Geography Of M'Sila Province on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar
 For something to exist in the realm of geography, it must be able to be described spatially. Thus, space is the most fundamental concept at the foundation of geography. The concept is so basic, that geographers often have difficulty defining exactly what it is, and instead assume that everyone knows what they are talking about. At its most fundamental, absolute space is the exact site, or spatial coordinates, of objects, persons, places, or phenomena under investigation. We exist in space. Absolute space leads to the view of the world as a photograph, with everything frozen in place when the coordinates were recorded. Today, geographers are trained to remember that the world is not the static image that appears on a map; and instead, the dynamic space where all processes interact and take place.
For something to exist in the realm of geography, it must be able to be described spatially. Thus, space is the most fundamental concept at the foundation of geography. The concept is so basic, that geographers often have difficulty defining exactly what it is, and instead assume that everyone knows what they are talking about. At its most fundamental, absolute space is the exact site, or spatial coordinates, of objects, persons, places, or phenomena under investigation. We exist in space. Absolute space leads to the view of the world as a photograph, with everything frozen in place when the coordinates were recorded. Today, geographers are trained to remember that the world is not the static image that appears on a map; and instead, the dynamic space where all processes interact and take place.
 Time is usually thought to be within the domain of history, however, it is of significant concern in the discipline of geography. In physics, space and time are not separated, and are combined into the concept of spacetime.
Geography is subject to the laws of physics, and in studying things that occur in space, time must be considered. Time in geography is more than just the historical record of events that occurred at various discrete coordinates; but also includes modeling the dynamic movement of people, organisms, and things through space. Time facilitates movement through space, ultimately allowing things to flow through a system. The amount of time an individual, or group of people, spends in a place will often shape their attachment and perspective to that place. Time constrains the possible paths that can be taken through space, given a starting point, possible routes, and rate of travel. Visualizing time over space is challenging in terms of cartography, and includes Space-Prism, advanced 3D geovisualizations, and animated maps.
Time is usually thought to be within the domain of history, however, it is of significant concern in the discipline of geography. In physics, space and time are not separated, and are combined into the concept of spacetime.
Geography is subject to the laws of physics, and in studying things that occur in space, time must be considered. Time in geography is more than just the historical record of events that occurred at various discrete coordinates; but also includes modeling the dynamic movement of people, organisms, and things through space. Time facilitates movement through space, ultimately allowing things to flow through a system. The amount of time an individual, or group of people, spends in a place will often shape their attachment and perspective to that place. Time constrains the possible paths that can be taken through space, given a starting point, possible routes, and rate of travel. Visualizing time over space is challenging in terms of cartography, and includes Space-Prism, advanced 3D geovisualizations, and animated maps.
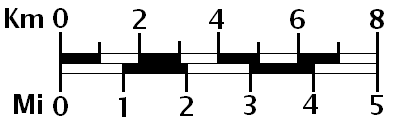 Scale in the context of a map is the ratio between a distance measured on the map and the corresponding distance as measured on the ground. This concept is fundamental to the discipline of geography, not just cartography, in that phenomena being investigated appear different depending on the scale used. Scale is the frame that geographers use to measure space, and ultimately to try and understand a place.
Scale in the context of a map is the ratio between a distance measured on the map and the corresponding distance as measured on the ground. This concept is fundamental to the discipline of geography, not just cartography, in that phenomena being investigated appear different depending on the scale used. Scale is the frame that geographers use to measure space, and ultimately to try and understand a place.
File:Línea de Wallace.jpg,
File:Spatial Contextual Awareness Fig 2.png, Cognitive geography
File:Qichwa conchucos 01.jpg, Cultural geography
File:Pepsi in India.jpg, Development geography
File:Christaller model 1.jpg, Economic geography
File:Star of life.svg, Health geography
File:British Empire 1897.jpg, Historical geography
File:UN General Assembly.jpg,
Various approaches to the study of human geography have also arisen through time and include:
* Behavioral geography
* Culture theory
*
File:The Cartographic Process.png, Cartography
File:Australian Census 2011 demographic map - Australia by SLA - BCP field 2715 Christianity Anglican Persons.svg, Digital mapping
File:Worldwind.png, Geoinformatics
File:Fig 4.4.png,
 Geomatics is concerned with the application of computers to the traditional spatial techniques used in cartography and topography. Similar to the terms
Geomatics is concerned with the application of computers to the traditional spatial techniques used in cartography and topography. Similar to the terms
 Cartography is the art, science, and technology of making maps. Cartographers study the Earth's surface representation with abstract symbols (map making). Although other subdisciplines of geography rely on maps for presenting their analyses, the actual making of maps is abstract enough to be regarded separately. Cartography has grown from a collection of drafting techniques into an actual science.
Cartographers must learn
Cartography is the art, science, and technology of making maps. Cartographers study the Earth's surface representation with abstract symbols (map making). Although other subdisciplines of geography rely on maps for presenting their analyses, the actual making of maps is abstract enough to be regarded separately. Cartography has grown from a collection of drafting techniques into an actual science.
Cartographers must learn
 During the Middle Ages, the fall of the Roman empire led to a shift in the evolution of geography from Europe to the
During the Middle Ages, the fall of the Roman empire led to a shift in the evolution of geography from Europe to the  The European Age of Discovery during the 16th and the 17th centuries, where many new lands were discovered and accounts by European explorers such as Christopher Columbus,
The European Age of Discovery during the 16th and the 17th centuries, where many new lands were discovered and accounts by European explorers such as Christopher Columbus,
 * Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859) – published '' Cosmos'' and founder of the sub-field biogeography.
* Anne Kelly Knowles (Born 1957) – influential in the use of GIS and geographic methods in History.
* Arnold Henry Guyot (1807–1884) – noted the structure of glaciers and advanced understanding in glacier motion, especially in fast ice flow.
* Carl O. Sauer (1889–1975) – cultural geographer.
* Carl Ritter (1779–1859) – occupied the first chair of geography at Berlin University.
