Georgia Superior Court on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The
The
Official website for Georgia Superior Courts, retrieved November 20, 2020
Georgia (U.S. state) state courts Georgia Courts and tribunals with year of establishment missing
 The
The Superior Court
In common law systems, a superior court is a court of general jurisdiction over civil and criminal legal cases. A superior court is "superior" in relation to a court with limited jurisdiction (see small claims court), which is restricted to civil ...
is Georgia's general jurisdiction trial court. It has exclusive, constitutional, authority over felony cases, divorce, equity
Equity may refer to:
Finance, accounting and ownership
* Equity (finance), ownership of assets that have liabilities attached to them
** Stock, equity based on original contributions of cash or other value to a business
** Home equity, the dif ...
and cases regarding title to land. The exclusive jurisdiction of this court also covers such matters as declaratory judgments, habeas corpus, mandamus
(; ) is a judicial remedy in the form of an order from a court to any government, subordinate court, corporation, or public authority, to do (or forbear from doing) some specific act which that body is obliged under law to do (or refrain from ...
, quo warranto and prohibition. The Superior Court corrects errors made by lower courts by issuing writs of certiorari
In law, ''certiorari'' is a court process to seek judicial review of a decision of a lower court or government agency. ''Certiorari'' comes from the name of an English prerogative writ, issued by a superior court to direct that the record of ...
; for some lower courts, the right to direct review by the Superior Court applies.
Organization
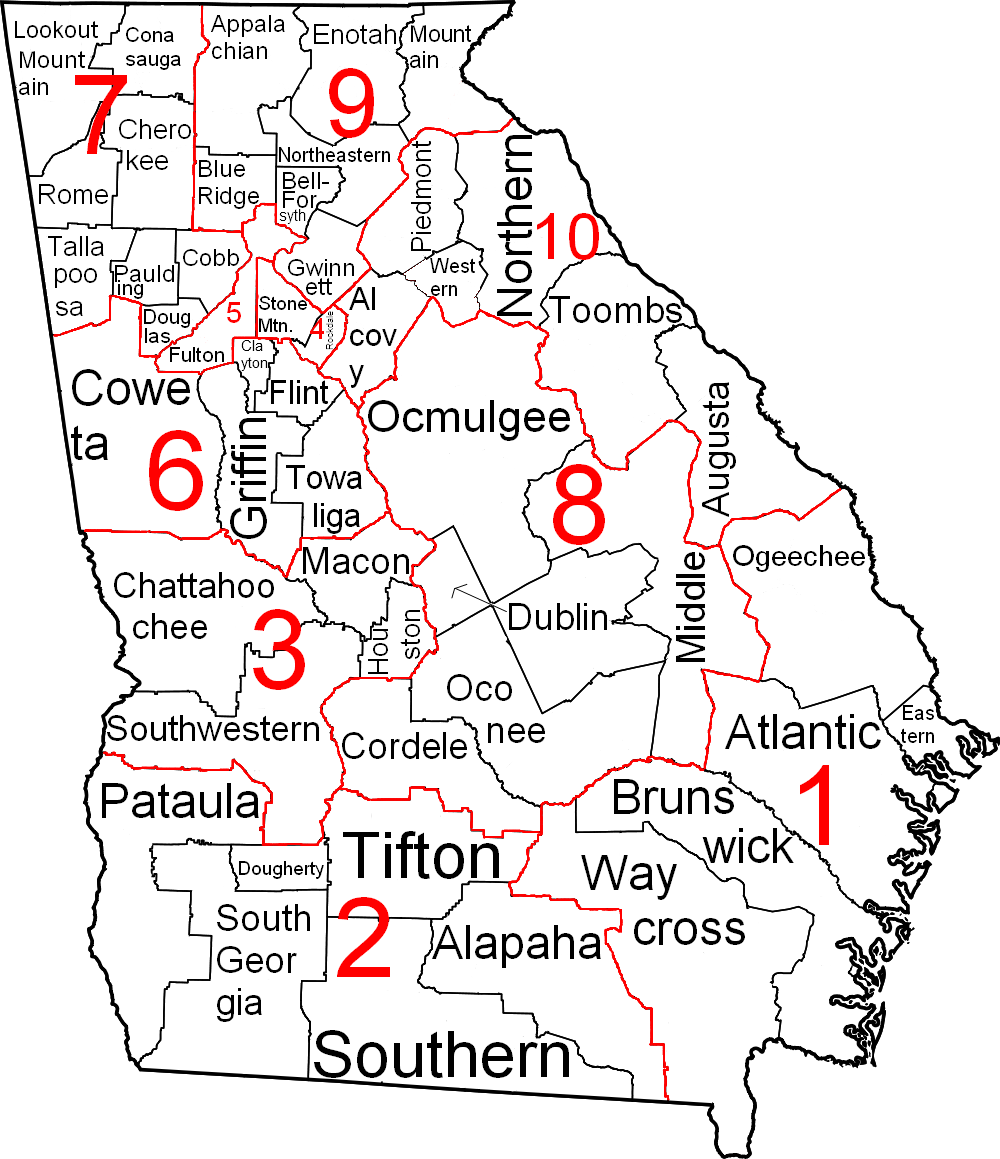
Superior Courts are organized into 10 Judicial Districts, comprising 50 judicial circuits. Each county has its own Superior Court, though a judge may serve more than one county. A chief judge handles the administrative tasks for each circuit.Election of judges
Superior Court judges are elected to four-year terms innonpartisan
Nonpartisanism is a lack of affiliation with, and a lack of bias towards, a political party.
While an Oxford English Dictionary definition of ''partisan'' includes adherents of a party, cause, person, etc., in most cases, nonpartisan refers sp ...
, circuit-wide races. To qualify as a Superior Court judge, a candidate must be at least 30 years old, a citizen of Georgia for at least three years, and have practiced law for at least seven years. Superior Court judges who have retired and taken senior status may hear cases in any circuit at the request of a local judge, an administrative judge, or the governor.
See also
*Judiciary of Georgia (U.S. state) The Judiciary of Georgia is a branch of the government of the State of Georgia established in Article Six of the Georgia constitution. This Article contains ten Sections which discuss the different courts, their powers and jurisdictions, and the ro ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
Official website for Georgia Superior Courts, retrieved November 20, 2020
Georgia (U.S. state) state courts Georgia Courts and tribunals with year of establishment missing