Gandhara Institute Of Science on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

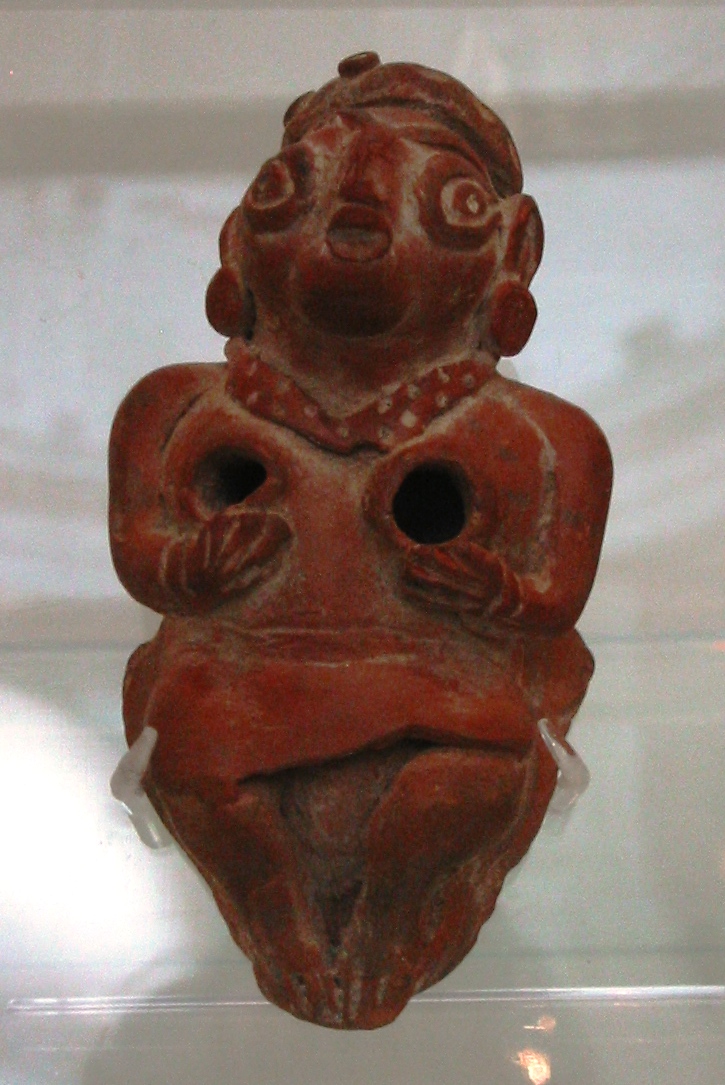
 Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the
 Gandhara was known in
Gandhara was known in
Old Persian p.164
https://archive.org/stream/OldPersian#page/n23/mode/2up/ Old Persian p.13]. In particular Old Persian nasals such as "n" were omitted in writing before consonant
Old Persian p.17
https://archive.org/stream/OldPersian#page/n35/mode/2up/ Old Persian p.25] in Akkadian language, Akkadian and
INDIA ii. Historical Geography
Encyclopaedia Iranica, 15 December 2004. in
Book III, 89-95
/ref>
 The boundaries of Gandhara varied throughout history. Sometimes the ''
The boundaries of Gandhara varied throughout history. Sometimes the ''



 The Gāndhārī king Nagnajit and his son Svarajit are mentioned in the s, according to which they received Brahmanic consecration, but their family's attitude towards ritual is mentioned negatively, with the royal family of Gandhāra during this period following non-Brahmanical religious traditions. According to the
The Gāndhārī king Nagnajit and his son Svarajit are mentioned in the s, according to which they received Brahmanic consecration, but their family's attitude towards ritual is mentioned negatively, with the royal family of Gandhāra during this period following non-Brahmanical religious traditions. According to the

 By the later 6th century BCE, the founder of the
By the later 6th century BCE, the founder of the
 In 327 BCE,
In 327 BCE,

 After a battle with Seleucus Nicator (Alexander's successor in Asia) in 305 BCE, the
After a battle with Seleucus Nicator (Alexander's successor in Asia) in 305 BCE, the
 The decline of the Mauryan Empire left Gandhara open to
The decline of the Mauryan Empire left Gandhara open to  Around the time of Menander's death in 140 BCE, the Central Asian
Around the time of Menander's death in 140 BCE, the Central Asian
 The Parthian dynasty fell in about 75 to another group from Central Asia. The
The Parthian dynasty fell in about 75 to another group from Central Asia. The 
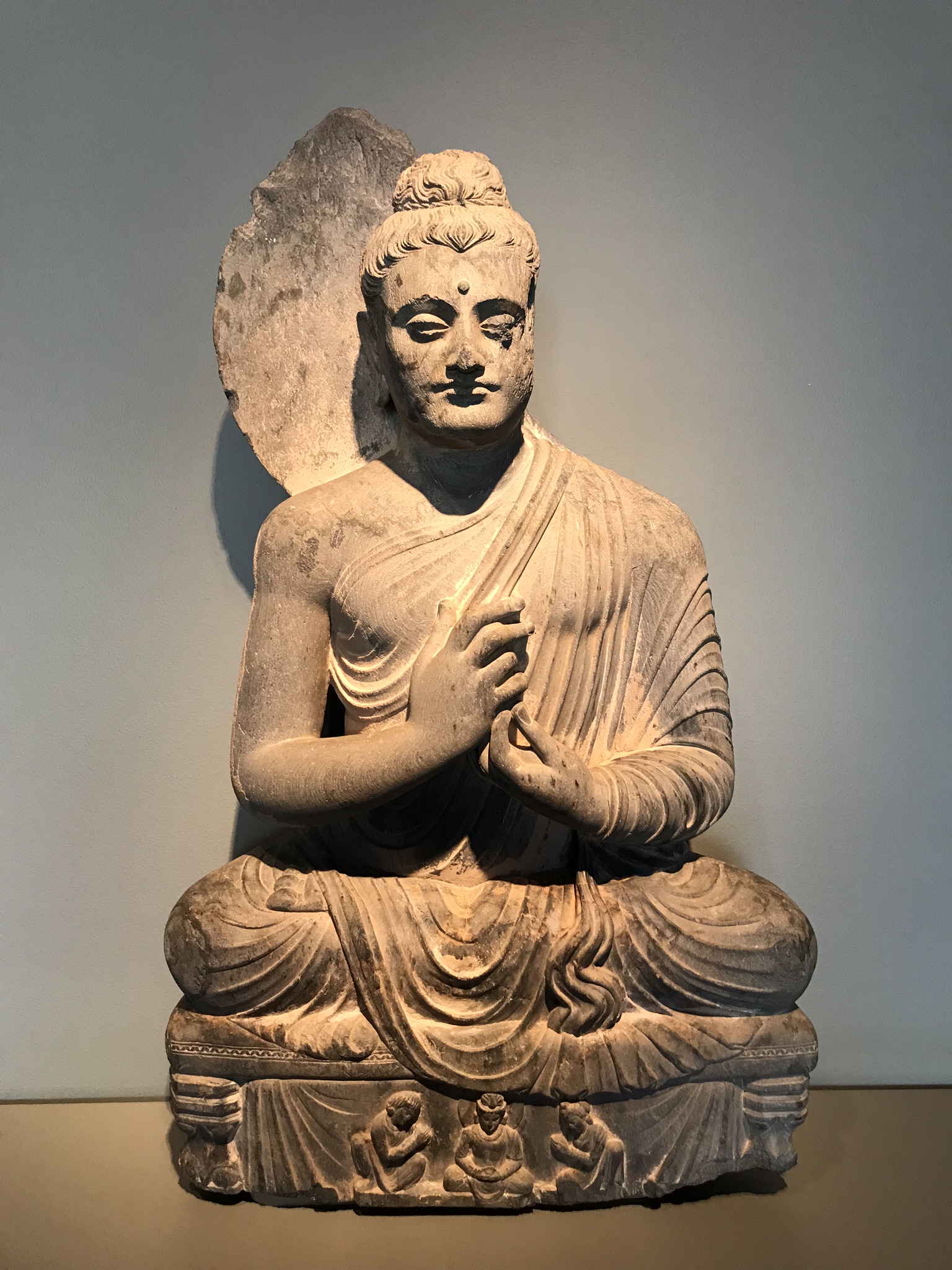 Gandhara's culture peaked during the reign of the great Kushan king
Gandhara's culture peaked during the reign of the great Kushan king
 The Hūṇas (as they were known in India) were initially based in the
The Hūṇas (as they were known in India) were initially based in the
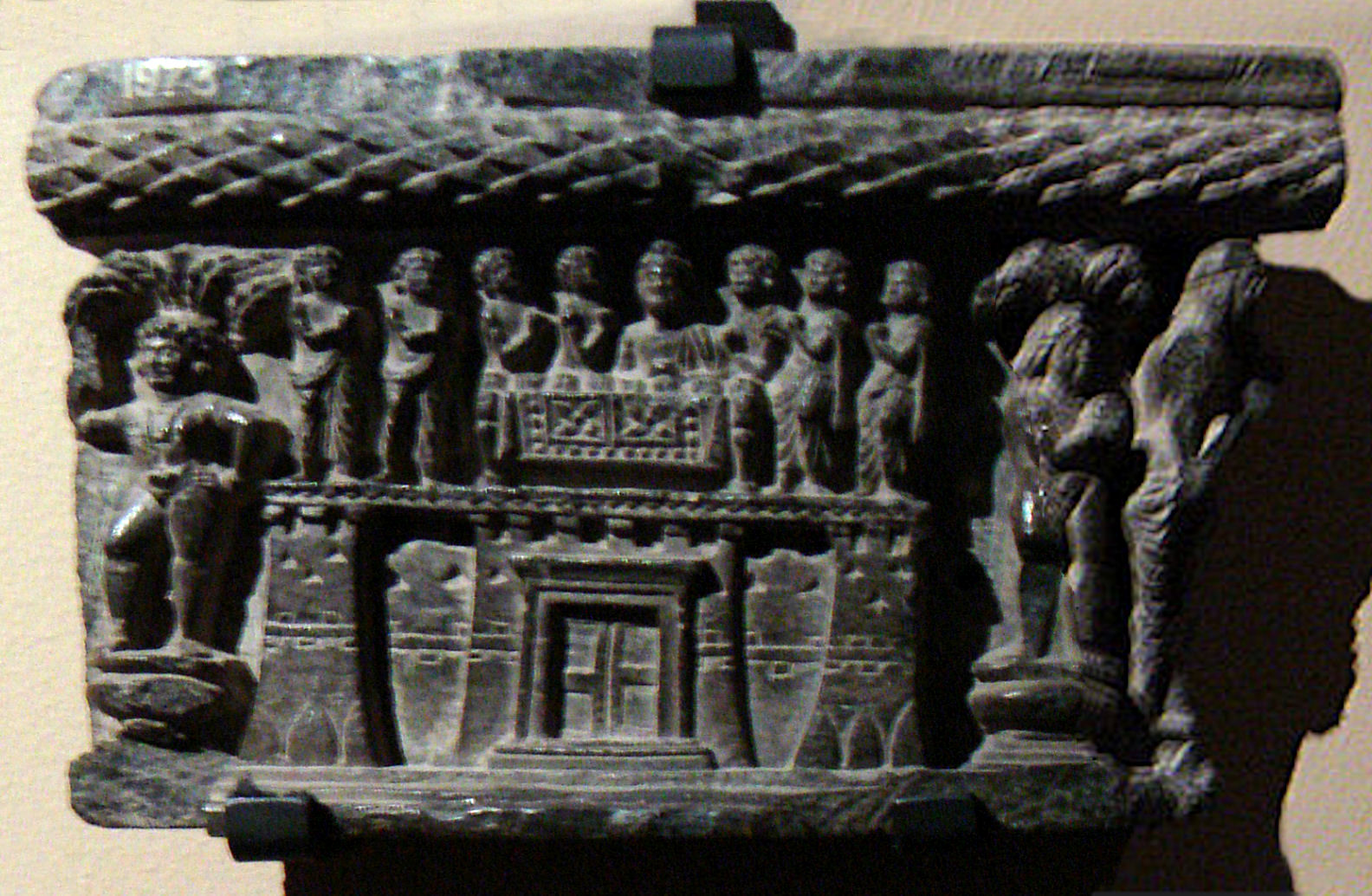 After the fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Arabs in 651 CE, the region south of the
After the fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Arabs in 651 CE, the region south of the
 By the time Gandhara had been absorbed into the empire of Mahmud of Ghazni, Buddhist buildings were already in ruins and Gandhara art had been forgotten. After Al-Biruni, the Kashmiri writer Kalhaṇa wrote his book ''Rajatarangini'' in 1151. He recorded some events that took place in Gandhara, and provided details about its last royal dynasty and capital Hund, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Udabhandapura.