* Cynthia Brewer – cartographic theorist that created the Apache 2.0 licensed web application ColorBrewer.
*
* Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859) – published '' Cosmos'' and founder of the sub-field biogeography.
* Anne Kelly Knowles (Born 1957) – influential in the use of GIS and geographic methods in History.
* Arnold Henry Guyot (1807–1884) – noted the structure of glaciers and advanced understanding in glacier motion, especially in fast ice flow.
* Carl O. Sauer (1889–1975) – cultural geographer.
* Carl Ritter (1779–1859) – occupied the first chair of geography at Berlin University.
* Cynthia Brewer – cartographic theorist that created the Apache 2.0 licensed web application ColorBrewer.
*
Definition of geography at Dictionary.com
Definition of geography by Lexico
Origin and meaning of geography by Online Etymology Dictionary
Topic Dictionaries at Oxford Learner's Dictionaries
{{Use British English Oxford spelling, date=August 2016 Earth sciences Social sciences Main topic articles
Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria ...
(276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of their f ...
. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and the physical sciences."
Introduction
Geography is a systematic study of the Earth, its features, and phenomena that take place on it. For something to fall into the domain of geography, it generally needs some sort of spatial component that can be placed on a map, such ascoordinates
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is sig ...
, place names, or addresses. This has led to geography being associated with cartography and place names. Although many geographers are trained in toponymy and cartology, this is not their main preoccupation. Geographers study the Earth's spatial and temporal distribution of phenomena, processes, and features as well as the interaction of humans and their environment. Because space and place affect a variety of topics, such as economics, health, climate, plants, and animals, geography is highly interdisciplinary. The interdisciplinary nature of the geographical approach depends on an attentiveness to the relationship between physical and human phenomena and their spatial patterns. Geography is specific to the planet Earth, and other celestial bodies are specified, such as "geography of Mars," or given another name, such as areography in the case of Mars.
Geography as a discipline can be split broadly into three main branches: human geography, physical geography, and technical geography. Human geography largely focuses on the built environment and how humans create, view, manage, and influence space. Physical geography examines the natural environment, and how organisms, climate, soil, water, and landform
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, ...
s produce and interact. The difference between these approaches led to the development of integrated geography, which combines physical and human geography and concerns the interactions between the environment and humans. Technical geography involves studying and developing the tools and techniques used by geographers, such as remote sensing, cartography, and geographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
.
Core concepts
Space
Place
Place is one of the most complex terms in geography. In human geography, place is the synthesis of the coordinates on the Earth's surface, the activity and use that occurs, has occurred, and will occur at the coordinates, and the meaning ascribed to the space by human individuals and groups. This can be extraordinarily complex, as different spaces may have different uses at different times and mean different things to different people. In physical geography, a place includes all of the physical phenomena that occur in space, including the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Places do not exist in a vacuum and instead have complex spatial relationships with each other, and place is concerned how a location is situated in relation to all other locations. As a discipline then, the term place in geography includes all spatial phenomena occurring at a location, the diverse uses and meanings humans ascribe to that location, and how that location impacts and is impacted by all other locations on Earth.Time
 Time is usually thought to be within the domain of history, however, it is of significant concern in the discipline of geography. In physics, space and time are not separated, and are combined into the concept of spacetime.
Geography is subject to the laws of physics, and in studying things that occur in space, time must be considered. Time in geography is more than just the historical record of events that occurred at various discrete coordinates; but also includes modeling the dynamic movement of people, organisms, and things through space. Time facilitates movement through space, ultimately allowing things to flow through a system. The amount of time an individual, or group of people, spends in a place will often shape their attachment and perspective to that place. Time constrains the possible paths that can be taken through space, given a starting point, possible routes, and rate of travel. Visualizing time over space is challenging in terms of cartography, and includes Space-Prism, advanced 3D geovisualizations, and animated maps.
Time is usually thought to be within the domain of history, however, it is of significant concern in the discipline of geography. In physics, space and time are not separated, and are combined into the concept of spacetime.
Geography is subject to the laws of physics, and in studying things that occur in space, time must be considered. Time in geography is more than just the historical record of events that occurred at various discrete coordinates; but also includes modeling the dynamic movement of people, organisms, and things through space. Time facilitates movement through space, ultimately allowing things to flow through a system. The amount of time an individual, or group of people, spends in a place will often shape their attachment and perspective to that place. Time constrains the possible paths that can be taken through space, given a starting point, possible routes, and rate of travel. Visualizing time over space is challenging in terms of cartography, and includes Space-Prism, advanced 3D geovisualizations, and animated maps.
Scale
 Scale in the context of a map is the ratio between a distance measured on the map and the corresponding distance as measured on the ground. This concept is fundamental to the discipline of geography, not just cartography, in that phenomena being investigated appear different depending on the scale used. Scale is the frame that geographers use to measure space, and ultimately to try and understand a place.
Scale in the context of a map is the ratio between a distance measured on the map and the corresponding distance as measured on the ground. This concept is fundamental to the discipline of geography, not just cartography, in that phenomena being investigated appear different depending on the scale used. Scale is the frame that geographers use to measure space, and ultimately to try and understand a place.
