression of the Bulgarian April uprising. Gladstone made clear his hostility focused on the Turkish people, rather than on the Muslim religion. The Turks he said:
 The historian
The historian Geoffrey Alderman
Geoffrey Alderman (born 10 February 1944) is a British historian that specialises in 19th and 20th centuries Jewish community in England. He is also a political adviser and journalist.
Life
Born in Middlesex, Alderman was educated at Hackney D ...
has described Gladstone as "unleashing the full fury of his oratorical powers against Jews and Jewish influence" during the Bulgarian Crisis (1885–88) Bulgarian Crisis may refer to:
*Bulgarian Crisis (1885–88)
*Bulgarian Declaration of Independence (1908)
*Negotiations of Bulgaria with the Central Powers and the Entente (1915)
*Incident at Petrich (1925)
*Bulgarian financial crisis of 1996–97 ...
, telling a journalist in 1876 that: "I deeply deplore the manner in which, what I may call Judaic sympathies, beyond as well as within the circle of professed Judaism, are now acting on the question of the East".[Alderman, Geoffrey. ''Modern British Jewry''. Oxford: Clarendon, 1992, p. 100] Gladstone similarly refused to speak out against the persecution of Romanian Jews in the 1870s and Russian Jews in the early 1880s.Jewish Chronicle
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
'' attacked Gladstone in 1888, arguing that "Are we, because there was once a Liberal Party, to bow down and worship Gladstone—the great Minister who was too Christian in his charity, too Russian in his proclivities, to raise voice or finger" to defend Russian Jews
The history of the Jews in Russia and areas historically connected with it goes back at least 1,500 years. Jews in Russia have historically constituted a large religious and ethnic diaspora; the Russian Empire at one time hosted the largest pop ...
... Alderman attributes these developments, along with other factors, to the collapse of the previously strong ties between British Jews and Liberalism.Midlothian campaign
The Midlothian campaign of 1878–80 was a series of foreign policy speeches given by William Gladstone, leader of Britain's Liberal Party. It is often cited as the first modern political campaign. It also set the stage for Gladstone's comeback ...
, he rousingly denounced Disraeli's foreign policies during the ongoing Second Anglo-Afghan War
The Second Anglo-Afghan War (Dari: جنگ دوم افغان و انگلیس, ps, د افغان-انګرېز دويمه جګړه) was a military conflict fought between the British Raj and the Emirate of Afghanistan from 1878 to 1880, when the l ...
in Afghanistan. (See Great Game
The Great Game is the name for a set of political, diplomatic and military confrontations that occurred through most of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century – involving the rivalry of the British Empire and the Russian Empi ...
). He saw the war as "great dishonour" and also criticised British conduct in the Zulu War
The Anglo-Zulu War was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Following the passing of the British North America Act of 1867 forming a federation in Canada, Lord Carnarvon thought that a similar political effort, coup ...
. Gladstone also (on 29 November) condemned what he saw as the Conservative government's profligate spending:
...the Chancellor of the Exchequer shall boldly uphold economy in detail; and it is the mark ... of ... a chicken-hearted Chancellor of the Exchequer, when he shrinks from upholding economy in detail, when, because it is a question of only £2,000 or £3,000, he says that is no matter. He is ridiculed, no doubt, for what is called saving candle-ends and cheese-parings. No Chancellor of the Exchequer is worth his salt who is not ready to save what are meant by candle-ends and cheese-parings in the cause of his country. No Chancellor of the Exchequer is worth his salt who makes his own popularity either his first consideration, or any consideration at all, in administrating the public purse. You would not like to have a housekeeper or steward who made her or his popularity with the tradesmen the measure of the payments that were to be delivered to them. In my opinion the Chancellor of the Exchequer is the trusted and confidential steward of the public. He is under a sacred obligation with regard to all that he consents to spend.... I am bound to say hardly ever in the six years that Sir Stafford Northcote has been in office have I heard him speak a resolute word on behalf of economy.
Second premiership (1880–1885)
 In 1880, the Liberals won again and the Liberal leaders,
In 1880, the Liberals won again and the Liberal leaders, Lord Hartington
Spencer Compton Cavendish, 8th Duke of Devonshire, (23 July 183324 March 1908), styled Lord Cavendish of Keighley between 1834 and 1858 and Marquess of Hartington between 1858 and 1891, was a British statesman. He has the distinction of having ...
(leader in the House of Commons) and Lord Granville, retired in Gladstone's favour. Gladstone won his constituency election in Midlothian (UK Parliament constituency) (1708–1918), Midlothian and also in Leeds (UK Parliament constituency), Leeds, where he had also been adopted as a candidate. As he could lawfully only serve as MP for one constituency, Leeds was passed to his son Herbert Gladstone, Herbert. One of his other sons, William Henry Gladstone, Henry, was also elected as an MP. Queen Victoria asked Lord Hartington to form a ministry, but he persuaded her to send for Gladstone. Gladstone's second administration—both as Prime Minister and again as Chancellor of the Exchequer until 1882—lasted from June 1880 to June 1885. He originally intended to retire at the end of 1882, the 50th anniversary of his entry into politics, but did not do so.
Foreign policy
Historians have debated the wisdom of Gladstone's foreign-policy during his second ministry. Paul Hayes says it "provides one of the most intriguing and perplexing tales of muddle and incompetence in foreign affairs, unsurpassed in modern political history until the days of Edward Grey, 1st Viscount Grey of Fallodon, Grey and, later, Neville Chamberlain." Gladstone opposed himself to the "colonialism, colonial lobby" pushing for the scramble for Africa. His term saw the end of the Second Anglo-Afghan War, the First Boer War, and the Mahdist War, war against the Muhammad Ahmad, Mahdi in Sudan.
On 11 July 1882, Gladstone ordered the bombardment of Alexandria, starting the 1882 Anglo-Egyptian War, short, Anglo-Egyptian War of 1882. The British won decisively, and although they repeatedly promised to depart in a few years, the actual result was British control of Egypt for four decades, largely ignoring Ottoman nominal ownership. France was seriously unhappy, having lost control of the canal that it built and financed and had dreamed of for decades. Gladstone's role in the decision to invade was described as relatively hands-off, and the ultimate responsibility was borne by certain members of his cabinet such as Lord Hartington, Secretary of State for India, Thomas Baring, 1st Earl of Northbrook, First Lord of the Admiralty, Hugh Childers, Secretary of State for War, and Granville Leveson-Gower, 2nd Earl Granville, the Foreign Secretary.
Historian A.J.P. Taylor says that the seizure of Egypt "was a great event; indeed, the only real event in international relations between the Battle of Sedan and the defeat of Russia in the Russo-Japanese war."
Taylor emphasizes long-term impact:
Gladstone and the Liberals had a reputation for strong opposition to imperialism, so historians have long debated the explanation for this reversal of policy. The most influential was a study by John Robinson and Ronald Gallagher, ''Africa and the Victorians'' (1961) which focused on The Imperialism of Free Trade and was promoted by the Cambridge School of historiography. They argue there was no long-term Liberal plan in support of imperialism. Instead they saw the urgent necessity to act to protect the Suez Canal in the face of what appeared to be a radical collapse of law and order, and a nationalist revolt focused on expelling the Europeans, regardless of the damage it would do to international trade and the British Empire. Gladstone's decision came against strained relations with France, and maneuvering by "men on the spot" in Egypt. Critics such as Cain and Hopkins have stressed the need to protect large sums invested by British financiers and Egyptian bonds, while downplaying the risk to the viability of the Suez Canal. Unlike the Marxists, they stress "gentlemanly" financial and commercial interests, not the industrial capitalism that Marxists believe was always central. More recently, specialists on Egypt have been interested primarily in the internal dynamics among Egyptians that produce the failed Urabi Revolt.
Ireland
In 1881 he established the Irish Coercion Act, which permitted the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland to detain people for as "long as was thought necessary", as there was rural disturbance in Ireland between landlords and tenants as Lord Frederick Cavendish, Cavendish, the Irish Secretary, had been Phoenix Park Murders, assassinated by Irish rebels in Dublin. He also passed the Second Land Act (the Landlord and Tenant (Ireland) Act 1870, First, in 1870, had entitled Irish tenants, if evicted, to compensation for improvements which they had made on their property, but had little effect) which gave Irish tenants the "3Fs"—fair rent, fixity of tenure and free sale. He was elected a List of Fellows of the Royal Society elected in 1881, Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS) in 1881.
Franchise
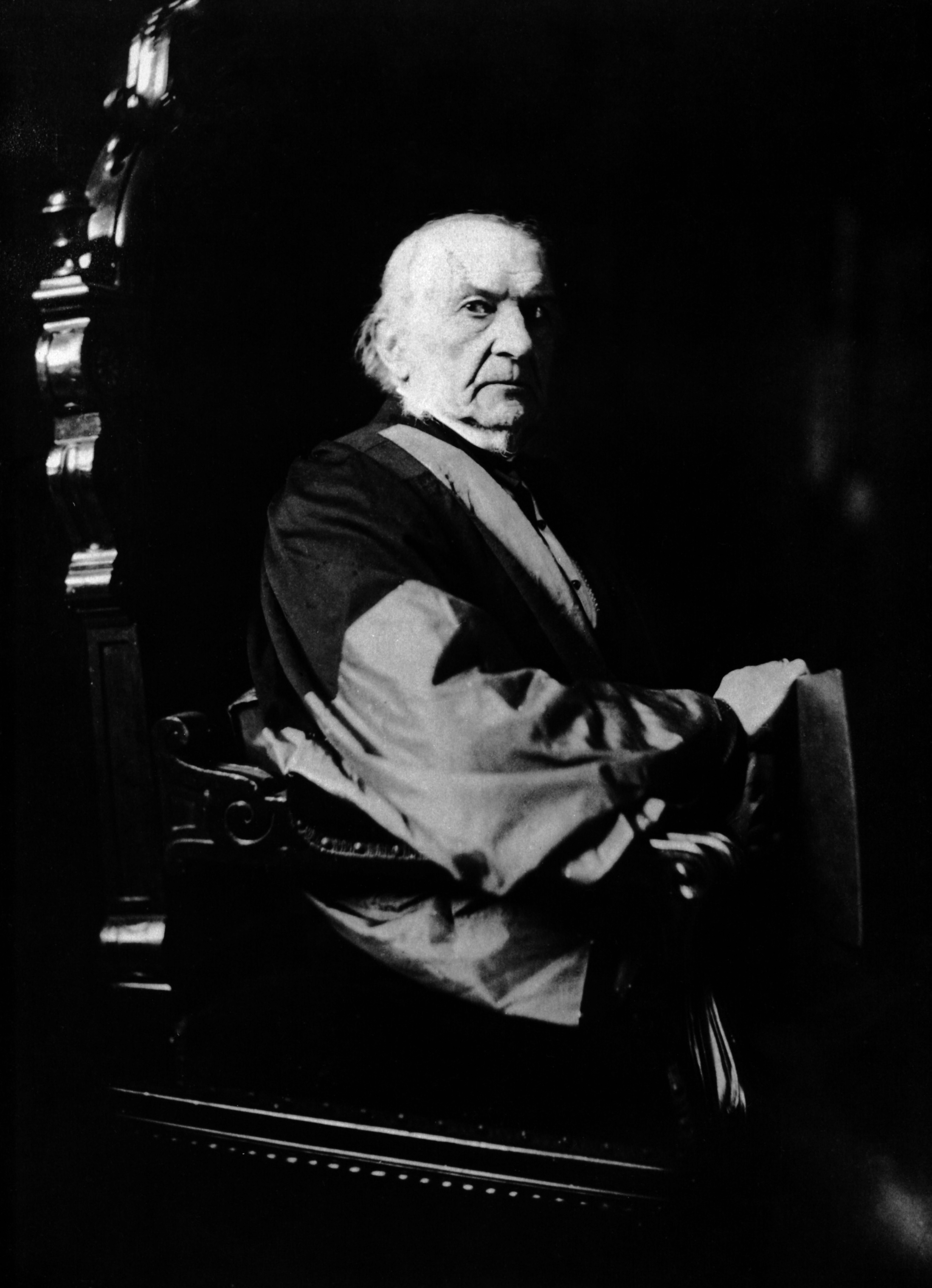 Gladstone extended the vote to agricultural labourers and others in the Representation of the People Act 1884, 1884 Reform Act, which gave the counties the same franchise as the boroughs—adult male householders and £10 lodgers—and added six million to the total number of people who could vote in parliamentary elections. Parliamentary reform continued with the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885.
