Geography of Slovakia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The highest point is at the summit of
The highest point is at the summit of
 There are 9 national parks in Slovakia, covering 6.5% of the Slovak land surface.
There are 9 national parks in Slovakia, covering 6.5% of the Slovak land surface.
 The Tatra Mountains, with 29 peaks higher than
The Tatra Mountains, with 29 peaks higher than
 Slovakia has hundreds of caves and caverns under its mountains, of which 30 are open to the public. Most of the caves have
Slovakia has hundreds of caves and caverns under its mountains, of which 30 are open to the public. Most of the caves have
 Most of the rivers arise in the Slovak mountains. Some only pass through Slovakia, while others make a natural border with surrounding countries (more than ). For example, the
Most of the rivers arise in the Slovak mountains. Some only pass through Slovakia, while others make a natural border with surrounding countries (more than ). For example, the

Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
is a landlocked Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area' ...
an country with mountainous regions in the north and flat terrain in the south. During much of the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
, Slovakia was much more forested than today. Decline of the forest occurred in as consequence of the Valachian colonization and the development of mining in the territory.
Statistics
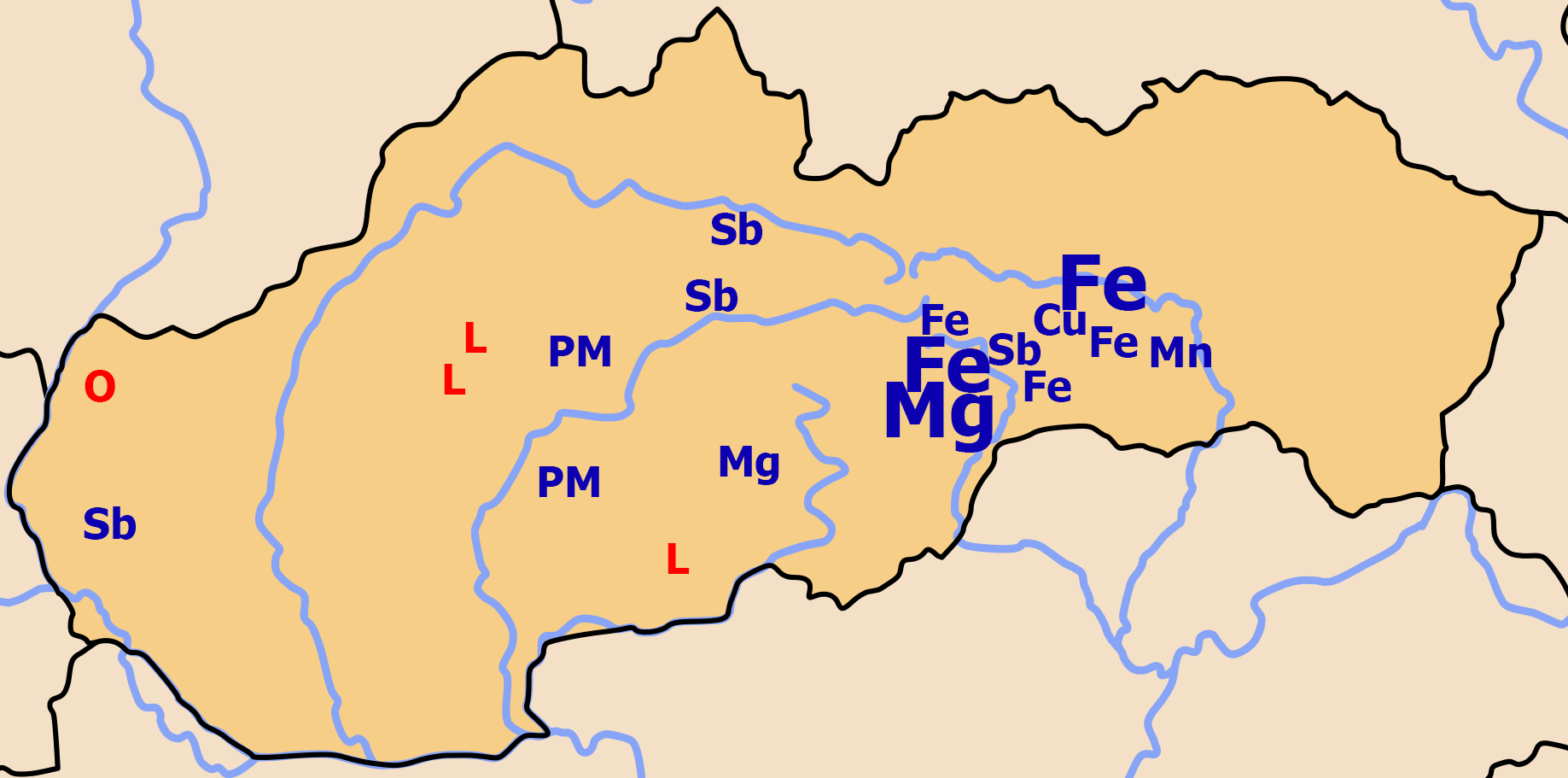
Land use: ''agricultural land'': 40.1% ''arable land'': 28.9%; permanent crops: 0.4%; permanent pasture: 10.8% ''forest'': 40.2% ''other'': 19.7% (2011 est.) Natural resources: Lignite, small amounts of iron ore, copper and manganese ore; salt; arable land Natural Hazards: Flooding Environment-international agreements: ''Party to'': Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling. ''Signed, but not ratified'': none of the selected agreementsArea
Slovakia lies between 49°36'48" and 47°44'21" northern latitude and 16°50'56" and 22°33'53" eastern longitude. The northernmost point is near Beskydok, a mountain on the border with Poland near the village ofOravská Polhora
Oravská Polhora ( hu, Polhora) is a large village and municipality in Námestovo District in the Žilina Region of northern Slovakia. The northernmost point of Slovakia is located close to the village.
History
In historical records the village ...
in the Beskids
The Beskids or Beskid Mountains ( pl, Beskidy, cs, Beskydy, sk, Beskydy, rue, Бескиды (''Beskydŷ''), ua, Бескиди (''Beskydy'')) are a series of mountain ranges in the Carpathians, stretching from the Czech Republic in the west a ...
