Giuseppe Galli Bibiena on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Giuseppe Galli Bibiena (5 January 1696 - 12 March 1757),"Galli-Bibiena, Giuseppe" (dates, with
Giuseppe Galli Bibiena (5 January 1696 - 12 March 1757),"Galli-Bibiena, Giuseppe" (dates, with
aeiou-FerdinandoGBibiena
. Italian designer, became the most distinguished artist of the
EB-Bibienas
 Giuseppe Galli Bibiena (5 January 1696 - 12 March 1757),"Galli-Bibiena, Giuseppe" (dates, with
Giuseppe Galli Bibiena (5 January 1696 - 12 March 1757),"Galli-Bibiena, Giuseppe" (dates, with Friedrich the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
),
''Encyclopedia of Austria'', 2006, aeiou-Austria webpage:
aeiou-FerdinandoGBibiena
. Italian designer, became the most distinguished artist of the
Galli da Bibiena family
The Galli–Bibiena family, or Galli da Bibiena (also spelled "Bibbiena"), was a family of Italian artists of the 17th and 18th centuries, including:
"Ferdinando Galli Bibiena Online" (overview), John Malyon,
''Artcyclopedia'', 2005, Artcycl ...
.
"Bibiena, Galli da, Family" (history),
''Encyclopædia Britannica Online'', 18-November-2006, Britannica.com webpage:
EB-Bibienas
Life
He was born inParma
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, Giuseppe Verdi, music, art, prosciutto (ham), Parmigiano-Reggiano, cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 ...
, the second son of Ferdinando Galli Bibiena
Ferdinando Galli-Bibiena (18 August 1657 – 3 January 1743),"Galli-Bibiena, Ferdinando" (dates, Farnese dynasty, to Barcelona for Karl VI),''Encyclopedia of Austria'', 2006, aeiou.iicm.tugraz.at webpag."Ferdinando Galli Bibiena Online" (overview ...
. In 1708, Ferdinando was called to Barcelona by Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to ...
of Habsburg to help organize and decorate his wedding to Elisabeth Christine of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Queen of Prussia
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
and Giuseppe accompanied him. Later Giuseppe traveled with his father to the courts of Charles VI the Holy Roman Emperor (reigned 1711-1740) who hired Fernando to be the court's scenographer and painter. There, when his father left in 1717, he became the chief organizer of the court festivities and official functions and named "His Majesty's Second Theatrical Engineer". It was not until 1723 that Giuseppe was officially promoted to "His Majesty's First Theatrical Engineer" and kept the position until 1747. After receiving his position in court, Giuseppe became involved in decorating all the Habsburgs' celebratory festivities. He did parties, weddings, funerals, painted in monasteries and various countries. He also did work for religious venues as in Melk Abbey (Pulpit and High Altar) and in Prague when he built a decorative arch in 1729 for the celebration of John of Nepomuk
John of Nepomuk (or John Nepomucene) ( cs, Jan Nepomucký; german: Johannes Nepomuk; la, Ioannes Nepomucenus) ( 1345 – 20 March 1393)
was the saint of Bohemia (Czech Republic) who was drowned in the Vltava river at the behest of Wenceslaus IV ...
. His younger brother Antonio Galli Bibiena was also hired by the Vienna court and worked alongside Giuseppe. Together Antonio and Giuseppe designed theater decorations and for festivities in Vienna, also Linz
Linz ( , ; cs, Linec) is the capital of Upper Austria and third-largest city in Austria. In the north of the country, it is on the Danube south of the Czech border. In 2018, the population was 204,846.
In 2009, it was a European Capital of ...
, Graz
Graz (; sl, Gradec) is the capital city of the Austrian state of Styria and second-largest city in Austria after Vienna. As of 1 January 2021, it had a population of 331,562 (294,236 of whom had principal-residence status). In 2018, the popul ...
, and Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
(1723 "Costanza e Fortezza" at Hradčany
Hradčany (; german: Hradschin), the Castle District, is the district of the city of Prague, Czech Republic surrounding Prague Castle.
The castle is one of the biggest in the world at about in length and an average of about wide. Its history ...
castle).
