George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and
Founding Father
The following list of national founding figures is a record, by country, of people who were credited with establishing a state. National founders are typically those who played an influential role in setting up the systems of governance, (i.e. ...
who served as the first
president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
as commander of the
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
, Washington led the
Patriot
A patriot is a person with the quality of patriotism.
Patriot may also refer to:
Political and military groups United States
* Patriot (American Revolution), those who supported the cause of independence in the American Revolution
* Patriot m ...
forces to victory in the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
and served as the president of the
Constitutional Convention of 1787, which created the
Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
and the American federal government. Washington has been called the "
Father of his Country" for his manifold leadership in the formative days of the country.
Washington's first public office was serving as the official
surveyor
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ca ...
of
Culpeper County, Virginia
Culpeper County is a county located along the borderlands of the northern and central region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 52,552. Its county seat and only incorporated community is Culp ...
, from 1749 to 1750. Subsequently, he received his first military training (as well as a command with the
Virginia Regiment
The Virginia Regiment was formed in 1754 by Virginia's Royal Governor Robert Dinwiddie, as a provincial corps. The regiment served in the French and Indian War, with members participating in actions at Jumonville Glen and Fort Necessity in 1754, ...
) during the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
. He was later elected to the Virginia
House of Burgesses
The House of Burgesses was the elected representative element of the Virginia General Assembly, the legislative body of the Colony of Virginia. With the creation of the House of Burgesses in 1642, the General Assembly, which had been established ...
and was named a delegate to the Continental Congress where he was appointed
Commanding General
The commanding officer (CO) or sometimes, if the incumbent is a general officer, commanding general (CG), is the officer in command of a military unit. The commanding officer has ultimate authority over the unit, and is usually given wide latitu ...
of the Continental Army. With this title, he commanded American forces (allied with
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
) in the defeat and surrender of the British at the
Siege of Yorktown
The Siege of Yorktown, also known as the Battle of Yorktown, the surrender at Yorktown, or the German battle (from the presence of Germans in all three armies), beginning on September 28, 1781, and ending on October 19, 1781, at Yorktown, Virgi ...
during the American Revolutionary War. He
resigned his commission after the
Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
was signed in 1783.
Washington played an indispensable role in adopting and ratifying the Constitution of the United States, which was a replacement of the original constitution, the
Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
. He was then twice elected president by the
Electoral College unanimously. As president, he implemented a strong, well-financed national government while remaining impartial in a fierce rivalry between cabinet members
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
and
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
. During the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, he
proclaimed a policy of neutrality while sanctioning the
Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
. He set enduring precedents for the office of president, including the title "
Mr. President", and swearing the
Oath of Office
An oath of office is an oath or affirmation a person takes before assuming the duties of an office, usually a position in government or within a religious body, although such oaths are sometimes required of officers of other organizations. Such ...
on the Bible. His
Farewell Address is widely regarded as a pre-eminent statement on
republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology centered on citizenship in a state organized as a republic. Historically, it emphasises the idea of self-rule and ranges from the rule of a representative minority or oligarchy to popular sovereignty. It ...
.
Washington was a slave owner who had a complicated relationship with
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. During his lifetime he owned a cumulative total of over 577 slaves, who were forced to work on his farms and wherever he lived, including the
President's House in Philadelphia. As president, he signed laws passed by Congress that both protected and curtailed slavery. His will said that one of his slaves,
William Lee, should be freed upon his death and that the other 123 slaves must work for his wife and be freed on her death. She freed them during her lifetime to remove the incentive for hastening her death.
He endeavored to
assimilate Native Americans into the
Anglo-American
Anglo-Americans are people who are English-speaking inhabitants of Anglo-America. It typically refers to the nations and ethnic groups in the Americas that speak English as a native language, making up the majority of people in the world who spe ...
culture. However, he waged military campaigns against hostile Native American nations during the Revolutionary War and the
Northwest Indian War
The Northwest Indian War (1786–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native American nations known today as the Northwestern ...
. He was a member of the
Anglican Church
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
and the
Freemasons
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
, and he urged broad religious freedom in his roles as general and president. Upon his death, he was eulogized by
Henry "Light-Horse Harry" Lee as "first in war, first in peace, and first in the hearts of his countrymen".
Washington has been
memorialized by monuments, a
federal holiday
Federal holidays in the United States are the eleven calendar dates that are designated by the U.S. government as holidays. On U.S. federal holidays, non-essential federal government offices are closed and federal government employees are paid ...
,
various media depictions, geographical locations, including
the national capital, the
State of Washington
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George Washington—the first U.S. president—the state was formed from the western part of the Washington ...
,
stamps
Stamp or Stamps or Stamping may refer to:
Official documents and related impressions
* Postage stamp, used to indicate prepayment of fees for public mail
* Ration stamp, indicating the right to rationed goods
* Revenue stamp, used on documents to ...
, and
currency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general def ...
, and many scholars and ordinary Americans alike rank him among
the greatest U.S. presidents. In 1976, Washington was
posthumous
Posthumous may refer to:
* Posthumous award - an award, prize or medal granted after the recipient's death
* Posthumous publication – material published after the author's death
* Posthumous (album), ''Posthumous'' (album), by Warne Marsh, 1987
* ...
ly promoted to the rank of
General of the Armies of the United States
General of the Armies of the United States, more commonly referred to as General of the Armies, is the highest military rank in the United States Army. The rank has been conferred three times: to John J. Pershing in 1919, as a personal accola ...
, the highest rank in the United States Army.
Early life (1732–1752)

The
Washington family
The Washington family is an American family of English origins that was part of both the British landed gentry and the American gentry. It was prominent in colonial America and rose to great economic and political eminence especially in the Col ...
was a wealthy Virginia
planter family that had made its fortune through
land speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. (It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.)
Many s ...
and the
cultivation of tobacco
The cultivation of tobacco usually takes place annually. The tobacco is germinated in cold frames or hotbeds and then transplanted to the field until it matures. It is grown in warm climates with rich, well-drained soil. About ''4.2 million'' hec ...
. Washington's great-grandfather
John Washington
John Washington (1633–1677) was an English merchant who emigrated across the Atlantic Ocean and became a planter, soldier and politician in colonial Virginia. In addition to leading the local militia, and running his own plantations, Washin ...
emigrated
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
in 1656 from
Sulgrave
Sulgrave is a village and civil parish in West Northamptonshire, England, about north of Brackley. The village is just south of a stream that rises in the parish and flows east to join the River Tove, a tributary of the Great Ouse.
The village ...
,
Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire (; abbreviated Northants.) is a county in the East Midlands of England. In 2015, it had a population of 723,000. The county is administered by
two unitary authorities: North Northamptonshire and West Northamptonshire. It is ...
,
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, to the English
colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colonial empire, English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertG ...
where he accumulated of land, including
Little Hunting Creek
Little Hunting Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 primarily tidal tributary of the Potomac River located in Fairfax County, Virginia, not to be c ...
on the
Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augus ...
. George Washington was born on February 22, 1732, at
Popes Creek in
Westmoreland County, in the British colony of Virginia, and was the first of six children of
Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berbers, Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia (Roman pr ...
and
Mary Ball Washington
Mary Washington (; born sometime between 1707 and 1709 – August 25, 1789), was the second wife of Augustine Washington, a planter in Virginia, the mother-in-law of Martha Washington, the paternal grandmother of Bushrod Washington, and ...
. His father was a
justice of the peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or ''puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sa ...
and a prominent public figure who had four additional children from his first marriage to Jane Butler. The family moved to Little Hunting Creek in 1735. In 1738, they moved to
Ferry Farm
Ferry Farm, also known as the George Washington Boyhood Home Site or the Ferry Farm Site, is the farm and home where George Washington spent much of his childhood. The site is located in Stafford County, Virginia, along the northern bank of the Ra ...
near
Fredericksburg, Virginia
Fredericksburg is an independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 27,982. The Bureau of Economic Analysis of the United States Department of Commerce combines the city of Fredericksburg wi ...
, on the
Rappahannock River
The Rappahannock River is a river in eastern Virginia, in the United States, approximately in length.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 It traverses the entir ...
. When Augustine died in 1743, Washington inherited Ferry Farm and ten slaves; his older half-brother
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
inherited Little Hunting Creek and renamed it
Mount Vernon
Mount Vernon is an American landmark and former plantation of Founding Father, commander of the Continental Army in the Revolutionary War, and the first president of the United States George Washington and his wife, Martha. The estate is on ...
.
Washington did not have the formal education his elder brothers received at
Appleby Grammar School
Appleby Grammar School is a mixed secondary school and sixth form in Appleby-in-Westmorland, Cumbria for students aged 11 to 18. Since 2011, it has been an Academy. Until 2013, the school was a registered charity.
History
The origins of Ap ...
in England, but he did attend the
Lower Church
Lower Church is a historic Episcopal church located near Hartfield, Middlesex County, Virginia. It was constructed in 1717, and is a one-story, rectangular brick building with a clipped gable roof. It measures 56 feet by 34 feet. an''Accompany ...
School in
Hartfield
Hartfield is a village and civil parish in the Wealden district of East Sussex, England. The parish also includes the settlements of Colemans Hatch, Hammerwood and Holtye, all lying on the northern edge of Ashdown Forest.
Geography
The main ...
. He learned mathematics,
trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. T ...
, and land
surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ca ...
and became a talented draftsman and
map-maker. By early adulthood, he was writing with "considerable force" and "precision". In his pursuit of admiration, status, and power, his writing displayed little wit or humor.
Washington often visited Mount Vernon and
Belvoir, the plantation that belonged to Lawrence's father-in-law
William Fairfax
William Fairfax (1691–1757) was a political appointee of the British Crown in several colonies as well as a planter and politician in the Colony of Virginia. Fairfax served as Collector of Customs in Barbados, Chief Justice and governor of the ...
. Fairfax became Washington's patron and surrogate father, and Washington spent a month in 1748 with a team surveying Fairfax's
Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley () is a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia. The valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge- ...
property. The following year he received a surveyor's license from the
College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William III ...
when he was 17 years old. Even though Washington had not served the customary apprenticeship, Fairfax appointed him surveyor of
Culpeper County, Virginia
Culpeper County is a county located along the borderlands of the northern and central region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 52,552. Its county seat and only incorporated community is Culp ...
, and he appeared in Culpeper County to take his oath of office July 20, 1749. He subsequently familiarized himself with the frontier region, and though he resigned from the job in 1750, he continued to do surveys west of the
Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States, and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virgin ...
. By 1752 he had bought almost in the Valley and owned .
In 1751, Washington made his only trip abroad when he accompanied Lawrence to
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). ...
, hoping the climate would cure his brother's tuberculosis. Washington contracted
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
during that trip, which immunized him and left his face slightly scarred. Lawrence died in 1752, and Washington leased Mount Vernon from his widow Anne; he inherited it outright after her death in 1761.
Colonial military career (1752–1758)
Lawrence Washington's service as adjutant general of the
Virginia militia inspired his half-brother George to seek a commission. Virginia's lieutenant governor,
Robert Dinwiddie
Robert Dinwiddie (1692 – 27 July 1770) was a British colonial administrator who served as lieutenant governor of colonial Virginia from 1751 to 1758, first under Governor Willem Anne van Keppel, 2nd Earl of Albemarle, and then, from July 1756 ...
, appointed George Washington as a major and commander of one of the four militia districts. The British and French were competing for control of the
Ohio Valley
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinoi ...
. While the British were constructing forts along the Ohio River, the French were doing the same—constructing forts between the Ohio River and Lake Erie.
In October 1753, Dinwiddie appointed Washington as a special envoy. He had sent George to demand French forces to vacate land that was being claimed by the British. Washington was also appointed to make peace with the
Iroquois Confederacy
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
, and to gather further intelligence about the French forces. Washington met with Half-King
Tanacharison
Tanacharison (; c. 1700 – 4 October 1754), also called Tanaghrisson (), was a Native American leader who played a pivotal role in the beginning of the French and Indian War. He was known to European-Americans as the Half-King, a title also ...
, and other Iroquois chiefs, at
Logstown
"extensive flats"
, settlement_type = Historic Native American village
, image_skyline = Image:Logstown1.jpg
, imagesize = 220px
, image_alt =
, image_map1 = Pennsylvania in United States ...
, and gathered information about the numbers and locations of the French forts, as well as intelligence concerning individuals taken prisoner by the French. Washington was given the nickname
Conotocaurius (town destroyer or devourer of villages) by Tanacharison. The nickname had previously been given to his great-grandfather
John Washington
John Washington (1633–1677) was an English merchant who emigrated across the Atlantic Ocean and became a planter, soldier and politician in colonial Virginia. In addition to leading the local militia, and running his own plantations, Washin ...
in the late seventeenth century by the
Susquehannock
The Susquehannock people, also called the Conestoga by some English settlers or Andastes were Iroquoian Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries, ranging from its upper reaches in the southern p ...
.
Washington's party reached the Ohio River in November 1753, and was intercepted by a French patrol. The party was escorted to
Fort Le Boeuf
Fort Le Bœuf (often referred to as Fort de la Rivière au Bœuf) was a fort established by the French during 1753 on a fork of French Creek (in the drainage area of the River Ohio), in present-day Waterford, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort ...
, where Washington was received in a friendly manner. He delivered the British demand to vacate to the French commander
Saint-Pierre, but the French refused to leave. Saint-Pierre gave Washington his official answer in a sealed envelope after a few days' delay, as well as food and extra winter clothing for his party's journey back to Virginia. Washington completed the precarious mission in 77 days, in difficult winter conditions, achieving a measure of distinction when his report was published in Virginia and in London.
French and Indian War
In February 1754, Dinwiddie promoted Washington to lieutenant colonel and second-in-command of the 300-strong
Virginia Regiment
The Virginia Regiment was formed in 1754 by Virginia's Royal Governor Robert Dinwiddie, as a provincial corps. The regiment served in the French and Indian War, with members participating in actions at Jumonville Glen and Fort Necessity in 1754, ...
, with orders to confront French forces at the
Forks of the Ohio
Point State Park (locally known as The Point) is a Pennsylvania state park on in Downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, forming the Ohio River.
Built on land acqu ...
. Washington set out for the Forks with half the regiment in April and soon learned a French force of 1,000 had begun construction of
Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
there. In May, having set up a
defensive position
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
at Great Meadows, he learned that the French had made camp seven miles (11 km) away; he decided to take the offensive.

The French detachment proved to be only about fifty men, so Washington advanced on May 28 with a small force of Virginians and Indian allies to ambush them. What took place, known as the
Battle of Jumonville Glen
The Battle of Jumonville Glen, also known as the Jumonville affair, was the opening battle of the French and Indian War, fought on May 28, 1754, near present-day Hopwood and Uniontown in Fayette County, Pennsylvania. A company of provincial ...
or the "Jumonville affair", was disputed, and French forces were killed outright with muskets and hatchets. French commander
Joseph Coulon de Jumonville
Joseph Coulon de Villiers, Sieur de Jumonville (September 8, 1718 – May 28, 1754) was a French Canadian military officer. His defeat and killing at the Battle of Jumonville Glen by forces led by George Washington was one of the sparks that igni ...
, who carried a diplomatic message for the British to evacuate, was killed. French forces found Jumonville and some of his men dead and scalped and assumed Washington was responsible. Washington blamed his translator for not communicating the French intentions. Dinwiddie congratulated Washington for his victory over the French. This incident ignited the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
, which later became part of the larger
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
.
The full Virginia Regiment joined Washington at Fort Necessity the following month with news that he had been promoted to command of the regiment and colonel upon the regimental commander's death. The regiment was reinforced by an
independent company of a hundred South Carolinians led by Captain
James Mackay, whose royal commission outranked that of Washington, and a conflict of command ensued. On July 3, a French force attacked with 900 men, and the
ensuing battle ended in Washington's surrender. In the aftermath, Colonel
James Innes took command of intercolonial forces, the Virginia Regiment was divided, and Washington was offered a captaincy which he refused, with the resignation of his commission.

In 1755, Washington served voluntarily as an aide to General
Edward Braddock
Major-General Edward Braddock (January 1695 – 13 July 1755) was a British officer and commander-in-chief for the Thirteen Colonies during the start of the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the North American front of what is known in Europe ...
, who led a British
expedition to expel the French from Fort Duquesne and the Ohio Country. On Washington's recommendation, Braddock split the army into one main column and a lightly equipped "flying column". Suffering from a severe case of
dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
, Washington was left behind, and when he rejoined Braddock at Monongahela the French and their Indian allies
ambushed the divided army. Two-thirds of the British force became casualties, including the mortally wounded Braddock. Under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Thomas Gage, Washington, still very ill, rallied the survivors and formed a rear guard, allowing the remnants of the force to disengage and retreat. During the engagement, he had two horses shot from under him, and his hat and coat were bullet-pierced. His conduct under fire redeemed his reputation among critics of his command in the Battle of Fort Necessity, but he was not included by the succeeding commander (Colonel Thomas Dunbar) in planning subsequent operations.
The Virginia Regiment was reconstituted in August 1755, and Dinwiddie appointed Washington its commander, again with the rank of colonel. Washington clashed over seniority almost immediately, this time with
John Dagworthy, another captain of superior royal rank, who commanded a detachment of Marylanders at the regiment's headquarters in
Fort Cumberland
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
. Washington, impatient for an offensive against Fort Duquesne, was convinced Braddock would have granted him a royal commission and pressed his case in February 1756 with Braddock's successor as
Commander-in-Chief,
William Shirley
William Shirley (2 December 1694 – 24 March 1771) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator who served as the governor of the British American colonies of Massachusetts Bay and the Bahamas. He is best known for his role in organi ...
, and again in January 1757 with Shirley's successor,
Lord Loudoun
General John Campbell, 4th Earl of Loudoun (5 May 1705 – 27 April 1782) was a Scottish nobleman and British army officer.
Early career
Born in Scotland two years before the creation of the Kingdom of Great Britain, in which his father Hugh ...
. Shirley ruled in Washington's favor only in the matter of Dagworthy; Loudoun humiliated Washington, refused him a royal commission and agreed only to relieve him of the responsibility of manning Fort Cumberland.
In 1758, the Virginia Regiment was assigned to the British
Forbes Expedition
The Forbes Expedition was a British military expedition to capture Fort Duquesne, led by Brigadier-General John Forbes in 1758, during the French and Indian War. While advancing to the fort, the expedition built the now historic trail, the Forbes ...
to capture Fort Duquesne. Washington disagreed with General
John Forbes' tactics and chosen route. Forbes nevertheless made Washington a
brevet
Brevet may refer to:
Military
* Brevet (military), higher rank that rewards merit or gallantry, but without higher pay
* Brevet d'état-major, a military distinction in France and Belgium awarded to officers passing military staff college
* Aircre ...
brigadier general and gave him command of one of the three brigades that would assault the fort. The French abandoned the fort and the valley before the assault was launched; Washington saw only a friendly fire incident which left 14 dead and 26 injured. The war lasted another four years, and Washington resigned his commission and returned to Mount Vernon.
Under Washington, the Virginia Regiment had defended of frontier against twenty Indian attacks in ten months. He increased the professionalism of the regiment as it increased from 300 to 1,000 men, and Virginia's frontier population suffered less than other colonies. Some historians have said this was Washington's "only unqualified success" during the war. Though he failed to realize a royal commission, he did gain self-confidence, leadership skills, and invaluable knowledge of British military tactics. The destructive competition Washington witnessed among colonial politicians fostered his later support of a strong central government.
Marriage, civilian, and political life (1755–1775)
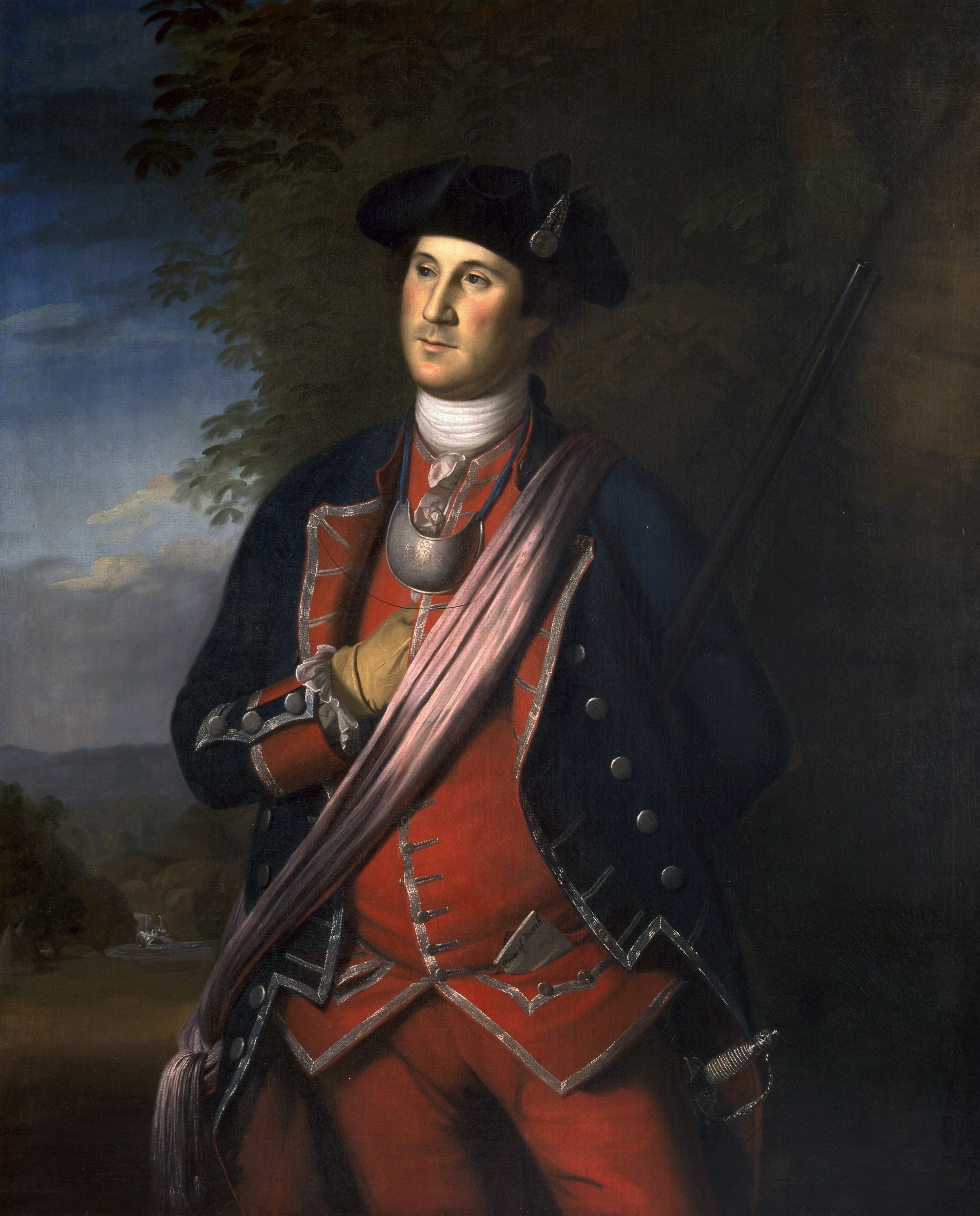