Gladstone was increasingly uneasy about the direction in which British politics was moving. In a letter to John Dalberg-Acton, 1st Baron Acton, Lord Acton on 11 February 1885, Gladstone criticised Tory Democracy as "demagogism" that "put down pacific, law-respecting, economic elements that ennobled the old Conservatism" but "still, in secret, as obstinately attached as ever to the evil principle of class interests". He found contemporary Liberalism better, "but far from being good". Gladstone claimed that this Liberalism's "pet idea is what they call construction,—that is to say, taking into the hands of the state the business of the individual man". Both Tory Democracy and this new Liberalism, Gladstone wrote, had done "much to estrange me, and had for many, many years".
Gladstone extended the vote to agricultural labourers and others in the Representation of the People Act 1884, 1884 Reform Act, which gave the counties the same franchise as the boroughs—adult male householders and £10 lodgers—and added six million to the total number of people who could vote in parliamentary elections. Parliamentary reform continued with the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885.
Gladstone was increasingly uneasy about the direction in which British politics was moving. In a letter to John Dalberg-Acton, 1st Baron Acton, Lord Acton on 11 February 1885, Gladstone criticised Tory Democracy as "demagogism" that "put down pacific, law-respecting, economic elements that ennobled the old Conservatism" but "still, in secret, as obstinately attached as ever to the evil principle of class interests". He found contemporary Liberalism better, "but far from being good". Gladstone claimed that this Liberalism's "pet idea is what they call construction,—that is to say, taking into the hands of the state the business of the individual man". Both Tory Democracy and this new Liberalism, Gladstone wrote, had done "much to estrange me, and had for many, many years".
Failure
Historian Sneh Mahajan has concluded, "Gladstone's second ministry remained barren of any achievement in the domestic sphere." His downfall came in Africa, where he delayed the mission to rescue Charles George Gordon, General Gordon's force which had been Siege of Khartoum, under siege in Khartoum for 10 months. It arrived in January 1885 two days after a massacre killed approximately 7,000 British and Egyptian soldiers and 4,000 civilians. The disaster proved a major blow to Gladstone's popularity. Queen Victoria sent him a telegram of rebuke which found its way into the press. Critics said Gladstone had neglected military affairs and had not acted promptly enough to save the besieged Gordon. Critics inverted his acronym, "G.O.M." (for "Grand Old Man"), to "M.O.G." (for "Murderer of Gordon"). He resigned as Prime Minister in June 1885 and declined Queen Victoria's offer of an earldom.
Third premiership (1886)
 The Hawarden Kite was a December 1885 press release by Gladstone's son and aide Herbert Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, Herbert Gladstone announcing that he had become convinced that Ireland needed a separate parliament. The bombshell announcement resulted in the fall of Lord Salisbury's Conservative government. Irish Nationalists, led by Charles Stewart Parnell, Charles Parnell's Irish Parliamentary Party, held the balance of power in Parliament. Gladstone's conversion to Home Rule convinced them to switch away from the Conservatives and support the Liberals using the 86 seats in Parliament they controlled. The main purpose of this administration was to deliver Ireland a reform which would give it a devolved assembly, similar to those which would be eventually put in place in Scotland and Wales in 1999. In 1886 Gladstone's party allied with Irish Nationalists to defeat Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury, Lord Salisbury's government. Gladstone regained his position as Prime Minister and combined the office with that of Lord Privy Seal. During this administration he first introduced his Home Rule Bill for Ireland. The issue split the Liberal Party (a breakaway group went on to create the Liberal Unionist party) and the bill was thrown out on the second reading, ending his government after only a few months and inaugurating another headed by Lord Salisbury.
Gladstone, says his biographer, "totally rejected the widespread English view that the Irish had no taste for justice, common sense, moderation or national prosperity and looked only to perpetual strife and dissension". The problem for Gladstone was that his rural English supporters would not support home rule for Ireland. A large faction of Liberals, led by Joseph Chamberlain, formed a Unionist faction that supported the Conservative party. Whenever the Liberals were out of power, home rule proposals languished.
The Hawarden Kite was a December 1885 press release by Gladstone's son and aide Herbert Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, Herbert Gladstone announcing that he had become convinced that Ireland needed a separate parliament. The bombshell announcement resulted in the fall of Lord Salisbury's Conservative government. Irish Nationalists, led by Charles Stewart Parnell, Charles Parnell's Irish Parliamentary Party, held the balance of power in Parliament. Gladstone's conversion to Home Rule convinced them to switch away from the Conservatives and support the Liberals using the 86 seats in Parliament they controlled. The main purpose of this administration was to deliver Ireland a reform which would give it a devolved assembly, similar to those which would be eventually put in place in Scotland and Wales in 1999. In 1886 Gladstone's party allied with Irish Nationalists to defeat Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury, Lord Salisbury's government. Gladstone regained his position as Prime Minister and combined the office with that of Lord Privy Seal. During this administration he first introduced his Home Rule Bill for Ireland. The issue split the Liberal Party (a breakaway group went on to create the Liberal Unionist party) and the bill was thrown out on the second reading, ending his government after only a few months and inaugurating another headed by Lord Salisbury.
Gladstone, says his biographer, "totally rejected the widespread English view that the Irish had no taste for justice, common sense, moderation or national prosperity and looked only to perpetual strife and dissension". The problem for Gladstone was that his rural English supporters would not support home rule for Ireland. A large faction of Liberals, led by Joseph Chamberlain, formed a Unionist faction that supported the Conservative party. Whenever the Liberals were out of power, home rule proposals languished.
Opposition (1886–1892)
 Gladstone supported the London dockers in their London Dock Strike of 1889, strike of 1889. After their victory he gave a speech at Hawarden on 23 September in which he said: "In the common interests of humanity, this remarkable strike and the results of this strike, which have tended somewhat to strengthen the condition of labour in the face of capital, is the record of what we ought to regard as satisfactory, as a real social advance [that] tends to a fair principle of division of the fruits of industry".
Gladstone supported the London dockers in their London Dock Strike of 1889, strike of 1889. After their victory he gave a speech at Hawarden on 23 September in which he said: "In the common interests of humanity, this remarkable strike and the results of this strike, which have tended somewhat to strengthen the condition of labour in the face of capital, is the record of what we ought to regard as satisfactory, as a real social advance [that] tends to a fair principle of division of the fruits of industry".[Michael Barker, ''Gladstone and Radicalism. The Reconstruction of Liberal Policy in Britain. 1885–1894'' (The Harvester Press, 1975), p. 92.] This speech has been described by Eugenio Biagini as having "no parallel in the rest of Europe except in the rhetoric of the toughest socialist leaders". Visitors at Hawarden in October were "shocked...by some rather wild language on the Dock labourers question"....come generally...to the conclusion that there is something painful in the condition of the rural labourer in this great respect, that it is hard even for the industrious and sober man, under ordinary conditions, to secure a provision for his own old age. Very large propositions, involving, some of them, very novel and very wide principles, have been submitted to the public, for the purpose of securing such a provision by means independent of the labourer himself....our duty [is] to develop in the first instance, every means that we may possibly devise whereby, if possible, the labourer may be able to make this provision for himself, or to approximate towards making such provision far more efficaciously and much more closely than he can now do.
Gladstone wrote on 16 July 1892 in ''autobiographica'' that "In 1834 the Government...did themselves high honour by the new Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, Poor Law Act, which rescued the English peasantry from the total loss of their independence". There were many who disagreed with him.
Gladstone wrote to Herbert Spencer, who contributed the introduction to a collection of anti-socialist essays (''A Plea for Liberty'', 1891), that "I ask to make reserves, and of one passage, which will be easily guessed, I am unable even to perceive the relevancy. But speaking generally, I have read this masterly argument with warm admiration and with the earnest hope that it may attract all the attention which it so well deserves".[David Duncan, ''The Life and Letters of Herbert Spencer'' (Methuen, 1908), p. 302.] The passage Gladstone alluded to was one where Spencer had spoken of "the behaviour of the so-called Liberal party".
Fourth premiership (1892–1894)
 The 1892 United Kingdom general election, general election of 1892 resulted in a minority Liberal government with Gladstone as Prime Minister. The electoral address had promised Irish Home Rule and the disestablishment of the Scottish and Welsh Churches. In February 1893 he introduced the Irish Government Bill 1893, Second Home Rule Bill, which was passed in the Commons at second reading on 21 April by 43 votes and third reading on 1 September by 34 votes. The House of Lords defeated the bill by voting against by 419 votes to 41 on 8 September.
The Elementary Education (Blind and Deaf Children) Act, passed in 1893, required local authorities to provide separate education for blind and deaf children.
Conservative MP Colonel Howard Vincent questioned Gladstone in the Commons on what his government would do about unemployment on 1 September 1893. Gladstone replied:
The 1892 United Kingdom general election, general election of 1892 resulted in a minority Liberal government with Gladstone as Prime Minister. The electoral address had promised Irish Home Rule and the disestablishment of the Scottish and Welsh Churches. In February 1893 he introduced the Irish Government Bill 1893, Second Home Rule Bill, which was passed in the Commons at second reading on 21 April by 43 votes and third reading on 1 September by 34 votes. The House of Lords defeated the bill by voting against by 419 votes to 41 on 8 September.
The Elementary Education (Blind and Deaf Children) Act, passed in 1893, required local authorities to provide separate education for blind and deaf children.
Conservative MP Colonel Howard Vincent questioned Gladstone in the Commons on what his government would do about unemployment on 1 September 1893. Gladstone replied: I cannot help regretting that the honourable and gallant Gentleman has felt it his duty to put the question. It is put under circumstances that naturally belong to one of those fluctuations in the condition of trade which, however unfortunate and lamentable they may be, recur from time to time. Undoubtedly I think that questions of this kind, whatever be the intention of the questioner, have a tendency to produce in the minds of people, or to suggest to the people, that these fluctuations can be corrected by the action of the Executive Government. Anything that contributes to such an impression inflicts an injury upon the labouring population.