. The southernmost point is near the village of Patince on the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
on the border with Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
. The westernmost point is on the Morava River
Morava may refer to:
Rivers
* Great Morava (''Velika Morava''; or only Morava), a river in central Serbia, and its tributaries:
** South Morava (''Južna Morava'')
*** Binač Morava (''Binačka Morava'')
** West Morava (''Zapadna Morava'')
* Mo ...
near Záhorská Ves on the Austrian border. The easternmost point is close to the summit of Kremenec, a mountain near the village of Nová Sedlica at the meeting point of Slovak, Polish, and Ukrainian borders.
 The highest point is at the summit of
The highest point is at the summit of Gerlachovský štít
Gerlachovský štít (, translated into English as ''Gerlachov Peak'', German: ''Gerlsdorfer Spitze'', Hungarian: ''Gerlachfalvi-csúcs''), informally referred to as Gerlach, is the highest peak in the High Tatras, in Slovakia, and in the Carpat ...
in the High Tatras
The High Tatras or High Tatra Mountains ( Slovak: Vysoké Tatry; pl, Tatry Wysokie; rue, Высокі Татри,'' Vysoki Tatry''; hu, Magas-Tátra; german: Hohe Tatra; french: Hautes Tatras), are a mountain range along the border of norther ...
, , the lowest point is the surface of the Bodrog River
The Bodrog is a river in eastern Slovakia and north-eastern Hungary. It is a tributary to the river Tisza. The Bodrog is formed by the confluence of the rivers Ondava and Latorica near Zemplín in eastern Slovakia. It crosses the Slovak–Hu ...
on the Hungarian border at .
The country's area is . 31% is arable land, 17% pastures, 41% forests, 3% cultivated land. The remaining 8% is mostly covered with human structures and infrastructure, and partly with rocky mountain ridges and other unimproved land.
Slovakia borders Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
in the north - , Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
in the east - , Hungary in the south - , Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
in the south-west - , and the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
in the north-west - for a total border length of .
The village of Veľké Slemence
Veľké Slemence (; hu, Nagyszelmenc) is a village and municipality in Michalovce District in the Košice Region of southeastern Slovakia.
History
In historical records the village was first mentioned in 1332. It was a single village named Sze ...
(Ukrainian: Mali Slementsi/Малі Селменці, Hungarian: Szelmenc) is an anomaly, as it is a village with a majority of Hungarians, but it is split between Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
.
