Georg BĂĽchner on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Karl Georg Büchner (17 October 1813 – 19 February 1837) was a German dramatist and writer of poetry and prose, considered part of the
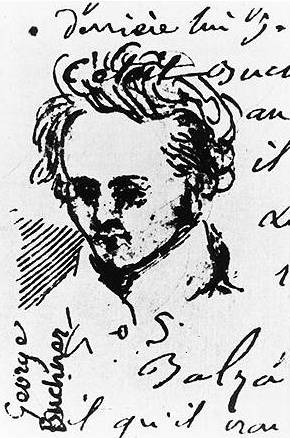 While BĂĽchner continued his studies in GieĂźen, he established a secret society dedicated to the revolutionary cause. In July 1834, with the help of evangelical theologian
While BĂĽchner continued his studies in GieĂźen, he established a secret society dedicated to the revolutionary cause. In July 1834, with the help of evangelical theologian
Red Yucca – German Poetry in Translation
(trans. Eric Plattner) *Georg BĂĽchner, ''Complete Plays and Prose'', trans. Carl Richard Mueller (Hill and Wang, 1963) *Georg BĂĽchner, ''The Complete Plays: Danton's Death; Leonce and Lena; Woyzeck; Lenz; the Hessian Messenger; on Cranial Nerves; Selected Letters'' trans. John Reddick (Penguin Classics, 1993) . *Georg BĂĽchner, ''Danton's Death, Leonce and Lena and Woyzeck'', trans. Victor Price, (Oxford World's Classics, 1998). .
â€
â€
â€
â€
{{DEFAULTSORT:Buchner, Georg 1813 births 1837 deaths People from GroĂź-Gerau (district) People from the Grand Duchy of Hesse German non-fiction writers German medical writers German Expressionist writers Writers from Hesse 19th-century German dramatists and playwrights People associated with the University of Zurich University of Strasbourg alumni Deaths from typhus Infectious disease deaths in Switzerland German male dramatists and playwrights German-language poets 19th-century German poets German male poets 19th-century German male writers German male non-fiction writers
Young Germany
Young Germany (german: Junges Deutschland) was a group of German writers which existed from about 1830 to 1850. It was essentially a youth ideology, similar to those that had swept France, Ireland, the United States and Italy. Its main proponents ...
movement. He was also a revolutionary and the brother of physician and philosopher Ludwig BĂĽchner
Friedrich Karl Christian Ludwig Büchner (29 March 1824 – 30 April 1899) was a German philosopher, physiologist and physician who became one of the exponents of 19th-century scientific materialism.
Biography
BĂĽchner was born at Darmstadt on ...
. His literary achievements, though few in number, are generally held in great esteem in Germany and it is widely believed that, had it not been for his early death, he might have joined such central German literary figures as Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as trea ...
and Friedrich Schiller
Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (, short: ; 10 November 17599 May 1805) was a German playwright, poet, and philosopher. During the last seventeen years of his life (1788–1805), Schiller developed a productive, if complicated, friends ...
at the summit of their profession.
Life and career
Born in Goddelau (now part ofRiedstadt
Riedstadt, with its municipal area of 73.76 km² is Groß-Gerau district's biggest town by land area. It lies in Hesse, Germany, about 12 km southwest of Darmstadt.
Geography
Location
Riedstadt is shaped not only by its preserved rur ...
) in the Grand Duchy of Hesse
The Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine (german: link=no, GroĂźherzogtum Hessen und bei Rhein) was a grand duchy in western Germany that existed from 1806 to 1918. The Grand Duchy originally formed from the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1806 ...
as the son of a physician, BĂĽchner attended the Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it th ...
gymnasium, a humanistic secondary school."BĂĽchner, Georg." Garland, Henry and Mary (Eds.). ''The Oxford Companion to German Literature''. 2nd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1986. p. 121.
In 1828, he became interested in politics and joined a circle of William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
aficionados, which later on probably became the GieĂźen
Giessen, spelled GieĂźen in German (), is a town in the German state (''Bundesland'') of Hesse, capital of both the district of Giessen and the administrative region of Giessen. The population is approximately 90,000, with roughly 37,000 univers ...
and Darmstadt section of the Society for Human Rights ().
In 1831, at age 18, he began to study medicine in Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: StraĂźburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the Eu ...