On January 6, 1759, Washington, at age 26, married
Martha Dandridge Custis
Martha Dandridge Custis Washington (June 21, 1731 — May 22, 1802) was the wife of George Washington, the first president of the United States. Although the title was not coined until after her death, Martha Washington served as the inaugural ...
, the 27-year-old widow of wealthy plantation owner
Daniel Parke Custis
Daniel Parke Custis (October 15, 1711 – July 8, 1757) was an American planter and politician who was the first husband of Martha Dandridge. After his death, Dandridge married George Washington, who later became the first president of the Unite ...
. The marriage took place at Martha's estate; she was intelligent, gracious, and experienced in managing a planter's estate, and the couple created a happy marriage. They raised
John Parke Custis
John Parke Custis (November 27, 1754 – November 5, 1781) was an American planter. He was a son of Martha Washington and stepson of George Washington.
Childhood
A son of Daniel Parke Custis, a wealthy planter with nearly three hundred enslaved ...
(Jacky) and
Martha Parke Custis
Martha "Patsy" Parke Custis (1756 – June 19, 1773) was the stepdaughter of George Washington who died from an epileptic seizure at the age of 17, fifteen years before he was elected as the first president of the United States in 1788. She was ...
(Patsy), children from her previous marriage, and later Jacky's children
Eleanor Parke Custis Eleanor Parke Custis may refer to:
* Eleanor Parke Custis Lewis (1779–1854), known as Nelly, step-granddaughter of George Washington
* Eleanor Parke Custis (artist) (1897–1983), American painter and photographer
{{disambig ...
(Nelly) and
George Washington Parke Custis
George Washington Parke Custis (April 30, 1781 – October 10, 1857) was an American plantation owner, antiquarian, author, and playwright. His father John Parke Custis was the stepson of George Washington. He and his sister Eleanor grew u ...
(Washy). Washington's 1751 bout with smallpox is thought to have rendered him sterile, though it is equally likely that "Martha may have sustained injury during the birth of Patsy, her final child, making additional births impossible." The couple lamented not having any children together. They moved to Mount Vernon, near
Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
, where he took up life as a planter of tobacco and wheat and emerged as a political figure.
The marriage gave Washington control over Martha's one-third
dower
Dower is a provision accorded traditionally by a husband or his family, to a wife for her support should she become widowed. It was settled on the bride (being gifted into trust) by agreement at the time of the wedding, or as provided by law.
...
interest in the
Custis estate, and he managed the remaining two-thirds for Martha's children; the estate also included 84 slaves. He became one of Virginia's wealthiest men, which increased his social standing.
At Washington's urging, Governor
Lord Botetourt
Baron Botetourt ( ) is an abeyant title in the Peerage of England. It was created by writ of summons on 19 June 1305. It became abeyant in 1406, was recalled from abeyance in 1764 for Norborne Berkeley. However, it became abeyant again on his dea ...
fulfilled Dinwiddie's 1754 promise of land bounties to all-volunteer militia during the French and Indian War. In late 1770, Washington inspected the lands in the
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
and
Great Kanawha
The Kanawha River ( ) is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 97 mi (156 km) long, in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The largest inland waterway in West Virginia, its valley has been a significant industrial region of the stat ...
regions, and he engaged surveyor
William Crawford William Crawford may refer to:
Entertainment
* William Broderick Crawford (1911–1986), American film actor
* Bill Crawford (cartoonist) (1913–1982), American editorial cartoonist
* William L. Crawford (1911–1984), U.S. publisher and editor
...
to subdivide it. Crawford allotted to Washington; Washington told the veterans that their land was hilly and unsuitable for farming, and he agreed to purchase , leaving some feeling they had been duped. He also doubled the size of Mount Vernon to and increased its slave population to more than a hundred by 1775.
Washington's political activities included supporting the candidacy of his friend
George William Fairfax
George William Fairfax (January 2, 1724April 3, 1787) was a Planter (American South), planter in colonial Virginia who represented then-vast Frederick County, Virginia, Frederick County and later Fairfax County, Virginia, Fairfax County in the Hou ...
in his 1755 bid to represent the region in the
Virginia House of Burgesses
The House of Burgesses was the elected representative element of the Virginia General Assembly, the legislative body of the Colony of Virginia. With the creation of the House of Burgesses in 1642, the General Assembly, which had been established ...
. This support led to a dispute which resulted in a physical altercation between Washington and another Virginia planter,
William Payne. Washington defused the situation, including ordering officers from the
Virginia Regiment
The Virginia Regiment was formed in 1754 by Virginia's Royal Governor Robert Dinwiddie, as a provincial corps. The regiment served in the French and Indian War, with members participating in actions at Jumonville Glen and Fort Necessity in 1754, ...
to stand down. Washington apologized to Payne the following day at a tavern. Payne had been expecting to be challenged to a duel.
As a respected military hero and large landowner, Washington held local offices and was elected to the Virginia provincial legislature, representing Frederick County in the House of Burgesses for seven years beginning in 1758. He plied the voters with beer, brandy, and other beverages, although he was absent while serving on the Forbes Expedition. He won the election with roughly 40 percent of the vote, defeating three other candidates with the help of several local supporters. He rarely spoke in his early legislative career, but he became a prominent critic of Britain's taxation policy and mercantilist policies towards the American colonies starting in the 1760s.

By occupation, Washington was a planter, and he imported luxuries and other goods from England, paying for them by exporting tobacco. His profligate spending combined with low tobacco prices left him £1,800 in debt by 1764, prompting him to diversify his holdings. In 1765, because of erosion and other soil problems, he changed Mount Vernon's primary cash crop from tobacco to wheat and expanded operations to include corn
flour milling
A gristmill (also: grist mill, corn mill, flour mill, feed mill or feedmill) grinds cereal grain into flour and Wheat middlings, middlings. The term can refer to either the Mill (grinding), grinding mechanism or the building that holds it. Grist i ...
and fishing. Washington also took time for leisure with fox hunting, fishing, dances, theater, cards, backgammon, and billiards.
Washington soon was counted among the political and social elite in Virginia. From 1768 to 1775, he invited some 2,000 guests to his Mount Vernon estate, mostly those whom he considered people of rank, and was known to be exceptionally cordial toward his guests. He became more politically active in 1769, presenting legislation in the
Virginia Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, the first elected legislative assembly in the New World, and was established on July 30, 1619 ...
to establish an embargo on goods from Great Britain.
Washington's step-daughter Patsy Custis suffered from epileptic attacks from age 12, and she died in his arms in 1773. The following day, he wrote to
Burwell Bassett
Burwell Bassett, Jr. (March 18, 1764 – February 26, 1841) was an American planter and politician from New Kent County and for two decades from Williamsburg in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Like his father, he served in both chambers of the ...
: "It is easier to conceive, than to describe, the distress of this Family". He canceled all business activity and remained with Martha every night for three months.
Opposition to British Parliament and Crown
Washington played a central role before and during the
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
. His distrust of the British military had begun when he was passed over for promotion into the Regular Army. Opposed to taxes imposed by the British Parliament on the Colonies without
proper representation, he and other colonists were also angered by the
Royal Proclamation of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The Procla ...
which banned American settlement west of the
Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range (; also spelled Alleghany or Allegany), informally the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada and posed a significant barrier to land travel in less devel ...
and protected the
British fur trade.
Washington believed the
Stamp Act of 1765
The Stamp Act 1765, also known as the Duties in American Colonies Act 1765 (5 Geo. III c. 12), was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain which imposed a direct tax on the British colonies in America and required that many printed materials ...
was an "Act of Oppression", and he celebrated its repeal the following year. In March 1766, Parliament passed the
Declaratory Act
The American Colonies Act 1766 (6 Geo. III c 12), commonly known as the Declaratory Act, was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain which accompanied the repeal of the Stamp Act 1765 and the amendment of the Sugar Act. Parliament repealed ...
asserting that Parliamentary law superseded colonial law. In the late 1760s, the interference of the British Crown in American lucrative western land speculation spurred on the American Revolution.
Washington himself was a prosperous land speculator, and in 1767, he encouraged "adventures" to acquire backcountry western lands.
Washington helped lead widespread protests against the
Townshend Acts
The Townshend Acts () or Townshend Duties, were a series of British acts of Parliament passed during 1767 and 1768 introducing a series of taxes and regulations to fund administration of the British colonies in America. They are named after the ...
passed by Parliament in 1767, and he introduced a proposal in May 1769 drafted by
George Mason
George Mason (October 7, 1792) was an American planter, politician, Founding Father, and delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787, one of the three delegates present who refused to sign the Constitution. His writings, including s ...
which called Virginians to boycott British goods; the Acts were mostly repealed in 1770.
Parliament sought to punish Massachusetts colonists for their role in the
Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was an American political and mercantile protest by the Sons of Liberty in Boston, Massachusetts, on December 16, 1773. The target was the Tea Act of May 10, 1773, which allowed the British East India Company to sell tea ...
in 1774 by passing the
Coercive Acts
The Intolerable Acts were a series of punitive laws passed by the British Parliament in 1774 after the Boston Tea Party. The laws aimed to punish Massachusetts colonists for their defiance in the Tea Party protest of the Tea Act, a tax measure ...
, which Washington referred to as "an invasion of our rights and privileges". He said Americans must not submit to acts of tyranny since "custom and use shall make us as tame and abject slaves, as the blacks we rule over with such arbitrary sway". That July, he and George Mason drafted a list of resolutions for the
Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is part of Northern Virginia and borders both the city of Alexandria and Arlington County and forms part of the suburban ring of Washington, D.C. ...
committee which Washington chaired, and the committee adopted the
Fairfax Resolves
The Fairfax Resolves were a set of resolutions adopted by a committee in Fairfax County in the colony of Virginia on July 18, 1774, in the early stages of the American Revolution. Written at the behest of George Washington and others, they were a ...
calling for a Continental Congress, and an end to the slave trade. On August 1, Washington attended the
First Virginia Convention
The Virginia Conventions have been the assemblies of delegates elected for the purpose of establishing constitutions of fundamental law for the Commonwealth of Virginia superior to General Assembly legislation. Their constitutions and subseque ...
, where he was selected as a delegate to the
First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
, September 5 to October 26, 1774, which he also attended. As tensions rose in 1774, he helped train county militias in Virginia and organized enforcement of the
Continental Association
The Continental Association, also known as the Articles of Association or simply the Association, was an agreement among the American colonies adopted by the First Continental Congress on October 20, 1774. It called for a trade boycott against ...
boycott of British goods instituted by the Congress.
The
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
began on April 19, 1775, with the
Battles of Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord ...
and the
Siege of Boston
The siege of Boston (April 19, 1775 – March 17, 1776) was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War. New England militiamen prevented the movement by land of the British Army, which was garrisoned in what was then the peninsular town ...
. The colonists were divided over breaking away from British rule and split into two factions:
Patriots who rejected British rule, and
Loyalists
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cr ...
who desired to remain subject to the King. General
Thomas Gage
General Thomas Gage (10 March 1718/192 April 1787) was a British Army general officer and colonial official best known for his many years of service in North America, including his role as British commander-in-chief in the early days of the ...
was commander of British forces in America at the beginning of the war. Upon hearing the shocking news of the onset of war, Washington was "sobered and dismayed", and he hastily departed Mount Vernon on May 4, 1775, to join the
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
in
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
.
Commander in chief (1775–1783)

Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
created the
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
on June 14, 1775, and
Samuel
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bibl ...
and
John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
nominated Washington to become its
commander-in-chief. Washington was chosen over
John Hancock
John Hancock ( – October 8, 1793) was an American Founding Father, merchant, statesman, and prominent Patriot of the American Revolution. He served as president of the Second Continental Congress and was the first and third Governor of the ...
because of his military experience and the belief that a Virginian would better unite the colonies. He was considered an incisive leader who kept his "ambition in check". He was unanimously elected commander in chief by Congress the next day.
Washington appeared before Congress in uniform and gave an acceptance speech on June 16, declining a salary—though he was later reimbursed expenses. He was commissioned on June 19 and was roundly praised by Congressional delegates, including John Adams, who proclaimed that he was the man best suited to lead and unite the colonies. Congress appointed Washington "General & Commander in chief of the army of the
United Colonies
The "United Colonies" was the name used by the Second Continental Congress for the emerging nation comprising the Thirteen Colonies in 1775 and 1776, before and as independence was declared. Continental currency banknotes displayed the name 'The ...
and of all the forces raised or to be raised by them", and instructed him to take charge of the siege of Boston on June 22, 1775.
Congress chose his primary staff officers, including Major General
Artemas Ward
Artemas Ward (November 26, 1727 – October 28, 1800) was an American major general in the American Revolutionary War and a Congressman from Massachusetts. He was considered an effective political leader, President John Adams describing him as ...
, Adjutant General
Horatio Gates
Horatio Lloyd Gates (July 26, 1727April 10, 1806) was a British-born American army officer who served as a general in the Continental Army during the early years of the Revolutionary War. He took credit for the American victory in the Battles ...
, Major General
Charles Lee, Major General
Philip Schuyler
Philip John Schuyler (; November 18, 1804) was an American general in the Revolutionary War and a United States Senator from New York. He is usually known as Philip Schuyler, while his son is usually known as Philip J. Schuyler.
Born in Alba ...
, Major General
Nathanael Greene
Nathanael Greene (June 19, 1786, sometimes misspelled Nathaniel) was a major general of the Continental Army in the American Revolutionary War. He emerged from the war with a reputation as General George Washington's most talented and dependabl ...
, Colonel
Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806), a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the ...
, and Colonel
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
. Washington was impressed by Colonel
Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold ( Brandt (1994), p. 4June 14, 1801) was an American military officer who served during the Revolutionary War. He fought with distinction for the American Continental Army and rose to the rank of major general before defect ...
and gave him responsibility for launching an invasion of Canada. He also engaged French and Indian War compatriot Brigadier General
Daniel Morgan
Daniel Morgan (1735–1736July 6, 1802) was an American pioneer, soldier, and politician from Virginia. One of the most respected battlefield tacticians of the American Revolutionary War of 1775–1783, he later commanded troops during the sup ...
. Henry Knox impressed Adams with ordnance knowledge, and Washington promoted him to colonel and chief of artillery.
At the start of the war, Washington opposed the recruiting of blacks, both free and enslaved, into the Continental Army. After his appointment, Washington banned their enlistment. The British saw an opportunity to divide the colonies, and the colonial governor of Virginia issued
a proclamation, which promised freedom to slaves if they joined the British. Desperate for manpower by late 1777, Washington relented and overturned his ban. By the end of the war, around one-tenth of Washington's army were blacks. Following the British surrender, Washington sought to enforce terms of the preliminary
Treaty of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed in Paris by representatives of George III, King George III of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and representatives of the United States, United States of America on September 3, 1783, officially ended the Ame ...
by reclaiming slaves freed by the British and returning them to servitude. He arranged to make this request to
Sir Guy Carleton
Guy Carleton, 1st Baron Dorchester (3 September 1724 – 10 November 1808), known between 1776 and 1786 as Sir Guy Carleton, was an Anglo-Irish soldier and administrator. He twice served as Governor of the Province of Quebec, from 1768 to 17 ...
on May 6, 1783. Instead, Carleton issued 3,000 freedom certificates and all former slaves in New York City were able to leave before the city was evacuated by the British in late November 1783.
Siege of Boston

Early in 1775, in response to the growing rebellious movement, London sent British troops, commanded by
General Thomas Gage
General (United Kingdom), General Thomas Gage (10 March 1718/192 April 1787) was a British Army general officer and Colonialism, colonial official best known for his many years of service in North America, including his role as British Comman ...
, to occupy Boston. They set up fortifications about the city, making it impervious to attack. Various local militias surrounded the city and effectively trapped the British, resulting in a standoff.
As Washington headed for Boston, word of his march preceded him, and he was greeted everywhere; gradually, he became a symbol of the Patriot cause. Upon arrival on July 2, 1775, two weeks after the Patriot defeat at nearby
Bunker Hill, he set up his
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston, ...
headquarters and inspected the new army there, only to find an undisciplined and badly outfitted militia. After consultation, he initiated
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
's suggested reforms—drilling the soldiers and imposing strict discipline, floggings, and incarceration. Washington ordered his officers to identify the skills of recruits to ensure military effectiveness, while removing incompetent officers. He petitioned Gage, his former superior, to release captured Patriot officers from prison and treat them humanely. In October 1775, King
George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
declared that the colonies were in open rebellion and relieved General Gage of command for incompetence, replacing him with General
William Howe.
The Continental Army, further diminished by expiring short-term enlistments, and by January 1776 reduced by half to 9,600 men, had to be supplemented with the militia, and was joined by
Knox with heavy artillery captured from
Fort Ticonderoga
Fort Ticonderoga (), formerly Fort Carillon, is a large 18th-century star fort built by the French at a narrows near the south end of Lake Champlain, in northern New York, in the United States. It was constructed by Canadian-born French mi ...
. When the
Charles River
The Charles River ( Massachusett: ''Quinobequin)'' (sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles) is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton to Boston along a highly meandering route, that doubles b ...
froze over, Washington was eager to cross and storm Boston, but General Gates and others were opposed to untrained militia striking well-garrisoned fortifications. Washington reluctantly agreed to
secure the Dorchester Heights, 100 feet above Boston, in an attempt to force the British out of the city. On March 9, under cover of darkness, Washington's troops brought up Knox's big guns and bombarded British ships in Boston harbor. On
March 17
Events Pre-1600
* 45 BC – In his last victory, Julius Caesar defeats the Pompeian forces of Titus Labienus and Pompey the Younger in the Battle of Munda.
* 180 – Commodus becomes sole emperor of the Roman Empire at the age of eigh ...
, 9,000 British troops and Loyalists began a chaotic ten-day evacuation of Boston aboard 120 ships. Soon after, Washington entered the city with 500 men, with explicit orders not to plunder the city. He ordered
variolation
Variolation was the method of inoculation first used to immunize individuals against smallpox (''Variola'') with material taken from a patient or a recently variolated individual, in the hope that a mild, but protective, infection would result. Var ...
against smallpox to great effect, as he did later in Morristown, New Jersey. He refrained from exerting military authority in Boston, leaving civilian matters in the hands of local authorities.
Invasion of Quebec (1775)
The Invasion of Quebec (June 1775 – October 1776, French: Invasion du Québec) was the first major military initiative by the newly formed Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. On June 27, 1775, Congress authorized General Philip Schuyler to investigate, and, if it seemed appropriate, begin an invasion. Benedict Arnold, passed over for its command, went to Boston and convinced General George Washington to send a supporting force to Quebec City under his command. The objective of the campaign was to seize the Province of Quebec (part of modern-day Canada) from Great Britain, and persuade French-speaking
Canadiens
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fren ...
to join the revolution on the side of the Thirteen Colonies. One expedition left Fort Ticonderoga under Richard Montgomery, besieged and captured Fort St. Johns, and very nearly captured British General Guy Carleton when taking Montreal. The other expedition, under Benedict Arnold, left Cambridge, Massachusetts and traveled with great difficulty through the wilderness of Maine to Quebec City. The two forces joined there, but they were defeated at the Battle of Quebec in December 1775, where Montgomery died.
Battle of Long Island
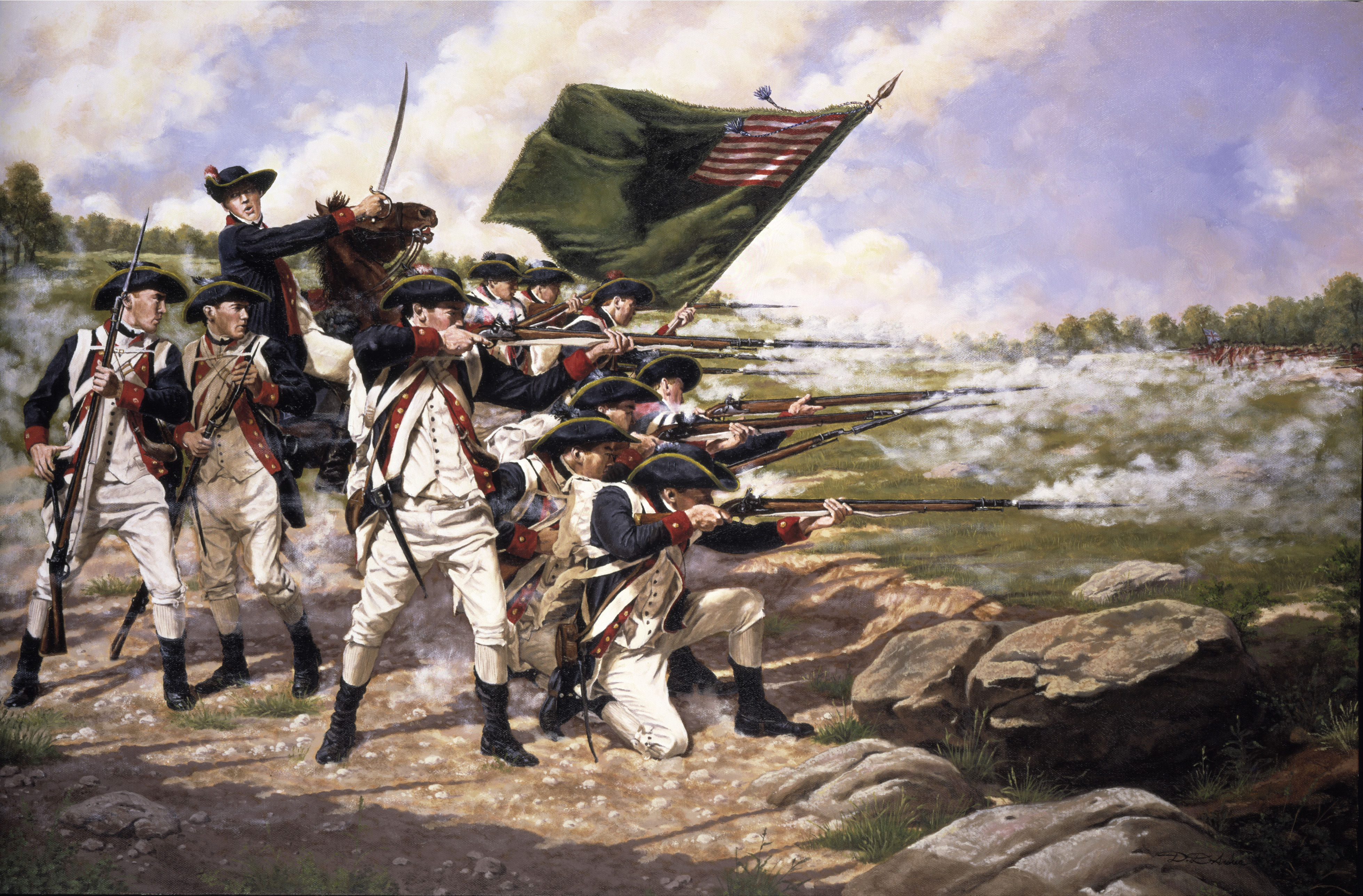