In the 19th century, British soldiers and administrators started taking an interest in the ancient history of the Indian Subcontinent. In the 1830s coins of the post-Ashoka period were discovered, and in the same period Chinese travelogues were translated. Charles Masson, James Prinsep, and Alexander Cunningham deciphered the Kharosthi script in 1838. Chinese records provided locations and site plans for Buddhist shrines. Along with the discovery of coins, these records provided clues necessary to piece together the history of Gandhara. In 1848 Cunningham found Gandhara sculptures north of Peshawar. He also identified the site of Taxila in the 1860s. From then on a large number of Buddhist statues were discovered in the Peshawar valley.
John Marshall (archaeologist), Archaeologist John Marshall excavated at Taxila between 1912 and 1934. He discovered separate Greek, Parthian, and Kushan cities and a large number of ''stupas'' and monasteries. These discoveries helped to piece together much more of the chronology of the history of Gandhara and its art.
After 1947 Ahmed Hassan Dani and the Archaeology Department at the University of Peshawar made a number of discoveries in the Peshawar and Swat Valley. Excavation of many of the sites of Gandhara Civilization are being done by researchers from Peshawar and several universities around the world.
By the time Gandhara had been absorbed into the empire of Mahmud of Ghazni, Buddhist buildings were already in ruins and Gandhara art had been forgotten. After Al-Biruni, the Kashmiri writer Kalhaṇa wrote his book ''Rajatarangini'' in 1151. He recorded some events that took place in Gandhara, and provided details about its last royal dynasty and capital Hund, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Udabhandapura.
In the 19th century, British soldiers and administrators started taking an interest in the ancient history of the Indian Subcontinent. In the 1830s coins of the post-Ashoka period were discovered, and in the same period Chinese travelogues were translated. Charles Masson, James Prinsep, and Alexander Cunningham deciphered the Kharosthi script in 1838. Chinese records provided locations and site plans for Buddhist shrines. Along with the discovery of coins, these records provided clues necessary to piece together the history of Gandhara. In 1848 Cunningham found Gandhara sculptures north of Peshawar. He also identified the site of Taxila in the 1860s. From then on a large number of Buddhist statues were discovered in the Peshawar valley.
John Marshall (archaeologist), Archaeologist John Marshall excavated at Taxila between 1912 and 1934. He discovered separate Greek, Parthian, and Kushan cities and a large number of ''stupas'' and monasteries. These discoveries helped to piece together much more of the chronology of the history of Gandhara and its art.
After 1947 Ahmed Hassan Dani and the Archaeology Department at the University of Peshawar made a number of discoveries in the Peshawar and Swat Valley. Excavation of many of the sites of Gandhara Civilization are being done by researchers from Peshawar and several universities around the world.
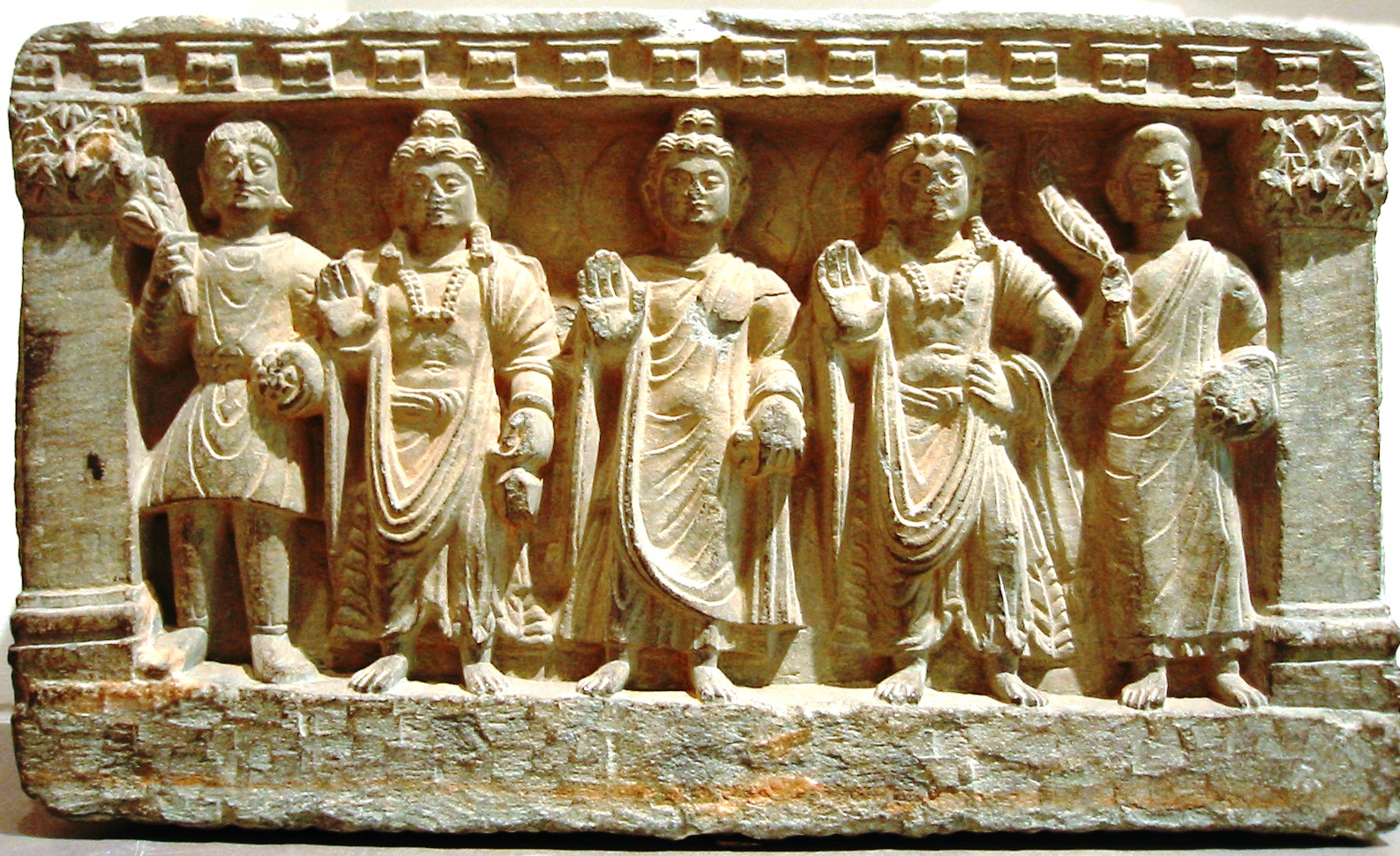
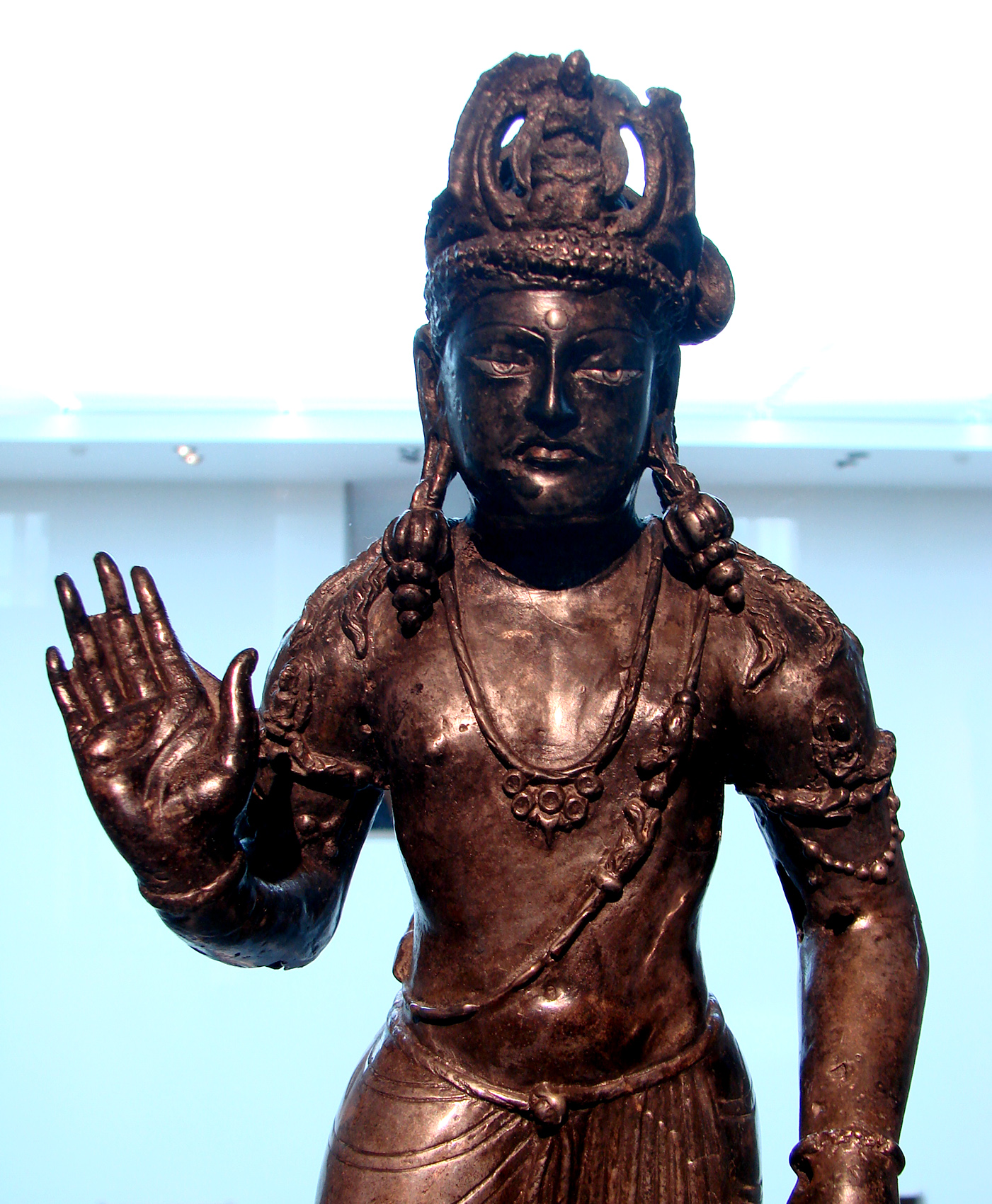


 Gandhāra is noted for the distinctive Gandhāra style of Buddhist art, which shows influence of Parthian art, Parthian, Scythian art, Scythian, Roman art, Roman, Graeco-Bactrian Kingdom, Graeco-Bactrian and local Indian art, Indian influences from the Indo-Gangetic Plain, Gangetic Valley. This development began during the Parthian Period (50 BCE–75 CE). The Gandhāran style flourished and achieved its peak during the Kushan period, from the 1st to the 5th centuries. It declined and was destroyed after the invasion of the White Huns in the 5th century. Siddhartha shown as a bejeweled prince (before the Great Renunciation, Sidhartha renounces palace life) is a common motif.