Laws of geography
In general, some dispute the entire concept of laws in geography and the social sciences. These criticisms have been addressed by Tobler and others. However, this is an ongoing source of debate in geography and is unlikely to be resolved anytime soon. Several laws have been proposed, and Tobler's first law of geography is the most generally accepted in geography. Some have argued that geographic laws do not need to be numbered. The existence of a first invites a second, and many have proposed themselves as that. It has also been proposed that Tobler's first law of geography should be moved to the second and replaced with another. A few of the proposed laws of geography are below: * Tobler's first law of geography: "Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant" * Tobler's second law of geography: "The phenomenon external to a geographic area of interest affects what goes on inside." * Arbia's law of geography: "Everything is related to everything else, but things observed at a coarse spatial resolution are more related than things observed at a finer resolution." * The uncertainty principle: "That the geographic world is infinitely complex and that any representation must therefore contain elements of uncertainty, that many definitions used in acquiring geographic data contain elements of vagueness, and that it is impossible to measure location on the Earth's surface exactly."Sub-disciplines
Geography is a branch of inquiry that focuses on spatial information on Earth. It is an extremely broad topic and can be broken down multiple ways. There have been several approaches to doing this, including "four traditions of geography" and into distinct branches. The Four traditions of geography are often used to divide the different historical approaches geographers have taken to the discipline. In contrast, the branches of geography are used to describe contemporary geographers' approaches.Four traditions of geography
Geography is an extremely broad field. Because of this, many view the various definitions of geography proposed over the decades as inadequate. To address this,William D. Pattison
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
proposed the concept of the "Four traditions of Geography" in 1964. These traditions are the Spatial or Locational Tradition, the Man-Land or Human-Environment Interaction Tradition, the Area Studies or Regional Tradition, and the Earth Science Tradition. These concepts are broad sets of geography philosophies bound together within the discipline. They are one of many ways geographers organize the major sets of thoughts and philosophies within the discipline.
Spatial or locational tradition
The spatial or locational tradition is concerned with employing quantitative methods to describe the spatial characteristics of a location. The spatial tradition seeks to use the spatial characteristics of a location or phenomena to understand and explain it. The contributors to this tradition were historically cartographers, but it now encompasses what we call technical geography and geographic information science.Area studies or regional tradition
The area studies or regional tradition is concerned with the description of the unique characteristics of the earth's surface, resulting in each area from the combination of its complete natural or elements, as of physical and human environment. The main aim is to understand, or define the uniqueness, or character of a particular region that consists of natural as well as human elements. Attention is paid also to regionalization, which covers the proper techniques of space delimitation into regions.Human-Environment interaction tradition
The Human Environment Interaction tradition (originally the Man-Land), also known as Integrated geography, is concerned with the description of the spatial interactions between humans and the natural world. It requires an understanding of the traditional aspects of physical and human geography, like how human societies conceptualize the environment. Integrated geography has emerged as a bridge between human and physical geography due to the increasing specialization of the two sub-fields. Since the changing of the human relationship with the environment as a result of globalization and technological change, a new approach was needed to understand the changing and dynamic relationship. Examples of areas of research in environmental geography include:emergency management
Emergency management or disaster management is the managerial function charged with creating the framework within which communities reduce vulnerability to hazards and cope with disasters. Emergency management, despite its name, does not actuall ...
, environmental management
Environmental resource management is the management of the interaction and impact of human societies on the environment. It is not, as the phrase might suggest, the management of the environment itself. Environmental resources management aims ...
, sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livi ...
, and political ecology.
Earth science tradition
TheEarth science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres ...
tradition is largely concerned with what is generally referred to as physical geography. The tradition focuses on understanding the spatial characteristics of natural phenomena. Some argue the Earth science tradition is a subset of the spatial tradition, however the two are different enough in their focus and objectives to warrant separation.
Branches of geography
Research and careers in geography today are highly multidisciplinary. Geography is often organized into three branches: human geography, physical geography, and technical geography. Geographers rarely focus on just one of these topics, often using one as their primary focus and then incorporating data and methods from the other branches. Geographers are more likely to identify closely with a specific branch when describing themselves to lay people than with grand traditions. Human geography is concerned with studying people and their communities, cultures, economies, and interactions with the environment by studying their relations with and across space and place. Physical geography is concerned with the study of processes and patterns in the natural environment like theatmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. Technical geography is interested in studying and applying techniques and methods to store, process, analyze, visualize, and use spatial data. These branches use similar geographic philosophies, concepts, and tools and often overlap significantly.
Physical
Physical geography (or physiography) focuses on geography as anEarth science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres ...
. It aims to understand the physical problems and the issues of lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time sca ...
, hydrosphere, atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
, pedosphere, and global flora and fauna patterns ( biosphere). Physical geography is the study of earth's seasons, climate, atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
, soil, streams, landforms, and oceans. Physical geographers will often work in identifying and monitoring the use of natural resources.
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
File:Cyclone Catarina from the ISS on March 26 2004.JPG, Climatology and meteorology
File:90 mile beach.jpg, Coastal geography
Coastal geography is the study of the constantly changing region between the ocean and the land, incorporating both the physical geography (i.e. coastal geomorphology, climatology and oceanography) and the human geography (sociology and history) ...
File:Gavin Plant.JPG, Environmental management
Environmental resource management is the management of the interaction and impact of human societies on the environment. It is not, as the phrase might suggest, the management of the environment itself. Environmental resources management aims ...
File:Delicate Arch LaSalle.jpg, Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or n ...
File:Receding glacier-en.svg, Glaciology
File:Meander.svg, Hydrology and hydrography
File:Khajuraho-landscape.jpg, Landscape ecology
File:World11.jpg, Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
File:Pangea interpretacion.png, alt=a view of the supercontinent of pangea breaking up, Palaeogeography
File:Soil profile.jpg, Pedology
File:Milankovitch Variations sv.png, Quaternary science
Human
Human geography (or anthropogeography) is a branch of geography that focuses on studying patterns and processes that shape human society. It encompasses the human, political,cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human Society, societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, and habits of the ...
, social, and economic aspects. In industry, human geographers often work in city planning, public health, or business analysis.
Political geography
Political geography is concerned with the study of both the spatially uneven outcomes of political processes and the ways in which political processes are themselves affected by spatial structures. Conventionally, for the purposes of analysis, po ...
and Geopolitics
Geopolitics (from Greek γῆ ''gê'' "earth, land" and πολιτική ''politikḗ'' "politics") is the study of the effects of Earth's geography (human and physical) on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to ...
File:Pyramide Comores.PNG, Population geography or Demography
File:ReligionSymbol.svg, Religion geography
Religion and geography is the study of the impact of geography, i.e. place and space, on religious belief.
Another aspect of the relationship between religion and geography is ''religious geography'', in which geographical ideas are influenced by ...