. In Strasbourg, he immersed himself in French literature
French literature () generally speaking, is literature written in the French language, particularly by citizens of France; it may also refer to literature written by people living in France who speak traditional languages of France other than F ...
and political thought. He was influenced by the utopian communist theories of François-Noël Babeuf
François-Noël Babeuf (; 23 November 1760 – 27 May 1797), also known as Gracchus Babeuf, was a French proto-communist, revolutionary, and journalist of the French Revolutionary period. His newspaper ''Le tribun du peuple'' (''The Tribune of ...
and Claude Henri de Saint-Simon
Claude Henri de Rouvroy, comte de Saint-Simon (17 October 1760 – 19 May 1825), often referred to as Henri de Saint-Simon (), was a French political, economic and socialist theorist and businessman whose thought had a substantial influence on ...
. In 1833 he moved to GieĂźen and continued his studies at the local university
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
.
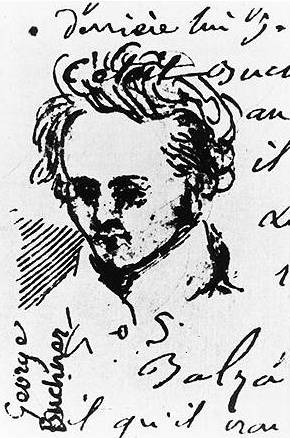 While BĂĽchner continued his studies in GieĂźen, he established a secret society dedicated to the revolutionary cause. In July 1834, with the help of evangelical theologian
While BĂĽchner continued his studies in GieĂźen, he established a secret society dedicated to the revolutionary cause. In July 1834, with the help of evangelical theologian Friedrich Ludwig Weidig
Friedrich Ludwig Weidig (15 February 1791 – 23 February 1837) was a German Protestant theologian, pastor, activist, teacher and journalist. Initially working as a teacher in Butzbach, he then spent a short time as a pastor in Ober-Gleen, a dis ...
, he published the leaflet '' Der Hessische Landbote'', a revolutionary pamphlet critical of social injustice in the Grand Duchy of Hesse
The Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine (german: link=no, GroĂźherzogtum Hessen und bei Rhein) was a grand duchy in western Germany that existed from 1806 to 1918. The Grand Duchy originally formed from the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1806 ...
. The authorities charged them with treason and issued a warrant for their arrest. Weidig was arrested, tortured and later died in prison in Darmstadt; BĂĽchner managed to flee across the border to Strasbourg where he wrote most of his literary work and translated two French plays by Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
, ''Lucrèce Borgia
''Lucrèce Borgia'' (also known as ''Lucretia Borgia'' or ''Sins of the Borgias'') is a 1953 French drama film starring Martine Carol and Pedro Armendáriz. The film was directed by Christian-Jaque, who co-wrote screenplay with Cécil Saint-Laur ...
'' and ''Marie Tudor
''Marie Tudor'' is an 1833 play by the French writer Victor Hugo. It is a historical work portraying the rise, fall and execution of Fabiano Fabiani, a fictional favourite of Mary I of England (1516–1558). Mary has Fabiani thrown in the Tower o ...
''. Two years later, his medical dissertation, "Mémoire sur le Système Nerveux du Barbeaux (Cyprinus barbus L.)" was published in Paris and Strasbourg. In October 1836, after receiving his M.D. and being appointed by the University of Zürich
The University of Zürich (UZH, german: Universität Zürich) is a public research university located in the city of Zürich, Switzerland. It is the largest university in Switzerland, with its 28,000 enrolled students. It was founded in 1833 f ...
as a lecturer in anatomy, BĂĽchner relocated to ZĂĽrich
ZĂĽrich () is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of ZĂĽrich. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake ZĂĽrich. As of January 2020, the municipality has 43 ...
where he spent his final months writing and teaching until his death from typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure.
...
at the age of twenty-three.
His first play, ''Dantons Tod'' (''Danton's Death
''Danton's Death'' (''Dantons Tod'') was the first play written by Georg BĂĽchner, set during the French Revolution.
History
Georg Büchner wrote his works in the period between Romanticism and Realism in the so-called Vormärz era in German hi ...
''), about the French revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, was published in 1835, followed by ''Lenz Lenz may refer to:
Places
* Lenasia, Gauteng Province, South Africa, a township often called Lenz
* Lantsch/Lenz, Canton of Grisons, Switzerland, a municipality
* Lenz, Hood River County, Oregon, an unincorporated community
* Lenz, Klamath County, ...