Washington then proceeded to
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, arriving on April 13, 1776, and began constructing fortifications to thwart the expected British attack. He ordered his occupying forces to treat civilians and their property with respect, to avoid the abuses which Bostonian citizens suffered at the hands of British troops during their occupation. A plot to assassinate or capture him was discovered and thwarted, resulting in the arrest of 98 people involved or complicit (56 of which were from Long Island (
Kings (Brooklyn) and
Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
counties)), including the Loyalist Mayor of New York
David Mathews
David Mathews ( – July 28, 1800) was an American lawyer and politician from New York City. He was a Loyalist during the American Revolutionary War and was the 43rd and last Colonial Mayor of New York City from 1776 until 1783. As New York City ...
. Washington's bodyguard,
Thomas Hickey, was hanged for mutiny and sedition. General Howe transported his resupplied army, with the British fleet, from
Halifax to New York, knowing the city was key to securing the continent.
George Germain, who ran the British war effort in England, believed it could be won with one "decisive blow". The British forces, including more than a hundred ships and thousands of troops, began arriving on
Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull an ...
on July2 to lay siege to the city. After the
Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
was adopted on July 4, Washington informed his troops in his general orders of July9 that Congress had declared the united colonies to be "free and independent states".
Howe's troop strength totaled 32,000 regulars and
Hessian auxiliaries, and Washington's consisted of 23,000, mostly raw recruits and militia. In August, Howe landed 20,000 troops at
Gravesend, Brooklyn
Gravesend is a neighborhood in the south-central section of the New York City borough of Brooklyn, on the southwestern edge of Long Island in the U.S. state of New York. It is bounded by the Belt Parkway to the south, Bay Parkway to the west, ...
, and approached Washington's fortifications, as George III proclaimed the rebellious American colonists to be traitors. Washington, opposing his generals, chose to fight, based upon inaccurate information that Howe's army had only 8,000-plus troops. In the
Battle of Long Island
The Battle of Long Island, also known as the Battle of Brooklyn and the Battle of Brooklyn Heights, was an action of the American Revolutionary War fought on August 27, 1776, at the western edge of Long Island in present-day Brooklyn, New Yo ...
, Howe
assaulted Washington's flank and inflicted 1,500 Patriot casualties, the British suffering 400. Washington retreated, instructing General
William Heath
William Heath (March 2, 1737 – January 24, 1814) was an American farmer, soldier, and political leader from Massachusetts who served as a major general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War.
Life and career
Heath m ...
to acquisition river craft in the area. On August 30, General
William Alexander held off the British and gave cover while the army crossed the
East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Queens ...
under darkness to
Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
Island without loss of life or materiel, although Alexander was captured.
Howe, emboldened by his Long Island victory, dispatched Washington as "George Washington, Esq." in futility to negotiate peace. Washington declined, demanding to be addressed with diplomatic protocol, as general and fellow belligerent, not as a "rebel", lest his men are hanged as such if captured. The
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
bombarded the unstable earthworks on lower Manhattan Island. Washington, with misgivings, heeded the advice of Generals Greene and
Putnam to defend
Fort Washington. They were unable to hold it, and Washington abandoned it despite General
Lee
Lee may refer to:
Name
Given name
* Lee (given name), a given name in English
Surname
* Chinese surnames romanized as Li or Lee:
** Li (surname 李) or Lee (Hanzi ), a common Chinese surname
** Li (surname 利) or Lee (Hanzi ), a Chinese ...
's objections, as his army retired north to the
White Plains. Howe's pursuit forced Washington to retreat across the
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
to
Fort Lee to avoid encirclement. Howe landed his troops on Manhattan in November and
captured Fort Washington, inflicting high casualties on the Americans. Washington was responsible for delaying the retreat, though he blamed Congress and General Greene. Loyalists in New York considered Howe a liberator and spread a rumor that Washington had set fire to the city. Patriot morale reached its lowest when Lee was captured. Now reduced to 5,400 troops, Washington's army retreated through
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
, and Howe broke off pursuit, delaying his advance on Philadelphia, and set up winter quarters in New York.
Crossing the Delaware, Trenton, and Princeton
Washington crossed the
Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
into Pennsylvania, where Lee's replacement
John Sullivan joined him with 2,000 more troops. The future of the Continental Army was in doubt for lack of supplies, a harsh winter, expiring enlistments, and desertions. Washington was disappointed that many New Jersey residents were Loyalists or skeptical about the prospect of independence.
Howe split up his British Army and posted a
Hessian
A Hessian is an inhabitant of the German state of Hesse.
Hessian may also refer to:
Named from the toponym
*Hessian (soldier), eighteenth-century German regiments in service with the British Empire
**Hessian (boot), a style of boot
**Hessian f ...
garrison at
Trenton to hold western New Jersey and the east shore of the Delaware, but the army appeared complacent, and Washington and his generals devised a surprise attack on the Hessians at Trenton, which he codenamed "Victory or Death". The army was to cross the Delaware River to Trenton in three divisions: one led by Washington (2,400 troops), another by General
James Ewing (700), and the third by Colonel
John Cadwalader (1,500). The force was to then split, with Washington taking the
Pennington Road and General Sullivan traveling south on the river's edge.

Washington first ordered a 60-mile search for
Durham boat
The Durham boat was a large wooden, flat-bottomed, double-ended freight boat which was in use on many of the interior waterways of North America beginning in the middle of the eighteenth century. They were replaced by larger, more efficient canal ...
s to transport his army, and he ordered the destruction of vessels that could be used by the British. Washington
crossed the Delaware River on
Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus, Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by country, around t ...
night, December 25, 1776, while he personally risked capture staking out the Jersey shoreline. His men followed across the ice-obstructed river in sleet and snow from
McConkey's Ferry
Washington Crossing Historic Park is a 500-acre (2 km2) state park operated by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources in partnership with the Friends of Washington Crossing Park. The park is divided into two sectio ...
, with 40 men per vessel. The wind churned up the waters, and they were pelted with hail, but by 3:00a.m. on December 26, they made it across with no losses. Henry Knox was delayed, managing frightened horses and about 18 field guns on flat-bottomed ferries. Cadwalader and Ewing failed to cross due to the ice and heavy currents, and awaiting Washington doubted his planned attack on Trenton. Once Knox arrived, Washington proceeded to Trenton to take only his troops against the Hessians, rather than risk being spotted returning his army to Pennsylvania.
The troops spotted Hessian positions a mile from Trenton, so Washington split his force into two columns, rallying his men: "Soldiers keep by your officers. For God's sake, keep by your officers." The two columns were separated at the Birmingham crossroads. General Nathanael Greene's column took the upper Ferry Road, led by Washington, and General John Sullivan's column advanced on River Road. (
See map.) The Americans marched in sleet and snowfall. Many were shoeless with bloodied feet, and two died of exposure. Meanwhile, Hessian Commander
Johann Rall
Johann Gottlieb Rall (also spelled Rahl) (December 27, 1776) was a German colonel best known for his command of Hessian troops at the Battle of Trenton during the American Revolutionary War.
Early life and education
Rall was born as a so-called ...
was held up at the home of
Abraham Hunt
Abraham Hunt (1741–1821) was a wealthy American merchant and farmer in Trenton, New Jersey, first Postmaster of Trenton, and served in the American Revolutionary War as a Lieutenant Colonel in the Hunterton County militia. He was a prominent ...
, of Trenton, who had placated Rall and some of his officers with plenty of food and drink into the late hours of the evening and morning. At sunrise, Washington, aided by Major General Knox and artillery, led his men in a surprise attack on an unsuspecting Rall. The Hessians had 22 killed, including Colonel Rall, 83 wounded, and 850 captured with supplies.

Washington retreated across the Delaware River to Pennsylvania and returned to New Jersey on January 3, 1777, launching
an attack on British regulars at
Princeton
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the nine ...
, with 40 Americans killed or wounded and 273 British killed or captured. American Generals
Hugh Mercer
Hugh Mercer (16 January 1726 – 12 January 1777) was a Scottish-born American military officer and physician who participated in the Seven Years' War and Revolutionary War. Born in Pitsligo, Scotland, he studied medicine in his home country ...
and John Cadwalader were being driven back by the British when Mercer was mortally wounded, then Washington arrived and led the men in a counterattack which advanced to within of the British line.
Some British troops retreated after a brief stand, while others took refuge in
Nassau Hall
Nassau Hall, colloquially known as Old Nassau, is the oldest building at Princeton University in Princeton, Mercer County, New Jersey, United States. In 1783 it served as the United States Capitol building for four months. At the time it was built ...
, which became the target of Colonel
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
's cannons. Washington's troops charged, the British surrendered in less than an hour, and 194 soldiers laid down their arms. Howe retreated to New York City where his army remained inactive until early the next year. From January to May, Washington took up winter headquarters in
Jacob Arnold's Tavern in
, while he received munition from
Hibernia mines
The Hibernia mines are a series of iron mines in and around Rockaway Township, in Morris County, New Jersey, United States, that were worked from pre- Revolutionary times until 1916. The mines worked a vein extending for more than . Several compa ...
. Meanwhile, "his troops stayed in
ocals�� homes" or camped in the
Loantaka Valley to the east. While in Morristown, Washington disrupted British supply lines and expelled them from parts of New Jersey. Washington later said the British could have successfully counterattacked his encampment before his troops were dug in. The victories at Trenton and Princeton by Washington revived Patriot morale and changed the course of the war.
The British still controlled New York, and many Patriot soldiers did not re-enlist or deserted after the harsh winter campaign. Congress instituted greater rewards for re-enlisting and punishments for desertion to effect greater troop numbers. Strategically, Washington's victories were pivotal for the Revolution and quashed the British strategy of showing overwhelming force followed by offering generous terms. In February 1777, word reached London of the American victories at Trenton and Princeton, and the British realized the Patriots were in a position to demand unconditional independence.
Brandywine, Germantown, and Saratoga
In July 1777, British General
John Burgoyne
General John Burgoyne (24 February 1722 – 4 August 1792) was a British general, dramatist and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1761 to 1792. He first saw action during the Seven Years' War when he participated in several batt ...
led the
Saratoga campaign
The Saratoga campaign in 1777 was an attempt by the British high command for North America to gain military control of the strategically important Hudson River valley during the American Revolutionary War. It ended in the surrender of the British ...
south from Quebec through
Lake Champlain
, native_name_lang =
, image = Champlainmap.svg
, caption = Lake Champlain-River Richelieu watershed
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = New York/Vermont in the United States; and Quebec in Canada
, coords =
, type =
, ...
and
recaptured Fort Ticonderoga intending to divide
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
, including control of the
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
. However, General Howe in British-occupied New York blundered, taking his army south to Philadelphia rather than up the Hudson River to join Burgoyne near
Albany. Meanwhile, Washington and
Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de Lafayette
Marie-Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de La Fayette (6 September 1757 – 20 May 1834), known in the United States as Lafayette (, ), was a French aristocrat, freemasonry, freemason and military officer who fought in the Ameri ...
rushed to Philadelphia to engage Howe and were shocked to learn of Burgoyne's progress in upstate New York, where the Patriots were led by General
Philip Schuyler
Philip John Schuyler (; November 18, 1804) was an American general in the Revolutionary War and a United States Senator from New York. He is usually known as Philip Schuyler, while his son is usually known as Philip J. Schuyler.
Born in Alba ...
and successor
Horatio Gates
Horatio Lloyd Gates (July 26, 1727April 10, 1806) was a British-born American army officer who served as a general in the Continental Army during the early years of the Revolutionary War. He took credit for the American victory in the Battles ...
. Washington's army of less experienced men were defeated in the
pitched battles at Philadelphia.
Howe outmaneuvered Washington at the
Battle of Brandywine
The Battle of Brandywine, also known as the Battle of Brandywine Creek, was fought between the American Continental Army of General George Washington and the British Army of General Sir William Howe on September 11, 1777, as part of the Ame ...
on September 11, 1777, and marched unopposed into the nation's capital at Philadelphia. A Patriot
attack failed against the British at
Germantown Germantown or German Town may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Germantown, Queensland, a locality in the Cassowary Coast Region
United States
* Germantown, California, the former name of Artois, a census-designated place in Glenn County
* Ger ...
in October. Major General
Thomas Conway
Thomas Conway (February 27, 1735 – c. 1800) served as a major general in the American Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. He became involved with the alleged Conway Cabal with Horatio Gates. He later served with Émigré for ...
prompted some members of Congress (referred to as the
Conway Cabal
The Conway Cabal was a group of senior Continental Army officers in late 1777 and early 1778 who aimed to have George Washington replaced as commander-in-chief of the Army during the American Revolutionary War. It was named after Brigadier Gen ...
) to consider removing Washington from command because of the losses incurred at Philadelphia. Washington's supporters resisted, and the matter was finally dropped after much deliberation. Once the plot was exposed, Conway wrote an apology to Washington, resigned, and returned to France.
Washington was concerned with Howe's movements during the Saratoga campaign to the north, and he was also aware that Burgoyne was moving south toward Saratoga from Quebec. Washington took some risks to support Gates' army, sending reinforcements north with Generals
Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold ( Brandt (1994), p. 4June 14, 1801) was an American military officer who served during the Revolutionary War. He fought with distinction for the American Continental Army and rose to the rank of major general before defect ...
, his most aggressive field commander, and
Benjamin Lincoln
Benjamin Lincoln (January 24, 1733 ( O.S. January 13, 1733) – May 9, 1810) was an American army officer. He served as a major general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. Lincoln was involved in three major surrender ...
. On October 7, 1777, Burgoyne tried to take
Bemis Heights
The Battles of Saratoga (September 19 and October 7, 1777) marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War. British General John Burgoyne led an invasion ...
but was isolated from support by Howe. He was forced to retreat to Saratoga and ultimately surrendered after the
Battles of Saratoga
The Battles of Saratoga (September 19 and October 7, 1777) marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War. British General John Burgoyne led an invasion ...
. As Washington suspected, Gates' victory emboldened his critics. Biographer John Alden maintains, "It was inevitable that the defeats of Washington's forces and the concurrent victory of the forces in upper New York should be compared." The admiration for Washington was waning, including little credit from John Adams. British commander Howe resigned in May 1778, left America forever, and was replaced by
Sir Henry Clinton.
Valley Forge and Monmouth

Washington's army of 11,000 went into winter quarters at
Valley Forge
Valley Forge functioned as the third of eight winter encampments for the Continental Army's main body, commanded by General George Washington, during the American Revolutionary War. In September 1777, Congress fled Philadelphia to escape the B ...
north of Philadelphia in December 1777. They suffered between 2,000 and 3,000 deaths in the extreme cold over six months, mostly from disease and lack of food, clothing, and shelter. Meanwhile, the British were comfortably quartered in Philadelphia, paying for supplies in
pounds sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO 4217, ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of #Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories, its associated territori ...
, while Washington struggled with a devalued
American paper currency. The woodlands were soon exhausted of game, and by February, lowered morale and increased desertions ensued.
Washington made repeated petitions to the Continental Congress for provisions. He received a congressional delegation to check the Army's conditions and expressed the urgency of the situation, proclaiming: "Something must be done. Important alterations must be made." He recommended that Congress expedite supplies, and Congress agreed to strengthen and fund the army's supply lines by reorganizing the commissary department. By late February, supplies began arriving.

Baron
Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben
Friedrich Wilhelm August Heinrich Ferdinand von Steuben (born Friedrich Wilhelm Ludolf Gerhard Augustin Louis von Steuben; September 17, 1730 – November 28, 1794), also referred to as Baron von Steuben (), was a Prussian military officer who p ...
's incessant drilling soon transformed Washington's recruits into a disciplined fighting force, and the revitalized army emerged from Valley Forge early the following year. Washington promoted Von Steuben to Major General and made him chief of staff.
In early 1778, the French responded to Burgoyne's defeat and entered into a
Treaty of Alliance with the Americans. The Continental Congress ratified the treaty in May, which amounted to a French declaration of war against Britain.
The British evacuated Philadelphia for New York that June and Washington summoned a war council of American and French Generals. He chose a partial attack on the retreating British at the
Battle of Monmouth
The Battle of Monmouth, also known as the Battle of Monmouth Court House, was fought near Monmouth Court House in modern-day Freehold Borough, New Jersey on June 28, 1778, during the American Revolutionary War. It pitted the Continental Army, co ...
; the British were commanded by Howe's successor General
Henry Clinton. Generals
Charles Lee and Lafayette moved with 4,000 men, without Washington's knowledge, and bungled their first attack on June 28. Washington relieved Lee and achieved a draw after an expansive battle. At nightfall, the British continued their retreat to New York, and Washington moved his army outside the city. Monmouth was Washington's last battle in the North; he valued the safety of his army more than towns with little value to the British.
West Point espionage
Washington became "America's first spymaster" by designing an espionage system against the British. In 1778, Major
Benjamin Tallmadge
Benjamin Tallmadge (February 25, 1754 – March 7, 1835) was an American military officer, spymaster, and politician. He is best known for his service as an officer in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. He acted as leade ...
formed the
Culper Ring
The Culper Ring was a network of spies active during the American Revolutionary War, organized by Major Benjamin Tallmadge and General George Washington in 1778 during the British occupation of New York City. The name "Culper" was suggested by ...
at Washington's direction to covertly collect information about the British in New York. Washington had disregarded incidents of disloyalty by
Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold ( Brandt (1994), p. 4June 14, 1801) was an American military officer who served during the Revolutionary War. He fought with distinction for the American Continental Army and rose to the rank of major general before defect ...
, who had distinguished himself in many battles.
During mid-1780, Arnold began supplying British spymaster
John André
John André (2 May 1750/1751[''Gravesite–Memorial''](_blank)
Westmi ...
with sensitive information intended to compromise Washington and capture
West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known Metonymy, metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a f ...
, a key American defensive position on the
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
. Historians have noted as possible reasons for Arnold's defection to be his anger at losing promotions to junior officers, or repeated slights from Congress. He was also deeply in debt, profiteering from the war, and disappointed by Washington's lack of support during his eventual
court-martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of memb ...
.

