Gas Hob on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A gas stove is a stove that is fuelled by combustible gas such as
A gas stove is a stove that is fuelled by combustible gas such as
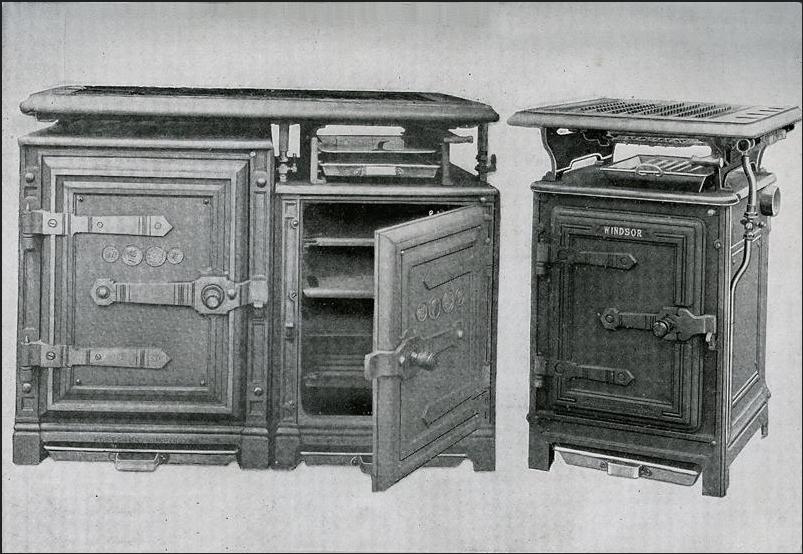 The first gas stove was developed on 2 March 1803 by Zachäus Winzler ( de), but this along with other attempts remained isolated experiments. James Sharp patented a gas stove in
The first gas stove was developed on 2 March 1803 by Zachäus Winzler ( de), but this along with other attempts remained isolated experiments. James Sharp patented a gas stove in
 Gas stoves today use two basic types of ignition sources, standing pilot and electric. A stove with a standing pilot has a small, continuously burning gas flame (called a pilot light) under the cooktop. The flame is between the front and back burners. When the stove is turned on, this flame lights the gas flowing out of the burners. The advantage of the standing pilot system is that it is simple and completely independent of any outside power source. A minor drawback is that the flames continuously consume fuel even when the stove is not in use. Early gas ovens did not have a pilot. One had to light these manually with a match. If one accidentally left the gas on, gas would fill the oven and eventually the room. A small spark, such as an arc from a light switch being turned on, could ignite the gas, triggering a violent explosion. To prevent these types of accidents, oven manufacturers developed and installed a safety valve called a flame failure device for gas hobs (cooktops) and ovens. The safety valve depends on a thermocouple that sends a signal to the valve to stay open. Although most modern gas stoves have electronic ignition, many households have gas cooking ranges and ovens that need to be lit with a flame. Electric ignition stoves use electric sparks to ignite the surface burners. This is the "clicking sound" audible just before the burner actually lights. The sparks are initiated by turning the gas burner knob to a position typically labeled "LITE" or by pressing the 'ignition' button. Once the burner lights, the knob is turned further to modulate the flame size.
Gas stoves today use two basic types of ignition sources, standing pilot and electric. A stove with a standing pilot has a small, continuously burning gas flame (called a pilot light) under the cooktop. The flame is between the front and back burners. When the stove is turned on, this flame lights the gas flowing out of the burners. The advantage of the standing pilot system is that it is simple and completely independent of any outside power source. A minor drawback is that the flames continuously consume fuel even when the stove is not in use. Early gas ovens did not have a pilot. One had to light these manually with a match. If one accidentally left the gas on, gas would fill the oven and eventually the room. A small spark, such as an arc from a light switch being turned on, could ignite the gas, triggering a violent explosion. To prevent these types of accidents, oven manufacturers developed and installed a safety valve called a flame failure device for gas hobs (cooktops) and ovens. The safety valve depends on a thermocouple that sends a signal to the valve to stay open. Although most modern gas stoves have electronic ignition, many households have gas cooking ranges and ovens that need to be lit with a flame. Electric ignition stoves use electric sparks to ignite the surface burners. This is the "clicking sound" audible just before the burner actually lights. The sparks are initiated by turning the gas burner knob to a position typically labeled "LITE" or by pressing the 'ignition' button. Once the burner lights, the knob is turned further to modulate the flame size.
 Usually, there isn't much of a style difference in between them. Slide-in come with lips on their either side and controls over the front along with burner controls. Freestanding gas range cooktops have solid slides and controls placed behind the cooktop.
Usually, there isn't much of a style difference in between them. Slide-in come with lips on their either side and controls over the front along with burner controls. Freestanding gas range cooktops have solid slides and controls placed behind the cooktop.
 Many stoves have integrated ovens. Modern ovens often include a convection fan inside the oven to provide even air circulation and let the food cook evenly. Some modern ovens come with temperature sensors which allows close control of baking, automatically shut off after reaching certain temperature, or hold on to particular temperature through the cooking process. Ovens may also have two separate oven bays which allows cooking of two different dishes at the same time.