File:US-hoosier-family.jpg, Social geography
Social geography is the branch of human geography that is interested in the relationships between society and space, and is most closely related to social theory in general and sociology in particular, dealing with the relation of social phenomena ...
File:Gare du Nord USFRT (Paris Metro).png, Transportation geography
File:Tourists-2.jpg, Tourism geography
File:New-York-Jan2005.jpg, Urban geography
Feminist geography
Feminist geography is a sub-discipline of human geography that applies the theories, methods, and critiques of feminism to the study of the human environment, society, and geographical space. Feminist geography emerged in the 1970s, when members ...
* Geosophy Geosophy is a concept introduced to geography by J.K. Wright in 1947. The word is a compound of ‘geo’ (Greek for earth) and ‘sophia’ (Greek for wisdom). Wright defined it thus:
:Geosophy ... is the study of geographical knowledge from any ...
Technical
Technical geography concerns studying and developing tools, techniques, and statistical methods employed to collect, analyze, use, and understand spatial data. Technical geography is the most recently recognized of the branches. As academic fields increasingly specialize in their nature, technical geography has emerged as a branch of geography specializing in geographic methods and thought. The emergence of technical geography has brought new relevance to the broad discipline of geography by serving as a set of unique methods for managing the interdisciplinary nature of the discipline. While human and physical geographers use the techniques employed by technical geographers, technical geography is more concerned with the fundamental spatial concepts and technologies than the nature of the data. A technical geographer might work as a GIS analyst or create general reference maps incorporating human and natural features.Geographic information science Geographic information science or geographical information science (GIScience or GISc) is the scientific discipline that studies geographic information, including how it represents phenomena in the real world, how it represents the way humans unders ...
File:Geoservices server with apps.png, Geographic information systems
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a br ...
File:Euclidean Voronoi diagram.svg, Geostatistics
File:Survey instruments-2.png, Geomatics
File:gislayers.jpg, Geovisualization
File:GPS-IIR.jpg, Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
File:Meridian convergence and spehrical excess.png, Geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
File:World map of submarine cables.png, Internet GIS
File:MapAlgebra.png, Map algebra
Image:Alpha2000.jpg, Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant ima ...
File:Remote Sensing Illustration.jpg, Remote Sensing
File:Example_krig.png, Spatial analysis
File:Sample of time geographical description.png, Time geography
File:Smartphone with navigation map app.jpg, Web mapping
Related fields
*Planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of their f ...
: While the discipline of geography is normally concerned with the Earth, the term can also be informally used to describe the study of other worlds, such as the planets of the Solar System and even beyond. The study of systems larger than the Earth itself usually forms part of Astronomy or Cosmology. The study of other planets is usually called planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of their f ...
. Alternative terms such as areography (geography of Mars)
Areography, also known as the geography of Mars, is a subfield of planetary science that entails the delineation and characterization of regions on Mars. Areography is mainly focused on what is called physical geography on Earth; that is the dis ...
have been employed to describe the study of other celestial objects. Ultimately, geography may be considered a subdiscipline within planetary science.
Techniques
All geographic research and analysis start with asking the question "where," followed by "why there." Geographers start with the fundamental assumption set forth in Tobler's first law of geography, that "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." As spatial interrelationships are key to this synoptic science, maps are a key tool. Classical cartography has been joined by a more modern approach to geographical analysis, computer-basedgeographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
s (GIS).
In their study, geographers use four interrelated approaches:
* Analytical – Asks ''why'' we find features and populations in a specific geographic area.
* Descriptive – Simply specifies the locations of features and populations.
* Regional – Examines systematic relationships between categories for a specific region or location on the planet.
* Systematic – Groups geographical knowledge into categories that can be explored globally.
Quantitative methods
Quantitative methods in geography became particularly influential in the discipline during the 1950s and 60s. These methods revitalized the discipline in many ways, allowing scientific testing of hypotheses and proposing scientific geographic theories and laws.Geomatics
 Geomatics is concerned with the application of computers to the traditional spatial techniques used in cartography and topography. Similar to the terms
Geomatics is concerned with the application of computers to the traditional spatial techniques used in cartography and topography. Similar to the terms geographic information science Geographic information science or geographical information science (GIScience or GISc) is the scientific discipline that studies geographic information, including how it represents phenomena in the real world, how it represents the way humans unders ...
and technical geography, geomatics emerged from the quantitative revolution
The quantitative revolution (QR) was a paradigm shift that sought to develop a more rigorous and systematic methodology for the discipline of geography. It came as a response to the inadequacy of regional geography to explain general spatial dynam ...
in geography in the mid-1950s. Today, geomatics methods include spatial analysis, geographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
s (GIS), remote sensing, and global positioning system
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
s (GPS). Geomatics has revitalized some geography departments, especially in Northern America, where the subject had a declining status during the 1950s. Because of this, many have proposed it may be a third branch in geography, in addition to physical and human.
Quantitative cartography
 Cartography is the art, science, and technology of making maps. Cartographers study the Earth's surface representation with abstract symbols (map making). Although other subdisciplines of geography rely on maps for presenting their analyses, the actual making of maps is abstract enough to be regarded separately. Cartography has grown from a collection of drafting techniques into an actual science.
Cartographers must learn
Cartography is the art, science, and technology of making maps. Cartographers study the Earth's surface representation with abstract symbols (map making). Although other subdisciplines of geography rely on maps for presenting their analyses, the actual making of maps is abstract enough to be regarded separately. Cartography has grown from a collection of drafting techniques into an actual science.
Cartographers must learn cognitive psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning.
Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which ...
and ergonomics to understand which symbols convey information about the Earth most effectively and behavioural psychology to induce the readers of their maps to act on the information. They must learn geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
and fairly advanced mathematics to understand how the shape of the Earth
Figure of the Earth is a term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A sphere is a well-known historical approxim ...
affects the distortion of map symbols projected onto a flat surface for viewing. It can be said, without much controversy, that cartography is the seed from which the larger field of geography grew. Most geographers will cite a childhood fascination with maps as an early sign they would end up in the field.
