Geography of Wyoming on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The U.S. state of Wyoming lies in the Mountain West subregion of the
The U.S. state of Wyoming lies in the Mountain West subregion of the
Public Land Ownership by State, 1995 Main Environment.org Federal lands within Wyoming include two national parks (
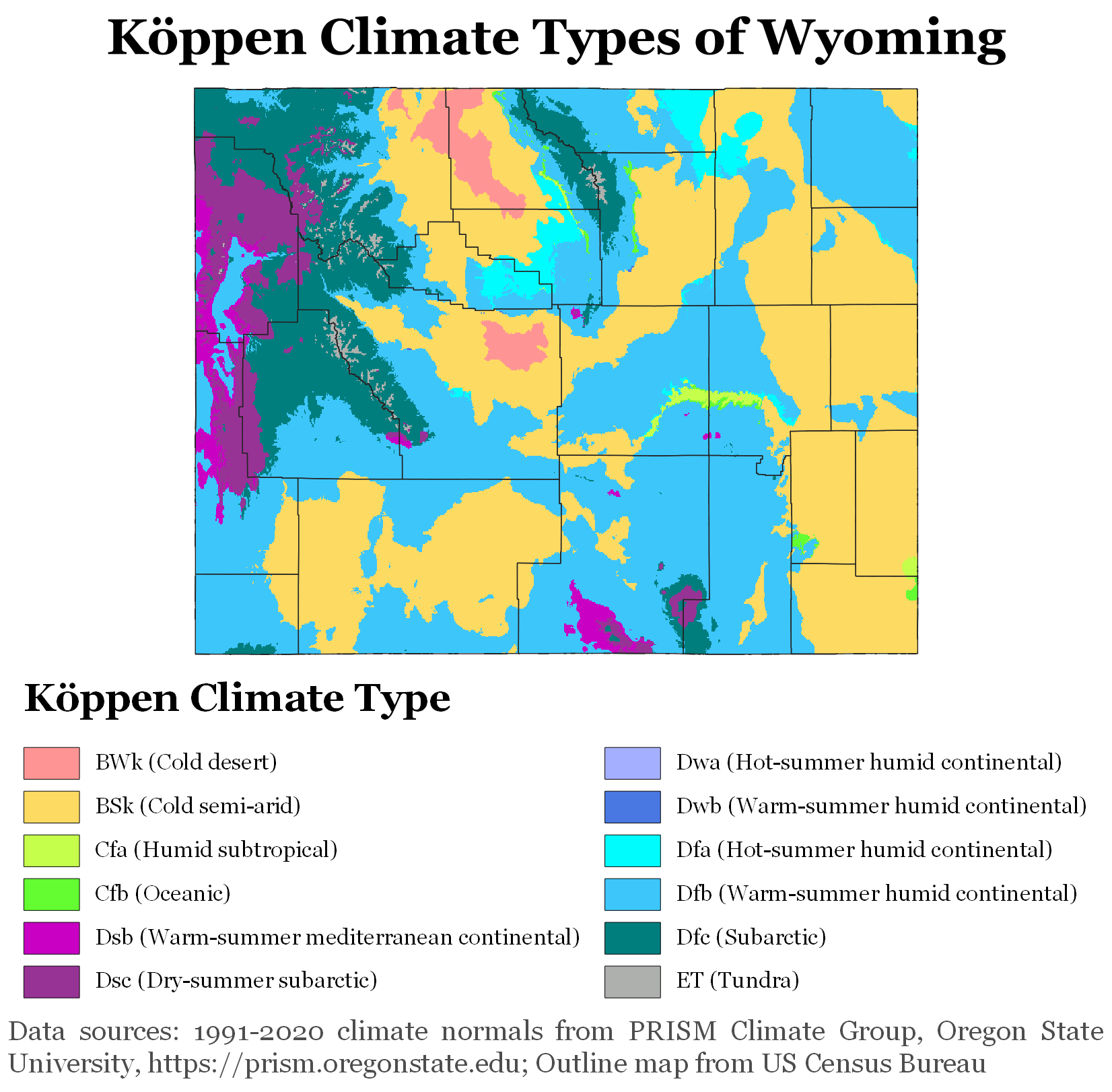
 Wyoming's climate is generally
Wyoming's climate is generally
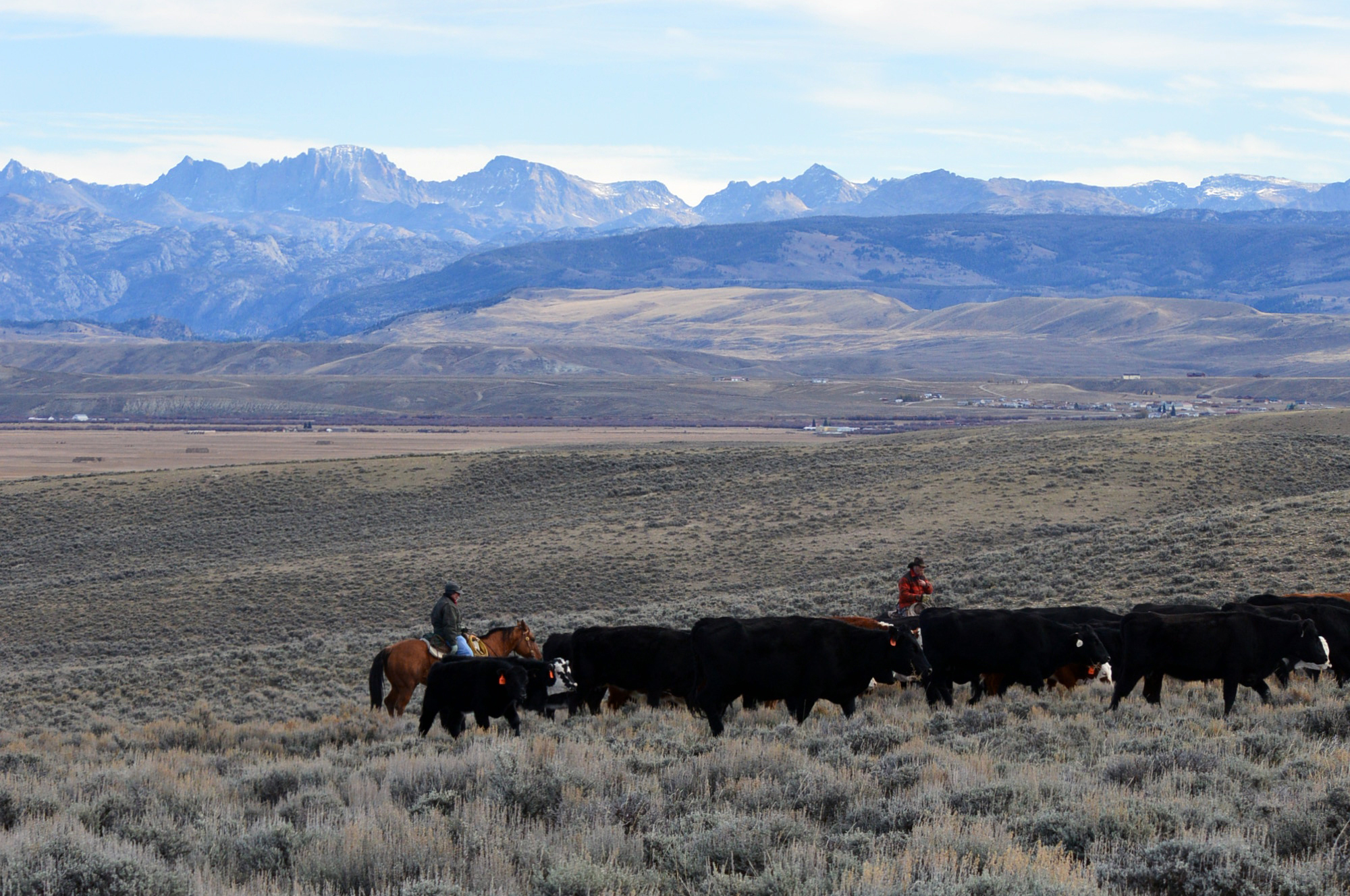
 The Great Plains meet the
The Great Plains meet the
 Wyoming license plates have a number on the left that indicates the county where the vehicle is registered, ranked by an earlier census. Specifically, the numbers are representative of the property values of the counties in 1930. The county license plate numbers are:
Wyoming license plates have a number on the left that indicates the county where the vehicle is registered, ranked by an earlier census. Specifically, the numbers are representative of the property values of the counties in 1930. The county license plate numbers are:





 The State of Wyoming has 99 incorporated municipalities.
