Genlisea aurea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
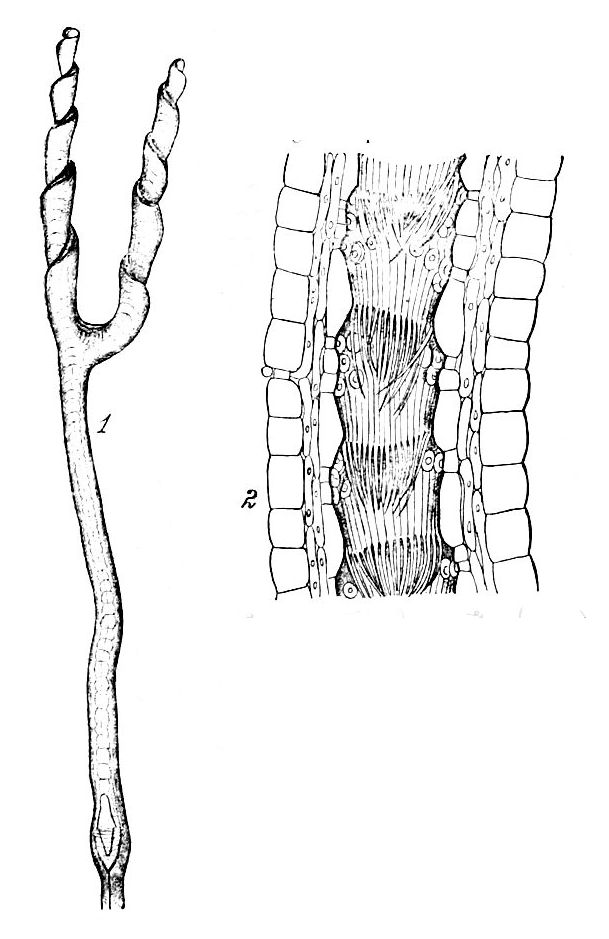 ''Genlisea aurea'' is one of the largest carnivorous species in the
''Genlisea aurea'' is one of the largest carnivorous species in the
 ''Genlisea aurea'' is one of the largest carnivorous species in the
''Genlisea aurea'' is one of the largest carnivorous species in the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Genlisea
''Genlisea'' ( ) is a genus of carnivorous plants also known as corkscrew plants. The 30 or so species grow in wet terrestrial to semi-aquatic environments distributed throughout Africa and Central and South America. The plants use highly modifi ...
'' (family Lentibulariaceae
Lentibulariaceae is a family of carnivorous plants containing three genera: ''Genlisea'', the corkscrew plants; ''Pinguicula'', the butterworts; and ''Utricularia'', the bladderworts.
The genera ''Polypompholyx'' (two species of pink petticoats ...
). It has pale bundles of root-like organs up to about 15 cm long under ground that attract, trap, and digest protozoans. These organs are subterranean leaves, which lack chlorophyll. ''G. aurea'' is endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
to Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, where it grows with several other species of ''Genlisea''. It possesses an exceptionally small genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
for a flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
.
Characteristics
''Genlisea aurea'' is a perennial herb that forms small, compact rosettes composed of nearly linear leaves about 2 mm wide. Leaves are typically 5–50 mm in length, but most of that length, including the petiole, is hidden beneath the soil. The rosettes can grow to be as big as 5 cm wide. It has no true roots and instead has highly modified subterranean leaves that act as the carnivorous trapping mechanism. The up to 40 cm tallinflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a Plant stem, stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphology (biology), Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of sperma ...
produces one to three flowers at its apex that are typically 15–20 mm long and are the largest of the yellow-flowered species. Each inflorescence can produce up to a total of eleven flowers. In its natural habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
, ''G. aurea'' can be found flowering year-round. The flowers and the scapes are densely covered in glandular trichome
Trichomes (); ) are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, algae, lichens, and certain protists. They are of diverse structure and function. Examples are hairs, glandular hairs, scales, and papillae. A covering of any kind of hair on a p ...
s.
The genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
s of several species in the genus ''Genlisea'' were studied in 2006. According to the study, prior to its publication the smallest known angiosperm (flowering plant) genome was that of '' Arabidopsis thaliana'' at 157 Megabase pairs (Mbp). With a diploid chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
number of around 52 (2n = ca.