In December 1893, an Opposition motion proposed by Lord George Hamilton called for an expansion of the Royal Navy. Gladstone opposed increasing public expenditure on the naval estimates, in the tradition of free trade liberalism of his earlier political career as Chancellor. All his Cabinet colleagues believed in some expansion of the navy. He declared in the Commons on 19 December that naval rearmament would commit the government to expenditure over a number of years and would subvert "the principle of annual account, annual proposition, annual approval by the House of Commons, which...is the only way of maintaining regularity, and that regularity is the only talisman which will secure Parliamentary control". In January 1894, Gladstone wrote that he would not "break to pieces the continuous action of my political life, nor trample on the tradition received from every colleague who has ever been my teacher" by supporting naval rearmament. Gladstone also opposed Chancellor Sir William Vernon Harcourt (politician), William Harcourt's proposal to implement a graduated death duty. In a fragment of autobiography dated 25 July 1894, Gladstone denounced the tax as
...by far the most Radical measure of my lifetime. I do not object to the principle of graduated taxation: for the just principle of ability to pay is not determined simply by the amount of income.... But, so far as I understand the present measure of finance from the partial reports I have received, I find it too violent. It involves a great departure from the methods of political action established in this country, where reforms, and especially financial reforms, have always been considerate and even tender.... I do not yet see the ground on which it can be justly held that any one description of ''property'' should be more heavily burdened than others, unless moral and social grounds can be shown first: but in this case the reasons drawn from those sources seem rather to verge in the opposite direction, for real property has more of presumptive connection with the discharge of duty than that which is ranked as personal...the aspect of the measure is not satisfactory to a man of my traditions (and these traditions lie near the roots of my being).... For the sudden introduction of such change there is I think no precedent in the history of this country. And the severity of the blow is greatly aggravated in moral effect by the fact that it is dealt only to a handful of individuals.
Gladstone had his last audience with Queen Victoria on 28 February 1894 and chaired his last Cabinet on 1 March—the last of 556 he had chaired. On that day he gave his last speech to the House of Commons, saying that the government would withdraw opposition to the Lords' amendments to the Local Government Bill "under protest" and that it was "a controversy which, when once raised, must go forward to an issue". He resigned from the premiership on 2 March. The Queen did not ask Gladstone who should succeed him, but sent for Archibald Primrose, 5th Earl of Rosebery, Lord Rosebery (Gladstone would have advised on John Spencer, 5th Earl Spencer, Lord Spencer). He retained his seat in the House of Commons until 1895. He was not offered a peerage, having earlier declined an earldom.
Gladstone is both the oldest person to form a government—aged 82 at his appointment—and the oldest person to occupy the Premiership—being 84 at his resignation.
Final years (1894–1898)
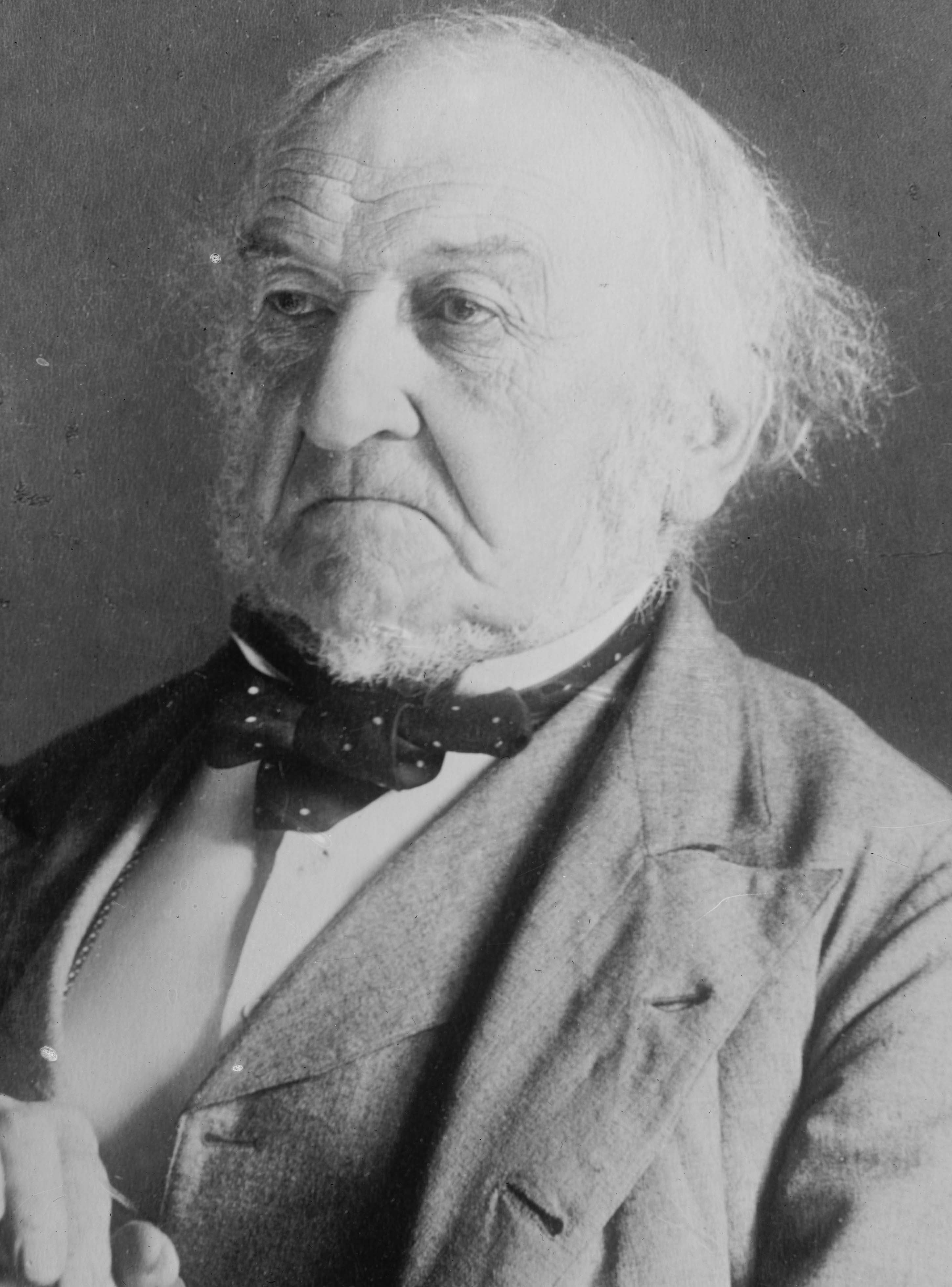 In 1895, at the age of 85, Gladstone bequeathed Pound sterling, £40,000 (equivalent to approximately £ today) and much of his 32,000 volume library to found St Deiniol's Library in
In 1895, at the age of 85, Gladstone bequeathed Pound sterling, £40,000 (equivalent to approximately £ today) and much of his 32,000 volume library to found St Deiniol's Library in Hawarden
Hawarden (; cy, Penarlâg) is a village, community (Wales), community and Wards and electoral divisions of the United Kingdom, electoral ward in Flintshire, Wales. It is part of the Deeside conurbation on the Wales-England border and is home ...
, Wales. It had begun with just 5,000 items at his father's home Fasque, which were transferred to Hawarden for research in 1851.
On 8 January 1896, in conversation with L.A. Tollemache, Gladstone explained that: "I am not so much afraid of Democracy or of Science as of the love of money. This seems to me to be a growing evil. Also, there is a danger from the growth of that dreadful military spirit". On 13 January, Gladstone claimed he had strong Conservative instincts and that "In all matters of custom and tradition, even the Tories look upon me as the chief Conservative that is". On 15 January Gladstone wrote to James Bryce, 1st Viscount Bryce, James Bryce, describing himself as "a dead man, one fundamentally a Peel–Cobden man". In 1896, in his last noteworthy speech, he denounced Hamidian massacres, Armenian massacres by Ottomans in a talk delivered at Liverpool. On 2 January 1897, Gladstone wrote to Francis Hirst on being unable to draft a preface to a book on liberalism: "I venture on assuring you that I regard the design formed by you and your friends with sincere interest, and in particular wish well to all the efforts you may make on behalf of individual freedom and independence as opposed to what is termed Collectivism".
In the early months of 1897, Gladstone and his wife stayed in Cannes. Gladstone met Queen Victoria, and she shook hands with him for (to his recollection) the first time in the 50 years he had known her. One of the Gladstones' neighbours observed that "He and his devoted wife never missed the morning service on Sunday ... One Sunday, returning from the altar rail, the old, partially blind man stumbled at the chancel step. One of the clergy sprang involuntarily to his assistance, but retreated with haste, so withering was the fire which flashed from those failing eyes." The Gladstones returned to Hawarden Castle at the end of March and he received the Colonial Premiers in their visit for the Diamond Jubilee of Queen Victoria, Queen's Jubilee. At a dinner in November with Edward Hamilton, his former private secretary, Hamilton noted that "What is now uppermost in his mind is what he calls the spirit of jingoism under the name of Imperialism which is now so prevalent". Gladstone riposted "It was enough to make Peel and Cobden turn in their graves".
On the advice of his doctor Samuel Habershon in the aftermath of an attack of facial neuralgia, Gladstone stayed at Cannes from the end of November 1897 to mid-February 1898. He gave an interview for ''The Daily Telegraph''. Gladstone then travelled to Bournemouth, where a swelling on his palate was diagnosed as cancer by the leading cancer surgeon Sir Thomas Smith on 18 March. On 22 March, he retired to Hawarden Castle. Despite being in pain he received visitors and quoted hymns, especially John Henry Newman, Cardinal Newman's "The Dream of Gerontius (poem), Praise to the Holiest in the Height".
 His last public statement was dictated to his daughter Helen in reply to receiving the Vice-Chancellor of the University of Oxford's "sorrow and affection": "There is no expression of Christian sympathy that I value more than that of the ancient University of Oxford, the God-fearing and God-sustaining University of Oxford. I served her perhaps mistakenly, but to the best of my ability. My most earnest prayers are hers to the uttermost and to the last". He left the house for the last time on 9 April. After 18 April he did not come down to the ground floor but still came out of bed to lie on the sofa. The Bishop of St Andrews, Dunkeld and Dunblane George Wilkinson (bishop), George Wilkinson recorded when he ministered to him along with Stephen Gladstone:
His last public statement was dictated to his daughter Helen in reply to receiving the Vice-Chancellor of the University of Oxford's "sorrow and affection": "There is no expression of Christian sympathy that I value more than that of the ancient University of Oxford, the God-fearing and God-sustaining University of Oxford. I served her perhaps mistakenly, but to the best of my ability. My most earnest prayers are hers to the uttermost and to the last". He left the house for the last time on 9 April. After 18 April he did not come down to the ground floor but still came out of bed to lie on the sofa. The Bishop of St Andrews, Dunkeld and Dunblane George Wilkinson (bishop), George Wilkinson recorded when he ministered to him along with Stephen Gladstone: Shall I ever forget the last Friday in Passion Week, when I gave him the last Holy Communion that I was allowed to administer to him? It was early in the morning. He was obliged to be in bed, and he was ordered to remain there, but the time had come for the confession of sin and the receiving of absolution. Out of his bed he came. Alone he knelt in the presence of his God till the absolution has been spoken, and the sacred elements received.
 Gladstone died on 19 May 1898 at Hawarden Castle, Hawarden, aged 88. He had been cared for by his daughter Helen Gladstone, Helen who had resigned her job to care for her father and mother. The cause of death is officially recorded as "Syncope, Senility". "Syncope" meant failure of the heart and "senility" in the 19th century was an infirmity of advanced old age, rather than a loss of mental faculties. The House of Commons adjourned on the afternoon of Gladstone's death, with A.J. Balfour giving notice for an Address to the Queen praying for a public funeral and a public memorial in Westminster Abbey. The day after, both Houses of Parliament approved the Address and Herbert Gladstone accepted a public funeral on behalf of the Gladstone family. His coffin was transported on the London Underground before his State funerals in the United Kingdom, state funeral at Westminster Abbey, at which the Prince of Wales (the future King Edward VII) and the Duke of York (the future King George V) acted as pallbearers. His wife, Catherine Gladstone (''née'' Glynne), died two years later on 14 June 1900 and was buried next to him.