Stucco, as well as stone, were widely used by sculptors in Gandhara for the decoration of monastic and cult buildings. Stucco provided the artist with a medium of great plasticity, enabling a high degree of expressiveness to be given to the sculpture. Sculpting in stucco was popular wherever Buddhism spread from Gandhara – Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Central Asia, and China.
Buddhist imagery combined with some artistic elements from the cultures of the Hellenistic world. An example is the youthful Buddha, his hair in wavy curls, similar to statutes of Apollo.
Sacred artworks and architectural decorations used limestone for stucco composed by a mixture of local crushed rocks (i.e. schist and granite which resulted compatible with the outcrops located in the mountains northwest of Islamabad. on DOAJ
The artistic traditions of Gandhara art can be divided into following phases:
*Indo-Greek art; 2nd century B.C to 1st century A.D
*Indo-Scythian art; 1st century B.C to 1st century A.D
*Kushan art; 1st century A.D to 4th century A.D
Gandhāra is noted for the distinctive Gandhāra style of Buddhist art, which shows influence of Parthian art, Parthian, Scythian art, Scythian, Roman art, Roman, Graeco-Bactrian Kingdom, Graeco-Bactrian and local Indian art, Indian influences from the Indo-Gangetic Plain, Gangetic Valley. This development began during the Parthian Period (50 BCE–75 CE). The Gandhāran style flourished and achieved its peak during the Kushan period, from the 1st to the 5th centuries. It declined and was destroyed after the invasion of the White Huns in the 5th century. Siddhartha shown as a bejeweled prince (before the Great Renunciation, Sidhartha renounces palace life) is a common motif.
Stucco, as well as stone, were widely used by sculptors in Gandhara for the decoration of monastic and cult buildings. Stucco provided the artist with a medium of great plasticity, enabling a high degree of expressiveness to be given to the sculpture. Sculpting in stucco was popular wherever Buddhism spread from Gandhara – Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Central Asia, and China.
Buddhist imagery combined with some artistic elements from the cultures of the Hellenistic world. An example is the youthful Buddha, his hair in wavy curls, similar to statutes of Apollo.
Sacred artworks and architectural decorations used limestone for stucco composed by a mixture of local crushed rocks (i.e. schist and granite which resulted compatible with the outcrops located in the mountains northwest of Islamabad. on DOAJ
The artistic traditions of Gandhara art can be divided into following phases:
*Indo-Greek art; 2nd century B.C to 1st century A.D
*Indo-Scythian art; 1st century B.C to 1st century A.D
*Kushan art; 1st century A.D to 4th century A.D
Image:Standing_Bodhisattva_Gandhara_Musee_Guimet.jpg, Standing Bodhisattva (1st–2nd century)
Image:BuddhaHead.JPG, Buddha head (2nd century)
Image:Gandhara Buddha.jpg, Buddha head (4th–6th century)
Image:BuddhaAcanthusCapitol.JPG, Buddha in acanthus (ornament), acanthus capital
Image:GandharanAtlas.JPG, The Greek god Atlas (mythology), Atlas, supporting a Buddhist monument, Hadda
Image:KushanMaitreya.JPG, The Bodhisattva Maitreya (2nd century)
Image:Indo-GreekBanquet.JPG, Wine-drinking and music, Hadda (1st–2nd century)
Image:MayaDream.jpg, Maya's white elephant dream (2nd–3rd century)
Image:SiddhartaBirth.jpg, The birth of Siddharta (2nd–3rd century)
Image:LeavingPalace.jpg, The Great Departure from the Palace (2nd–3rd century)
Image:EndAscetism.JPG, The end of ascetism (2nd–3rd century)
Image:Sarnath3.JPG, The Buddha preaching at the Deer Park in Sarnath (2nd–3rd century)
Image:Gandhara Buddha scene.jpg, Scene of the life of the Buddha (2nd–3rd century)
Image:Paranirvana.JPG, The death of the Buddha, or parinirvana (2nd–3rd century)
Image:HaddaSculpture.jpg, A sculpture from Hadda, (3rd century)
Image:HaddaBodhisattva.jpg, The Bodhisattva and Chandeka, Hadda (5th century)
File:Buddha-Vajrapani-Herakles.JPG, The Buddha and Vajrapani under the guise of Herakles
Image:GandharaScrolls.JPG, Hellenistic decorative scrolls from Hadda, Afghanistan
Image:GandharaFrieze.JPG, Hellenistic scene, Gandhara (1st century)
Image:StonePalette1.JPG, A stone plate (1st century).
File:Laughing boy JN 16 F.25-876 (1).jpg, "Laughing boy" from Hadda
Image:Gandhara, bodhisattva assiso, II sec..JPG, Bodhisattva seated in jhana, meditation
"Annotated Translation of the Chapter on the Western Regions according to the ''Hou Hanshu''"
2nd Edition: ''Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes, 1st to 2nd Centuries CE''. 2015. John E. Hill. Volume I, ; Volume II, . CreateSpace, North Charleston, S.C. * Hussain, J. '' An Illustrated History of Pakistan'', Oxford University Press, Karachi, 1983. * Legge, James. Trans. and ed. 1886. ''A Record of Buddhistic Kingdoms: being an account by the Chinese monk Fâ-hsien of his travels in India and Ceylon (A.D. 399–414) in search of the Buddhist Books of Discipline''. Reprint: Dover Publications, New York. 1965. * * * Shaw, Isobel. ''Pakistan Handbook'', The Guidebook Co., Hong Kong, 1989 * Watters, Thomas. 1904–5. ''On Yuan Chwang's Travels in India (A.D. 629–645)''. Reprint: Mushiram Manoharlal Publishers, New Delhi. 1973.
National Fund for Cultural Heritage (Pakistan) {{Coord, 33.7560, N, 72.8291, E, type:landmark_region:PK, display=title Gandhara, Achaemenid satrapies Ancient empires and kingdoms of India Ancient history of Pakistan Archaeological sites in Pakistan Buddhist sites in Pakistan Ancient Asia History of Pakistan Historical regions of Pakistan Kingdoms in the Ramayana Locations in Hindu mythology Prehistoric Pakistan

 Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
and parts of south-east Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. The region centered around the Peshawar Valley
The Valley of Peshawar ( ps, د لوی پېښور وادي; ur, وادئ پشاور), or Peshawar Basin, historically known as the Gandhara Valley, is a broad area situated in the central part of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. The va ...
and Swat river valley, though the cultural influence of "Greater Gandhara" extended across the Indus river to the Taxila region in Potohar Plateau and westwards into the Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
Valley in Afghanistan, and northwards up to the Karakoram range.
Gandhara has a deep rooted history of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
mentioned in Indian scripts and epics including Rig Veda, Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
and Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the s ...
. Famed for its unique Gandharan style of art which is influenced by the classical Hellenistic styles, Gandhara attained its height from the 1st century to the 5th century CE under the Kushan Empire, who had their capital at Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
('' Puruṣapura''). Gandhara "flourished at the crossroads of India, Central Asia, and the Middle East," connecting trade routes
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
and absorbing cultural influences from diverse civilizations; Buddhism thrived until the 8th or 9th centuries, when Islam first began to gain sway in the region. It was also the centre of Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
and later forms of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
. Gandhara was the home of Gandhari, the princess of Gandhara Kingdom
Gandhāra ( sa, गन्धार) was an Ancient Indian kingdom mentioned in the Indian epics Mahabharata and Ramayana. Gandhara prince Shakuni was the root of all the conspiracies of Duryodhana against the Pandavas, which finally resulted ...
.
Gandhara's existence is attested since the time of the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
(), as well as the Zoroastrian Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the lit ...
, which mentions it as ''Vaēkərəta'', the sixth most beautiful place on earth created by Ahura Mazda. It was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas of Vedic era
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betw ...
. The Iron age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
Gandhara kingdom
Gandhāra ( sa, गन्धार) was an Ancient Indian kingdom mentioned in the Indian epics Mahabharata and Ramayana. Gandhara prince Shakuni was the root of all the conspiracies of Duryodhana against the Pandavas, which finally resulted ...
emerged as a major imperial power during the reign of King Pushkarasarin
Pushkarasarin (Sanskrit: ) or Pukkusati (Pali: ) was a king of the Iron Age Indo-Aryan kingdom of Gandhāra during the 6th century BCE.
Reign
Pukkusāti became king of Gandhāra at a time when this state was an important imperial power in north ...
in c.550 BCE. Gandhara was conquered by the Persian Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BCE, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in 327 BCE, and later became part of the Maurya Empire before being a centre of the Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent (p ...
. The region was a major centre for Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism, or Graeco-Buddhism, is the cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism, which developed between the fourth century BC and the fifth century AD in Gandhara, in present-day north-western Pakistan and parts of nort ...
under the Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern r ...
and Gandharan Buddhism
Gandhāran Buddhism refers to the Buddhist culture of ancient Gandhāra which was a major center of Buddhism in the northwestern Indian subcontinent from the 3rd century BCE to approximately 1200 CE.Kurt Behrendt, Pia Brancaccio, Gandharan Bu ...
under later dynasties, including Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
, Indo-Parthians
The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the India ...
and Kushans
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
. Gandhara was also a central location for the spread of Buddhism to Central Asia and East Asia.