The death of Charles VI in 1740 made a significant shift in Giuseppe Bibiena's career. Charles VI's daughter and successor Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position ''suo jure'' (in her own right). ...
did not see theatre as representative of her reign as her father did. Especially after her marriage to Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
, his French tastes overturned Italian prominence in the Vienna court. Giuseppe stayed in Vienna, organized Maria Theresa's wedding and festivities and still continued to find various jobs in the area, but his significance in the Vienna court diminished. This caused Giuseppe to take various jobs outside Vienna. In 1753 Giuseppe was hired by Frederick the Great of Prussia
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
in his court in Berlin. There Giuseppe spent the last three years of his life and died at the age of 61 on March 12, 1757.
Works
::* in 1722, Giuseppe Galli Bibiena worked inMunich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the States of Germany, German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the List of cities in Germany by popu ...
::* in 1723, he designed religious venues in Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
::* in 1735, he designed the Pulpit and High Altar for The Abbey Church, Melk Abbey
Melk Abbey (german: Stift Melk) is a Benedictine abbey above the town of Melk, Lower Austria, Austria, on a rocky outcrop overlooking the Danube river, adjoining the Wachau valley. The abbey contains the tomb of Saint Coloman of Stockerau and the ...
::* in 1742, he designed the decorations for the Vienna state opera
::* in 1744, he designed the interior of the Margrave's Opera House
The Margravial Opera House (german: Markgräfliches Opernhaus) is a Baroque opera house in the town of Bayreuth, Germany. Built between 1745 and 1750, it is one of Europe's few surviving theatres of the period and has been extensively restored. On ...
at Bayreuth
Bayreuth (, ; bar, Bareid) is a town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtelgebirge Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital of U ...
::* in 1747, Giuseppe was employed at the opera in Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth larg ...
, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
::* in 1750, he renovated the Dresden opera (which burned in 1849)
::* in 1751, Giuseppe received occasional orders from Friedrich the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
::* in 1753, worked permanently for Friedrich the Great in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
.
Style
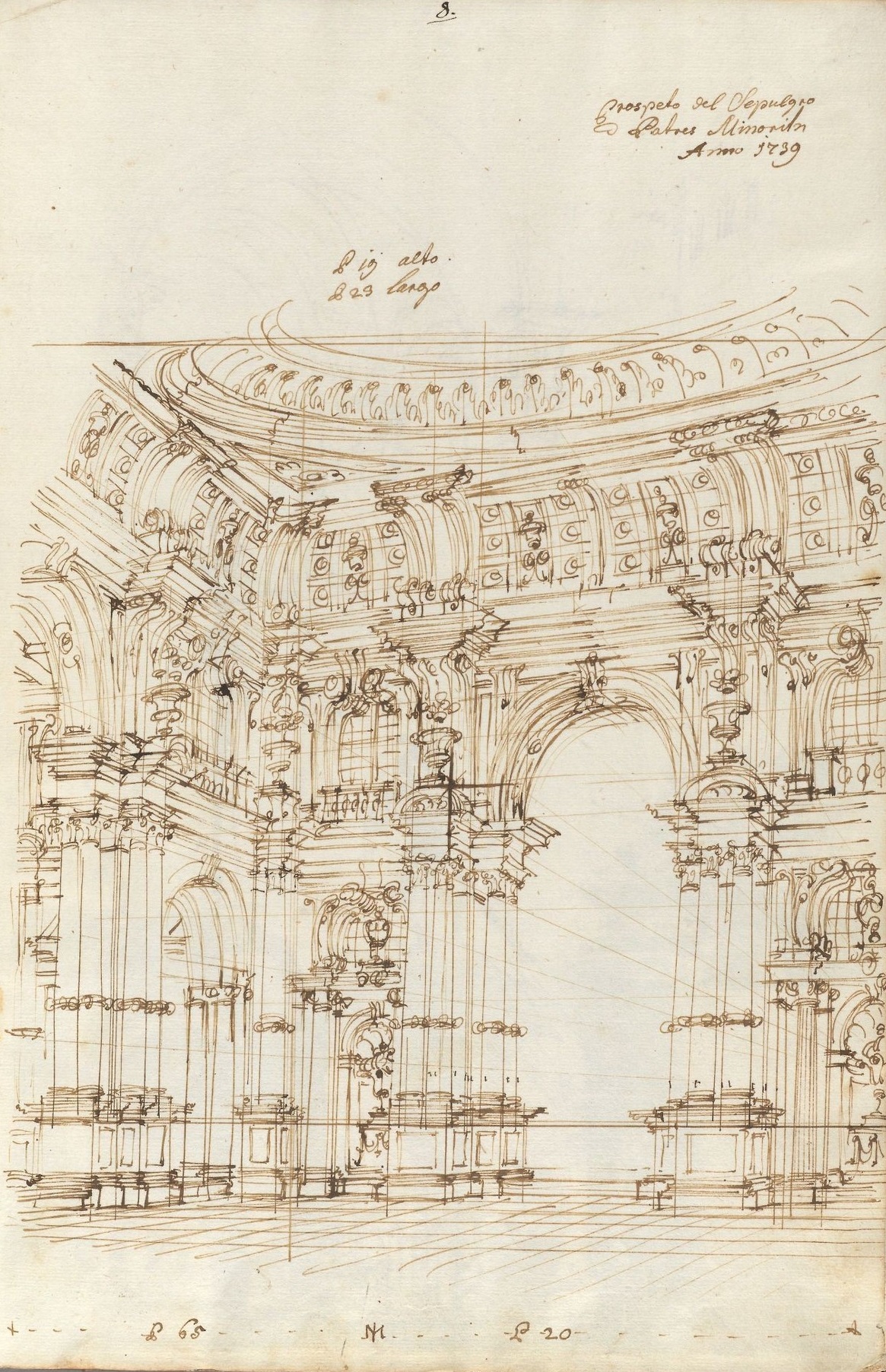