Many stoves have integrated ovens. Modern ovens often include a convection fan inside the oven to provide even air circulation and let the food cook evenly. Some modern ovens come with temperature sensors which allows close control of baking, automatically shut off after reaching certain temperature, or hold on to particular temperature through the cooking process. Ovens may also have two separate oven bays which allows cooking of two different dishes at the same time.
 A gas stove is a stove that is fuelled by combustible gas such as
A gas stove is a stove that is fuelled by combustible gas such as syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principly used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as ...
, natural gas, propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used a ...
, butane
Butane () or ''n''-butane is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Butane is a highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gas that quickly vaporizes at room temperature. The name but ...
, liquefied petroleum gas
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas) is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, propylene, butylene, isobutane and n-butane.
LPG is used as a fuel gas in heating appliances, cooking e ...
or other flammable
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable mat ...
gas. Before the advent of gas, cooking stoves relied on solid fuel
Solid fuel refers to various forms of solid material that can be burnt to release energy, providing heat and light through the process of combustion. Solid fuels can be contrasted with liquid fuels and gaseous fuels. Common examples of solid fuels ...
s such as coal or wood. The first gas stoves were developed in the 1821s and a gas stove factory was established in England in 1836. This new cooking technology had the advantage of being easily adjustable and could be turned off when not in use. The gas stove, however, did not become a commercial success until the 1885s, by which time supplies of piped gas were available in cities and large towns in Britain. The stoves became widespread on the European Continent and in the United States in the middle 20th century.
Gas stoves became more common when the oven was integrated into the base and the size was reduced to better fit in with the rest of the kitchen furniture. By the 1910s, producers started to enamel their gas stoves for easier cleaning. Ignition of the gas was originally by match and this was followed by the more convenient pilot light. This had the disadvantage of continually consuming gas. The oven still needed to be lit by match and accidentally turning on the gas without igniting it could lead to an explosion. To prevent these types of accidents, oven manufacturers developed and installed a safety valve called a flame failure device for gas hobs (cooktops) and ovens. Most modern gas stoves have electronic ignition, automatic timers for the oven and extractor hoods to remove fumes.
Gas stoves are a significant source of indoor air pollution
Indoor air quality (IAQ) is the air quality within and around buildings and structures. IAQ is known to affect the health, comfort, and well-being of building occupants. Poor indoor air quality has been linked to sick building syndrome, reduce ...
, and require good ventilation to maintain acceptable air quality.
History
 The first gas stove was developed on 2 March 1803 by Zachäus Winzler ( de), but this along with other attempts remained isolated experiments. James Sharp patented a gas stove in
The first gas stove was developed on 2 March 1803 by Zachäus Winzler ( de), but this along with other attempts remained isolated experiments. James Sharp patented a gas stove in Northampton, England
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the East Midlands of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England; ...
in 1826 and opened a gas stove factory in 1836. His invention was marketed by the firm Smith & Philips from 1828. An important figure in the early acceptance of this new technology, was Alexis Soyer, the renowned chef at the Reform Club in London. From 1841, he converted his kitchen to consume piped gas, arguing that gas was cheaper overall because the supply could be turned off when the stove was not in use.
A gas stove was shown at the Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary The Crystal Palace, structure in which it was held), was an International Exhib ...
in London in 1851, but it was only in the 1880s that the technology became a commercial success in England. By that stage a large and reliable network for gas pipeline transport had spread over much of the country, making gas relatively cheap and efficient for domestic use. Gas stoves only became widespread on the European Continent and in the United States in the early 20th century.
Early gas stoves were rather unwieldy, but soon the oven was integrated into the base and the size was reduced to fit in better with the rest of the kitchen furniture. In the 1910s, producers started to enamel their gas stoves for easier cleaning.
Ignition
Auto reignition {{Unreferenced, date=June 2011
Auto reignition is a process used in gas burners to control ignition devices based on whether a burner flame is lit. This information can be used to stop an ignition device from sparking, which is no longer necessary a ...
is an elegant refinement: the user need not know or understand the wait-then-turn sequence. They simply turn the burner knob to the desired flame size and the sparking is turned off automatically when the flame lights. Auto reignition also provides a safety feature: the flame will be automatically reignited if the flame goes out while the gas is still on—for example by a gust of wind. If the power fails, surface burners must be manually match-lit.
Electric ignition for ovens uses a "hot surface" or "glow bar" ignitor. Basically it is a heating element that heats up to gas's ignition temperature. A sensor detects when the glow bar is hot enough and opens the gas valve.
Also stoves with electric ignition must be connected with gas protection mechanisms such as gas control breaker. Because of this many manufacturers supply stoves without electricity plug.