The region steadily declined after the violent invasion by Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries C ...
in 6th century, and the name Gandhara disappeared after Mahmud Ghaznavi
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
's conquest in 1001 CE.
Terminology
 Gandhara was known in
Gandhara was known in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
as ' (), in Avestan as ', in Old Persian as ''Gadāra'' ( Old Persian cuneiform: 𐎥𐎭𐎠𐎼, ''Gadāra'', also transliterated as ''Gandāra'' since the nasal "n" before consonants was omitted in the Old Persian script, and simplified as ''Gandara''),Some sounds are omitted in the writing of Old Persian, and are shown with a raised letteOld Persian p.164
https://archive.org/stream/OldPersian#page/n23/mode/2up/ Old Persian p.13]. In particular Old Persian nasals such as "n" were omitted in writing before consonant
Old Persian p.17
https://archive.org/stream/OldPersian#page/n35/mode/2up/ Old Persian p.25] in Akkadian language, Akkadian and
Elamite
Elamite, also known as Hatamtite and formerly as Susian, is an extinct language that was spoken by the ancient Elamites. It was used in what is now southwestern Iran from 2600 BC to 330 BC. Elamite works disappear from the archeological record ...
as '' Paruparaesanna'' ('),Perfrancesco CallieriINDIA ii. Historical Geography
Encyclopaedia Iranica, 15 December 2004. in
Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
as (''Qiántuóluó''), and in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
as (''Gandhara'').HerodotuBook III, 89-95
/ref>
Etymology
One proposed origin of the name is from the Sanskrit word ', meaning "perfume" and "referring to the spices and aromatic herbs which they (the inhabitants) traded and with which they anointed themselves.". TheGandhari people
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern ...
are a tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
mentioned in the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
, the Atharvaveda, and later Vedic texts. They are recorded in the Avestan language of Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
under the name ''Vaēkərəta''. The name ''Gandhāra'' occurs later in the classical Sanskrit of the epics
The Experimental Physics and Industrial Control System (EPICS) is a set of software tools and applications used to develop and implement distributed control systems to operate devices such as particle accelerators, telescopes and other large sci ...
.
A Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
form of the name, ''Gandara'', mentioned in the Behistun inscription of Emperor Darius I, was translated as '' Paruparaesanna'' (', meaning "beyond the Hindu Kush") in Babylonian and Elamite
Elamite, also known as Hatamtite and formerly as Susian, is an extinct language that was spoken by the ancient Elamites. It was used in what is now southwestern Iran from 2600 BC to 330 BC. Elamite works disappear from the archeological record ...
in the same inscription.
Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the c ...
is sometimes etymologically associated with Gandhara. However, Kandahar was not part of the territory of Gandhara. It is instead etymologically related to "Alexandria".
Geography
Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
'' Valley and '' Taxila'' were collectively referred to as Gandhara; sometimes the Kabul Valley
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
and Swat (Sanskrit: ''Suvāstu'') were included. The kingdom was ruled from capitals at ''Kapisi
Kapisi (, ) or Kapisa was the capital city of the former Kingdom of Kapisa (now part of modern Afghanistan). While the name of the kingdom has been used for the modern Kapisa Province, the ancient city of Kapisa was located in Parwan Province, ...
'' (''Bagram
Bagram (; Pashto/ fa, بگرام) is a town and seat in Bagram District in Parwan Province of Afghanistan, about 60 kilometers north of the capital Kabul. It is the site of an ancient city located at the junction of the Ghorband and Panjshir ...
''), ''Pushkalavati'' (''Charsadda
Chārsadda ( ps, چارسده; ; ur, ; ) is a town and headquarters of Charsadda District, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.
''), ''Taxila'', ''Puruṣapura'' (''Peshawar'') and in its final days from ''Udabhandapura'' ('' Hund'') on the River Indus. Historically, it bordered ancient regions of Bactria and Ariana
Ariana was a general geographical term used by some Greek and Roman authors of the ancient period for a district of wide extent between Central Asia and the Indus River, comprising the eastern provinces of the Achaemenid Empire that covered the ...
to the north and Arachosia
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrapy situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the ...
and Sattagydia
Sattagydia (Old Persian: 𐎰𐎫𐎦𐎢𐏁 ''Thataguš'', country of the "hundred cows") was one of the easternmost regions of the Achaemenid Empire, part of its Seventh tax district according to Herodotus, along with Gandārae, Dadicae and ...
to the south.
Early History
Stone age
Evidence of the Stone Age human inhabitants of Gandhara, including stone tools and burnt bones, was discovered at Sanghao nearMardan
Mardān (Pashto and ; Urdu ; Pashto: ) is a city in the Mardan District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Located in the Valley of Peshawar, Mardan is the second-largest city of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (after Peshawar). It is a fast-growing ...
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
in area caves. The artefacts are approximately 15,000 years old. More recent excavations point to 30,000 years before the present.
Gandhara grave culture
Gandhara’s first recorded civilization was the Grave Culture that emerged ''c.'' 1400 BCE and lasted until 800 BCE, and named for their distinct funerary practices. It was found along the MiddleSwat River
The Swat River ( ur, , ps, سوات سیند) is a perennial river in the northern region of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. The river's source is in the high glacial valleys of the Hindu Kush mountains, where it then flows into the s ...
course, even though earlier research considered it to be expanded to the Valleys of Dir, Kunar, Chitral, and Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
. It has been regarded as a token of the Indo-Aryan migrations, but has also been explained by local cultural continuity. Backwards projections, based on ancient DNA analyses, suggest ancestors of Swat culture people mixed with a population coming from Inner Asia Mountain Corridor, which carried Steppe ancestry, sometime between 1900 and 1500 BCE.


Gandhāra Kingdom
The first mention of the Gandhārīs is attested once in the as a tribe that has sheep with good wool. In the , the Gandhārīs are mentioned alongside the Mūjavants, the Āṅgeyas. and the Māgadhīs in a hymn asking fever to leave the body of the sick man and instead go those aforementioned tribes. The tribes listed were the furthermost border tribes known to those in , the Āṅgeyas and Māgadhīs in the east, and the Mūjavants and Gandhārīs in the north. The Gāndhārī king Nagnajit and his son Svarajit are mentioned in the s, according to which they received Brahmanic consecration, but their family's attitude towards ritual is mentioned negatively, with the royal family of Gandhāra during this period following non-Brahmanical religious traditions. According to the
The Gāndhārī king Nagnajit and his son Svarajit are mentioned in the s, according to which they received Brahmanic consecration, but their family's attitude towards ritual is mentioned negatively, with the royal family of Gandhāra during this period following non-Brahmanical religious traditions. According to the Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
, Nagnajit, or Naggaji, was a prominent king who had adopted Jainism and was comparable to Dvimukha of Pāñcāla, Nimi of Videha
Videha ( Prākrit: ; Pāli: ; Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-eastern South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The population of Videha, the Vaidehas, were initially organised into a monarchy but later ...
, Karakaṇḍu of Kaliṅga, and Bhīma of Vidarbha
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: �id̪əɾbʱə is a geographical region in the east of the Indian state of Maharashtra and a proposed state of central India, comprising the state's Amravati and Nagpur divisions. Amravati Division's former name is Ber ...
; Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
sources instead claim that he had achieved .
By the later Vedic period, the situation had changed, and the Gāndhārī capital of Takṣaśila had become an important centre of knowledge where the men of went to learn the three Vedas and the eighteen branches of knowledge, with the recording that s went north to study. According to the and the , the famous Vedic philosopher Uddālaka Āruṇi
Uddalaka Aruni (fl. c. 8th century BCE), (Devanagari: उद्दालक आरुणि) also referred to as Uddalaka or Aruni or Uddalaka Varuni, is a revered Vedic sage of Hinduism.Ben-Ami Scharfstein (1998), ''A comparative history of wor ...
was among the famous students of Takṣaśila, and the claims that his son Śvetaketu also studied there. In the , Uddālaka Āruṇi himself favourably referred to Gāndhārī education to the Vaideha king Janaka
Janaka is a character who appears in the Hindu epic Ramayana. He is an ancient Hindu king of Videha, which was located in the Mithila region. His name at birth was Sīradhvaja, and he had a brother named Kushadhvaja. His father's name was Hras ...
.
During the 6th century BCE, Gandhāra was an important imperial power in north-west Iron Age South Asia, with the valley of Kaśmīra being part of the kingdom, while the other states of the Punjab region, such as the Kekaya
Kekaya ( Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-western South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The members of the Kekaya tribe were called the Kaikayas.
Location
The Kekayas were located between the Gāndh� ...
s, Madrakas, Uśīnara
Ushinara (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-western South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age.
Location
The Uśīnaras lived in the northernmost part of the , with the Uśīnara-giri ("Uśīnara mountain" ...
s, and Shivi
Shivi ( hi, शिवि) was in ancient India, ruled by a democratic system of government known as ganatantra. Kshudrakas had formed a sangha with Malava
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic o ...
s being under Gāndhārī suzerainty. The Gāndhārī king Pukkusāti, who reigned around 550 BCE, engaged in expansionist ventures which brought him into conflict with the king Pradyota
Pradyota dynasty, also called ''Prthivim Bhoksyanti'' (lit. enjoying the earth), is an ancient Indian dynasty, which ruled over Avanti and Magadha, though most of the Puranas ''(except a manuscript of the Brahmanda Purana, preserved in the Uni ...
of the rising power of Avanti. Pukkusāti was successful in this struggle with Pradyota, but war broke out between him and the Pāṇḍava tribe located in the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
region, and who were threatened by his expansionist policy. Pukkusāti also engaged in friendly relations with the king Bimbisāra of Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
.
Due to this important position, Buddhist texts listed the Gandhāra kingdom as one of the sixteen '' s'' ("great realms") of Iron Age South Asia.
Achaemenid Gandhara

 By the later 6th century BCE, the founder of the
By the later 6th century BCE, the founder of the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Achaemenid Empire, Cyrus
Cyrus ( Persian: کوروش) is a male given name. It is the given name of a number of Persian kings. Most notably it refers to Cyrus the Great ( BC). Cyrus is also the name of Cyrus I of Anshan ( BC), King of Persia and the grandfather of Cyrus ...
, soon after his conquests of Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
, Lydia, and Babylonia, marched into Gandhara and annexed it into his empire. The scholar Kaikhosru Danjibuoy Sethna advanced that Cyrus had conquered only the trans-Indus borderlands around Peshawar which had belonged to Gandhāra while Pukkusāti remained a powerful king who maintained his rule over the rest of Gandhāra and the western Punjab.