In 2005, 50.6% of Wyomingites lived in one of the 13 most populous Wyoming municipalities.
The State of Wyoming has 99 incorporated municipalities.
In 2005, 50.6% of Wyomingites lived in one of the 13 most populous Wyoming municipalities.
 The U.S. state of Wyoming lies in the Mountain West subregion of the
The U.S. state of Wyoming lies in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the We ...
and has a varied geography. It is bordered by Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
to the north and northwest, South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large porti ...
and Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
to the east, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyomi ...
to the west, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
to the southwest, and Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
to the south. Wyoming is the least populous U.S. state and has the second-lowest population density behind Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
.
Wyoming's western half is covered mostly by the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
, while the eastern half of the state is high-elevation prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
called the High Plains High Plains refers to one of two distinct land regions:
* High Plains (United States), land region of the western Great Plains
*High Plains (Australia)
The High Plains of south-eastern Australia are a sub-region, or more strictly a string of adja ...
. It is drier and windier than the rest of the country, being split between semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi- ...
and continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
climates with greater temperature extremes. Almost half of the land in Wyoming is owned by the federal government, generally protected for public uses. The state ranks 6th by area and fifth by proportion of a state's land owned by the federal government.MainEnvironment.orgPublic Land Ownership by State, 1995 Main Environment.org Federal lands within Wyoming include two national parks (
Grand Teton
Grand Teton is the highest mountain in Grand Teton National Park, in Northwest Wyoming, and a classic destination in American mountaineering.
Geography
Grand Teton, at , is the highest point of the Teton Range, and the second highest peak in t ...
and Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
), two national recreation areas, two national monuments, several national forests, historic sites, fish hatcheries, and wildlife refuges.
Climate


semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi- ...
and continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
'' ''BSk''''), and is drier and windier in comparison to most of the United States with greater temperature extremes. Much of this is due to the topography of the state. Summers in Wyoming are warm with July high temperatures averaging between in most of the state. With increasing elevation, however, this average drops rapidly with locations above averaging around . Summer nights throughout the state are characterized by a rapid cooldown with even the hottest locations averaging in the range at night. In most of the state, most of the precipitation tends to fall in the late spring and early summer. Winters are cold, but are variable with periods of sometimes extreme cold interspersed between generally mild periods, with Chinook winds providing unusually warm temperatures in some locations.
Wyoming is a dry state with much of the land receiving less than of rainfall per year. Precipitation depends on elevation with lower areas in the Big Horn Basin
The Bighorn Basin is a plateau region and intermontane basin, approximately 100 miles (160 km) wide, in north-central Wyoming in the United States. It is bounded by the Absaroka Range on the west, the Pryor Mountains on the north, the Bighor ...
averaging , making the area nearly a true desert. The lower areas in the North and on the eastern plains typically average around , making the climate there semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi- ...
. Some mountain areas do receive a good amount of precipitation, or more, much of it as snow, sometimes or more annually. The state's highest recorded temperature is at Basin on July 12, 1900, and the lowest recorded temperature is at Riverside on February 9, 1933.
The number of thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are some ...
days vary across the state with the southeastern plains of the state having the most days of thunderstorm activity. Thunderstorm activity in the state is highest during the late spring and early summer. The southeastern corner of the state is the most vulnerable part of the state to tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, altho ...
activity. Moving away from that point and westwards, the incidence of tornadoes drops dramatically with the west part of the state showing little vulnerability. Tornadoes, where they occur, tend to be small and brief, unlike some of those that occur farther east. The most destructive tornado to occur in Wyoming happened on July 16, 1979 in Cheyenne and caused one death and 40 injuries.
Climate data
Location and size
As specified in the designating legislation for theTerritory of Wyoming
The Territory of Wyoming was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 25, 1868, until July 10, 1890, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Wyoming. Cheyenne was the territorial capital. The bo ...