Gladstone died on 19 May 1898 at Hawarden Castle, Hawarden, aged 88. He had been cared for by his daughter Helen Gladstone, Helen who had resigned her job to care for her father and mother. The cause of death is officially recorded as "Syncope, Senility". "Syncope" meant failure of the heart and "senility" in the 19th century was an infirmity of advanced old age, rather than a loss of mental faculties. The House of Commons adjourned on the afternoon of Gladstone's death, with A.J. Balfour giving notice for an Address to the Queen praying for a public funeral and a public memorial in Westminster Abbey. The day after, both Houses of Parliament approved the Address and Herbert Gladstone accepted a public funeral on behalf of the Gladstone family. His coffin was transported on the London Underground before his State funerals in the United Kingdom, state funeral at Westminster Abbey, at which the Prince of Wales (the future King Edward VII) and the Duke of York (the future King George V) acted as pallbearers. His wife, Catherine Gladstone (''née'' Glynne), died two years later on 14 June 1900 and was buried next to him.
Religion
Gladstone's intensely religious mother was an evangelical of Scottish Episcopal Church, Scottish Episcopal origins, and his father joined the Church of England, having been a Church of Scotland, Presbyterian when he first settled in Liverpool. As a boy William was baptised into the Church of England. He rejected a call to enter the ministry, and on this his conscience always tormented him. In compensation he aligned his politics with the evangelical faith in which he fervently believed. In 1838 Gladstone nearly ruined his career when he tried to force a religious mission upon the Conservative Party. His book ''The State in its Relations with the Church'' argued that England had neglected its great duty to the Church of England. He announced that since that church possessed a monopoly of religious truth, nonconformists and Roman Catholics ought to be excluded from all government positions. The historian Thomas Babington Macaulay, 1st Baron Macaulay, Thomas Babington Macaulay and other critics ridiculed his arguments and refuted them. Robert Peel, Sir Robert Peel, Gladstone's chief, was outraged because this would upset the delicate political issue of Catholic Emancipation and anger the Nonconformists. Since Peel greatly admired his protégé, he redirected his focus from theology to finance.
Gladstone altered his approach to religious problems, which always held first place in his mind. Before entering Parliament he had already substituted a high church Anglican attitude, with its dependence on authority and tradition, for the evangelical outlook of his boyhood, with its reliance upon the direct inspiration of the Bible. In middle life he decided that the individual conscience would have to replace authority as the inner citadel of the Church. That view of the individual conscience affected his political outlook and changed him gradually from a Conservative into a Liberal.
Marriage and family
 Gladstone's early attempts to find a wife proved unsuccessful, having been rejected in 1835 by Caroline Eliza Farquhar (daughter of Sir Thomas Harvie Farquhar, 2nd Baronet) and again in 1837 by Lady Frances Harriet Douglas (daughter of George Douglas, 17th Earl of Morton).
The following year, having met her in 1834 at the London home of Old Etonian friend and then fellow-Conservative MP James Milnes Gaskell,
Gladstone's early attempts to find a wife proved unsuccessful, having been rejected in 1835 by Caroline Eliza Farquhar (daughter of Sir Thomas Harvie Farquhar, 2nd Baronet) and again in 1837 by Lady Frances Harriet Douglas (daughter of George Douglas, 17th Earl of Morton).
The following year, having met her in 1834 at the London home of Old Etonian friend and then fellow-Conservative MP James Milnes Gaskell,
Descendants
 Two of Gladstone's sons and a grandson, William Glynne Charles Gladstone, followed him into parliament, making for four generations of MPs in total. One of his collateral descendants, George Freeman (politician), George Freeman, has been the Conservative Member of Parliament for Mid Norfolk since 2010.
Two of Gladstone's sons and a grandson, William Glynne Charles Gladstone, followed him into parliament, making for four generations of MPs in total. One of his collateral descendants, George Freeman (politician), George Freeman, has been the Conservative Member of Parliament for Mid Norfolk since 2010.
Legacy
The historian H. C. G. Matthew states that Gladstone's chief legacy lay in three areas: his financial policy, his support for Home Rule (devolution) that modified the view of the unitary state of the United Kingdom and his idea of a progressive, reforming party broadly based and capable of accommodating and conciliating varying interests, along with his speeches at mass public meetings.
Historian Walter L. Arnstein concludes:
Lord Acton wrote in 1880 that he considered Gladstone one "of the three greatest Liberals" (along with Edmund Burke and Lord Macaulay).
In 1909 the Liberal Chancellor David Lloyd George introduced his "People's Budget", the first budget which aimed to redistribute wealth. The Liberal statesman Archibald Primrose, 5th Earl of Rosebery, Lord Rosebery ridiculed it by asserting Gladstone would reject it, "Because in his eyes, and in my eyes, too as his humble disciple, Liberalism and Liberty were cognate terms; they were twin-sisters."
Lloyd George had written in 1913 that the Liberals were "carving the last few columns out of the Gladstonian quarry".[Chris Wrigley, "‘Carving the Last Few Columns out of the Gladstonian Quarry’: The Liberal Leaders and the Mantle of Gladstone, 1898–1929", in David Bebbington and Roger Swift (eds), ''Gladstone Centenary Essays'' (Liverpool University Press, 2000), p. 247.]
Lloyd George said of Gladstone in 1915: "What a man he was! Head and shoulders above anyone else I have ever seen in the House of Commons. I did not like him much. He hated Nonconformists and Welsh Nonconformists in particular and he had no real sympathy with the working classes. But he was far and away the best Parliamentary speaker I have ever heard. He was not so good in exposition."
Rivalry with Disraeli
Historical writers have often played Disraeli and Gladstone against each other as great rivals. Roland Quinault, however, cautions us not to exaggerate the confrontation:
Monuments and archives
Archives
* Thomas Edison's European agent, Colonel Gouraud, recorded Gladstone's voice several times on phonograph. The accent on one of the recordings is North Welsh.
* The National Library of Wales holds many pamphlets that were sent to Gladstone during his political career. These pamphlets show the concerns of people from all strands of society and together form a historical resource of the social and economical conditions of mid to late nineteenth century Britain. Many of the pamphlets bear the handwriting of Gladstone, which provides direct evidence of Gladstone's interest in various topics.
Statues
 * A statue of Gladstone by Albert Bruce-Joy and erected in 1882, stands near the front gate of Bow Church, St. Marys Church in Bow, London, Bow, London. Paid for by the industrialist Theodore Bryant, it is viewed as a symbol of the later London matchgirls strike of 1888, 1888 match girls strike, which took place at the nearby Bow Quarter, Bryant & May Match Factory. Led by the socialist Annie Besant, hundreds of women working in the factory, where many sickened and died from poisoning from the white phosphorus used in the matches, went on strike to demand improved working conditions and pay, eventually winning their cause. In recent years, the statue of Gladstone has been repeatedly daubed with red paint, suggesting that it was paid for with the "blood of the match girls".
* A statue of Gladstone in bronze by Sir Thomas Brock, erected in 1904, stands in St John's Gardens, Liverpool, St John's Gardens, Liverpool.
* The Gladstone Memorial, London, Gladstone Memorial erected in 1905 stands at Aldwych, London, near the Royal Courts of Justice.
* A Grade II listed statue of Gladstone stands in Albert Square, Manchester, Albert Square, Manchester.
* A statue of Gladstone by Albert Bruce-Joy and erected in 1882, stands near the front gate of Bow Church, St. Marys Church in Bow, London, Bow, London. Paid for by the industrialist Theodore Bryant, it is viewed as a symbol of the later London matchgirls strike of 1888, 1888 match girls strike, which took place at the nearby Bow Quarter, Bryant & May Match Factory. Led by the socialist Annie Besant, hundreds of women working in the factory, where many sickened and died from poisoning from the white phosphorus used in the matches, went on strike to demand improved working conditions and pay, eventually winning their cause. In recent years, the statue of Gladstone has been repeatedly daubed with red paint, suggesting that it was paid for with the "blood of the match girls".
* A statue of Gladstone in bronze by Sir Thomas Brock, erected in 1904, stands in St John's Gardens, Liverpool, St John's Gardens, Liverpool.
* The Gladstone Memorial, London, Gladstone Memorial erected in 1905 stands at Aldwych, London, near the Royal Courts of Justice.
* A Grade II listed statue of Gladstone stands in Albert Square, Manchester, Albert Square, Manchester.Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
in 1917 (and moved to its present location in 1955). It stands in Atholl Crescent Gardens.Hawarden
Hawarden (; cy, Penarlâg) is a village, community (Wales), community and Wards and electoral divisions of the United Kingdom, electoral ward in Flintshire, Wales. It is part of the Deeside conurbation on the Wales-England border and is home ...
in the town of Mancot, there is a small hospital named after Catherine Gladstone. A statue of Gladstone stands prominently in the front grounds of the eponymous Gladstone's Library (formerly known as St. Deiniol's), near the commencement of Gladstone Way at Hawarden.
* A statue of Gladstone stands in front of the Kapodistrian University building in the centre of Athens.
* There is a Gladstone statue at Glenalmond College
Glenalmond College is a co-educational independent boarding school in Perth and Kinross, Scotland, for children aged between 12 and 18 years. It is situated on the River Almond near the village of Methven, about west of the city of Perth. T ...
, unveiled in 2010, which is located in Front Quad.
* A Gladstone memorial was unveiled on 23 February 2013 in Seaforth, Liverpool by MP Frank Field (British politician), Frank Field. It is located in the grounds of Our Lady Star of the Sea Church facing the former site of St Thomas's Church where Gladstone was educated from 1816 to 1821. The Seaglam (Seaforth Gladstone Memorial) Project, whose chairman is local historian Brenda Murray (British Empire Medal, BEM), was started to raise the profile of Seaforth Village by installing a memorial to Gladstone. Funds for the memorial were raised by voluntary effort and additional funding was provided by the Heritage Lottery Fund. Sculptor Tom Murphy (artist), Tom Murphy created the bronze bust.
Namesakes
 * Gladstone Park, London, Gladstone Park in the Municipal Borough of Willesden, London was named after him in 1899. Dollis Hill House, within what later became the park, was occupied by Dudley Marjoribanks, 1st Baron Tweedmouth, Sir Dudley Coutts Marjoribanks, who subsequently became Lord Tweedmouth. In 1881 Lord Tweedmouth's daughter and her husband, John Hamilton-Gordon, 1st Marquess of Aberdeen and Temair, Lord Aberdeen, took up residence. They often had Gladstone to stay as a guest. In 1897 Lord Aberdeen was appointed Governor-General of Canada and the Aberdeens moved out. When Willesden acquired the house and land in 1899, they named the park Gladstone Park after the old Prime Minister.
* Gladstone Rock, a large boulder about 12 ft high in Cwm Llan on the Watkin Path on the south side of Snowdon where Gladstone made a speech in 1892, was named for him. A plaque on the rock states that he "addressed the people of Eryri upon justice to Wales".
* Gladstone, Oregon; Gladstone, New Jersey; Gladstone, Michigan; Gladstone, Missouri; and Gladstone, New Mexico, in the United States are named for him. The city of Gladstone, Queensland, Australia, was named after him and has a 19th-century marble statue on display in its town museum.