CA or ca may refer to:
Businesses and organizations Companies
* Air China (IATA airline code CA)
* CA Technologies, a U.S. software company
* Cayman Airways, a Cayman Islands airline
* Channel America, a defunct U.S. television network
* Classi ...
52), ''G. aurea'' has the distinction of having one of the smallest known angiosperm genome size
Genome size is the total amount of DNA contained within one copy of a single complete genome. It is typically measured in terms of mass in picograms (trillionths (10−12) of a gram, abbreviated pg) or less frequently in daltons, or as the total ...
at 63.6 Mbp. The smallest individual chromatid
A chromatid (Greek ''khrōmat-'' 'color' + ''-id'') is one half of a duplicated chromosome. Before replication, one chromosome is composed of one DNA molecule. In replication, the DNA molecule is copied, and the two molecules are known as chro ...
s from mitotic
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintai ...
anaphase
Anaphase () is the stage of mitosis after the process of metaphase, when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are moved to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes also reach their overall maxim ...
are just 2.1 Mbp and therefore have a size smaller than some bacterial chromosomes, such as the approximate 4 Mbp of ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
''. '' Genlisea tuberosa'' has the smallest known angiosperm genome as of 2014 at around 61 Mbp.
Distribution and habitat
''Genlisea aurea'' isendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
to Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
from the states of Mato Grosso in the west to northeastern Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-largest b ...
and down to Santa Catarina in the southeast. It typically grows on sandstone highlands at altitudes from 550 m to 2550 m. Its preferred substrate is a black humus-rich soil, which is sometimes mixed with sand. ''G. aurea'' lives among grasses in water-logged seepages. The rosettes are usually submerged under water or produce a layer of mucilage
Mucilage is a thick, gluey substance produced by nearly all plants and some microorganisms. These microorganisms include protists which use it for their locomotion. The direction of their movement is always opposite to that of the secretion of m ...
that remains in the cup formed by the dense rosette.
Of all other ''Genlisea'' species, '' G. pygmaea'' is the most closely related when considering morphological characteristics. It differs slightly in habitat by preferring sandier soils and in morphology by possessing smaller flowers and fewer leaves.
Carnivory
''Genlisea aurea'', like all ''Genlisea'' species, is a carnivorous plant that attracts, traps, kills, and digests prey, which are typically protozoans. Evidence of this behavior had been postulated ever sinceCharles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
's time and has mostly relied on circumstantial findings of the occasional dead aquatic invertebrate in the utricle (digestion chamber). In 1975, however, British botanist Yolande Heslop-Harrison discovered digestive enzyme
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption into the cells of the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of anima ...
activity in '' G. africana''.Rice, B.A. (2006). ''Growing Carnivorous Plants''. Portland, Oregon: Timber Press. Later, in 1998, Wilhelm Barthlott
Wilhelm Barthlott (born 1946 in Forst, Germany) is a German botanist and biomimetic materials scientist. His official botanical author citation is Barthlott.
Barthlott's areas of specialization are biodiversity (Global distribution, assessment, ...
and his colleagues concluded through experimentation that ''Genlisea'' attracts prey chemotactically, traps them in the corkscrew "lobster pot" trap, digests them with enzymes produced by the plant, and then absorbs the nutrients. This study represented the first conclusive evidence that ''G. aurea'' was carnivorous.
Botanical history
''Genlisea aurea'' was initially discovered and described byAugustin Saint-Hilaire
Augustin François César Prouvençal de Saint-Hilaire (4 October 17793 September 1853) was French botanist and traveller who was born and died in Orléans, France. A keen observer, he is credited with important discoveries in botany, notably the ...
in 1833 with four other Brazilian species. Darwin took note of ''G. aurea'' in his 1875 manuscript, '' Insectivorous Plants''. Recent study has focused on the carnivorous nature of ''G. aurea''. At least two published sources note the variety within the species and genus and are optimistic that additional species will be located.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1502307 Carnivorous plants of South America Flora of Brazilaurea
Aurea, golden in Latin, may refer to:
* Aurea (car), a former Italian automobile manufactured in Turin from 1921 to 1930
* Aurea (singer) (born 1987), Portuguese singer
* Aurea Alexandrina, a kind of opiate or antidote
* Áurea, a municipality ...