National parks
Geographical features
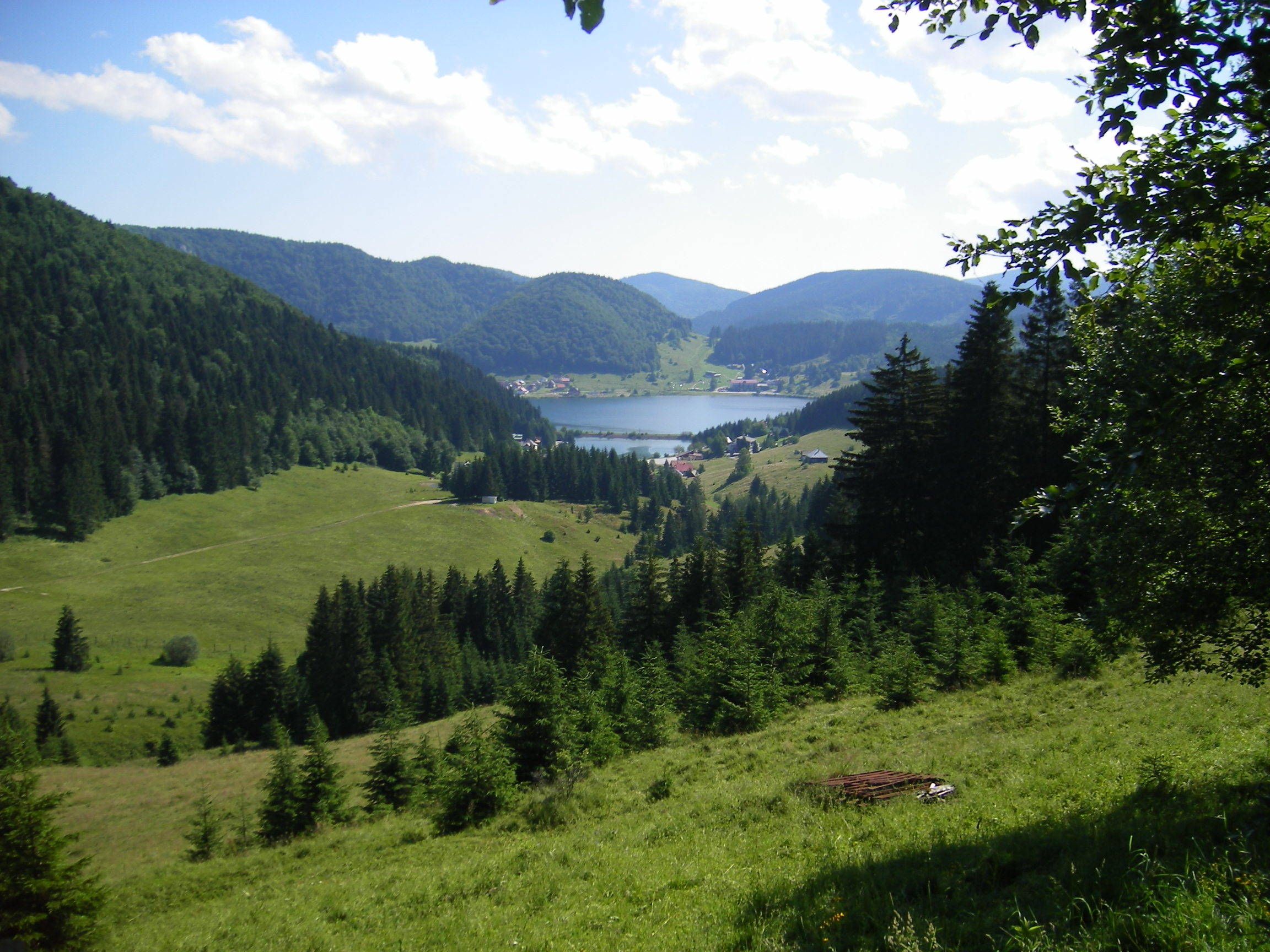
Tatra mountains
 The Tatra Mountains, with 29 peaks higher than
The Tatra Mountains, with 29 peaks higher than AMSL
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, are the highest mountain range in the Carpathian Mountains. The Tatras occupy an area of , of which the greater part lies in Slovakia. They are divided into several parts.