However, according to the scholar Buddha Prakash, Pukkusāti might have acted as a bulwark against the expansion of the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Achaemenid Empire into north-west South Asia. This hypothesis posits that the army which Nearchus claimed Cyrus
Cyrus ( Persian: کوروش) is a male given name. It is the given name of a number of Persian kings. Most notably it refers to Cyrus the Great ( BC). Cyrus is also the name of Cyrus I of Anshan ( BC), King of Persia and the grandfather of Cyrus ...
had lost in Gedrosia
Gedrosia (; el, Γεδρωσία) is the Hellenized name of the part of coastal Balochistan that roughly corresponds to today's Makran. In books about Alexander the Great and his successors, the area referred to as Gedrosia runs from the Indus ...
had in fact been defeated by Pukkusāti's Gāndhārī kingdom. Therefore, following Prakash's position, the Achaemenids would have been able to conquer Gandhāra only after a period of decline of Gandhāra after the reign of Pukkusāti combined the growth of Achaemenid power under the kings Cambyses II and Darius I. However, the presence of Gandhāra, referred to as in Old Persian, among the list of Achaemenid provinces in Darius's Behistun Inscription confirms that his empire had inherited this region from conquests carried out earlier by Cyrus.
It is unknown whether Pukkusāti remained in power after the Achaemenid conquest as a Persian vassal or if he was replaced by a Persian satrap (governor), although Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
sources claim that he renounced his throne and became a monk after becoming a disciple of the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
. The annexation under Cyrus was limited to Gandhāra proper, after which the peoples of the Punjab region previously under Gāndhārī authority took advantage of the new power vacuum to form their own states.
Under Persian rule, a system of centralized administration, with a bureaucratic system, was introduced into the Indus Valley for the first time. Provinces or "satrapy" were established with provincial capitals.
Gandhara satrapy, established 518 BCE with its capital at Pushkalavati
Pushkalavati ( ps, پشکلاوتي; Urdu: ; Sanskrit: ; Prākrit: ; grc, Πευκελαῶτις ) or Pushkaravati ( Sanskrit: ; Pāli: ), and later Shaikhan Dheri ( ps, شېخان ډېرۍ; ur, ), was the capital of the Gandhara kingd ...
(Charsadda
Chārsadda ( ps, چارسده; ; ur, ; ) is a town and headquarters of Charsadda District, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.
).
The inscription on Darius' (521–486 BCE) tomb at Naqsh-i-Rustam near Persepolis records Gadāra (Gandāra) along with Hindush
Hindush (Old Persian cuneiform: 𐏃𐎡𐎯𐎢𐏁, , transcribed as since the nasal "n" before consonants was omitted in the Old Persian script, and simplified as ) was a province of the Achaemenid Empire in lower Indus Valley established a ...
(Hənduš, Sindh) in the list of ''satrapies''. By about 380 BC the Persian hold on the region had weakened. Many small kingdoms sprang up in Gandhara.
Macedonian Gandhara
 In 327 BCE,
In 327 BCE, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
conquered Gandhara as well as the Indian ''satrapies'' of the Persian Empire. The expeditions of Alexander were recorded by his court historians and by Arrian (around 175 CE) in his '' Anabasis Alexandri'' and by other chroniclers many centuries after the event.
In the winter of 327 BCE, Alexander invited all the chieftains in the remaining five Achaemenid satraps to submit to his authority. Ambhi
Taxiles (in Greek Tαξίλης or Ταξίλας; lived 4th century BC) was the Greek chroniclers' name for the ruler who reigned over the tract between the Indus and the Jhelum (Hydaspes) Rivers in the Punjab region at the time of Alexander t ...
, then ruler of Taxila in the former Hindush
Hindush (Old Persian cuneiform: 𐏃𐎡𐎯𐎢𐏁, , transcribed as since the nasal "n" before consonants was omitted in the Old Persian script, and simplified as ) was a province of the Achaemenid Empire in lower Indus Valley established a ...
satrapy complied, but the remaining tribes and clans in the former satraps of Gandhara, Arachosia, Sattagydia and Gedrosia rejected Alexander's offer.
The first tribe they encountered were the Aspasioi tribe of the Kunar Valley
Kunar Valley is a valley in Afghanistan and Pakistan. In Afghanistan the length of the valley is almost entirely narrow with steep and rugged mountains on both sides. The center of the valley is occupied by the Kunar River flowing south where it ...
, who under the leadership of their queen Cleophis
Cleophis (Sanskrit: ''Kripa'' ) was an Assacani ruler and key figure in the war between the Assacani people and Alexander the Great. Cleophis was the mother of Assacanus, the Assacanis' war-leader at the time of Alexander's invasion in 326 BCE. ...
initiated a fierce battle against Alexander, in which he himself was wounded in the shoulder by a dart. However, the Aspasioi eventually lost and 40,000 people were enslaved. Alexander then continued in a southwestern direction where he encountered the Assakenoi tribe of the Swat & Buner
Buner District ( ps, بونیر ولسوالۍ, ur, ) is a district in Malakand Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province in Pakistan. Before becoming a district in 1991, it was a tehsil within Swat District.
History
The Buner Valley lies bet ...
valleys in April 326 BCE. The Assakenoi fought bravely and offered stubborn resistance to Alexander and his army in the cities of Ora, Bazira (Barikot
Barikot ( ur, بریکوٹ) (Pashto: بریکوټ) is a town located in the middle course of the Swat River in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is located about away from Mingora and the Butkara Stupa. It is the entrance town to the central ...
) and Massaga. So enraged was Alexander about the resistance put up by the Assakenoi that he killed the entire population of Massaga and reduced its buildings to rubble. A similar slaughter then followed at Ora, another stronghold of the Assakenoi. The stories of these slaughters reached numerous Assakenians, who began fleeing to Aornos, a hill-fort located between Shangla
Shangla District ( ps, شانګله ولسوالۍ, ur, ) is a district in Malakand Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. The district's headquarter is located at Alpuri, while the largest city and commercial center is Besham. The district ...
and Kohistan. Alexander followed close behind their heels and besieged the strategic hill-fort, eventually capturing and destroying the fort and killing everyone inside. The remaining smaller tribes either surrendered or like the Astanenoi tribe of Pushkalavati (Charsadda
Chārsadda ( ps, چارسده; ; ur, ; ) is a town and headquarters of Charsadda District, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.
) were quickly neutralized where 38,000 soldiers and 230,000 oxen were captured by Alexander. Eventually Alexander's smaller force would meet with the larger force which had come through the Khyber Pass met at Attock
Attock ( Punjabi and Urdu: ), formerly known as Campbellpur (), is a historical city located in the north of Pakistan's Punjab Province, not far from the country's capital Islamabad. It is the headquarters of the Attock District and is 61st lar ...
. With the conquest of Gandhara complete, Alexander switched to strengthening his military supply line, which by now stretched dangerously vulnerable over the Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
back to Balkh in Bactria.
After conquering Gandhara and solidifying his supply line back to Bactria, Alexander combined his forces with the King Ambhi of Taxila and crossed the River Indus in July 326 BCE to begin the Archosia (Punjab) campaign. Alexander nominated officers as Satraps of the new provinces, and in Gandhara, Oxyartes
Oxyartes (Old Persian: 𐎢𐎺𐎧𐏁𐎫𐎼, Greek: ''Ὀξυάρτης'', in fa, وخشارد ("Vaxš-ard"), from an unattested form in an Old Iranian language: ''*Huxšaθra-'') was a Sogdian or Bactrian nobleman of Bactria, father o ...
was nominated to the position of Satrap in 326 BCE.
Mauryan Gandhara
 After a battle with Seleucus Nicator (Alexander's successor in Asia) in 305 BCE, the
After a battle with Seleucus Nicator (Alexander's successor in Asia) in 305 BCE, the Mauryan
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
Emperor extended his domain up to and including present Southern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. With the completion of the Empire's Grand Trunk Road, the region prospered as a centre of trade. Gandhara remained a part of the Mauryan Empire for about a century and a half.
Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
, the grandson of Chandragupta, was one of the greatest Indian rulers. Like his grandfather, Ashoka also started his career in Gandhara as a governor. Later he became a Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
and promoted Buddhism. He built many ''stupas'' in Gandhara. Mauryan control over the northwestern frontier, including the Yona
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit and Yavanar in Tamil, were words used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for " Ionians" ( grc, ...
s, Kambojas
Kamboja ( sa, कम्बोज) was a kingdom of Iron Age India that spanned parts of South and Central Asia, frequently mentioned in Sanskrit and Pali literature. Eponymous with the kingdom name, the Kambojas were an Indo-Iranian people o ...
, and the Gandharas, is attested from the Rock Edicts left by Ashoka.
According to one school of scholars, the Gandharas and Kambojas were cognate people. It is also contended that the Kurus, Kambojas
Kamboja ( sa, कम्बोज) was a kingdom of Iron Age India that spanned parts of South and Central Asia, frequently mentioned in Sanskrit and Pali literature. Eponymous with the kingdom name, the Kambojas were an Indo-Iranian people o ...
, Gandharas and Bahlikas were cognate people and all had Iranian affinities, or that the Gandhara and Kamboja were nothing but two provinces of one empire and hence influencing each other's language. However, the local language of Gandhara is represented by Panini's conservative ''bhāṣā'' ("language"), which is entirely different from the Iranian (Late Avestan) language of the Kamboja that is indicated by Patanjali's quote of Kambojan śavati 'to go' (= Late Avestan šava(i)ti).
Ancient Era
Indo-Greek Kingdom
 The decline of the Mauryan Empire left Gandhara open to
The decline of the Mauryan Empire left Gandhara open to Greco-Bactrian
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the India ...
invasions. Present-day southern Afghanistan was absorbed by Demetrius I of Bactria
Demetrius I Anicetus ( grc, Δημήτριος Ἀνίκητος, Dēmētrios Anikētos, "the unconquered"), also called Damaytra was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek king (Yona in Pali language, "Yavana" in Sanskrit) (reigned c. 200–167 ...
in 180 BCE. Around about 185 BCE, Demetrius moved into Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
; he invaded and conquered Gandhara and the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
. Later, wars between different groups of Bactrian Greeks resulted in the independence of Gandhara from Bactria and the formation of the Indo-Greek kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent (p ...
. Menander I
Menander I Soter ( grc, Μένανδρος Σωτήρ, Ménandros Sōtḗr, Menander the Saviour; pi, मिलिन्दो, Milinda), was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek King (reigned c.165/155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectivel ...
was its most famous king. He ruled from Taxila and later from Sagala
Sagala, Sakala ( sa, साकला), or Sangala ( grc, Σάγγαλα) was a city in ancient India, which was the predecessor of the modern city of Sialkot that is located in what is now Pakistan's northern Punjab province. The city was the ...
(Sialkot). He rebuilt Taxila (Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and pnb, ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. ...
) and Pushkalavati. He became a Buddhist and is remembered in Buddhist records for his discussions with the great Buddhist philosopher, Nāgasena
Nāgasena was a Sarvastivadan Buddhist sage who lived around 150 BC. His answers to questions about Buddhism posed by Menander I (Pali: ''Milinda''), the Indo-Greek king of northwestern India, are recorded in the '' Milinda Pañha'' and the Sa ...