Arnold repeatedly asked for command of West Point, and Washington finally agreed in August. Arnold met André on September 21, giving him plans to take over the garrison. Militia forces captured André and discovered the plans, but Arnold escaped to New York. Washington recalled the commanders positioned under Arnold at key points around the fort to prevent any complicity, but he did not suspect Arnold's wife
Peggy. Washington assumed personal command at West Point and reorganized its defenses. André's trial for espionage ended in a death sentence, and Washington offered to return him to the British in exchange for Arnold, but
Clinton refused. André was hanged on October 2, 1780, despite his last request being to face a firing squad, to deter other spies.
Southern theater and Yorktown
In late 1778, General Clinton shipped 3,000 troops from New York to Georgia and launched a Southern invasion against
Savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the Canopy (forest), canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to rea ...
, reinforced by 2,000 British and Loyalist troops. They repelled an attack by Patriots and
French naval forces, which bolstered the British war effort.
In June 1778,
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
warriors joined with
Loyalist
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cro ...
rangers led by
Walter Butler and killed more than 200 frontiersmen in June, laying waste to the
Wyoming Valley
The Wyoming Valley is a historic industrialized region of Northeastern Pennsylvania. The region is historically notable for its influence in helping fuel the American Industrial Revolution with its many anthracite coal-mines. As a metropolitan are ...
in Pennsylvania. In mid-1779, in response to this and other attacks on New England towns, Washington ordered General John Sullivan to lead an expedition to force the Iroquois out of New York by effecting "the total destruction and devastation" of their villages and by taking their women and children hostage. The expedition systematically destroyed Iroquois villages and food stocks, and forced at least 5,036 Iroquois to flee to British Canada. The campaign directly killed a few hundred Iroquois, but according to anthropologist
Anthony F. C. Wallace
Anthony Francis Clarke Wallace (April 15, 1923 – October 5, 2015) was a Canadian-American anthropologist who specialized in Native American cultures, especially the Iroquois. His research expressed an interest in the intersection of cultural a ...
, the net effect of the campaign was to reduce the Iroquois by half, who became unable to support themselves or survive the harsh winter of 1779–1780. Rhiannon Koehler estimates that as many as 5,500 Iroquois, around 55.5% of the population, may have perished as a result of the campaign, which some historians have described as genocidal.
Washington's troops went into quarters at Morristown, New Jersey during the winter of 1779–1780 and suffered their worst winter of the war, with temperatures well below freezing.
New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in t ...
was frozen over, snow and ice covered the ground for weeks, and the troops again lacked provisions.
Clinton assembled 12,500 troops and attacked
Charlestown, South Carolina
Charleston is the largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina, the county seat of Charleston County, and the principal city in the Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint of ...
in January 1780, defeating General
Benjamin Lincoln
Benjamin Lincoln (January 24, 1733 ( O.S. January 13, 1733) – May 9, 1810) was an American army officer. He served as a major general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. Lincoln was involved in three major surrender ...
who had only 5,100 Continental troops. The British went on to occupy the
South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
in June, with no Patriot resistance. Clinton returned to New York and left 8,000 troops commanded by General
Charles Cornwallis
Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis, (31 December 1738 – 5 October 1805), styled Viscount Brome between 1753 and 1762 and known as the Earl Cornwallis between 1762 and 1792, was a British Army general and official. In the United S ...
. Congress replaced Lincoln with Horatio Gates; he failed in South Carolina and was replaced by Washington's choice of Nathaniel Greene, but the British already had the South in their grasp. Washington was reinvigorated, however, when Lafayette returned from France with more ships, men, and supplies, and 5,000 veteran French troops led by Marshal
Rochambeau arrived at
Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is an American seaside city on Aquidneck Island in Newport County, Rhode Island. It is located in Narragansett Bay, approximately southeast of Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, south of Fall River, Massachusetts, south of Boston, ...
in July 1780. French naval forces then landed, led by Admiral
Grasse
Grasse (; Provençal dialect, Provençal oc, Grassa in classical norm or in Mistralian norm ; traditional it, Grassa) is the only Subprefectures in France, subprefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes Departments of France, department in the Provence- ...
, and Washington encouraged Rochambeau to move his fleet south to launch a joint land and naval attack on Arnold's troops.
Washington's army went into winter quarters at
New Windsor, New York
New Windsor is a town in Orange County, New York, United States.
History
The region was originally inhabited by the Munsee
The Munsee (or Minsi or Muncee) or mə́n'si·w ( del, Monsiyok)Online Lenape Talking Dictionary, "Munsee Indians"L ...
in December 1780, and Washington urged Congress and state officials to expedite provisions in hopes that the army would not "continue to struggle under the same difficulties they have hitherto endured". On March 1, 1781, Congress ratified the
Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
, but the government that took effect on March2 did not have the power to levy taxes, and it loosely held the states together.
General Clinton sent Benedict Arnold, now a British Brigadier General with 1,700 troops, to Virginia to capture
Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
and conduct raids on Patriot forces from there; Washington responded by sending Lafayette south to counter Arnold's efforts. Washington initially hoped to bring the fight to New York, drawing off British forces from Virginia and ending the war there, but Rochambeau advised Grasse that
Cornwallis
Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis, (31 December 1738 – 5 October 1805), styled Viscount Brome between 1753 and 1762 and known as the Earl Cornwallis between 1762 and 1792, was a British Army general and official. In the United S ...
in Virginia was the better target. Grasse's fleet arrived off the Virginia coast, and Washington saw the advantage. He made a feint towards Clinton in New York, then headed south to Virginia.
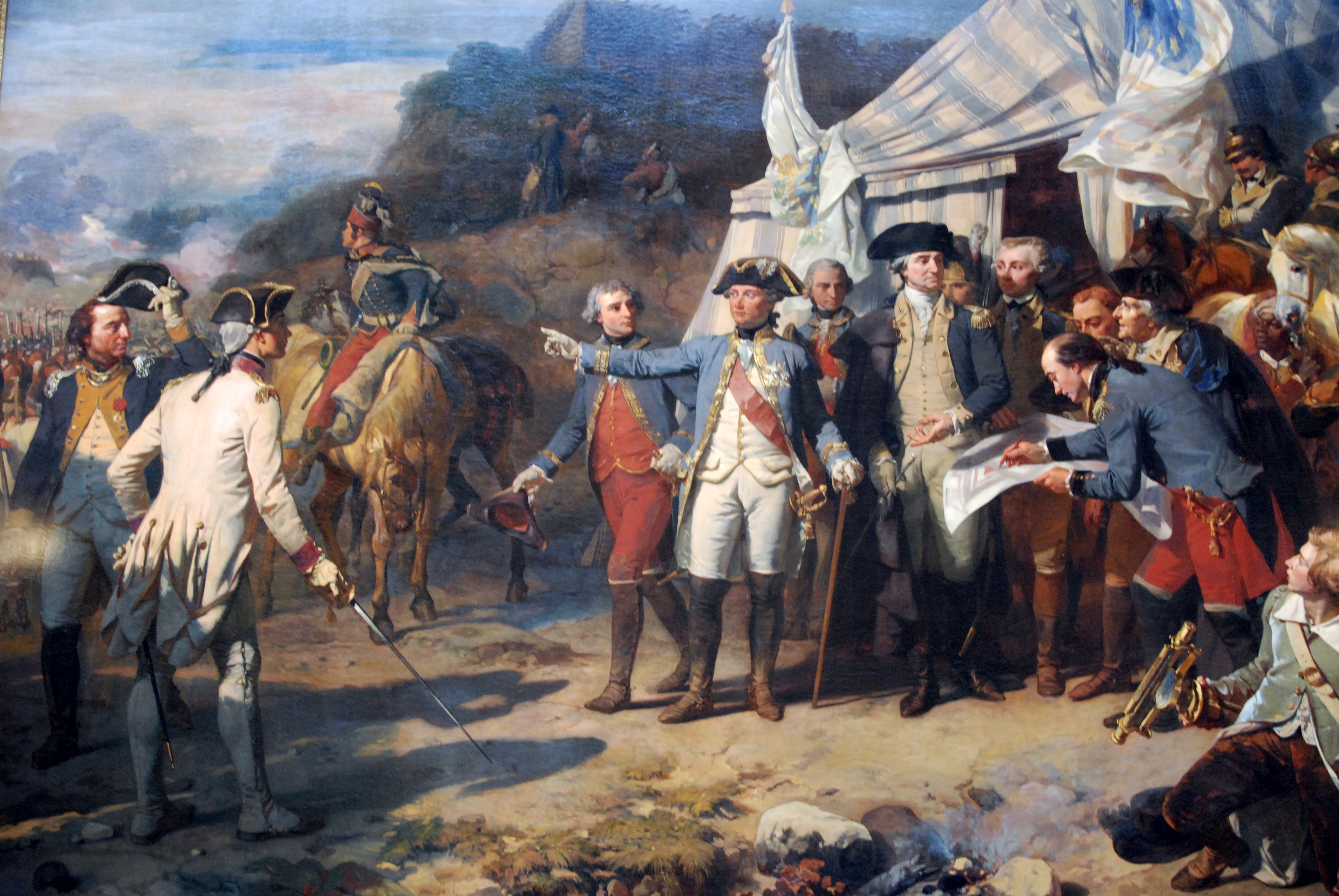

The
Siege of Yorktown
The Siege of Yorktown, also known as the Battle of Yorktown, the surrender at Yorktown, or the German battle (from the presence of Germans in all three armies), beginning on September 28, 1781, and ending on October 19, 1781, at Yorktown, Virgi ...
was a decisive Allied victory by the combined forces of the Continental Army commanded by General Washington, the French Army commanded by the General Comte de Rochambeau, and the French Navy commanded by Admiral
de Grasse, in the defeat of Cornwallis' British forces. On August 19, the march to Yorktown led by Washington and Rochambeau began, which is known now as the
"celebrated march". Washington was in command of an army of 7,800 Frenchmen, 3,100 militia, and 8,000 Continentals. Not well experienced in siege warfare, Washington often referred to the judgment of General Rochambeau and used his advice about how to proceed; however, Rochambeau never challenged Washington's authority as the battle's commanding officer.
By late September, Patriot-French forces surrounded Yorktown, trapped the British army, and prevented British reinforcements from Clinton in the North, while the French navy emerged victorious at the
Battle of the Chesapeake
The Battle of the Chesapeake, also known as the Battle of the Virginia Capes or simply the Battle of the Capes, was a crucial naval battle in the American Revolutionary War that took place near the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay on 5 September 17 ...
. The final American offensive was begun with a shot fired by Washington. The siege ended with a British surrender on October 19, 1781; over 7,000 British soldiers were made
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
, in the last major land battle of the American Revolutionary War. Washington negotiated the terms of surrender for two days, and the official signing ceremony took place on October 19; Cornwallis claimed illness and was absent, sending General
Charles O'Hara
General Charles O'Hara (1740 – 25 February 1802) was a British Army officer who served in the Seven Years' War, the American War of Independence, and the French Revolutionary War and later served as governor of Gibraltar. He served with di ...
as his proxy. As a gesture of goodwill, Washington held a dinner for the American, French, and British generals, all of whom fraternized on friendly terms and identified with one another as members of the same professional military
caste
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultura ...
.
Asgill Affair
After the surrender at Yorktown, a situation developed that threatened relations between the newly independent America and Britain. Following a series of retributive executions between
Patriots and
Loyalists
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cr ...
, Washington, on May 18, 1782, wrote in a letter to General
Moses Hazen
Moses Hazen (June 1, 1733 – February 5, 1803) was a brigadier general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. Born in the Province of Massachusetts Bay, he saw action in the French and Indian War with Rogers' Rang ...
that a British captain would be executed in retaliation for the execution of
Joshua Huddy
Joshua "Jack" Huddy (November 8, 1735April 12, 1782) was a captain in the Monmouth militia and of the privateer ship ''The Black Snake'' during the American Revolutionary War. Following his capture, Huddy was controversially executed by irregular ...
, a popular Patriot leader, who was
hanged
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging in ...
at the direction of the Loyalist
Richard Lippincott. Washington wanted Lippincott himself to be executed but was rebuffed. Subsequently,
Charles Asgill was chosen instead, by a drawing of lots from a hat. This was a violation of the 14th article of the Yorktown Articles of Capitulation, which protected prisoners of war from acts of retaliation.
Later, Washington's feelings on matters changed and in a letter of November 13, 1782, to Asgill, he acknowledged Asgill's letter and situation, expressing his desire not to see any harm come to him. After much consideration between the
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
,
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
, Washington, and appeals from the
French Crown
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the firs ...
, Asgill was finally released, where Washington issued Asgill a pass that allowed his passage to New York.
Demobilization and resignation
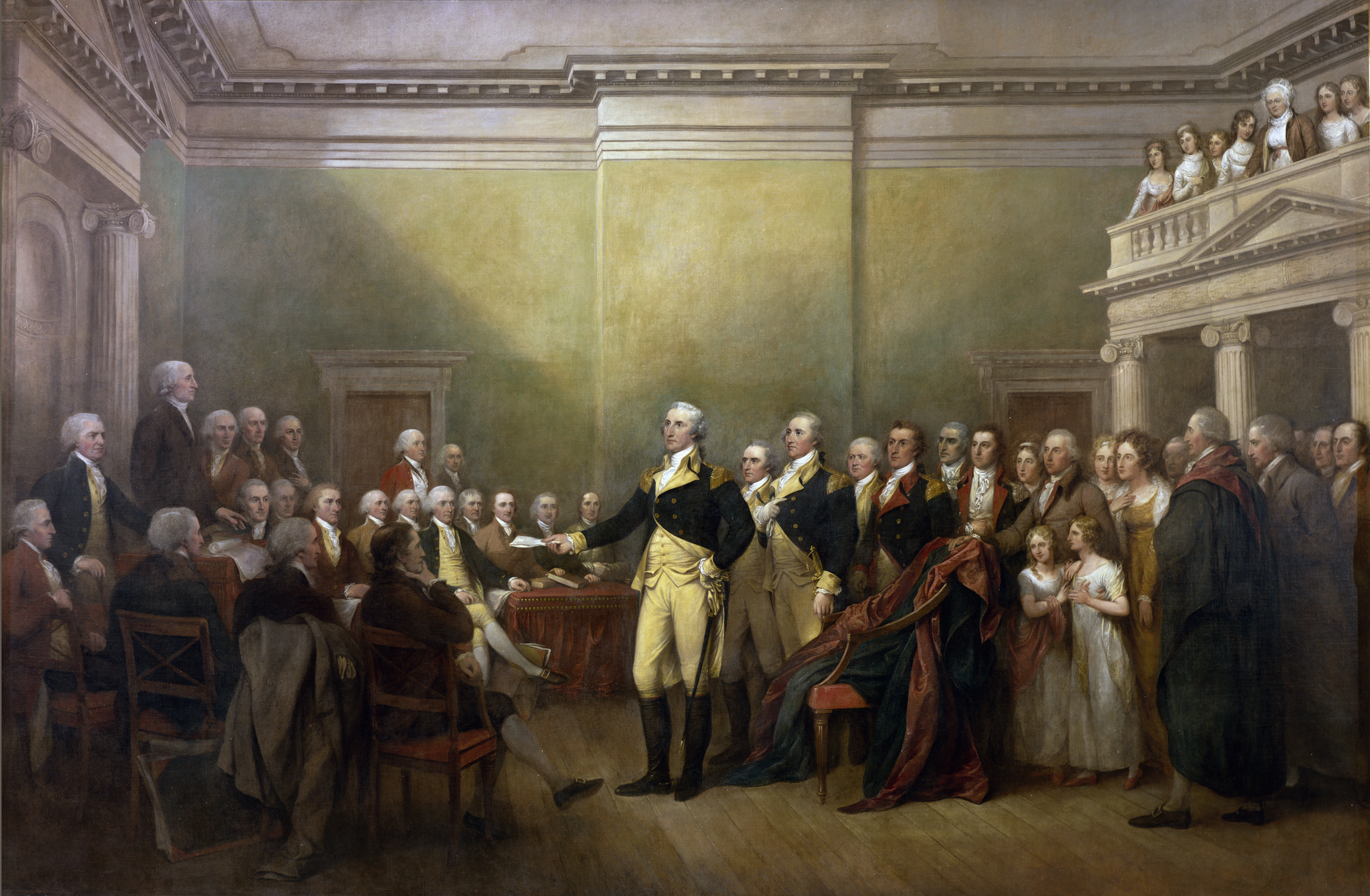

When peace negotiations began in April 1782, both the British and French began gradually evacuating their forces. The American treasury was empty, unpaid, and mutinous soldiers forced the adjournment of Congress, and Washington dispelled unrest by suppressing the
Newburgh Conspiracy
The Newburgh Conspiracy was a failed apparent threat by leaders of the Continental Army in March 1783, at the end of the American Revolutionary War. The Army's commander, George Washington, successfully calmed the soldiers and helped secure back ...
in March 1783; Congress promised officers a five-year bonus. Washington submitted an account of $450,000 in expenses which he had advanced to the army. The account was settled, though it was allegedly vague about large sums and included expenses his wife had incurred through visits to his headquarters.
The following month, a Congressional committee led by
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
began adapting the army for peacetime. In August 1783, Washington gave the Army's perspective to the committee in his ''Sentiments on a Peace Establishment'', which advised Congress to keep a standing army, create a "national militia" of separate state units, and establish a navy and a national military academy.
The
Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
was signed on September 3, 1783, and Great Britain officially recognized the independence of the United States. Washington then disbanded his army, giving a farewell address to his soldiers on November 2. During this time, Washington oversaw the
evacuation of British forces in New York and was greeted by parades and celebrations. There he announced that Colonel Henry Knox had been promoted commander-in-chief. Washington and Governor
George Clinton took formal possession of the city on November 25.
In early December 1783, Washington bade farewell to his officers at
Fraunces Tavern
Fraunces Tavern is a museum and restaurant in New York City, situated at 54 Pearl Street (Manhattan), Pearl Street at the corner of Broad Street (Manhattan), Broad Street in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhatt ...
and
resigned as commander-in-chief soon thereafter, refuting Loyalist predictions that he would not relinquish his military command. In a final appearance in uniform, he gave a statement to the Congress: "I consider it an indispensable duty to close this last solemn act of my official life, by commending the interests of our dearest country to the protection of Almighty God, and those who have the superintendence of them, to his holy keeping." Washington's resignation was acclaimed at home and abroad and showed a skeptical world that the new republic would not degenerate into chaos.
The same month, Washington was appointed president-general of the
Society of the Cincinnati
The Society of the Cincinnati is a fraternal, hereditary society founded in 1783 to commemorate the American Revolutionary War that saw the creation of the United States. Membership is largely restricted to descendants of military officers wh ...
, a newly established hereditary fraternity of Revolutionary War officers. He served in this capacity for the remainder of his life.
Early republic (1783–1789)
Return to Mount Vernon
Washington was longing to return home after spending just ten days at Mount Vernon out of years of war. He arrived on Christmas Eve, delighted to be "free of the bustle of a camp and the busy scenes of public life". He was a celebrity and was
fêted during a visit to his mother at Fredericksburg in February 1784, and he received a constant stream of visitors wishing to pay their respects to him at Mount Vernon.
Washington reactivated his interests in the
Great Dismal Swamp
The Great Dismal Swamp is a large swamp in the Coastal Plain Region of southeastern Virginia and northeastern North Carolina, between Norfolk, Virginia, and Elizabeth City, North Carolina. It is located in parts of the southern Virginia inde ...
and
Potomac canal
The Patowmack Canal, sometimes called the Potomac Canal, is a series of five inoperative canals located in Maryland and Virginia, United States, that was designed to bypass rapids in the Potomac River upstream of the present Washington, D.C., ar ...
projects begun before the war, though neither paid him any dividends, and he undertook a 34-day, 680-mile (1090 km) trip to check on his land holdings in the Ohio Country. He oversaw the completion of the remodeling work at Mount Vernon, which transformed his residence into the mansion that survives to this day—although his financial situation was not strong. Creditors paid him in depreciated wartime currency, and he owed significant amounts in taxes and wages. Mount Vernon had made no profit during his absence, and he saw persistently poor crop yields due to pestilence and poor weather. His estate recorded its eleventh year running at a deficit in 1787, and there was little prospect of improvement. Washington undertook a new landscaping plan and succeeded in cultivating a range of fast-growing trees and shrubs that were native to North America. He also began
breeding
Breeding is sexual reproduction that produces offspring, usually animals or plants. It can only occur between a male and a female animal or plant.
Breeding may refer to:
* Animal husbandry, through selected specimens such as dogs, horses, and rab ...
mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two pos ...
s after having been gifted a Spanish
jack
Jack may refer to:
Places
* Jack, Alabama, US, an unincorporated community
* Jack, Missouri, US, an unincorporated community
* Jack County, Texas, a county in Texas, USA
People and fictional characters
* Jack (given name), a male given name, ...
by
King Charles III of Spain
Charles III (born Charles Sebastian; es, Carlos Sebastián; 20 January 1716 – 14 December 1788) was King of Spain (1759–1788). He also was Duchy of Parma and Piacenza, Duke of Parma and Piacenza, as Charles I (1731–1735); Kingdom of Naples, ...
in 1784. There were few mules in the United States at that time, and he believed that properly bred mules would revolutionize
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and
transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
.
Constitutional Convention of 1787

Before returning to private life in June 1783, Washington called for a strong union. Though he was concerned that he might be criticized for meddling in civil matters, he sent a circular letter to all the states, maintaining that the
Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
was no more than "a rope of sand" linking the states. He believed the nation was on the verge of "anarchy and confusion", was vulnerable to foreign intervention, and that a national constitution would unify the states under a strong central government. When
Shays' Rebellion
Shays Rebellion was an armed uprising in Western Massachusetts and Worcester in response to a debt crisis among the citizenry and in opposition to the state government's increased efforts to collect taxes both on individuals and their trades. The ...
erupted in Massachusetts on August 29, 1786, over taxation, Washington was further convinced that a national constitution was needed. Some nationalists feared that the new republic had descended into lawlessness, and they met together on September 11, 1786, at
Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
to ask Congress to revise the Articles of Confederation. One of their biggest efforts, however, was getting Washington to attend. Congress agreed to a Constitutional Convention to be held in Philadelphia in Spring 1787, and each state was to send delegates.
On December 4, 1786, Washington was chosen to lead the Virginia delegation, but he declined on December 21. He had concerns about the legality of the convention and consulted
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
,
Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806), a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the ...
, and others. They persuaded him to attend it, however, as his presence might induce reluctant states to send delegates and smooth the way for the ratification process. On March 28, Washington told Governor
Edmund Randolph
Edmund Jennings Randolph (August 10, 1753 September 12, 1813) was a Founding Father of the United States, attorney, and the 7th Governor of Virginia. As a delegate from Virginia, he attended the Constitutional Convention and helped to create ...
that he would attend the convention but made it clear that he was urged to attend.
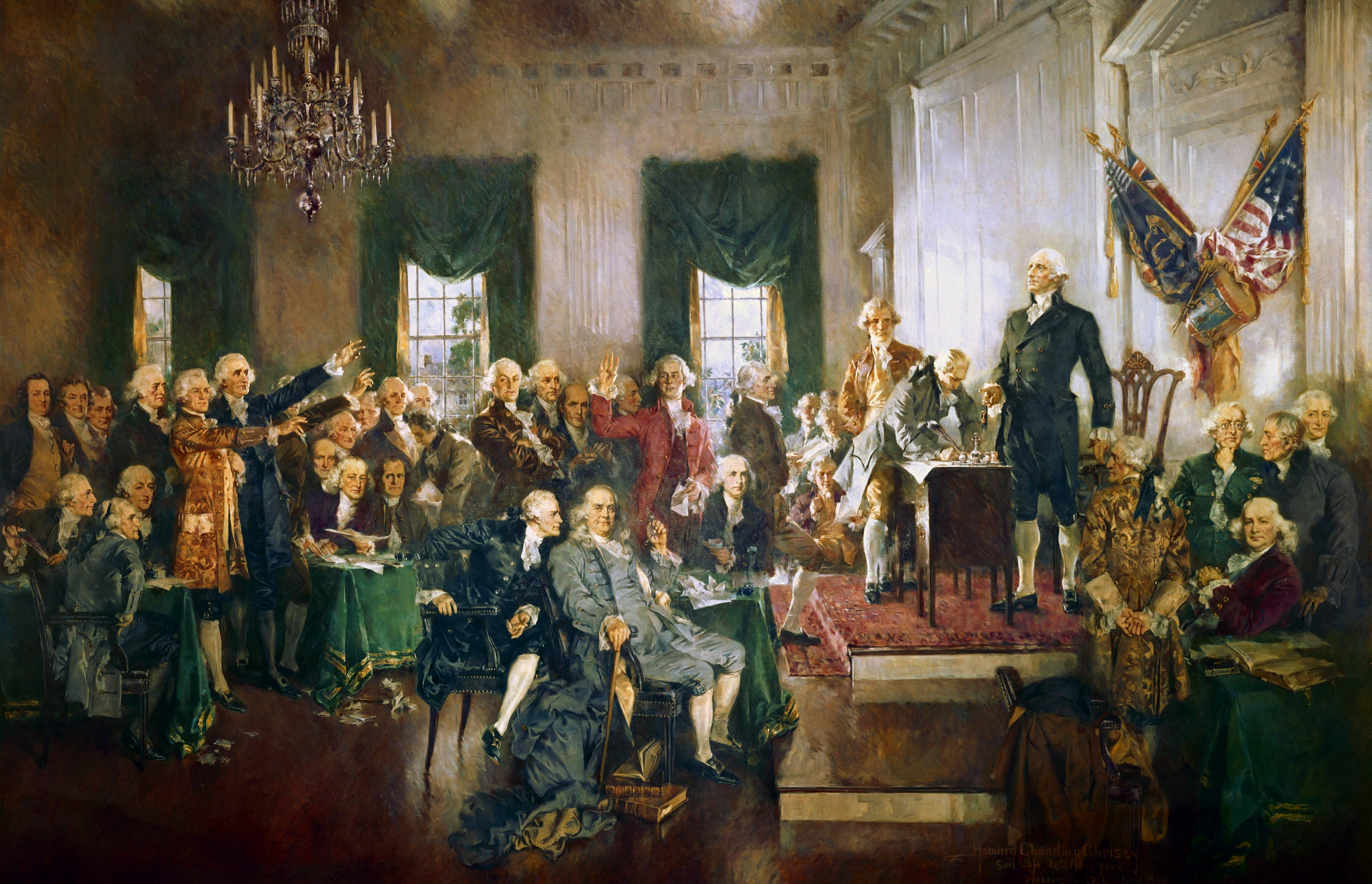