To the north, close to the Polish border, are the High Tatras
The High Tatras or High Tatra Mountains ( Slovak: Vysoké Tatry; pl, Tatry Wysokie; rue, Высокі Татри,'' Vysoki Tatry''; hu, Magas-Tátra; german: Hohe Tatra; french: Hautes Tatras), are a mountain range along the border of norther ...
which are a popular hiking
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A Histor ...
and skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IO ...
destination and home to many scenic lakes and valleys as well as the highest point in Slovakia, the Gerlachovský štít
Gerlachovský štít (, translated into English as ''Gerlachov Peak'', German: ''Gerlsdorfer Spitze'', Hungarian: ''Gerlachfalvi-csúcs''), informally referred to as Gerlach, is the highest peak in the High Tatras, in Slovakia, and in the Carpat ...
at and the country's highly symbolic mountain Kriváň Kriváň can refer to:
* Kriváň (peak), peak in the High Tatras, Slovakia
* Veľký Kriváň, the highest peak in Malá Fatra, Slovakia
* Kriváň (village)
Kriváň ( hu, Krivány) is a village and municipality in Detva District, in the Bansk� ...
. To the west are the Western Tatras
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
with their highest peak of Bystrá at and to the east are the Belianske Tatras
, photo = Belianske Tatry from Jahňaci štít-captions sk.svg
, photo_size = 250px
, photo_caption = Muráň, Nový, Havran, Ždiarska Vidla peaks – beginning from the left
, count ...
, smallest by area.
Separated from the Tatras proper by the valley of the Váh
The Váh (; german: Waag, ; hu, Vág; pl, WagWag
w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów ...
river are the w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów ...
Low Tatras
The Low Tatras or Low Tatra ( sk, Nízke Tatry; hu, Alacsony-Tátra) is a mountain range of the Inner Western Carpathians in central Slovakia.
It is located south of the Tatras proper, from which it is separated by the valleys of the Váh ...
, with their highest peak of Ďumbier
Ďumbier (2,043 m or 6,703 ft) is the highest mountain in the Low Tatra range, in central Slovakia. Despite the remains of medieval mines (gold, iron, antimony), the massif is now protected as a part of the Low Tatras National Park.
The ea ...
at .
The Tatra mountain range is represented as one of the three hills on the coat of arms of Slovakia
The coat of arms of the Slovak Republic consists of a red (''gules'') shield, in early Gothic style, charged with a silver (''argent'') double cross standing on the middle peak of a dark blue mountain consisting of three peaks. Extremities of th ...
.
Caves
 Slovakia has hundreds of caves and caverns under its mountains, of which 30 are open to the public. Most of the caves have
Slovakia has hundreds of caves and caverns under its mountains, of which 30 are open to the public. Most of the caves have stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling")
is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically ...
s rising from the ground and stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via
''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble an ...
s hanging from above. There are currently five Slovak caves under UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
's World Heritage Site status. They are Dobšiná Ice Cave
Dobšiná Ice Cave ( sk, Dobšinská ľadová jaskyňa; hu, Dobsinai-jégbarlang) is an ice cave in Slovakia, near the mining town of Dobšiná in the Slovak Paradise. Since 2000 it has been included on the UNESCO World Heritage list as a part of ...
, Domica
The Domica cave is situated on the south-western border of the ''Silicka planina Plateau'' south-east of Plesivec in the Rožňava District of the Košice Region in southern Slovakia and in combination with the Baradla cave represents the most ...
, Gombasek Cave, Jasovská Cave and Ochtinská Aragonite Cave
Ochtinská Aragonite Cave ( sk, Ochtinská aragonitová jaskyňa, hu, Martonházi-aragonitbarlangthe Magyar Wikipedia article uses a different title) is a unique aragonite cave situated in southern Slovakia, near Rožňava. Although only 300 m lo ...
. Other caves open to the public include Belianska Cave
Belianska Cave ( sk, Belianska jaskyňa, ) is a stalactite cave in the Slovak part of the Tatra mountains
The Tatra Mountains (), Tatras, or Tatra (''Tatry'' either in Slovak () or in Polish () - '' plurale tantum''), are a series of moun ...
, Demänovská Cave of Liberty, Demänovská Ice Cave or Bystrianska Cave.