, in the book ''Milinda Panha
The ''Milinda Pañha'' () is a Buddhist text which dates from sometime between 100 BC and 200 AD. It purports to record a dialogue between the Indian Buddhist sage Nāgasena, and the 2nd century BC Indo-Greek king Menander I (Pali: ''Milinda'' ...
''.
 Around the time of Menander's death in 140 BCE, the Central Asian
Around the time of Menander's death in 140 BCE, the Central Asian Kushans
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
overran Bactria and ended Greek rule there.
Indo-Scythian Kingdom
Around 80 BCE, theSaka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
s, diverted by their Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
n cousins from Iran, moved into Gandhara and other parts of Pakistan and Western India. The most famous king of the Sakas, Maues
Maues (Greek: ; (epigraphic); Kharosthi: , , called , on the Taxila copper plate; also called , in the Mathura lion capital inscription,) was the first Indo-Scythian king, ruling from 98/85 to 60/57 BCE. He invaded India and establi ...
, established himself in Gandhara.
Indo-Parthian Kingdom
By 90 BCE theParthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
ns had taken control of eastern Iran and, around 50 BCE, they put an end to the last remnants of Greek rule in today's Afghanistan. Eventually an Indo-Parthian dynasty succeeded in taking control of Gandhara. The Parthians continued to support Greek artistic traditions. The start of the Gandharan Greco-Buddhist art is dated to about 75–50 BCE. Links between Rome and the Indo-Parthian kingdoms existed. There is archaeological evidence that building techniques were transmitted between the two realms. Christian records claim that around 40 CE Thomas the Apostle
Thomas the Apostle ( arc, 𐡀𐡌𐡅𐡕𐡌, hbo, תוֹמא הקדוש or תוֹמָא שליחא (''Toma HaKadosh'' "Thomas the Holy" or ''Toma Shlikha'' "Thomas the Messenger/Apostle" in Hebrew-Aramaic), syc, ܬܐܘܡܐ, , meaning "twi ...
visited the Indian subcontinent and encountered the Indo-Parthian king Gondophares.
Kushan Gandhara
Kushans
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
, known as Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
in the Chinese source Hou Han Shu (argued by some to be ethnically Asii
The Asii, Osii, Ossii, Asoi, Asioi, Asini or Aseni were an ancient Indo-European people of Central Asia, during the 2nd and 1st centuries BCE. Known only from Classical Greek and Roman sources, they were one of the peoples held to be responsible ...
) moved from Central Asia to Bactria, where they stayed for a century. Around 75 CE, one of their tribes, the Kushan (Kuṣāṇa), under the leadership of Kujula Kadphises gained control of Gandhara. The Kushan empire began as a Central Asian kingdom, and expanded into Afghanistan and northwestern India in the early centuries CE.
The Kushan period is considered the Golden Period of Gandhara. Peshawar Valley and Taxila are littered with ruins of ''stupas'' and monasteries of this period. Gandharan art flourished and produced some of the best pieces of sculpture from the Indian subcontinent. Many monuments were created to commemorate the Jataka
The Jātakas (meaning "Birth Story", "related to a birth") are a voluminous body of literature native to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, th ...
s.

 Gandhara's culture peaked during the reign of the great Kushan king
Gandhara's culture peaked during the reign of the great Kushan king Kanishka the Great
Kanishka I (Sanskrit: कनिष्क, '; Greco-Bactrian: Κανηϸκε ''Kanēške''; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨞𐨁𐨮𐨿𐨐 '; Brahmi: '), or Kanishka, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (c. 127–150 CE) the empire r ...
(127 CE – 150 CE). The cities of Taxila (Takṣaśilā) at Sirsukh and Purushapura (modern day Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
) reached new heights. Purushapura along with Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
became the capital of the great empire stretching from Central Asia to Northern India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
with Gandhara being in the midst of it. Emperor Kanishka
Kanishka I (Sanskrit: कनिष्क, '; Greco-Bactrian: Κανηϸκε ''Kanēške''; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨞𐨁𐨮𐨿𐨐 '; Brahmi: '), or Kanishka, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (c. 127–150 CE) the empire ...
was a great patron of the Buddhist faith; Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
spread from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
to Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
and the Far East across Bactria and Sogdia, where his empire met the Han Empire
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
of China. Buddhist art spread from Gandhara to other parts of Asia. Under Kanishka
Kanishka I (Sanskrit: कनिष्क, '; Greco-Bactrian: Κανηϸκε ''Kanēške''; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨞𐨁𐨮𐨿𐨐 '; Brahmi: '), or Kanishka, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (c. 127–150 CE) the empire ...
, Gandhara became a holy land of Buddhism and attracted Chinese pilgrims eager to view the monuments associated with many Jatakas.
In Gandhara, Mahayana Buddhism flourished and Buddha was represented in human form. Under the Kushans new Buddhists ''stupas'' were built and old ones were enlarged. Huge statues of the Buddha were erected in monasteries and carved into the hillsides. Kanishka also built a great 400-foot tower at Peshawar. This tower was reported by Chinese monks Faxian
Faxian (法顯 ; 337 CE – c. 422 CE), also referred to as Fa-Hien, Fa-hsien and Sehi, was a Chinese Buddhist monk and translator who traveled by foot from China to India to acquire Buddhist texts. Starting his arduous journey about age 60, h ...
, Song Yun
Song Yun () was a Chinese Buddhist monk who was sent by the pious Buddhist Empress Dowager Hu (Northern Wei), Empress Hu (, ?-528 CE) of the Northern Wei, Northern Wei Dynasty with other monastic companions including Hui Zheng, Fa Li and Zheng (o ...
, and Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
who visited the country. This structure was destroyed and rebuilt many times until it was finally destroyed by Mahmud of Ghazni in the 11th century.
Kidarites
The Kidarites conqueredPeshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
and parts of northwest Indian subcontinent including Gandhara probably sometime between 390 and 410 from Kushan empire, around the end of the rule of Gupta Emperor Chandragupta II or beginning of the rule of Kumaragupta I
Kumaragupta I (Gupta script: ''Ku-ma-ra-gu-pta'', r. c. 415–455 CE) was an emperor of the Gupta Empire of Ancient India. A son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta II and queen Dhruvadevi, he seems to have maintained control of his inherited te ...
. It is probably the rise of the Hephthalites and the defeats against the Sasanians which pushed the Kidarites into northern India. Their last ruler in Gandhara was Kandik, around 500 CE.
Alchon Huns
The Alchon invasion of theIndian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
eradicated the Kidarite Huns who had preceded them by about a century, and contributed to the fall of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
, in a sense bringing an end to Classical India
The middle kingdoms of India were the political entities in the Indian subcontinent from 200 BCE to 1200 CE. The period begins after the decline of the Maurya Empire and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, starting with Simuka, ...
.
Hephthalite Empire
 The Hūṇas (as they were known in India) were initially based in the
The Hūṇas (as they were known in India) were initially based in the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
basin in Central Asia and established their control over Gandhara in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent by about 465 CE. From there, they fanned out into various parts of northern, western, and central India. The Hūṇas are mentioned in several ancient texts such as the Rāmāyaṇa
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th to 4th centuries BCE, and later stages ...
, Mahābhārata, Purāṇas, and Kalidasa's Raghuvaṃśa.
Numerous incidents of violence were reported during this period. The Dharmarajika Stupa
The Dharmarajika Stupa ( ur, ), also referred to as the Great Stupa of Taxila, is a Buddhist stupa near Taxila, Pakistan. It was built over the relics of the Buddha by Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE. The stupa, along with the large monastic c ...
at Takṣaśilā has evidence of a massacre there by the Huns. Mihirakula
Mihirakula (Gupta script: , ''Mi-hi-ra-ku-la'', Chinese: 摩酰逻矩罗 ''Mo-hi-lo-kiu-lo''), sometimes referred to as Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was the second and last Alchon Hun king of northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent betwee ...
is said to have become a "terrible persecutor" of Buddhism which may have contributed to decline of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
in the Gandhara region. Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
tells us that initially Mihirakula
Mihirakula (Gupta script: , ''Mi-hi-ra-ku-la'', Chinese: 摩酰逻矩罗 ''Mo-hi-lo-kiu-lo''), sometimes referred to as Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was the second and last Alchon Hun king of northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent betwee ...
was interested in learning about Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
, and asked the monks to send him a teacher; the monks insulted him by recommending a servant of his own household for the purpose. This incident is said to have turned Mihirakula
Mihirakula (Gupta script: , ''Mi-hi-ra-ku-la'', Chinese: 摩酰逻矩罗 ''Mo-hi-lo-kiu-lo''), sometimes referred to as Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was the second and last Alchon Hun king of northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent betwee ...
virulently anti-Buddhist, although some have suggested the anti-Buddhist reputation was exaggerated. It is possible that Mihirakula
Mihirakula (Gupta script: , ''Mi-hi-ra-ku-la'', Chinese: 摩酰逻矩罗 ''Mo-hi-lo-kiu-lo''), sometimes referred to as Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was the second and last Alchon Hun king of northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent betwee ...
, who may have been inclined toward Shaivism
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions rangi ...
(although his coins also have representations of other deities such as the goddess Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism. She is the goddess of wealth, fortune, power, beauty, fertility and prosperity, and associated with ''Maya'' ("Illusion"). Alo ...
), was inimical toward both Buddhists and Jainas.
The travel records of many Chinese Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
pilgrims record that Gandhara was going through a transformation during these centuries. Buddhism was declining, and Hinduism was rising. Faxian
Faxian (法顯 ; 337 CE – c. 422 CE), also referred to as Fa-Hien, Fa-hsien and Sehi, was a Chinese Buddhist monk and translator who traveled by foot from China to India to acquire Buddhist texts. Starting his arduous journey about age 60, h ...
traveled around 400, when Prakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usu ...
was the language of the people, and Buddhism was flourishing. 100 years later, when Song Yun
Song Yun () was a Chinese Buddhist monk who was sent by the pious Buddhist Empress Dowager Hu (Northern Wei), Empress Hu (, ?-528 CE) of the Northern Wei, Northern Wei Dynasty with other monastic companions including Hui Zheng, Fa Li and Zheng (o ...
visited in 520, a different situation was described: the area had been destroyed by the White Huns and was ruled by Lae-Lih, who did not practice the laws of the Buddha. Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
visited India around 644 CE and found Buddhism on the wane in Gandhara and Hinduism in the ascendant. Gandhara was ruled by a king from Kabul, who respected Buddha's law, but Taxila was in ruins, and Buddhist monasteries were deserted.
Later History
Kabul Shahi
 After the fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Arabs in 651 CE, the region south of the
After the fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Arabs in 651 CE, the region south of the Hindukush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
along with Gandhara came under pressure from Muslims. After failure of multiple campaigns by Arabs they failed to extend their rule to Gandhara.