Washington arrived in Philadelphia on May 9, 1787, though a quorum was not attained until Friday, May 25. Benjamin Franklin nominated Washington to preside over the convention, and he was unanimously elected to serve as president general. The convention's state-mandated purpose was to revise the Articles of Confederation with "all such alterations and further provisions" required to improve them, and the new government would be established when the resulting document was "duly confirmed by the several states".
Governor Edmund Randolph of Virginia introduced Madison's
Virginia Plan
The ''Virginia Plan'' (also known as the Randolph Plan, after its sponsor, or the Large-State Plan) was a proposal to the United States Constitutional Convention for the creation of a supreme national government with three branches and a bicam ...
on May 27, the third day of the convention. It called for an entirely new constitution and a sovereign national government, which Washington highly recommended.
Washington wrote
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
on July 10: "I almost despair of seeing a favorable issue to the proceedings of our convention and do therefore repent having had any agency in the business." Nevertheless, he lent his prestige to the goodwill and work of the other delegates. He unsuccessfully lobbied many to support ratification of the
Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
, such as anti-federalist
Patrick Henry
Patrick Henry (May 29, 1736June 6, 1799) was an American attorney, planter, politician and orator known for declaring to the Second Virginia Convention (1775): " Give me liberty, or give me death!" A Founding Father, he served as the first an ...
; Washington told him "the adoption of it under the present circumstances of the Union is in my opinion desirable" and declared the alternative would be anarchy. Washington and Madison then spent four days at Mount Vernon evaluating the new government's transition.
Chancellor of William & Mary
In 1788, the Board of Visitors of the
College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William III ...
decided to re-establish the position of Chancellor, and elected Washington to the office on January 18.
The College Rector Samuel Griffin wrote to Washington inviting him to the post, and in a letter dated April 30, 1788, Washington accepted the position of the 14th
Chancellor of the College of William & Mary
The chancellor of the College of William & Mary is the ceremonial head of the College of William & Mary in Williamsburg, Virginia, United States, chosen by the university's Board of Visitors. The office was created by the college's Royal Charter, ...
.
He continued to serve in the post through his presidency until his death on December 14, 1799.
First presidential election
The delegates to the Convention anticipated a Washington presidency and left it to him to define the office once elected. The state electors under the Constitution voted for the president on February 4, 1789, and Washington suspected that most republicans had not voted for him. The mandated March4 date passed without a Congressional quorum to count the votes, but a quorum was reached on April 5. The votes were tallied the next day, and Congressional Secretary
Charles Thomson
Charles Thomson (November 29, 1729 – August 16, 1824) was an Irish-born Patriot leader in Philadelphia during the American Revolution and the secretary of the Continental Congress (1774–1789) throughout its existence. As secretary, Thomson ...
was sent to Mount Vernon to tell Washington he had been elected president. Washington won the majority of every state's electoral votes; John Adams received the next highest number of votes and therefore became vice president. Washington had "anxious and painful sensations" about leaving the "domestic felicity" of Mount Vernon, but departed for
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
on April 16 to be inaugurated.
Presidency (1789–1797)

Washington was
inaugurated
In government and politics, inauguration is the process of swearing a person into office and thus making that person the incumbent. Such an inauguration commonly occurs through a formal ceremony or special event, which may also include an inaugu ...
on April 30, 1789, taking the
oath of office
An oath of office is an oath or affirmation a person takes before assuming the duties of an office, usually a position in government or within a religious body, although such oaths are sometimes required of officers of other organizations. Such ...
at
Federal Hall
Federal Hall is a historic building at 26 Wall Street in the Financial District of Manhattan in New York City. The current Greek Revival–style building, completed in 1842 as the Custom House, is operated by the National Park Service as a nati ...
in New York City. His coach was led by militia and a marching band and followed by statesmen and foreign dignitaries in an inaugural parade, with a crowd of 10,000. Chancellor
Robert R. Livingston
Robert Robert Livingston (November 27, 1746 (Old Style November 16) – February 26, 1813) was an American lawyer, politician, and diplomat from New York, as well as a Founding Father of the United States. He was known as "The Chancellor", afte ...
administered the oath, using a
Bible provided by the Masons, after which the militia fired a 13-gun salute. Washington read a speech in the Senate Chamber, asking "that Almighty Being who rules over the universe, who presides in the councils of nations—and whose providential aids can supply every human defect, consecrate the liberties and happiness of the people of the United States". Though he wished to serve without a salary, Congress insisted adamantly that he accept it, later providing Washington $25,000 per year to defray costs of the presidency.
Washington wrote to James Madison: "As the first of everything in our situation will serve to establish a precedent, it is devoutly wished on my part that these precedents be fixed on true principles." To that end, he preferred the title "Mr. President" over more majestic names proposed by the Senate, including "His Excellency" and "His Highness the President". His executive precedents included the inaugural address, messages to Congress, and the
cabinet form of the
executive branch
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a State (polity), state.
In poli ...
.
Washington had planned to resign after his first term, but the political strife in the nation convinced him he should remain in office. He was an able administrator and a judge of talent and character, and he regularly talked with department heads to get their advice. He tolerated opposing views, despite fears that a democratic system would lead to political violence, and he conducted a smooth transition of power to his successor. He remained non-partisan throughout his presidency and opposed the divisiveness of political parties, but he favored a strong central government, was sympathetic to a Federalist form of government, and leery of the Republican opposition.
Washington dealt with major problems. The old
Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
lacked the powers to handle its workload and had weak leadership, no executive, a small bureaucracy of clerks, a large debt, worthless paper money, and no power to establish taxes. He had the task of assembling an executive department and relied on
Tobias Lear
Tobias Lear (September 19, 1762 – October 11, 1816) was the personal secretary to President of the United States, President George Washington. Lear served Washington from 1784 until the former-President's death in 1799. Lear's journal details Was ...
for advice selecting its officers. Great Britain refused to relinquish its forts in the American West, and
Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known i ...
preyed on American merchant ships in the Mediterranean before the United States even had a navy.
Cabinet and executive departments
Congress created executive departments in 1789, including the
State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
in July, the
Department of War War Department may refer to:
* War Department (United Kingdom)
* United States Department of War (1789–1947)
See also
* War Office, a former department of the British Government
* Ministry of defence
* Ministry of War
* Ministry of Defence
* D ...
in August, and the
Treasury Department in September. Washington appointed fellow Virginian
Edmund Randolph
Edmund Jennings Randolph (August 10, 1753 September 12, 1813) was a Founding Father of the United States, attorney, and the 7th Governor of Virginia. As a delegate from Virginia, he attended the Constitutional Convention and helped to create ...
as Attorney General,
Samuel Osgood
Samuel Osgood (February 3, 1747 – August 12, 1813) was an American merchant and statesman born in Andover, Massachusetts, currently a part of North Andover, Massachusetts. His family home still stands at 440 Osgood Street in North Andover ...
as Postmaster General,
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
as Secretary of State, and
Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806), a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the ...
as
Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
. Finally, he appointed
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
as
Secretary of the Treasury
The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal a ...
. Washington's cabinet became a consulting and advisory body, not mandated by the Constitution.
Washington's cabinet members formed rival parties with sharply opposing views, most fiercely illustrated between Hamilton and Jefferson. Washington restricted cabinet discussions to topics of his choosing, without participating in the debate. He occasionally requested cabinet opinions in writing and expected department heads to agreeably carry out his decisions.
Domestic issues
Washington was apolitical and opposed the formation of parties, suspecting that conflict would undermine republicanism. He exercised great restraint in using
his veto power, writing that "I give my Signature to many Bills with which my Judgment is at variance…."
His closest advisors formed two factions, portending the
First Party System
The First Party System is a model of American politics used in history and political science to periodize the political party system that existed in the United States between roughly 1792 and 1824. It featured two national parties competing for ...
. Secretary of the Treasury
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
formed the
Federalist Party
The Federalist Party was a Conservatism in the United States, conservative political party which was the first political party in the United States. As such, under Alexander Hamilton, it dominated the national government from 1789 to 1801.
De ...
to promote national credit and a financially powerful nation. Secretary of State
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
opposed Hamilton's agenda and founded the
Jeffersonian Republicans
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
. Washington favored Hamilton's agenda, however, and it ultimately went into effect—resulting in bitter controversy.
Washington proclaimed November 26 as a day of
Thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in the United States, Canada, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Philippines. It is also observed in the Netherlander town of Leiden and ...
to encourage national unity. "It is the duty of all nations to acknowledge the providence of Almighty God, to obey His will, to be grateful for His benefits, and humbly to implore His protection and favor." He spent that day fasting and visiting debtors in prison to provide them with food and beer.
African Americans
In response to two antislavery petitions that were presented to Congress in 1790, slaveholders in Georgia and South Carolina objected and threatened to "blow the trumpet of civil war". Washington and Congress responded with a series of racist measures:
naturalized citizenship was denied to black immigrants;
blacks were barred from serving in state militias; the
Southwest Territory
The Territory South of the River Ohio, more commonly known as the Southwest Territory, was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 26, 1790, until June 1, 1796, when it was admitted to the United States a ...
that would soon become the state of Tennessee was permitted to maintain slavery; and two more slave states were admitted (Kentucky in 1792, and Tennessee in 1796). On February 12, 1793, Washington signed into law the
Fugitive Slave Act
A fugitive (or runaway) is a person who is fleeing from custody, whether it be from jail, a government arrest, government or non-government questioning, vigilante violence, or outraged private individuals. A fugitive from justice, also kno ...
, which overrode state laws and courts, allowing agents to cross state lines to capture and return escaped slaves. Many free blacks in the north decried the law believing it would allow bounty hunting and the kidnappings of blacks. The Fugitive Slave Act gave effect to the Constitution's
Fugitive Slave Clause
The Fugitive Slave Clause in the United States Constitution, also known as either the Slave Clause or the Fugitives From Labor Clause, is Article IV, Section 2, Clause 3, which requires a "person held to service or labor" (usually a slave, appre ...
, and the Act was passed overwhelmingly in Congress (e.g. the vote was 48 to 7 in the House).
On the anti-slavery side of the ledger, in 1789 Washington signed a reenactment of the
Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Co ...
which had freed all slaves brought after 1787 into a vast expanse of federal territory north of the
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
, except for slaves escaping from slave states. That 1787 law lapsed when the new U.S. Constitution was ratified in 1789. The
Slave Trade Act of 1794
The Slave Trade Act of 1794 was a law passed by the United States Congress that prohibited American ships from engaging the international slave trade. It was signed into law by President George Washington on March 22, 1794. This was the first of ...
, which sharply limited American involvement in the
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
, was also signed by Washington. And, Congress acted on February 18, 1791, to admit the free state of Vermont into the Union as the 14th state as of March 4, 1791.
National Bank

Washington's first term was largely devoted to economic concerns, in which Hamilton had devised various plans to address matters. The establishment of public credit became a primary challenge for the federal government. Hamilton submitted a report to a deadlocked Congress, and he, Madison, and Jefferson reached the
Compromise of 1790
The Compromise of 1790 was a compromise between Alexander Hamilton, Thomas Jefferson, and James Madison, where Hamilton won the decision for the national government to take over and pay the state debts, and Jefferson and Madison obtained the nati ...
in which Jefferson agreed to Hamilton's debt proposals in exchange for moving the nation's capital temporarily to Philadelphia and then south near
Georgetown on the
Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augus ...
. The terms were legislated in the
Funding Act of 1790
The Funding Act of 1790, the full title of which is An Act making provision for the ayment of theDebt of the United States, was passed on August 4, 1790, by the United States Congress as part of the Compromise of 1790, to address the issue of fu ...
and the
Residence Act
The Residence Act of 1790, officially titled An Act for establishing the temporary and permanent seat of the Government of the United States (), is a United States federal statute adopted during the second session of the First United States Co ...
, both of which Washington signed into law. Congress authorized the assumption and payment of the nation's debts, with funding provided by customs duties and excise taxes.
Hamilton created controversy among Cabinet members by advocating establishing the
First Bank of the United States
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
. Madison and Jefferson objected, but the bank easily passed Congress. Jefferson and
Randolph Randolph may refer to:
Places In the United States
* Randolph, Alabama, an unincorporated community
* Randolph, Arizona, a populated place
* Randolph, California, a village merged into the city of Brea
* Randolph, Illinois, an unincorporated commun ...
insisted that the new bank was beyond the authority granted by the constitution, as Hamilton believed. Washington sided with Hamilton and signed the legislation on February 25, and the rift became openly hostile between Hamilton and Jefferson.
The nation's
first financial crisis occurred in March 1792. Hamilton's Federalists exploited large loans to gain control of U.S. debt securities, causing a run on the national bank; the markets returned to normal by mid-April. Jefferson believed Hamilton was part of the scheme, despite Hamilton's efforts to ameliorate, and Washington again found himself in the middle of a feud.
Jefferson–Hamilton feud
Jefferson and Hamilton adopted diametrically opposed political principles. Hamilton believed in a strong national government requiring a national bank and foreign loans to function, while Jefferson believed the states and the farm element should primarily direct the government; he also resented the idea of banks and foreign loans. To Washington's dismay, the two men persistently entered into disputes and infighting. Hamilton demanded that Jefferson resign if he could not support Washington, and Jefferson told Washington that Hamilton's fiscal system would lead to the overthrow of the republic. Washington urged them to call a truce for the nation's sake, but they ignored him.
Washington reversed his decision to retire after his first term to minimize party strife, but the feud continued after his re-election. Jefferson's political actions, his support of Freneau's ''National Gazette'', and his attempt to undermine Hamilton nearly led Washington to dismiss him from the cabinet; Jefferson ultimately resigned his position in December 1793, and Washington forsook him from that time on.
The feud led to the well-defined Federalist and Republican parties, and party affiliation became necessary for election to Congress by 1794. Washington remained aloof from congressional attacks on Hamilton, but he did not publicly protect him, either. The
Hamilton–Reynolds sex scandal opened Hamilton to disgrace, but Washington continued to hold him in "very high esteem" as the dominant force in establishing federal law and government.
Whiskey Rebellion
In March 1791, at Hamilton's urging, with support from Madison, Congress imposed an excise tax on distilled spirits to help curtail the national debt, which took effect in July. Grain farmers strongly protested in Pennsylvania's frontier districts; they argued that they were unrepresented and were shouldering too much of the debt, comparing their situation to excessive British taxation before the Revolutionary War. On August 2, Washington assembled his cabinet to discuss how to deal with the situation. Unlike Washington, who had reservations about using force, Hamilton had long waited for such a situation and was eager to suppress the rebellion by using federal authority and force. Not wanting to involve the federal government if possible, Washington called on Pennsylvania state officials to take the initiative, but they declined to take military action. On August 7, Washington issued his first proclamation for calling up state militias. After appealing for peace, he reminded the protestors that, unlike the rule of the British crown, the Federal law was issued by state-elected representatives.
Threats and violence against tax collectors, however, escalated into defiance against federal authority in 1794 and gave rise to the
Whiskey Rebellion
The Whiskey Rebellion (also known as the Whiskey Insurrection) was a violent tax protest in the United States beginning in 1791 and ending in 1794 during the presidency of George Washington. The so-called "whiskey tax" was the first tax impo ...
. Washington issued a final proclamation on September 25, threatening the use of military force to no avail. The federal army was not up to the task, so Washington invoked the Militia Acts of 1792, Militia Act of 1792 to summon state militias. Governors sent troops, initially commanded by Washington, who gave the command to Henry Lee III, Light-Horse Harry Lee to lead them into the rebellious districts. They took 150 prisoners, and the remaining rebels dispersed without further fighting. Two of the prisoners were condemned to death, but Washington exercised his Constitutional authority for the first time and pardoned them.
Washington's forceful action demonstrated that the new government could protect itself and its tax collectors. This represented the first use of federal military force against the states and citizens, and remains the only time an incumbent president has commanded troops in the field. Washington justified his action against "certain self-created societies", which he regarded as "subversive organizations" that threatened the national union. He did not dispute their right to protest, but he insisted that their dissent must not violate federal law. Congress agreed and extended their congratulations to him; only Madison and Jefferson expressed indifference.
Foreign affairs

In April 1792, the French Revolutionary Wars began between Great Britain and France, and Washington declared America's neutrality. The revolutionary government of France sent diplomat Edmond-Charles Genêt, Citizen Genêt to America, and he was welcomed with great enthusiasm. He created a network of new Democratic-Republican Societies promoting France's interests, but Washington denounced them and demanded that the French recall Genêt. The National Assembly of France granted Washington honorary French citizenship on August 26, 1792, during the early stages of the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
. Hamilton formulated the
Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
to normalize trade relations with Great Britain while removing them from western forts, and also to resolve financial debts remaining from the Revolution. Chief Justice John Jay acted as Washington's negotiator and signed the treaty on November 19, 1794; critical Jeffersonians, however, supported France. Washington deliberated, then supported the treaty because it avoided war with Britain, but was disappointed that its provisions favored Britain. He mobilized public opinion and secured ratification in the Senate but faced frequent public criticism.
The British agreed to abandon their forts around the Great Lakes, and the United States modified the boundary with Canada. The government liquidated numerous pre-Revolutionary debts, and the British opened the British West Indies to American trade. The treaty secured peace with Britain and a decade of prosperous trade. Jefferson claimed that it angered France and "invited rather than avoided" war. Relations with France deteriorated afterward, leaving succeeding president
John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
with prospective war. James Monroe was the American Minister to France, but Washington recalled him for his opposition to the Treaty. The French refused to accept his replacement Charles Cotesworth Pinckney, and the French Directory declared the authority to seize American ships two days before Washington's term ended.
Native American affairs

Ron Chernow describes Washington as always trying to be even-handed in dealing with the Natives. He states that Washington hoped they would abandon their itinerant hunting life and adapt to fixed agricultural communities in the manner of white settlers. He also maintains that Washington never advocated outright confiscation of tribal land or the forcible removal of tribes and that he berated American settlers who abused natives, admitting that he held out no hope for pacific relations with the natives as long as "frontier settlers entertain the opinion that there is not the same crime (or indeed no crime at all) in killing a native as in killing a white man."
By contrast, Colin G. Calloway writes that "Washington had a lifelong obsession with getting Indian land, either for himself or for his nation, and initiated policies and campaigns that had devastating effects in Indian country." "The growth of the nation," Galloway has stated, "demanded the dispossession of Indian people. Washington hoped the process could be bloodless and that Indian people would give up their lands for a "fair" price and move away. But if Indians refused and resisted, as they often did, he felt he had no choice but to "extirpate" them and that the expeditions he sent to destroy Indian towns were therefore entirely justified."
During the fall of 1789, Washington had to contend with the British refusing to evacuate their forts in the Northwest frontier and their Northwest Indian War, concerted efforts to incite hostile Indian tribes to attack European Americans, American settlers. The Northwest tribes under Miami people, Miami chief Little Turtle allied with the British Army to resist American expansion, and killed 1,500 settlers between 1783 and 1790.
As documented by Harless (2018), Washington declared that "The Government of the United States are determined that their Administration of Indian Affairs shall be directed entirely by the great principles of Justice and humanity", and provided that treaties should negotiate their land interests. The administration regarded powerful tribes as foreign nations, and Washington even smoked a Ceremonial pipe, peace pipe and drank wine with them at the President's House (Philadelphia), Philadelphia presidential house. He made numerous attempts to conciliate them; he equated killing indigenous peoples with killing whites and sought to integrate them into European Americans, European American culture. Secretary of War
Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806), a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the ...
also attempted to encourage agriculture among the tribes.
In the Southwest, negotiations failed between federal commissioners and raiding Indian tribes seeking retribution. Washington invited Muscogee, Creek Chief Alexander McGillivray and 24 leading chiefs to New York to negotiate a treaty and treated them like foreign dignitaries. Knox and McGillivray concluded the Treaty of New York (1790), Treaty of New York on August 7, 1790, in
Federal Hall
Federal Hall is a historic building at 26 Wall Street in the Financial District of Manhattan in New York City. The current Greek Revival–style building, completed in 1842 as the Custom House, is operated by the National Park Service as a nati ...
, which provided the tribes with agricultural supplies and McGillivray with a rank of Brigadier General Army and a salary of $1,500.