'' (first partly published in Karl Gutzkow
Karl Ferdinand Gutzkow ( in Berlin – in Sachsenhausen) was a German writer notable in the Young Germany movement of the mid-19th century.
Life
Gutzkow was born of an extremely poor family, not proletarian, but of the lowest and most meni ...
's and Wienberg's ''Deutsche Revue'', which was quickly banned). ''Lenz'' is a novella based on the life of the Sturm und Drang
''Sturm und Drang'' (, ; usually translated as "storm and stress") was a proto- Romantic movement in German literature and music that occurred between the late 1760s and early 1780s. Within the movement, individual subjectivity and, in particul ...
poet Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz
Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz (23 January 1751, or 12 January in the Julian calendar – 4 June 1792, or 24 May in the Julian calendar) was a Baltic German writer of the ''Sturm und Drang'' movement.
Life
Lenz was born in Sesswegen (Cesvaine), ...
. In 1836 his second play, ''Leonce and Lena
''Leonce and Lena'' (german: Leonce und Lena) is a play by German dramatist Georg Büchner (1813–1837) which is considered a comedy, but is actually a satire veiled in humor. It was written in the spring of 1836 for a competition 'for the best ...
'', satirized the nobility. His unfinished and most famous play, ''Woyzeck
''Woyzeck'' () is a stage play written by Georg BĂĽchner. BĂĽchner wrote the play between July and October 1836, yet left it incomplete at his death in February 1837. The play first appeared in 1877 in a heavily edited version by Karl Emil Fr ...
'', exists only in fragments and was published posthumously.
Legacy
By the 1870s, BĂĽchner was nearly forgotten in Germany whenKarl Emil Franzos
Karl Emil Franzos (25 October 184828 January 1904) was a popular Austrian novelist of the late 19th century. His works, both reportage and fiction, concentrate on the multi-ethnic corner of Galicia, Podolia and Bukovina, now largely in western U ...
edited his works; these later became a major influence on the naturalist and expressionist
Expressionism is a modernist movement, initially in poetry and painting, originating in Northern Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. Its typical trait is to present the world solely from a subjective perspective, distorting it rad ...
movements. Arnold Zweig
Arnold Zweig (10 November 1887 – 26 November 1968) was a German writer, pacifist and socialist.
He is best known for his six-part cycle on World War I.
Life and work
Zweig was born in Glogau, Prussian Silesia (now GĹ‚ogĂłw, Poland), the son ...
described ''Lenz'', BĂĽchner's only work of prose fiction, as "the beginning of modern European prose".
The play ''Woyzeck'' became the basis for many adaptations including Alban Berg
Alban Maria Johannes Berg ( , ; 9 February 1885 – 24 December 1935) was an Austrian composer of the Second Viennese School. His compositional style combined Romantic lyricism with the twelve-tone technique. Although he left a relatively sma ...
's landmark atonal
Atonality in its broadest sense is music that lacks a tonal center, or key. ''Atonality'', in this sense, usually describes compositions written from about the early 20th-century to the present day, where a hierarchy of harmonies focusing on a ...
opera ''Wozzeck
''Wozzeck'' () is the first opera by the Austrian composer Alban Berg. It was composed between 1914 and 1922 and first performed in 1925. The opera is based on the drama ''Woyzeck'', which the German playwright Georg BĂĽchner left incomplete at h ...
'' which premiered in 1925, and Werner Herzog
Werner Herzog (; born 5 September 1942) is a German film director, screenwriter, author, actor, and opera director, regarded as a pioneer of New German Cinema. His films often feature ambitious protagonists with impossible dreams, people with u ...
's 1979 film ''Woyzeck
''Woyzeck'' () is a stage play written by Georg BĂĽchner. BĂĽchner wrote the play between July and October 1836, yet left it incomplete at his death in February 1837. The play first appeared in 1877 in a heavily edited version by Karl Emil Fr ...
'' (see main article, ''Woyzeck
''Woyzeck'' () is a stage play written by Georg BĂĽchner. BĂĽchner wrote the play between July and October 1836, yet left it incomplete at his death in February 1837. The play first appeared in 1877 in a heavily edited version by Karl Emil Fr ...
'', for a full list).
A literary prize in Germany, the Georg BĂĽchner Prize
The Georg BĂĽchner Prize (german: link=no, Georg-BĂĽchner-Preis) is the most important literary prize for German language literature, along with the Goethe Prize. The award is named after dramatist and writer Georg BĂĽchner, author of '' Woyzeck ...