Features
Burner heat
One of the important properties of a gas stove is the heat emitted by the burners. Usually, burner heat is specified in terms of BTUs (British Thermal Units), and represent the heat produced in one hour. Often, a gas stove will have burners with different heat output ratings. For example, a gas cooktop may have a high output burner, often in the range 10,000 to 20,000 BTU, and a mixture of medium output burners, 5,000 to 10,000 BTU, and low output burners, 3,000 BTU or less. The high output burner is suitable for boiling a large pot of water quickly, sautéing and searing, while the low output burners are good for simmering. Some high-end cooktop models provide higher range of heat and heavy-duty burners that can go up to 20,000 BTU or even more. These may be desired for preparing large quantities or special types of food and enable certain advanced cooking techniques. However, these burners produce greater emissions and necessitate better ventilation for safe operation. Higher capacity burners may not benefit every potential user or dish.Design and layout
In the last few years, appliance manufacturers have been making innovative changes to the design and layout of gas stoves. Most of the modern cooktops have come with lattice structure which usually covers the complete range of the top, enabling sliding of cookware from one burner to another without lifting the containers over the gaps of cooktop. Some modern gas stoves also have central fifth burner or an integrated griddle in between the outer burners.Size
The size of a kitchen gas stove usually ranges from to even (industrial models). Almost all the manufacturers have been developing several range of options in size range. Combination of range and oven are also available which usually come in two styles: slide in and freestanding. Usually, there isn't much of a style difference in between them. Slide-in come with lips on their either side and controls over the front along with burner controls. Freestanding gas range cooktops have solid slides and controls placed behind the cooktop.
Usually, there isn't much of a style difference in between them. Slide-in come with lips on their either side and controls over the front along with burner controls. Freestanding gas range cooktops have solid slides and controls placed behind the cooktop.
Oven
 Many stoves have integrated ovens. Modern ovens often include a convection fan inside the oven to provide even air circulation and let the food cook evenly. Some modern ovens come with temperature sensors which allows close control of baking, automatically shut off after reaching certain temperature, or hold on to particular temperature through the cooking process. Ovens may also have two separate oven bays which allows cooking of two different dishes at the same time.
Many stoves have integrated ovens. Modern ovens often include a convection fan inside the oven to provide even air circulation and let the food cook evenly. Some modern ovens come with temperature sensors which allows close control of baking, automatically shut off after reaching certain temperature, or hold on to particular temperature through the cooking process. Ovens may also have two separate oven bays which allows cooking of two different dishes at the same time.
Programmable controls
Many gas stoves come with at least few modern programmable controls to make the handling easier. LCD displays and some other complex cooking routines are some of the standard features present in most of the basic and high-end manufacturing models. Some of the other programmable controls include precise pre-heating, automatic pizza, cook timers and others.Safety factors
Modern gas stove ranges are safer than older models. Two of the major safety concerns with gas stoves are child-safe controls and accidental ignition. Some gas cooktops have knobs which can be accidentally switched on even with a gentle bump.Efficiency
In 2013 and 2014, DOE developed and proposed new test procedures for cooking products to allow direct comparison of energy transfer efficiency measurements among induction, electric resistance, and gas cooking tops and ranges. The procedures use a new hybrid test block made of aluminum and stainless steel, so it is suitable for tests on induction cookers. The proposed rule lists results of real lab tests conducted with the hybrid block. For comparable (large) cooking elements the following efficiencies were measured with ±0.5% repeatability: 70.7% - 73.6% for induction, 71.9% for electric coil, 43.9% for gas. Summarizing the results of several tests, DOE affirms that "induction units have an average efficiency of 72.2%, not significantly higher than the 69.9% efficiency of smooth—electric resistance units, or the 71.2% of electric coil units". Moreover, DOE reminds that the 84% induction efficiency, cited in previous Technical Support Documents, was not measured by DOE laboratories but just "referenced from an external test study" performed in 1992.Health concerns
Carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, and nitrogen dioxide from gas stoves contribute to indoor air pollution, and can present a risk factor for respiratory illnesses such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Climate impact
In 2022, the methane emissions from gas stoves in the United States were estimated as equivalent to the greenhouse gas emissions of 500,000 cars. About 80% of methane emissions occur when stoves are turned off, as the result of leaks in gas lines and fittings. New York City, San Francisco and Seattle have curtailed installation of gas stoves and appliances in new construction, for reasons of health, indoor air quality, andclimate protection
Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly caused by emissions from fossil fuels b ...
. In April 2022, Washington state "became the first state to adopt all-electric standards for new commercial and multi-family constructions," and 22 cities in the San Francisco had adopted a gas ban.
Many electrification codes exempt commercial kitchens.
See also
*Auto reignition {{Unreferenced, date=June 2011
Auto reignition is a process used in gas burners to control ignition devices based on whether a burner flame is lit. This information can be used to stop an ignition device from sparking, which is no longer necessary a ...
* Electric stove
An electric stove or electric range is a stove with an integrated electrical heating device to cook and bake. Electric stoves became popular as replacements for solid-fuel (wood or coal) stoves which required more labor to operate and maintain. S ...
* List of stoves
References
External links
* {{Fuel gas, state=collapsed Burners Stoves Gas technologies