In 1790, Washington sent Brigadier General Josiah Harmar to pacify the Northwest tribes, but Little Turtle routed him twice and forced him to withdraw. The Northwestern Confederacy of tribes used guerrilla tactics and were an effective force against the sparsely manned American Army. Washington sent Major General Arthur St. Clair from Fort Washington (Ohio), Fort Washington on an expedition to restore peace in the territory in 1791. On November 4, St. Clair's forces were ambushed and St. Clair's defeat, soundly defeated by tribal forces with few survivors, despite Washington's warning of surprise attacks. Washington was outraged over what he viewed to be excessive Native American brutality and execution of captives, including women and children.
St. Clair resigned his commission, and Washington replaced him with the Revolutionary War hero General Anthony Wayne. From 1792 to 1793, Wayne instructed his troops on Native American warfare tactics and instilled discipline which was lacking under St. Clair. In August 1794, Washington sent Wayne into tribal territory with authority to drive them out by burning their villages and crops in the Maumee, Ohio, Maumee Valley. On August 24, the American army under Wayne's leadership defeated the western confederacy at the Battle of Fallen Timbers, and the Treaty of Greenville in August 1795 opened up two-thirds of the Ohio Country for American settlement.
Second term
Originally, Washington had planned to retire after his first term, while many Americans could not imagine anyone else taking his place. After nearly four years as president, and dealing with the infighting in his own cabinet and with partisan critics, Washington showed little enthusiasm in running for a second term, while Martha also wanted him not to run. James Madison urged him not to retire, that his absence would only allow the dangerous political rift in his cabinet and the House to worsen. Jefferson also pleaded with him not to retire and agreed to drop his attacks on Hamilton, or he would also retire if Washington did. Hamilton maintained that Washington's absence would be "deplored as the greatest evil" to the country at this time. Washington's close nephew George Augustine Washington, his manager at Mount Vernon, was critically ill and had to be replaced, further increasing Washington's desire to retire and return to Mount Vernon.
When the 1792 United States presidential election, election of 1792 neared, Washington did not publicly announce his presidential candidacy. Still, he silently consented to run to prevent a further political-personal rift in his cabinet. The
Electoral College unanimously elected him president on February 13, 1793, and
John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
as vice president by a vote of 77 to 50. Washington, with nominal fanfare, arrived alone at Presidency of George Washington, his inauguration in his carriage. Sworn into office by Associate Justice William Cushing on March 4, 1793, in the Senate Chamber of Congress Hall in Philadelphia, Washington gave a brief address and then immediately retired to his Philadelphia presidential house, weary of office and in poor health.
On April 22, 1793, during the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, Washington issued his famous Proclamation of Neutrality, Neutrality Proclamation and was resolved to pursue "a conduct friendly and impartial toward the belligerent Powers" while he warned Americans not to intervene in the international conflict. Although Washington recognized France's revolutionary government, he would eventually ask French minister to the United States Edmond-Charles Genêt be recalled over the Citizen Genêt affair. Genêt was a diplomatic troublemaker who was openly hostile toward Washington's neutrality policy. He procured four American ships as privateers to strike at Spanish forces (British allies) in Florida while organizing militias to strike at other British possessions. However, his efforts failed to draw America into the French Revolutionary Wars, foreign campaigns during Washington's presidency. On July 31, 1793, Jefferson submitted his resignation from Washington's cabinet. Washington signed the Naval Act of 1794 and commissioned the first six federal frigates to combat Barbary pirates.
In January 1795, Hamilton, who desired more income for his family, resigned office and was replaced by Washington appointment Oliver Wolcott Jr. Washington and Hamilton remained friends. However, Washington's relationship with his Secretary of War Henry Knox deteriorated. Knox resigned office on the rumor he profited from construction contracts on U.S. Frigates.
In the final months of his presidency, Washington was assailed by his political foes and a partisan press who accused him of being ambitious and greedy, while he argued that he had taken no salary during the war and had risked his life in battle. He regarded the press as a disuniting, "diabolical" force of falsehoods, sentiments that he expressed in his
Farewell Address. At the end of his second term, Washington retired for personal and political reasons, dismayed with personal attacks, and to ensure that a truly contested presidential election could be held. He did not feel bound to a two-term limit, but his retirement set a significant precedent. Washington is often credited with setting the principle of a two-term presidency, but it was Thomas Jefferson who first refused to run for a third term on political grounds.
Farewell Address

In 1796, Washington declined to run for a third term of office, believing his death in office would create an image of a lifetime appointment. The precedent of a two-term limit was created by his retirement from office. In May 1792, in anticipation of his retirement, Washington instructed
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
to prepare a "Valedictorian, valedictory address", an initial draft of which was entitled the "Farewell Address". In May 1796, Washington sent the manuscript to his Secretary of Treasury
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
who did an extensive rewrite, while Washington provided final edits. On September 19, 1796, David Claypoole's ''Pennsylvania Packet, American Daily Advertiser'' published the final version of the address.
Washington stressed that national identity was paramount, while a united America would safeguard freedom and prosperity. He warned the nation of three eminent dangers: regionalism, partisanship, and foreign entanglements, and said the "name of AMERICAN, which belongs to you, in your national capacity, must always exalt the just pride of patriotism, more than any appellation derived from local discriminations." Washington called for men to move beyond partisanship for the common good, stressing that the United States must concentrate on its own interests. He warned against foreign alliances and their influence in domestic affairs, and bitter partisanship and the dangers of political parties. He counseled friendship and commerce with all nations, but advised against involvement in European wars. He stressed the importance of religion, asserting that "religion and morality are indispensable supports" in a republic. Washington's address favored Hamilton's Federalist ideology and economic policies.
Washington closed the address by reflecting on his legacy:
After initial publication, many Republicans, including Madison, criticized the Address and believed it was an anti-French campaign document. Madison believed Washington was strongly pro-British. Madison also was suspicious of who authored the Address.
In 1839, Washington biographer Jared Sparks maintained that Washington's "...Farewell Address was Early American publishers and printers, printed and published with the laws, by order of the legislatures, as an evidence of the value they attached to its political precepts, and of their affection for its author." In 1972, Washington scholar James Thomas Flexner, James Flexner referred to the Farewell Address as receiving as much acclaim as Thomas Jefferson's
Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
and Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address. In 2010, historian Ron Chernow reported the ''Farewell Address'' proved to be one of the most influential statements on republicanism.
Post-presidency (1797–1799)
Retirement
Washington retired to Mount Vernon in March 1797 and devoted time to his plantations and other business interests, including his :File:George Washington's Distillery.JPG, distillery. His plantation operations were only minimally profitable, and his lands in the west (
Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
) were under Indian attacks and yielded little income, with the squatters there refusing to pay rent. He attempted to sell these but without success. He became an even more committed Federalist. He vocally supported the Alien and Sedition Acts and convinced Federalist John Marshall to run for Congress to weaken the Jeffersonian hold on Virginia.
Washington grew restless in retirement, prompted by tensions with France, and he wrote to Secretary of War James McHenry offering to organize President Adams' army. In a continuation of the French Revolutionary Wars, French privateers began seizing American ships in 1798, and relations deteriorated with France and led to the "Quasi-War". Without consulting Washington, Adams nominated him for a lieutenant general commission on July 4, 1798, and the position of commander-in-chief of the armies. Washington chose to accept, replacing James Wilkinson, and he served as the commanding general from July 13, 1798, until his death 17 months later. He participated in planning for a provisional army, but he avoided involvement in details. In advising McHenry of potential officers for the army, he appeared to make a complete break with Jefferson's Democratic-Republicans: "you could as soon scrub the blackamoor white, as to change the principles of a profest Democrat; and that he will leave nothing unattempted to overturn the government of this country." Washington delegated the active leadership of the army to Hamilton, a major general. No army invaded the United States during this period, and Washington did not assume a field command.
Washington was known to be rich because of the well-known "glorified façade of wealth and grandeur" at Mount Vernon, but nearly all his wealth was in the form of land and slaves rather than ready cash. To supplement his income, he erected a :File:George Washington's Distillery.JPG, distillery for substantial whiskey production. Historians estimate that the estate was worth about $1million in 1799 dollars, . He bought land parcels to spur development around the new Washington, D.C., Federal City named in his honor, and he sold individual lots to middle-income investors rather than multiple lots to large investors, believing they would more likely commit to making improvements.
Final days and death

On December 12, 1799, Washington inspected his farms on horseback. He returned home late and had guests over for dinner. He had a sore throat the next day but was well enough to mark trees for cutting. That evening, he complained of chest congestion but was still cheerful. On Saturday, he awoke to an inflamed throat and difficulty breathing, so he ordered estate overseer George Rawlins to remove nearly a pint of his blood; bloodletting was a common practice of the time. His family summoned Drs. James Craik, Gustavus Richard Brown, and Elisha C. Dick. Dr. William Thornton arrived some hours after Washington died.
Dr. Brown thought Washington had Peritonsillar abscess, quinsy; Dr. Dick thought the condition was a more serious "violent inflammation of the throat". They continued the process of bloodletting to approximately five pints, and Washington's condition deteriorated further. Dr. Dick proposed a tracheotomy, but the others were not familiar with that procedure and therefore disapproved. Washington instructed Brown and Dick to leave the room, while he assured Craik, "Doctor, I die hard, but I am not afraid to go."
Washington's death came more swiftly than expected. On his deathbed, he instructed his private secretary
Tobias Lear
Tobias Lear (September 19, 1762 – October 11, 1816) was the personal secretary to President of the United States, President George Washington. Lear served Washington from 1784 until the former-President's death in 1799. Lear's journal details Was ...
to wait three days before his burial, out of fear of being entombed alive. According to Lear, he died between 10 and 11 p.m. on December 14, 1799, with Martha seated at the foot of his bed. His last words were "'Tis well", from his conversation with Lear about his burial. He was 67.

Congress immediately adjourned for the day upon news of Washington's death, and the Speaker's chair was shrouded in black the next morning. The funeral was held four days after his death on December 18, 1799, at Mount Vernon, where his body was interred. Cavalry and foot soldiers led the procession, and six colonels served as the pallbearers. The Mount Vernon funeral service was restricted mostly to family and friends. Reverend Thomas Davis read the funeral service by the vault with a brief address, followed by a ceremony performed by various members of Washington's Masonic lodge in Alexandria, Virginia. Congress chose Henry Lee III, Light-Horse Harry Lee to deliver the eulogy. Word of his death traveled slowly; church bells rang in the cities, and many places of business closed. People worldwide admired Washington and were saddened by his death, and memorial processions were held in major cities of the United States. Martha wore a black mourning cape for one year, and she burned their correspondence to protect their privacy. Only five letters between the couple are known to have survived: two from Martha to George and three from him to her.
The diagnosis of Washington's illness and the immediate cause of his death have been subjects of debate since the day he died. The published account of Drs. Craik and Brown stated that his symptoms had been consistent with ''cynanche trachealis'' (tracheal inflammation), a term of that period used to describe severe inflammation of the upper windpipe, including quinsy. Accusations have persisted since Washington's death concerning medical malpractice, with some believing he had been bled to death. Various modern medical authors have speculated that he died from a severe case of epiglottitis complicated by the given treatments, most notably the massive blood loss which almost certainly caused hypovolemia, hypovolemic shock.
Burial, net worth, and aftermath

Washington was buried in the old Washington family vault at Mount Vernon, situated on a grassy slope overspread with willow, juniper, cypress, and chestnut trees. It contained the remains of his brother Lawrence and other family members, but the decrepit brick vault needed repair, prompting Washington to leave instructions in his will for the construction of a new vault. Washington's estate at the time of his death was worth an estimated $780,000 in 1799, approximately equivalent to $17.82million in 2021. Washington's peak net worth was $587.0 million, including his 300 slaves. Washington held title to more than 65,000 acres of land in 37 different locations.
In 1830, a disgruntled ex-employee of the estate Attempted theft of George Washington's skull, attempted to steal what he thought was Washington's skull, prompting the construction of a more secure vault. The next year, the new vault was constructed at Mount Vernon to receive the remains of George and Martha and other relatives. In 1832, a joint Congressional committee debated moving his body from Mount Vernon to a crypt in the Capitol. The crypt had been built by architect Charles Bulfinch in the 1820s during the reconstruction of the burned-out capital, after the Burning of Washington by the British during the War of 1812. Southern opposition was intense, antagonized by an ever-growing rift between North and South; many were concerned that Washington's remains could end up on "a shore foreign to his native soil" if the country became divided, and Washington's remains stayed in Mount Vernon.
On October 7, 1837, Washington's remains were placed, still in the original lead coffin, within a marble sarcophagus designed by William Strickland (architect), William Strickland and constructed by John Struthers earlier that year. The sarcophagus was sealed and encased with planks, and an outer vault was constructed around it. The outer vault has the sarcophagi of both George and Martha Washington; the inner vault has the remains of other Washington family members and relatives.
Personal life

Washington was somewhat reserved in personality, but he generally had a strong presence among others. He made speeches and announcements when required, but he was not a noted orator or debater. He was taller than most of his contemporaries; accounts of his height vary from to tall, he weighed between as an adult, and he was known for his great strength. He had grey-blue eyes and long reddish-brown hair. He did not wear a wig#19th and 20th centuries, powdered wig; instead he wore his hair curled, powdered and tied in a queue in the 1775–1795 in Western fashion#Men's fashion, fashion of the day.
Washington frequently suffered from severe tooth decay and ultimately lost all George Washington's teeth, his teeth but one. He had several sets of false teeth, which he wore during his presidency, made using a variety of materials including both animal and human teeth, but wood was not used despite common lore. These dental problems left him in constant pain, for which he took laudanum. As a public figure, he relied upon the strict confidence of his dentist.
Washington was a talented equestrian early in life. He collected thoroughbreds at Mount Vernon, and his two favorite horses were Blueskin (horse), Blueskin and Nelson (horse), Nelson. Fellow Virginian
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
said Washington was "the best horseman of his age and the most graceful figure that could be seen on horseback"; he also hunted foxes, deer, ducks, and other game. He was an excellent dancer and attended the theater frequently. He drank in moderation but was morally opposed to excessive drinking, smoking tobacco, gambling, and profanity.
Religion and Freemasonry
Washington was descended from Anglican minister Lawrence Washington (1602–1652), Lawrence Washington (his great-great-grandfather), whose troubles with the Church of England may have prompted his heirs to emigrate to America. Washington was baptized as an infant in April 1732 and became a devoted member of the Church of England (the Anglican Church). He served more than 20 years as a vestryman and churchwarden for Fairfax Parish, Virginia, Fairfax Parish and Truro Parish, Virginia. He privately prayed and read the Bible daily, and he publicly encouraged people and the nation to pray. He may have taken communion on a regular basis prior to the Revolutionary War, but he did not do so following the war, for which he was admonished by Pastor James Abercrombie (Episcopal priest), James Abercrombie.

Washington believed in a "wise, inscrutable, and irresistible" Creator God who was active in the Universe, contrary to deism, deistic thought. He referred to God by the Enlightenment terms ''divine providence, Providence'', the ''Creator'', or the ''Almighty'', and also as the ''Divine Author'' or the ''Supreme Being''. He believed in a divine power who watched over battlefields, was involved in the outcome of war, was protecting his life, and was involved in American politics—and specifically in the creation of the United States. Modern historian Ron Chernow has posited that Washington avoided evangelistic Christianity or hellfire-and-brimstone speech along with communion and anything inclined to "flaunt his religiosity". Chernow has also said Washington "never used his religion as a device for partisan purposes or in official undertakings". No mention of Jesus Christ appears in The Washington Papers, his private correspondence, and such references are rare in his public writings. He frequently quoted from the Bible or paraphrased it, and often referred to the Anglican ''Book of Common Prayer''. There is debate on whether he is best classed as a Christian or a theistic rationalism, theistic rationalist—or both.
Washington emphasized religious toleration in a nation with numerous denominations and religions. He publicly attended services of different Christian denominations and prohibited anti-Catholic celebrations in the Army. He engaged workers at Mount Vernon without regard for religious belief or affiliation. While president, he acknowledged major religious sects and gave speeches on religious toleration. He was distinctly rooted in the ideas, values, and modes of thinking of the Enlightenment, but he harbored no contempt of organized Christianity and its clergy, "being no bigot myself to any mode of worship". In 1793, speaking to members of the The New Church (Swedenborgian), New Church in Baltimore, Washington proclaimed, "We have abundant reason to rejoice that in this Land the light of truth and reason has triumphed over the power of bigotry and superstition."
Freemasonry was a widely accepted institution in the late 18th century, known for advocating moral teachings. Washington was attracted to the Masons' dedication to the Enlightenment principles of rationality, reason, and brotherhood. The American Masonic lodges did not share the anti-clerical perspective of the anticlericalism and Freemasonry, controversial European lodges. A Masonic lodge was established in Fredericksburg in September 1752, and Washington was initiated two months later at the age of 20 as one of its first Entered Apprentices. Within a year, he progressed through its ranks to become a Master Mason. Washington had high regard for the Masonic Order, but his personal lodge attendance was sporadic. In 1777, a convention of Virginia lodges asked him to be the Grand Master of the newly established Grand Lodge of Virginia, but he declined due to his commitments leading the Continental Army. After 1782, he frequently corresponded with Masonic lodges and members, and he was listed as Master in the Virginia charter of George Washington Masonic National Memorial, Alexandria Lodge No. 22 in 1788.
Slavery

In Washington's lifetime, slavery was History of slavery in Virginia, deeply ingrained in the economic and social fabric of Virginia. Slavery was Slavery in the colonial history of the United States, legal in all of the Thirteen Colonies prior to the American Revolution.
Washington's slaves
Washington owned and rented Slavery in the United States, enslaved African Americans, and during his lifetime over 577 slaves lived and worked at Mount Vernon.
He acquired them through inheritance, gaining control of 84 Dowry, dower slaves upon his marriage to Martha, and purchased at least 71 slaves between 1752 and 1773. From 1786 he rented slaves, at his death he was renting 41.
His early views on slavery were no different from any Virginia
planter of the time. From the 1760s his attitudes underwent a slow evolution. The first doubts were prompted by his transition from tobacco to grain crops, which left him with a costly surplus of slaves, causing him to question the system's economic efficiency. His growing disillusionment with the institution was spurred by the principles of the American Revolution and revolutionary friends such as Lafayette and Hamilton. Most historians agree the Revolution was central to the evolution of Washington's attitudes on slavery; "After 1783", Kenneth Morgan writes, "...[Washington] began to express inner tensions about the problem of slavery more frequently, though always in private..."
The many contemporary reports of slave treatment at Mount Vernon are varied and conflicting. Historian Kenneth Morgan (2000) maintains that Washington was frugal on spending for clothes and bedding for his slaves, and only provided them with just enough food, and that he maintained strict control over his slaves, instructing his overseers to keep them working hard from dawn to dusk year-round. However, historian Dorothy Twohig (2001) said: "Food, clothing, and housing seem to have been at least adequate". Washington faced growing debts involved with the costs of supporting slaves. He held an "engrained sense of racial superiority" towards African Americans but harbored no ill feelings toward them. Some enslaved families worked at different locations on the plantation but were allowed to visit one another on their days off. Washington's slaves received two hours off for meals during the workday and were given time off on Sundays and religious holidays.
Some accounts report that Washington opposed flogging but at times sanctioned its use, generally as a last resort, on both men and women slaves. Washington used both reward and punishment to encourage discipline and productivity in his slaves. He tried appealing to an individual's sense of pride, gave better blankets and clothing to the "most deserving", and motivated his slaves with cash rewards. He believed "watchfulness and admonition" to be often better deterrents against transgressions but would punish those who "will not do their duty by fair means". Punishment ranged in severity from demotion back to fieldwork, through whipping and beatings, to permanent separation from friends and family by sale. Historian Ron Chernow maintains that overseers were required to warn slaves before resorting to the lash and required Washington's written permission before whipping, though his extended absences did not always permit this. Washington remained dependent on slave labor to work his farms and negotiated the purchase of more slaves in 1786 and 1787.

Washington brought several of his slaves with him and his family to the federal capital during his presidency. When the capital moved from New York City to Philadelphia in 1791, the president began rotating his slave household staff periodically between the capital and Mount Vernon. This was done deliberately to circumvent Pennsylvania's An Act for the Gradual Abolition of Slavery, Slavery Abolition Act, which, in part, automatically freed any slave who moved to the state and lived there for more than six months. In May 1796, Martha's personal and favorite slave Oney Judge escaped to Portsmouth, New Hampshire, Portsmouth. At Martha's behest, Washington attempted to capture Ona, using a Treasury agent, but this effort failed. In February 1797, Washington's personal slave Hercules Posey, Hercules escaped to Philadelphia and was never found.
In February 1786, Washington took a census of Mount Vernon and recorded 224 slaves. By 1799, slaves at Mount Vernon totaled 317, including 143 children. Washington owned 124 slaves, leased 40, and held 153 for his wife's dower interest. Washington supported many slaves who were too young or too old to work, greatly increasing Mount Vernon's slave population and causing the plantation to operate at a loss.
Abolition and manumission
Based on his letters, diary, documents, accounts from colleagues, employees, friends, and visitors, Washington slowly developed a cautious sympathy toward Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionism that eventually ended with his will manumission, freeing his military/war valet William Lee (valet), Billy Lee, and then subsequently freeing the rest of his personally-owned slaves outright upon Martha's death. As president, he remained publicly silent on the topic of slavery, believing it was a nationally divisive issue which could destroy the union.
During the American Revolutionary War, Washington began to change his views on slavery.
In a 1778 letter to Lund Washington, he made clear his desire "to get quit of Negroes" when discussing the exchange of slaves for the land he wanted to buy. The next year, Washington stated his intention not to separate enslaved families as a result of "a change of masters". During the 1780s, Washington privately expressed his support for the gradual emancipation of slaves. Between 1783 and 1786, he gave moral support to a plan proposed by Lafayette to purchase land and free slaves to work on it, but declined to participate in the experiment. Washington privately expressed support for emancipation to prominent Methodists Thomas Coke (bishop), Thomas Coke and Francis Asbury in 1785 but declined to sign their petition. In personal correspondence the next year, he made clear his desire to see the institution of slavery ended by a gradual legislative process, a view that correlated with the mainstream antislavery literature published in the 1780s that Washington possessed. He significantly reduced his purchases of slaves after the war but continued to acquire them in small numbers.