* Gladstone, Manitoba, was named after him in 1882.
* Streets in the cities of Athens, Sofia (including a school), Plovdiv, Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, Burgas, Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse, Stara Zagora, Limassol, Springs, Gauteng, Springs, Newark-on-Trent, Waterford City, Clonmel, Baltimore, MD., Brighton, Bradford, Scarborough, North Yorkshire, Scarborough, Swindon, Vancouver (including a school), Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ottawa, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax and Brisbane, Queensland, Brisbane are named for him. There is also Gladstone Avenue and adjoining Ewart Road in his hometown of Liverpool in a part of the city where he was a landowner.
* There is an imposing "Arts and Crafts" pub in Dulwich Hill NSW Australia named for him on the corner of Marrickville Road and New Canterbury Road; also a street is named for him in Dulwich Hill (Ewart Street) which crosses into the adjoining suburb of Marrickville. In Ewart Street there is a mansion called Gladstone Hall built in 1870 by William Starkey founder of Starkey's Ginger Beer and cordial factory in 1838 which became the largest of its type in the southern hemisphere for some time.There is a Gladstone Park in the Sydney suburb of Balmain.
* At the University of Liverpool, there is Gladstone Hall of residence, and the Gladstone Professor of Greek.
* A Gladstone bag, a light travelling bag, is named after him.
* Gladstone Park, London, Gladstone Park in the Municipal Borough of Willesden, London was named after him in 1899. Dollis Hill House, within what later became the park, was occupied by Dudley Marjoribanks, 1st Baron Tweedmouth, Sir Dudley Coutts Marjoribanks, who subsequently became Lord Tweedmouth. In 1881 Lord Tweedmouth's daughter and her husband, John Hamilton-Gordon, 1st Marquess of Aberdeen and Temair, Lord Aberdeen, took up residence. They often had Gladstone to stay as a guest. In 1897 Lord Aberdeen was appointed Governor-General of Canada and the Aberdeens moved out. When Willesden acquired the house and land in 1899, they named the park Gladstone Park after the old Prime Minister.
* Gladstone Rock, a large boulder about 12 ft high in Cwm Llan on the Watkin Path on the south side of Snowdon where Gladstone made a speech in 1892, was named for him. A plaque on the rock states that he "addressed the people of Eryri upon justice to Wales".
* Gladstone, Oregon; Gladstone, New Jersey; Gladstone, Michigan; Gladstone, Missouri; and Gladstone, New Mexico, in the United States are named for him. The city of Gladstone, Queensland, Australia, was named after him and has a 19th-century marble statue on display in its town museum.
* Gladstone, Manitoba, was named after him in 1882.
* Streets in the cities of Athens, Sofia (including a school), Plovdiv, Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, Burgas, Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse, Stara Zagora, Limassol, Springs, Gauteng, Springs, Newark-on-Trent, Waterford City, Clonmel, Baltimore, MD., Brighton, Bradford, Scarborough, North Yorkshire, Scarborough, Swindon, Vancouver (including a school), Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ottawa, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax and Brisbane, Queensland, Brisbane are named for him. There is also Gladstone Avenue and adjoining Ewart Road in his hometown of Liverpool in a part of the city where he was a landowner.
* There is an imposing "Arts and Crafts" pub in Dulwich Hill NSW Australia named for him on the corner of Marrickville Road and New Canterbury Road; also a street is named for him in Dulwich Hill (Ewart Street) which crosses into the adjoining suburb of Marrickville. In Ewart Street there is a mansion called Gladstone Hall built in 1870 by William Starkey founder of Starkey's Ginger Beer and cordial factory in 1838 which became the largest of its type in the southern hemisphere for some time.There is a Gladstone Park in the Sydney suburb of Balmain.
* At the University of Liverpool, there is Gladstone Hall of residence, and the Gladstone Professor of Greek.
* A Gladstone bag, a light travelling bag, is named after him.
Gallery
File:Gladstone Statue, London.jpg, Statue at Aldwych, London, near to the Royal Courts of Justice and opposite Australia House
File:William Ewart Gladstone statue, Albert Square.jpg, Statue in Albert Square, Manchester, Manchester
File:Gladstone Monument statue, Coates Crescent Gardens, Edinburgh.JPG, Statue on the Gladstone Monument in Coates Crescent Gardens, Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
File:From Vladaya to Chalite b 20090407 010.JPG, A high school named after Gladstone in Sofia, Bulgaria, Sofia, Bulgaria
In popular culture
Gladstone was popularly known in his later years as the "Grand Old Man" or "G.O.M.". The term was used occasionally during the Midlothian election campaign, first became widely associated with him during the 1880 general election, and was ubiquitous in the press by 1882. Henry Labouchère and Sir Stafford Northcote have both been credited with coining it; it appears to have been in use before either of them used it publicly, though they may have helped popularise it. While it was originally used to show affectionate reverence, it was quickly adopted more sarcastically by his opponents, using it to emphasise his age. The acronym was sometimes satirised as "God's Only Mistake", or after the fall of Khartoum, inverted to "M.O.G.", "Murderer of Gordon". (Disraeli is often credited with the former, but Lord Salisbury is a more likely origin). The term is still widely used today and is virtually synonymous with Gladstone.
Gladstone's burial in 1898 was commemorated in a poem by William McGonagall.
Portrayal in film and television
Since 1937, Gladstone has been portrayed some 37 times in film and television.
Portrayals include:
* Montagu Love in the film ''Parnell (film), Parnell'' (1937)
* Arthur Young (actor), Arthur Young in the films ''Victoria the Great'' (1937) and ''The Lady with a Lamp'' (1951)
* Malcolm Keen in the film ''Sixty Glorious Years'' (1938)
* Stephen Murray (actor), Stephen Murray in the film ''The Prime Minister (film), The Prime Minister'' (1941)
* Gordon Richards in the film ''The Imperfect Lady (1947 film), The Imperfect Lady'' (1947)
* Ralph Richardson in the film ''Khartoum (film), Khartoum'' (1966)
Works
*
*
volume 1volume 2volume 3
*
*
*
*
* A treatise on the storing of books and the design of bookshelves as employed in his personal library.
*
* (Volume 51, Issue 4 of new series, Transactions of the American Philosophical Society) (Original from the University of California)
See also
* Foreign Policy of William Ewart Gladstone
* Liberalism in the United Kingdom
Notes
References
Further reading
Biographies
 * Bebbington, D.W. ''William Ewart Gladstone'' (1993).
* Biagini, Eugenio F. ''Gladstone'' (2000).
* Brand, Eric. ''William Gladstone'' (1986) .
* Feuchtwanger, E.J. ''Gladstone'' (1975). 272 pp.
* Feuchtwanger, E.J. "Gladstone and the Rise and Fall of Victorian Liberalism" ''History Review'' (Dec 1996) v. 2
* Bebbington, D.W. ''William Ewart Gladstone'' (1993).
* Biagini, Eugenio F. ''Gladstone'' (2000).
* Brand, Eric. ''William Gladstone'' (1986) .
* Feuchtwanger, E.J. ''Gladstone'' (1975). 272 pp.
* Feuchtwanger, E.J. "Gladstone and the Rise and Fall of Victorian Liberalism" ''History Review'' (Dec 1996) v. 2
online
also online
* Jagger, Peter J., ed. ''Gladstone'' (2007), 256 pp.
* Jenkins, Roy. ''Gladstone: A Biography'' (2002)
* Philip Magnus (historian), Magnus, Philip
Gladstone: A biography
' (1954) London, John Murray.
* Matthew, H.C.G. "Gladstone, William Ewart (1809–1898)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography,'' (2004
online edition, May 2006.
* Matthew, H.C.G. ''Gladstone, 1809–1874'' (1988); ''Gladstone, 1875–1898'' (1995
online complete
** Matthew, ''Gladstone: 1809–1898'' (1997) is an unabridged one-volume version
online
*
volume Ivolume IIvolume III
via Internet Archive.
* Partridge, M. ''Gladstone'' (2003)
* .
* .
* Russell, Michael. ''Gladstone: A Bicentenary Portrait'' (2009).
* Richard Shannon (historian), Shannon, Richard. ''Gladstone: Peel's Inheritor, 1809–1865'' (1985), ; ''Gladstone: Heroic Minister, 1865–1898'' (1999), , a scholarly biograph
vol 1 online
*
Special studies
* Aldous, Richard. ''The Lion and the Unicorn: Gladstone vs Disraeli'' (2007).
* Barker, Michael. ''Gladstone and Radicalism. The Reconstruction of Liberal Policy in Britain. 1885–1894'' (The Harvester Press, 1975).
* Beales, Derek. ''From Castlereagh to Gladstone, 1815–1885'' (1969), survey of political histor
online
* Bebbington, D.W. ''The Mind of Gladstone: Religion, Homer and Politics'' (2004).
* Bebbington, David and Roger Swift (eds.), ''Gladstone Centenary Essays'' (Liverpool University Press, 2000).
* Biagini, E.F. ''Liberty, Retrenchment and Reform. Popular Liberalism in the Age of Gladstone, 1860–1880'' (Cambridge University Press, 1992).
* Biagini, Eugenio. and Alastair Reid (eds.), ''Currents of Radicalism. Popular Radicalism, Organised Labour and Party Politics in Britain, 1850–1914'' (Cambridge University Press, 1991).
* Boyce, D. George and Alan O'Day, eds. ''Gladstone and Ireland: Politics, Religion, and Nationality in the Victorian Age'' (Palgrave Macmillan; 2011), 307 pp.
* Bright, J. Franck. ''A History Of England. Period 4: Growth Of Democracy: Victoria 1837–1880'' (190
online
608pp; highly detailed older political narrative
** ''A History of England: Period V. Imperial Reaction, Victoria, 1880‒1901'' (1904
online
* Butler, P. ''Gladstone, church, state, and Tractarianism: a study of his religious ideas and attitudes, 1809–1859'' (1982).
* Dewey, Clive. “Celtic Agrarian Legislation and the Celtic Revival: Historicist Implications of Gladstone’s Irish and Scottish Land Acts 1870–1886.” ''Past & Present'', no. 64, (1974), pp. 30–70
online
* Gopal, S. "Gladstone and the Italian Question." ''History'' 41#141 (1956): 113–121
in JSTOR
* Guedalla, Philip. ''Queen and Mr. Gladstone'' (2 vols, 1933
online edition
* Hirst, F.W. ''Gladstone as Financier and Economist'' (1931).
* Hirst, F.W. ''In the Golden Days'' (Frederick Muller, 1947).
* Isba, Anne. ''Gladstone and Women'' (2006), London: Hambledon Continuum, .
* John Lawrence Hammond, Hammond, J.L. ''Gladstone and the Irish nation'' (1938
online edition.
* Jenkins, T.A. ''Gladstone, whiggery and the liberal party, 1874–1886'' (1988).
* Keith A. P. Sandiford. “W. E. Gladstone and Liberal-Nationalist Movements.” ''Albion'' 13#1 (1981), pp. 27–42
online
* Langer, William L. ''The Diplomacy of Imperialism: 1890–1902'' (2nd ed. 1950), a standard diplomatic history of Europe
* Loughlin, J. ''Gladstone, home rule and the Ulster question, 1882–1893'' (1986)
online
* Machin, G. I. T. "Gladstone and Nonconformity in the 1860s: The Formation of an Alliance." ''Historical Journal'' 17, no. 2 (1974): 347–364
online
.