Geographic information systems
Geographic information systems (GIS) deal with storing information about the Earth for automatic retrieval by a computer in an accurate manner appropriate to the information's purpose. In addition to all of the other subdisciplines of geography, GIS specialists must understand computer science and database systems. GIS has revolutionized the field of cartography: nearly all mapmaking is now done with the assistance of some form of GIS software. The science of using GIS software and GIS techniques to represent, analyse, and predict the spatial relationships is called ''geographic information science Geographic information science or geographical information science (GIScience or GISc) is the scientific discipline that studies geographic information, including how it represents phenomena in the real world, how it represents the way humans unders ...
'' (GISc).
Remote sensing
Remote sensing is the art, science, and technology of obtaining information about Earth's features from measurements made at a distance. Remotely sensed data comes in many forms, such assatellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell ima ...
, aerial photography, and data obtained from hand-held sensors. Geographers increasingly use remotely sensed data to obtain information about the Earth's land surface, ocean, and atmosphere, because it: (a) supplies objective information at a variety of spatial scales (local to global), (b) provides a synoptic view of the area of interest, (c) allows access to distant and inaccessible sites, (d) provides spectral information outside the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and (e) facilitates studies of how features/areas change over time. Remotely sensed data may be analyzed independently or in conjunction with other digital data layers (e.g., in a geographic information system). Remote sensing aids in land use, land cover (LULC) mapping, by helping to determine both what is naturally occurring on a piece of land and what human activities are taking place on it.
Geostatistics
Geostatistics deal with quantitative data analysis, specifically the application of a statistical methodology to the exploration of geographic phenomena. Geostatistics is used extensively in a variety of fields, including hydrology, geology, petroleum exploration, weather analysis, urban planning, logistics, and epidemiology. The mathematical basis for geostatistics derives fromcluster analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of ...
, linear discriminant analysis
Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), normal discriminant analysis (NDA), or discriminant function analysis is a generalization of Fisher's linear discriminant, a method used in statistics and other fields, to find a linear combination of features ...
and non-parametric statistical tests, and a variety of other subjects. Applications of geostatistics rely heavily on geographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
s, particularly for the interpolation
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one often has a n ...
(estimate) of unmeasured points. Geographers are making notable contributions to the method of quantitative techniques.
Qualitative methods
Qualitative geography is descriptive rather than numerical or statistical in nature. They add context to concepts, and explore human concepts like beliefs and perspective that are difficult or impossible to quantify. Human geography is much more likely to employ qualitative methods than physical. Increasingly, technical geographers are attempting to employ GIS methods to qualitative datasets.Qualitative cartography
Qualitative cartography employs many of the same software and techniques as quantitative. It may be employed to inform on map practices, or to visualize perspectives and ideas that are not strictly quantitative in nature.Ethnography
Ethnographical research techniques are used by human geographers. In cultural geography, there is a tradition of employing qualitative research techniques, also used in anthropology and sociology.Participant observation
Participant observation is one type of data collection method by practitioner-scholars typically used in qualitative research and ethnography. This type of methodology is employed in many disciplines, particularly anthropology (incl. cultural an ...
and in-depth interviews provide human geographers with qualitative data.
History
The concept of geography is present in all cultures, and therefore the history of the discipline is a series of competing narratives, with concepts emerging at various points across space and time. The oldest known world maps date back to ancient Babylon from the 9th century BC. The best knownBabylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
n world map, however, is the ''Imago Mundi
''Imago Mundi'', or in full ''Imago Mundi: International Journal for the History of Cartography'', is a semiannual peer-reviewed academic journal about mapping, established in 1935 by Leo Bagrow. It covers the history of early maps, cartography, ...
'' of 600 BC. The map as reconstructed by Eckhard Unger shows Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
on the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
, surrounded by a circular landmass showing Assyria, Urartu, and several cities, in turn surrounded by a "bitter river" (Oceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus (; grc-gre, , Ancient Greek pronunciation: , also Ὠγενός , Ὤγενος , or Ὠγήν ) was a Titan son of Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys, and the father of the river gods a ...
), with seven islands arranged around it so as to form a seven-pointed star. The accompanying text mentions seven outer regions beyond the encircling ocean. The descriptions of five of them have survived. In contrast to the ''Imago Mundi'', an earlier Babylonian world map dating back to the 9th century BC depicted Babylon as being further north from the center of the world, though it is not certain what that center was supposed to represent.
The ideas of Anaximander
Anaximander (; grc-gre, Ἀναξίμανδρος ''Anaximandros''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 403. a city of Ionia (in moder ...
(c. 610–545 BC): considered by later Greek writers to be the true founder of geography, come to us through fragments quoted by his successors. Anaximander is credited with the invention of the gnomon
A gnomon (; ) is the part of a sundial that casts a shadow. The term is used for a variety of purposes in mathematics and other fields.
History
A painted stick dating from 2300 BC that was excavated at the astronomical site of Taosi is the ol ...
, the simple, yet efficient Greek instrument that allowed the early measurement of latitude. Thales is also credited with the prediction of eclipses. The foundations of geography can be traced to ancient cultures, such as the ancient, medieval, and early modern Chinese. The Greeks, who were the first to explore geography as both art and science, achieved this through Cartography, Philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, and Literature, or through Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
. There is some debate about who was the first person to assert that the Earth is spherical in shape, with the credit going either to Parmenides
Parmenides of Elea (; grc-gre, Παρμενίδης ὁ Ἐλεάτης; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Elea in Magna Graecia.
Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Elea, from a wealthy and illustrious family. His dates a ...
or Pythagoras. Anaxagoras
Anaxagoras (; grc-gre, Ἀναξαγόρας, ''Anaxagóras'', "lord of the assembly"; 500 – 428 BC) was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, ...
was able to demonstrate that the profile of the Earth was circular by explaining eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ce ...
s. However, he still believed that the Earth was a flat disk, as did many of his contemporaries. One of the first estimates of the radius of the Earth was made by Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria ...