, is awarded annually. It was created in 1923.
Works
* ''The Hessian Courier
''The Hessian Courier'' (German'': Der Hessische Landbote'') is an eight-page pamphlet, written by Georg BĂĽchner in 1834, in which he argues against the social injustices of his time. It was printed and published following editorial revision by ...
'', 1834 – in cooperation with Friedrich Ludwig Weidig
Friedrich Ludwig Weidig (15 February 1791 – 23 February 1837) was a German Protestant theologian, pastor, activist, teacher and journalist. Initially working as a teacher in Butzbach, he then spent a short time as a pastor in Ober-Gleen, a dis ...
(Flugschrift)
* ''Danton's Death
''Danton's Death'' (''Dantons Tod'') was the first play written by Georg BĂĽchner, set during the French Revolution.
History
Georg Büchner wrote his works in the period between Romanticism and Realism in the so-called Vormärz era in German hi ...
'', 1835 (Drama)
* ''Lenz Lenz may refer to:
Places
* Lenasia, Gauteng Province, South Africa, a township often called Lenz
* Lantsch/Lenz, Canton of Grisons, Switzerland, a municipality
* Lenz, Hood River County, Oregon, an unincorporated community
* Lenz, Klamath County, ...
'', 1835 (Short story)
* ''Leonce and Lena
''Leonce and Lena'' (german: Leonce und Lena) is a play by German dramatist Georg Büchner (1813–1837) which is considered a comedy, but is actually a satire veiled in humor. It was written in the spring of 1836 for a competition 'for the best ...
'', 1836 (Comedy)
* ''Woyzeck
''Woyzeck'' () is a stage play written by Georg BĂĽchner. BĂĽchner wrote the play between July and October 1836, yet left it incomplete at his death in February 1837. The play first appeared in 1877 in a heavily edited version by Karl Emil Fr ...
'', 1837 (Drama – fragment)
* ''Pietro Aretino'', his drama about Pietro Aretino
Pietro Aretino (, ; 19 or 20 April 1492 – 21 October 1556) was an Italian author, playwright, poet, satirist and blackmailer, who wielded influence on contemporary art and politics. He was one of the most influential writers of his time and a ...
, has been lost.
* Translations:
** ''Lucrezia Borgia'', 1835 (Of the play by Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
)
** ''Maria Tudor'', 1835 (Of the play by Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
)
Editions
*Georg BĂĽchner, ''Werke und Briefe. MĂĽnchner Ausgabe'' (dtv, 1997). .Translations
Red Yucca – German Poetry in Translation
(trans. Eric Plattner) *Georg BĂĽchner, ''Complete Plays and Prose'', trans. Carl Richard Mueller (Hill and Wang, 1963) *Georg BĂĽchner, ''The Complete Plays: Danton's Death; Leonce and Lena; Woyzeck; Lenz; the Hessian Messenger; on Cranial Nerves; Selected Letters'' trans. John Reddick (Penguin Classics, 1993) . *Georg BĂĽchner, ''Danton's Death, Leonce and Lena and Woyzeck'', trans. Victor Price, (Oxford World's Classics, 1998). .
Notes
References
* Garland, Henry and Mary (Eds.). ''The Oxford Companion to German Literature''. 2nd ed. by Mary Garland. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1986. "Büchner, Georg", p. 121. * Heiner Boehncke, Peter Brunner, Hans Sarkowicz. ''Die Büchners oder der Wunsch, die Welt zu verändern''. Societäts-Verlag, Frankfurt am Main, 2008.External links
* * * * * Series on life of Georg BĂĽchner, by Sybille Fuchs, reviewing ''Georg BĂĽchner: Revolutionary with pen and scalpel'', an exhibition from 13 October 2013 to 16 February 2014 at the Darmstadium Conference Centre, Darmstadt:â€
â€
â€
â€
{{DEFAULTSORT:Buchner, Georg 1813 births 1837 deaths People from GroĂź-Gerau (district) People from the Grand Duchy of Hesse German non-fiction writers German medical writers German Expressionist writers Writers from Hesse 19th-century German dramatists and playwrights People associated with the University of Zurich University of Strasbourg alumni Deaths from typhus Infectious disease deaths in Switzerland German male dramatists and playwrights German-language poets 19th-century German poets German male poets 19th-century German male writers German male non-fiction writers