Giuseppe's innovation in theatre and in architecture embodied the Baroque/Classical style of the time period. His designs focused on detail, majesty, grandeur, and demonstrated a classical theme which was considered “true art” in the society of that time. Because of this, Giuseppe thrived as an artist. Although most of Giuseppe's designs were made to be temporary and are no longer accessible, many of his drawings were published. His efforts to combine architecture and painting through the perspective can easily be seen in three series of engravings: ''Alcina'' (in 1716), ''Costanza e Fortezza'' (1723 "Constancy and Fortitude"); and ''Architetture e prospettive'' (1740 "Architecture and Perspective"). The baroque style and attention to detail made the Bibiena style of scenography stand out. The multifaceted backdrops gave the audience a more realistic experience and added to the overall aesthetic of the play or opera. They not only impacted the scenery designs inside the theatre but also the architecture of the theatre itself.Collections
Giuseppe's drawings are held in the permanent collections of several institutions, including theNelson-Atkins Museum of Art
The Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art is an art museum in Kansas City, Missouri, known for its encyclopedic collection of art from nearly every continent and culture, and especially for its extensive collection of Asian art.
In 2007, ''Time'' magaz ...
, the Smart Museum of Art
The David and Alfred Smart Museum of Art is an art museum located on the campus of the University of Chicago in Chicago, Illinois. The permanent collection has over 15,000 objects. Admission is free and open to the general public.
The Smart Muse ...
, the Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
, the University of Michigan Museum of Art
The University of Michigan Museum of Art in Ann Arbor, Michigan with is one of the largest university art museums in the United States. Built as a war memorial in 1909 for the university's fallen alumni from the Civil War, Alumni Memorial Hall ori ...
, the Victoria and Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (often abbreviated as the V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.27 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and nam ...
, the Museo Nacional del Prado
The Prado Museum ( ; ), officially known as Museo Nacional del Prado, is the main Spanish national art museum, located in central Madrid. It is widely considered to house one of the world's finest collections of European art, dating from the ...
, the Detroit Institute of Arts
The Detroit Institute of Arts (DIA), located in Midtown Detroit, Michigan, has one of the list of largest art museums, largest and most significant art collections in the United States. With over 100 galleries, it covers with a major renovation a ...
, the La Salle University Art Museum
The La Salle University Art Museum is located in the basement of Olney Hall at La Salle University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The museum features six galleries. Collections include European and American art from the Renaissance to the present. ...
, and the Cooper Hewitt.
Notes
{{DEFAULTSORT:Galli Bibiena, Giuseppe 1696 births 1757 deaths Italian designers Italian scenic designers 18th-century Italian artists 18th-century Italian male artists