Rivers
 Most of the rivers arise in the Slovak mountains. Some only pass through Slovakia, while others make a natural border with surrounding countries (more than ). For example, the
Most of the rivers arise in the Slovak mountains. Some only pass through Slovakia, while others make a natural border with surrounding countries (more than ). For example, the Dunajec
The Dunajec (); Goral dialects: ''Dónajec'') is a river running through northeastern Slovakia and southern Poland. It is also regarded as the main river of the Goral Lands. It is a right tributary of the Vistula River. It begins in Nowy Targ at t ...
() to the north, the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
() to the south or the Morava () to the West. The total length of the rivers on Slovak territory is .
The longest river in Slovakia is the Váh
The Váh (; german: Waag, ; hu, Vág; pl, WagWag
w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów ...
(), the shortest is the Čierna voda. Other important and large rivers are the w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów ...
Myjava
Myjava (; historically also Miava, german: Miawa, hu, Miava) is a town in Trenčín Region, Slovakia.
Geography
It is located in the Myjava Hills at the foothills of the White Carpathians and nearby the Little Carpathians. The river Myjava flow ...
, the Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of about 78,353, it is the fifth la ...
(), the Orava, the Hron
The Hron ( sk, Hron; german: Gran; hu, Garam; la, Granus) is a long left tributary of the DanubeHornád
Hornád ( Slovak, ) or Hernád ( Hungarian, ) is a river in eastern Slovakia and north-eastern Hungary.
It is a tributary to the river Slaná (Sajo). The source of the Hornád is the eastern slopes of Kráľova hoľa hill, south of Šuňava.
...
(), the Slaná (), the Ipeľ
The Ipeľ ( Slovak; ) or Ipoly ( Hungarian) (German: ''Eipel'', archaic Slovak: ''Jupoľ'', Latin: ''Bolia'') is a long river in Slovakia and Hungary, a tributary of the Danube River. Its source is in central Slovakia in the Slovak Ore Mountai ...
(, forming the border with Hungary), the Bodrog
The Bodrog is a river in eastern Slovakia and north-eastern Hungary. It is a tributary to the river Tisza. The Bodrog is formed by the confluence of the rivers Ondava and Latorica near Zemplín in eastern Slovakia. It crosses the Slovak–Hun ...
, the Laborec
The Laborec ( ukr, Лаборець; hu, Laborc) is a river in eastern Slovakia that flows through the districts of Medzilaborce, Humenné, and Michalovce in the Košice Region, and the Prešov Region. The river drains the Laborec Highlands. ...
, the Latorica
Latorica ( hu, Latorca; sk, Latorica, pronounced: ''Latoritsa''; uk, Латориця, translit.: ''Latorytsia'') is a river in the watershed of the Danube. Its source is in the Ukrainian Carpathians (Eastern Carpathian Mountains), near the vil ...
and the Ondava
The Ondava is a river in eastern Slovakia, the northern source river of the Bodrog. Its source is in the Low Beskids (Eastern Carpathian Mountains), near the village Nižná Polianka, close to the border with Poland. The Ondava flows south throu ...
.
The biggest volume of discharge in Slovak rivers is during spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season)
Spring, also known as springtime, is one of the four temperate seasons, succeeding winter and preceding summer. There are various technical definitions of spring, but local usage of ...
, when the snow melts from the mountains. The only exception is the Danube, whose discharge is the greatest during summer when the snow melts in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
. The Danube is the largest river that flows through Slovakia.
Climate
The Slovak climate lies between the temperate andcontinental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
zones with relatively warm summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
s and cold, cloudy and humid winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures ...
s. Temperature extremes are between although temperatures below are rare. The weather differs from the mountainous north to the plains in the south.
The warmest region is Bratislava
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Preßburg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 — approxim ...
and Southern Slovakia where the temperatures may reach in summer, occasionally to in Hurbanovo
Hurbanovo (until 1948 ''Stará Ďala'', hu, Ógyalla, german: Altdala) is a town and large municipality in the Komárno District in the Nitra Region of south-west Slovakia. In 1948, its Slovak name was changed to Hurbanovo, named after Slovak wri ...
. During night, the temperatures drop to . The daily temperatures in winter average in the range of to . During night it may be freezing, but usually not below .
In Slovakia, there are four season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and pol ...
s, each season (spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season)
Spring, also known as springtime, is one of the four temperate seasons, succeeding winter and preceding summer. There are various technical definitions of spring, but local usage of ...
, summer, autumn
Autumn, also known as fall in American English and Canadian English, is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September ( Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Sou ...
and winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures ...