In 1788, Washington declined a suggestion from a leading French abolitionist, Jacques Pierre Brissot, Jacques Brissot, to establish an abolitionist society in Virginia, stating that although he supported the idea, the time was not yet right to confront the issue. The historian Henry Wiencek (2003) believes, based on a remark that appears in the notebook of his biographer David Humphreys (soldier), David Humphreys, that Washington considered making a public statement by freeing his slaves on the eve of his presidency in 1789. The historian Philip D. Morgan (2005) disagrees, believing the remark was a "private expression of remorse" at his inability to free his slaves. Other historians agree with Morgan that Washington was determined not to risk national unity over an issue as divisive as slavery. Washington never responded to any of the antislavery petitions he received, and the subject was not mentioned in either his last address to Congress or his Farewell Address.
The first clear indication that Washington seriously intended to free his slaves appears in a letter written to his secretary,
Tobias Lear
Tobias Lear (September 19, 1762 – October 11, 1816) was the personal secretary to President of the United States, President George Washington. Lear served Washington from 1784 until the former-President's death in 1799. Lear's journal details Was ...
, in 1794. Washington instructed Lear to find buyers for his land in western Virginia, explaining in a private coda that he was doing so "to liberate a certain species of property which I possess, very repugnantly to my own feelings". The plan, along with others Washington considered in 1795 and 1796, could not be realized because he failed to find buyers for his land, his reluctance to break up slave families, and the refusal of the Custis heirs to help prevent such separations by freeing their dower slaves at the same time.
On July 9, 1799, Washington finished making his last will; the longest provision concerned slavery. All his slaves were to be freed after the death of his wife, Martha. Washington said he did not free them immediately because his slaves intermarried with his wife's dower slaves. He forbade their sale or transportation out of Virginia. His will provided that old and young freed people be taken care of indefinitely; younger ones were to be taught to read and write and placed in suitable occupations. Washington freed more than 160 slaves, including about 25 he had acquired from his wife's brother Bartholomew Dandridge in payment of a debt. He was among the few large slave-holding Virginians during the Revolutionary Era who emancipated their slaves.
On January 1, 1801, one year after George Washington's death, Martha Washington signed an order to free his slaves. Many of them, having never strayed far from Mount Vernon, were naturally reluctant to try their luck elsewhere; others refused to abandon spouses or children still held as dower slaves (the Custis estate) and also stayed with or near Martha. Following George Washington's instructions in his will, funds were used to feed and clothe the young, aged, and infirm slaves until the early 1830s.
Historical reputation and legacy

Washington's legacy endures as one of the most influential in American history since he served as commander-in-chief of the
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
, a hero of the American Revolution, Revolution, and the first
president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
. Various historians maintain that he also was a dominant factor in America's founding, the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, and the
Constitutional Convention. American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War comrade Henry Lee III, Light-Horse Harry Lee s:The Father of His Country, eulogized him as "First in war—first in peace—and first in the hearts of his countrymen". Lee's words became the hallmark by which Washington's reputation was impressed upon the American memory, with some biographers regarding him as the great exemplar of republicanism. He set many precedents for the national government and the presidency in particular, and he was called the "Father of His Country" as early as 1778.
In 1879, Congress proclaimed Presidents' Day, Washington's Birthday to be a federal holiday. Twentieth-century biographer Douglas Southall Freeman concluded, "The great big thing stamped across that man is character." Modern historian David Hackett Fischer has expanded upon Freeman's assessment, defining Washington's character as "integrity, self-discipline, courage, absolute honesty, resolve, and decision, but also forbearance, decency, and respect for others".

Washington became an international symbol for liberation and nationalism as the leader of the first successful revolution against a colonial empire. The Federalist Party, Federalists made him the symbol of their party, but the Democratic-Republican Party, Jeffersonians continued to distrust his influence for many years and delayed building the Washington Monument. Washington was elected a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences on January 31, 1781, before he had even begun his presidency. He was posthumously appointed to the grade of General of the Armies of the United States during the United States Bicentennial to ensure he would never be outranked; this was accomplished by the congressional joint resolution s:Public Law 94-479, Public Law 94-479 passed on January 19, 1976, with an effective appointment date of July 4, 1976. On March 13, 1978, Washington was militarily promoted to the rank of General of the Armies of the United States, General of the Armies.
Mason Locke Weems, Parson Weems wrote a Hagiography, hagiographic biography in 1809 to honor Washington. Historian Ron Chernow maintains that Weems attempted to humanize Washington, making him look less stern, and to inspire "patriotism and morality" and to foster "enduring myths", such as Washington's refusal to lie about damaging his father's cherry tree. Weems' accounts have never been proven or disproven. Historian John Ferling, however, maintains that Washington remains the only founder and president ever to be referred to as "godlike", and points out that his character has been the most scrutinized by historians, past and present. Historian Gordon S. Wood concludes that "the greatest act of his life, the one that gave him his greatest fame, was his resignation as commander-in-chief of the American forces." Chernow suggests that Washington was "burdened by public life" and divided by "unacknowledged ambition mingled with self-doubt". A 1993 review of presidential polls and surveys consistently ranked Washington number 4, 3, or2 among presidents. A 2018 Siena College Research Institute survey ranked him number1 among presidents.
In the 21st century, Washington's reputation has been critically scrutinized. Along with various other Founding Fathers, he has been condemned for holding enslaved human beings. Though he expressed the desire to see the abolition of slavery come through legislation, he did not initiate or support any initiatives for bringing about its end. This has led to calls from some activists to remove his name from public buildings and his statue from public spaces. Nonetheless, Washington maintains his place among the highest-ranked U.S. Presidents, listed second (after Abraham Lincoln, Lincoln) in a 2021 C-SPAN poll.
Memorials