* O’Day, Alan. “Gladstone and Irish Nationalism: Achievement and Reputation.” in ''Gladstone Centenary Essays,'' edited by David Bebbington and Roger Swift, (Liverpool University Press, 2000), pp. 163–183
online
* Parry, J. P. ''Democracy and religion: Gladstone and the liberal party, 1867–1875'' (1986).
* Quinault, Roland, et al. eds ''William Gladstone: New Studies and Perspectives'' (2012).
* Quinault, Roland. "Chamberlain and Gladstone: An Overview of Their Relationship." in ''Joseph Chamberlain: International Statesman, National Leader, Local Icon'' ed. by I. Cawood, C. Upton, (Palgrave Macmillan UK, 2016). 97–115.
* Quinault, Roland. "Gladstone and slavery." ''The Historical Journal'' 52.2 (2009): 363–383. DOI
Gladstone and Slavery
* Schreuder, D. M. ''Gladstone and Kruger: Liberal government and colonial ‘home rule’, 1880–85'' (1969).
* Schreuder, D. M. "Gladstone and Italian unification, 1848–70: the making of a Liberal?", ''The English historical review'', (1970) vol. 85 (n. 336), pp. 475–501
in JSTOR
* Schumpeter, Joseph A. ''History of Economic Analysis'' (George Allen & Unwin Ltd, 1954).
* Seton-Watson, R.W. ''Disraeli, Gladstone and the eastern question: a study in diplomacy and party politics'' (1935).
* Shannon, Richard. ''The crisis of imperialism, 1865–1915'' (1976), pp. 76–100, 142–198.
* Shannon, Richard. ''Gladstone and the Bulgarian agitation, 1876'' (1975
online
* Taylor, Michael. "The British West India interest and its allies, 1823–1833." ''English Historical Review'' 133.565 (2018): 1478–1511
The British West India Interest and Its Allies, 1823–1833*
focus on slavery
* Vincent, J. ''Gladstone and Ireland'' (1978).
* Vincent, J. ''The Formation of the Liberal Party, 1857–1868'' (1966
online
Midlothian campaign
* Blair, Kirstie. "The People’s William and the People’s Poets: William Gladstone and the Midlothian Campaign." ''The People’s Voice'' (2018
online
.
* Brooks, David. "Gladstone and Midlothian: The Background to the First Campaign," ''Scottish Historical Review'' (1985) 64#1 pp 42–67.
* Fitzsimons, M. A. "Midlothian: the Triumph and Frustration of the British Liberal Party," ''Review of Politics'' (1960) 22#2 pp 187–201
in JSTOR
* Kelley, Robert. "Midlothian: A Study In Politics and Ideas," ''Victorian Studies'' (1960) 4#2 pp 119–140.
* Matthew, H. C. G ''Gladstone: 1809–1898'' (1997) pp 293–313
* Whitehead, Cameron Ean Alfred. "The Bulgarian Horrors: culture and the international history of the Great Eastern Crisis, 1876–1878" (PhD. Dissertation, University of British Columbia, 2014
online
* Yildizeli, Fahriye Begum. "W.E. Gladstone and British Policy Towards the Ottoman Empire." (PhD dissertation, University of Exeter, 2016
online
.
Historiography
* St. John, Ian. ''The Historiography of Gladstone and Disraeli'' (Anthem Press, 2016) 402 p
excerpt
Primary sources
* Gladstone, W.E. ''Midlothian Speeches. 1879'' (Leicester University Press, 1971).
* Gladstone, William E. ''Midlothian Speeches 1884'' with an Introduction by M. R. D. Foot, (New York: Humanities Press, 1971
online
* Guedalla, Philip, ed. ''Gladstone and Palmerston: Being the Correspondence of Lord Palmerston with Mr. Gladstone, 1851–1865'' (1928)
* Guedalla, Philip, ed. ''Queen And Mr. Gladstone'' (1933
online
* Lord Kilbracken, ''Reminiscences of Lord Kilbracken'' (Macmillan, 1931).
* .
* .
* Matthew, H.C.G. and M.R.D. Foot, eds. ''Gladstone Diaries. With Cabinet Minutes & Prime-Ministerial Correspondence'' (13 vol; vol 14 is the index; 1968–1994); includes diaries, important selections from cabinet minutes and key political correspondence
online, vol 1, 4, 6, 7, and 11–14
; vol 14, pp. 1–284 includes brief identification of the 20,000+ people mentioned by Gladstone.
* Partridge, Michael, and Richard Gaunt, eds. ''Lives of Victorian Political Figures Part 1: Palmerston, Disraeli and Gladstone'' (4 vol. Pickering & Chatto. 2006) reprints 27 original pamphlets on Gladstone.
* Ramm, Agatha, ed. ''The Political Correspondence of Gladstone and Lord Granville 1876–1886.'' (2 vol Clarendon, 1962
online
* Temperley, Harold and L.M. Penson, eds. ''Foundations of British Foreign Policy: From Pitt (1792) to Salisbury (1902)'' (1938), primary source
online
External links
*
BBC Radio – Programme Two contains a recording of Gladstone's voice.
*
More about William Ewart Gladstone
on the Downing Street website.
Mr. Gladstone
(character sketch by William Thomas Stead, W.T. Stead, in the ''Review of Reviews'', 1892).
*
William Ewart Gladstone 1809–98
biography from the Liberal Democrat History Group.
William Gladstone – Harry Furniss Caricatures – UK Parliament Living Heritage
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gladstone, William Ewart
William Ewart Gladstone,
1809 births
1898 deaths
19th-century prime ministers of the United Kingdom
19th-century British writers
Alumni of Christ Church, Oxford
April Uprising of 1876
British classical liberals
Burials at Westminster Abbey
Chancellors of the Exchequer of the United Kingdom
Conservative Party (UK) MPs for English constituencies
English Anglicans
English people of Scottish descent
Founders of Scottish schools and colleges
Gladstone family, William Ewart Gladstone
Home rule in Ireland
Leaders of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom
Leaders of the Liberal Party (UK)
Lords Privy Seal
Liberal Party (UK) MPs for English constituencies
Separation of church and state
Scottish Liberal Party MPs
Members of the Parliament of the United Kingdom for the University of Oxford
Members of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom
People educated at Eton College
People of the Victorian era
Politicians from Liverpool
Presidents of the Oxford Union
Prime Ministers of the United Kingdom
Secretaries of State for War and the Colonies
Tory MPs (pre-1834)
UK MPs 1832–1835
UK MPs 1835–1837
UK MPs 1837–1841
UK MPs 1841–1847
UK MPs 1847–1852
UK MPs 1852–1857
UK MPs 1857–1859
UK MPs 1859–1865
UK MPs 1865–1868
UK MPs 1868–1874
UK MPs 1874–1880
UK MPs 1880–1885
UK MPs 1885–1886
UK MPs 1886–1892
UK MPs 1892–1895
Younger sons of baronets
Liberal Party prime ministers of the United Kingdom
Presidents of the Board of Trade
 Following the success of his double first, William travelled with his brother
Following the success of his double first, William travelled with his brother  In 1852, following the appointment of
In 1852, following the appointment of  The Conservative Leader
The Conservative Leader  In 1859, Lord Palmerston formed a new mixed government with Radicals included, and Gladstone again joined the government (with most of the other remaining Peelites) as Chancellor of the Exchequer, to become part of the new
In 1859, Lord Palmerston formed a new mixed government with Radicals included, and Gladstone again joined the government (with most of the other remaining Peelites) as Chancellor of the Exchequer, to become part of the new  Gladstone instituted abolition of the
Gladstone instituted abolition of the  In the wake of
In the wake of 
 The historian
The historian  In 1880, the Liberals won again and the Liberal leaders,
In 1880, the Liberals won again and the Liberal leaders,  Gladstone extended the vote to agricultural labourers and others in the Representation of the People Act 1884, 1884 Reform Act, which gave the counties the same franchise as the boroughs—adult male householders and £10 lodgers—and added six million to the total number of people who could vote in parliamentary elections. Parliamentary reform continued with the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885.
Gladstone was increasingly uneasy about the direction in which British politics was moving. In a letter to John Dalberg-Acton, 1st Baron Acton, Lord Acton on 11 February 1885, Gladstone criticised Tory Democracy as "demagogism" that "put down pacific, law-respecting, economic elements that ennobled the old Conservatism" but "still, in secret, as obstinately attached as ever to the evil principle of class interests". He found contemporary Liberalism better, "but far from being good". Gladstone claimed that this Liberalism's "pet idea is what they call construction,—that is to say, taking into the hands of the state the business of the individual man". Both Tory Democracy and this new Liberalism, Gladstone wrote, had done "much to estrange me, and had for many, many years".
Gladstone extended the vote to agricultural labourers and others in the Representation of the People Act 1884, 1884 Reform Act, which gave the counties the same franchise as the boroughs—adult male householders and £10 lodgers—and added six million to the total number of people who could vote in parliamentary elections. Parliamentary reform continued with the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885.
Gladstone was increasingly uneasy about the direction in which British politics was moving. In a letter to John Dalberg-Acton, 1st Baron Acton, Lord Acton on 11 February 1885, Gladstone criticised Tory Democracy as "demagogism" that "put down pacific, law-respecting, economic elements that ennobled the old Conservatism" but "still, in secret, as obstinately attached as ever to the evil principle of class interests". He found contemporary Liberalism better, "but far from being good". Gladstone claimed that this Liberalism's "pet idea is what they call construction,—that is to say, taking into the hands of the state the business of the individual man". Both Tory Democracy and this new Liberalism, Gladstone wrote, had done "much to estrange me, and had for many, many years".
 The Hawarden Kite was a December 1885 press release by Gladstone's son and aide Herbert Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, Herbert Gladstone announcing that he had become convinced that Ireland needed a separate parliament. The bombshell announcement resulted in the fall of Lord Salisbury's Conservative government. Irish Nationalists, led by Charles Stewart Parnell, Charles Parnell's Irish Parliamentary Party, held the balance of power in Parliament. Gladstone's conversion to Home Rule convinced them to switch away from the Conservatives and support the Liberals using the 86 seats in Parliament they controlled. The main purpose of this administration was to deliver Ireland a reform which would give it a devolved assembly, similar to those which would be eventually put in place in Scotland and Wales in 1999. In 1886 Gladstone's party allied with Irish Nationalists to defeat Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury, Lord Salisbury's government. Gladstone regained his position as Prime Minister and combined the office with that of Lord Privy Seal. During this administration he first introduced his Home Rule Bill for Ireland. The issue split the Liberal Party (a breakaway group went on to create the Liberal Unionist party) and the bill was thrown out on the second reading, ending his government after only a few months and inaugurating another headed by Lord Salisbury.
Gladstone, says his biographer, "totally rejected the widespread English view that the Irish had no taste for justice, common sense, moderation or national prosperity and looked only to perpetual strife and dissension". The problem for Gladstone was that his rural English supporters would not support home rule for Ireland. A large faction of Liberals, led by Joseph Chamberlain, formed a Unionist faction that supported the Conservative party. Whenever the Liberals were out of power, home rule proposals languished.