, Wyoming's borders are lines of latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
41°N and 45°N, and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
104°3'W and 111°3'W (27 and 34 west of the Washington Meridian
The Washington meridians are four meridians that were used as prime meridians in the United States and pass through Washington, D.C. The four which have been specified are:
# through the Capitol
# through the White House
# through the old Naval Ob ...
)—a geodesic quadrangle. Wyoming is one of only three states (the others being Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
and Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
) to have borders defined by ''only'' "straight" lines. Due to surveying inaccuracies during the 19th century, Wyoming's legal border deviates from the true latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
lines by up to half of a mile (0.8 km) in some spots, especially in the mountainous region along the 45th parallel. Wyoming is bordered on the north by Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
, on the east by South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large porti ...
and Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
, on the south by Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, on the southwest by Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, and on the west by Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyomi ...
. It is the tenth largest state in the United States in total area, containing and is made up of 23 counties. From the north border to the south border it is ; and from the east to the west border is at its south end and at the north end.
Natural landforms
Mountain ranges

 The Great Plains meet the
The Great Plains meet the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
in Wyoming. The state is a great plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
broken by many mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
s. Surface elevations range from the summit of Gannett Peak in the Wind River Mountain Range, at , to the Belle Fourche River
The Belle Fourche River (pronounced ''bel FOOSH''; lkt, Šahíyela Wakpá) is a tributary of the Cheyenne River, approximately long, in the U.S. states of Wyoming and South Dakota. It is part of the Mississippi River watershed via the Cheyen ...
valley in the state's northeast corner, at . In the northwest are the Absaroka, Owl Creek, Gros Ventre
The Gros Ventre ( , ; meaning "big belly"), also known as the Aaniiih, A'aninin, Haaninin, Atsina, and White Clay, are a historically Algonquian-speaking Native American tribe located in north central Montana. Today the Gros Ventre people are ...
, Wind River, and the Teton ranges. In the north central are the Big Horn Mountains
The Bighorn Mountains ( cro, Basawaxaawúua, lit=our mountains or cro, Iisaxpúatahchee Isawaxaawúua, label=none, lit=bighorn sheep's mountains) are a mountain range in northern Wyoming and southern Montana in the United States, forming a nort ...
; in the northeast, the Black Hills
The Black Hills ( lkt, Ȟe Sápa; chy, Moʼȯhta-voʼhonáaeva; hid, awaxaawi shiibisha) is an isolated mountain range rising from the Great Plains of North America in western South Dakota and extending into Wyoming, United States. Black ...
; and in the southern region the Laramie, Snowy, and Sierra Madre
Sierra Madre (Spanish, 'mother mountain range') may refer to:
Places and mountains Mexico
*Sierra Madre Occidental, a mountain range in northwestern Mexico and southern Arizona
*Sierra Madre Oriental, a mountain range in northeastern Mexico
*S ...
ranges.
The Snowy Range in the south central part of the state is an extension of the Colorado Rockies
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
both in geology and in appearance. The Wind River Range in the west central part of the state is remote and includes more than 40 mountain peaks in excess of tall in addition to Gannett Peak, the highest peak in the state. The Big Horn Mountains in the north central portion are somewhat isolated from the bulk of the Rocky Mountains.
The Teton Range in the northwest extends for , part of which is included in Grand Teton National Park
Grand Teton National Park is an American national park in northwestern Wyoming. At approximately , the park includes the major peaks of the Teton Range as well as most of the northern sections of the valley known as Jackson Hole. Grand Teton ...
. The park includes the Grand Teton
Grand Teton is the highest mountain in Grand Teton National Park, in Northwest Wyoming, and a classic destination in American mountaineering.
Geography
Grand Teton, at , is the highest point of the Teton Range, and the second highest peak in t ...
, the second highest peak in the state.
The Continental Divide spans north–south across the central portion of the state. Rivers east of the divide drain into the Missouri River Basin and eventually the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
. They are the North Platte
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' is ...
, Wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ho ...