) lasts three months. The dry continental air brings in the summer heat and winter frosts. In contrast, oceanic air brings rainfalls and reduces summer temperatures. In the lowlands and valleys, there is often fog, especially in winter.
Spring starts with 21 March and is characterised by colder weather with an average daily temperature of in the first weeks and about in May and in June. In Slovakia, the weather and climate in the spring are very unstable.
Summer starts on 22 June and is usually characterised by hot weather with daily temperatures exceeding . July is the warmest month with temperatures up to about , especially in regions of southern Slovakia - in the urban area of Komárno, Hurbanovo or Štúrovo. Showers or thunderstorms may occur because of the summer monsoon called Medardova kvapka (Medard drop - 40 days of rain). Summer in Northern Slovakia is usually mild with temperatures around (less in the mountains).
Autumn in Slovakia starts on 23 September and is mostly characterised by wet weather and wind, although the first weeks can be very warm and sunny. The average temperature in September is around , in November to . Late September and early October is a dry and sunny time of year (so-called Indian summer
An Indian summer is a period of unseasonably warm, dry weather that sometimes occurs in autumn in temperate regions of the northern hemisphere. Several sources describe a true Indian summer as not occurring until after the first frost, or more s ...
).
Winter starts on 21 December with temperatures around . In December and January, it is usually snowing, these are the coldest months of the year. At lower altitudes, snow does not stay the whole winter, it changes into the thaw and frost. Winters are colder in the mountains, where the snow usually lasts until March or April and the night temperatures fall to and colder.
Examples
Biodiversity
Slovakia signed the RioConvention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
on 19 May 1993, and became a party to the convention on 25 August 1994. It has subsequently produced a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan, which was received by the convention on 2 November 1998.
The biodiversity of Slovakia comprises animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s (such as annelids, arthropods, molluscs, nematodes and vertebrates), fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
(Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The def ...
, Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basi ...
, Chytridiomycota
Chytridiomycota are a division of zoosporic organisms in the kingdom Fungi, informally known as chytrids. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased zoöspores. Chytrids ...
, Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota (often referred to as glomeromycetes, as they include only one class, Glomeromycetes) are one of eight currently recognized divisions within the kingdom Fungi,
with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycot ...
and Zygomycota
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla: the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living i ...
), micro-organisms (including Mycetozoa
Mycetozoa is a polyphyletic grouping of slime molds. It was originally thought to be a monophyletic clade, but recently it was discovered that protostelia are a polyphyletic group within Conosa.
Classification
It can be divided into dictyostelid ...
), and plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s. The geographical position of Slovakia determines the richness of the diversity of fauna and flora. More than 11,000 plant species have been described throughout its territory, nearly 29,000 animal species and over 1,000 species of protozoa. Endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsew ...
biodiversity is also common.
Slovakia is located in the biome of temperate broadleaf and mixed forest
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.
These for ...
s and terrestrial ecoregions of Pannonian mixed forests
The Pannonian mixed forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in Europe. It covers an area of 307,720 km2 in Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Czech Republic, Hungary, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Ukraine, and Croatia.
...
and Carpathian montane conifer forests
The Carpathian montane conifer forests, also known as Carpathian montane forests, is a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion in the Carpathian Mountains of the Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, Ukraine, and Romania.
Geography
The ecoregion cove ...
. As the altitude changes, the vegetation associations and animal communities are forming height levels (oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
, beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
, spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfami ...
, scrub pine
''Pinus virginiana'', the Virginia pine, scrub pine, Jersey pine, Possum pine, is a medium-sized tree, often found on poorer soils from Long Island in southern New York south through the Appalachian Mountains to western Tennessee and Alabama. T ...
, alpine meadows
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets ...
and subsoil
Subsoil is the layer of soil under the topsoil on the surface of the ground. Like topsoil, it is composed of a variable mixture of small particles such as sand, silt and clay, but with a much lower percentage of organic matter and humus, and it ...
). Forests cover 44% of the territory of Slovakia. The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 4.34/10, ranking it 129th globally out of 172 countries. In terms of forest stands, 60% are broadleaf trees and 40% are coniferous trees
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant ...
. The occurrence of animal species is strongly connected to the appropriate types of plant associations and biotopes.
Over 4,000 species of fungi have been recorded from Slovakia. Of these, nearly 1,500 are lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Lakes of Slovakia
* Baňur
References
{{Danube