.
The first rigorous system of latitude and longitude lines is credited to Hipparchus. He employed a sexagesimal system that was derived from Babylonian mathematics. The meridians were subdivided into 360°, with each degree further subdivided into 60 (minutes
Minutes, also known as minutes of meeting (abbreviation MoM), protocols or, informally, notes, are the instant written record of a meeting or hearing. They typically describe the events of the meeting and may include a list of attendees, a state ...
). To measure the longitude at different locations on Earth, he suggested using eclipses to determine the relative difference in time. The extensive mapping by the Romans as they explored new lands would later provide a high level of information for Ptolemy to construct detailed atlases. He extended the work of Hipparchus, using a grid system on his maps and adopting a length of 56.5 miles for a degree.
From the 3rd century onwards, Chinese methods of geographical study and writing of geographical literature became much more comprehensive than what was found in Europe at the time (until the 13th century). Chinese geographers such as Liu An, Pei Xiu, Jia Dan, Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo (; 1031–1095) or Shen Gua, courtesy name Cunzhong (存中) and pseudonym Mengqi (now usually given as Mengxi) Weng (夢溪翁),Yao (2003), 544. was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman of the Song dynasty (960–1279). Shen wa ...
, Fan Chengda, Zhou Daguan, and Xu Xiake wrote important treatises, yet by the 17th century advanced ideas and methods of Western-style geography were adopted in China.
 During the Middle Ages, the fall of the Roman empire led to a shift in the evolution of geography from Europe to the
During the Middle Ages, the fall of the Roman empire led to a shift in the evolution of geography from Europe to the Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
. Muslim geographers such as Muhammad al-Idrisi produced detailed world maps (such as Tabula Rogeriana), while other geographers such as Yaqut al-Hamawi, Abu Rayhan Biruni, Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
, and Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun (; ar, أبو زيد عبد الرحمن بن محمد بن خلدون الحضرمي, ; 27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732-808 AH) was an Arab
The Historical Muhammad', Irving M. Zeitlin, (Polity Press, 2007), p. 21; "It is, of ...
provided detailed accounts of their journeys and the geography of the regions they visited. Turkish geographer Mahmud al-Kashgari
Mahmud ibn Husayn ibn Muhammed al-Kashgari, ''Maḥmūd ibnu 'l-Ḥusayn ibn Muḥammad al-Kāšġarī'', , tr, Kaşgarlı Mahmûd, ug, مەھمۇد قەشقىرى, ''Mehmud Qeshqiri'' / Мәһмуд Қәшқири uz, Mahmud Qashg'ariy / М ...
drew a world map on a linguistic basis, and later so did Piri Reis ( Piri Reis map). Further, Islamic scholars translated and interpreted the earlier works of the Romans and the Greeks and established the House of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom ( ar, بيت الحكمة, Bayt al-Ḥikmah), also known as the Grand Library of Baghdad, refers to either a major Abbasid public academy and intellectual center in Baghdad or to a large private library belonging to the Abba ...
in Baghdad for this purpose. Abū Zayd al-Balkhī
Abu Zayd Ahmed ibn Sahl Balkhi ( fa, ابو زید احمد بن سهل بلخی) was a Persian people, Persian Muslim polymath: a Islamic geography, geographer, Islamic mathematics, mathematician, Islamic medicine, physician, Islamic psychologic ...
, originally from Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
, founded the "Balkhī school" of terrestrial mapping in Baghdad. Suhrāb, a late tenth century Muslim geographer accompanied a book of geographical coordinates, with instructions for making a rectangular world map with equirectangular projection
The equirectangular projection (also called the equidistant cylindrical projection or la carte parallélogrammatique projection), and which includes the special case of the plate carrée projection (also called the geographic projection, lat/lon ...
or cylindrical equidistant projection.
Abu Rayhan Biruni (976–1048) first described a polar equi- azimuthal equidistant projection of the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
. He was regarded as the most skilled when it came to mapping cities and measuring the distances between them, which he did for many cities in the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent. He often combined astronomical readings and mathematical equations to develop methods of pin-pointing locations by recording degrees of latitude and longitude. He also developed similar techniques when it came to measuring the heights of mountains, depths of the valleys, and expanse of the horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
. He also discussed human geography and the planetary habitability of the Earth. He also calculated the latitude of Kath, Khwarezm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ...
, using the maximum altitude of the Sun, and solved a complex geodesic
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a connection. ...
equation to accurately compute the Earth's circumference, which was close to modern values of the Earth's circumference. His estimate of 6,339.9 km for the Earth radius was only 16.8 km less than the modern value of 6,356.7 km. In contrast to his predecessors, who measured the Earth's circumference by sighting the Sun simultaneously from two different locations, al-Biruni developed a new method of using trigonometric calculations based on the angle between a plain and mountain top, which yielded more accurate measurements of the Earth's circumference, and made it possible for it to be measured by a single person from a single location.
 The European Age of Discovery during the 16th and the 17th centuries, where many new lands were discovered and accounts by European explorers such as Christopher Columbus,
The European Age of Discovery during the 16th and the 17th centuries, where many new lands were discovered and accounts by European explorers such as Christopher Columbus, Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
, and James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
revived a desire for both accurate geographic detail and more solid theoretical foundations in Europe. The problem facing both explorers and geographers was finding the latitude and longitude of a geographic location. The problem of latitude was solved long ago, but that of longitude remained; agreeing on what zero meridians should be was only part of the problem. It was left to John Harrison to solve it by inventing the chronometer H-4 in 1760, and later in 1884 for the International Meridian Conference to adopt by convention the Greenwich meridian
The historic prime meridian or Greenwich meridian is a geographical reference line that passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, Royal Observatory, Greenwich, in London, England. The modern IERS Reference Meridian widely used today ...
as zero meridians.