The Hawarden Kite was a December 1885 press release by Gladstone's son and aide Herbert Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, Herbert Gladstone announcing that he had become convinced that Ireland needed a separate parliament. The bombshell announcement resulted in the fall of Lord Salisbury's Conservative government. Irish Nationalists, led by Charles Stewart Parnell, Charles Parnell's Irish Parliamentary Party, held the balance of power in Parliament. Gladstone's conversion to Home Rule convinced them to switch away from the Conservatives and support the Liberals using the 86 seats in Parliament they controlled. The main purpose of this administration was to deliver Ireland a reform which would give it a devolved assembly, similar to those which would be eventually put in place in Scotland and Wales in 1999. In 1886 Gladstone's party allied with Irish Nationalists to defeat Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury, Lord Salisbury's government. Gladstone regained his position as Prime Minister and combined the office with that of Lord Privy Seal. During this administration he first introduced his Home Rule Bill for Ireland. The issue split the Liberal Party (a breakaway group went on to create the Liberal Unionist party) and the bill was thrown out on the second reading, ending his government after only a few months and inaugurating another headed by Lord Salisbury.
Gladstone, says his biographer, "totally rejected the widespread English view that the Irish had no taste for justice, common sense, moderation or national prosperity and looked only to perpetual strife and dissension". The problem for Gladstone was that his rural English supporters would not support home rule for Ireland. A large faction of Liberals, led by Joseph Chamberlain, formed a Unionist faction that supported the Conservative party. Whenever the Liberals were out of power, home rule proposals languished.
 Gladstone supported the London dockers in their London Dock Strike of 1889, strike of 1889. After their victory he gave a speech at Hawarden on 23 September in which he said: "In the common interests of humanity, this remarkable strike and the results of this strike, which have tended somewhat to strengthen the condition of labour in the face of capital, is the record of what we ought to regard as satisfactory, as a real social advance [that] tends to a fair principle of division of the fruits of industry".Michael Barker, ''Gladstone and Radicalism. The Reconstruction of Liberal Policy in Britain. 1885–1894'' (The Harvester Press, 1975), p. 92. This speech has been described by Eugenio Biagini as having "no parallel in the rest of Europe except in the rhetoric of the toughest socialist leaders". Visitors at Hawarden in October were "shocked...by some rather wild language on the Dock labourers question". Gladstone was impressed with workers unconnected with the dockers' dispute who "intended to make common cause" in the interests of justice.
On 23 October at Southport, Gladstone delivered a speech where he said that the right to combination, which in London was "innocent and lawful, in Ireland would be penal and...punished by imprisonment with hard labour". Gladstone believed that the right to combination used by British workers was in jeopardy when it could be denied to Irish workers. In October 1890 Gladstone at Midlothian claimed that competition between capital and labour, "where it has gone to sharp issues, where there have been strikes on one side and lock-outs on the other, I believe that in the main and as a general rule, the labouring man has been in the right".
On 11 December 1891 Gladstone said that: "It is a lamentable fact if, in the midst of our civilisation, and at the close of the nineteenth century, the workhouse is all that can be offered to the industrious labourer at the end of a long and honourable life. I do not enter into the question now in detail. I do not say it is an easy one; I do not say that it will be solved in a moment; but I do say this, that until society is able to offer to the industrious labourer at the end of a long and blameless life something better than the workhouse, society will not have discharged its duties to its poorer members". On 24 March 1892 Gladstone said that the Liberals had:
Gladstone supported the London dockers in their London Dock Strike of 1889, strike of 1889. After their victory he gave a speech at Hawarden on 23 September in which he said: "In the common interests of humanity, this remarkable strike and the results of this strike, which have tended somewhat to strengthen the condition of labour in the face of capital, is the record of what we ought to regard as satisfactory, as a real social advance [that] tends to a fair principle of division of the fruits of industry".Michael Barker, ''Gladstone and Radicalism. The Reconstruction of Liberal Policy in Britain. 1885–1894'' (The Harvester Press, 1975), p. 92. This speech has been described by Eugenio Biagini as having "no parallel in the rest of Europe except in the rhetoric of the toughest socialist leaders". Visitors at Hawarden in October were "shocked...by some rather wild language on the Dock labourers question". Gladstone was impressed with workers unconnected with the dockers' dispute who "intended to make common cause" in the interests of justice.
On 23 October at Southport, Gladstone delivered a speech where he said that the right to combination, which in London was "innocent and lawful, in Ireland would be penal and...punished by imprisonment with hard labour". Gladstone believed that the right to combination used by British workers was in jeopardy when it could be denied to Irish workers. In October 1890 Gladstone at Midlothian claimed that competition between capital and labour, "where it has gone to sharp issues, where there have been strikes on one side and lock-outs on the other, I believe that in the main and as a general rule, the labouring man has been in the right".
On 11 December 1891 Gladstone said that: "It is a lamentable fact if, in the midst of our civilisation, and at the close of the nineteenth century, the workhouse is all that can be offered to the industrious labourer at the end of a long and honourable life. I do not enter into the question now in detail. I do not say it is an easy one; I do not say that it will be solved in a moment; but I do say this, that until society is able to offer to the industrious labourer at the end of a long and blameless life something better than the workhouse, society will not have discharged its duties to its poorer members". On 24 March 1892 Gladstone said that the Liberals had:
 The 1892 United Kingdom general election, general election of 1892 resulted in a minority Liberal government with Gladstone as Prime Minister. The electoral address had promised Irish Home Rule and the disestablishment of the Scottish and Welsh Churches. In February 1893 he introduced the Irish Government Bill 1893, Second Home Rule Bill, which was passed in the Commons at second reading on 21 April by 43 votes and third reading on 1 September by 34 votes. The House of Lords defeated the bill by voting against by 419 votes to 41 on 8 September.
The Elementary Education (Blind and Deaf Children) Act, passed in 1893, required local authorities to provide separate education for blind and deaf children.
Conservative MP Colonel Howard Vincent questioned Gladstone in the Commons on what his government would do about unemployment on 1 September 1893. Gladstone replied:
The 1892 United Kingdom general election, general election of 1892 resulted in a minority Liberal government with Gladstone as Prime Minister. The electoral address had promised Irish Home Rule and the disestablishment of the Scottish and Welsh Churches. In February 1893 he introduced the Irish Government Bill 1893, Second Home Rule Bill, which was passed in the Commons at second reading on 21 April by 43 votes and third reading on 1 September by 34 votes. The House of Lords defeated the bill by voting against by 419 votes to 41 on 8 September.
The Elementary Education (Blind and Deaf Children) Act, passed in 1893, required local authorities to provide separate education for blind and deaf children.
Conservative MP Colonel Howard Vincent questioned Gladstone in the Commons on what his government would do about unemployment on 1 September 1893. Gladstone replied:  In 1895, at the age of 85, Gladstone bequeathed Pound sterling, £40,000 (equivalent to approximately £ today) and much of his 32,000 volume library to found St Deiniol's Library in
In 1895, at the age of 85, Gladstone bequeathed Pound sterling, £40,000 (equivalent to approximately £ today) and much of his 32,000 volume library to found St Deiniol's Library in  His last public statement was dictated to his daughter Helen in reply to receiving the Vice-Chancellor of the University of Oxford's "sorrow and affection": "There is no expression of Christian sympathy that I value more than that of the ancient University of Oxford, the God-fearing and God-sustaining University of Oxford. I served her perhaps mistakenly, but to the best of my ability. My most earnest prayers are hers to the uttermost and to the last". He left the house for the last time on 9 April. After 18 April he did not come down to the ground floor but still came out of bed to lie on the sofa. The Bishop of St Andrews, Dunkeld and Dunblane George Wilkinson (bishop), George Wilkinson recorded when he ministered to him along with Stephen Gladstone:
His last public statement was dictated to his daughter Helen in reply to receiving the Vice-Chancellor of the University of Oxford's "sorrow and affection": "There is no expression of Christian sympathy that I value more than that of the ancient University of Oxford, the God-fearing and God-sustaining University of Oxford. I served her perhaps mistakenly, but to the best of my ability. My most earnest prayers are hers to the uttermost and to the last". He left the house for the last time on 9 April. After 18 April he did not come down to the ground floor but still came out of bed to lie on the sofa. The Bishop of St Andrews, Dunkeld and Dunblane George Wilkinson (bishop), George Wilkinson recorded when he ministered to him along with Stephen Gladstone:  Gladstone died on 19 May 1898 at Hawarden Castle, Hawarden, aged 88. He had been cared for by his daughter Helen Gladstone, Helen who had resigned her job to care for her father and mother. The cause of death is officially recorded as "Syncope, Senility". "Syncope" meant failure of the heart and "senility" in the 19th century was an infirmity of advanced old age, rather than a loss of mental faculties. The House of Commons adjourned on the afternoon of Gladstone's death, with A.J. Balfour giving notice for an Address to the Queen praying for a public funeral and a public memorial in Westminster Abbey. The day after, both Houses of Parliament approved the Address and Herbert Gladstone accepted a public funeral on behalf of the Gladstone family. His coffin was transported on the London Underground before his State funerals in the United Kingdom, state funeral at Westminster Abbey, at which the Prince of Wales (the future King Edward VII) and the Duke of York (the future King George V) acted as pallbearers. His wife, Catherine Gladstone (''née'' Glynne), died two years later on 14 June 1900 and was buried next to him.
Gladstone died on 19 May 1898 at Hawarden Castle, Hawarden, aged 88. He had been cared for by his daughter Helen Gladstone, Helen who had resigned her job to care for her father and mother. The cause of death is officially recorded as "Syncope, Senility". "Syncope" meant failure of the heart and "senility" in the 19th century was an infirmity of advanced old age, rather than a loss of mental faculties. The House of Commons adjourned on the afternoon of Gladstone's death, with A.J. Balfour giving notice for an Address to the Queen praying for a public funeral and a public memorial in Westminster Abbey. The day after, both Houses of Parliament approved the Address and Herbert Gladstone accepted a public funeral on behalf of the Gladstone family. His coffin was transported on the London Underground before his State funerals in the United Kingdom, state funeral at Westminster Abbey, at which the Prince of Wales (the future King Edward VII) and the Duke of York (the future King George V) acted as pallbearers. His wife, Catherine Gladstone (''née'' Glynne), died two years later on 14 June 1900 and was buried next to him.
 Gladstone's early attempts to find a wife proved unsuccessful, having been rejected in 1835 by Caroline Eliza Farquhar (daughter of Sir Thomas Harvie Farquhar, 2nd Baronet) and again in 1837 by Lady Frances Harriet Douglas (daughter of George Douglas, 17th Earl of Morton).
The following year, having met her in 1834 at the London home of Old Etonian friend and then fellow-Conservative MP James Milnes Gaskell, he married Catherine Gladstone, Catherine Glynne, to whom he remained married until his death 59 years later. They had eight children together:
* William Henry Gladstone MP (1840–1891); married Hon. Gertrude Stuart (daughter of Charles Stuart, 12th Lord Blantyre) in 1875. They had three children.
* Agnes Gladstone (1842–1931); she married Very Rev. Edward Wickham in 1873. They had three children.
* The Rev. Stephen Edward Gladstone (1844–1920); he married Annie Wilson in 1885. They had five children: their eldest son Albert Gladstone, Albert, inherited the Gladstone baronets, Gladstone baronetcy in 1945.
* Catherine Jessy Gladstone (1845–1850)
* Mary Gladstone (1847–1927); she married Reverend Harry Drew in 1886. They had one daughter, Dorothy.
* Helen Gladstone (1849–1925), Vice-Principal of Newnham College, Cambridge
* Henry Neville Gladstone, 1st Baron Gladstone of Hawarden, Henry Neville Gladstone (1852–1935); he married Hon. Maud Rendel in 1890.
* Herbert Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, Herbert John Gladstone MP (1854–1930); he married Dorothy Paget in 1901.