Gandhara was ruled from Kabul by the Kabul Shahi Kabul Shahi is a term used to denote two former non-Muslim dynasties in Kabul:
*Turk Shahis (665–850 CE)
*Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway ...
for next 200 years. Sometime in the 9th century the Kabul Shahi Kabul Shahi is a term used to denote two former non-Muslim dynasties in Kabul:
*Turk Shahis (665–850 CE)
*Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway ...
were replaced by the Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details ...
.
Hindu Shahi and Decline
Based on various records it is estimated thatHindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details ...
was formed in 850 CE. According to Al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
(973–1048), Kallar, a Brahmin minister, founded the Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details ...
dynasty around 843 CE. The dynasty ruled from Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, later moved their capital to Udabhandapura. They built great temples all over their kingdoms. Some of these buildings are still in good condition in the Salt Range
The Salt Range ( pnb, ) is a mountain range in the north of Punjab province of Pakistan, deriving its name from its extensive deposits of rock salt. The range extends along the south of the Potohar Plateau and the north of the Jhelum River. The ...
of the Punjab.
Jayapala
Jayapala or Jaipal was a ruler of the Hindu Shahi dynasty from 964 to 1001 CE.
His kingdom stretched from Laghman to Kashmir and Sirhind to Multan, with Peshawar being in the center. He was the son of Hutpal and the father of Anandapala. Epi ...
was the last great king of the Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details ...
dynasty. His empire extended from west of Kabul to the river Sutlej. However, this expansion of Gandhara kingdom coincided with the rise of the powerful Ghaznavid Empire
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwes ...
under Sabuktigin
Abu Mansur Nasir al-Din Sabuktigin ( fa, ابو منصور سبکتگین) ( 942 – August 997), also spelled as Sabuktagin, Sabuktakin, Sebüktegin and Sebük Tigin, was the founder of the Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 367 A.H/977 A.D to 3 ...
. Defeated twice by Sabuktigin and then by Mahmud of Ghazni in the Kabul valley, Jayapala gave his life on a funeral pyre
A pyre ( grc, πυρά; ''pyrá'', from , ''pyr'', "fire"), also known as a funeral pyre, is a structure, usually made of wood, for burning a body as part of a funeral rite or execution. As a form of cremation, a body is placed upon or under the ...
. Anandapala
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details r ...
, a son of Jayapala, moved his capital near Nandana
Nandana or Nandna ( pnb, ) was a fort built at strategic location on a hilly range on the eastern flanks of the Salt Range in Punjab Pakistan. Its ruins, including those of a town and a temple, are present. It was ruled by the Hindu Shahi king ...
in the Salt Range. In 1021 the last king of this dynasty, Trilochanapala, was assassinated by his own troops which spelled the end of Gandhara. Subsequently, some Shahi princes moved to Kashmir and became active in local politics.
The city of Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the c ...
in Afghanistan is said to have been named after Gandhara. According to H.W. Bellow, an emigrant from the collapsing Gandhara region in the 5th century brought this name to modern Kandahar.
Writing in , Al Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
reported on the devastation caused during the conquest of Gandhara and much of north-west India by Mahmud of Ghazni following his defeat of Jayapala in the Battle of Peshawar (1001), Battle of Peshawar at Peshawar in 1001:
Rediscovery
 By the time Gandhara had been absorbed into the empire of Mahmud of Ghazni, Buddhist buildings were already in ruins and Gandhara art had been forgotten. After Al-Biruni, the Kashmiri writer Kalhaṇa wrote his book ''Rajatarangini'' in 1151. He recorded some events that took place in Gandhara, and provided details about its last royal dynasty and capital Hund, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Udabhandapura.
In the 19th century, British soldiers and administrators started taking an interest in the ancient history of the Indian Subcontinent. In the 1830s coins of the post-Ashoka period were discovered, and in the same period Chinese travelogues were translated. Charles Masson, James Prinsep, and Alexander Cunningham deciphered the Kharosthi script in 1838. Chinese records provided locations and site plans for Buddhist shrines. Along with the discovery of coins, these records provided clues necessary to piece together the history of Gandhara. In 1848 Cunningham found Gandhara sculptures north of Peshawar. He also identified the site of Taxila in the 1860s. From then on a large number of Buddhist statues were discovered in the Peshawar valley.
John Marshall (archaeologist), Archaeologist John Marshall excavated at Taxila between 1912 and 1934. He discovered separate Greek, Parthian, and Kushan cities and a large number of ''stupas'' and monasteries. These discoveries helped to piece together much more of the chronology of the history of Gandhara and its art.
After 1947 Ahmed Hassan Dani and the Archaeology Department at the University of Peshawar made a number of discoveries in the Peshawar and Swat Valley. Excavation of many of the sites of Gandhara Civilization are being done by researchers from Peshawar and several universities around the world.
By the time Gandhara had been absorbed into the empire of Mahmud of Ghazni, Buddhist buildings were already in ruins and Gandhara art had been forgotten. After Al-Biruni, the Kashmiri writer Kalhaṇa wrote his book ''Rajatarangini'' in 1151. He recorded some events that took place in Gandhara, and provided details about its last royal dynasty and capital Hund, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Udabhandapura.
In the 19th century, British soldiers and administrators started taking an interest in the ancient history of the Indian Subcontinent. In the 1830s coins of the post-Ashoka period were discovered, and in the same period Chinese travelogues were translated. Charles Masson, James Prinsep, and Alexander Cunningham deciphered the Kharosthi script in 1838. Chinese records provided locations and site plans for Buddhist shrines. Along with the discovery of coins, these records provided clues necessary to piece together the history of Gandhara. In 1848 Cunningham found Gandhara sculptures north of Peshawar. He also identified the site of Taxila in the 1860s. From then on a large number of Buddhist statues were discovered in the Peshawar valley.
John Marshall (archaeologist), Archaeologist John Marshall excavated at Taxila between 1912 and 1934. He discovered separate Greek, Parthian, and Kushan cities and a large number of ''stupas'' and monasteries. These discoveries helped to piece together much more of the chronology of the history of Gandhara and its art.
After 1947 Ahmed Hassan Dani and the Archaeology Department at the University of Peshawar made a number of discoveries in the Peshawar and Swat Valley. Excavation of many of the sites of Gandhara Civilization are being done by researchers from Peshawar and several universities around the world.
Language
Gandhara's language was aPrakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usu ...
or "Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan" dialect, usually called Gandhari language, Gāndhārī. Hindko from Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
, which was the capital of Gandhara, came from Shauraseni Prakrit, Shuraseni prakrit a language spoken in Gandhara. Under the Kushan Empire, Gāndhārī spread into adjoining regions of South and Central Asia. It used the Kharosthi script, which is derived from the Aramaic alphabet, Aramaic script, and it died out about in the 4th century CE.
Linguistic evidence links some groups of the Dardic languages with Gandhari. The Kohistani languages, now all being displaced from their original homelands, were once more widespread in the region and most likely descend from the ancient dialects of the region of Gandhara. The last to disappear was Tirahi language, Tirahi, still spoken some years ago in a few villages in the vicinity of Jalalabad in eastern Afghanistan, by descendants of migrants expelled from Tirah by the Afridi Pashtuns in the 19th century. Georg Morgenstierne claimed that Tirahi is "probably the remnant of a dialect group extending from Tirah through the Peshawar District, Peshawar district into Swat and Dir". Nowadays, it must be entirely extinct and the region is now dominated by Iranian languages brought in by later migrants, such as Pashto. Among the modern day Indo-Aryan languages still spoken today, Torwali language, Torwali shows the closest linguistic affinity possible to ''Niya'', a dialect of Gāndhārī.
Religion
Buddhism

Mahāyāna Buddhism
Mahāyāna Buddhist sutras#Pure Land Sutras, Pure Land sutras were brought from the Gandhāra region to China as early as 147 CE, when the Kushan monk Lokaksema (Buddhist monk), Lokakṣema began translating some of the first Buddhist sutras into Chinese. The earliest of these translations show evidence of having been translated from the Gāndhārī language. Lokakṣema translated important Mahayana sutras, Mahāyāna sūtras such as the ''Prajñāpāramitā, Aṣṭasāhasrikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra'', as well as rare, early Mahāyāna sūtras on topics such as Samādhi (Buddhism), samādhi, and meditation on the Buddha Akshobhya, Akṣobhya. Lokaksema's translations continue to provide insight into the early period of Mahāyāna Buddhism. This corpus of texts often includes and emphasizes ascetic practices and forest dwelling, and absorption in states of meditative concentration: Some scholars believe that the Mahāyāna ''Infinite Life Sutra, Longer Sukhāvatīvyūha Sūtra'' was compiled in the age of the Kushan Empire in the 1st and 2nd centuries CE, by an order of Mahisasaka, Mahīśāsaka bhikkhu, bhikṣus which flourished in the Gandhāra region.Nakamura, Hajime. ''Indian Buddhism: A Survey With Biographical Notes.'' 1999. p. 205 However, it is likely that the longer ''Sukhāvatīvyūha'' owes greatly to the Mahāsāṃghika-Lokottaravāda sect as well for its compilation, and in this sutra there are many elements in common with the Lokottaravādin ''Mahavastu, Mahāvastu''. There are also images of Amitābha Buddha with the bodhisattvas Avalokiteśvara and Mahāsthāmaprāpta which were made in Gandhāra during the Kushan era. The ''Mañjuśrīmūlakalpa'' records that Kaniṣka of the Kushan Empire presided over the establishment of the Mahāyāna Prajnaparamita, Prajñāpāramitā teachings in the northwest.Ray, Reginald. ''Buddhist Saints in India: A Study in Buddhist Values and Orientations.'' 1999. p. 410 Taranatha, Tāranātha wrote that in this region, 500 bodhisattvas attended the council at Jālandhra monastery during the time of Kaniṣka, suggesting some institutional strength for Mahāyāna in the north-west during this period. Edward Conze goes further to say that Prajñāpāramitā had great success in the north-west during the Kushan period, and may have been the "fortress and hearth" of early Mahāyāna, but not its origin, which he associates with the Mahāsāṃghika branch of Buddhism.Destruction of Buddhist relics by Taliban