The 18th and 19th centuries were the times when geography became recognized as a discrete academic discipline, and became part of a typical university curriculum in Europe (especially Paris and Berlin). The development of many geographic societies also occurred during the 19th century, with the foundations of the Société de Géographie in 1821, the Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers), often shortened to RGS, is a learned society and professional body for geography based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical scien ...
in 1830, Russian Geographical Society
The Russian Geographical Society (russian: Ру́сское географи́ческое о́бщество «РГО»), or RGO, is a learned society based in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It promotes geography, exploration and nature protection wi ...
in 1845, American Geographical Society in 1851, and the National Geographic Society in 1888. The influence of Immanuel Kant, Alexander von Humboldt, Carl Ritter, and Paul Vidal de la Blache can be seen as a major turning point in geography from philosophy to an academic subject.
Over the past two centuries, the advancements in technology with computers have led to the development of geomatics and new practices such as participant observation and geostatistics being incorporated into geography's portfolio of tools. In the West during the 20th century, the discipline of geography went through four major phases: environmental determinism, regional geography
Regional geography is a major branch of geography. It focuses on the interaction of different cultural and natural geofactors in a specific land or landscape, while its counterpart, systematic geography, concentrates on a specific geofactor at the ...
, the quantitative revolution
The quantitative revolution (QR) was a paradigm shift that sought to develop a more rigorous and systematic methodology for the discipline of geography. It came as a response to the inadequacy of regional geography to explain general spatial dynam ...
, and critical geography. The strong interdisciplinary links between geography and the sciences of geology and botany, as well as economics, sociology, and demographics, have also grown greatly, especially as a result of earth system science that seeks to understand the world in a holistic view. New concepts and philosophies have emerged from the rapid advancement of computers, quantitative methods, and interdisciplinary approaches. In 1970, Waldo Tobler proposed the first law of geography, "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." This law summarizes the first assumption geographers make about the world.
Notable geographers
 * Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859) – published '' Cosmos'' and founder of the sub-field biogeography.
* Anne Kelly Knowles (Born 1957) – influential in the use of GIS and geographic methods in History.
* Arnold Henry Guyot (1807–1884) – noted the structure of glaciers and advanced understanding in glacier motion, especially in fast ice flow.
* Carl O. Sauer (1889–1975) – cultural geographer.
* Carl Ritter (1779–1859) – occupied the first chair of geography at Berlin University.
* Cynthia Brewer – cartographic theorist that created the Apache 2.0 licensed web application ColorBrewer.
*
* Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859) – published '' Cosmos'' and founder of the sub-field biogeography.
* Anne Kelly Knowles (Born 1957) – influential in the use of GIS and geographic methods in History.
* Arnold Henry Guyot (1807–1884) – noted the structure of glaciers and advanced understanding in glacier motion, especially in fast ice flow.
* Carl O. Sauer (1889–1975) – cultural geographer.
* Carl Ritter (1779–1859) – occupied the first chair of geography at Berlin University.
* Cynthia Brewer – cartographic theorist that created the Apache 2.0 licensed web application ColorBrewer.
* Dana Tomlin
Charles Dana Tomlin is an author, professor, and originator of Map Algebra, a vocabulary and conceptual framework for classifying ways to combine map data to produce new maps. Tomlin's teaching and research focus on the development and application ...
(1779–1859) – originator of map algebra
* David Harvey (born 1935) – Marxist geographer and author of theories on spatial and urban geography, winner of the Vautrin Lud Prize
The ''Prix International de Géographie Vautrin Lud'', known in English as the Vautrin Lud Prize, is the highest award in the field of geography. Established in 1991, the award is named after the 16th Century French scholar . The award is given in ...
.
* Doreen Massey (1944–2016) – scholar in the space and places of globalization and its pluralities; winner of the Vautrin Lud Prize
The ''Prix International de Géographie Vautrin Lud'', known in English as the Vautrin Lud Prize, is the highest award in the field of geography. Established in 1991, the award is named after the 16th Century French scholar . The award is given in ...
.
* Edward Soja (1940–2015) – worked on regional development, planning, and governance and coined the terms Synekism Synekism is a concept in urban studies coined by Edward Soja. It refers to the dynamic formation of the polis state — the union of several small urban settlements under the rule of a "capital" city (or so-called city-state or urban system). Soja's ...
and Postmetropolis; winner of the Vautrin Lud Prize
The ''Prix International de Géographie Vautrin Lud'', known in English as the Vautrin Lud Prize, is the highest award in the field of geography. Established in 1991, the award is named after the 16th Century French scholar . The award is given in ...
.
* Ellen Churchill Semple
Ellen Churchill Semple (January 8, 1863 – May 8, 1932) was an American geographer and the first female president of the Association of American Geographers. She contributed significantly to the early development of the discipline of geography i ...
(1863–1932) – first female president of the Association of American Geographers.
* Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria ...
( 276–c. 195/194 BC) – calculated the size of the Earth.
* Ernest Burgess (1886–1966) – creator of the concentric zone model.
* Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented ...
(1512–1594) – cartographer
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an im ...
who produced the mercator projection
The Mercator projection () is a cylindrical map projection presented by Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. It became the standard map projection for navigation because it is unique in representing north as up and sou ...
* John Francon Williams (1854–1911) – author of ''The Geography of the Oceans''.
* Karl Butzer (1934–2016) – German-American geographer, cultural ecologist, and environmental archaeologist.
* Mark Monmonier (born 1943) – cartographic theorist that wrote numerous books contributing to Geographic Information Systems.
* Michael Frank Goodchild (born 1944) – GIS scholar and winner of the RGS founder's medal in 2003.
* Muhammad al-Idrisi (Arabic: أبو عبد الله محمد الإدريسي; Latin: Dreses) (1100–1165) – author of Nuzhatul Mushtaq.
* Nigel Thrift (born 1949) – originator of non-representational theory.
* Paul Vidal de La Blache (1845–1918) – founder of the French school of geopolitics, wrote the principles of human geography.
* Ptolemy (c. 100–c. 170) – compiled Greek and Roman knowledge into the book Geographia.
* Radhanath Sikdar (1813–1870) – calculated the height of Mount Everest.