Gladstone's eldest son William Henry Gladstone, William (known as "Willy" to distinguish him from his father), and youngest, Herbert Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, Herbert, both became Members of Parliament. William Henry predeceased his father by seven years. Gladstone's private secretary was his nephew Spencer Lyttelton.
Gladstone's early attempts to find a wife proved unsuccessful, having been rejected in 1835 by Caroline Eliza Farquhar (daughter of Sir Thomas Harvie Farquhar, 2nd Baronet) and again in 1837 by Lady Frances Harriet Douglas (daughter of George Douglas, 17th Earl of Morton).
The following year, having met her in 1834 at the London home of Old Etonian friend and then fellow-Conservative MP James Milnes Gaskell, he married Catherine Gladstone, Catherine Glynne, to whom he remained married until his death 59 years later. They had eight children together:
* William Henry Gladstone MP (1840–1891); married Hon. Gertrude Stuart (daughter of Charles Stuart, 12th Lord Blantyre) in 1875. They had three children.
* Agnes Gladstone (1842–1931); she married Very Rev. Edward Wickham in 1873. They had three children.
* The Rev. Stephen Edward Gladstone (1844–1920); he married Annie Wilson in 1885. They had five children: their eldest son Albert Gladstone, Albert, inherited the Gladstone baronets, Gladstone baronetcy in 1945.
* Catherine Jessy Gladstone (1845–1850)
* Mary Gladstone (1847–1927); she married Reverend Harry Drew in 1886. They had one daughter, Dorothy.
* Helen Gladstone (1849–1925), Vice-Principal of Newnham College, Cambridge
* Henry Neville Gladstone, 1st Baron Gladstone of Hawarden, Henry Neville Gladstone (1852–1935); he married Hon. Maud Rendel in 1890.
* Herbert Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, Herbert John Gladstone MP (1854–1930); he married Dorothy Paget in 1901.
Gladstone's eldest son William Henry Gladstone, William (known as "Willy" to distinguish him from his father), and youngest, Herbert Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, Herbert, both became Members of Parliament. William Henry predeceased his father by seven years. Gladstone's private secretary was his nephew Spencer Lyttelton.
 Two of Gladstone's sons and a grandson, William Glynne Charles Gladstone, followed him into parliament, making for four generations of MPs in total. One of his collateral descendants, George Freeman (politician), George Freeman, has been the Conservative Member of Parliament for Mid Norfolk since 2010.
Albert Gladstone, Sir Albert Gladstone, 5th baronet and Charles Gladstone, Sir Charles Gladstone, 6th baronet (from whom the Sir William Gladstone, 7th Baronet, 7th and Gladstone baronets, 8th baronets are descended) were also grandsons.
Two of Gladstone's sons and a grandson, William Glynne Charles Gladstone, followed him into parliament, making for four generations of MPs in total. One of his collateral descendants, George Freeman (politician), George Freeman, has been the Conservative Member of Parliament for Mid Norfolk since 2010.
Albert Gladstone, Sir Albert Gladstone, 5th baronet and Charles Gladstone, Sir Charles Gladstone, 6th baronet (from whom the Sir William Gladstone, 7th Baronet, 7th and Gladstone baronets, 8th baronets are descended) were also grandsons.
 * A statue of Gladstone by Albert Bruce-Joy and erected in 1882, stands near the front gate of Bow Church, St. Marys Church in Bow, London, Bow, London. Paid for by the industrialist Theodore Bryant, it is viewed as a symbol of the later London matchgirls strike of 1888, 1888 match girls strike, which took place at the nearby Bow Quarter, Bryant & May Match Factory. Led by the socialist Annie Besant, hundreds of women working in the factory, where many sickened and died from poisoning from the white phosphorus used in the matches, went on strike to demand improved working conditions and pay, eventually winning their cause. In recent years, the statue of Gladstone has been repeatedly daubed with red paint, suggesting that it was paid for with the "blood of the match girls".
* A statue of Gladstone in bronze by Sir Thomas Brock, erected in 1904, stands in St John's Gardens, Liverpool, St John's Gardens, Liverpool.
* The Gladstone Memorial, London, Gladstone Memorial erected in 1905 stands at Aldwych, London, near the Royal Courts of Justice.
* A Grade II listed statue of Gladstone stands in Albert Square, Manchester, Albert Square, Manchester.
* A monument to Gladstone, Member of Parliament for Midlothian (UK Parliament constituency), Midlothian 1880–1895 was unveiled in
* A statue of Gladstone by Albert Bruce-Joy and erected in 1882, stands near the front gate of Bow Church, St. Marys Church in Bow, London, Bow, London. Paid for by the industrialist Theodore Bryant, it is viewed as a symbol of the later London matchgirls strike of 1888, 1888 match girls strike, which took place at the nearby Bow Quarter, Bryant & May Match Factory. Led by the socialist Annie Besant, hundreds of women working in the factory, where many sickened and died from poisoning from the white phosphorus used in the matches, went on strike to demand improved working conditions and pay, eventually winning their cause. In recent years, the statue of Gladstone has been repeatedly daubed with red paint, suggesting that it was paid for with the "blood of the match girls".
* A statue of Gladstone in bronze by Sir Thomas Brock, erected in 1904, stands in St John's Gardens, Liverpool, St John's Gardens, Liverpool.
* The Gladstone Memorial, London, Gladstone Memorial erected in 1905 stands at Aldwych, London, near the Royal Courts of Justice.
* A Grade II listed statue of Gladstone stands in Albert Square, Manchester, Albert Square, Manchester.
* A monument to Gladstone, Member of Parliament for Midlothian (UK Parliament constituency), Midlothian 1880–1895 was unveiled in  * Gladstone Park, London, Gladstone Park in the Municipal Borough of Willesden, London was named after him in 1899. Dollis Hill House, within what later became the park, was occupied by Dudley Marjoribanks, 1st Baron Tweedmouth, Sir Dudley Coutts Marjoribanks, who subsequently became Lord Tweedmouth. In 1881 Lord Tweedmouth's daughter and her husband, John Hamilton-Gordon, 1st Marquess of Aberdeen and Temair, Lord Aberdeen, took up residence. They often had Gladstone to stay as a guest. In 1897 Lord Aberdeen was appointed Governor-General of Canada and the Aberdeens moved out. When Willesden acquired the house and land in 1899, they named the park Gladstone Park after the old Prime Minister.
* Gladstone Rock, a large boulder about 12 ft high in Cwm Llan on the Watkin Path on the south side of Snowdon where Gladstone made a speech in 1892, was named for him. A plaque on the rock states that he "addressed the people of Eryri upon justice to Wales".
* Gladstone, Oregon; Gladstone, New Jersey; Gladstone, Michigan; Gladstone, Missouri; and Gladstone, New Mexico, in the United States are named for him. The city of Gladstone, Queensland, Australia, was named after him and has a 19th-century marble statue on display in its town museum.
* Gladstone, Manitoba, was named after him in 1882.
* Streets in the cities of Athens, Sofia (including a school), Plovdiv, Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, Burgas, Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse, Stara Zagora, Limassol, Springs, Gauteng, Springs, Newark-on-Trent, Waterford City, Clonmel, Baltimore, MD., Brighton, Bradford, Scarborough, North Yorkshire, Scarborough, Swindon, Vancouver (including a school), Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ottawa, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax and Brisbane, Queensland, Brisbane are named for him. There is also Gladstone Avenue and adjoining Ewart Road in his hometown of Liverpool in a part of the city where he was a landowner.
* There is an imposing "Arts and Crafts" pub in Dulwich Hill NSW Australia named for him on the corner of Marrickville Road and New Canterbury Road; also a street is named for him in Dulwich Hill (Ewart Street) which crosses into the adjoining suburb of Marrickville. In Ewart Street there is a mansion called Gladstone Hall built in 1870 by William Starkey founder of Starkey's Ginger Beer and cordial factory in 1838 which became the largest of its type in the southern hemisphere for some time.There is a Gladstone Park in the Sydney suburb of Balmain.
* At the University of Liverpool, there is Gladstone Hall of residence, and the Gladstone Professor of Greek.
* A Gladstone bag, a light travelling bag, is named after him.
* Gladstone Park, London, Gladstone Park in the Municipal Borough of Willesden, London was named after him in 1899. Dollis Hill House, within what later became the park, was occupied by Dudley Marjoribanks, 1st Baron Tweedmouth, Sir Dudley Coutts Marjoribanks, who subsequently became Lord Tweedmouth. In 1881 Lord Tweedmouth's daughter and her husband, John Hamilton-Gordon, 1st Marquess of Aberdeen and Temair, Lord Aberdeen, took up residence. They often had Gladstone to stay as a guest. In 1897 Lord Aberdeen was appointed Governor-General of Canada and the Aberdeens moved out. When Willesden acquired the house and land in 1899, they named the park Gladstone Park after the old Prime Minister.
* Gladstone Rock, a large boulder about 12 ft high in Cwm Llan on the Watkin Path on the south side of Snowdon where Gladstone made a speech in 1892, was named for him. A plaque on the rock states that he "addressed the people of Eryri upon justice to Wales".
* Gladstone, Oregon; Gladstone, New Jersey; Gladstone, Michigan; Gladstone, Missouri; and Gladstone, New Mexico, in the United States are named for him. The city of Gladstone, Queensland, Australia, was named after him and has a 19th-century marble statue on display in its town museum.
* Gladstone, Manitoba, was named after him in 1882.
* Streets in the cities of Athens, Sofia (including a school), Plovdiv, Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, Burgas, Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse, Stara Zagora, Limassol, Springs, Gauteng, Springs, Newark-on-Trent, Waterford City, Clonmel, Baltimore, MD., Brighton, Bradford, Scarborough, North Yorkshire, Scarborough, Swindon, Vancouver (including a school), Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ottawa, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax and Brisbane, Queensland, Brisbane are named for him. There is also Gladstone Avenue and adjoining Ewart Road in his hometown of Liverpool in a part of the city where he was a landowner.
* There is an imposing "Arts and Crafts" pub in Dulwich Hill NSW Australia named for him on the corner of Marrickville Road and New Canterbury Road; also a street is named for him in Dulwich Hill (Ewart Street) which crosses into the adjoining suburb of Marrickville. In Ewart Street there is a mansion called Gladstone Hall built in 1870 by William Starkey founder of Starkey's Ginger Beer and cordial factory in 1838 which became the largest of its type in the southern hemisphere for some time.There is a Gladstone Park in the Sydney suburb of Balmain.
* At the University of Liverpool, there is Gladstone Hall of residence, and the Gladstone Professor of Greek.
* A Gladstone bag, a light travelling bag, is named after him.
 * Bebbington, D.W. ''William Ewart Gladstone'' (1993).
* Biagini, Eugenio F. ''Gladstone'' (2000).
* Brand, Eric. ''William Gladstone'' (1986) .
* Feuchtwanger, E.J. ''Gladstone'' (1975). 272 pp.
* Feuchtwanger, E.J. "Gladstone and the Rise and Fall of Victorian Liberalism" ''History Review'' (Dec 1996) v. 2
* Bebbington, D.W. ''William Ewart Gladstone'' (1993).
* Biagini, Eugenio F. ''Gladstone'' (2000).
* Brand, Eric. ''William Gladstone'' (1986) .
* Feuchtwanger, E.J. ''Gladstone'' (1975). 272 pp.
* Feuchtwanger, E.J. "Gladstone and the Rise and Fall of Victorian Liberalism" ''History Review'' (Dec 1996) v. 2