Swat Valley in Pakistan has many Buddhist carvings, and ''stupas'', and jehanabad (Pakistan), Jehanabad contains a Seated Buddha statue. Kushan era Buddhist ''stupas'' and statues in Swat valley were demolished after two attempts by the Taliban and the Jehanabad Buddha's face was dynamited. Only the Buddhas of Bamiyan were larger than the carved giant Buddha statues in Swat near Manglawar, Manglore which the Taliban attacked. The government did nothing to safeguard the statue after the initial attempts to destroy the Buddha, which did not cause permanent harm. But when a second attack took place on the statue, the feet, shoulders, and face were demolished. Taliban and looters destroyed many of Pakistan's Buddhist artefacts from the Buddhist Gandhara civilization especially in the Swat Valley.Buddhist translators
Gandharan Buddhist missionaries were active, with other monks from Central Asia, from the 2nd century CE in the Han Dynasty, Han-dynasty (202 BC – 220 CE) at China's capital of Luoyang, and particularly distinguished themselves by their translation work. They promoted scriptures from Early Buddhist schools as well as those from the Mahāyāna. These translators included: * Lokaksema (Buddhist monk), Lokakṣema, a Kushan and the first to translate Mahāyāna scriptures into Chinese language, Chinese (167–186) * Zhi Yao (monk), Zhi Yao (), a Kushan monk, second generation of translators after Lokakṣema * Zhi Qian (220–252), a Kushan monk whose grandfather had settled in China during 168–190 * Zhi Yue (), a Kushan monk who worked at Nanjing * Dharmaraksa, Dharmarakṣa (265–313), a Kushan whose family had lived for generations at Dunhuang * Jnanagupta, Jñānagupta (561–592), a monk and translator from Gandhāra * Śikṣānanda (652–710), a monk and translator from Oddiyana, Oḍḍiyāna, Gandhāra * Prajna (Buddhist Monk), Prajñā (), a monk and translator fromKabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, who educated the Japanese Kūkai in Sanskrit texts
Textual finds
The Chinese Buddhist monkXuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
visited a Lokottaravāda monastery in the 7th century, at Bamiyan, Afghanistan. The site of this monastery has since been rediscovered by archaeologists. Birchbark and palm leaf manuscripts of texts in this monastery's collection, including Mahāyāna sūtras, have been discovered at the site, and these are now located in the Schoyen Collection, Schøyen Collection. Some manuscripts are in the Gāndhārī language and Kharoṣṭhī script, while others are in Sanskrit and written in forms of the Gupta script. Manuscripts and fragments that have survived from this monastery's collection include the following source texts:
* ''Pratimoksa, Pratimokṣa Vibhaṅga'' of the Mahāsāṃghika-Lokottaravāda (MS 2382/269)
* ''Mahaparinibbana Sutta, Mahāparinirvāṇa Sūtra'', a sūtra from the Āgama (Buddhism), Āgamas (MS 2179/44)
* ''Caṃgī Sūtra'', a sūtra from the Āgamas (MS 2376)
* ''Diamond Sutra, Vajracchedikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra'', a Mahāyāna sūtra (MS 2385)
* ''Bhaisajyaguru, Bhaiṣajyaguru Sūtra'', a Mahāyāna sūtra (MS 2385)
* ''Śrīmālādevī Sūtra, Śrīmālādevī Siṃhanāda Sūtra'', a Mahāyāna sūtra (MS 2378)
* ''Pravāraṇa Sūtra'', a Mahāyāna sūtra (MS 2378)
* ''Sarvadharmapravṛttinirdeśa Sūtra'', a Mahāyāna sūtra (MS 2378)
* ''Ajātaśatrukaukṛtyavinodana Sūtra'', a Mahāyāna sūtra (MS 2378)
* ''Śāriputrābhidharma, Śāriputrābhidharma Śāstra'' (MS 2375/08)
A Sanskrit manuscript of the ''Bhaiṣajyaguruvaiḍūryaprabhārāja Sūtra'' was among the textual finds at Gilgit, Pakistan, attesting to the popularity of the Medicine Buddha in Gandhāra.Bakshi, S.R. ''Kashmir: History and People.'' 1998. p. 194 The manuscripts in this find are dated before the 7th century, and are written in the upright Gupta script.
Art
Important Gandharans
Important people from ancient region of Gandhara are as follows; *Pāṇini (4th century BCE), he was aSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
philologist, grammarian, and a revered scholar from Gandhara. Pāṇini is known for his text Aṣṭādhyāyī, a sutra-style treatise on Sanskrit grammar.
*Chanakya (4th century BCE), he was an ancient Gandharan teacher, philosopher, economist, jurist and royal advisor. Chanakya assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta Maurya, Chandragupta in his rise to power, and his work Arthashastra is considered Pioneer of field of political science in India.
*Garab Dorje (1st century CE), founder of Dzogchen (Great Perfection) tradition.
*Kumāralāta (3rd century), Kumāralāta was the founder of Sautrāntika school of Buddhism.
*Vasubandhu (4th century), Vasubandhu is considered one of the most influential thinkers in the Gandharan Buddhist philosophical tradition. In Jōdo Shinshū, he is considered the Second Patriarch; in Chan Buddhism, he is the 21st Patriarch. His writing Abhidharmakośakārikā ("Commentary on the Treasury of the Abhidharma") is widely used in Tibetan and East Asian Buddhism.
*Asanga (4th century), he was "one of the most important spiritual figures" of Mahayana Buddhism and the "founder of the Yogachara school". His book Mahāyānasaṃgraha (MSg) is the key work of the Yogācāra school of Mahāyāna Buddhist philosophy.
*Padmasambhāva (8th century), he is considered the Second Buddha by the Nyingma school, the oldest Buddhist school in Tibet known as "the ancient one".
Major cities
Major cities of ancient Gandhara are as follows: *Pushkalavati, Puṣkalavati (Charsadda
Chārsadda ( ps, چارسده; ; ur, ; ) is a town and headquarters of Charsadda District, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.
), Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
*Takshashila ( Taxila), Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
* Puruṣapura (Peshawer), Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
*Sagala
Sagala, Sakala ( sa, साकला), or Sangala ( grc, Σάγγαλα) was a city in ancient India, which was the predecessor of the modern city of Sialkot that is located in what is now Pakistan's northern Punjab province. The city was the ...
(Sialkot), Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
*Oddiyana (Swat district, Swat), Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
*Chiniotis (Chiniot), Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
*Kapisi
Kapisi (, ) or Kapisa was the capital city of the former Kingdom of Kapisa (now part of modern Afghanistan). While the name of the kingdom has been used for the modern Kapisa Province, the ancient city of Kapisa was located in Parwan Province, ...
(Bagram
Bagram (; Pashto/ fa, بگرام) is a town and seat in Bagram District in Parwan Province of Afghanistan, about 60 kilometers north of the capital Kabul. It is the site of an ancient city located at the junction of the Ghorband and Panjshir ...
), Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
Timeline
* c. 2300 – c. 1400 BCE Indus Valley civilization * c. 1400 – c. 800 BCE Gandhara grave culture * c. 1200 – c. 800 BCEGandhari people
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern ...
mentioned in Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
and Atharvaveda.
* c. 800 – c. 518 BCE Gandhara Kingdom
Gandhāra ( sa, गन्धार) was an Ancient Indian kingdom mentioned in the Indian epics Mahabharata and Ramayana. Gandhara prince Shakuni was the root of all the conspiracies of Duryodhana against the Pandavas, which finally resulted ...
* c. 518 – c. 326 BCE Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire. Under direct Persian control and/or local control under Achaemenid suzerainty.
* c. 326 – c. 305 BCE Occupied by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
and Macedonian generals
* c. 305 – c. 185 BCE Controlled by the Maurya dynasty, founded by Chandragupta Maurya, Chandragupta. Converted to Buddhism under King Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
(273–232 BC)
* c. 185 – c. 97 BCE Under control of the Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent (p ...
, with some incursions of the Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
from around 100 BC
* c. 97 BCE – c. 7 CE Saka (Indo-Scythian) Rule
* c. 7 – c. 75 CE Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
n invasion and Indo-Parthian Kingdom, Rule of Commander Aspavarman?.
* c. 75 – c. 230 CE Kushan Empire
* c. 230 – c. 440 CE Kushanshas under Persian Sassanid suzerainty
* c. 450 – c. 565 CE White Huns (Hephthalites)
* c. 565 – c. 644 CE Nezak kingdom, ruled from Kapisa and Udabhandapura
* c. 644 – c. 870 CE Kabul Shahi Kabul Shahi is a term used to denote two former non-Muslim dynasties in Kabul:
*Turk Shahis (665–850 CE)
*Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway ...
, ruled from Kabul
* c. 870 – 1021 CE Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details ...
, ruled from Udabhandapura
* c. 1021 – c. 1100 CE Conquered and controlled by the Ghaznavids, Ghaznavid empire
See also
*Gandhari people
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern ...
*History of India
*History of Pakistan
*Kambojas
Kamboja ( sa, कम्बोज) was a kingdom of Iron Age India that spanned parts of South and Central Asia, frequently mentioned in Sanskrit and Pali literature. Eponymous with the kingdom name, the Kambojas were an Indo-Iranian people o ...
*Kashmir Smast
* Mahajanapadas
*Mankiala
Notes
References
Sources
* Beal, Samuel. 1884. ''Si-Yu-Ki: Buddhist Records of the Western World, by Hiuen Tsiang.'' 2 vols. Trans. by Samuel Beal. London. Reprint: Delhi. Oriental Books Reprint Corporation. 1969. * Beal, Samuel. 1911. ''The Life of Hiuen-Tsiang by the Shaman Hwui Li, with an Introduction containing an account of the Works of I-Tsing''. Trans. by Samuel Beal. London. 1911. Reprint: Munshiram Manoharlal, New Delhi. 1973. * Bellew, H.W. ''Kashmir and Kashgar''. London, 1875. Reprint: Sang-e-Meel Publications 1999 * Caroe, Sir Olaf, '' The Pathans'', Oxford University Press, Karachi, 1958. * * * Hill, John E. 2003"Annotated Translation of the Chapter on the Western Regions according to the ''Hou Hanshu''"
2nd Edition: ''Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes, 1st to 2nd Centuries CE''. 2015. John E. Hill. Volume I, ; Volume II, . CreateSpace, North Charleston, S.C. * Hussain, J. '' An Illustrated History of Pakistan'', Oxford University Press, Karachi, 1983. * Legge, James. Trans. and ed. 1886. ''A Record of Buddhistic Kingdoms: being an account by the Chinese monk Fâ-hsien of his travels in India and Ceylon (A.D. 399–414) in search of the Buddhist Books of Discipline''. Reprint: Dover Publications, New York. 1965. * * * Shaw, Isobel. ''Pakistan Handbook'', The Guidebook Co., Hong Kong, 1989 * Watters, Thomas. 1904–5. ''On Yuan Chwang's Travels in India (A.D. 629–645)''. Reprint: Mushiram Manoharlal Publishers, New Delhi. 1973.
Further reading
* * * * Rienjang, Wannaporn, and Peter Stewart (eds), ''The Rediscovery and Reception of Gandharan Art'' (Archaeopress, 2022) ISBN 978-1-80327-233-7.External links
National Fund for Cultural Heritage (Pakistan) {{Coord, 33.7560, N, 72.8291, E, type:landmark_region:PK, display=title Gandhara, Achaemenid satrapies Ancient empires and kingdoms of India Ancient history of Pakistan Archaeological sites in Pakistan Buddhist sites in Pakistan Ancient Asia History of Pakistan Historical regions of Pakistan Kingdoms in the Ramayana Locations in Hindu mythology Prehistoric Pakistan