* Roger Tomlinson (1933 – 2014) – the primary originator of modern geographic information systems
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a br ...
.
* Sir Halford Mackinder (1861–1947) – co-founder of the LSE, Geographical Association.
* Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
(64/63 BC – c. AD 24) – wrote Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (Ancient Greek: Γεωγραφικά ''Geōgraphiká''), or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Ancient Greek, Greek and attributed to Strabo, an educated citizen ...
, one of the first books outlining the study of geography.
* Waldo Tobler (1930-2018) – coined the first law of geography and second law of geography.
* Walter Christaller (1893–1969) – human geographer and inventor of Central place theory.
* William Morris Davis (1850–1934) – father of American geography and developer of the cycle of erosion.
* Yi-Fu Tuan (1930-2022) – Chinese-American scholar credited with starting Humanistic Geography as a discipline.
Institutions and societies
* American Association of Geographers (AAG) * American Geographical Society (US) * Anton Melik Geographical Institute (Slovenia) *Gamma Theta Upsilon
Gamma Theta Upsilon ( or GTU) is an international honor society in geography.
History
On May 15, 1928, a local professional fraternity by the name of Gamma Theta Upsilon was formed at Illinois State University under the guidance of Dr. R. G. B ...
(international)
* Institute of Geographical Information Systems
The Institute of Geographical Information Systems (IGIS) was established by the National University of Sciences and Technology, Pakistan (NUST) to focus on the educational needs of students in Geographical Information Systems (GIS) and Remote ...
(Pakistan)
* International Geographical Union (International)
* Karachi Geographical Society (Pakistan)
* National Geographic Society (US)
* Royal Canadian Geographical Society (Canada)
* Royal Danish Geographical Society
The Royal Danish Geographical Society (RDGS, da, Det Kongelige Danske Geografiske Selskab) is a scientific society aimed at furthering the knowledge of the Earth and its inhabitants and to disseminate interest in the science of geography.
It was ...
(Denmark)
* Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers), often shortened to RGS, is a learned society and professional body for geography based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical scien ...
(UK)
* Russian Geographical Society
The Russian Geographical Society (russian: Ру́сское географи́ческое о́бщество «РГО»), or RGO, is a learned society based in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It promotes geography, exploration and nature protection wi ...
(Russia)
Publications
* '' Annals of the American Association of Geographers'' * ''Antipode'' * '' Applied Geography'' * '' Concepts and Techniques in Modern Geography'' * ''Dialogues in Human Geography
''Dialogues in Human Geography'' is a triannual peer-reviewed academic journal covering human geography. It was established in 2011 and is published by SAGE Publishing. The journal's founding editor was Rob Kitchin (Maynooth University) and the cur ...
''
* '' Economic Geography''
* ''Geographia Technica
''Geographia Technica'' is a biannual open-access peer-reviewed academic journal.
The journal focuses on quantitative and technical methods in the discipline of geography. The editor-in-chief is Ionel Haidu of the University of Lorraine, France.
...
''
* '' Geographical Review''
* ''Geographical Bulletin
The ''Geographical Bulletin'' is a biannual open-access peer-reviewed academic journal published by the international geographic honor society Gamma Theta Upsilon ( or GTU). It covers all aspects of geography and focuses on student-written and stu ...
''
* ''Geography Compass
Geography (from Ancient Greek, Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, i ...
''
* ''GeoHumanities
The American Association of Geographers (AAG) is a non-profit scientific and educational society aimed at advancing the understanding, study, and importance of geography and related fields. Its headquarters is located in Washington, D.C. The ...
''
* '' International Journal of Geographical Information Science''
* ''Journal of Maps
The ''Journal of Maps'' (JoM) is a biannual open-access peer-reviewed academic journal published by Taylor and Francis. While heavily focused on geography and cartography, the JoM is interdisciplinary and publishes maps and other visualizations ...
''
* '' Journal of Rural Studies''
* ''Journal of Transport Geography
The ''Journal of Transport Geography'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier in association with the Transport Geography Research Group of the Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers). T ...
''
* ''National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
''
* ''Professional Geographer
''The Professional Geographer'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal publishing short articles on all aspects of geography. The journal is published by Taylor and Francis on behalf of the American Association of Geographers. According to t ...
''
* '' Progress in Human Geography''
* '' The Geographical Journal''
* '' The Professional Geographer''
See also
* American Association of Geographers * Arbia's law of geography *Areography (geography of Mars)
Areography, also known as the geography of Mars, is a subfield of planetary science that entails the delineation and characterization of regions on Mars. Areography is mainly focused on what is called physical geography on Earth; that is the dis ...
* Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
* Cartography
* Climatology
* Concepts and Techniques in Modern Geography
* Cultural geography
* Demography
* Development geography
* Economic geography
* Gamma Theta Upsilon
Gamma Theta Upsilon ( or GTU) is an international honor society in geography.
History
On May 15, 1928, a local professional fraternity by the name of Gamma Theta Upsilon was formed at Illinois State University under the guidance of Dr. R. G. B ...
* Geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
* Geographic information science Geographic information science or geographical information science (GIScience or GISc) is the scientific discipline that studies geographic information, including how it represents phenomena in the real world, how it represents the way humans unders ...
* Geographic information systems
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a br ...
* Geographical space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider ...
* Geomatics
* Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or n ...
* Geovisualization
* Glaciology
* Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
* Health geography
* Historical geography
* Hydrology
* Landscape ecology
* National Council for Geographic Education
* Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
* Palaeogeography
* Pedology
* Planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of their f ...
* Remote sensing
* Technical geography
* Time geography
* Tobler's first law of geography
* Tobler's second law of geography
* Transportation geography
* Urban geography
References
External links
Definition of geography at Dictionary.com
Definition of geography by Lexico
Origin and meaning of geography by Online Etymology Dictionary
Topic Dictionaries at Oxford Learner's Dictionaries
{{Use British English Oxford spelling, date=August 2016 Earth sciences Social sciences Main topic articles