, Big Horn and the Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
rivers. The Snake River in northwest Wyoming eventually drains into the Columbia River and the Pacific Ocean, as does the Green River Green River may refer to:
Rivers
Canada
* Green River (British Columbia), a tributary of the Lillooet River
*Green River, a tributary of the Saint John River, also known by its French name of Rivière Verte
*Green River (Ontario), a tributary of ...
through the Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. s ...
Basin.
The Continental Divide forks in the south central part of the state in an area known as the Great Divide Basin
The Great Divide Basin or Great Divide Closed Basin is an area of land in the Red Desert (Wyoming), Red Desert of Wyoming where none of the water falling as rain to the ground drains into any ocean, directly or indirectly. It is thus an endorheic ...
where water that precipitates onto or flows into it cannot reach an ocean—it ''all'' sinks into the soil and eventually evaporates.
Several rivers begin in or flow through the state, including the Yellowstone River, Bighorn River, Green River, and the Snake River.
Basins
Much of Wyoming is covered with large basins containing different eco-regions, from shrublands to smaller patches of desert. Regions of the state classified as basins contain everything from large geologic formations to sand dunes and vast unpopulated spaces. Basin landscapes are typically at lower elevations and include rolling hills, valleys, mesas, terraces and other rugged terrain, but also include natural springs as well as rivers and artificial reservoirs. They have common plant species such as various subspecies ofsagebrush
Sagebrush is the common name of several woody and herbaceous species of plants in the genus '' Artemisia''. The best known sagebrush is the shrub '' Artemisia tridentata''. Sagebrushes are native to the North American west.
Following is an al ...
, juniper and grasses such as wheatgrass
Wheatgrass is the freshly sprouted first leaves of the common wheat plant (''Triticum aestivum''), used as a food, drink, or dietary supplement. Wheatgrass is served freeze dried or fresh, and so it differs from wheat malt, which is convect ...
, but basins are known for their diversity of plant and animal species.
Islands
Wyoming has 32 named islands; the majority are in Jackson Lake andYellowstone Lake
Yellowstone Lake is the largest body of water in Yellowstone National Park. The lake is above sea level and covers with of shoreline. While the average depth of the lake is , its greatest depth is at least . Yellowstone Lake is the largest fre ...
, within Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowst ...
in the northwest portion of the state. The Green River Green River may refer to:
Rivers
Canada
* Green River (British Columbia), a tributary of the Lillooet River
*Green River, a tributary of the Saint John River, also known by its French name of Rivière Verte
*Green River (Ontario), a tributary of ...
in the southwest also contains a number of islands.
Regions and Administration
Counties
The state of Wyoming has 23counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
. Thirteen were there when Wyoming became a state in 1890 and ten more have been created since then.
 Wyoming license plates have a number on the left that indicates the county where the vehicle is registered, ranked by an earlier census. Specifically, the numbers are representative of the property values of the counties in 1930. The county license plate numbers are:
Wyoming license plates have a number on the left that indicates the county where the vehicle is registered, ranked by an earlier census. Specifically, the numbers are representative of the property values of the counties in 1930. The county license plate numbers are:
Cities and towns





 The State of Wyoming has 99 incorporated municipalities.
In 2005, 50.6% of Wyomingites lived in one of the 13 most populous Wyoming municipalities.
The State of Wyoming has 99 incorporated municipalities.
In 2005, 50.6% of Wyomingites lived in one of the 13 most populous Wyoming municipalities.
Metropolitan areas
TheUnited States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of t ...
has defined two Metropolitan Statistical Areas
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally incorporated as a city or tow ...
(MSA) and seven Micropolitan Statistical Areas (MiSA) for the State of Wyoming. In 2008, 30.4% of Wyomingites lived in either of the Metropolitan Statistical Areas
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally incorporated as a city or tow ...
, and 73% lived in either a Metropolitan Statistical Area
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally incorporated as a city or tow ...
or a Micropolitan Statistical Area.
See also
*Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
* Geography of Montana
Montana is one of the eight Mountain States, located in the north of the region known as the Western United States. It borders North Dakota and South Dakota to the east. Wyoming is to the south, Idaho is to the west and southwest, and the Canadia ...
* Continental Divide
Notes
References
{{reflist Geography of Wyoming