Jared Sparks began collecting and publishing Washington's documentary record in the 1830s in ''Life and Writings of George Washington'' (12 vols., 1834–1837). ''The Writings of George Washington from the Original Manuscript Sources, 1745–1799'' (1931–1944) is a 39-volume set edited by John Clement Fitzpatrick, whom the George Washington Bicentennial Commission commissioned. It contains more than 17,000 letters and documents and is available online from the University of Virginia.
Educational institutions
Numerous secondary schools are named in honor of Washington, as are many universities, including George Washington University and Washington University in St. Louis.
Places and monuments
Many places and monuments have been named in honor of Washington, most notably the capital of the United States, Washington, D.C. The state of Washington (state), Washington is the only US state to be named after a president.
Washington appears as one of four U.S. presidents in a colossal statue by Gutzon Borglum on Mount Rushmore in South Dakota.
Currency and postage
George Washington appears on contemporary U.S. currency, including the United States one-dollar bill, one-dollar bill, the Presidential dollar coins, Presidential one-dollar coin and the Quarter (United States coin), quarter-dollar coin (the Washington quarter). Washington and
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
appeared on the :File:First US Postage stamps of 1847.tiff, nation's first postage stamps in 1847. Washington has since appeared on many postage issues, more than any other person.
Washington 1862 Issue-24c.jpg, Washington issue of 1862
Washington WF 1917 Issue-5c (cropped).jpg, Washington–Franklin Issues, Washington–Franklin issue of 1917
2006 Quarter Proof.png, Washington Quarter (United States coin), quarter dollar
George Washington Presidential $1 Coin obverse.png, George Washington Presidential dollar coins, Presidential one-dollar coin
One dollar 1928.jpg, Washington on the 1928 United States one-dollar bill, dollar bill
See also
* British Army during the American War of Independence, British Army during the American Revolutionary War
* Founders Online
* List of American Revolutionary War battles
* List of Continental Forces in the American Revolutionary War
* Timeline of the American Revolution
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
Print sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Primary sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Online sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
''Copies of the wills of General George Washington: the first president of the United States and of Martha Washington, his wife''(1904), edited by E. R. Holbrook
George Washington Personal ManuscriptsGeorge Washington Resourcesat the University of Virginia Library
George Washington's Speeches: Quote-search-toolOriginal Digitized Letters of George Washington Shapell Manuscript Foundation
The Papers of George Washington subset o
Founders Onlinefrom the National Archives and Records Administration, National Archives
*
Washington & the American Revolution BBC Radio4 discussion with Carol Berkin, Simon Middleton & Colin Bonwick (''In Our Time'', June 24, 2004)
*
Guide to the George Washington Collection 1776–1792at th
University of Chicago Special Collections Research Center
{{DEFAULTSORT:Washington, George
George Washington,
1732 births
1799 deaths
Washington family, George
People from Mount Vernon, Virginia
People from Westmoreland County, Virginia
Presidents of the United States
18th-century American Episcopalians
18th-century American politicians
18th-century American writers
18th-century presidents of the United States
18th-century United States Army personnel
American cartographers
American foreign policy writers
American Freemasons
American male non-fiction writers
American military personnel of the Seven Years' War
American militia officers
American people of English descent
American planters
American rebels
American slave owners
American surveyors
British America army officers
Burials at Mount Vernon
Candidates in the 1789 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1792 United States presidential election
Chancellors of the College of William & Mary
Commanders in chief
Commanding Generals of the United States Army
Congressional Gold Medal recipients
Continental Army generals
Continental Army officers from Virginia
Continental Congressmen from Virginia
Respiratory disease deaths in Virginia
Episcopalians from Virginia
Farmers from Virginia
Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
Free speech activists
Hall of Fame for Great Americans inductees
House of Burgesses members
Members of the American Philosophical Society
People of the American Enlightenment
People of Virginia in the French and Indian War
Signers of the Continental Association
Signers of the United States Constitution
United States Army generals
Virginia Independents
Virginia militiamen in the American Revolution
Washington and Lee University people
Washington College people
Virginia dynasty
 The
The  The French detachment proved to be only about fifty men, so Washington advanced on May 28 with a small force of Virginians and Indian allies to ambush them. What took place, known as the
The French detachment proved to be only about fifty men, so Washington advanced on May 28 with a small force of Virginians and Indian allies to ambush them. What took place, known as the  In 1755, Washington served voluntarily as an aide to General
In 1755, Washington served voluntarily as an aide to General  On January 6, 1759, Washington, at age 26, married
On January 6, 1759, Washington, at age 26, married  By occupation, Washington was a planter, and he imported luxuries and other goods from England, paying for them by exporting tobacco. His profligate spending combined with low tobacco prices left him £1,800 in debt by 1764, prompting him to diversify his holdings. In 1765, because of erosion and other soil problems, he changed Mount Vernon's primary cash crop from tobacco to wheat and expanded operations to include corn
By occupation, Washington was a planter, and he imported luxuries and other goods from England, paying for them by exporting tobacco. His profligate spending combined with low tobacco prices left him £1,800 in debt by 1764, prompting him to diversify his holdings. In 1765, because of erosion and other soil problems, he changed Mount Vernon's primary cash crop from tobacco to wheat and expanded operations to include corn 
 Early in 1775, in response to the growing rebellious movement, London sent British troops, commanded by
Early in 1775, in response to the growing rebellious movement, London sent British troops, commanded by  Washington then proceeded to
Washington then proceeded to  Washington first ordered a 60-mile search for
Washington first ordered a 60-mile search for  Washington retreated across the Delaware River to Pennsylvania and returned to New Jersey on January 3, 1777, launching an attack on British regulars at
Washington retreated across the Delaware River to Pennsylvania and returned to New Jersey on January 3, 1777, launching an attack on British regulars at  Washington's army of 11,000 went into winter quarters at
Washington's army of 11,000 went into winter quarters at  Baron
Baron  Arnold repeatedly asked for command of West Point, and Washington finally agreed in August. Arnold met André on September 21, giving him plans to take over the garrison. Militia forces captured André and discovered the plans, but Arnold escaped to New York. Washington recalled the commanders positioned under Arnold at key points around the fort to prevent any complicity, but he did not suspect Arnold's wife Peggy. Washington assumed personal command at West Point and reorganized its defenses. André's trial for espionage ended in a death sentence, and Washington offered to return him to the British in exchange for Arnold, but Clinton refused. André was hanged on October 2, 1780, despite his last request being to face a firing squad, to deter other spies.
Arnold repeatedly asked for command of West Point, and Washington finally agreed in August. Arnold met André on September 21, giving him plans to take over the garrison. Militia forces captured André and discovered the plans, but Arnold escaped to New York. Washington recalled the commanders positioned under Arnold at key points around the fort to prevent any complicity, but he did not suspect Arnold's wife Peggy. Washington assumed personal command at West Point and reorganized its defenses. André's trial for espionage ended in a death sentence, and Washington offered to return him to the British in exchange for Arnold, but Clinton refused. André was hanged on October 2, 1780, despite his last request being to face a firing squad, to deter other spies.
 When peace negotiations began in April 1782, both the British and French began gradually evacuating their forces. The American treasury was empty, unpaid, and mutinous soldiers forced the adjournment of Congress, and Washington dispelled unrest by suppressing the
When peace negotiations began in April 1782, both the British and French began gradually evacuating their forces. The American treasury was empty, unpaid, and mutinous soldiers forced the adjournment of Congress, and Washington dispelled unrest by suppressing the  Before returning to private life in June 1783, Washington called for a strong union. Though he was concerned that he might be criticized for meddling in civil matters, he sent a circular letter to all the states, maintaining that the
Before returning to private life in June 1783, Washington called for a strong union. Though he was concerned that he might be criticized for meddling in civil matters, he sent a circular letter to all the states, maintaining that the  Washington arrived in Philadelphia on May 9, 1787, though a quorum was not attained until Friday, May 25. Benjamin Franklin nominated Washington to preside over the convention, and he was unanimously elected to serve as president general. The convention's state-mandated purpose was to revise the Articles of Confederation with "all such alterations and further provisions" required to improve them, and the new government would be established when the resulting document was "duly confirmed by the several states". Governor Edmund Randolph of Virginia introduced Madison's
Washington arrived in Philadelphia on May 9, 1787, though a quorum was not attained until Friday, May 25. Benjamin Franklin nominated Washington to preside over the convention, and he was unanimously elected to serve as president general. The convention's state-mandated purpose was to revise the Articles of Confederation with "all such alterations and further provisions" required to improve them, and the new government would be established when the resulting document was "duly confirmed by the several states". Governor Edmund Randolph of Virginia introduced Madison's  Washington was
Washington was  Washington's first term was largely devoted to economic concerns, in which Hamilton had devised various plans to address matters. The establishment of public credit became a primary challenge for the federal government. Hamilton submitted a report to a deadlocked Congress, and he, Madison, and Jefferson reached the
Washington's first term was largely devoted to economic concerns, in which Hamilton had devised various plans to address matters. The establishment of public credit became a primary challenge for the federal government. Hamilton submitted a report to a deadlocked Congress, and he, Madison, and Jefferson reached the  In April 1792, the French Revolutionary Wars began between Great Britain and France, and Washington declared America's neutrality. The revolutionary government of France sent diplomat Edmond-Charles Genêt, Citizen Genêt to America, and he was welcomed with great enthusiasm. He created a network of new Democratic-Republican Societies promoting France's interests, but Washington denounced them and demanded that the French recall Genêt. The National Assembly of France granted Washington honorary French citizenship on August 26, 1792, during the early stages of the
In April 1792, the French Revolutionary Wars began between Great Britain and France, and Washington declared America's neutrality. The revolutionary government of France sent diplomat Edmond-Charles Genêt, Citizen Genêt to America, and he was welcomed with great enthusiasm. He created a network of new Democratic-Republican Societies promoting France's interests, but Washington denounced them and demanded that the French recall Genêt. The National Assembly of France granted Washington honorary French citizenship on August 26, 1792, during the early stages of the  Ron Chernow describes Washington as always trying to be even-handed in dealing with the Natives. He states that Washington hoped they would abandon their itinerant hunting life and adapt to fixed agricultural communities in the manner of white settlers. He also maintains that Washington never advocated outright confiscation of tribal land or the forcible removal of tribes and that he berated American settlers who abused natives, admitting that he held out no hope for pacific relations with the natives as long as "frontier settlers entertain the opinion that there is not the same crime (or indeed no crime at all) in killing a native as in killing a white man."
By contrast, Colin G. Calloway writes that "Washington had a lifelong obsession with getting Indian land, either for himself or for his nation, and initiated policies and campaigns that had devastating effects in Indian country." "The growth of the nation," Galloway has stated, "demanded the dispossession of Indian people. Washington hoped the process could be bloodless and that Indian people would give up their lands for a "fair" price and move away. But if Indians refused and resisted, as they often did, he felt he had no choice but to "extirpate" them and that the expeditions he sent to destroy Indian towns were therefore entirely justified."
During the fall of 1789, Washington had to contend with the British refusing to evacuate their forts in the Northwest frontier and their Northwest Indian War, concerted efforts to incite hostile Indian tribes to attack European Americans, American settlers. The Northwest tribes under Miami people, Miami chief Little Turtle allied with the British Army to resist American expansion, and killed 1,500 settlers between 1783 and 1790.
As documented by Harless (2018), Washington declared that "The Government of the United States are determined that their Administration of Indian Affairs shall be directed entirely by the great principles of Justice and humanity", and provided that treaties should negotiate their land interests. The administration regarded powerful tribes as foreign nations, and Washington even smoked a Ceremonial pipe, peace pipe and drank wine with them at the President's House (Philadelphia), Philadelphia presidential house. He made numerous attempts to conciliate them; he equated killing indigenous peoples with killing whites and sought to integrate them into European Americans, European American culture. Secretary of War
Ron Chernow describes Washington as always trying to be even-handed in dealing with the Natives. He states that Washington hoped they would abandon their itinerant hunting life and adapt to fixed agricultural communities in the manner of white settlers. He also maintains that Washington never advocated outright confiscation of tribal land or the forcible removal of tribes and that he berated American settlers who abused natives, admitting that he held out no hope for pacific relations with the natives as long as "frontier settlers entertain the opinion that there is not the same crime (or indeed no crime at all) in killing a native as in killing a white man."
By contrast, Colin G. Calloway writes that "Washington had a lifelong obsession with getting Indian land, either for himself or for his nation, and initiated policies and campaigns that had devastating effects in Indian country." "The growth of the nation," Galloway has stated, "demanded the dispossession of Indian people. Washington hoped the process could be bloodless and that Indian people would give up their lands for a "fair" price and move away. But if Indians refused and resisted, as they often did, he felt he had no choice but to "extirpate" them and that the expeditions he sent to destroy Indian towns were therefore entirely justified."
During the fall of 1789, Washington had to contend with the British refusing to evacuate their forts in the Northwest frontier and their Northwest Indian War, concerted efforts to incite hostile Indian tribes to attack European Americans, American settlers. The Northwest tribes under Miami people, Miami chief Little Turtle allied with the British Army to resist American expansion, and killed 1,500 settlers between 1783 and 1790.
As documented by Harless (2018), Washington declared that "The Government of the United States are determined that their Administration of Indian Affairs shall be directed entirely by the great principles of Justice and humanity", and provided that treaties should negotiate their land interests. The administration regarded powerful tribes as foreign nations, and Washington even smoked a Ceremonial pipe, peace pipe and drank wine with them at the President's House (Philadelphia), Philadelphia presidential house. He made numerous attempts to conciliate them; he equated killing indigenous peoples with killing whites and sought to integrate them into European Americans, European American culture. Secretary of War  In 1790, Washington sent Brigadier General Josiah Harmar to pacify the Northwest tribes, but Little Turtle routed him twice and forced him to withdraw. The Northwestern Confederacy of tribes used guerrilla tactics and were an effective force against the sparsely manned American Army. Washington sent Major General Arthur St. Clair from Fort Washington (Ohio), Fort Washington on an expedition to restore peace in the territory in 1791. On November 4, St. Clair's forces were ambushed and St. Clair's defeat, soundly defeated by tribal forces with few survivors, despite Washington's warning of surprise attacks. Washington was outraged over what he viewed to be excessive Native American brutality and execution of captives, including women and children.
St. Clair resigned his commission, and Washington replaced him with the Revolutionary War hero General Anthony Wayne. From 1792 to 1793, Wayne instructed his troops on Native American warfare tactics and instilled discipline which was lacking under St. Clair. In August 1794, Washington sent Wayne into tribal territory with authority to drive them out by burning their villages and crops in the Maumee, Ohio, Maumee Valley. On August 24, the American army under Wayne's leadership defeated the western confederacy at the Battle of Fallen Timbers, and the Treaty of Greenville in August 1795 opened up two-thirds of the Ohio Country for American settlement.
In 1790, Washington sent Brigadier General Josiah Harmar to pacify the Northwest tribes, but Little Turtle routed him twice and forced him to withdraw. The Northwestern Confederacy of tribes used guerrilla tactics and were an effective force against the sparsely manned American Army. Washington sent Major General Arthur St. Clair from Fort Washington (Ohio), Fort Washington on an expedition to restore peace in the territory in 1791. On November 4, St. Clair's forces were ambushed and St. Clair's defeat, soundly defeated by tribal forces with few survivors, despite Washington's warning of surprise attacks. Washington was outraged over what he viewed to be excessive Native American brutality and execution of captives, including women and children.
St. Clair resigned his commission, and Washington replaced him with the Revolutionary War hero General Anthony Wayne. From 1792 to 1793, Wayne instructed his troops on Native American warfare tactics and instilled discipline which was lacking under St. Clair. In August 1794, Washington sent Wayne into tribal territory with authority to drive them out by burning their villages and crops in the Maumee, Ohio, Maumee Valley. On August 24, the American army under Wayne's leadership defeated the western confederacy at the Battle of Fallen Timbers, and the Treaty of Greenville in August 1795 opened up two-thirds of the Ohio Country for American settlement.
 On April 22, 1793, during the
On April 22, 1793, during the  In 1796, Washington declined to run for a third term of office, believing his death in office would create an image of a lifetime appointment. The precedent of a two-term limit was created by his retirement from office. In May 1792, in anticipation of his retirement, Washington instructed
In 1796, Washington declined to run for a third term of office, believing his death in office would create an image of a lifetime appointment. The precedent of a two-term limit was created by his retirement from office. In May 1792, in anticipation of his retirement, Washington instructed  On December 12, 1799, Washington inspected his farms on horseback. He returned home late and had guests over for dinner. He had a sore throat the next day but was well enough to mark trees for cutting. That evening, he complained of chest congestion but was still cheerful. On Saturday, he awoke to an inflamed throat and difficulty breathing, so he ordered estate overseer George Rawlins to remove nearly a pint of his blood; bloodletting was a common practice of the time. His family summoned Drs. James Craik, Gustavus Richard Brown, and Elisha C. Dick. Dr. William Thornton arrived some hours after Washington died.
Dr. Brown thought Washington had Peritonsillar abscess, quinsy; Dr. Dick thought the condition was a more serious "violent inflammation of the throat". They continued the process of bloodletting to approximately five pints, and Washington's condition deteriorated further. Dr. Dick proposed a tracheotomy, but the others were not familiar with that procedure and therefore disapproved. Washington instructed Brown and Dick to leave the room, while he assured Craik, "Doctor, I die hard, but I am not afraid to go."
Washington's death came more swiftly than expected. On his deathbed, he instructed his private secretary
On December 12, 1799, Washington inspected his farms on horseback. He returned home late and had guests over for dinner. He had a sore throat the next day but was well enough to mark trees for cutting. That evening, he complained of chest congestion but was still cheerful. On Saturday, he awoke to an inflamed throat and difficulty breathing, so he ordered estate overseer George Rawlins to remove nearly a pint of his blood; bloodletting was a common practice of the time. His family summoned Drs. James Craik, Gustavus Richard Brown, and Elisha C. Dick. Dr. William Thornton arrived some hours after Washington died.
Dr. Brown thought Washington had Peritonsillar abscess, quinsy; Dr. Dick thought the condition was a more serious "violent inflammation of the throat". They continued the process of bloodletting to approximately five pints, and Washington's condition deteriorated further. Dr. Dick proposed a tracheotomy, but the others were not familiar with that procedure and therefore disapproved. Washington instructed Brown and Dick to leave the room, while he assured Craik, "Doctor, I die hard, but I am not afraid to go."
Washington's death came more swiftly than expected. On his deathbed, he instructed his private secretary  Congress immediately adjourned for the day upon news of Washington's death, and the Speaker's chair was shrouded in black the next morning. The funeral was held four days after his death on December 18, 1799, at Mount Vernon, where his body was interred. Cavalry and foot soldiers led the procession, and six colonels served as the pallbearers. The Mount Vernon funeral service was restricted mostly to family and friends. Reverend Thomas Davis read the funeral service by the vault with a brief address, followed by a ceremony performed by various members of Washington's Masonic lodge in Alexandria, Virginia. Congress chose Henry Lee III, Light-Horse Harry Lee to deliver the eulogy. Word of his death traveled slowly; church bells rang in the cities, and many places of business closed. People worldwide admired Washington and were saddened by his death, and memorial processions were held in major cities of the United States. Martha wore a black mourning cape for one year, and she burned their correspondence to protect their privacy. Only five letters between the couple are known to have survived: two from Martha to George and three from him to her.
The diagnosis of Washington's illness and the immediate cause of his death have been subjects of debate since the day he died. The published account of Drs. Craik and Brown stated that his symptoms had been consistent with ''cynanche trachealis'' (tracheal inflammation), a term of that period used to describe severe inflammation of the upper windpipe, including quinsy. Accusations have persisted since Washington's death concerning medical malpractice, with some believing he had been bled to death. Various modern medical authors have speculated that he died from a severe case of epiglottitis complicated by the given treatments, most notably the massive blood loss which almost certainly caused hypovolemia, hypovolemic shock.
Congress immediately adjourned for the day upon news of Washington's death, and the Speaker's chair was shrouded in black the next morning. The funeral was held four days after his death on December 18, 1799, at Mount Vernon, where his body was interred. Cavalry and foot soldiers led the procession, and six colonels served as the pallbearers. The Mount Vernon funeral service was restricted mostly to family and friends. Reverend Thomas Davis read the funeral service by the vault with a brief address, followed by a ceremony performed by various members of Washington's Masonic lodge in Alexandria, Virginia. Congress chose Henry Lee III, Light-Horse Harry Lee to deliver the eulogy. Word of his death traveled slowly; church bells rang in the cities, and many places of business closed. People worldwide admired Washington and were saddened by his death, and memorial processions were held in major cities of the United States. Martha wore a black mourning cape for one year, and she burned their correspondence to protect their privacy. Only five letters between the couple are known to have survived: two from Martha to George and three from him to her.
The diagnosis of Washington's illness and the immediate cause of his death have been subjects of debate since the day he died. The published account of Drs. Craik and Brown stated that his symptoms had been consistent with ''cynanche trachealis'' (tracheal inflammation), a term of that period used to describe severe inflammation of the upper windpipe, including quinsy. Accusations have persisted since Washington's death concerning medical malpractice, with some believing he had been bled to death. Various modern medical authors have speculated that he died from a severe case of epiglottitis complicated by the given treatments, most notably the massive blood loss which almost certainly caused hypovolemia, hypovolemic shock.
 Washington was buried in the old Washington family vault at Mount Vernon, situated on a grassy slope overspread with willow, juniper, cypress, and chestnut trees. It contained the remains of his brother Lawrence and other family members, but the decrepit brick vault needed repair, prompting Washington to leave instructions in his will for the construction of a new vault. Washington's estate at the time of his death was worth an estimated $780,000 in 1799, approximately equivalent to $17.82million in 2021. Washington's peak net worth was $587.0 million, including his 300 slaves. Washington held title to more than 65,000 acres of land in 37 different locations.
In 1830, a disgruntled ex-employee of the estate Attempted theft of George Washington's skull, attempted to steal what he thought was Washington's skull, prompting the construction of a more secure vault. The next year, the new vault was constructed at Mount Vernon to receive the remains of George and Martha and other relatives. In 1832, a joint Congressional committee debated moving his body from Mount Vernon to a crypt in the Capitol. The crypt had been built by architect Charles Bulfinch in the 1820s during the reconstruction of the burned-out capital, after the Burning of Washington by the British during the War of 1812. Southern opposition was intense, antagonized by an ever-growing rift between North and South; many were concerned that Washington's remains could end up on "a shore foreign to his native soil" if the country became divided, and Washington's remains stayed in Mount Vernon.
On October 7, 1837, Washington's remains were placed, still in the original lead coffin, within a marble sarcophagus designed by William Strickland (architect), William Strickland and constructed by John Struthers earlier that year. The sarcophagus was sealed and encased with planks, and an outer vault was constructed around it. The outer vault has the sarcophagi of both George and Martha Washington; the inner vault has the remains of other Washington family members and relatives.
Washington was buried in the old Washington family vault at Mount Vernon, situated on a grassy slope overspread with willow, juniper, cypress, and chestnut trees. It contained the remains of his brother Lawrence and other family members, but the decrepit brick vault needed repair, prompting Washington to leave instructions in his will for the construction of a new vault. Washington's estate at the time of his death was worth an estimated $780,000 in 1799, approximately equivalent to $17.82million in 2021. Washington's peak net worth was $587.0 million, including his 300 slaves. Washington held title to more than 65,000 acres of land in 37 different locations.
In 1830, a disgruntled ex-employee of the estate Attempted theft of George Washington's skull, attempted to steal what he thought was Washington's skull, prompting the construction of a more secure vault. The next year, the new vault was constructed at Mount Vernon to receive the remains of George and Martha and other relatives. In 1832, a joint Congressional committee debated moving his body from Mount Vernon to a crypt in the Capitol. The crypt had been built by architect Charles Bulfinch in the 1820s during the reconstruction of the burned-out capital, after the Burning of Washington by the British during the War of 1812. Southern opposition was intense, antagonized by an ever-growing rift between North and South; many were concerned that Washington's remains could end up on "a shore foreign to his native soil" if the country became divided, and Washington's remains stayed in Mount Vernon.
On October 7, 1837, Washington's remains were placed, still in the original lead coffin, within a marble sarcophagus designed by William Strickland (architect), William Strickland and constructed by John Struthers earlier that year. The sarcophagus was sealed and encased with planks, and an outer vault was constructed around it. The outer vault has the sarcophagi of both George and Martha Washington; the inner vault has the remains of other Washington family members and relatives.
 Washington was somewhat reserved in personality, but he generally had a strong presence among others. He made speeches and announcements when required, but he was not a noted orator or debater. He was taller than most of his contemporaries; accounts of his height vary from to tall, he weighed between as an adult, and he was known for his great strength. He had grey-blue eyes and long reddish-brown hair. He did not wear a wig#19th and 20th centuries, powdered wig; instead he wore his hair curled, powdered and tied in a queue in the 1775–1795 in Western fashion#Men's fashion, fashion of the day.
Washington frequently suffered from severe tooth decay and ultimately lost all George Washington's teeth, his teeth but one. He had several sets of false teeth, which he wore during his presidency, made using a variety of materials including both animal and human teeth, but wood was not used despite common lore. These dental problems left him in constant pain, for which he took laudanum. As a public figure, he relied upon the strict confidence of his dentist.
Washington was a talented equestrian early in life. He collected thoroughbreds at Mount Vernon, and his two favorite horses were Blueskin (horse), Blueskin and Nelson (horse), Nelson. Fellow Virginian
Washington was somewhat reserved in personality, but he generally had a strong presence among others. He made speeches and announcements when required, but he was not a noted orator or debater. He was taller than most of his contemporaries; accounts of his height vary from to tall, he weighed between as an adult, and he was known for his great strength. He had grey-blue eyes and long reddish-brown hair. He did not wear a wig#19th and 20th centuries, powdered wig; instead he wore his hair curled, powdered and tied in a queue in the 1775–1795 in Western fashion#Men's fashion, fashion of the day.
Washington frequently suffered from severe tooth decay and ultimately lost all George Washington's teeth, his teeth but one. He had several sets of false teeth, which he wore during his presidency, made using a variety of materials including both animal and human teeth, but wood was not used despite common lore. These dental problems left him in constant pain, for which he took laudanum. As a public figure, he relied upon the strict confidence of his dentist.
Washington was a talented equestrian early in life. He collected thoroughbreds at Mount Vernon, and his two favorite horses were Blueskin (horse), Blueskin and Nelson (horse), Nelson. Fellow Virginian  Washington believed in a "wise, inscrutable, and irresistible" Creator God who was active in the Universe, contrary to deism, deistic thought. He referred to God by the Enlightenment terms ''divine providence, Providence'', the ''Creator'', or the ''Almighty'', and also as the ''Divine Author'' or the ''Supreme Being''. He believed in a divine power who watched over battlefields, was involved in the outcome of war, was protecting his life, and was involved in American politics—and specifically in the creation of the United States. Modern historian Ron Chernow has posited that Washington avoided evangelistic Christianity or hellfire-and-brimstone speech along with communion and anything inclined to "flaunt his religiosity". Chernow has also said Washington "never used his religion as a device for partisan purposes or in official undertakings". No mention of Jesus Christ appears in The Washington Papers, his private correspondence, and such references are rare in his public writings. He frequently quoted from the Bible or paraphrased it, and often referred to the Anglican ''Book of Common Prayer''. There is debate on whether he is best classed as a Christian or a theistic rationalism, theistic rationalist—or both.
Washington emphasized religious toleration in a nation with numerous denominations and religions. He publicly attended services of different Christian denominations and prohibited anti-Catholic celebrations in the Army. He engaged workers at Mount Vernon without regard for religious belief or affiliation. While president, he acknowledged major religious sects and gave speeches on religious toleration. He was distinctly rooted in the ideas, values, and modes of thinking of the Enlightenment, but he harbored no contempt of organized Christianity and its clergy, "being no bigot myself to any mode of worship". In 1793, speaking to members of the The New Church (Swedenborgian), New Church in Baltimore, Washington proclaimed, "We have abundant reason to rejoice that in this Land the light of truth and reason has triumphed over the power of bigotry and superstition."
Freemasonry was a widely accepted institution in the late 18th century, known for advocating moral teachings. Washington was attracted to the Masons' dedication to the Enlightenment principles of rationality, reason, and brotherhood. The American Masonic lodges did not share the anti-clerical perspective of the anticlericalism and Freemasonry, controversial European lodges. A Masonic lodge was established in Fredericksburg in September 1752, and Washington was initiated two months later at the age of 20 as one of its first Entered Apprentices. Within a year, he progressed through its ranks to become a Master Mason. Washington had high regard for the Masonic Order, but his personal lodge attendance was sporadic. In 1777, a convention of Virginia lodges asked him to be the Grand Master of the newly established Grand Lodge of Virginia, but he declined due to his commitments leading the Continental Army. After 1782, he frequently corresponded with Masonic lodges and members, and he was listed as Master in the Virginia charter of George Washington Masonic National Memorial, Alexandria Lodge No. 22 in 1788.
Washington believed in a "wise, inscrutable, and irresistible" Creator God who was active in the Universe, contrary to deism, deistic thought. He referred to God by the Enlightenment terms ''divine providence, Providence'', the ''Creator'', or the ''Almighty'', and also as the ''Divine Author'' or the ''Supreme Being''. He believed in a divine power who watched over battlefields, was involved in the outcome of war, was protecting his life, and was involved in American politics—and specifically in the creation of the United States. Modern historian Ron Chernow has posited that Washington avoided evangelistic Christianity or hellfire-and-brimstone speech along with communion and anything inclined to "flaunt his religiosity". Chernow has also said Washington "never used his religion as a device for partisan purposes or in official undertakings". No mention of Jesus Christ appears in The Washington Papers, his private correspondence, and such references are rare in his public writings. He frequently quoted from the Bible or paraphrased it, and often referred to the Anglican ''Book of Common Prayer''. There is debate on whether he is best classed as a Christian or a theistic rationalism, theistic rationalist—or both.
Washington emphasized religious toleration in a nation with numerous denominations and religions. He publicly attended services of different Christian denominations and prohibited anti-Catholic celebrations in the Army. He engaged workers at Mount Vernon without regard for religious belief or affiliation. While president, he acknowledged major religious sects and gave speeches on religious toleration. He was distinctly rooted in the ideas, values, and modes of thinking of the Enlightenment, but he harbored no contempt of organized Christianity and its clergy, "being no bigot myself to any mode of worship". In 1793, speaking to members of the The New Church (Swedenborgian), New Church in Baltimore, Washington proclaimed, "We have abundant reason to rejoice that in this Land the light of truth and reason has triumphed over the power of bigotry and superstition."
Freemasonry was a widely accepted institution in the late 18th century, known for advocating moral teachings. Washington was attracted to the Masons' dedication to the Enlightenment principles of rationality, reason, and brotherhood. The American Masonic lodges did not share the anti-clerical perspective of the anticlericalism and Freemasonry, controversial European lodges. A Masonic lodge was established in Fredericksburg in September 1752, and Washington was initiated two months later at the age of 20 as one of its first Entered Apprentices. Within a year, he progressed through its ranks to become a Master Mason. Washington had high regard for the Masonic Order, but his personal lodge attendance was sporadic. In 1777, a convention of Virginia lodges asked him to be the Grand Master of the newly established Grand Lodge of Virginia, but he declined due to his commitments leading the Continental Army. After 1782, he frequently corresponded with Masonic lodges and members, and he was listed as Master in the Virginia charter of George Washington Masonic National Memorial, Alexandria Lodge No. 22 in 1788.
 In Washington's lifetime, slavery was History of slavery in Virginia, deeply ingrained in the economic and social fabric of Virginia. Slavery was Slavery in the colonial history of the United States, legal in all of the Thirteen Colonies prior to the American Revolution.
In Washington's lifetime, slavery was History of slavery in Virginia, deeply ingrained in the economic and social fabric of Virginia. Slavery was Slavery in the colonial history of the United States, legal in all of the Thirteen Colonies prior to the American Revolution.
 Washington brought several of his slaves with him and his family to the federal capital during his presidency. When the capital moved from New York City to Philadelphia in 1791, the president began rotating his slave household staff periodically between the capital and Mount Vernon. This was done deliberately to circumvent Pennsylvania's An Act for the Gradual Abolition of Slavery, Slavery Abolition Act, which, in part, automatically freed any slave who moved to the state and lived there for more than six months. In May 1796, Martha's personal and favorite slave Oney Judge escaped to Portsmouth, New Hampshire, Portsmouth. At Martha's behest, Washington attempted to capture Ona, using a Treasury agent, but this effort failed. In February 1797, Washington's personal slave Hercules Posey, Hercules escaped to Philadelphia and was never found.
In February 1786, Washington took a census of Mount Vernon and recorded 224 slaves. By 1799, slaves at Mount Vernon totaled 317, including 143 children. Washington owned 124 slaves, leased 40, and held 153 for his wife's dower interest. Washington supported many slaves who were too young or too old to work, greatly increasing Mount Vernon's slave population and causing the plantation to operate at a loss.
Washington brought several of his slaves with him and his family to the federal capital during his presidency. When the capital moved from New York City to Philadelphia in 1791, the president began rotating his slave household staff periodically between the capital and Mount Vernon. This was done deliberately to circumvent Pennsylvania's An Act for the Gradual Abolition of Slavery, Slavery Abolition Act, which, in part, automatically freed any slave who moved to the state and lived there for more than six months. In May 1796, Martha's personal and favorite slave Oney Judge escaped to Portsmouth, New Hampshire, Portsmouth. At Martha's behest, Washington attempted to capture Ona, using a Treasury agent, but this effort failed. In February 1797, Washington's personal slave Hercules Posey, Hercules escaped to Philadelphia and was never found.
In February 1786, Washington took a census of Mount Vernon and recorded 224 slaves. By 1799, slaves at Mount Vernon totaled 317, including 143 children. Washington owned 124 slaves, leased 40, and held 153 for his wife's dower interest. Washington supported many slaves who were too young or too old to work, greatly increasing Mount Vernon's slave population and causing the plantation to operate at a loss.
 In 1788, Washington declined a suggestion from a leading French abolitionist, Jacques Pierre Brissot, Jacques Brissot, to establish an abolitionist society in Virginia, stating that although he supported the idea, the time was not yet right to confront the issue. The historian Henry Wiencek (2003) believes, based on a remark that appears in the notebook of his biographer David Humphreys (soldier), David Humphreys, that Washington considered making a public statement by freeing his slaves on the eve of his presidency in 1789. The historian Philip D. Morgan (2005) disagrees, believing the remark was a "private expression of remorse" at his inability to free his slaves. Other historians agree with Morgan that Washington was determined not to risk national unity over an issue as divisive as slavery. Washington never responded to any of the antislavery petitions he received, and the subject was not mentioned in either his last address to Congress or his Farewell Address.
The first clear indication that Washington seriously intended to free his slaves appears in a letter written to his secretary,
In 1788, Washington declined a suggestion from a leading French abolitionist, Jacques Pierre Brissot, Jacques Brissot, to establish an abolitionist society in Virginia, stating that although he supported the idea, the time was not yet right to confront the issue. The historian Henry Wiencek (2003) believes, based on a remark that appears in the notebook of his biographer David Humphreys (soldier), David Humphreys, that Washington considered making a public statement by freeing his slaves on the eve of his presidency in 1789. The historian Philip D. Morgan (2005) disagrees, believing the remark was a "private expression of remorse" at his inability to free his slaves. Other historians agree with Morgan that Washington was determined not to risk national unity over an issue as divisive as slavery. Washington never responded to any of the antislavery petitions he received, and the subject was not mentioned in either his last address to Congress or his Farewell Address.
The first clear indication that Washington seriously intended to free his slaves appears in a letter written to his secretary,  Washington's legacy endures as one of the most influential in American history since he served as commander-in-chief of the
Washington's legacy endures as one of the most influential in American history since he served as commander-in-chief of the  Washington became an international symbol for liberation and nationalism as the leader of the first successful revolution against a colonial empire. The Federalist Party, Federalists made him the symbol of their party, but the Democratic-Republican Party, Jeffersonians continued to distrust his influence for many years and delayed building the Washington Monument. Washington was elected a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences on January 31, 1781, before he had even begun his presidency. He was posthumously appointed to the grade of General of the Armies of the United States during the United States Bicentennial to ensure he would never be outranked; this was accomplished by the congressional joint resolution s:Public Law 94-479, Public Law 94-479 passed on January 19, 1976, with an effective appointment date of July 4, 1976. On March 13, 1978, Washington was militarily promoted to the rank of General of the Armies of the United States, General of the Armies.
Mason Locke Weems, Parson Weems wrote a Hagiography, hagiographic biography in 1809 to honor Washington. Historian Ron Chernow maintains that Weems attempted to humanize Washington, making him look less stern, and to inspire "patriotism and morality" and to foster "enduring myths", such as Washington's refusal to lie about damaging his father's cherry tree. Weems' accounts have never been proven or disproven. Historian John Ferling, however, maintains that Washington remains the only founder and president ever to be referred to as "godlike", and points out that his character has been the most scrutinized by historians, past and present. Historian Gordon S. Wood concludes that "the greatest act of his life, the one that gave him his greatest fame, was his resignation as commander-in-chief of the American forces." Chernow suggests that Washington was "burdened by public life" and divided by "unacknowledged ambition mingled with self-doubt". A 1993 review of presidential polls and surveys consistently ranked Washington number 4, 3, or2 among presidents. A 2018 Siena College Research Institute survey ranked him number1 among presidents.
In the 21st century, Washington's reputation has been critically scrutinized. Along with various other Founding Fathers, he has been condemned for holding enslaved human beings. Though he expressed the desire to see the abolition of slavery come through legislation, he did not initiate or support any initiatives for bringing about its end. This has led to calls from some activists to remove his name from public buildings and his statue from public spaces. Nonetheless, Washington maintains his place among the highest-ranked U.S. Presidents, listed second (after Abraham Lincoln, Lincoln) in a 2021 C-SPAN poll.
Washington became an international symbol for liberation and nationalism as the leader of the first successful revolution against a colonial empire. The Federalist Party, Federalists made him the symbol of their party, but the Democratic-Republican Party, Jeffersonians continued to distrust his influence for many years and delayed building the Washington Monument. Washington was elected a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences on January 31, 1781, before he had even begun his presidency. He was posthumously appointed to the grade of General of the Armies of the United States during the United States Bicentennial to ensure he would never be outranked; this was accomplished by the congressional joint resolution s:Public Law 94-479, Public Law 94-479 passed on January 19, 1976, with an effective appointment date of July 4, 1976. On March 13, 1978, Washington was militarily promoted to the rank of General of the Armies of the United States, General of the Armies.
Mason Locke Weems, Parson Weems wrote a Hagiography, hagiographic biography in 1809 to honor Washington. Historian Ron Chernow maintains that Weems attempted to humanize Washington, making him look less stern, and to inspire "patriotism and morality" and to foster "enduring myths", such as Washington's refusal to lie about damaging his father's cherry tree. Weems' accounts have never been proven or disproven. Historian John Ferling, however, maintains that Washington remains the only founder and president ever to be referred to as "godlike", and points out that his character has been the most scrutinized by historians, past and present. Historian Gordon S. Wood concludes that "the greatest act of his life, the one that gave him his greatest fame, was his resignation as commander-in-chief of the American forces." Chernow suggests that Washington was "burdened by public life" and divided by "unacknowledged ambition mingled with self-doubt". A 1993 review of presidential polls and surveys consistently ranked Washington number 4, 3, or2 among presidents. A 2018 Siena College Research Institute survey ranked him number1 among presidents.
In the 21st century, Washington's reputation has been critically scrutinized. Along with various other Founding Fathers, he has been condemned for holding enslaved human beings. Though he expressed the desire to see the abolition of slavery come through legislation, he did not initiate or support any initiatives for bringing about its end. This has led to calls from some activists to remove his name from public buildings and his statue from public spaces. Nonetheless, Washington maintains his place among the highest-ranked U.S. Presidents, listed second (after Abraham Lincoln, Lincoln) in a 2021 C-SPAN poll.
 Jared Sparks began collecting and publishing Washington's documentary record in the 1830s in ''Life and Writings of George Washington'' (12 vols., 1834–1837). ''The Writings of George Washington from the Original Manuscript Sources, 1745–1799'' (1931–1944) is a 39-volume set edited by John Clement Fitzpatrick, whom the George Washington Bicentennial Commission commissioned. It contains more than 17,000 letters and documents and is available online from the University of Virginia.
Jared Sparks began collecting and publishing Washington's documentary record in the 1830s in ''Life and Writings of George Washington'' (12 vols., 1834–1837). ''The Writings of George Washington from the Original Manuscript Sources, 1745–1799'' (1931–1944) is a 39-volume set edited by John Clement Fitzpatrick, whom the George Washington Bicentennial Commission commissioned. It contains more than 17,000 letters and documents and is available online from the University of Virginia.